TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT
|
|
|
- Opal Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Performance Analysis of PNNI Routing in ATM Networks: Hierarchical Reduced Load Approximation by Hui Xie John S. Baras CSHCN T.R (ISR T.R ) The Center for Satellite and Hybrid Communication Networks is a NASA-sponsored Commercial Space Center also supported by the Department of Defense (DOD) industry the State of Maryland the University of Maryland and the Institute for Systems Research. This document is a technical report in the CSHCN series originating at the University of Maryland. Web site
2 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response including the time for reviewing instructions searching existing data sources gathering and maintaining the data needed and completing and reviewing the collection of information. Send comments regarding this burden estimate or any other aspect of this collection of information including suggestions for reducing this burden to Washington Headquarters Services Directorate for Information Operations and Reports 1215 Jefferson Davis Highway Suite 1204 Arlington VA Respondents should be aware that notwithstanding any other provision of law no person shall be subject to a penalty for failing to comply with a collection of information if it does not display a currently valid OMB control number. 1. REPORT DATE REPORT TYPE 3. DATES COVERED - 4. TITLE AND SUBTITLE Performance Analysis of PNNI Routing in ATM Networks: Hierarchical Reduced Load Approximation 5a. CONTRACT NUMBER 5b. GRANT NUMBER 5c. PROGRAM ELEMENT NUMBER 6. AUTHOR(S) 5d. PROJECT NUMBER 5e. TASK NUMBER 5f. WORK UNIT NUMBER 7. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) Army Research Laboratory2800 Powder Mill RoadAdelphiMD PERFORMING ORGANIZATION REPORT NUMBER 9. SPONSORING/MONITORING AGENCY NAME(S) AND ADDRESS(ES) 10. SPONSOR/MONITOR S ACRONYM(S) 12. DISTRIBUTION/AVAILABILITY STATEMENT Approved for public release; distribution unlimited 13. SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES The original document contains color images. 14. ABSTRACT see report 15. SUBJECT TERMS 11. SPONSOR/MONITOR S REPORT NUMBER(S) 16. SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF: 17. LIMITATION OF ABSTRACT a. REPORT unclassified b. ABSTRACT unclassified c. THIS PAGE unclassified 18. NUMBER OF PAGES 6 19a. NAME OF RESPONSIBLE PERSON Standard Form 298 (Rev. 8-98) Prescribed by ANSI Std Z39-18
3 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF PNNI ROUTING IN ATM NETWORKS: HIERARCHICAL REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION * Hui Xie John S. Baras Electrical Engineering Department Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland College Park MD ABSTRACT In this paper we investigate the performance issue of PNNI routing for ATM networks. A brief introduction to PNNI routing protocol is given. We extend the reduced load approximation algorithm to ATM networks with PNNI routing. A hierarchical reduced load approximation scheme is proposed. The scheme includes two steps: the reduced load approximation algorithm is first applied on the aggregated network at upper level; then the approximation is refined at the lower level as needed using the results from the upper level. This hierarchical scheme follows the PNNI routing framework and results a fast and scaleable algorithm. 1 INTRODUCTION The commercial communications infrastructure continues to experience dramatic growth. To modernize current military legacy communications systems it is very important to leverage commercial leadership and expertise in communication technology arena. Recently a program is setup to extend advanced commercial telecommunications and information distribution to a wireless mobile battlefield environment [11]. One major trend of evolution of telecommunications networks is the rapid growth of ATM networks that are gradually covering more and more of the world. A lot of research is going on to incorporate ATM technology into wireless mobile environment. The difference between commercial and military communication systems are the environment and performance requirements. It is crucial to have an in-depth understanding of the performance of a communication system under different environment. In this paper we consider the performance issue of PNNI (Private Network-to-Network Interface) routing protocol from ATM Forum. PNNI specifies a topology state routing protocol in which nodes flood quality of service (QoS) and reachability information so that all nodes obtain knowledge about the state of the network and available network resources. To reduce the complexity PNNI uses a hierarchical model for topology aggregation [1]. Some important performance metrics for PNNI routing are call setup delay call blocking probability and resource utilization efficiency. However only the call blocking probabilities for PNNI-routed ATM networks are discussed in this paper. The reduced load approximation algorithms [2][3][4] are extended to ATM network with PNNI routing. A hierarchical reduced load approximation algorithm is proposed. Section 2 of this paper describes the reduced load approximation for general loss network. A brief introduction of PNNI routing is given in section 3. In section 4 the reduced load approximation algorithms are extended to ATM networks with PNNI routing and the hierarchical approximation algorithm is presented. The paper concludes with section 5. 2 REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION FOR MULTIRATE LOSS NETWORK Traditionally the loss probability of a telephone system is estimated using Erlang s formula which is applicable to a single link and a single call type system. Recently a generalization of Erlang s model was proposed [2] which treats multirate integrated service networks with state dependent admission control and routing. However the generalization leads to a combinatorial explosion in systems of equations. Indeed the computational complexity is exponential in the number of routes between node pairs and is exponential in the number of bandwidth classes. To circumvent the numerical complexity researchers have developed an approximation called the Erlang fixed point approximation or reduced load approximation [3][4][5]. This technique applies to synchronous transfer mode (circuit-switched) services and to asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) services. It provides an appealing alternative and complement to discrete event simulations. Consider a network with N nodes. A link ( i j ) between nodes i and j has capacity C ij counted in bandwidth units termed trunks. Calls offered to the network fall into S classes. A call of class s has bandwidth b s meaning that if the call is admitted to the network then it is allocated b s trunks on each link of a path from its source to its destination. A link s state is characterized by the number of calls in progress n s of each call class. Consider routing policies where each node pair ( i j ) is assigned an ordered list P ij of paths between nodes i and j: *This work was supported in part by the Advanced Telecommunications/Information Distribution Research Program (ATIRP) Consortium sponsored by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory under Cooperative Agreement DAAL
4 () 1 ( 2) Pij Pij....The call is admitted on the first path in the list where it is admissible. If the call is not admissible on any path then it is blocked. Calls of class s are assumed to arrive to node pair ( i j ) according to a Poisson process with rate λ ij (). s If admitted to the network the call holds for an exponential period of time with mean µ ij (). s Thus these calls constitute a load of ρij () s = λ ij ()/ s µ ij () s. The performance metrics that we are interested in are the blocking probabilities or equivalently the admissibility probabilities. The fixed point approximation is based on assuming that a call is blocked independently by the different links along its path and that arrivals of calls of a given class to a given link are described by a Poisson process. The resulting system of equations whose unknown are for each link ( i j ) and call class s: arrival rates υ ij () s of calls of class s from any node pair that includes link ( i j ) on some route given that link ( i j ) is in a state that admits calls of class s and probabilities aij () s that link ( i j ) is in a state that admits calls of class s. The fixed point formulation essentially consists of two mappings. One is for every node pair ( i j ) from probabilities a kl () s (with k and l dependent on the routing structure) to rates υ ij (). s The other mapping is for each link ( i j ) from rates υ ij () s to probabilities aij (). s Let υ ( m ij ) ( kls ) be the rate that node pair (kl) admits class s calls on its mth route if that route contains link ( i j ); otherwise υ ( m ij ) ( kls )=0. Thus the aggregate arrival rate of calls of class s at link ( i j ) is given by υij () s = υij ( m k l s m kl ) ( ) (1) and by the link independence assumption ( υij m ) ( m) ( kls ) = λkl ( s) R ( kls ) auv ( s) ( uv ) P ( m uv i j kl ) ( ) ( ) (2) ( m) where R ( k l s ) is the probability that a call of class s is not admissible on the first m-1 paths given that the mth path is admissible. An algorithm based on two-terminal reliability ( m) problem was proposed in [3] to compute R ( k l s ). Two ( m) additional approximation of R ( k l s ) was also proposed in [3]: m 1 ( m) R ( k l s) = 1 auv ( s) (3) r= 1 ( uv ) P ( r kl ) ( uv ) ( i j ) with the assumption that admission of a call on a given path is statistically independent of its admission on any other path. m 1 ( m) R ( k l s) = 1 auv ( s) r= 1 ( uv ) P ( r) kl P ( m) kl ( uv ) ( i j) (4) ( r) with the assumption that the events A r = m 1 are kl ( r) ( r) statistically independent where A kl is the event that Pk l is ( m) admissible given P kl is admissible. To complete the fixed point approximation we need a mapping from arrival rates to admissibility probabilities. An approximation first introduced in [67] will be used. The probability of admitting a call of class s to link ( i j ) is C ij aij () s = 1 Eij () n n= C ij b s r s + 1 where Eij ( n) is the equilibrium distribution of the following one-dimensional Markov chain: Letting α ij () s denote the average number of calls of type s in progress on link ( i j ) αij () s = aij () s υ ij ()/ s µ ij () s (6) consider the one-dimensional Markov chain which for any state n and call class s jumps to: state n+ b s with rate λ ij ()( sic ij n r s + b s ) where r s is the trunk reservation parameter and to αij () s state n b s with rate υij () sn In ( bs). tαij () t We can obtain the admissibility probabilities aij () s by solving the above small system of fixed point approximation. It is shown in [67] that this approximation becomes asymptotically exact in overload conditions. More refined approximations are also discussed in [67]. 3 PNNI ROUTING PNNI is the protocol that enables the building of multivendor interoperable ATM networks. PNNI is a hierarchical dynamic link-state routing protocol for building large-scale ATM-based network. In addition PNNI defines signaling requests to establish point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections. (5) 2
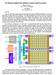
5 UPPER LEVEL N.2 N.1 N.4 N.3 N.5 N.6 PG(2) N.2.3 N.2.2 PG(1) 2.1 PG(5) PG(6) N.1.3 N.5.1 N.6.1 N.1.2 PG(4) PG(3) N.5.2 N.6.2 N.1.1 N.4.1 N.4.2 N.3.1 N.4.3 N.5.3 N.6.3 N.6.4 N.6.5 N.4.4 N.3.4 N.3.2 LOWER LEVEL N.4.5 N.4.6 N.3.3 Figure 1. Hierarchical ATM Network with Two Levels Like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) PNNI is a hierarchical link-state routing protocol that organizes switching systems into logical collections called peer group. Neighboring nodes form a peer group by exchanging their peer group identifiers (PGIDs) via Hello packets using a protocol that makes nodes known to each other. If the nodes have the same PGID they belong to the peer group defined by that particular ID; if their PGIDs are different they belong to different peer groups. A border node has at least one link that crosses the peer group boundary. Hello protocol exchange occur over logical links (physical link or VPC or SVCC). PNNI defines the creation and distribution of a topology database that describes the elements of the routing domain as seen by a node. This database provides all the information required to compute a route from the node to any address that is reachable in or through that routing domain. Nodes exchange database information using PTSEs (PNNI Topology State Elements). PTSEs contain topology characteristics derived from link or node state parameter information. The state parameter information could be either metrics or attributes. PTSEs are grouped to form PTSP (PNNI Topology State Packet) and PTSPs are flooded throughout the peer group so all nodes in one peer group will have an identical database. Every peer group has a node called peer group leader (PGL). There is at most one active PGL per peer group. The PGL will represent current peer group in the parent peer group as a single node. The PGL will also flood the PTSEs in parent peer group to the current peer group. Apart from its specific role in aggregation and distribution of information for maintaining the PNNI hierarchy the PGL does not have any special role in the peer group. Currently PNNI support 104 hierarchical levels. Call establishment in PNNI consists of two operations: the selection of a path and the setup of the connection state at each point along that path. PNNI uses source routing for all connection setup requests. The path is encoded as a Designated Transit List (DTL) which is explicitly included in the connection setup request. The PNNI network can be described by a hierarchical model. The network is represented by a graph G(VE) where V is the set of layer 1 nodes and E is the set of links interconnecting them. G(VE) will be referred as the actual network. Layer 1 nodes are clustered to form layer 2 nodes which are clustered into layer 3 nodes etc. up to the highest. Say L-th layer. The PNNI routing hierarchy also allows asymmetries in the sense that a set of layer i nodes can be directly clustered into a layer i+ n node with 1 n L i so for a given lower level peer group its parent peer group can simultaneously be a grandparent or great-grandparent peer group to some other lower level peer group. Completion is achieved until the entire network is encompassed in a single highest level peer group. 4 A HIERARCHICAL REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION FOR PNNI ROUTING We now describe a reduced load approximation method for ATM networks with PNNI routing. We assume that the effective bandwidths are used for admission control and routing. PNNI routing designed for ATM networks has a hierarchical structure. Currently up to 104 levels are allowed but 3-6 levels 3
6 are suffice to a large network. For simplicity we will only consider the case of two level hierarchies. Figure 1 shows a two level hierarchical ATM network. At the lower level each node represents a switching system. At upper level each node represents a collection of one or more nodes at lower level (or called a peer group). A path in PNNI routing is called a hierarchically complete source route. Such a path is not a fully detailed source route because it does not contain the details of the path outside the originator s peer group. Instead those portions of the path are abstracted as a sequence of logical group nodes to be transited. When the call setup arrives at the entry switching system of a peer group that switching system is responsible for selecting a source route describing the transit across that peer group. Consider a path between node N.1.2 and node N.6.4 in Figure 1. PNNI routing algorithm will build following DTLs: DTL:[N.1.2 N.1.1] DTL:[N.1N.2N.3N.5N.6] which includes nodes (and links) in lower level and logical nodes (and logical links) in upper level. A two step method is needed to estimate the admissibility probabilities and arrival rates on links along this path. A. Approximation at Upper Level (Step 1) A logical link at upper level represents one or more links between the same peer groups at lower level. The bandwidth of one logical link is the sum of the bandwidth of each link it includes. A logical node at upper level represents a peer group at lower level. In the reduced load approximation model a physical node does not contribute to the end-to-end blocking probability estimation. Since a logical node may include a set of nodes and links it will contribute to the end-to-end blocking probability. For the purpose of reduced load approximation a nodal aggregation mechanism that captures the blocking probability of the logical node is needed. There are some conventional methods for topology aggregation [8-10]. In the Symmetric-Node approach a given topology with multiple nodes is collapsed into one virtual node. This approach offers the greatest reduction of information but it does not adequately reflect any connectivity information in the original topology. The Full-Mesh approach uses a logical link between each pair of border nodes to construct the aggregated topology. The draw back of this approach is the number of internal links increases as the square of the number of border nodes. A compromise between the two extreme approaches is a Star approach. In the Star approach the virtual node that is the center of the star is explicitly connected to the border nodes via logical links which are not necessarily identical. This approach has the complexity of an order that is linear in the number of the border nodes. However it offers a limited flexibility for reflecting asymmetric topology information. We use the Complex Node Representation [1] for our purpose of reduced load approximation at upper level hierarchy. The complex node representation provides aggregated topology information not only for traversing the logical node but also routing to and from the inside of the logical node. The interior reference point of a logical node is referred to as a nucleus. A border reference point of a logical node is known as port. A logical connectivity between the nucleus and a port is refereed to as a spoke. Exceptions can be used to represent particular ports whose connectivity to the nucleus is significantly different from the default. Two ports may also be connected via a bypass. The complex node representation of logical node N.4 or peer group PG(4) is shown in Figure 2. BYPASS Port 1 on link (N.4--N.1) SPOKE Port 2 on link (N.4--N.2) NUCLEUS SPOKE Port 3 on link (N.4--N.3) Figure 2. Complex node representation of N.4 in Figure 1 Now replace all the logical node in upper level with their corresponding complex node representations we get a network with N nodes. A node is either a nucleus or a port of a logical node. A link ( ( u ) ( u i j ) ) is a logical link between peer groups or a spoke or bypass within a complex node representation. Suppose node i of the N nodes ( represents a set of lower level nodes Gi ( u ) ). Then the arrival rate between node pair ( ( u ) ( u i j ) ) is λ i j = i G( i ) j G( j ) λ ij The computation of link capacity C i j depends on the type of the link. For logical link between peer groups the capacity is the summation of the capacity of the lower level links that the logical link represents. For spoke or bypass within complex node representation the guideline of PNNI topology aggregation [1][9] should be followed. We use a conservative scheme that uses worst case parameter i.e. the smallest capacity between a nucleus and a port (spoke case) or a port and a port (bypass case). With these parameters the reduced load approximation algorithm described in section 2 can be used to calculate the 4
7 admissibility probabilities a i j and aggregated link arrival rates υ i j for the upper level network with complex node representations. B. Refinement at Lower Level (Step 2) Step 1 gives us the reduced load approximation of the upper level network so we can compute the blocking probabilities between logical nodes. Now suppose we want to compute the blocking probability between two lower level nodes such as N.1.2 and N.6.4 some refinements are needed. For originating and destination peer group no aggregation is used i.e. the logical node N.1 and N.6 will be represented by their corresponding lower level peer groups. For intermediate logical nodes aggregation is used i.e. complex node representation is used to represent the intermediate logical nodes. The resulting network is shown in Figure 3. PG(1) N.1.3 N.1.2 N.1.1 N.4 N.2 N.3 N.5 N.6.2 N.6.3 PG(6) N.6.4 N.6.1 N.6.5 Figure 3. Refinement for Originating and Destination Peer Groups Now the reduced load approximation algorithm described in section 2 is used to refine the estimation for originating and destination peer groups (PG(1) and PG(6) in Figure 1) i.e. the admissibility probabilities and aggregated link arrival rates for links in originating and destination peer groups are estimated. The admissibility probabilities and aggregated link arrival rates for links other than the originating and destination peer groups will not be estimated and the values we get from step 1 will be used instead. The same refinement call be done for any originating and destination peer group pairs. This hierarchical scheme follows the PNNI routing framework and results a fast and scaleable reduced load approximation for ATM networks with PNNI routing. 5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE RESEARCH The hierarchical approximation scheme proposed in this paper extend the reduced load approximation algorithm to ATM networks with PNNI routing. Compared to original reduced load approximation algorithm this scheme uses coarse to fine iteration so it is fast and scaleable to large networks. One possible future area of research is to extend the scheme to multiple level of hierarchies. Another interesting problem is to take into account the traffic of topology database flooding and build a more realistic blocking probability model for PNNI routing in ATM networks. REFERENCES [1] ATM Forum PNNI Specification 1.0 af-pnni March [2] F.P. Kelly Loss Networks The Annals of Applied Probability Vol. 1 No. 3 pp Aug [3] A.G. Greenberg and R. Srikant Computational Techniques for Accurate Performance Evaluation of Multirate Multihop Communication Networks preprint [4] S.P. Chung and K.W. Ross Reduced Load Approximations for Multirate Loss Networks IEEE Trans. on Communications Vol. 41 No. 8 pp Aug [5] S.P. Chung A. Kashper and K.W. Ross Computing Approximate Blocking Probabilities for Large Loss Networks with State-Dependent Routing IEEE/ACM Trans. On Networking Vol. 1 No. 1 pp Feb [6] N. Bean R.J. Gibbens and S. Zachary Analysis of large single resource loss systems under heavy traffic with applications to integrated networks Adv. Appl. Prob. March [7] N. Bean R.J. Gibbens and S. Zachary The Performance of single resource loss systems in multiservice networks preprints [8] Whay Lee Topology Aggregation in PNNI Routing ATM Forum atm Sept [9] Whay Lee Some Guidelines for PNNI Topology Aggregation ATM Forum atm Feb [10] Whay C. Lee Topology Aggregation for Hierarchical Routing in ATM Networks ACM SIGCOMM pp [11] ARL Advanced Telecommunications /Information Distribution Research Program (ATIRP) Annual Conference Proceedings Vol. I & II January
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF PNNI ROUTING IN ATM NETWORKS: HIERARCHICAL REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION*
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF PNNI ROUTING IN ATM NETWORKS: HIERARCHICAL REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION* Hui Xie John S. Baras Electrical Engineering Department Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF PNNI ROUTING IN ATM NETWORKS: HIERARCHICAL REDUCED LOAD APPROXIMATION* Hui Xie John S. Baras Electrical Engineering Department Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland
DoD Common Access Card Information Brief. Smart Card Project Managers Group
 DoD Common Access Card Information Brief Smart Card Project Managers Group 12 July, 2001 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burder for this collection of information
DoD Common Access Card Information Brief Smart Card Project Managers Group 12 July, 2001 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burder for this collection of information
Service Level Agreements: An Approach to Software Lifecycle Management. CDR Leonard Gaines Naval Supply Systems Command 29 January 2003
 Service Level Agreements: An Approach to Software Lifecycle Management CDR Leonard Gaines Naval Supply Systems Command 29 January 2003 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting
Service Level Agreements: An Approach to Software Lifecycle Management CDR Leonard Gaines Naval Supply Systems Command 29 January 2003 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting
Using Model-Theoretic Invariants for Semantic Integration. Michael Gruninger NIST / Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland
 Using Model-Theoretic Invariants for Semantic Integration Michael Gruninger NIST / Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
Using Model-Theoretic Invariants for Semantic Integration Michael Gruninger NIST / Institute for Systems Research University of Maryland Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
Dana Sinno MIT Lincoln Laboratory 244 Wood Street Lexington, MA phone:
 Self-Organizing Networks (SONets) with Application to Target Tracking Dana Sinno 244 Wood Street Lexington, MA 02420-9108 phone: 781-981-4526 email: @ll.mit.edu Abstract The growing interest in large arrays
Self-Organizing Networks (SONets) with Application to Target Tracking Dana Sinno 244 Wood Street Lexington, MA 02420-9108 phone: 781-981-4526 email: @ll.mit.edu Abstract The growing interest in large arrays
Empirically Based Analysis: The DDoS Case
 Empirically Based Analysis: The DDoS Case Jul 22 nd, 2004 CERT Analysis Center Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 The CERT Analysis Center is part of the
Empirically Based Analysis: The DDoS Case Jul 22 nd, 2004 CERT Analysis Center Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 The CERT Analysis Center is part of the
Multi-Modal Communication
 Multi-Modal Communication 14 November 2011 Victor S. Finomore, Jr., Ph.D. Research Psychologist Battlespace Acoustic Branch Air Force Research Laboratory DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT D. Distribution authorized
Multi-Modal Communication 14 November 2011 Victor S. Finomore, Jr., Ph.D. Research Psychologist Battlespace Acoustic Branch Air Force Research Laboratory DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT D. Distribution authorized
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF HALON- REPLACEMENT FIRE EXTINGUISHING SYSTEMS (PHASE II)
 AL/EQ-TR-1997-3104 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF HALON- REPLACEMENT FIRE EXTINGUISHING SYSTEMS (PHASE II) D. Nickolaus CFD Research Corporation 215 Wynn Drive Huntsville,
AL/EQ-TR-1997-3104 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF HALON- REPLACEMENT FIRE EXTINGUISHING SYSTEMS (PHASE II) D. Nickolaus CFD Research Corporation 215 Wynn Drive Huntsville,
4. Lessons Learned in Introducing MBSE: 2009 to 2012
 4. Lessons Learned in Introducing MBSE: 2009 to 2012 Abstract A. Peter Campbell University of South Australia An overview of the lessons that are emerging from recent efforts to employ MBSE in the development
4. Lessons Learned in Introducing MBSE: 2009 to 2012 Abstract A. Peter Campbell University of South Australia An overview of the lessons that are emerging from recent efforts to employ MBSE in the development
Topology Control from Bottom to Top
 Topology Control from Bottom to Top M. Steenstrup Stow Research L.L.C. Clemson University steenie@rcn.com This work was funded in part by DARPA and by ONR MURI. Report Documentation Page Form Approved
Topology Control from Bottom to Top M. Steenstrup Stow Research L.L.C. Clemson University steenie@rcn.com This work was funded in part by DARPA and by ONR MURI. Report Documentation Page Form Approved
Setting the Standard for Real-Time Digital Signal Processing Pentek Seminar Series. Digital IF Standardization
 Setting the Standard for Real-Time Digital Signal Processing Pentek Seminar Series Digital IF Standardization Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection
Setting the Standard for Real-Time Digital Signal Processing Pentek Seminar Series Digital IF Standardization Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection
High-Assurance Security/Safety on HPEC Systems: an Oxymoron?
 High-Assurance Security/Safety on HPEC Systems: an Oxymoron? Bill Beckwith Objective Interface Systems, Inc. Phone: 703-295-6519 Email Address: bill.beckwith@ois.com W. Mark Vanfleet National Security
High-Assurance Security/Safety on HPEC Systems: an Oxymoron? Bill Beckwith Objective Interface Systems, Inc. Phone: 703-295-6519 Email Address: bill.beckwith@ois.com W. Mark Vanfleet National Security
Simulation of Routing Protocol with CoS/QoS Enhancements in Heterogeneous Communication Network
 UNCLASSIFIED/UNLIMITED Simulation of Routing Protocol with CoS/QoS Enhancements in Heterogeneous Communication Network M. Sc. Eng. Emil Kubera M. Sc. Eng. Joanna Sliwa M. Sc. Eng. Krzysztof Zubel Eng.
UNCLASSIFIED/UNLIMITED Simulation of Routing Protocol with CoS/QoS Enhancements in Heterogeneous Communication Network M. Sc. Eng. Emil Kubera M. Sc. Eng. Joanna Sliwa M. Sc. Eng. Krzysztof Zubel Eng.
Architecting for Resiliency Army s Common Operating Environment (COE) SERC
 Architecting for Resiliency Army s Common Operating Environment (COE) SERC 5 October 2011 Mr. Terry Edwards Director, ASA(ALT) Office of the Chief Systems Engineer (OCSE) (703) 614-4540 terry.edwards@us.army.mil
Architecting for Resiliency Army s Common Operating Environment (COE) SERC 5 October 2011 Mr. Terry Edwards Director, ASA(ALT) Office of the Chief Systems Engineer (OCSE) (703) 614-4540 terry.edwards@us.army.mil
Accuracy of Computed Water Surface Profiles
 US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center Accuracy of Computed Water Surface Profiles Appendix D Data Management and Processing Procedures February 1987 Approved for Public Release. Distribution
US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center Accuracy of Computed Water Surface Profiles Appendix D Data Management and Processing Procedures February 1987 Approved for Public Release. Distribution
Kathleen Fisher Program Manager, Information Innovation Office
 Kathleen Fisher Program Manager, Information Innovation Office High Assurance Systems DARPA Cyber Colloquium Arlington, VA November 7, 2011 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
Kathleen Fisher Program Manager, Information Innovation Office High Assurance Systems DARPA Cyber Colloquium Arlington, VA November 7, 2011 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Hierarchical Loss Network Model for Performance Evaluation by Mingyan Liu, John S. Baras CSHCN T.R. 2000-1 (ISR T.R. 2000-2) Sponsored by: NASA A Hierarchical Loss Network Model
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Hierarchical Loss Network Model for Performance Evaluation by Mingyan Liu, John S. Baras CSHCN T.R. 2000-1 (ISR T.R. 2000-2) Sponsored by: NASA A Hierarchical Loss Network Model
FUDSChem. Brian Jordan With the assistance of Deb Walker. Formerly Used Defense Site Chemistry Database. USACE-Albuquerque District.
 FUDSChem Formerly Used Defense Site Chemistry Database Brian Jordan With the assistance of Deb Walker USACE-Albuquerque District 31 March 2011 1 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
FUDSChem Formerly Used Defense Site Chemistry Database Brian Jordan With the assistance of Deb Walker USACE-Albuquerque District 31 March 2011 1 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
Dr. Stuart Dickinson Dr. Donald H. Steinbrecher Naval Undersea Warfare Center, Newport, RI May 10, 2011
 Environment, Energy Security & Sustainability Symposium & Exhibition Dr. Stuart Dickinson Dr. Donald H. Steinbrecher Naval Undersea Warfare Center, Newport, RI Stuart.dickinson@navy.mil May 10, 2011 Approved
Environment, Energy Security & Sustainability Symposium & Exhibition Dr. Stuart Dickinson Dr. Donald H. Steinbrecher Naval Undersea Warfare Center, Newport, RI Stuart.dickinson@navy.mil May 10, 2011 Approved
PNNI: Routing in ATM Networks
 PNNI: Routing in ATM Networks Professor of CIS Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@ACM.Org http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview Distribution of topology information Hierarchical groups Source routing Designated
PNNI: Routing in ATM Networks Professor of CIS Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@ACM.Org http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview Distribution of topology information Hierarchical groups Source routing Designated
73rd MORSS CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation
 CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation 712CD For office use only 41205 21-23 June 2005, at US Military Academy, West Point, NY Please complete this form 712CD as your cover page to
CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation 712CD For office use only 41205 21-23 June 2005, at US Military Academy, West Point, NY Please complete this form 712CD as your cover page to
Dr. ing. Rune Aasgaard SINTEF Applied Mathematics PO Box 124 Blindern N-0314 Oslo NORWAY
 Do You Have to See Everything All the Time? Or is it at All Possible? Handling Complex Graphics Using Multiple Levels of Detail Examples from Geographical Applications Dr. ing. Rune Aasgaard SINTEF PO
Do You Have to See Everything All the Time? Or is it at All Possible? Handling Complex Graphics Using Multiple Levels of Detail Examples from Geographical Applications Dr. ing. Rune Aasgaard SINTEF PO
NATO-IST-124 Experimentation Instructions
 ARL-TN-0799 NOV 2016 US Army Research Laboratory NATO-IST-124 Experimentation Instructions by Kelvin M Marcus NOTICES Disclaimers The findings in this report are not to be construed as an official Department
ARL-TN-0799 NOV 2016 US Army Research Laboratory NATO-IST-124 Experimentation Instructions by Kelvin M Marcus NOTICES Disclaimers The findings in this report are not to be construed as an official Department
Information, Decision, & Complex Networks AFOSR/RTC Overview
 Information, Decision, & Complex Networks AFOSR/RTC Overview 06 MAR 2013 Integrity Service Excellence Robert J. Bonneau, Ph.D. Division Chief AFOSR/RTC Air Force Research Laboratory Report Documentation
Information, Decision, & Complex Networks AFOSR/RTC Overview 06 MAR 2013 Integrity Service Excellence Robert J. Bonneau, Ph.D. Division Chief AFOSR/RTC Air Force Research Laboratory Report Documentation
A Distributed Parallel Processing System for Command and Control Imagery
 A Distributed Parallel Processing System for Command and Control Imagery Dr. Scott E. Spetka[1][2], Dr. George O. Ramseyer[3], Dennis Fitzgerald[1] and Dr. Richard E. Linderman[3] [1] ITT Industries Advanced
A Distributed Parallel Processing System for Command and Control Imagery Dr. Scott E. Spetka[1][2], Dr. George O. Ramseyer[3], Dennis Fitzgerald[1] and Dr. Richard E. Linderman[3] [1] ITT Industries Advanced
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Computer Aided Munitions Storage Planning
 Computer Aided Munitions Storage Planning Robert F. Littlefield and Edward M. Jacobs Integrated Systems Analysts, Inc. (904) 862-7321 Mr. Joseph Jenus, Jr. Manager, Air Force Explosives Hazard Reduction
Computer Aided Munitions Storage Planning Robert F. Littlefield and Edward M. Jacobs Integrated Systems Analysts, Inc. (904) 862-7321 Mr. Joseph Jenus, Jr. Manager, Air Force Explosives Hazard Reduction
David W. Hyde US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Vicksburg, Mississippi ABSTRACT
 MICROCOMPUTER ADAPTATION OF A TECHNICAL MANUAL David W. Hyde US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Vicksburg, Mississippi 39180 ABSTRACT The Tri-Service Manual "Structures to Resist the Effects
MICROCOMPUTER ADAPTATION OF A TECHNICAL MANUAL David W. Hyde US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Vicksburg, Mississippi 39180 ABSTRACT The Tri-Service Manual "Structures to Resist the Effects
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF LIQUID MOLDING PROCESSES. Pavel Simacek Center for Composite Materials University of Delaware
 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF LIQUID MOLDING PROCESSES Pavel Simacek Center for Composite Materials University of Delaware UD-CCM 1 July 2003 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF LIQUID MOLDING PROCESSES Pavel Simacek Center for Composite Materials University of Delaware UD-CCM 1 July 2003 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public
Technological Advances In Emergency Management
 Technological Advances In Emergency Management Closing the gap between Preparation and Recovery Will Fontan, P.E. Regional Director, ONRG Americas Office Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No.
Technological Advances In Emergency Management Closing the gap between Preparation and Recovery Will Fontan, P.E. Regional Director, ONRG Americas Office Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No.
ARINC653 AADL Annex Update
 ARINC653 AADL Annex Update Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Julien Delange AADL Meeting February 15 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
ARINC653 AADL Annex Update Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Julien Delange AADL Meeting February 15 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
Title: An Integrated Design Environment to Evaluate Power/Performance Tradeoffs for Sensor Network Applications 1
 Title: An Integrated Design Environment to Evaluate Power/Performance Tradeoffs for Sensor Network Applications 1 Authors Mr. Amol B. Bakshi (first author, corresponding author) 3740 McClintock Ave, EEB
Title: An Integrated Design Environment to Evaluate Power/Performance Tradeoffs for Sensor Network Applications 1 Authors Mr. Amol B. Bakshi (first author, corresponding author) 3740 McClintock Ave, EEB
Corrosion Prevention and Control Database. Bob Barbin 07 February 2011 ASETSDefense 2011
 Corrosion Prevention and Control Database Bob Barbin 07 February 2011 ASETSDefense 2011 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information
Corrosion Prevention and Control Database Bob Barbin 07 February 2011 ASETSDefense 2011 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information
Parallelization of a Electromagnetic Analysis Tool
 Parallelization of a Electromagnetic Analysis Tool Milissa Benincasa Black River Systems Co. 162 Genesee Street Utica, NY 13502 (315) 732-7385 phone (315) 732-5837 fax benincas@brsc.com United States Chris
Parallelization of a Electromagnetic Analysis Tool Milissa Benincasa Black River Systems Co. 162 Genesee Street Utica, NY 13502 (315) 732-7385 phone (315) 732-5837 fax benincas@brsc.com United States Chris
I R TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT. A Local Optimization Algorithm for Logical Topology Design and Traffic Grooming in IP over WDM Networks
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Local Optimization Algorithm for Logical Topology Design and Traffic Grooming in IP over WDM Networks by Kwang-Il Lee, Mark Shayman TR 2003-3 I R INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Local Optimization Algorithm for Logical Topology Design and Traffic Grooming in IP over WDM Networks by Kwang-Il Lee, Mark Shayman TR 2003-3 I R INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH
Basing a Modeling Environment on a General Purpose Theorem Prover
 Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375-5320 NRL/MR/5546--06-8952 Basing a Modeling Environment on a General Purpose Theorem Prover Myla Archer Center for High Assurance Computer Systems Information
Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375-5320 NRL/MR/5546--06-8952 Basing a Modeling Environment on a General Purpose Theorem Prover Myla Archer Center for High Assurance Computer Systems Information
Distributed Real-Time Embedded Video Processing
 Distributed Real-Time Embedded Processing Tiehan Lv Wayne Wolf Dept. of EE, Princeton University Phone: (609) 258-1424 Fax: (609) 258-3745 Email: wolf@princeton.edu Burak Ozer Verificon Corp. Abstract:
Distributed Real-Time Embedded Processing Tiehan Lv Wayne Wolf Dept. of EE, Princeton University Phone: (609) 258-1424 Fax: (609) 258-3745 Email: wolf@princeton.edu Burak Ozer Verificon Corp. Abstract:
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction
 Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Introducing I 3 CON. The Information Interpretation and Integration Conference
 Introducing I 3 CON The Information Interpretation and Integration Conference Todd Hughes, Ph.D. Senior Member, Engineering Staff Advanced Technology Laboratories 10/7/2004 LOCKHEED MARTIN 1 Report Documentation
Introducing I 3 CON The Information Interpretation and Integration Conference Todd Hughes, Ph.D. Senior Member, Engineering Staff Advanced Technology Laboratories 10/7/2004 LOCKHEED MARTIN 1 Report Documentation
Use of the Polarized Radiance Distribution Camera System in the RADYO Program
 Use of the Polarized Radiance Distribution Camera System in the RADYO Program Kenneth J. Voss Physics Department, University of Miami Coral Gables, Fl. 33124 phone: (305) 284-2323 ext 2 fax: (305) 284-4222
Use of the Polarized Radiance Distribution Camera System in the RADYO Program Kenneth J. Voss Physics Department, University of Miami Coral Gables, Fl. 33124 phone: (305) 284-2323 ext 2 fax: (305) 284-4222
Data Reorganization Interface
 Data Reorganization Interface Kenneth Cain Mercury Computer Systems, Inc. Phone: (978)-967-1645 Email Address: kcain@mc.com Abstract: This presentation will update the HPEC community on the latest status
Data Reorganization Interface Kenneth Cain Mercury Computer Systems, Inc. Phone: (978)-967-1645 Email Address: kcain@mc.com Abstract: This presentation will update the HPEC community on the latest status
AFRL-ML-WP-TM
 AFRL-ML-WP-TM-2004-4157 NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION (NDE) TECHNOLOGY INITIATIVES PROGRAM (NTIP) Delivery Order 0043: Upgrade of Computed Tomography Facility By: S. Trent Neel Advanced Research and Applications
AFRL-ML-WP-TM-2004-4157 NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION (NDE) TECHNOLOGY INITIATIVES PROGRAM (NTIP) Delivery Order 0043: Upgrade of Computed Tomography Facility By: S. Trent Neel Advanced Research and Applications
A Review of the 2007 Air Force Inaugural Sustainability Report
 Headquarters U.S. Air Force A Review of the 2007 Air Force Inaugural Sustainability Report Lt Col Wade Weisman SAF/IEE 703-693-9544 wade.weisman@pentagon.af.mil Ms. Krista Goodale Booz Allen Hamilton 757-466-3251
Headquarters U.S. Air Force A Review of the 2007 Air Force Inaugural Sustainability Report Lt Col Wade Weisman SAF/IEE 703-693-9544 wade.weisman@pentagon.af.mil Ms. Krista Goodale Booz Allen Hamilton 757-466-3251
Better Contextual Suggestions in ClueWeb12 Using Domain Knowledge Inferred from The Open Web
 Better Contextual Suggestions in ClueWeb12 Using Domain Knowledge Inferred from The Open Web Thaer Samar 1, Alejandro Bellogín 2, and Arjen P. de Vries 1 1 Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, {samar,arjen}@cwi.nl
Better Contextual Suggestions in ClueWeb12 Using Domain Knowledge Inferred from The Open Web Thaer Samar 1, Alejandro Bellogín 2, and Arjen P. de Vries 1 1 Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, {samar,arjen}@cwi.nl
Space and Missile Systems Center
 Space and Missile Systems Center M-Code Benefits and Availability Capt Travis Mills, SMC/GPEP 29 Apr 15 UNCLASSIFIED/APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
Space and Missile Systems Center M-Code Benefits and Availability Capt Travis Mills, SMC/GPEP 29 Apr 15 UNCLASSIFIED/APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
Balancing Transport and Physical Layers in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks: Jointly Optimal Congestion Control and Power Control
 Balancing Transport and Physical Layers in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks: Jointly Optimal Congestion Control and Power Control Mung Chiang Electrical Engineering Department, Princeton University NRL/NATO Workshop
Balancing Transport and Physical Layers in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks: Jointly Optimal Congestion Control and Power Control Mung Chiang Electrical Engineering Department, Princeton University NRL/NATO Workshop
U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command (IDAS) Briefer: Jason Morse ARMED Team Leader Ground System Survivability, TARDEC
 U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command Integrated Defensive Aid Suites (IDAS) Briefer: Jason Morse ARMED Team Leader Ground System Survivability, TARDEC Report Documentation Page Form
U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command Integrated Defensive Aid Suites (IDAS) Briefer: Jason Morse ARMED Team Leader Ground System Survivability, TARDEC Report Documentation Page Form
UMass at TREC 2006: Enterprise Track
 UMass at TREC 2006: Enterprise Track Desislava Petkova and W. Bruce Croft Center for Intelligent Information Retrieval Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract
UMass at TREC 2006: Enterprise Track Desislava Petkova and W. Bruce Croft Center for Intelligent Information Retrieval Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract
Exploring the Query Expansion Methods for Concept Based Representation
 Exploring the Query Expansion Methods for Concept Based Representation Yue Wang and Hui Fang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware 140 Evans Hall, Newark, Delaware, 19716,
Exploring the Query Expansion Methods for Concept Based Representation Yue Wang and Hui Fang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware 140 Evans Hall, Newark, Delaware, 19716,
Vision Protection Army Technology Objective (ATO) Overview for GVSET VIP Day. Sensors from Laser Weapons Date: 17 Jul 09 UNCLASSIFIED
 Vision Protection Army Technology Objective (ATO) Overview for GVSET VIP Day DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release. Vision POC: Rob Protection Goedert, ATO: TARDEC Protection ATO manager
Vision Protection Army Technology Objective (ATO) Overview for GVSET VIP Day DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release. Vision POC: Rob Protection Goedert, ATO: TARDEC Protection ATO manager
NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES
 NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES Paramsothy Jayakumar, Mike Letherwood US Army RDECOM TARDEC Ulysses Contreras, Ashraf M. Hamed, Abdel-Nasser A. Mohamed,
NEW FINITE ELEMENT / MULTIBODY SYSTEM ALGORITHM FOR MODELING FLEXIBLE TRACKED VEHICLES Paramsothy Jayakumar, Mike Letherwood US Army RDECOM TARDEC Ulysses Contreras, Ashraf M. Hamed, Abdel-Nasser A. Mohamed,
2013 US State of Cybercrime Survey
 2013 US State of Cybercrime Survey Unknown How 24 % Bad is the Insider Threat? Insiders 51% 2007-2013 Carnegie Mellon University Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting
2013 US State of Cybercrime Survey Unknown How 24 % Bad is the Insider Threat? Insiders 51% 2007-2013 Carnegie Mellon University Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting
Data Replication in the CNR Environment:
 Data Replication in the CNR Environment: The Harsh Reality of a Harsh Communications Environment presented by Tim Johnson, IP Unwired 11 Sept 2002 UNCLASSIFIED - APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE 1 Report Documentation
Data Replication in the CNR Environment: The Harsh Reality of a Harsh Communications Environment presented by Tim Johnson, IP Unwired 11 Sept 2002 UNCLASSIFIED - APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE 1 Report Documentation
73rd MORSS CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation
 CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation 712CD For office use only 41205 21-23 June 2005, at US Military Academy, West Point, NY Please complete this form 712CD as your cover page to
CD Cover Page UNCLASSIFIED DISCLOSURE FORM CD Presentation 712CD For office use only 41205 21-23 June 2005, at US Military Academy, West Point, NY Please complete this form 712CD as your cover page to
A Performance Evaluation Architecture for Hierarchical PNNI and Performance Evaluation of Different Aggregation Algorithms in Large ATM Networks
 A Performance Evaluation Architecture for Hierarchical PNNI and Performance Evaluation of Different Aggregation Algorithms in Large ATM Networks Gowri Dhandapani 07/17/2000 Organization PNNI Basics Motivation
A Performance Evaluation Architecture for Hierarchical PNNI and Performance Evaluation of Different Aggregation Algorithms in Large ATM Networks Gowri Dhandapani 07/17/2000 Organization PNNI Basics Motivation
Energy Security: A Global Challenge
 A presentation from the 2009 Topical Symposium: Energy Security: A Global Challenge Hosted by: The Institute for National Strategic Studies of The National Defense University 29-30 September 2009 By SCOTT
A presentation from the 2009 Topical Symposium: Energy Security: A Global Challenge Hosted by: The Institute for National Strategic Studies of The National Defense University 29-30 September 2009 By SCOTT
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction
 Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Automation Middleware and Algorithms for Robotic Underwater Sensor Networks
 Automation Middleware and Algorithms for Robotic Underwater Sensor Networks Fumin Zhang ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology 210 Technology Circle, Savannah, GA 31407 phone: (912) 963-6905 fax: (912) 966-7928
Automation Middleware and Algorithms for Robotic Underwater Sensor Networks Fumin Zhang ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology 210 Technology Circle, Savannah, GA 31407 phone: (912) 963-6905 fax: (912) 966-7928
ASSESSMENT OF A BAYESIAN MODEL AND TEST VALIDATION METHOD
 ASSESSMENT OF A BAYESIAN MODEL AND TEST VALIDATION METHOD Yogita Pai, Michael Kokkolaras, Greg Hulbert, Panos Papalambros, Univ. of Michigan Michael K. Pozolo, US Army RDECOM-TARDEC Yan Fu, Ren-Jye Yang,
ASSESSMENT OF A BAYESIAN MODEL AND TEST VALIDATION METHOD Yogita Pai, Michael Kokkolaras, Greg Hulbert, Panos Papalambros, Univ. of Michigan Michael K. Pozolo, US Army RDECOM-TARDEC Yan Fu, Ren-Jye Yang,
SURVIVABILITY ENHANCED RUN-FLAT
 SURVIVABILITY ENHANCED RUN-FLAT VARIABLE FOOTPRINT TIRES Presented by: James Capouellez (US ARMY, RDE-COM, TARDEC) Dr. Jon Gerhardt (American Engineering Group) Date: August 2010 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT
SURVIVABILITY ENHANCED RUN-FLAT VARIABLE FOOTPRINT TIRES Presented by: James Capouellez (US ARMY, RDE-COM, TARDEC) Dr. Jon Gerhardt (American Engineering Group) Date: August 2010 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT
VICTORY VALIDATION AN INTRODUCTION AND TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
 2012 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM VEHICLE ELECTRONICS AND ARCHITECTURE (VEA) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 14-16 TROY, MICHIGAN VICTORY VALIDATION AN INTRODUCTION AND TECHNICAL
2012 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM VEHICLE ELECTRONICS AND ARCHITECTURE (VEA) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 14-16 TROY, MICHIGAN VICTORY VALIDATION AN INTRODUCTION AND TECHNICAL
Space and Missile Systems Center
 Space and Missile Systems Center GPS Control Segment Improvements Mr. Tim McIntyre GPS Product Support Manager GPS Ops Support and Sustainment Division Peterson AFB CO 2015 04 29 _GPS Control Segment Improvements
Space and Missile Systems Center GPS Control Segment Improvements Mr. Tim McIntyre GPS Product Support Manager GPS Ops Support and Sustainment Division Peterson AFB CO 2015 04 29 _GPS Control Segment Improvements
HEC-FFA Flood Frequency Analysis
 US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center Generalized Computer Program HEC-FFA Flood Frequency Analysis User's Manual May 1992 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. CPD-13
US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center Generalized Computer Program HEC-FFA Flood Frequency Analysis User's Manual May 1992 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. CPD-13
Shallow Ocean Bottom BRDF Prediction, Modeling, and Inversion via Simulation with Surface/Volume Data Derived from X-Ray Tomography
 Shallow Ocean Bottom BRDF Prediction, Modeling, and Inversion via Simulation with Surface/Volume Data Derived from X-Ray Tomography G. C. Boynton Physics Dept, University of Miami, PO Box 248046, Coral
Shallow Ocean Bottom BRDF Prediction, Modeling, and Inversion via Simulation with Surface/Volume Data Derived from X-Ray Tomography G. C. Boynton Physics Dept, University of Miami, PO Box 248046, Coral
New Dimensions in Microarchitecture Harnessing 3D Integration Technologies
 New Dimensions in Microarchitecture Harnessing 3D Integration Technologies Kerry Bernstein IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, NY 6 March, 27 San Jose, California DARPA Microsystems Technology
New Dimensions in Microarchitecture Harnessing 3D Integration Technologies Kerry Bernstein IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, NY 6 March, 27 San Jose, California DARPA Microsystems Technology
Running CyberCIEGE on Linux without Windows
 Running CyberCIEGE on Linux without Windows May, 0 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 070-0 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average hour per response,
Running CyberCIEGE on Linux without Windows May, 0 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 070-0 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average hour per response,
MATREX Run Time Interface (RTI) DoD M&S Conference 10 March 2008
 U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command MATREX Run Time Interface (RTI) DoD M&S Conference 10 March 2008 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command MATREX Run Time Interface (RTI) DoD M&S Conference 10 March 2008 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
Current Threat Environment
 Current Threat Environment Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, PhD Technical Director, CERT mssherman@sei.cmu.edu 29-Aug-2014 Report Documentation Page Form
Current Threat Environment Software Engineering Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, PhD Technical Director, CERT mssherman@sei.cmu.edu 29-Aug-2014 Report Documentation Page Form
Sparse Linear Solver for Power System Analyis using FPGA
 Sparse Linear Solver for Power System Analyis using FPGA J. R. Johnson P. Nagvajara C. Nwankpa 1 Extended Abstract Load flow computation and contingency analysis is the foundation of power system analysis.
Sparse Linear Solver for Power System Analyis using FPGA J. R. Johnson P. Nagvajara C. Nwankpa 1 Extended Abstract Load flow computation and contingency analysis is the foundation of power system analysis.
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL MICROWAVE RADAR SYSTEM USING ANGULAR CORRELATION FOR THE DETECTION OF BURIED OBJECTS IN SANDY SOILS
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL MICROWAVE RADAR SYSTEM USING ANGULAR CORRELATION FOR THE DETECTION OF BURIED OBJECTS IN SANDY SOILS Leung Tsang Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington Box
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL MICROWAVE RADAR SYSTEM USING ANGULAR CORRELATION FOR THE DETECTION OF BURIED OBJECTS IN SANDY SOILS Leung Tsang Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington Box
An Update on CORBA Performance for HPEC Algorithms. Bill Beckwith Objective Interface Systems, Inc.
 An Update on CORBA Performance for HPEC Algorithms Bill Beckwith Objective Interface Systems, Inc. Email: bill.beckwith@ois.com CORBA technology today surrounds HPEC-oriented subsystems. In recent years
An Update on CORBA Performance for HPEC Algorithms Bill Beckwith Objective Interface Systems, Inc. Email: bill.beckwith@ois.com CORBA technology today surrounds HPEC-oriented subsystems. In recent years
CASE STUDY: Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays in a Beowulf Cluster
 CASE STUDY: Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays in a Beowulf Cluster Mr. Matthew Krzych Naval Undersea Warfare Center Phone: 401-832-8174 Email Address: krzychmj@npt.nuwc.navy.mil The Robust Passive Sonar
CASE STUDY: Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays in a Beowulf Cluster Mr. Matthew Krzych Naval Undersea Warfare Center Phone: 401-832-8174 Email Address: krzychmj@npt.nuwc.navy.mil The Robust Passive Sonar
An Efficient Architecture for Ultra Long FFTs in FPGAs and ASICs
 HPEC 2004 Abstract Submission Dillon Engineering, Inc. www.dilloneng.com An Efficient Architecture for Ultra Long FFTs in FPGAs and ASICs Tom Dillon Dillon Engineering, Inc. This presentation outlines
HPEC 2004 Abstract Submission Dillon Engineering, Inc. www.dilloneng.com An Efficient Architecture for Ultra Long FFTs in FPGAs and ASICs Tom Dillon Dillon Engineering, Inc. This presentation outlines
ASPECTS OF USE OF CFD FOR UAV CONFIGURATION DESIGN
 ASPECTS OF USE OF CFD FOR UAV CONFIGURATION DESIGN Presentation at UAV Workshop, Bath University, November 2002 Tim Pemberton, Senior Specialist, BAE SYSTEMS Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB
ASPECTS OF USE OF CFD FOR UAV CONFIGURATION DESIGN Presentation at UAV Workshop, Bath University, November 2002 Tim Pemberton, Senior Specialist, BAE SYSTEMS Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB
COUNTERING IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICES
 COUNTERING IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICES FEBRUARY 26, 2013 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour
COUNTERING IMPROVISED EXPLOSIVE DEVICES FEBRUARY 26, 2013 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour
Uniform Tests of File Converters Using Unit Cubes
 Uniform Tests of File Converters Using Unit Cubes by Steven J Nichols ARL-CR-0770 March 2015 Under contract W911NF-10-2-0076 Approved for public release; distribution unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The
Uniform Tests of File Converters Using Unit Cubes by Steven J Nichols ARL-CR-0770 March 2015 Under contract W911NF-10-2-0076 Approved for public release; distribution unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The
BUPT at TREC 2009: Entity Track
 BUPT at TREC 2009: Entity Track Zhanyi Wang, Dongxin Liu, Weiran Xu, Guang Chen, Jun Guo Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System Lab, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China,
BUPT at TREC 2009: Entity Track Zhanyi Wang, Dongxin Liu, Weiran Xu, Guang Chen, Jun Guo Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System Lab, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China,
The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing
 The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing Abstract Martin Vorbach PACT XPP Technologies Leo Mirkin Sky Computers, Inc. The new ISR mobile autonomous sensor platforms present a difficult
The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing Abstract Martin Vorbach PACT XPP Technologies Leo Mirkin Sky Computers, Inc. The new ISR mobile autonomous sensor platforms present a difficult
Creating, Positioning, and Rotating Rectangles Using C++
 Creating, Positioning, and Rotating Rectangles Using C++ by Robert J. Yager ARL-TN-558 August 2013 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The findings in this report
Creating, Positioning, and Rotating Rectangles Using C++ by Robert J. Yager ARL-TN-558 August 2013 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The findings in this report
Web Site update. 21st HCAT Program Review Toronto, September 26, Keith Legg
 Web Site update 21st HCAT Program Review Toronto, September 26, 2002 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to
Web Site update 21st HCAT Program Review Toronto, September 26, 2002 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to
Office of Global Maritime Situational Awareness
 Global Maritime Awareness Office of Global Maritime Situational Awareness Capt. George E McCarthy, USN October 27 th 2009 Office of Global Maritime Situational Awareness A National Coordination Office
Global Maritime Awareness Office of Global Maritime Situational Awareness Capt. George E McCarthy, USN October 27 th 2009 Office of Global Maritime Situational Awareness A National Coordination Office
Ross Lazarus MB,BS MPH
 Innovations in Public Health Surveillance: The National Bioterrorism Syndromic Surveillance Demonstration Project Ross Lazarus MB,BS MPH Director of Bioinformatics, Channing Laboratory Brigham and Women
Innovations in Public Health Surveillance: The National Bioterrorism Syndromic Surveillance Demonstration Project Ross Lazarus MB,BS MPH Director of Bioinformatics, Channing Laboratory Brigham and Women
Lessons Learned in Adapting a Software System to a Micro Computer
 Lessons Learned in Adapting a Software System to a Micro Computer ABSTRACT: A system was developed in a laboratory on a desktop computer to evaluate armor health. The system uses sensors embedded in the
Lessons Learned in Adapting a Software System to a Micro Computer ABSTRACT: A system was developed in a laboratory on a desktop computer to evaluate armor health. The system uses sensors embedded in the
US Army Industry Day Conference Boeing SBIR/STTR Program Overview
 US Army Industry Day Conference Boeing SBIR/STTR Program Overview Larry Pionke, DSc Associate Technical Fellow Product Standards - Technology & Services Boeing Research & Technology Ft. Leonard Wood (FLW)
US Army Industry Day Conference Boeing SBIR/STTR Program Overview Larry Pionke, DSc Associate Technical Fellow Product Standards - Technology & Services Boeing Research & Technology Ft. Leonard Wood (FLW)
Speaker Verification Using SVM
 Mr. Rastoceanu Florin / Mrs. Lazar Marilena Military Equipment and Technologies Research Agency Aeroportului Street, No. 16, CP 19 OP Bragadiru 077025, Ilfov ROMANIA email: rastoceanu_florin@yahoo.com
Mr. Rastoceanu Florin / Mrs. Lazar Marilena Military Equipment and Technologies Research Agency Aeroportului Street, No. 16, CP 19 OP Bragadiru 077025, Ilfov ROMANIA email: rastoceanu_florin@yahoo.com
SETTING UP AN NTP SERVER AT THE ROYAL OBSERVATORY OF BELGIUM
 SETTING UP AN NTP SERVER AT THE ROYAL OBSERVATORY OF BELGIUM Fabian Roosbeek, Pascale Defraigne, and André Somerhausen Royal Observatory of Belgium Abstract This paper describes the setup of an NTP server
SETTING UP AN NTP SERVER AT THE ROYAL OBSERVATORY OF BELGIUM Fabian Roosbeek, Pascale Defraigne, and André Somerhausen Royal Observatory of Belgium Abstract This paper describes the setup of an NTP server
The C2 Workstation and Data Replication over Disadvantaged Tactical Communication Links
 The C2 Workstation and Data Replication over Disadvantaged Tactical Communication Links Presentation held at the NATO RTO-IST Taskgroup 12 Workshop on September 11 th &12 th in Quebec, Canada TNO Physics
The C2 Workstation and Data Replication over Disadvantaged Tactical Communication Links Presentation held at the NATO RTO-IST Taskgroup 12 Workshop on September 11 th &12 th in Quebec, Canada TNO Physics
Folded Shell Projectors and Virtual Optimization
 Folded Shell Projectors and Virtual Optimization David Powell 1, Greg Wojcik 1, Victor Pereyra 1, Laura Carcione 1, Paul Reynolds 1, Chris Purcell 2, Craig Near 3 1 Weidlinger Associates Inc., 4410 El
Folded Shell Projectors and Virtual Optimization David Powell 1, Greg Wojcik 1, Victor Pereyra 1, Laura Carcione 1, Paul Reynolds 1, Chris Purcell 2, Craig Near 3 1 Weidlinger Associates Inc., 4410 El
Towards a Formal Pedigree Ontology for Level-One Sensor Fusion
 Towards a Formal Pedigree Ontology for Level-One Sensor Fusion Christopher J. Matheus David Tribble Referentia Systems, Inc. Mieczyslaw M. Kokar Northeaster University Marion Ceruti and Scott McGirr Space
Towards a Formal Pedigree Ontology for Level-One Sensor Fusion Christopher J. Matheus David Tribble Referentia Systems, Inc. Mieczyslaw M. Kokar Northeaster University Marion Ceruti and Scott McGirr Space
ENHANCED FRAGMENTATION MODELING
 ENHANCED FRAGMENTATION MODELING Peter Rottinger*, Richard Fong, William Ng U.S. ARMY ARDEC Picatinny Arsenal, NJ, 07806 ABSTRACT Enhancing the fragmentation capability of current and future projectiles
ENHANCED FRAGMENTATION MODELING Peter Rottinger*, Richard Fong, William Ng U.S. ARMY ARDEC Picatinny Arsenal, NJ, 07806 ABSTRACT Enhancing the fragmentation capability of current and future projectiles
75th Air Base Wing. Effective Data Stewarding Measures in Support of EESOH-MIS
 75th Air Base Wing Effective Data Stewarding Measures in Support of EESOH-MIS Steve Rasmussen Hill Air Force Base (AFB) Air Quality Program Manager 75 CEG/CEVC (801) 777-0359 Steve.Rasmussen@hill.af.mil
75th Air Base Wing Effective Data Stewarding Measures in Support of EESOH-MIS Steve Rasmussen Hill Air Force Base (AFB) Air Quality Program Manager 75 CEG/CEVC (801) 777-0359 Steve.Rasmussen@hill.af.mil
Concept of Operations Discussion Summary
 TSPG Common Dataset Standard Concept of Operations Discussion Summary Tony DalSasso 677 AESG/EN 15 May 2007 1 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection
TSPG Common Dataset Standard Concept of Operations Discussion Summary Tony DalSasso 677 AESG/EN 15 May 2007 1 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection
SINOVIA An open approach for heterogeneous ISR systems inter-operability
 SINOVIA An open approach for heterogeneous ISR systems inter-operability Pr C. Moreno, Dr S. Belot Paris, June 2002 UAV 2002 Paris www.sinovia.com Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
SINOVIA An open approach for heterogeneous ISR systems inter-operability Pr C. Moreno, Dr S. Belot Paris, June 2002 UAV 2002 Paris www.sinovia.com Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188
INTEGRATING LOCAL AND GLOBAL NAVIGATION IN UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLES
 INTEGRATING LOCAL AND GLOBAL NAVIGATION IN UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLES Juan Pablo Gonzalez*, William Dodson, Robert Dean General Dynamics Robotic Systems Westminster, MD Alberto Lacaze, Leonid Sapronov Robotics
INTEGRATING LOCAL AND GLOBAL NAVIGATION IN UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLES Juan Pablo Gonzalez*, William Dodson, Robert Dean General Dynamics Robotic Systems Westminster, MD Alberto Lacaze, Leonid Sapronov Robotics
Cyber Threat Prioritization
 Cyber Threat Prioritization FSSCC Threat and Vulnerability Assessment Committee Jay McAllister Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information
Cyber Threat Prioritization FSSCC Threat and Vulnerability Assessment Committee Jay McAllister Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Resource Reservation Scheme for Synchronized Distributed Multimedia Sessions by W. Zhao, S.K. Tripathi T.R. 97-14 ISR INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH Sponsored by the National
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Resource Reservation Scheme for Synchronized Distributed Multimedia Sessions by W. Zhao, S.K. Tripathi T.R. 97-14 ISR INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS RESEARCH Sponsored by the National
Monte Carlo Techniques for Estimating Power in Aircraft T&E Tests. Todd Remund Dr. William Kitto EDWARDS AFB, CA. July 2011
 AFFTC-PA-11244 Monte Carlo Techniques for Estimating Power in Aircraft T&E Tests A F F T C Todd Remund Dr. William Kitto AIR FORCE FLIGHT TEST CENTER EDWARDS AFB, CA July 2011 Approved for public release
AFFTC-PA-11244 Monte Carlo Techniques for Estimating Power in Aircraft T&E Tests A F F T C Todd Remund Dr. William Kitto AIR FORCE FLIGHT TEST CENTER EDWARDS AFB, CA July 2011 Approved for public release
Army Research Laboratory
 Army Research Laboratory Arabic Natural Language Processing System Code Library by Stephen C. Tratz ARL-TN-0609 June 2014 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The
Army Research Laboratory Arabic Natural Language Processing System Code Library by Stephen C. Tratz ARL-TN-0609 June 2014 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. NOTICES Disclaimers The
Wireless Connectivity of Swarms in Presence of Obstacles
 Wireless Connectivity of Swarms in Presence of Obstacles Joel Esposito US Naval Academy Thomas Dunbar Naval Postgraduate School Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 070-088 Public reporting
Wireless Connectivity of Swarms in Presence of Obstacles Joel Esposito US Naval Academy Thomas Dunbar Naval Postgraduate School Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 070-088 Public reporting
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Fixed Point Approximation for Multirate Multihop Loss Networks with Adaptive Routing by Mingyan Liu, John S. Baras CSHCN T.R. 99-21 (ISR T.R. 99-44) Sponsored by: NASA Fixed Point
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT Fixed Point Approximation for Multirate Multihop Loss Networks with Adaptive Routing by Mingyan Liu, John S. Baras CSHCN T.R. 99-21 (ISR T.R. 99-44) Sponsored by: NASA Fixed Point
