CIS 83 Lab Assignment
|
|
|
- Lionel Erick Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIS 83 Lab Assignment Open the Packet Tracer Scenario STP Configuration Lab-1.pkt. Before proceeding, save as STP Configuration Lab-1-working.pkt. To demonstrate completion of the lab you will be asked at various points during the lab to copy and paste configurations into a lab completion document. Save the document as STP Configuration Lab 1. To get credit for completing the lab the document to grollinson2017@gmail.com and indicate the following in the subject line of the . CIS 83 STP configuration lab 1 Spanning Tree Configuration Lab Spanning Tree Protocol Overview: The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is designed to prevent layer 2 loops. In a bridge or switch topology (for purposes of STP, bridges and switches are identical in operation), it is desirable to physically cable redundant paths to provide fault tolerance. This creates a layer 2 loop, however, and causes undesirable effects. Normally, when a broadcast frame is received by a bridge, it is forwarded out all other ports. Each bridge in the loop forwards the broadcast and a broadcast storm results. If a loop were allowed to exist, then, the first broadcast frame would essentially shut down the network. The solution is STP. STP operation will result in one port in each loop being blocked. STP monitors the environment as well, so that a blocked port can be re-opened if a failure occurs in the working path. STP accomplishes these functions by exchanging STP information in frames called Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). A switch compares the values in BPDUs received with the values in BPDUs being sent - lower values are preferred over higher values. In order to fully understand BPDUs and how they work, it is first necessary to understand certain aspects of the STP environment. First, every bridge has a Bridge Identifier (BID) that consists of the bridge STP priority and the MAC address assigned to the bridge itself. The default STP priority is (Cisco switches use Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), a variation of the original version of STP. With PVST, an instance of STP is run for each configured VLAN. The VLAN number is added to the default priority for each instance. For VLAN 1, then, the default priority is 32769). Second, links are assigned a cost based on their speed. A 100 Mb link has a STP cost of 19, a 1 Gb link has a STP cost of 4. Finally, each port has a port ID and priority. These parameters are used by STP to ultimately determine which port to block in the loop. Again, when using these parameters, lower values are considered better than higher values. Below is an example of a BPDU sent out port Fa0/3 by a switch with the default priority for VLAN 1 of
2 32769, a MAC address of 000B and a cost to root of 19. The root switch has been determined to be 000A The row descriptions are above the fields. Root ID (RID) Cost Bridge ID (BID) Port ID (PID) Root priority Root MAC to root Bridge priority Bridge MAC Port priority Port number A B Direction of BPDU STP goes through a three step process to establish the role of each bridge (Root Bridge or non-root bridge) as well as the role and status of each operational port on each switch. A port s role can be either a root port, designated port or alternate port. Root ports and designated ports have a forwarding status while an alternate port has a blocking status. The three STP steps are- 1. Determine the root bridge 2. Determine the root port on each non-root bridge 3. Determine the designated port for each segment. Determining the root bridge Spanning Tree elects the root bridge by determining the bridge with the lowest bridge ID. First, each bridge compares its STP priority. The bridge with the lowest priority will become the root bridge. If all bridges have the same bridge priority, the bridge with lowest MAC address becomes the root bridge. All ports on the root bridge are automatically designated ports. Designated ports are put in a forwarding state so all root bridge ports are forwarding. Determining the root port on each non-root bridge Each non-root bridge will determine the port through which its cost to the root bridge is lowest. The cost to root for each port is determined by adding the cost-to-root value advertised in BPDUs received on the port to the cost assigned to the port. The port with the lowest total value will be made the root port. Root ports are put in a forwarding state. Determining the designated port for each segment. To determine the designated port for a segment, the bridges on the segment compare information in exchanged BPDUs. The bridge closest to root will have its port become
3 the designated port for the segment. If two or more bridges have the same lowest cost to root, the bridge with the lowest BID will have its port become the designated port for the segment. Designated ports are put in a forwarding state. Once a switch has determined its root port and any designated ports, all other ports are put in a blocking state. No traffic is sent out blocked ports nor is any traffic received on a blocked port forwarded out any other port. Lab steps You will look start by looking at the spanning tree behavior in the network. Wait at least 30 seconds and then issue the show spanning-tree command on all switches. From the output, you can see that SwitchA is the spanning-tree root bridge. Since all the switches have the same default bridge priority number of 32769, the switch with lowest MAC address became the root bridge. Notice that on the root bridge all interfaces are designated forwarding ports. Optimizing the Spanning Tree environment STP has successfully closed off the layer 2 loops without any configuration changes being made. This is its strength leave it alone and it works However, it does not necessarily optimize the environment. Administrator intervention is needed to accomplish that task. Note that a server is connected to SwitchC. Because the links between SwitchB and SwitchC are blocked, data destined for the server from hosts connected to SwitchB must pass through SwitchA. This isn t optimal for two reasons it induces propagation delay and burdens the link between SwitchA and SwitchC. If SwitchC were the root switch, however, the link between SwitchB and SwitchC would be forwarding this would eliminate both issues. You will now make SwitchC the root with the command, spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary. This command lowers the default priority on the switch thus making it the root bridge. SwitchC#config t SwitchC(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary You will now confirm that the link between SwitchB and SwitchC is in a forwarding state. SwitchB#show spanning-tree
4 1. Copy and paste the output from the command into your lab completion document In the topology with which you are working SwitchA is also at the distribution layer. Accordingly, it generally considered a good practice to make such a switch the secondary root switch. SwitchA#config t SwitchA(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root secondary SwitchA(config)#exit SwitchA# The command, spanning-tree vlan 1 root secondary sets a switch s priority number higher than the primary root bridge s priority number but lower than the default setting. This causes the switch to become the secondary root bridge. On SwitchC and SwitchA issue the show run command to display the primary and secondary root bridge priority numbers. Examples are below - SwitchC#show run spanning-tree vlan 1 priority SwitchA#show run spanning-tree vlan 1 priority Copy and paste the portion of the SwitchC configuration that relates to its spanning tree configuration. The command you entered was spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary. However, in the running configuration, the real command is spanning-tree vlan 1 priority You could have also used this command to manually configure root bridges as well. The priority number must be in increments of Please Note: The following configuration in this step is only an example. Do not use the command spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 4096 in this lab. SwitchB#config t SwitchB(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 4096 SwitchB(config)#exit SwitchB# Now that you have made SwitchC the primary root and SwitchA the secondary root, view the spanning tree environment by issuing the show spanning-tree command on all switches.
5 Now, all the switches see SwitchC as the root bridge. Look at the MAC address under the Root ID for each switch. The MAC address for the Root ID belongs to SwitchC. 3. Determine the MAC address for SwitchC and enter that MAC address into your lab completion document. Host port optimization Normally, when a switch port is brought up it takes the port approximately 30 seconds for spanning-tree to go through an initialization process. The purpose of this process is to make sure that any bridging loop is closed before packets are forwarded. Accordingly, during this time the switch port is in a blocking state and does not forward packets. Where a host (server, workstation, printer, router, iphone or other non-switch device) is connected to the port, no bridging loop can actually occur so it is not necessary to have STP go through this initialization process. In fact, it is often undesirable to have the port effectively shut down during the initial 30 seconds as it can be during this time that a network device is seeking an address through DHCP. To remedy this, the portfast command can be entered on a port directly connected to a host. Configuring portfast allows the switch port to immediately transition to a forwarding state and skip the spanning-tree initialization process. Portfast does entirely disable STP, however. Should a switch be connected to the port and a BPDU is received, the port will immediately transition to a blocking state and go through the STP initialization process. Lab steps- In the following steps you will configure portfast on the appropriate port on each switch. SwitchB#config t SwitchB(config)#interface fastethernet 0/8 SwitchB(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast SwitchB(config-if)#exit SwitchB(config)#exit SwitchB# SwitchA#config t SwitchA(config)#interface fastethernet 0/8 SwitchA(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast SwitchA(config-if)#exit SwitchA(config)#exit SwitchA# SwitchC#config t SwitchC(config)#interface fastethernet 0/8
6 SwitchC(config-if)#spanning-tree portfast SwitchC(config-if)#exit SwitchC(config)#exit SwitchC# Confirm the configuration with the show run command on each switch. 4. Paste into your lab completion document the portion of the configuration on SwitchC that relates to its portfast configuration.
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Chapter 5: STP. * What is STP? How does STP work?
 Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Chapter 5. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I
 Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Objectives. 1. Introduction:
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.5 Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Objectives 1. Explain the role of redundancy
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.5 Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Objectives 1. Explain the role of redundancy
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching
 CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 15 Objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 15 Objectives (con
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 15 Objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 15 Objectives (con
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
EIGRP Features and Operation
 EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)
 Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP)
 3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol
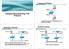 Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree
 Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior
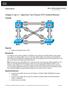 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q
 Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Chapter 3 Reading Organizer
 Name Date Chapter 3 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: 3.1 Compare the types of switches used in an enterprise network. Explain how Spanning Tree Protocol prevents
Name Date Chapter 3 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: 3.1 Compare the types of switches used in an enterprise network. Explain how Spanning Tree Protocol prevents
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]
![Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]](/thumbs/85/92420323.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging
 Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Lab VTP Client and Server Configurations
 Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
Lab Selecting the Root Bridge
 Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
CCNP Switch Questions/Answers Labs
 Acme is small export company that has an existing enterprise network comprised of 5 switches; CORE, DSW1, DSW2, ASW1 and ASW2. The topology diagram indicates their desired pre-vlan spanning tree mapping.
Acme is small export company that has an existing enterprise network comprised of 5 switches; CORE, DSW1, DSW2, ASW1 and ASW2. The topology diagram indicates their desired pre-vlan spanning tree mapping.
Lecture (08) STP - CDP. Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee CDP STP. tweak this simple design to make it more resilient by adding
 Lecture (08) STP - CDP STP CDP Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Such design creates a single point of failure. We could easily tweak this simple design to make it more resilient by adding an extra path between
Lecture (08) STP - CDP STP CDP Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Such design creates a single point of failure. We could easily tweak this simple design to make it more resilient by adding an extra path between
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Introduction to OSPF
 Campus Networking Introduction to OSPF Workshop Campus Layer-2 Networking Network Workshop Design These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license
Campus Networking Introduction to OSPF Workshop Campus Layer-2 Networking Network Workshop Design These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2
 Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial
 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior
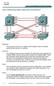 Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Chapter 5. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part II
 Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
examcollection.premium.exam.157q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version 15.0
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan
 isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
Campus Networking Workshop. Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs
 Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
Lab STP configuration on Catalyst 1900 Command Line Interface
 Lab STP configuration on Catalyst 1900 Command Line Interface Estimated Time: 30 mins Objectives: Background: To gain a better understanding of how STP works. To be able to configure and monitor STP on
Lab STP configuration on Catalyst 1900 Command Line Interface Estimated Time: 30 mins Objectives: Background: To gain a better understanding of how STP works. To be able to configure and monitor STP on
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Configuring Flex Links
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Spanning Tree
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
 CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
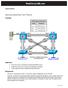 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Configuring STP Extensions
 Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
Lab Verifying VLAN Configurations
 Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Configuring STP Extensions
 This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Exam Questions
 Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Configuring STP and Prestandard IEEE 802.1s MST
 20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CS IT. Lecture (06) STP (I) Problem statement. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
 Lecture (06) STP (I) By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Problem statement If your network consists of layer 2 switches that allow computers connect and exchange data, you will need to consider the design that
Lecture (06) STP (I) By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Problem statement If your network consists of layer 2 switches that allow computers connect and exchange data, you will need to consider the design that
Describing the STP. IEEE Documents. Download this file. Enhancements to STP. Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt STP
 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
Cisco.Actualtests v by.Watson.314q. Exam Code: Exam Name: CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (803)
 Cisco.Actualtests.200-120.v2013-12-09.by.Watson.314q Number: 200-120 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 14.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam Code: 200-120 Exam Name: CCNA Cisco Certified
Cisco.Actualtests.200-120.v2013-12-09.by.Watson.314q Number: 200-120 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 14.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam Code: 200-120 Exam Name: CCNA Cisco Certified
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Exam4Tests. Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily
 Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : 200-101 Title : Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) Vendor : Cisco Version
Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : 200-101 Title : Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) Vendor : Cisco Version
The Spanning Tree Protocol
 Università Ca Foscari di Venezia Dipartimento di Informatica Corso di Sistemi Distribuiti 2009 Presentation outline Introduction 1 Introduction Local internetworking Motivations 2 High level description
Università Ca Foscari di Venezia Dipartimento di Informatica Corso di Sistemi Distribuiti 2009 Presentation outline Introduction 1 Introduction Local internetworking Motivations 2 High level description
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Index. Numerics. Index p priority (QoS) definition Q VLAN standard w as a region 5-54
 Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Managing Network Spanning Trees
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment - Packet Tracer
 CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment - Packet Tracer A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close
CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment - Packet Tracer A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close
CCNA Layer 2 switching. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
STP Optional Characteristic Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
Implementing Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
 Implementing Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol This module provides conceptual and configuration information for Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers. Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Implementing Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol This module provides conceptual and configuration information for Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers. Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Vendor: Cisco. Exam Code: Exam Name: Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Version: Demo
 Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 200-120 Exam Name: Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Version: Demo Exam A QUESTION 1 Refer to the exhibit: What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose
Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 200-120 Exam Name: Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Version: Demo Exam A QUESTION 1 Refer to the exhibit: What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
ICND2. Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol. These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions.
 ICND2 Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol TOPOLOGY 5x2950 (Layer 2 Switches) These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions. Lab Exercise 1: Rapid Spanning-Tree Configuration
ICND2 Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol TOPOLOGY 5x2950 (Layer 2 Switches) These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions. Lab Exercise 1: Rapid Spanning-Tree Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement
 Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
Lab Spanning-Tree Recalculation
 Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Chapter 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks 1.0.1.2 Class Activity Network by Design 1.0.1.2 Class Activity Network by Design 1 Objective Explain the need to design a hierarchical network that is scalable.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks 1.0.1.2 Class Activity Network by Design 1.0.1.2 Class Activity Network by Design 1 Objective Explain the need to design a hierarchical network that is scalable.
CISCO FOR DUMMIES 3. LAN SWITCHING FAST TRACK!
 CISCO FOR DUMMIES 3. LAN SWITCHING FAST TRACK! ZANIM ZACZNIEMY 26/04/15 2 AGENDA Kilka słów o switchach Podstawy konfiguracji switchy L2 i L3, Logiczna separacja sieci lokalnej VLANy Komunikacja między
CISCO FOR DUMMIES 3. LAN SWITCHING FAST TRACK! ZANIM ZACZNIEMY 26/04/15 2 AGENDA Kilka słów o switchach Podstawy konfiguracji switchy L2 i L3, Logiczna separacja sieci lokalnej VLANy Komunikacja między
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
PrepKing. PrepKing
 PrepKing Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 180 min File Version: 9.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ PrepKing 350-001 Sections 1. Section 1.00 - Implement Layer 2 2. Section 2.00 - Implement IPv4
PrepKing Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 180 min File Version: 9.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ PrepKing 350-001 Sections 1. Section 1.00 - Implement Layer 2 2. Section 2.00 - Implement IPv4
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
Configuring Private VLANs Using NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
: Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks
 Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Exam : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Title : Version : DEMO
 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Version : DEMO 1.Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the "Serial0/0 is down" interface status? (Choose two.) A. A Layer
Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Version : DEMO 1.Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the "Serial0/0 is down" interface status? (Choose two.) A. A Layer
Command Reference for Voice VLAN
 APPENDIX A This section provides reference information for the following voice VLAN commands: interface range, page A-1 interface vlan, page A-3 monitor session, page A-4 spanning-tree, page A-6 spanning-tree
APPENDIX A This section provides reference information for the following voice VLAN commands: interface range, page A-1 interface vlan, page A-3 monitor session, page A-4 spanning-tree, page A-6 spanning-tree
Spanning Tree Protocol, from a feature CCNA s Perspective.
 Spanning Tree Protocol, from a feature CCNA s Perspective. written by Gerald C. Paciello Jan. 29, 2015 A little bit of history. Before we talk about Spanning Tree Protocol, let's organize the different
Spanning Tree Protocol, from a feature CCNA s Perspective. written by Gerald C. Paciello Jan. 29, 2015 A little bit of history. Before we talk about Spanning Tree Protocol, let's organize the different
Operation Manual VRRP. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VRRP... 1-1 1.2 Configuring VRRP... 1-2 1.2.1 Configuring the Function of Pinging the Virtual IP Address... 1-3 1.2.2 Configuring the TTL
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to VRRP... 1-1 1.2 Configuring VRRP... 1-2 1.2.1 Configuring the Function of Pinging the Virtual IP Address... 1-3 1.2.2 Configuring the TTL
