Differential program verification
|
|
|
- Sharleen Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Differential program verification Shuvendu K. Lahiri Research in Software Engineering (RiSE), Microsoft Research Redmond, WA
2 Involved in building static assertion checkers HAVOC [POPL 06, 08, 09, CAV 09, VSTTE 10, S&P 13] Heap logics, efficient memory modeling for C NTFS object management(~50 bugs, 300KLOC) Variants of MSRC Security Vulnerabilities in IE/Kernel (~100 bugs, ~2MLOC) Uses components Z3, Boogie, Corral, Houdini, STORM [CAV 09] Reducing concurrency analysis to sequential Concurrency bugs in Drivers (~10 bugs, 10KLOC) Angelic Verifier [PLDI 13,CAV 15] Configurable angelic environment specification inference Assertion checker (memory safety, type-state) on Drivers/Kernel (~100+ bugs, ~100KLOC) with minimal env modeling Will ships in a future release of Windows DK
3 Challenges for static assertion checkers Ability to find new bugs in large unannotated code bases (without hand holding) Not cost-effective for legacy developers Costly upfront investment Need for specifications Need for environment specifications Need for help with program-specific invariants Scalability of (precise) interprocedural analysis Issue of false alarms Users get discouraged after a few dumb warnings [Coverity report 10]
4 Motivation(s) How can program verifiers be used by any developer cost-effectively? Tap (active) research in PL, FM, SE, conferences Answer questions that devs care about (even late in development) Does modern software engineering process create new ways to apply/leverage/extend program verifiers?
5 One direction: differential verification Goal Preserve the quality of existing code across evolution (no regressions ) Idea: Verify properties of program differences Highlight semantic differences that are unintended Research question What properties of differences are interesting? Which of them are amenable to automated verification? This talk Some problems in this space Some ongoing solutions
6 Motivation: Verifying StringCopy Need precondition relating dst,src, size, nullterminated Check all dereferences are in bound Need a programspecific loop invariant void StringCopy2 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;i<size-1 && *src; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0;
7 False alarms from no preconditions size ==2, ==1,!Valid(src)!Valid(dst) assert(valid(x)) before every *x void StringCopy2 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;i<size-1 && *src; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0;
8 Weaken the soundness: relative correctness void StringCopy1 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;*src && i<size-1; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0; void StringCopy2 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;i<size-1 && *src; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0; Is there any input that passes StringCopy1 but fails StringCopy2?
9 Relative correctness (Proof) void StringCopy1 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;*src && i<size-1; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0; void StringCopy2 (char* dst, char*src, int size) { int i=0; for(;i<size-1 && *src; i++) *dst++ = *src++; *dst = 0; No need for any preconditions Mutual loop invariants: src.1=src.2, dst.1=dst.2, size.1=size.2, i.1=i.2, Mem_char.1 == Mem_char.2, ok1 ok2
10 Problems Procedure-level equivalence rarely holds for feature-additions, bug-fixes, refactoring Equivalence checking for evolving compilers FSE 13, CAV 15 Differential Assertion Checking and VMV FSE 13, PLDI 14 Relative bounds and termination Semantic Diff for Concurrent Programs Semantic Merge Semantic Change Impact Analysis Explored in a tool SymDiff
11 Problems Procedure-level equivalence rarely holds for feature-additions, bug-fixes, refactoring Equivalence checking for evolving compilers FSE 13, CAV 15 Differential Assertion Checking and VMV FSE 13, PLDI 14 Relative bounds and termination Semantic Diff for Concurrent Programs Semantic Merge Semantic Change Impact Analysis Explored in a tool SymDiff
12 Reduce differential analysis single program analysis proc f1(x1): r1 modifies g1 { s1; L1: w1 := call h1(e1); t1 proc f2(x2): r2 modifies g2 { s2; L2: w2 := call h2(e2); t2 Novel product construction Off-theshelf program verifier + invariant inference
13 Verifying bug fixes Question: did a fix inadvertently introduce new bugs? Verisec suite: snippets of open source programs which contain buffer overflow vulnerabilities, as well as corresponding patched versions. Examples include apache, madwifi, sendmail, (~ LOC) Relative memory safety (buffer overflow) checking Automatic proof of relative correctness Using small space of relative invariants {x <= x, x >= x, x == x, x x,.. Applied similar ideas in Verification Modulo Versions (VMV) in CLOUSOT Conditions guaranteeing bug fix vs. regression (~100KLOC C#)
14 Problems Procedure-level equivalence rarely holds for feature-additions, bug-fixes, refactoring Equivalence checking for evolving compilers FSE 13, CAV 15 Differential Assertion Checking and VMV FSE 13, PLDI 14 Relative bounds and termination Semantic Diff for Concurrent Programs Semantic Merge Semantic Change Impact Analysis Explored in a tool SymDiff
15 Semantic merge Inconsistency can be introduced by (text-based) git merge Blamed for Apple SSL/TLS Goto Bug 2014 (led to security exploits) Questions Can we have a semantic formulation of conflict-freedom? [revive 90s work] Can we check such a property automatically?
16 Semantic merge Verifying conflict freedom for 3-way merge How to represent differences (using edit scripts) Formalize conflict-freedom A variable v in Merge agrees with the A (respectively B) if A (respectively B) changes v s value over Base Reduction to assertion checking Sound 4-way product construction Simulation relation inference using Horn Clause Solver (Duality) Next step: Semantic merge Synthesize verified merge when git merge fails or causes conflict
17 Problems Procedure-level equivalence rarely holds for feature-additions, bug-fixes, refactoring Equivalence checking for evolving compilers FSE 13, CAV 15 Differential Assertion Checking and VMV FSE 13, PLDI 14 Relative bounds and termination Semantic Diff for Concurrent Programs Semantic Merge Semantic Change Impact Analysis Explored in a tool SymDiff
18 Semantic change impact Problem Which statements are impacted by a change (soundly)? Current approaches don t exploit change semantics to contain changes Hard to localize change (even for refactoring parts) Solution Incorporate change semantics by inferring equivalences when they hold (SymDiff) More subtle than checking two procedures are equal Novel combination of data-flow and differential invariant inference Foo(x, z) { y = x + x 2x ; Bar(y); Complex(z); Bar(y) { Baz(y+1);. Baz(z) { Foo(.., z);.
19 Semantic change impact Problem Which statements are impacted by a change (soundly)? Current approaches don t exploit change semantics to contain changes Hard to localize change (even for refactoring parts) Solution Incorporate change semantics by inferring equivalences when they hold (SymDiff) More subtle than checking two procedures are equal Novel combination of data-flow and differential invariant inference Foo(x, z) { y = x + x 2x ; Bar(y); Complex(z); Bar(y) { Baz(y+1);. Baz(z) { Foo(.., z);.
20 Semantic change impact Questions How to formalize CI soundly, not dependent on syntactic diff What kind of semantic/relative facts can help prune impact How to leverage relative verification in a scalable manner with a lightweight static analysis Applied it to several GitHub projects using SMACK +SymDiff
21 Summary Differential verification Verify properties of difference (2+ programs) as opposed to a single program New domain of problems to apply verification Less reliance of specifications, environment modeling and program-specific invariants Use cases in software engineering High quality detection of regressions (e.g. relative memory safety) Help with refactorings (equivalence checking,..) Code review (understand change impact) Redundant tests (that only cover non-impacted statements) Safer merge (avoid cost regression and rollback later) Verifying approximations in compilers (relative assertion, termination safety) A new cost-effective way to use automatic verification! SymDiff
Differential Assertion Checking
 Differential Assertion Checking Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Kenneth L. McMillan Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Chris Hawblitzel Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Rahul
Differential Assertion Checking Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Kenneth L. McMillan Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Chris Hawblitzel Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA Rahul
Differential assertion checking
 Differential assertion checking S. K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA K. L. McMillan Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA C. Hawblitzel Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA R. Sharma Stanford
Differential assertion checking S. K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA K. L. McMillan Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA C. Hawblitzel Microsoft Research Redmond, WA, USA R. Sharma Stanford
Mutual Summaries: Unifying Program Comparison Techniques
 Mutual Summaries: Unifying Program Comparison Techniques Chris Hawblitzel 1, Ming Kawaguchi 2, Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1, and Henrique Rebêlo 3 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA 2 University of California,
Mutual Summaries: Unifying Program Comparison Techniques Chris Hawblitzel 1, Ming Kawaguchi 2, Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1, and Henrique Rebêlo 3 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA 2 University of California,
SymDiff: A language-agnostic semantic diff tool for imperative programs
 SymDiff: A language-agnostic semantic diff tool for imperative programs Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1, Chris Hawblitzel 1, Ming Kawaguchi 2, and Henrique Rebêlo 3 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA 2 University
SymDiff: A language-agnostic semantic diff tool for imperative programs Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1, Chris Hawblitzel 1, Ming Kawaguchi 2, and Henrique Rebêlo 3 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA 2 University
Model Checking and Its Applications
 Model Checking and Its Applications Orna Grumberg Technion, Israel Verification and Deduction Mentoring Workshop July 13, 2018 1 Personal data Ph.d. in (non-automated) verification Postdoc in Model Checking
Model Checking and Its Applications Orna Grumberg Technion, Israel Verification and Deduction Mentoring Workshop July 13, 2018 1 Personal data Ph.d. in (non-automated) verification Postdoc in Model Checking
Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step. NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000
 Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step David Wagner Eric A. Brewer Jeffrey S. Foster Alexander Aiken NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000 1 Introduction The state of computer security
Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step David Wagner Eric A. Brewer Jeffrey S. Foster Alexander Aiken NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000 1 Introduction The state of computer security
Abstract Semantic Differencing for Numerical Programs
 Abstract Semantic Differencing for Numerical Programs Nimrod Partush Eran Yahav Technion, Israel Semantic differencing Characterize semantic difference between similar programs 2 Motivating example 1.
Abstract Semantic Differencing for Numerical Programs Nimrod Partush Eran Yahav Technion, Israel Semantic differencing Characterize semantic difference between similar programs 2 Motivating example 1.
Static program checking and verification
 Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Automatic Generation of Program Specifications
 Automatic Generation of Program Specifications Jeremy Nimmer MIT Lab for Computer Science http://pag.lcs.mit.edu/ Joint work with Michael Ernst Jeremy Nimmer, page 1 Synopsis Specifications are useful
Automatic Generation of Program Specifications Jeremy Nimmer MIT Lab for Computer Science http://pag.lcs.mit.edu/ Joint work with Michael Ernst Jeremy Nimmer, page 1 Synopsis Specifications are useful
Combining the Logical and the Probabilistic in Program Analysis. Xin Zhang Xujie Si Mayur Naik University of Pennsylvania
 Combining the Logical and the Probabilistic in Program Analysis Xin Zhang Xujie Si Mayur Naik University of Pennsylvania What is Program Analysis? int f(int i) {... } Program Analysis x may be null!...
Combining the Logical and the Probabilistic in Program Analysis Xin Zhang Xujie Si Mayur Naik University of Pennsylvania What is Program Analysis? int f(int i) {... } Program Analysis x may be null!...
Scalable Program Analysis Using Boolean Satisfiability: The Saturn Project
 Scalable Program Analysis Using Boolean Satisfiability: The Saturn Project Alex Aiken Stanford University Saturn 1 The Idea Verify properties of large systems! Doesn t {SLAM, BLAST, CQual, ESP} already
Scalable Program Analysis Using Boolean Satisfiability: The Saturn Project Alex Aiken Stanford University Saturn 1 The Idea Verify properties of large systems! Doesn t {SLAM, BLAST, CQual, ESP} already
Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses. Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher
 Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher Overview Over- vs. underapproximating static analysis Path-based symbolic simulation Path merging Acceleration
Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher Overview Over- vs. underapproximating static analysis Path-based symbolic simulation Path merging Acceleration
Automatically Finding Patches Using Genetic Programming. Westley Weimer, Claire Le Goues, ThanVu Nguyen, Stephanie Forrest
 Automatically Finding Patches Using Genetic Programming Westley Weimer, Claire Le Goues, ThanVu Nguyen, Stephanie Forrest Motivation Software Quality remains a key problem Over one half of 1 percent of
Automatically Finding Patches Using Genetic Programming Westley Weimer, Claire Le Goues, ThanVu Nguyen, Stephanie Forrest Motivation Software Quality remains a key problem Over one half of 1 percent of
Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back
 Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back Bogdan Mihaila Technical University of Munich, Germany December 6, 2014 Name Lastname < name@mail.org > ()()()()()()()()()... ()()() 1 / 25 Abstract Interpretation
Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back Bogdan Mihaila Technical University of Munich, Germany December 6, 2014 Name Lastname < name@mail.org > ()()()()()()()()()... ()()() 1 / 25 Abstract Interpretation
Goal. Overflow Checking in Firefox. Sixgill. Sixgill (cont) Verifier Design Questions. Sixgill: Properties 4/8/2010
 Goal Overflow Checking in Firefox Brian Hackett Can we clean a code base of buffer overflows? Keep it clean? Must prove buffer accesses are in bounds Verification: prove a code base has a property Sixgill
Goal Overflow Checking in Firefox Brian Hackett Can we clean a code base of buffer overflows? Keep it clean? Must prove buffer accesses are in bounds Verification: prove a code base has a property Sixgill
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming
 Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language
 Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language http://cs.au.dk/~amoeller/spa/ Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, Aarhus University Questions about programs Does the program terminate
Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language http://cs.au.dk/~amoeller/spa/ Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, Aarhus University Questions about programs Does the program terminate
Pliny and Fixr Meeting. September 15, 2014
 Pliny and Fixr Meeting September 15, 2014 Fixr: Mining and Understanding Bug Fixes for App-Framework Protocol Defects (TA2) University of Colorado Boulder September 15, 2014 Fixr: Mining and Understanding
Pliny and Fixr Meeting September 15, 2014 Fixr: Mining and Understanding Bug Fixes for App-Framework Protocol Defects (TA2) University of Colorado Boulder September 15, 2014 Fixr: Mining and Understanding
ExplainHoudini: Making Houdini inference transparent
 ExplainHoudini: Making Houdini inference transparent Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1 and Julien Vanegue 2 1 Microsoft Research shuvendu@microsoft.com 2 Microsoft Corporation jvanegue@microsoft.com Abstract. Houdini
ExplainHoudini: Making Houdini inference transparent Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1 and Julien Vanegue 2 1 Microsoft Research shuvendu@microsoft.com 2 Microsoft Corporation jvanegue@microsoft.com Abstract. Houdini
An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking
 An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking Dirk Beyer, Thomas A. Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA Rupak Majumdar Computer Science
An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking Dirk Beyer, Thomas A. Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA Rupak Majumdar Computer Science
Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems
 Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems Karen Zee, Viktor Kuncak, and Martin Rinard MIT CSAIL Tuesday, March 13, 2007 Workshop on Runtime Verification 1 Background Jahob program verification
Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems Karen Zee, Viktor Kuncak, and Martin Rinard MIT CSAIL Tuesday, March 13, 2007 Workshop on Runtime Verification 1 Background Jahob program verification
Verifying the Safety of Security-Critical Applications
 Verifying the Safety of Security-Critical Applications Thomas Dillig Stanford University Thomas Dillig 1 of 31 Why Program Verification? Reliability and security of software is a huge problem. Thomas Dillig
Verifying the Safety of Security-Critical Applications Thomas Dillig Stanford University Thomas Dillig 1 of 31 Why Program Verification? Reliability and security of software is a huge problem. Thomas Dillig
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell. Anish Tondwalkar
 Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Static Analysis Techniques
 oftware Design (F28SD2): Static Analysis Techniques 1 Software Design (F28SD2) Static Analysis Techniques Andrew Ireland School of Mathematical and Computer Science Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh oftware
oftware Design (F28SD2): Static Analysis Techniques 1 Software Design (F28SD2) Static Analysis Techniques Andrew Ireland School of Mathematical and Computer Science Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh oftware
F-Soft: Software Verification Platform
 F-Soft: Software Verification Platform F. Ivančić, Z. Yang, M.K. Ganai, A. Gupta, I. Shlyakhter, and P. Ashar NEC Laboratories America, 4 Independence Way, Suite 200, Princeton, NJ 08540 fsoft@nec-labs.com
F-Soft: Software Verification Platform F. Ivančić, Z. Yang, M.K. Ganai, A. Gupta, I. Shlyakhter, and P. Ashar NEC Laboratories America, 4 Independence Way, Suite 200, Princeton, NJ 08540 fsoft@nec-labs.com
Modular and Verified Automatic Program Repairs
 Modular and Verified Automatic Program Repairs from Francesco Logozzo and Thomas Ball at Microsoft Research, Redmond presenter name(s) removed for FERPA considerations Introduction Your programs will have
Modular and Verified Automatic Program Repairs from Francesco Logozzo and Thomas Ball at Microsoft Research, Redmond presenter name(s) removed for FERPA considerations Introduction Your programs will have
Crash Course in Applied PL
 Crash Course in Applied PL (with applications to Networks) Software Reliability Lab Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich Overview of Applied PL techniques Static Analysis Program Synthesis ibgp, OSPF,
Crash Course in Applied PL (with applications to Networks) Software Reliability Lab Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich Overview of Applied PL techniques Static Analysis Program Synthesis ibgp, OSPF,
Verifying Relative Safety, Accuracy, and Termination for Program Approximations
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Verifying Relative Safety, Accuracy, and Termination for Program Approximations Shaobo He Shuvendu K. Lahiri Zvonimir Rakamarić the date of receipt
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Verifying Relative Safety, Accuracy, and Termination for Program Approximations Shaobo He Shuvendu K. Lahiri Zvonimir Rakamarić the date of receipt
BOOGIE. Presentation by Itsik Hefez A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH
 BOOGIE A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH Presentation by Itsik Hefez Introduction Boogie is an intermediate verification language, intended as a layer on which
BOOGIE A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH Presentation by Itsik Hefez Introduction Boogie is an intermediate verification language, intended as a layer on which
Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis
 Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
Now we are porting. (a short time ago in a company not so far away) Mihails Strasuns
 Now we are porting (a short time ago in a company not so far away) Some basics: Sociomantic Labs : Real-Time Bidding startup founded in 2009 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/real-time_bidding One of biggest
Now we are porting (a short time ago in a company not so far away) Some basics: Sociomantic Labs : Real-Time Bidding startup founded in 2009 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/real-time_bidding One of biggest
CodeContracts & Clousot. Francesco Logozzo - Microsoft Mehdi Bouaziz ENS
 CodeContracts & Clousot Francesco Logozzo - Microsoft Mehdi Bouaziz ENS CodeContracts? Specify code with code Advantages Language agnostic No new language/compiler Leverage existing tools IDE, Compiler
CodeContracts & Clousot Francesco Logozzo - Microsoft Mehdi Bouaziz ENS CodeContracts? Specify code with code Advantages Language agnostic No new language/compiler Leverage existing tools IDE, Compiler
Reachability Modulo Theories
 Reachability Modulo Theories Akash Lal and Shaz Qadeer Microsoft Research {akashl, qadeer@microsoft.com Abstract. Program verifiers that attempt to verify programs automatically pose the verification problem
Reachability Modulo Theories Akash Lal and Shaz Qadeer Microsoft Research {akashl, qadeer@microsoft.com Abstract. Program verifiers that attempt to verify programs automatically pose the verification problem
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java
 Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design
 Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design Prahlad Sampath (Prahlad.Sampath@mathworks.com) 2018 by The MathWorks, Inc., MATLAB, Simulink, Stateflow, are registered trademarks of The MathWorks,
Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design Prahlad Sampath (Prahlad.Sampath@mathworks.com) 2018 by The MathWorks, Inc., MATLAB, Simulink, Stateflow, are registered trademarks of The MathWorks,
Software Excellence via. at Microsoft
 Software Excellence via Program Analysis at Microsoft Used by permission for 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich, Instructor Manuvir Das Center for Software Excellence Microsoft
Software Excellence via Program Analysis at Microsoft Used by permission for 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich, Instructor Manuvir Das Center for Software Excellence Microsoft
Lightweight Verification of Array Indexing
 Lightweight Verification of Array Indexing Martin Kellogg*, Vlastimil Dort**, Suzanne Millstein*, Michael D. Ernst* * University of Washington, Seattle ** Charles University, Prague The problem: unsafe
Lightweight Verification of Array Indexing Martin Kellogg*, Vlastimil Dort**, Suzanne Millstein*, Michael D. Ernst* * University of Washington, Seattle ** Charles University, Prague The problem: unsafe
Seminar in Software Engineering Presented by Dima Pavlov, November 2010
 Seminar in Software Engineering-236800 Presented by Dima Pavlov, November 2010 1. Introduction 2. Overview CBMC and SAT 3. CBMC Loop Unwinding 4. Running CBMC 5. Lets Compare 6. How does it work? 7. Conclusions
Seminar in Software Engineering-236800 Presented by Dima Pavlov, November 2010 1. Introduction 2. Overview CBMC and SAT 3. CBMC Loop Unwinding 4. Running CBMC 5. Lets Compare 6. How does it work? 7. Conclusions
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Refining Interprocedural Change-Impact Analysis using Equivalence Relations
 Refining Interprocedural Change-Impact Analysis using Equivalence Relations Alex Gyori University of Illinois, USA gyori@illinois.edu Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research, USA shuvendu@microsoft.com Nimrod
Refining Interprocedural Change-Impact Analysis using Equivalence Relations Alex Gyori University of Illinois, USA gyori@illinois.edu Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research, USA shuvendu@microsoft.com Nimrod
Static Analysis in Practice
 in Practice 15-313: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich 1 Outline: in Practice Case study: Analysis at ebay Case study: Analysis at Microsoft Analysis Results and Process Example: Standard
in Practice 15-313: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich 1 Outline: in Practice Case study: Analysis at ebay Case study: Analysis at Microsoft Analysis Results and Process Example: Standard
A Comparison of SPARK with MISRA C and Frama-C
 A Comparison of SPARK with MISRA C and Frama-C Johannes Kanig, AdaCore October 2018 Abstract Both SPARK and MISRA C are programming languages intended for high-assurance applications, i.e., systems where
A Comparison of SPARK with MISRA C and Frama-C Johannes Kanig, AdaCore October 2018 Abstract Both SPARK and MISRA C are programming languages intended for high-assurance applications, i.e., systems where
Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar
 Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar John Plaice, Senior Scientist, GrammaTech jplaice@grammatech.com 25 July 2017, Meetup C++ de Montréal Abstract Static program analysis consists of the analysis
Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar John Plaice, Senior Scientist, GrammaTech jplaice@grammatech.com 25 July 2017, Meetup C++ de Montréal Abstract Static program analysis consists of the analysis
Testing Library Specifications by Verifying Conformance Tests
 Testing Library Specifications by Verifying Conformance Tests Joseph R. Kiniry, Daniel M. Zimmerman, Ralph Hyland ITU Copenhagen, UW Tacoma, UCD Dublin 6th International Conference on Tests & Proofs Prague,
Testing Library Specifications by Verifying Conformance Tests Joseph R. Kiniry, Daniel M. Zimmerman, Ralph Hyland ITU Copenhagen, UW Tacoma, UCD Dublin 6th International Conference on Tests & Proofs Prague,
Secure Programming. An introduction to Splint. Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E
 Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
CSSV: Towards a Realistic Tool for Statically Detecting All Buffer Overflows in C
 CSSV: Towards a Realistic Tool for Statically Detecting All Buffer Overflows in C Nurit Dor, Michael Rodeh, Mooly Sagiv PLDI 2003 DAEDALUS project Vulnerabilities of C programs /* from web2c [strpascalc]
CSSV: Towards a Realistic Tool for Statically Detecting All Buffer Overflows in C Nurit Dor, Michael Rodeh, Mooly Sagiv PLDI 2003 DAEDALUS project Vulnerabilities of C programs /* from web2c [strpascalc]
Program Verification (6EC version only)
 Program Verification (6EC version only) Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Overview Program Verification using Verification Condition Generators JML a formal specification language
Program Verification (6EC version only) Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Overview Program Verification using Verification Condition Generators JML a formal specification language
Failure-Directed Program Trimming
 Failure-Directed Program Trimming ABSTRACT Kostas Ferles The University of Texas at Austin, USA kferles@cs.utexas.edu Maria Christakis University of Kent, UK M.Christakis@kent.ac.uk This paper describes
Failure-Directed Program Trimming ABSTRACT Kostas Ferles The University of Texas at Austin, USA kferles@cs.utexas.edu Maria Christakis University of Kent, UK M.Christakis@kent.ac.uk This paper describes
Using Type Annotations to Improve Your Code
 Using Type Annotations to Improve Your Code Birds-of-a-Feather Session Werner Dietl, University of Waterloo Michael Ernst, University of Washington Open for questions Survey: Did you attend the tutorial?
Using Type Annotations to Improve Your Code Birds-of-a-Feather Session Werner Dietl, University of Waterloo Michael Ernst, University of Washington Open for questions Survey: Did you attend the tutorial?
Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning
 Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning Alex Summers, ETH Zurich Joint work with Uri Juhasz, Ioannis Kassios, Peter Müller, Milos Novacek, Malte Schwerhoff (and many students)
Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning Alex Summers, ETH Zurich Joint work with Uri Juhasz, Ioannis Kassios, Peter Müller, Milos Novacek, Malte Schwerhoff (and many students)
Overview AEG Conclusion CS 6V Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen. Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas
 CS 6V81.005 Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas February 20 th, 2012 Outline 1 Overview Introduction Considerations 2 AEG Challenges
CS 6V81.005 Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas February 20 th, 2012 Outline 1 Overview Introduction Considerations 2 AEG Challenges
Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability
 Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation void bar(foo f) { f.m();... } bar() expects functionality
Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation void bar(foo f) { f.m();... } bar() expects functionality
Introduction to CBMC. Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA Arie Gurfinkel December 5, 2011
 Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 December 5, 2011 based on slides by Daniel Kroening Bug Catching with SAT-Solvers Main Idea: Given a program and a claim use
Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 December 5, 2011 based on slides by Daniel Kroening Bug Catching with SAT-Solvers Main Idea: Given a program and a claim use
Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties
 Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties Brian Hackett Stanford University, CA bhackett@stanford.edu Shuvendu K. Lahiri, Shaz Qadeer, Thomas Ball Microsoft Research, WA {shuvendu,qadeer,tball@microsoft.com
Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties Brian Hackett Stanford University, CA bhackett@stanford.edu Shuvendu K. Lahiri, Shaz Qadeer, Thomas Ball Microsoft Research, WA {shuvendu,qadeer,tball@microsoft.com
A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity
 A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity Serdar Tasiran Koc University Istanbul, Turkey Tayfun Elmas Koc University Istanbul, Turkey RV 2007 March 13, 2007 Outline This paper: Define rollback
A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity Serdar Tasiran Koc University Istanbul, Turkey Tayfun Elmas Koc University Istanbul, Turkey RV 2007 March 13, 2007 Outline This paper: Define rollback
Static Analysis in Practice
 in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
Overview. Verification with Functions and Pointers. IMP with assertions and assumptions. Proof rules for Assert and Assume. IMP+: IMP with functions
 Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study. Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU
 Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
Towards practical reactive security audit using extended static checkers
 2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy Towards practical reactive security audit using extended static checkers Julien Vanegue Bloomberg L.P. New York, NY, USA jvanegue@bloomberg.net Shuvendu K. Lahiri
2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy Towards practical reactive security audit using extended static checkers Julien Vanegue Bloomberg L.P. New York, NY, USA jvanegue@bloomberg.net Shuvendu K. Lahiri
Statically Detecting Likely Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities
 Statically Detecting Likely Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities David Larochelle and David Evans USENIX'01 David Larochelle and David Evans IEEE Software Jan/Feb 2002 Presented by Adam Polyak 30.03.2014 Outline
Statically Detecting Likely Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities David Larochelle and David Evans USENIX'01 David Larochelle and David Evans IEEE Software Jan/Feb 2002 Presented by Adam Polyak 30.03.2014 Outline
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine
 The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties
 Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties Thomas Ball 1, Brian Hackett 2, Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1 Shaz Qadeer 1, and Julien Vanegue 1 1 Microsoft 2 Stanford University Abstract. Theorem-prover
Towards scalable modular checking of user-defined properties Thomas Ball 1, Brian Hackett 2, Shuvendu K. Lahiri 1 Shaz Qadeer 1, and Julien Vanegue 1 1 Microsoft 2 Stanford University Abstract. Theorem-prover
The Boogie Intermediate Language
 The Boogie Intermediate Language What is BoogiePL? A simplified C-like language that s structured for verification tasks Has constructs that allow specification of assumptions and axioms, as well as assertions
The Boogie Intermediate Language What is BoogiePL? A simplified C-like language that s structured for verification tasks Has constructs that allow specification of assumptions and axioms, as well as assertions
Program Verification. Aarti Gupta
 Program Verification Aarti Gupta 1 Agenda Famous bugs Common bugs Testing (from lecture 6) Reasoning about programs Techniques for program verification 2 Famous Bugs The first bug: A moth in a relay (1945)
Program Verification Aarti Gupta 1 Agenda Famous bugs Common bugs Testing (from lecture 6) Reasoning about programs Techniques for program verification 2 Famous Bugs The first bug: A moth in a relay (1945)
Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction
 Software Tools for Technology Transfer manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction Mikhail Y. R. Gadelha, Hussama I. Ismail, and
Software Tools for Technology Transfer manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction Mikhail Y. R. Gadelha, Hussama I. Ismail, and
Bounded Model Checking Of C Programs: CBMC Tool Overview
 Workshop on Formal Verification and Analysis Tools, CFDVS, IIT-Bombay - Feb 21,2017 Bounded Model Checking Of C Programs: CBMC Tool Overview Prateek Saxena CBMC Developed and Maintained by Dr Daniel Kröning
Workshop on Formal Verification and Analysis Tools, CFDVS, IIT-Bombay - Feb 21,2017 Bounded Model Checking Of C Programs: CBMC Tool Overview Prateek Saxena CBMC Developed and Maintained by Dr Daniel Kröning
Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1
 École de Recherche: Semantics and Tools for Low-Level Concurrent Programming ENS Lyon Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1 Alastair Donaldson Imperial College London www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~afd
École de Recherche: Semantics and Tools for Low-Level Concurrent Programming ENS Lyon Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1 Alastair Donaldson Imperial College London www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~afd
Lecture 1 Contracts. 1 A Mysterious Program : Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning
 Lecture 1 Contracts 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning In these notes we review contracts, which we use to collectively denote function contracts, loop invariants,
Lecture 1 Contracts 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning In these notes we review contracts, which we use to collectively denote function contracts, loop invariants,
Static Vulnerability Analysis
 Static Vulnerability Analysis Static Vulnerability Detection helps in finding vulnerabilities in code that can be extracted by malicious input. There are different static analysis tools for different kinds
Static Vulnerability Analysis Static Vulnerability Detection helps in finding vulnerabilities in code that can be extracted by malicious input. There are different static analysis tools for different kinds
SMT-Based Modular Analysis of Sequential Systems Code
 SMT-Based Modular Analysis of Sequential Systems Code Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Abstract. In this paper, we describe a few challenges that accompany SMTbased precise verification of systems
SMT-Based Modular Analysis of Sequential Systems Code Shuvendu K. Lahiri Microsoft Research Abstract. In this paper, we describe a few challenges that accompany SMTbased precise verification of systems
Software Excellence via Program Analysis at Microsoft. Manuvir Das
 Software Excellence via Program Analysis at Microsoft Used by permission for 17-654/17-754: Jonathan Aldrich, Instructor Manuvir Das Center for Software Excellence Microsoft Corporation Talking the talk
Software Excellence via Program Analysis at Microsoft Used by permission for 17-654/17-754: Jonathan Aldrich, Instructor Manuvir Das Center for Software Excellence Microsoft Corporation Talking the talk
David Glasser Michael D. Ernst CSAIL, MIT
 static dynamic intraprocedural interprocedural Shay Artzi, Adam Kiezun, David Glasser Michael D. Ernst CSAIL, MIT Parameter P of method M is: Mutable if some execution of M can change the state of P s
static dynamic intraprocedural interprocedural Shay Artzi, Adam Kiezun, David Glasser Michael D. Ernst CSAIL, MIT Parameter P of method M is: Mutable if some execution of M can change the state of P s
Appendix to The Health of Software Engineering Research
 Appendix to The Health of Software Engineering Research David Lo School of Information Systems Singapore Management University Singapore davidlo@smu.edu.sg Nachiappan Nagappan and Thomas Zimmermann Research
Appendix to The Health of Software Engineering Research David Lo School of Information Systems Singapore Management University Singapore davidlo@smu.edu.sg Nachiappan Nagappan and Thomas Zimmermann Research
Rubicon: Scalable Bounded Verification of Web Applications
 Joseph P. Near Research Statement My research focuses on developing domain-specific static analyses to improve software security and reliability. In contrast to existing approaches, my techniques leverage
Joseph P. Near Research Statement My research focuses on developing domain-specific static analyses to improve software security and reliability. In contrast to existing approaches, my techniques leverage
A Context-Sensitive Memory Model for Verification of C/C++ Programs
 A Context-Sensitive Memory Model for Verification of C/C++ Programs Arie Gurfinkel and Jorge A. Navas University of Waterloo and SRI International SAS 17, August 30th, 2017 Gurfinkel and Navas (UWaterloo/SRI)
A Context-Sensitive Memory Model for Verification of C/C++ Programs Arie Gurfinkel and Jorge A. Navas University of Waterloo and SRI International SAS 17, August 30th, 2017 Gurfinkel and Navas (UWaterloo/SRI)
HECTOR: Formal System-Level to RTL Equivalence Checking
 ATG SoC HECTOR: Formal System-Level to RTL Equivalence Checking Alfred Koelbl, Sergey Berezin, Reily Jacoby, Jerry Burch, William Nicholls, Carl Pixley Advanced Technology Group Synopsys, Inc. June 2008
ATG SoC HECTOR: Formal System-Level to RTL Equivalence Checking Alfred Koelbl, Sergey Berezin, Reily Jacoby, Jerry Burch, William Nicholls, Carl Pixley Advanced Technology Group Synopsys, Inc. June 2008
Automated Testing of Tableau Dashboards
 Kinesis Technical Whitepapers April 2018 Kinesis CI Automated Testing of Tableau Dashboards Abstract Companies make business critical decisions every day, based on data from their business intelligence
Kinesis Technical Whitepapers April 2018 Kinesis CI Automated Testing of Tableau Dashboards Abstract Companies make business critical decisions every day, based on data from their business intelligence
Synthesis of Synchronization using Uninterpreted Functions
 Synthesis of Synchronization using Uninterpreted Functions* October 22, 2014 Roderick Bloem, Georg Hofferek, Bettina Könighofer, Robert Könighofer, Simon Außerlechner, and Raphael Spörk * This work was
Synthesis of Synchronization using Uninterpreted Functions* October 22, 2014 Roderick Bloem, Georg Hofferek, Bettina Könighofer, Robert Könighofer, Simon Außerlechner, and Raphael Spörk * This work was
MEMORY MANAGEMENT TEST-CASE GENERATION OF C PROGRAMS USING BOUNDED MODEL CHECKING
 FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF AMAZONAS INSTITUTE OF COMPUTING GRADUATE PROGRAM IN COMPUTER SCIENCE MEMORY MANAGEMENT TEST-CASE GENERATION OF C PROGRAMS USING BOUNDED MODEL CHECKING Herbert Rocha, Raimundo Barreto,
FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF AMAZONAS INSTITUTE OF COMPUTING GRADUATE PROGRAM IN COMPUTER SCIENCE MEMORY MANAGEMENT TEST-CASE GENERATION OF C PROGRAMS USING BOUNDED MODEL CHECKING Herbert Rocha, Raimundo Barreto,
One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Language Security
 Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice
 Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Formal Methods for Java
 Formal Methods for Java Lecture 30: Conclusion Jochen Hoenicke Software Engineering Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg Feb 17, 2012 Jochen Hoenicke (Software Engineering) FM4J Feb 17, 2012 1 / 21 Topics
Formal Methods for Java Lecture 30: Conclusion Jochen Hoenicke Software Engineering Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg Feb 17, 2012 Jochen Hoenicke (Software Engineering) FM4J Feb 17, 2012 1 / 21 Topics
Software Security IV: Fuzzing
 1 Software Security IV: Fuzzing Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Homework1 Due: Friday Oct 27 11:59pm Questions regarding reading materials Talk Security R&D in a Security Company:
1 Software Security IV: Fuzzing Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Homework1 Due: Friday Oct 27 11:59pm Questions regarding reading materials Talk Security R&D in a Security Company:
Course Overview CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone
 Course Overview CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone Ras Bodik Emina Torlak Division of Computer Science University of California, Berkeley The name of the course this CS294 topics course has been listed
Course Overview CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone Ras Bodik Emina Torlak Division of Computer Science University of California, Berkeley The name of the course this CS294 topics course has been listed
Code Contracts. Pavel Parízek. CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics
 Code Contracts http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Pavel Parízek Code Contracts 2 Assertions Typically used as internal checks in the program
Code Contracts http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Pavel Parízek Code Contracts 2 Assertions Typically used as internal checks in the program
The Importance of Benchmarks for Tools that Find or Prevent Buffer Overflows
 The Importance of Benchmarks for Tools that Find or Prevent Buffer Overflows Richard Lippmann, Michael Zhivich Kendra Kratkiewicz, Tim Leek, Graham Baker, Robert Cunningham lippmann@ll.mit.edu To be presented
The Importance of Benchmarks for Tools that Find or Prevent Buffer Overflows Richard Lippmann, Michael Zhivich Kendra Kratkiewicz, Tim Leek, Graham Baker, Robert Cunningham lippmann@ll.mit.edu To be presented
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs. {livshits,
 Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Advanced Programming Methods. Introduction in program analysis
 Advanced Programming Methods Introduction in program analysis What is Program Analysis? Very broad topic, but generally speaking, automated analysis of program behavior Program analysis is about developing
Advanced Programming Methods Introduction in program analysis What is Program Analysis? Very broad topic, but generally speaking, automated analysis of program behavior Program analysis is about developing
Programming Languages Research at the University of Colorado, Boulder
 Amer Diwan Jeremy Siek Bor-Yuh Evan Chang Sriram Sankaranarayanan Programming Languages Research at the University of Colorado, Boulder PL research at CU has breadth! How do we effectively express computation?
Amer Diwan Jeremy Siek Bor-Yuh Evan Chang Sriram Sankaranarayanan Programming Languages Research at the University of Colorado, Boulder PL research at CU has breadth! How do we effectively express computation?
Lecture 1 Contracts : Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning
 Lecture 1 Contracts 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning In these notes we review contracts, which we use to collectively denote function contracts, loop invariants,
Lecture 1 Contracts 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning In these notes we review contracts, which we use to collectively denote function contracts, loop invariants,
WHITE PAPER. 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development
 WHITE PAPER 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development Overview Software is in everything. And in many embedded systems like flight control, medical devices, and powertrains, quality
WHITE PAPER 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development Overview Software is in everything. And in many embedded systems like flight control, medical devices, and powertrains, quality
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone
 Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
Selective Context-Sensitivity Guided by Impact Pre-Analysis
 Selective Context-Sensitivity Guided by Impact Pre-Analysis 1 1 1 Hakjoo Oh Wonchan Lee Kihong Heo 2 1 Hongseok Yang Kwangkeun Yi 1 Seoul National University 2University of Oxford PLDI 2014 @Edinburgh,
Selective Context-Sensitivity Guided by Impact Pre-Analysis 1 1 1 Hakjoo Oh Wonchan Lee Kihong Heo 2 1 Hongseok Yang Kwangkeun Yi 1 Seoul National University 2University of Oxford PLDI 2014 @Edinburgh,
Lecture Outline. COOL operational semantics. Operational Semantics of Cool. Motivation. Notation. The rules. Evaluation Rules So Far.
 Lecture Outline Operational Semantics of Cool COOL operational semantics Motivation Adapted from Lectures by Profs. Alex Aiken and George Necula (UCB) Notation The rules CS781(Prasad) L24CG 1 CS781(Prasad)
Lecture Outline Operational Semantics of Cool COOL operational semantics Motivation Adapted from Lectures by Profs. Alex Aiken and George Necula (UCB) Notation The rules CS781(Prasad) L24CG 1 CS781(Prasad)
The Spin Model Checker : Part I/II
 The Spin Model Checker : Part I/II Moonzoo Kim CS Dept. KAIST Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Motivation: Tragic Accidents Caused by SW Bugs 2 Cost of Software Errors June 2002 Software
The Spin Model Checker : Part I/II Moonzoo Kim CS Dept. KAIST Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Motivation: Tragic Accidents Caused by SW Bugs 2 Cost of Software Errors June 2002 Software
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
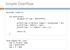 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C
 Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C David Bühler CEA LIST, Software Safety Lab Frama-C & SPARK Day 2017 May 30th, 2017 David
Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C David Bühler CEA LIST, Software Safety Lab Frama-C & SPARK Day 2017 May 30th, 2017 David
Test Automation. 20 December 2017
 Test Automation 20 December 2017 The problem of test automation Testing has repetitive components, so automation is justified The problem is cost-benefit evaluation of automation [Kaner] Time for: test
Test Automation 20 December 2017 The problem of test automation Testing has repetitive components, so automation is justified The problem is cost-benefit evaluation of automation [Kaner] Time for: test
