IPv6 Module 2 OSPF Areas
|
|
|
- Erika Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
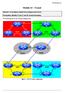
1 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 2 OSPF Areas Objective: To migrate from one flat OSPF topology to OSPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: IPv6 Module 1 and OSPF presentation Topology: Figure 1 OSPF Areas 1
2 Monday, March 24, 2014 Lab Notes This module provides an introduction to areas in OSPF as used in ISP networks. The module forms the basis for the Route Reflector Module which follows. It is strongly recommended that the OSPF presentation is reviewed prior to starting this module. Prerequisites for this Module are Module 1, and the OSPF presentation. As before, ask the workshop instructors or refer to the online documentation if there is any doubt. The topology shown in Figure 1 allows the student to configure the best combination for the study of OSPF areas. Functional assignments of routers in Figure 1:! Routers 5 to 10 represent the core network and the core interfaces are all in OSPF area 0. In a typical ISP backbone, these routers would carry all the internal link routes known in the ISPs network. Routers 5, 6, 9 and 10 are Area Border Routers, whereas Routers 7 and 8 are Internal Routers.! Routers 1 and 3 are completely in OSPF area 10. Router 5 is the boundary between area 0 and area 10, so requires configuration for both areas.! Routers 2 and 4 are completely in OSPF area 20. Router 6 is the boundary between area 0 and area 20, so requires configuration for both areas.! Routers 11 and 13 are completely in OSPF area 30. Router 9 is the boundary between area 0 and area 30, so requires configuration for both areas.! Routers 12 and 14 are completely in OSPF area 40. Router 10 is the boundary between area 0 and area 40, so requires configuration for both areas. Note: if this module is attempted without completing the IPv4 version, please remember to set the OSPF router-id first. Lab Exercise 1. OSPF Migration. This module is going to show the student how to migrate from a single area OSPF backbone to one using multiple areas. As ISP networks grow, quite often a single OSPF area ends up with an unmanageably large number of routers, resulting in reduced convergence rates impacting network performance. Of course, standard design advice is to start off with areas from day one, but many network designers unfortunately choose to ignore lessons well learnt by their predecessors. Before starting ensure that the configuration is exactly as it was at the end of Module 1. OSPFv3 adjacencies should all be properly established and ibgp should be running with each neighbour adjacency established and active. Also, shutdown or disconnect interfaces which are not being used for this Module. These include connections between Router1 and Router2, Router1 and Router13, Router2 and Router14, and Router13 and Router14. It makes no sense to have a physical connection between non-zero OSPF areas as traffic between two non-zero areas must always transit Area 0. Checkpoint #1: Call the lab assistant and show the router configuration and connectivity. 2. Migration strategy. Review the OSPF for ISPs presentation where one possible migration strategy was discussed. The best strategy is to start at the edge of the network and work inwards. 2
3 ISP Workshop Lab We want to migrate to using OSPF areas without causing too much downtime in the network in other words, we want to try and ensure that all the ibgp sessions remain active. To this end, the outermost links of the network are changed from OSPF Area 0 to the sub area first. We want to avoid having any islands of Area0 in the network this will result in partition of the network and disconnectivity for the stub Area 0. The following steps work through the process in detail. 3. Step 1: Network Outer Edge. The first links we will move from Area 0 are the links between Router1 and Router3, Router2 and Router4, Router11 and Router13, and Router12 and Router14. The Router teams at either side of each link MUST work together to coordinate the change. For example, Router1 and Router3 should coordinate to change the area on the link between them from Area0 to Area10 at exactly the same time. Example for Router1: interface serial 1/0 interface loopback 0 Example for Router3: interface serial 1/1 interface loopback 0 Once these two teams have changed the area for the link between them (don t forget to do the loopback interface as well!), the OSPF adjacency will re-establish in the new area, and the rest of the network will become visible again. The other teams mentioned above should do a similar thing for their interconnecting links and respective areas. 4. Step 2: Network Inner Edge. Once the outer edge links have been moved to the new areas, we are ready to change the area of the next links in from the outer edge; these are the links between Router3 and Router5, Router4 and Router6, Router11 and Router9, and Router12 and Router10. Again the Router teams at either side of each link MUST work together to coordinate the change. For example, Router4 and Router6 should coordinate to change the area on the link between them from Area0 to Area20 at exactly the same time. Example for Router4: interface serial 1/0 ipv6 ospf 41 area 20 interface loopback 0 ipv6 ospf 41 area 20 Example for Router6: interface serial 1/1 ipv6 ospf 41 area 20 Once these two teams have changed the area for the link between them, the OSPF adjacency will re-establish in the new area, and the rest of the network will become visible again. The other teams mentioned above should do a similar thing for their interconnecting links and respective areas. 3
4 Monday, March 24, 2014 Note that Routers 5, 6, 9 and 10 should only change the Area of the link to their outer neighbour they should NOT change the area of the loopback interface. 5. Further steps. Our lab network is not very large or complex, so the migration was quite simple. However, for larger networks, we would repeat the above steps, working from the outside in to the backbone Area, taking great care to ensure that no Area 0 islands are created as part of the process. Such a migration should have negligible impact on the network s operation. 6. All router teams should check their routing table. The routing table should look the same as it did in Module 1. All the prefixes in Area 0 will be available in Areas 10 through to 40. Although notice now that several of the routes will be marked as Inter Area (IA) routes. Here is an example of the typical output from show ipv6 route as seen from Router2: IPv6 Routing Table - 29 entries Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, R - RIP, B - BGP U - Per-user Static route I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary O - OSPF intra, OI - OSPF inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2 ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2 S 2001:DB8::/32 [1/0] via ::, Null0 OI 2001:DB8::1/128 [110/250] LC 2001:DB8::2/128 [0/0] via ::, Loopback0 OI 2001:DB8::3/128 [110/200] O 2001:DB8::4/128 [110/50] OI 2001:DB8::5/128 [110/150] OI 2001:DB8::6/128 [110/100] OI 2001:DB8::7/128 [110/200] OI 2001:DB8::8/128 [110/150] Traces through the network. Once you have analysed the routing table as it is now, and compared with any notes you made in Module 1, try some traceroutes through the network. Checkpoint #2: Call the lab instructors and show the function of your router. The inter-area OSPF peerings will now be up. If you have an area border router, demonstrate the neighbour relationships using sh ip ospf neigh. If you are not in an area border, you should now have a more complete routing table. STOP AND WAIT HERE 7. Intra Area Authentication. OSPF supports router authentication within areas. This is quite important inside ISP networks to prevent the introduction of improperly configured or unintended equipment. 4
5 ISP Workshop Lab Each area will turn on authentication within that area. Routers which are ABRs will naturally have to enter configuration to cover all areas the router has interfaces in. This first step will enable each area to support authentication using the area N authentication command set. We have to set a different Security Parameter Index (SPI) for each area. Please use the SPIs as listed below, otherwise each router team will have to negotiate SPIs for each area. Area0 500 Area Area Area Area An example configuration for Router6 might be: ipv6 router ospf 41 area 0 authentication ipsec spi 500 md ABCDEF ABCDEF area 20 authentication ipsec spi 2000 md ABCDEF ABCDEF! Notice now that the OSPF adjacencies do not come up unless the neighbouring router has also entered the same configuration and key. Notice also how the OSPF adjacencies timed out after the configuration was entered the adjacent router still had not set up OSPF neighbour authentication. Once they also have done this, the adjacency is re-established. Also, if we want to configure neighbour authentication per area but disable it on a per link basis, we need to used the authentication null option. The following example shows how to disable neighbour authentication on one specific interface, hssi 5/0. interface hssi 5/0 ipv6 ospf authentication null ipv6 ospf 1 area 10 Note: Wherever an OSPF session is configured from now on in the workshop, all Router Teams MUST use passwords on these OSPF sessions. Checkpoint #3: Call the lab instructors and demonstrate the OSPF is still working following the addition of neighbour authentication and that the OSPF routing table is still the same as it was previously. 8. Inter-area summarisation. It is fairly important, especially for larger ISP networks, to try and summarise the announcements going from sub-areas into Area 0 as much as is possible. Unfortunately we don t have an extensive lab network here, so it s going to be hard to see much benefit from summarisation, but we will try with the limited resources we have. Areas 10, 20, 30 and 40 can summarise the point-to-point links they announce into Area 0. Routers5, 6, 9 and 10, respectively, will introduce this configuration into the network. We will take the example of Area 20 and Router 6 below. Area 20 point to point subnets are 2001:db8:0:6::/64 (Router2-Router4) and 2001:db8:0:7::/64 (Router4-Router6). These can be aggregated into 2001:db8:0:6::/63 (even though we have addressed the links as /127, we have still reserved a /64 for each). The configuration which has to be introduced on Router6 therefore is: 5
6 Monday, March 24, 2014 ipv6 router ospf 41 area 20 range 2001:db8:0:6::/63 Once the team operating Router6 has done this, check the routing table. Everyone (apart from Area 20 routers) will see that the entries for 2001:db8:0:6::/64 and 2001:db8:0:7::/64 will have been replaced by the aggregate, 2001:db8:0:6::/ The other three router teams (5, 9 and 10) should do a similar thing for their areas, aggregating the point to point links between their area routers. Once complete, eight /127s in the routing table should have been replaced by four /63 aggregates 10. Final check. Use the various show ipv6 ospf commands to see the OSPF status of the lab network now. Check the routing of IPv6 traffic and the IPv6 routing table. If you are missing any adjacencies, work with your neighbouring routers to work out why, and what might have gone wrong with the neighbour authentication. Checkpoint #4: Call the lab instructors and show the routing table after the area summarisation was applied. 6
ISP Workshop Lab. Module 2 OSPF Areas
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
Module 5 Advanced OSPF
 Module 5 Advanced OSPF ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement different types of OSPF areas and use advanced OSPF Features in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module 1 and OSPF presentation
Module 5 Advanced OSPF ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement different types of OSPF areas and use advanced OSPF Features in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module 1 and OSPF presentation
Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp
 IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
Module 7 BGP Route Reflector Lab
 Module 7 BGP Route Reflector Lab ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement BGP route reflectors as an alternative to fully-meshed ibgp. Prerequisites: Module 1, the Scaling BGP presentation
Module 7 BGP Route Reflector Lab ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement BGP route reflectors as an alternative to fully-meshed ibgp. Prerequisites: Module 1, the Scaling BGP presentation
IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features
 IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour filtering and more
IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour filtering and more
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 (IS-IS)
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 (IS-IS)
Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 2, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 2, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate
Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
NIS Workshop - Ashgabad April Routing hands-on: Local Lab
 NIS Workshop - Ashgabad 25-27 April 2007 Routing hands-on: Local Lab Piers O'Hanlon Peter Kirstein Janos Mohacsi Nikolay Pakulin
NIS Workshop - Ashgabad 25-27 April 2007 Routing hands-on: Local Lab Piers O'Hanlon Peter Kirstein Janos Mohacsi Nikolay Pakulin
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point
 IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp
 2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp More ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Connect your ISP to a Transit provider and the Internet Exchange Point using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp More ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Connect your ISP to a Transit provider and the Internet Exchange Point using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
Module 1 Device and Infrastructure Security Lab
 Module 1 Device and structure Security Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic (No security) interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. Create
Module 1 Device and structure Security Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic (No security) interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. Create
Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Exchange Points Presentation
ISP Workshop Lab Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Exchange Points Presentation
2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp
 2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with IGP and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites:
2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with IGP and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites:
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab
 2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
BGP route filtering and advanced features
 2015/07/23 23:33 1/13 BGP route filtering and advanced features BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings
2015/07/23 23:33 1/13 BGP route filtering and advanced features BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings
IPv6 Module 1a OSPF. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module 1, knowledge of Cisco router CLI, and previous hands on experience.
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1a OSPF Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1a OSPF Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module
Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration
 IXP Workshop Lab Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration Objective: The focus of this lab is to connect 8 customers with IXP. Customers are connected with AS17821 as transit and received customer prefixes, also
IXP Workshop Lab Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration Objective: The focus of this lab is to connect 8 customers with IXP. Customers are connected with AS17821 as transit and received customer prefixes, also
Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs
 Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto two different upstream ISPs. Prerequisites: Module 12 and Multihoming
Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto two different upstream ISPs. Prerequisites: Module 12 and Multihoming
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS
 Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS ISP Workshops Last updated 25 th August 2015 1 Introduction p With the advent of IPv6 and dual stack networks, more ISPs expressing interest to migrate to IS-IS n Migration
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS ISP Workshops Last updated 25 th August 2015 1 Introduction p With the advent of IPv6 and dual stack networks, more ISPs expressing interest to migrate to IS-IS n Migration
LAB12: OSPF IPv6. OSPF: Redistribution. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
LAB20: EIGRP IPv6. EIGRP: Summarization. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB20: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB20: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 1 to 4, and the Exchange
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 1 to 4, and the Exchange
Module 18 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
Route Filtering. Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes. Downstream customers Internet prefixes
 1 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes 2 Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
1 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes 2 Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately
Module 14 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
Route Filtering. Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes. Downstream customers Internet prefixes
 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
IPv6 Module 1c ibgp. Prerequisites: IPv6 Module 1a (OSPF) or IPv6 Module 1b (ISIS).
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1c ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with chosen IGP and one BGP AS number running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1c ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with chosen IGP and one BGP AS number running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites:
IPv6 Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup
 IPv6 Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module 1, knowledge
IPv6 Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module 1, knowledge
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
LAB24: EIGRP IPv6. EIGRP: Load Balancing. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB24: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB24: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network concepts of Lab 1, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network concepts of Lab 1, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example
 Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp
 Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07
 Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration #2 Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Piers O'Hanlon (p.ohanlon@cs.ucl.ac.uk)
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration #2 Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Piers O'Hanlon (p.ohanlon@cs.ucl.ac.uk)
Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone The following will be the common topology used.
Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone The following will be the common topology used.
Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup
 Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab with IP addressing and essential router configuration. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working
Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab with IP addressing and essential router configuration. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE)
 Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE) Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6VPE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented
Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE) Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6VPE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented
Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab
 Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab Objective: Introduction to routing policy, the manipulation of BGP attributes to control traffic flow in a multihomed network. Prerequisite: Module 6 and 7 Topology
Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab Objective: Introduction to routing policy, the manipulation of BGP attributes to control traffic flow in a multihomed network. Prerequisite: Module 6 and 7 Topology
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS
 Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS Philip Smith philip@nsrc.org SAFNOG 2 7 th -8 th April 2015 Mbabane Last updated 27 March 2014 1 Presentation slides p Available at: n http://bgp4all.com/ftp/seminars/safnog2-
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS Philip Smith philip@nsrc.org SAFNOG 2 7 th -8 th April 2015 Mbabane Last updated 27 March 2014 1 Presentation slides p Available at: n http://bgp4all.com/ftp/seminars/safnog2-
Module 1b IS-IS. Prerequisites: The setup section of Module 1. The following will be the common topology used for the first series of labs.
 Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp
 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers 1 Wednesday,
Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers 1 Wednesday,
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv3 Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008
 Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to construct a working network.
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to construct a working network.
IPv6 Routing Protocols
 IPv6 Routing Protocols ITU/APNIC/PacNOG21 IPv6 Workshop 4 th 8 th December 2017 Nuku alofa These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
IPv6 Routing Protocols ITU/APNIC/PacNOG21 IPv6 Workshop 4 th 8 th December 2017 Nuku alofa These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
IPv6 Module 4 OSPF to IS-IS for IPv6
 IPv6 Module 4 OSPF to IS-IS for IPv6 Objective: To migrate the OSPF version of Module 1 (running IPv4) to using IS-IS as part of an IPv6 migration strategy. OSPF will be completely removed once the migration
IPv6 Module 4 OSPF to IS-IS for IPv6 Objective: To migrate the OSPF version of Module 1 (running IPv4) to using IS-IS as part of an IPv6 migration strategy. OSPF will be completely removed once the migration
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3
 Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Module 9 BGP Configuration Essentials Lab
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 9 BGP Configuration Essentials Lab Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, to introduce more BGP Configuration Essentials for application in ISP networks Prerequisite:
ISP Workshop Lab Module 9 BGP Configuration Essentials Lab Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, to introduce more BGP Configuration Essentials for application in ISP networks Prerequisite:
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five-day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP certification.
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five-day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP certification.
CS 43: Computer Networks. 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
Cisco CCNP ROUTE: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) 2.0. Upcoming Dates. Course Description. Course Outline
 Cisco CCNP ROUTE: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) 2.0 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP certification.
Cisco CCNP ROUTE: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) 2.0 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP certification.
All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with.
 Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab. Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within the AS.
 2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab Internal BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within
2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab Internal BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within
OSPF Exercises. All participants will work within a group as a team. Each group has three routers and four switches to work with.
 OSPF Exercises All participants will work within a group as a team. Each group has three routers and four switches to work with. These exercises are divided into several components: 1. Basic Router Configuration
OSPF Exercises All participants will work within a group as a team. Each group has three routers and four switches to work with. These exercises are divided into several components: 1. Basic Router Configuration
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Hands-On ROUTE Implementing Cisco IP Routing CCNP Course 1
 Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
OSPFv3 Commands. address-family (OSPFv3), page 4. authentication (OSPFv3), page 7
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
Any individual involved in implementation and verification of routing protocols in the enterprise networks
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING Information Length: 5 Days Courseware : Course code: Delivery Type Included CIS_ROUTE Classroom Description Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v1.0 is a five-day course
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING Information Length: 5 Days Courseware : Course code: Delivery Type Included CIS_ROUTE Classroom Description Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v1.0 is a five-day course
PREREQUISITES TARGET AUDIENCE. Length Days: 5
 Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Routing v2.0 (ROUTE) ROUTE v2.0 includes major updates and follows an updated blueprint. However, note that this course does not cover all items listed on the blueprint. Some
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Routing v2.0 (ROUTE) ROUTE v2.0 includes major updates and follows an updated blueprint. However, note that this course does not cover all items listed on the blueprint. Some
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6
 COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6. (P22) Suppose you are interested in detecting the number of hosts behind a NAT. You observe that the IP layer stamps an identification number sequentially on each
COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6. (P22) Suppose you are interested in detecting the number of hosts behind a NAT. You observe that the IP layer stamps an identification number sequentially on each
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp
 Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure). Prerequisites:
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure). Prerequisites:
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Routing v2.0 (ROUTE)
 Course Overview ROUTE v2.0, a five-day ILT course, includes major updates and follows an updated blueprint. (However, note that this course does not cover all items listed on the blueprint.) Some older
Course Overview ROUTE v2.0, a five-day ILT course, includes major updates and follows an updated blueprint. (However, note that this course does not cover all items listed on the blueprint.) Some older
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt)
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt)
Module 4 BGP-LS Configuration Lab
 APNIC SDN Workshop Lab Module 4 BGP-LS Configuration Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. As part
APNIC SDN Workshop Lab Module 4 BGP-LS Configuration Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. As part
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
DD2490 p Link-state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
Introduction to OSPF OSPF. Link State Routing. Link State. Fast Convergence. Low Bandwidth Utilisation
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
IETF RFCs Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x
 IETF Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x BGP, page 1 First-Hop Redundancy Protocols, page 2 IP Services, page 3 IPv6, page 3 IS-IS, page 4 OSPF, page 5 RIP, page 5 BGP RFC 1997 BGP Communities
IETF Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x BGP, page 1 First-Hop Redundancy Protocols, page 2 IP Services, page 3 IPv6, page 3 IS-IS, page 4 OSPF, page 5 RIP, page 5 BGP RFC 1997 BGP Communities
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points
 Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
KTHNOC, MPLS/RSVP lab, rev: 1.7 KTHNOC. MPLS/RSVP lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTHNOC MPLS/RSVP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 2.1RSVP concepts...3 3 Initial configuration...4
KTHNOC MPLS/RSVP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 2.1RSVP concepts...3 3 Initial configuration...4
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
BGP in the Internet Best Current Practices
 BGP in the Internet Best Current Practices 1 Recommended IOS Releases Which IOS?? 2 Which IOS? IOS is a feature rich and highly complex router control system ISPs should choose the IOS variant which is
BGP in the Internet Best Current Practices 1 Recommended IOS Releases Which IOS?? 2 Which IOS? IOS is a feature rich and highly complex router control system ISPs should choose the IOS variant which is
OSPF. About OSPF. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.4 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing.! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway Protocol! Route aggregation
 ! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing
Page1. Cisco IOS Software, Linux Software (I86BI_LINUX-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)M1, DEVELOPMENT TEST SOFTWARE
 BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
Configuring FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke
 Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network
 APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to construct
ISP Workshop Lab Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to construct
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013
 CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013 1 Reading Quiz Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013 1 Reading Quiz Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017
 CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
