(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
|
|
|
- Rebecca Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US 2004O A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1 Sekine (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 10, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR (75) Inventor: Hirokazu Sekine, Kanagawa-ken (JP) Correspondence Address: OBLON, SPIVAK, MCCLELLAND, MAIER & NEUSTADT, P.C DUKE STREET ALEXANDRIA, VA (US) (73) Assignee: KABUSHIKI KAISHA TOSHIBA, Tokyo (JP) (21) Appl. No.: 10/675,960 (22) Filed: Oct. 2, 2003 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 2, 2002 (JP) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... H01L 27/10 (52) U.S. Cl /202 (57) ABSTRACT In the pixel portions of the CMOS image sensor, a plurality of unit cells are arranged in the row and column directions at a predetermined pitch respectively in a two-dimensional plain forming a matrix. Each unit cell includes the first and second photodiodes PDa and PDb, the first and second transfer transistors Ta and Tb for transferring the stored charges of the photodiodes to their common floating junc tions FJ, the reset transistors R for resetting the potential of the floating junctions FJ, the driver transistors D whose output potential is controlled by the potential of the floating junctions FJ, and the address transistors A for Selectively driving the driver transistors D. The floating junction area FJ, the reset transistors R, the driver transistors D, and the address transistors A are com monly used for reading Signal charges Stored in the first and second photodiodes PDa and PDb. With the arrangement of the elements and wires in the pixel portions, the integration can be increased and the resolution in the horizontal and vertical directions can be improved.
2 Patent Application Publication Jun. 10, 2004 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2004/ A1
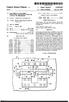
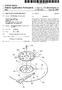
3 Patent Application Publication Jun. 10, 2004 Sheet 2 of 7 US 2004/ A1 Fig. 2 Fingle Pho, 2 h92 Ph 11 Gy o \ RDL1 SL1 RD-2 SL2 RDL3 S-3 RD D 3 Fis (RS) RS 3 RSL l t 12 f PO3a S13 ce F: Stega 3a TGL ICERS E 5EE 1 a fit TE V 2R TGL1 GibJ11 A r EEE 12b A12 13.b A13 h Pvo POb EE Y AD3a ROrigera2. ^S-2 Ceglished;is TG TG21stSR225SER E. IS2s L2a Fif T w EFEEE b TG2b J TG2b-22 es TG23b23 péire T2b A21 : 6 A22 E. A2 ADL2 AD2 AD22 23 SPEPs TGL3a TG3:SRTG : 5Rf Sid is "EEEEEE 3. T r G3b J3 TG3232 G33b A. r 33 3b A 32D A32, P33 A33 AD-3 PD31b AD AD32-' AD 33 RD - R2 RDs,
4
5
6
7
8
9 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, 2004 CMOS IMAGE SENSOR BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to a CMOS image Sensor having one unit cell composed of two pixels, which is Suited to a Solid image pick up device Such as a digital cameral or a camera System for mobile equipment As well known, a CMOS image sensor can be manufactured by the CMOS technology, which is widely used for manufacturing Semiconductor devices having a Small size and low power consumption and which can install a peripheral circuit Such as a signal processor together with the image Sensors in one chip. Thus, the CMOS image Sensor is noticed as an alternative device to a CCD device conventionally used as an image pick up device. 0003) A conventional CMOS image sensor is known, in which a unit cell Ce forming a pixel portion has two photodiodes PDa and PDb and one floating junction FJ, which is shared by the photodiodes PDa and PDb However, the conventional CMOS image sensor has pixels, which are arranged in a matrix having horizontal and vertical pitches of Ph and Pv respectively, which provide So long intervals between adjacent pixels in the horizontal and Vertical directions that information between pixels can not be picked up. Therefore, a problem arises that Sufficient resolution of the Sensor cannot be obtained. As a means for improving the resolution of the Sensor, high integration of the Sensor is conceivable. However, there is a limit in making the diodes and transistor elements constituting the pixel portion be reduced in their sizes and in making fine wires, thus there is also a limit in the improvement of the resolution of the Sensor The present invention is made in view of the above-mentioned circumstances and it is therefore one of the objects of the present invention is to provide a CMOS image Sensor, which make it possible to increase the integration by efficiently arranging elements and wires constituting the pixel portions without making the elements and wires Small or fine and thereby to improve the resolution in the hori Zontal and vertical directions. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION 0006 ACMOS image sensor according to an embodi ment of the present invention has a plurality of unit cells arranged in the row and column directions at a predeter mined pitch respectively in a two-dimensional plain forming a matrix, which include a first and a Second photoelectric conversion element, a first and a Second transfer transistor for transferring charges Stored by the photoelectric conver Sion elements at their common floating junctions, reset transistors for resetting the potential of the floating junc tions, driver transistors whose output potential is controlled by the potential of the floating junctions, and address tran sistors for selectively driving the driver transistors. The CMOS image sensor further includes reset drain voltage lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrange ment for resetting the potential of the common floating junctions included in the unit cell belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement, first transfer lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the first transfer transistor included in the unit cell belonging to each row, Second transfer lines in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the Second transfer tran Sistors included in the unit cells belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement, Signal output lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement to which the output voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement are Supplied, and address lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for Selectively driving the driver transistors included in the unit cell belonging to each row Further, a CMOS image sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention has a plurality of unit cells arranged in the row and column directions at a prede termined pitch respectively in a two-dimensional plain form ing a matrix, which include a first and a Second photoelectric conversion element, a first and a Second transfer transistor for transferring charges Stored by the photoelectric conver Sion elements at their common floating junctions, reset transistors for resetting the potential of the floating junc tions, driver transistors whose output potential is controlled by the potential of the floating junctions, and address tran sistors for selectively driving the driver transistors. The CMOS image sensor further includes reset drain voltage lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrange ment for resetting the potential of the common floating junctions included in the unit cell belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement, first transfer lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the first transfer transistor included in the unit cell belonging to each row, Second transfer lines in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the Second transfer tran Sistors included in the unit cells belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement, 0008 first signal output lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement to which the output Voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells arranged in the odd numbered rows are Supplied, Second Signal output lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement to which the output voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells arranged in the even numbered rows are Supplied, and address lines pro Vided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for Selectively driving the driver transistors included in the unit cell belonging to each row, wherein image Signals of the pixel arrays composed of the photoelectric conversion ele ments included in the unit cells arranged in the neighboring two columns are read Simultaneously using the first and Second Signal output lines Furthermore, in the CMOS image sensor according to Still another embodiment of the present invention, each gate of the address transistor included in the unit cell arranged in the first column is connected to each correspond ing gate of the reset transistor included in the unit cell arranged in the adjacent Second column, wherein while the image Signals from the Second photoelectric conversion elements included in the unit cells arranged in the first column are read, the floating junctions included in the unit cells arranged in the Second column, which should be read in the next time are reset, and thus the image Signal from the first photoelectric conversion elements included in the unit cells arranged in the Second column can be read.
10 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, 2004 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an entire structure of a CMOS image sensor in the embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of a pixel portion of the image sensor shown in FIG. 1, 0012 FIG. 3 is a drawing showing an IC circuit pattern constituting the pixel portion shown in FIG. 2, 0013 FIG. 4 is a circuit diagram showing a second embodiment of the pixel portion of the image Sensor shown in FIG. 1, FIG. 5 is a drawing showing another IC circuit pattern constituting a pixel portion shown in FIG. 4, FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing a third embodi ment of the pixel portion of the image sensor shown in FIG. 1, and 0016 FIG. 7 is a drawing showing further IC circuit pattern constituting a pixel portion shown in FIG. 6. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The preferred embodiments of the present inven tion will be explained below with reference to the accom panying drawings FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an entire structure of the CMOS image sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention The CMOS image sensor has a pixel portion 4, in which each of a plurality of unit cells Ce is composed of a pixel 2 including two photodiodes PDa and PDb and a pixel amplifier 3. In the pixel portion 4, the unit cells Ce are arranged in the row and column directions at a predeter mined pitch of Pho and Pvo respectively in a two-dimen Sional plain forming a matrix. 0020) Further, around the pixel portion 4, a timing gen eration circuit 5, a vertical line Scanning circuit 6, a noise cancel circuit 7, a horizontal line Scanning circuit 8 and an output amplifier 9 are arranged to form a reading unit FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram showing the pixel portion 4 of the image sensor shown in FIG. 1. In the drawing, a pixel portion 11 is a circuit diagram showing a part of the pixel portion 4 shown in FIG. 1. In the pixel portion 11, the photodiodes PDa and PDb respectively constitute one pixel and the two photodiodes PDa and PDb constitute one unit cell Ce. The unit cells Ce are arranged in the row and column directions at a predetermined pitch of PhO and Pv0 respectively in a two-dimensional plain form ing a matrix Further, each unit cell Ce in the pixel portion 11 further includes two transfer transistors Ta and Tb, a reset transistor R, a driver transistor I, and an address transistor A in addition to a pair of photodiodes PDa and PDb. The pixel portion 11 is formed on the same Semiconductor Substrate using the integrated circuit technology In FIG. 2, the two photodiodes included in each unit cell Ce are indicated as PD11a, PD1b, PD12a, PD12b, - - -, according to the position in the matrix arrangement. However, hereinafter, when the two photodiodes are repre Sentatively explained regardless of their positions, they are indicated as PDa and PDb. Further, the other elements constituting each unit cell Ce are also indicated in the same way In FIG. 2, the two photodiodes PDa and PDb are respectively connected to Source electrodes of the corre sponding transfer transistors Ta and Tb. Transfer pulses for reading pixel Signals are respectively applied to gates TGa and TGb of the transfer transistors Ta and Tb from transfer lines TGLa and TGLb. Further, the floating junctions FJ, which are drain electrodes of the transfer transistors Ta and Tb, are connected to the Source electrodes of the reset transistor R and a gate DR of the driver transistor D. 0025) Furthermore, the drain electrodes of the reset tran Sistor R are connected to a reset drain Voltage line RDL and a gate RS is connected to a reset line RSL. The reset line RSL applies a pulse for resetting the floating junction FJ to a predetermined reset drain Voltage to the gate RS Source electrodes of the driver transistors D are connected to a signal output line SL and drain electrodes of which are connected to Source electrodes of address tran Sistors. A via a junction areas J. Further, the drain electrodes of the address transistors A are connected to reset drain Voltage lines RDL and a gate AD of which are connected to address lines ADL. The address lines ADL provide the gate AD with address pulses for Selecting the address transistors A arranged in the horizontal direction. By Selecting the address transistorsa, pixel Signals are read out to the Signal output lines SL via the corresponding driver transistors D The pixel portion 11, as mentioned above, is com posed of a plurality of unit cells Ce arranged in a matrix. Noticing the photodiodes PDa and PDb, which are corre sponded to the respective pixels in the pixel portion 11, the photodiodes PDa constituting the respective unit cells Ce and arranged in a horizontal row form a first pixel line. Similarly, the photodiodes PDb constituting the respective unit cells Ce and arranged in a horizontal row form a Second pixel line adjacent to the first pixel line. Thus, the adjacent first and Second pixel lines are formed repeatedly in the Vertical direction The photodiodes PDa in the first pixel lines are arranged at predetermined pitches of PhO and Pv0, which are equal to the pitches of the unit cells Ce arrangement in the horizontal and vertical directions. The photodiodes PDb in the Second pixel lines are also arranged at the predetermined pitches of PhO and Pv0, which are equal to the pitches of the unit cells Ce arrangement in the horizontal and Vertical directions The photodiodes PDa arranged in the first pixel lines and the photodiodes PDb arranged in the second pixel lines are dislocated by PhO/2 and Pv0/2 respectively in the horizontal and vertical directions and are arranged checker wise as a whole. Further, when the unit cells Ce are arranged in a square matrix, PhO becomes equal to Pv0 and the pixel pitches in the horizontal and Vertical directions are made equal to each other. As a result, the photodiodes PDa and photodiodes PDb included in the respective unit cells Ce are Slanted by 45 degrees.
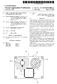
11 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, FIG. 3 shows an IC circuit pattern forming the pixel portion shown in FIG ) Noticing a unit cell Ce 22 positioned at the center in the drawing, a unit cell Ce 21 and a unit cell Ce 23 are located adjacent to the unit cell Ce 22 in the horizontal direction and a unit cell Ce 12 and a unit cell Ce 32 are located adjacent to the unit cell Ce 22 in the vertical direction. A pair of photodiodes PD22a and PD22b of the unit cell Ce 22 are spaced by PhO/2 and Pv0/2 in the horizontal and Vertical directions with each other and are indicated with a rectangle inclined by 45 degrees Between the two photodiodes PD22a and PD22b, gates TG22a and TG22b of the transfer transistors T22a and T22b a replaced side by side. Between the gates TG22a and TG22b, a floating junction FJ22 is placed. In the neighbor hood of the floating junction FJ22, a gate RS22 of the reset transistor R22 is placed. Source electrodes of the transistor R22 are connected to the floating junction FJ In the neighborhood of the gate RS22 of the reset transistor R22, a reset drain area RD22 is provided, to which drain electrodes of the reset transistor R22 are connected On the opposite side of the gate RS22 to the floating junction FJ22, a gate DR22 of the driver transistor D22 is adjacently placed on both sides of the gate DR22, a diffusion area S22 and a junction area J22 are placed. The diffusion area S22 corresponds to the connecting portion of the Source electrodes of the driver transistor D22 with the Signal output line S2. The junction area J22 corresponds to the connecting portion of the drain electrodes of the driver resistor D22 with the Source electrodes of the address transistor A22. Furthermore, in the neighborhood of the junction area J22, a gate AD22 of the address transistor A22 is placed. 0035) Further, the floating junction FJ22 and the gate DR22 of the driver transistor D22 are connected by a metallic line AL Such as aluminum The other unit cells Ce11, ce12, are also formed with the Same circuit pattern as the aforementioned. Furthermore, although not shown in FIG. 3 but shown in the circuit diagram in FIG. 2, transfer lines TGL1a, TGL1b, TGL2a, TGL2b, - - -, reset lines RSL1, RSL2, - - -, address lines ADL1, ADL2, - - -, reset drain voltage lines RDL1, RDL2, and Signal output lines SL1, SL2, are formed by metallic lines Such as aluminum in the corresponding respective positions Next, the operation of the CMOS image sensor having Such a configuration will be outlined. An optical image of an object is focused on the pixel portion 11 by the optical lens System (not shown in the drawing). The optical image is converted into an electric Signal by the photodiodes PDa and PDb, each of which provides at its output terminal a pixel Signal corresponding to the image. The image Signals are read for each pixel line constituting the pixel portion 11. For example, electric charges representing Signals generated by the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, arranged in the first row of the matrix arrangement are transferred and stored in the floating junctions FJ11, FJ12, FJ13, - - -, by applying transfer pulses to the gates TG11, TG12a, TC13a of the transfer transistors T11a, T12a, T13a, via the transfer line TGL1a and by opening the gates In this case, prior to reading Such signal charges, the floating junctions FJ11, FJ 12, FJ13, are reset to predetermined reset drain Voltages. Namely, the reset tran SistorS R11, R12, are turned from a non-conducting State to a conducting State, by providing the gates RS11, RS12, with a reset pulse via the reset line RSL1, thereby reset the floating junctions FJ11, FJ 12, FJ13, to a fixed voltage given to the reset drain voltage lines RD11, RDI2, beforehand The voltage levels of the floating junctions FJ11, FJ12, FJ13, - - -, which are thus put into the reset state, are changed by being Supplied with the Signal charges from the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, since the floating junctions FJ11, FJ12, FJ are respectively connected to the gates DR11, DR12, DR13, of the driver transistors D11, D12, D13, - - -, potential changes in the floating junctions FJ11, FJ12, FJ13, cause modulation of the channel potential at the gates DR11, DR12, DR13, of the driver transistors D11, D12, D13, Next, an address pulse is applied to the gates AD11, AD12, AD13, of the address transistors A11, A12, A13, via the address line ADL1, thus the address transistors All, A12, A13, turned from a non- conducting State to a conducting state. Thus, the driver transistors D11, D12, D13, with the channel potentials being modulated by potential changes of the floating junctions FJ11, FJ 12, FJ13, are connected to the reset drain voltage lines RDL1, RDL2, - - -, So that Signals corresponding to the Signal charges Stored in the floating junctions FJ11, FJ 12, FJ13, are taken out to the signal output lines SL1, SL2, ) When reading of the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, forming the first pixel line is completed, the floating junctions PJ11, FJ 12, FJ13, are connected again to the reset drain voltage lines RDL1, RDL2, via the reset transistors R11, R12, and are reset to the reset drain Voltages Next, a transfer pulse is applied to the gates TG11b, TG12b, TC13bb, of the transfer transistors T11b, T12b, T13b, via the transfer line TGL1b so as to open the gates, thus signal charges generated by the photodiodes PD11, PD12b, PD13b, --- forming the second pixel line are transferred to the floating junctions FJ11, FJ12, FJ13, and Stored therein. The Same operation as the reading Signals from the first pixel line is repeated, thus signals correspond ing to the charges generated by the Second pixel line are read out by the Signal output lines SL1, SL2, Furthermore, with respect to the photodiode lines forming the third and fourth pixel line, that is, the photo diodes PD21a, PD22a, PD23a, and PD11b, PD12b, PD13b, included in the unit cells Ce21, Ce22, - - -, the floating junctions FJ21, FJ22, FJ23, are shared for reading of the Signal charges in the Same way as with the first and Second image line Repeating the same reading operation, hereinafter, pixel Signals are read out for all the horizontal pixel lines constituting the pixel portion The above mentioned image sensor according to the embodiment of the present invention has a characteristic that the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, - - -, and PD11b, PD12b, PD13b, --- are arranged checker wise in the pixel portion 11, as shown in FIG. 2. Further, the embodi
12 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, 2004 ment has another characteristic that a pair of transfer lines TGL1a and TGL1b is provided between adjacent pixel lines, so that the floating junctions FJ21, FJ22, FJ23, are shared by the adjacent pixel lines. Furthermore, due to the above characteristic, the embodiment has further character istic that the reset line RSL and address line ADL are shared by the adjacent pixel lines. According to the embodiment of the image Sensor having these characteristics, the integration in manufacturing with the Semiconductor technology can be greatly improved without reducing the size of the elements or width of the wires In other aspect for the aforementioned embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to improve the integration of the IC by adopting the circuit pattern of the pixel portion 11 as shown in FIG. 3. The circuit pattern is characterized in that between the paired photodiodes, for example, photodiodes PD22a and PD22b, the gates TG22a and TG22b of the corresponding transfer transistors T22a and T22b, the floating junction FJ22, and the gate RS22 of the reset transistor R22 are placed, and that, in the neigh borhood of them, the reset drain area RD22, the diffusion area S22, the gate DR22 of the driver transistor 122, the junction area J22, and the gate AD22 of the address transistor A22 are placed Further, since the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, - - -,, and PD11b, PD12b, PD13b, --- are arranged in checker wise, the pitch between adjacent photodiodes in the vertical and horizontal directions can be reduced to about a half of the pitch in the conventional image Sensors having a matrix arrangement of the photodiodes and thus the resolution in the vertical and horizontal directions can be improved. In this case, the resolution in the oblique direction is reduced. However, reduction in the resolution is not questionable in particular for a regular object Since the resolution of human eyes is higher in the vertical and horizontal directions than in the oblique direction and a regular object has rather more components in the vertical and horizontal directions than in the oblique direction The second embodiment of the present invention will be explained by referring to FIGS. 4 and 5. FIG. 4 is a circuit diagram showing the pixel portion of the image sensor shown in FIG. 1 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a drawing showing the IC circuit pattern constituting the pixel portion shown in FIG. 4. In the following explanation, the same numerals are assigned to the same parts as those of the first embodiment, with which the detailed explanation thereof is omitted and the different parts from those of the first embodiment will be explained in detail In FIGS. 4 and 5, a pixel portion 12 indicates a part of the pixel portion 4 shown in FIG. 1. The basic constitution having the checker wise arrangement of the each unit cell Ce of the pixel portion 12 is the same as that of the first embodiment. Further, the circuit pattern of the unit cell Ce is also the same as that of the first embodiment However, the differences from the first embodi ment areas follows. In the first embodiment, the Signal output lines SL1, SL2, are provided only one for each unit cell Ce, while in this embodiment, for example, two lines such as SLo1 and SLe1 are provided for each unit cell Ce. The Signal output lines SLO1, SLO2, are connected to the diffusion areas S11, S12, S13, - - -, S31, S32, S33, - - -, which are connecting portions to the Source electrodes of the driver transistors D11, D12, D13, - - -, D31, D32, D33, - - -, included in the unit cells Cel1, Cel2, Ce13, - - -, Ce31, Ce32, Ce33, - - -, arranged in the odd numbered rows of the matrix In a similar way, the signal output lines SLe1, SLe2, are connected to the diffusion areas S21, S22, S23, - - -, S41, S42, S43, - - -, which are connecting portions to the Source electrodes of the driver transistors D21, D22, D23, - - -, D41, D42, D43, - - -, included in the unit cells Ce21, Ce22, Ce23, - - -, Ce41, Ce42, ce43, arranged in the even numbered rows of the matrix, although unit cells Ce41, Ce42, and Ce43 are not shown in the drawings The second difference from the first embodiment is described below taking the unit ce11 Ce22 shown in FIG. 5 as an example The gate TG22a of the transfer transistor T22a for reading the photodiode PD22a of the unit cell Ce22 is connected to the gate TG12b of the transfer transistor T12b for reading the photodiode PD12b of the unit cell Ce12 with a Second metallic line AL2 Such as aluminum In a similar way, the gate TG22b of the transfer transistor T22b for reading the photodiode PD22b is con nected to the gate TG32a of the transfer transistor T32a for reading the photodiode PD32a of the unit cell ce32 with the Second metallic line AL2 Such as aluminum. With respect to the other unit cells Ce, the same connection is provided In the CMOS image sensor relating to the second embodiment of the present invention having Such a consti tution, the Signal output lines SLO1, SLO2, are provided for the unit cells arranged in the neighboring odd numbered rows in the matrix arrangement, and the Signal output lines SLe1, SLe2, are provided for the unit cells arranged in the neighboring even numbered rows in the matrix arrange ment. With this arrangement, pixel Signals are read as indicated below With respect to the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, in the first pixel row, Signals corresponding to the charges Stored are read out in the same way as in the first embodiment. With respect to the photodiodes PD11b, PD12b, PD13b, in the second pixel row and the photodiodes PD21a, PD22a, PD23a, in the third pixel row, Signals are simultaneously output to the Signal output lines SLe1, SLe2, and the signal output lines SLo1, SLO2, The reason is that with respect to the gates TG11b, TG12b, TG13b, of the transfer transistors T11b, T12b, T13b, and the gates TG21a, TG22a, TG23a, of the transfer transistorst21a, T22a, T23a, - - -, the correspond ing gates are connected to each other and also mutually connected to the transfer line TGL1b and TGL2a, so that transfer pulses are simultaneously applied to the gates of the transfer transistors corresponding to the photodiodes con Stituting the Second pixel row and third pixel row As a result, in a signal processing for reproduction of a picture, in which Signals obtained by Scanning adjacent horizontal two lines are combined, there is no need to Store the Signals obtained by a first horizontal Scanning until a Second Scanning is completed for a horizontal Scanning period. Thus the external circuit Such as a horizontal line Scanning circuit is Simplified According to the above-described embodiment, the external reading circuit is simplified, with which the inte
13 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, 2004 gration of the circuit can be more improved, and with which the resolution in the Vertical and horizontal directions are improved as in the same reason as with the first embodiment The third embodiment will be explained by refer ring to FIGS. 6 and 7. FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing the third embodiment of the pixel portion of the image sensor shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 7 is a drawing showing an IC circuit pattern of the pixel portion shown in FIG. 6. In the following explanation, the same numerals are assigned to the same parts as those of the first embodiment, and the detailed explanation thereof is omitted, and the different parts from the first embodiment will be explained in detail In FIGS. 6 and 7, a pixel portion 13 shows a part of the pixel portion 4 of the CMOS image sensor shown in FIG. 1, au the pixel portion 11 in the first embodiment. The basic constitution having the checker wise arrangement of the each unit cell Ce of the pixel portion 13 is the same as that of the first embodiment Further, the circuit pattern of the unit cell Ce is also the same as that of the first embodiment However, the differences from the first embodi ment are as follows. Noting the unit cell Ce22, for example, in FIG. 7 of the embodiment, between a pair of unit cells Ce12 and Ce13 adjacent to each other in the vertical direction, the gate RS22 of the reset transistor R22 and the adjacently placed gate AD12 of the address transistor A12 in the unit cell Ce12 are connected in the pattern. Further, the gate AD22 of the address transistor A22 is connected to the adjacently placed gate RS22 of the reset transistor R32 of the unit cell Ce32 in the pattern. The same pattern configuration is applied to other unit cells Ce in the pixel portion 13 of the CMOS image sensor shown in FIG. 7 of the embodiment. This circuit pattern is indicated by mutual connections of the address line ADL1 with the reset line RSL1, of ADL2 with RSL2, or of ADL3 with RSL3, in FIG The reading operation of pixel signals in the CMOS image Sensor having above described configuration is explained below Firstly, in the same way as with the first and second embodiments, pixel signals of the photodiodes PD11a, PD12a, PD13a, of the unit cells Ce11, Ce12, Ce13, in the first pixel row are read into the Signal output lines SL1, SL2, SL3, Then, pixel signals of the photodiodes PD11b, PD12b, PD13b, --- in the second pixel row are read. In this process, the gates TG11b, TG12b, TG13b, of the transfer transistors T11b, T12b, T13b, are made open, and Signal charges are transferred to the floating junctions FJ11, FJI2, FJ13, ---. Furthermore, the gates AD11, AD12, AD13, of the address transistors A11, A12, A13, are made open, and Signals corresponding to the Stored charges are taken out via the diffusion areas S11, S12, S13, to the signal output lines SLI1, SL12, SL13, Simultaneously, the gates RS21, RS22, RS23, of the reset transistors R21, R22, R23, - - -, to which the gates AD1, AD12, AD13, of the address transistors A11, A12, A13, are connected, are made open by being applied with an address pulse operating as a reset pulse. The floating junctions FJ21, FJ22, FJ23, are thus reset to predetermined reset drain Voltages. The next third pixel row can be read. For reading the Subsequent pixel rows, the aforementioned process is repeated According to the embodiments mentioned above, in any adjacent two unit cells among the unit cells Ce11, Ce12, Ce 13, - - -, which are arranged in the vertical direction, the gates AD11, AD12, AD13, of the address transistors A11, A12, A13, and the gates RS21, RS22, RS23, of the reset transistors R21, R22, R23, are connected in the circuit pattern without connecting with metallic lines, So the integration can be improved more than that in the conventional device as in the first and Second embodiments. Further, the resolution in the vertical and horizontal directions can be also improved According to the embodiments of the present invention explained above, the elements and lines constitut ing the pixel portions can be arranged efficiently, and thus the circuit integration can be improved neither reducing the elements size nor forming fine wires, as well as the resolu tion in the horizontal and vertical directions can be improved. What is claimed is: 1. A CMOS image sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises, a plurality of unit cells arranged in the row and column directions at a predetermined pitch respectively in a two-dimensional plain forming a matrix, which include a first and a Second photoelectric conversion element, a first and a Second transfer transistor for transferring charges Stored by the photoelectric conversion ele ments at their common floating junctions, reset tran Sistors for resetting the potential of the floating junc tions, driver transistors whose output potential is controlled by the potential of the floating junctions, and address transistors for Selectively driving the driver transistors, reset drain Voltage lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement for resetting the potential of the common floating junctions included in the unit cell belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement; first transfer lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the first transfer transistor included in the unit cell belonging to each row, Second transfer lines in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the Second transfer tran Sistors included in the unit cells belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement; Signal output lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement to which the output Voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement are Supplied, and address lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for Selectively driving the driver transis tors included in the unit cell belonging to each row. 2. A CMOS image Sensor according to claim 1, wherein a first pixel line composed of the first photoelectric conver Sion element included in the unit cells belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement and a Second pixel lines com posed of the Second photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cells are independently read respectively by the first and Second transfer lines.
14 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, A CMOS image sensor according to claim 2, wherein the first pixel lines and the Second pixel lines are read by Switching the first and Second transfer transistors by the first and Second transfer lines. 4. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 3, wherein the driver transistors and the address transistors which are included in the respective unit cells are connected in Series, wherein the first and Second photoelectric conversion ele ments are connected to gate electrodes of the driver tran Sistors via the first and Second transfer transistors, and wherein Source electrodes of the reset transistors are con nected to the gate electrodes of the driver transistors. 5. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 4, wherein the first and Second photoelectric conversion elements are photodiodes. 6. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 5, wherein the first and Second photodiodes included in the unit cells are arranged in the oblique direction to the row or column direction of the matrix arrangement. 7. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 6, wherein the unit cells are formed as an integrated circuit on a Semiconductor Substrate and the first and Second photo diodes arranged in the oblique direction share the floating junction area, the reset drain area, the reset transistors, the driver transistors, the address transistors, the junction area between the driver transistors and the address transistors and the diffusion area at the connecting portion between the driver transistors and the Signal output line, thereby reading Signals of the first pixel row and the Second pixel row independently. 8. A CMOS image sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a plurality of unit cells arranged in the row and column directions at a predetermined pitch respectively in a two-dimensional plain forming a matrix, which include a first and a Second photoelectric conversion element, a first and a Second transfer transistor for transferring charges Stored by the photoelectric conversion ele ments at their common floating junctions, reset tran Sistors for resetting the potential of the floating junc tions, driver transistors whose output potential is controlled by the potential of the floating junctions, and address transistors for Selectively driving the driver transistors, reset drain Voltage lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement for resetting the potential of the common floating junctions included in the unit cell belonging to each column of the matrix arrangement; first transfer lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the first transfer transistor included in the unit cell belonging to each row, Second transfer lines in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for controlling the Second transfer tran Sistors included in the unit cells belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement; first signal output lines provided in the column direction of the matrix arrangement to which the output Voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells arranged in the odd numbered rows are Supplied; Second Signal output lines provided in the column direc tion of the matrix arrangement to which the output Voltages of the driver transistors included in the unit cells arranged in the even numbered rows are Supplied; and address lines provided in the row direction of the matrix arrangement for Selectively driving the driver transis tors included in the unit cell belonging to each row, wherein image Signals of the pixel arrays composed of the photoelectric conversion elements included in the unit cells arranged in the neighboring two columns are read Simultaneously using the first and Second Signal output lines. 9. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 8, wherein the adjacent pixel lines, which are read simultaneously, are a pixel row formed by the Second photoelectric conversion elements included in the unit cell belonging to the first row and a pixel row formed by the first photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cell belonging to the Second row, thereby simultaneously read the image Signals of the pixel of adjacent tow rows into the first and Second Signal output lines by respectively Supplying the same transfer pulse to the second transfer line provided for the unit cell belonging to the first row and the first transfer line provided for the unit cell belonging to the Second row. 10. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 9, a gate of the Second transfer transistor included in the unit cell belong to the first row and a gate of the first transfer transistor included in the unit cell belong to the Second row are connected to each other. 11. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 10, wherein the first pixel row composed of the first photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cells belonging to the respective rows of the matrix arrangement and the Second pixel row composed of the Second photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cells are indepen dently read respectively by the first and Second transfer lines. 12. ACMOS image Sensor according to claim 11, wherein the first pixel row and the Second pixel row are read by Switching the first and Second transfer transistors by the first and Second transfer lines. 13. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 12, wherein the driver transistors and the address transistors, which are included in the unit cells are connected in Series, wherein the first and Second photoelectric conversion elements are con nected to gate electrodes of the driver transistors via the first and Second transfer transistors, and wherein Source elec trodes of the reset transistors are connected to the gate electrodes of the driver transistors. 14. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 13, wherein the first and Second photoelectric conversion elements are photodiodes. 15. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 14, wherein the first and Second photodiodes included in the respective unit cells are arranged in the oblique direction to the row or column direction of the matrix arrangement. 16. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 15, wherein the unit cells are formed as an integrated circuit on a Semiconductor Substrate and wherein the first and Second photodiodes arranged in the oblique direction share the floating junction area, the reset drain area, the reset transis tors, the driver transistors, the address transistors, the junc tion area between the driver transistors and the address
15 US 2004/ A1 Jun. 10, 2004 transistors, and the diffusion area at the connecting portion between the driver transistors and the Signal output line, thereby reading Signals of the first pixel row and the Second pixel row independently. 17. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 1, wherein among unit cells arranged in adjacent two rows of the matrix arrangement, a gate of the address transistor included in the unit cell arranged in the first row and a gate of the reset transistor included in the unit cell arranged in the Second row are connected, and while an image Signal from the Second photoelectric conversion element included in the unit arranged in the first row is being read, the floating junction included in the unit cell arranged in the Second row to be read next is reset, thus an image Signal from the first photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cell arranged in the Second row can be read. 18. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 17, wherein a first pixel row composed of the first photoelectric conver Sion element included in the unit cell belonging to each row of the matrix arrangement and a Second pixel row composed of the Second photoelectric conversion element included in the unit cell are independently read by the first and Second transfer lines. 19. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 18, wherein the first pixel row and the Second pixel row are read by Switching the first and Second transfer transistors by the first and Second transfer lines. 20. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 19, wherein the driver transistors and the address transistors which are included in the unit cells are connected in Series, and the first and Second photoelectric conversion elements are connected to gate electrodes of the driver transistors via the first and Second transfer transistors, and Source electrodes of the reset transistors are connected to the gate electrodes of the driver transistors. 21. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 19, wherein the first and Second photoelectric conversion elements are photodiodes. 22. A CMOS image sensor according to claim 20, wherein the first and Second photodiodes included in the unit cells are arranged in the oblique direction to the row or column direction of the matrix arrangement. 23. ACMOS image sensor according to claim 21, wherein unit cells are formed as an integrated circuit on a Semicon ductor Substrate and the first and Second photodiodes arranged in the oblique direction share the floating junction area, the reset drain area, the reset transistors, the driver transistors, the address transistors, the junction area between the driver transistors and the address transistors and the diffusion area at the connecting portion between the driver transistors and the Signal output line, thereby read signals of the first pixel row and the Second pixel row independently.
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000
 US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
United States Patent (19) Haines
 United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,017,055 B1. H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006
 United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1
 USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) United States Patent
 US007110229B2 (12) United States Patent Yang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY PANELUSING THE SAME (76) Inventors: Sheng-Chieh Yang, No. 120, Jhenfu St.,
US007110229B2 (12) United States Patent Yang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY PANELUSING THE SAME (76) Inventors: Sheng-Chieh Yang, No. 120, Jhenfu St.,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2
 USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,879,518 B1. Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005
 United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996
 United States Patent (19) I I USOO5519242A 11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996 54 ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,357,126 10/1994 Jimenez... 257/173 PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR A NMOS
United States Patent (19) I I USOO5519242A 11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996 54 ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,357,126 10/1994 Jimenez... 257/173 PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR A NMOS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050092895A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0092895A1 FOSSum (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2005 (54) IN-PIXEL KTC NOISE SUPPRESSION USING Publication Classification
US 20050092895A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0092895A1 FOSSum (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2005 (54) IN-PIXEL KTC NOISE SUPPRESSION USING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008
 (19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O156442A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156442 A1 Origasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE AND MULT-CHIP MODULE
(19) United States US 2003O156442A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156442 A1 Origasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE AND MULT-CHIP MODULE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,172,601 B1. Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001
 USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247625 A1 Tomonariet al. US 2016O247625A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) COMMON MODE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247625 A1 Tomonariet al. US 2016O247625A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) COMMON MODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
United States Patent (19) Soshi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Soshi et al. 54 CAMERA WITH IMPROVED POSITIONING OF VEBRATION DETECTING SENSORS THEREN 75 Inventors: Isao Soshi, Tokyo; Hidenori Miyamoto, Urayasu; Seijiro Noda, Yokohama, all
United States Patent (19) Soshi et al. 54 CAMERA WITH IMPROVED POSITIONING OF VEBRATION DETECTING SENSORS THEREN 75 Inventors: Isao Soshi, Tokyo; Hidenori Miyamoto, Urayasu; Seijiro Noda, Yokohama, all
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O181685A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hasegawa (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) PROJECTOR, METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE PROJECTOR, PROGRAM FOR CONTROLLING
(19) United States US 2006O181685A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hasegawa (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) PROJECTOR, METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE PROJECTOR, PROGRAM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110242707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0242707 A1 YOON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) HARD DISK DRIVE Publication Classification (51) Int.
US 20110242707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0242707 A1 YOON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) HARD DISK DRIVE Publication Classification (51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
isits ar. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 (19) United States y(n) second sub-filter feedback equalizer
 (19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
United States Patent (19) Lee et al.
 United States Patent (19) Lee et al. 54) MICROMIRROR FOR A HYBRID OPTOELECTRONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUIT, A METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME, A MICROMIRROR-PHOTODETECTOR ASSEMBLY AND AN ASSEMBLY OF HYBRD OPTOELECTRONIC
United States Patent (19) Lee et al. 54) MICROMIRROR FOR A HYBRID OPTOELECTRONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUIT, A METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME, A MICROMIRROR-PHOTODETECTOR ASSEMBLY AND AN ASSEMBLY OF HYBRD OPTOELECTRONIC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
(19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O161600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0161600 A1 ELDADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) OPTICAL PHASED ARRAY LIDAR SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016O161600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0161600 A1 ELDADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) OPTICAL PHASED ARRAY LIDAR SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Moriwaki et al. USOO6819328B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) GRAPHIC ACCELERATOR WITH INTERPOLATE FUNCTION (75) Inventors: Shohei Moriwaki, Hyogo (JP);
(12) United States Patent Moriwaki et al. USOO6819328B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) GRAPHIC ACCELERATOR WITH INTERPOLATE FUNCTION (75) Inventors: Shohei Moriwaki, Hyogo (JP);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O177182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0177182 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) FLEXIBLE DISPLAY AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. MANUFACTURING
(19) United States US 2014O177182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0177182 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) FLEXIBLE DISPLAY AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. MANUFACTURING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008
 (19) United States US 2008.0095244A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0095244 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008 (54) DE-BLOCKING FILTERING METHOD OF Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2008.0095244A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0095244 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008 (54) DE-BLOCKING FILTERING METHOD OF Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170090624A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090624 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH DRIVING SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE, TOUCH DRIVING DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20170090624A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0090624 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TOUCH DRIVING SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE, TOUCH DRIVING DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 16/06
 US005920509A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,509 Hirano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) NONVOLATILE SEMICONDUCTOR 5,576,991 11/1996 Rady et al.... 365/185.24 MEMORY DEVICE
US005920509A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,509 Hirano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) NONVOLATILE SEMICONDUCTOR 5,576,991 11/1996 Rady et al.... 365/185.24 MEMORY DEVICE
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,103,736 B2. Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006
 United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008982274B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,982.274 B2 Kang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2015 (54) CAMERA MODULE INCLUDING 2011/0063741 A1 3/2011 Park et al.... 359,823 2011/0091193
(12) United States Patent US008982274B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,982.274 B2 Kang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2015 (54) CAMERA MODULE INCLUDING 2011/0063741 A1 3/2011 Park et al.... 359,823 2011/0091193
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006
 US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
US 7.663,338 B2. Feb. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Guthrie et al. used to receive a USB bus voltage from the USB interface and (51)
 USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
Printer. Data input/ Printout unit. processor) Control unit. (Raster image RIP. Display unit. Image
 (19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
75 Inventors: David J. Corisis, Meridian; Jerry M ,180 10/1997 Pederson et al..
 US006072233A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,072,233 C Orisis et tal al. (45) Date O of Patent C. Jun. 6, 2000 54 STACKABLE BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE 5,648,679 7/1997 Chillara et al.. 5,668,405
US006072233A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,072,233 C Orisis et tal al. (45) Date O of Patent C. Jun. 6, 2000 54 STACKABLE BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE 5,648,679 7/1997 Chillara et al.. 5,668,405
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150331513A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0331513 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCH DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 20150331513A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0331513 A1 LEE (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) TOUCH PANEL AND TOUCH DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 US008619055B2 (12) United States Patent Westerinen et al. (54) ACTIVE MATRIX TOUCH SENSING (75) Inventors: William J. Westerinen, Issaquah, WA (US); Craig Steven Ranta, Redmond, WA (US) (73) Assignee:
US008619055B2 (12) United States Patent Westerinen et al. (54) ACTIVE MATRIX TOUCH SENSING (75) Inventors: William J. Westerinen, Issaquah, WA (US); Craig Steven Ranta, Redmond, WA (US) (73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231580 A1 Hsu US 20080231580A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) LCD DEVICE DRIVEN BY PRE-CHARGE PROCEDURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231580 A1 Hsu US 20080231580A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) LCD DEVICE DRIVEN BY PRE-CHARGE PROCEDURE (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.009 1512A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0091512 A1 Mai (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING DEVICE, POWER (52) U.S. Cl. RECEIVING
(19) United States US 2015.009 1512A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0091512 A1 Mai (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING DEVICE, POWER (52) U.S. Cl. RECEIVING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
-Gorse III IEEEEEEEEE OFF-TIM -17B is 12 L=y 3 14 KB/Mouse 16- DSP-CONT. United States Patent 19 Yoshida 0 T 1 O LEVEL I LEVEL 10
 United States Patent 19 Yoshida 54 DISPLAY CONTROL METHOD AND DISPLAY CONTROLAPPARATUSADAPTED TO PORTABLE DATA PROCESSING EQUIPMENT PROVIDED WITH A BATTERY. DRIVABLE FLAT PANEL DISPLAY 75) Inventor: Norio
United States Patent 19 Yoshida 54 DISPLAY CONTROL METHOD AND DISPLAY CONTROLAPPARATUSADAPTED TO PORTABLE DATA PROCESSING EQUIPMENT PROVIDED WITH A BATTERY. DRIVABLE FLAT PANEL DISPLAY 75) Inventor: Norio
St SS 4 N 3 2/ N N S. 9 6.N&SNS. (12) United States Patent. 19b 16. (10) Patent No.: US 8,643,112 B2. 1Ob 5 1 Oa. (45) Date of Patent: Feb.
 USOO864.3112B2 (12) United States Patent Okushima (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (71) Applicant: Renesas Electronics Corporation, Kanagawa (JP) (72) Inventor: Mototsugu Okushima, Kanagawa (JP) (73) Assignee:
USOO864.3112B2 (12) United States Patent Okushima (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (71) Applicant: Renesas Electronics Corporation, Kanagawa (JP) (72) Inventor: Mototsugu Okushima, Kanagawa (JP) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7773440B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.773,440 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) ZQ CALIBRATION CONTROLLER AND (56) References Cited METHOD FOR ZQ CALIBRATION
(12) United States Patent USOO7773440B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.773,440 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) ZQ CALIBRATION CONTROLLER AND (56) References Cited METHOD FOR ZQ CALIBRATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,399,323 B1
 US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014009 7885A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0097885 A1 HL (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) CAPACITIVE TOUCH KEYBOARD (71) Applicant: TOUCHPLUS INFORMATION
(19) United States US 2014009 7885A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0097885 A1 HL (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) CAPACITIVE TOUCH KEYBOARD (71) Applicant: TOUCHPLUS INFORMATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140O85999A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0085999 A1 Kang (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE HAVING ADJUSTABLE REFRESH PERIOD,
(19) United States US 20140O85999A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0085999 A1 Kang (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2014 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE HAVING ADJUSTABLE REFRESH PERIOD,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
2c NCPURA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0182258A1 Sakamoto et al. US 2003O182258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003 (54) SEARCH SERVER AND METHOD FOR (75) (73) (21) (22)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0182258A1 Sakamoto et al. US 2003O182258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003 (54) SEARCH SERVER AND METHOD FOR (75) (73) (21) (22)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2. Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010
 USOO7643021B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2 Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) DRIVING SYSTEMAND DRIVING METHOD 6,215,468 B1 * 4/2001 Van Mourik... 345 605 FORMOTION
USOO7643021B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2 Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) DRIVING SYSTEMAND DRIVING METHOD 6,215,468 B1 * 4/2001 Van Mourik... 345 605 FORMOTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
(19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
