Cache Controller with Enhanced Features using Verilog HDL
|
|
|
- Irene Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cache Controller with Enhanced Features using Verilog HDL Prof. V. B. Baru 1, Sweety Pinjani 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon (BK), Pune, India 1 PG Student [VLSI & Embedded Systems], Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon (BK), Pune, India 2 ABSTRACT: The major role of cache controller is reduction in the data transfer access time between the CPU and cache. The fact that read request is more critical compared to write request is exploited in this paper. The paper presents a novel approach to cache controllers which uses read write partitioning wherein more read lines are maintained as compared to write lines. KEYWORDS: hit, miss, RWP, cache, controller. I.INTRODUCTION There is a drastic improvement in technology leading to improved processor speeds. However, the memory speed has not yet increased in order to match with the faster processing needs. As cache is the fastest memory, there is a need for cache controller enhancements. Some methods for improving cache controller have been proposed in the past. One of such methods is to design a pipelined cache controller which increases the circuit complexity. Another method is to increase the size of the cache. But, as the cache size increases, the cache access time also increases. So, there is a need of better and efficient techniques. Multi-core processor is the modern processor which can handle multiple applications simultaneously. Multiple cores on a single die share the cache resources in such processors. So, there is a need for the hierarchical cache with different cache levels like L1, L2 and LLC. Thus, the cache controller must be capable of handling hierarchical cache in the multi-core processor. Some prior works have proposed various insertion policies or algorithms for storing data inside the cache. Some attempted to differentiate between the critical and not-critical data. Some others focused on the likelihood of processor stall as the main criteria. Prior work focused only on distinguishing the lines that will be reused and those that will be not. It failed to distinguish between lines reused by reads versus those reused by writes. The criticality of read requests is more as compared to write request. This is due to the fact that write data can be temporarily stored inside a buffer. Hence, read must be favored compared to a write request. The technique proposed in this paper makes this distinction between read-write criticality. The controller design proposed in this paper applies multiple ways and block size to the cache dynamically. In order to further improve the system performance, the controller is designed to be capable of handling the multi-sized output. The cache management policy used increases the read request hit probability by causing less critical write requests to miss. It also distinguishes between the cache lines which will be read in future and those that will be write only. An attempt is made to increase the cache lines that will be read and eliminate those that will be write only. The contributions made in this paper are: Design a controller which can be used for multi-core processor where multiple cores share the cache. Capability to handle the multiple ways and block size for cache and provide multiple-sized output. Distinction between read and write requests criticality. Read Write Partitioning (RWP) is proposed as a cache management policy. Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
2 II.LITERATURE SURVEY The cache is replacement policies are optimizing instructions in order to manage a cache of information stored on a system. When the cache is full, the algorithm must choose which items to discard to make room for the new ones. Several such policies have been proposed in the past which are described below. The Least Recently Used (LRU) discards the least recently used items first. The algorithm need to track the past access history of the data maintained inside the cache. General technique used for this purpose is the use of age bits for cache lines. Every time a cache line is used, the age of all other cache lines changes. If CPU caches have large associativity (>4ways), the implementation cost of LRU becomes prohibitive. A scheme that discards one of the least recently used items is sufficient. So, CPU designers choose a Pseudo Least Recently Used (PLRU) algorithm which only needs one bit per cache item. It typically has a slightly worse miss ratio, better latency and uses less power than LRU. The Most Recently Used (MRU) is another cache replacement policy which discards the most recently used items first. It is the best replacement policy when a file is being repeatedly scanned in a reference pattern. MRU has more hits than LRU for random access patterns and repeated scans over large datasets. MRU has a tendency to retain old data. They are most useful in situations where the older item is more likely to be accessed. Random Replacement (RR) selects a candidate item randomly and discards it to make space when necessary. It does not need to store any information about the access history. It is relatively simple and admits stochastic simulation. Least Frequently Used (LFU) involves the system keeping track of the number of times a block is referenced in memory. When the system is full, the algorithm will replace the item with the lowest frequency. III.THE CACHE The cache is the fastest and the most expensive memory. It is the highest part in the memory hierarchy tree. A. The Architecture The cache implemented in this paper is a dynamic one. It is having a memory size of 4 MB and a hierarchical cache with L1, L2 and LLC. It may be implemented as a 16, 8, 4 or 2 way set associative cache. Also, the block size may vary from 16, 8, 4 or 2 bytes. The number of sets for each way and the data handling capability for each set will vary according to the way and block size chosen for the cache. B. Operation Two different operations are possible for the cache. These are to read the data from cache or to write the data inside the cache. They are explained below. 1) Write Operation Whenever there is a write request from the processor, the way and the cache line for cache write will be selected by RWP cache management policy. Only one way which is selected by RWP is enabled for write operation. The data needs to be converted according to the data alignment of the cache before performing this operation. 2) Read Operation All ways are enabled for cache read operation. The set address decides which set is to be accessed. The tag address is then compared using a comparator inside each way. If the tag address matches and the valid bit is set, it is an indication for the availability of data inside the cache. This is termed as hit. The way which asserted the hit is selected by the data multiplexer. The data is selected via data encoder. There will be only one hit at a time. If the tag address does not match, it is a miss indicating the data is not present inside the cache and no data will be provided by cache. The data inside the cache will be 16, 8, 4 or 2 byte. This data needs to be converted into 8 byte data as will be accepted by the processor. Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
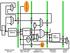
3 IV.THE CACHE CONTROLLER The main function of the cache controller is to increase the data access speed between cache memory and the processor. Whenever the controller receives the request from the processor for data access, it will check if the data is present inside the cache. If the data exists inside the cache, the controller will send the data from cache to the processor. However, if the data is not present inside the cache, the controller will fetch the data from the main memory and send a copy of data to the processor and to the cache according to the cache management policy used. A. The Architecture The controller will have stages like fetch data, read cache, read main memory, write cache, write main memory and provide data to the processor. These stages are designed using FSM. The stages are again divided into different states as shown in Figure.1. The controller is capable of handling the caches with multiple ways like 16, 8, 4 or 2 ways as well as various block size like 16, 8, 4 or 2 byte. Also, it is capable of delivering the data as multiple-sized output like 16, 8, 4, 2 or 1 byte. One of the major challenges for the cache controller is to align the variable data exchange between the processor, the cache and the main memory. The controller is designed to deal with three different agents or processors. In order to overcome the data transfer clashes, the controller will use a busy flag. Whenever the cache is being accessed the busy flag will be asserted. The processor can request data only if the busy flag is not asserted. B. Operation The controller consists of various states: Fetch Data, Read Cache, Read Memory, Write Cache, Write Memory and Give Data. 1) Fetch Data: At this state, the controller will check whether the request from the processor is read or write. This can be analyzed on the basis of the instruction opcode. The controller will maintain the busy flag low until it goes to any next state. 2) Read Cache: At this state, the controller will check the cache for the availability of the requested data. If the data is present inside the cache, it is a hit and the requested data is sent to the processor. Thus, the controller will go to the next state Give Data. This state also has other states for data alignment. If the data is not present inside the cache, it is a miss and the controller will now search for the data inside the main memory. The controller will then go to the next state Read Memory. 3) Read Memory: At this state, the main memory is checked for the availability of the requested data. Then one copy of the data is sent to the processor and the other one is sent to the cache according to the RWP cache replacement policy used by the controller. This state also involves the conversion of the data from the main memory to a 16, 8, 4 or 2 byte data as will be acceptable to the cache. It many involve a parallel to serial converter where multiple smaller data is combined into one big data or it may involve the serial to parallel converter where one big data is split into several small data. Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
4 Figure.1. State diagram of cache controller 4) Write Cache: At this state, the controller will write the data inside the cache. The cache line for writing the data will be selected with the help of RWP cache management policy. There are two conditions in which this state may be accessed. If this state is accessed due to cache miss, the controller will return back to the Read Cache followed by the Give Data state. If the state is accessed due to the write request sent by the processor, the controller will go to the Fetch Data state in order to fetch the next instruction from the processor. This state also needs some more additional states for data alignment between the processor, the cache and the main memory as will be required. 5) Write Memory: In this state the data from the processor is written to the main memory. This state occurs only if the processor requests from the write operation. This data may then be stored into the cache if it has a probability for read in future. V.THE CACHE MANAGEMENT POLICY This paper uses the Read-Write Partitioning (RWP) policy which distinguishes the criticality of read and writes, giving a higher priority to read. This is achieved by maximizing the hit probability for read at the cost of minimizing that hit for the write, if required. In order to distinguish between the cache lines which will be read and those that will be write in future, the cache lines are logically partitioned into two categories as described below: 1) Clean lines: These are the lines which will be read at least once before being evicted. 2) Dirty lines: These are the lines used for write, independent of the probability of future read request. Write-only lines, a subset of dirty lines are those lines that will be evicted without any read. Structure for a RWP is as shown in the Figure.2. Partition Size predictor predicts the best partition size for the clean and dirty partitions. In order to service the write request, either a clean or a dirty line will be evicted. The evicted line will be replaced by the new line. Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
5 Figure.2. Structure of RWP VI. THE RWP FRAMEWORK RWP framework partitions the cache into clean and dirty lines logically, not physically. In order to indicate this, a dirty status bit is used. Whenever a write is made to the clean line, its dirty bit is set and it logically becomes a part of the dirty partition. There is no strict enforcement on the partition sizes. They are adjusted only when a new cache line is allocated. RWP dynamically determines the cache line to be evicted and replaced with the new one. There can be three possible cases to determine the placement victim based on the current number of dirty lines in the cache set. They are described below: The current dirty lines are greater than the best predicted partition size: RWP picks the LRU line from the dirty partition as the replacement victim. The current dirty lines are smaller than the best predicted partition size: RWP picks the LRU line from the clean partition as the replacement victim. The current dirty lines are equal to the best predicted partition size: The replacement victim depends on the access type of the request. If the access type is read, RWP picks the victim from clean partition. However, for a write access, the replacement victim is picked from the dirty partition. RWP calculates the best partition sizes dynamically and makes a conclusion on the number of ways to be assigned for each partition. In order to achieve this, it needs to calculate the benefit of growing one partition size at the cost of shrinking another one. RWP compares the read reuse of clean and dirty lines as if given exclusive access to the entire cache. The Partition Size Predictor uses set sampling, wherein a small subset of total sets is extended with a shadow directory. Whenever there is a read miss, a cache line is allocated to the clean shadow directory. For a write miss, the cache line is allocated to the dirty shadow directory. Two counters are used for size prediction: clean age hit counter and dirty age hit counter. If a read request is made to the clean partition, clean age hit counter is incremented by 1. Similarly, if the read request is made to the dirty partition, dirty age hit counter is incremented by 1. These counter values are used to predict the number of additional hit/miss that cache will incur if one of the ways allocated to a partition is re-allocated to another. Thus, the best partition size is predicted. Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
6 VII.CONCLUSION The criticality of read requests is more as compared to the writes. Thus, the cache management policies that increase the probability of cache hits perform better. This is done by allocating more resources to the reads. RWP is a mechanism which distinguishes between read lines vs. write-only lines and also favors read lines. It protects the partition with read lines and evicts the partition with write-only lines. Thus, RWP can outperform many of the prior cache management mechanisms. REFERENCES [1] Samira Khan and Chris Wilkerson, Improving Cache Performance Using Read-Write Partitioning, IEEE, [2] Siti Lailatul Mohd Hassan, Multi-Sized Output Cache Controllers, International Conference on Technology, Informatics, Management, Engineering & Environment, pp , June [3] C. J. Lee, DRAM-aware last-level cache write back: Reducing write-caused interference in memory systems, Technical Report TR-HPS , pp. 1-25, December [4] M. Qureshi et al. Improving read performance of phase change memories via write cancellation and write pausing, HPCA, [5] M. Chaudhuri, Pseudo-LIFO: The foundation of a new family of replacement policies for last-level caches, MICRO, Copyright to IJAREEIE /ijareeie
CACHE OPTIMIZATION. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 is due on Mar. 27 th This lecture Cache
CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 is due on Mar. 27 th This lecture Cache
A Review on Cache Memory with Multiprocessor System
 A Review on Cache Memory with Multiprocessor System Chirag R. Patel 1, Rajesh H. Davda 2 1,2 Computer Engineering Department, C. U. Shah College of Engineering & Technology, Wadhwan (Gujarat) Abstract
A Review on Cache Memory with Multiprocessor System Chirag R. Patel 1, Rajesh H. Davda 2 1,2 Computer Engineering Department, C. U. Shah College of Engineering & Technology, Wadhwan (Gujarat) Abstract
Cache Memory COE 403. Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar. Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
 Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems. Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I)
 ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I) 1 Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I) 1 Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 Lecture 5a Caching Review Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 Lecture 5a Caching Review Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
Design and Functional Verification of Four Way Set Associative Cache Controller
 International Journal of Research in Computer and Communication Technology, Vol 4, Issue 3, March -2015 ISSN (Online) 2278-5841 ISSN (Print) 2320-5156 Design and Functional Verification of Four Way Set
International Journal of Research in Computer and Communication Technology, Vol 4, Issue 3, March -2015 ISSN (Online) 2278-5841 ISSN (Print) 2320-5156 Design and Functional Verification of Four Way Set
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
CACHE MEMORIES ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURES. Slides by: Pedro Tomás
 CACHE MEMORIES Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Chapter 2 and Appendix B, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
CACHE MEMORIES Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Chapter 2 and Appendix B, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
CSE 120. Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware. July 18, Day 5 Memory. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Software TLB Management
 CSE 120 July 18, 2006 Day 5 Memory Instructor: Neil Rhodes Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware Cache to map virtual page numbers to page frame Associative memory: HW looks up in
CSE 120 July 18, 2006 Day 5 Memory Instructor: Neil Rhodes Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware Cache to map virtual page numbers to page frame Associative memory: HW looks up in
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Memory System Design Part II. Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore.
 Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
Lecture 10: Large Cache Design III
 Lecture 10: Large Cache Design III Topics: Replacement policies, prefetch, dead blocks, associativity Sign up for class mailing list Pseudo-LRU has a 9% higher miss rate than true LRU 1 Overview 2 Set
Lecture 10: Large Cache Design III Topics: Replacement policies, prefetch, dead blocks, associativity Sign up for class mailing list Pseudo-LRU has a 9% higher miss rate than true LRU 1 Overview 2 Set
CACHE OPTIMIZATION. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st This
CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st This
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Advanced Computer Architecture
 ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Portland State University ECE 587/687. Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism
 Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory
 Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Caches Part 1. Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CHAPTER 6 Memory. CMPS375 Class Notes (Chap06) Page 1 / 20 Dr. Kuo-pao Yang
 CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Lecture 15: Large Cache Design III. Topics: Replacement policies, prefetch, dead blocks, associativity, cache networks
 Lecture 15: Large Cache Design III Topics: Replacement policies, prefetch, dead blocks, associativity, cache networks 1 LIN Qureshi et al., ISCA 06 Memory level parallelism (MLP): number of misses that
Lecture 15: Large Cache Design III Topics: Replacement policies, prefetch, dead blocks, associativity, cache networks 1 LIN Qureshi et al., ISCA 06 Memory level parallelism (MLP): number of misses that
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
Q3: Block Replacement. Replacement Algorithms. ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Improving System. Performance: Caches
 Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Operating Systems. Operating Systems Sina Meraji U of T
 Operating Systems Operating Systems Sina Meraji U of T Recap Last time we looked at memory management techniques Fixed partitioning Dynamic partitioning Paging Example Address Translation Suppose addresses
Operating Systems Operating Systems Sina Meraji U of T Recap Last time we looked at memory management techniques Fixed partitioning Dynamic partitioning Paging Example Address Translation Suppose addresses
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles. Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!)
 Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems
 CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
Introduction to cache memories
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches
 Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches S Coudert and R Pacalet January 23, 2019 Outline Introduction Localities principles Direct-mapped caches Increasing block size Set-associative caches
Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches S Coudert and R Pacalet January 23, 2019 Outline Introduction Localities principles Direct-mapped caches Increasing block size Set-associative caches
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6)
 Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Selective Fill Data Cache
 Selective Fill Data Cache Rice University ELEC525 Final Report Anuj Dharia, Paul Rodriguez, Ryan Verret Abstract Here we present an architecture for improving data cache miss rate. Our enhancement seeks
Selective Fill Data Cache Rice University ELEC525 Final Report Anuj Dharia, Paul Rodriguez, Ryan Verret Abstract Here we present an architecture for improving data cache miss rate. Our enhancement seeks
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
A Reconfigurable Cache Design for Embedded Dynamic Data Cache
 I J C T A, 9(17) 2016, pp. 8509-8517 International Science Press A Reconfigurable Cache Design for Embedded Dynamic Data Cache Shameedha Begum, T. Vidya, Amit D. Joshi and N. Ramasubramanian ABSTRACT Applications
I J C T A, 9(17) 2016, pp. 8509-8517 International Science Press A Reconfigurable Cache Design for Embedded Dynamic Data Cache Shameedha Begum, T. Vidya, Amit D. Joshi and N. Ramasubramanian ABSTRACT Applications
Locality and Data Accesses video is wrong one notes when video is correct
 Cache Review This lesson is a review of caches. Beginning with the structure of the cache itself, including set associative and direct mapped caches. Then the lesson discusses replacement policies, specifically
Cache Review This lesson is a review of caches. Beginning with the structure of the cache itself, including set associative and direct mapped caches. Then the lesson discusses replacement policies, specifically
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Chapter 8. Virtual Memory
 Operating System Chapter 8. Virtual Memory Lynn Choi School of Electrical Engineering Motivated by Memory Hierarchy Principles of Locality Speed vs. size vs. cost tradeoff Locality principle Spatial Locality:
Operating System Chapter 8. Virtual Memory Lynn Choi School of Electrical Engineering Motivated by Memory Hierarchy Principles of Locality Speed vs. size vs. cost tradeoff Locality principle Spatial Locality:
Improving Cache Performance by Exploi7ng Read- Write Disparity. Samira Khan, Alaa R. Alameldeen, Chris Wilkerson, Onur Mutlu, and Daniel A.
 Improving Cache Performance by Exploi7ng Read- Write Disparity Samira Khan, Alaa R. Alameldeen, Chris Wilkerson, Onur Mutlu, and Daniel A. Jiménez Summary Read misses are more cri?cal than write misses
Improving Cache Performance by Exploi7ng Read- Write Disparity Samira Khan, Alaa R. Alameldeen, Chris Wilkerson, Onur Mutlu, and Daniel A. Jiménez Summary Read misses are more cri?cal than write misses
Chapter 6 Memory 11/3/2015. Chapter 6 Objectives. 6.2 Types of Memory. 6.1 Introduction
 Chapter 6 Objectives Chapter 6 Memory Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Chapter 6 Objectives Chapter 6 Memory Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
Question?! Processor comparison!
 1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
CHAPTER 6 Memory. CMPS375 Class Notes Page 1/ 16 by Kuo-pao Yang
 CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 233 6.2 Types of Memory 233 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 235 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 237 6.4 Cache Memory 237 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 239 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 247
CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 233 6.2 Types of Memory 233 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 235 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 237 6.4 Cache Memory 237 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 239 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 247
Cache Policies. Philipp Koehn. 6 April 2018
 Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
High Performance Computer Architecture Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 High Performance Computer Architecture Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 23 Hierarchical Memory Organization (Contd.) Hello
High Performance Computer Architecture Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 23 Hierarchical Memory Organization (Contd.) Hello
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
Locality. CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture. Locality Example 2. Locality Example
 Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
COSC4201. Chapter 5. Memory Hierarchy Design. Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University
 COSC4201 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University 1 Memory Hierarchy The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating
COSC4201 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University 1 Memory Hierarchy The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating
Lecture notes for CS Chapter 2, part 1 10/23/18
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
a process may be swapped in and out of main memory such that it occupies different regions
 Virtual Memory Characteristics of Paging and Segmentation A process may be broken up into pieces (pages or segments) that do not need to be located contiguously in main memory Memory references are dynamically
Virtual Memory Characteristics of Paging and Segmentation A process may be broken up into pieces (pages or segments) that do not need to be located contiguously in main memory Memory references are dynamically
ECEC 355: Cache Design
 ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
CHAPTER 4 MEMORY HIERARCHIES TYPICAL MEMORY HIERARCHY TYPICAL MEMORY HIERARCHY: THE PYRAMID CACHE PERFORMANCE MEMORY HIERARCHIES CACHE DESIGN
 CHAPTER 4 TYPICAL MEMORY HIERARCHY MEMORY HIERARCHIES MEMORY HIERARCHIES CACHE DESIGN TECHNIQUES TO IMPROVE CACHE PERFORMANCE VIRTUAL MEMORY SUPPORT PRINCIPLE OF LOCALITY: A PROGRAM ACCESSES A RELATIVELY
CHAPTER 4 TYPICAL MEMORY HIERARCHY MEMORY HIERARCHIES MEMORY HIERARCHIES CACHE DESIGN TECHNIQUES TO IMPROVE CACHE PERFORMANCE VIRTUAL MEMORY SUPPORT PRINCIPLE OF LOCALITY: A PROGRAM ACCESSES A RELATIVELY
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II. Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies
 Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies 1 Page Coloring CACHE VIEW Bank number with Page-to-Bank Tag Set Index Bank number with Set-interleaving Block offset
Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies 1 Page Coloring CACHE VIEW Bank number with Page-to-Bank Tag Set Index Bank number with Set-interleaving Block offset
Let!s go back to a course goal... Let!s go back to a course goal... Question? Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies
 1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
Caches. Cache Memory. memory hierarchy. CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first
 Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology CACHE MEMORY. Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy.
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
CS 33. Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
Caches. Samira Khan March 23, 2017
 Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Memory Hierarchies &
 Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Structure of Computer Systems
 222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write)
 The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
William Stallings Copyright 2009
 A PPENDIX D V ICTIM C ACHE S TRATEGIES William Stallings Copyright 2009 D.1 VICTIM CACHE...2! D.2 SELECTIVE VICTIM CACHE...4! Incoming Blocks from Memory...4! Swap Between Direct-Mapped Cache and Victim
A PPENDIX D V ICTIM C ACHE S TRATEGIES William Stallings Copyright 2009 D.1 VICTIM CACHE...2! D.2 SELECTIVE VICTIM CACHE...4! Incoming Blocks from Memory...4! Swap Between Direct-Mapped Cache and Victim
Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design
 S 09 L17-1 18-447 Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design James C. Hoe Dept of ECE, CMU March 24, 2009 Announcements: Project 3 is due Midterm 2 is coming Handouts: Practice Midterm 2 solutions The
S 09 L17-1 18-447 Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design James C. Hoe Dept of ECE, CMU March 24, 2009 Announcements: Project 3 is due Midterm 2 is coming Handouts: Practice Midterm 2 solutions The
A Cache Hierarchy in a Computer System
 A Cache Hierarchy in a Computer System Ideally one would desire an indefinitely large memory capacity such that any particular... word would be immediately available... We are... forced to recognize the
A Cache Hierarchy in a Computer System Ideally one would desire an indefinitely large memory capacity such that any particular... word would be immediately available... We are... forced to recognize the
Lecture-16 (Cache Replacement Policies) CS422-Spring
 Lecture-16 (Cache Replacement Policies) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 From SPEC92 Miss rate: Still Applicable Today 0.14 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 1-way 2-way 4-way 8-way Capacity
Lecture-16 (Cache Replacement Policies) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 From SPEC92 Miss rate: Still Applicable Today 0.14 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 1-way 2-way 4-way 8-way Capacity
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Week 2: Tiina Niklander
 Virtual memory Operations and policies Chapters 3.4. 3.6 Week 2: 17.9.2009 Tiina Niklander 1 Policies and methods Fetch policy (Noutopolitiikka) When to load page to memory? Placement policy (Sijoituspolitiikka
Virtual memory Operations and policies Chapters 3.4. 3.6 Week 2: 17.9.2009 Tiina Niklander 1 Policies and methods Fetch policy (Noutopolitiikka) When to load page to memory? Placement policy (Sijoituspolitiikka
Lecture 16. Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay!
 Lecture 16 Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay! Note: There are no slides labeled Lecture 15. Nothing omitted, just that the numbering got out of sequence somewhere along the way. 1
Lecture 16 Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay! Note: There are no slides labeled Lecture 15. Nothing omitted, just that the numbering got out of sequence somewhere along the way. 1
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm
 SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm Jaafar Alghazo, Adil Akaaboune, Nazeih Botros Southern Illinois University at Carbondale Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carbondale, IL 6291 alghazo@siu.edu,
SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm Jaafar Alghazo, Adil Akaaboune, Nazeih Botros Southern Illinois University at Carbondale Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carbondale, IL 6291 alghazo@siu.edu,
CS 136: Advanced Architecture. Review of Caches
 1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
Page Replacement Algorithms
 Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Swapping. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Swapping Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Swapping Support processes when not enough physical memory User program should be independent
Swapping Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Swapping Support processes when not enough physical memory User program should be independent
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2...
 Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
Swapping. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Swapping Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu EEE0: Introduction to Operating Systems, Fall 07, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Swapping
Swapping Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu EEE0: Introduction to Operating Systems, Fall 07, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Swapping
Physical characteristics (such as packaging, volatility, and erasability Organization.
 CS 320 Ch 4 Cache Memory 1. The author list 8 classifications for memory systems; Location Capacity Unit of transfer Access method (there are four:sequential, Direct, Random, and Associative) Performance
CS 320 Ch 4 Cache Memory 1. The author list 8 classifications for memory systems; Location Capacity Unit of transfer Access method (there are four:sequential, Direct, Random, and Associative) Performance
(Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture. Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (4 th Week)
 + (Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (4 th Week) + Outline 2. The computer system 2.1 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection 2.2 Cache Memory
+ (Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (4 th Week) + Outline 2. The computer system 2.1 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection 2.2 Cache Memory
PAGE REPLACEMENT. Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo
 PAGE REPLACEMENT Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Today s Topics What if the physical memory becomes full? Page replacement algorithms How to manage memory among competing processes? Advanced
PAGE REPLACEMENT Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Today s Topics What if the physical memory becomes full? Page replacement algorithms How to manage memory among competing processes? Advanced
Fig 7.30 The Cache Mapping Function. Memory Fields and Address Translation
 7-47 Chapter 7 Memory System Design Fig 7. The Mapping Function Example: KB MB CPU Word Block Main Address Mapping function The cache mapping function is responsible for all cache operations: Placement
7-47 Chapter 7 Memory System Design Fig 7. The Mapping Function Example: KB MB CPU Word Block Main Address Mapping function The cache mapping function is responsible for all cache operations: Placement
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
