Get your hands dirty - Segment Routing on IOS-XR and IOS-XE
|
|
|
- Marlene Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Get your hands dirty - Segment Routing on IOS-XR and IOS-XE Nagendra Kumar Nainar Ashish Panda LTRRST-2500
3 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
4 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
5 Segment Routing Source Routing Source chooses a path and encodes it in the packet header as an ordered list of segments Rest of the network executes the encoded instructions without any further per-flow state Segment Identifier for any type of instruction Forwarding or service Control Plane Paradigm Distributed intelligence is used to build these segments Centralized intelligence maps application to path for resource optimization LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 5
6 IGP Prefix Segment Aka Node Segment ID Shortest-path to the IGP prefix Global Signaled by ISIS/OSPF Manually assigned or using centralized controller payload payload Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 6
7 IGP Adjacency Segment Forward on the IGP adjacency Locally Assigned Local significance Signaled by ISIS/OSPF Programmed only in originator s forwarding table payload payload Illustration: Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index 6 15 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 7
8 BGP Prefix SID Useful in DC based BGP designs Similar to Node SID Globally unique in the SRGB Manually assigned like node SID Transported through BGP LU Solves the unpredictability issue Controller knows which label to assign to exit through Node 3 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 8
9 BGP peer SID Egress Peer engineering Similar to adjacency SID Locally significant to assigning router Pop and Forward to the BGP peer BGP LS carries SID from egress peer to controller BGP LU transports the SID from controller to routers RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router_C# show bgp egress-engineering Egress Engineering Peer Set: /32 (10b87210) Nexthop: Version: 2, rn_version: 2 Flags: 0x Local ASN: 1 Remote ASN: 2 Local RID: Remote RID: First Hop: NHID: 3 Label: 24002, Refcount: 3 rpc_set: 10b9d408 Egress Engineering Peer Set: /32 (10be61d4) Nexthop: Version: 3, rn_version: 3 Flags: 0x Local ASN: 1 Remote ASN: 3 Local RID: Remote RID: First Hop: NHID: 4 Label: 24003, Refcount: 3 rpc_set: 10be6250 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 9
10 SR Data Plane Data Plane Forwarding actions: CONTINUE: Forwarding action based on active segment PUSH: Add segment to SR header NEXT: Mark the next segment as Active Segment Routing SR Header Active Segment PUSH NEXT CONTINUE MPLS Data Plane Label Stack Topmost Label Label Push Label Pop Label Swap LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 10
11 SR Control Plane Segment ID distribution IGP: OSPF, ISIS BGP: BGP-LU, BGP-LS Controller collects via BGP-LS IGP segments BGP segments Topology Flow to Segment sequence mapping instruction Distributed CSPF SDN Controller based approach Operator defined 11 Ctrl BGP-LS BGP-LS LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 11
12 SR Control Plane Segment ID Distribution Link State IGP (OSPF/ISIS) are extended to carry Segment Routing attributes ISIS implantation is based on draft-ietf-isis-segment-routing-extensions SR Capabilities TLV, SRGB, Algorithm Segment ID Sub-TLVs (Prefix, adjacency) SID binding TLV LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 12
13 OSPF Extensions Implementation is based on draft-ietf-ospf-prefix-link-attr-01 and draft-ietf-ospf-segment-routing-extensions-02 OSPF adds to the Router Information Opaque LSA (type 4): SR-Algorithm TLV (8) SID/Label Range TLV (9) OSPF defines new Opaque LSAs to advertise the SIDs OSPFv2 Extended Prefix Opaque LSA (type 7) OSPFv2 Extended Prefix TLV (1) Prefix SID Sub-TLV (2) OSPFv2 Extended Link Opaque LSA (type 8) OSPFv2 Extended Link TLV (1) Adj-SID Sub-TLV (2) LAN Adj-SID Sub-TLV (3) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 13
14 Segment Routing Use-Cases
15 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 15
16 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 16
17 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 17
18 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 18
19 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels FTP Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 19
20 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels FTP Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 20
21 Traffic Engineering using SR Tunnels FTP Voice Application or Controller triggered Flow mapping Instruction Voice Traffic File Transfer Ctrl 11 Voice Traffic with low latency requirement uses {18002, 24125, 18013, 30021} File Transfer Traffic with High BW requirement uses {18002, 24025, 18013, 30021} Link0 High BW High delay Link1 Low BW Low delay Illustration: Prefix-SID NodeX = X Adj-SID X Y = 24nXY, n is index Service-SID X = X DPI LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 21
22 Lets lab it up
23 Segment Routing Topology PCE SR Domain CE11 CE12 G0/0/0/0 G0/0/0/1 PCC & Mapping Server G0/0/0/2 XR_PCE G0/0/0/2 G0/0/0/3 G0/1 LDP Domain G0/1 G0/0/0/3 G0/0/0/1 G0/0/0/4 G0/0/0/2 G0/1 CE G0/2 Gi4 XR_PE G0/0/0/0 Gi2 XE_PE G0/0/0/1 Gi3 XR_P3 G0/0/0/3 G0/0/0/ Gi3 Gi5 Gi2 Gi4 XE_P G0/0/0/0 XR_PE G0/0/0/1 G0/0/0/1 G0/0/0/0 XR_P G0/0/0/2 G0/1 IOS_P G0/2 G0/3 Gi2 Gi3 XE_PE LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 23
24 Pre configurations All loopback addresses are of format x/32. x= node number All transit network are from 10.0.xy.x or y/24 network. e.g P2-P3 link has IPs /24 and /24 on respective sides ISIS is configured as the IGP across all devices LDP is configured on LDP domain devices. No segment routing configuration is done on SR domain CE routers and PE routers have all relevant(xr or XE) L3VPN configuration preconfigured. XR_PE5 is used as BGP VPNv4 RR. PE CE protocol is BGP. CE11 to CE12 loopback reachability using MPLS L3VPN is there as they are on LDP domain. CE10 reachability is not there from CE11 and CE12 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 24
25 POD access details Open cisco anyconnect. Connect to the firewall Username: ciscolive1, password: ciscolive1 After successful connection, open Remote Desktop client and login to your respective POD VM (IP address in the table in next slide). Username: admin, Password: cisco From your respective VM, open putty connection manager : you can connect to your Pre-saved POD routers by double click: Username: cisco, Password: cisco LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 25
26 POD access details - continued POD number Jump host Port ( ) VM IP Router name Router management IP CE CE CE IOS_P XE_P XE_PE XE_PE XR_P XR_P XR_PCE XR_PE XR_PE LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 26
27 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
28 Configuration Tasks 1. Enable Segment Routing on all nodes in SR domain 2. Enable IGP (ISIS) to advertise Segment ID on all SR nodes 3. Change the default segment routing Global Block to Use Index based Segment ID configuration on XR_PE1, XE_PE2, XR_P3 and XR_PCE5. Use Index = node number 5. Use Absolute value based SID Configuration on XE_P4, XR_PE6, XR_P7 6. Enable Explicit-null SID advertisement on XR_P7 and XE_P4 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 28
29 Enable Segment Routing On all XE node XE_PE2, XE_P4! segment-routing mpls! On all XR nodes XR_PE1, XR_P3, XR_PCE5, XR_PE6, XR_P7! segment-routing! Enables Segment Routing globally on the node. Does not assign or advertise any Segment ID. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 29
30 Enable IGP with Segment Routing On all XE nodes XE_PE2, XE_P4 router isis 1 metric-style wide segment-routing mpls! enable SR for the MPLS data plane Note: All nodes in the POD are enabled with ISIS instance 1 Enables IGP to assign and advertise Segment ID. Adjacency-SIDs are allocated automatically and distributed for all IGP Adjacencies MPLS forwarding is enabled on all non-passive IS-IS interfaces On all XR nodes XR_PE1, XR_P3, XR_PCE5, XR_PE6, XR_P7 router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast metric-style wide segment-routing mpls! enable SR for the MPLS data plane LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 30
31 Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) On all XE nodes XE_PE2, XE_P4 segment-routing mpls global-block ! On all XR nodes XR_PE1, XR_P3, XR_PCE5, XR_PE6, XR_P7 segment-routing global-block By default SRGB will be from to (8000 labels). It must be same on all devices in the same SR domain. The range can be changed using global-block We use global-block (2000 labels) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 31
32 Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) XE and XR Example segment-routing global-block ! router isis segment-routing mpls Configure a non-default global SRGB 18,000 19,999 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls label range Sun Nov 13 09:17: UTCRange for dynamic labels: Min/Max: 24000/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls label table det <SNIP> ISIS(A):1 InUse No (Lbl-blk SRGB, vers:0, (start_label=18000, size=2000) <SNIP> XR R9#show mpls label range Downstream Generic label region: Min/Max label: 16/ Range for Reserved labels: 1. Range ID: 0 Owner: SR-APP Min/Max label: 18000/19999 Clients Permitted: ISIS OSPF Clients In Use: ISIS Checkpoint Labels Unclaimed: FALSE XE LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 32
33 Prefix SID Configuration Index Value On all XE nodes segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map address-family ipv4 n.n.n.n/m index <index> range 1 exit-address-family XE On all XR nodes router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid index <index> Prefix-SID is globally unique within the domain. index (offset) Value based assignment is used to identify the Prefix SID value LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 33
34 Prefix SID Configuration Index Value On XE nodes XE_PE2: segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map address-family ipv /32 index 2 range 1 exit-address-family On XR nodes XR_PE1: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid index 1 XR_P3: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid index 3 XR_PCE5: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid index 5 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 34
35 Prefix SID Configuration Absolute Value On all XE nodes segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map address-family ipv4 n.n.n.n/m absolute <value> range 1 exit-address-family XE On all XR nodes router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid absolute <value> Prefix-SID is globally unique within the domain. Absolute value based assignment is used to identify the Prefix SID value LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 35
36 Prefix SID Configuration Absolute Value On XE nodes On XR nodes XE_P4: segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map address-family ipv /32 absolute range 1 exit-address-family XE XR_PE6: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid absolute XR_P7: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid absolute LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 36
37 Prefix SID Configuration Explicit Null (XE) On XE node XE_P4 XE_P4: conf t segment-routing mpls! set-attributes address-family ipv4 explicit-null exit-address-family XE_P4#show isis database XE_P verbose Tag 1: IS-IS Level-1 LSP XE_P LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL XE_P * 0x000006BC 0xA30D 748/* 0/0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xCC Router CAP: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 8000 Hostname: XE_P4 IP Address: Metric: 10 IP /32 Prefix-attr: X:0 R:0 N:1 Prefix-SID Index: 4, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:1 E:1 V:0 L:0 E Flag set to 1 P = 1 (don't pop) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 37
38 Prefix SID Configuration Explicit Null (XR) On XR node XR_P7 XR_P7: router isis 1 interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid absolute explicit-null RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P7#show isis database XR_P7 verbose detail Thu Jan 5 00:19: UTC IS-IS 1 (Level-1) Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL XR_P * 0x000006b9 0x9f1d /0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xcc Hostname: XR_P7 IP Address: Router Cap: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 <SNIP> E Flag set to 1 P = 1 (don't pop) Metric: 0 IP-Extended /32 Prefix-SID Index: 7, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:1 E:1 V:0 L:0 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 38
39 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
40 SR LDP inter operability Configure XR_PE1 as a Mapping Serve Advertises Prefix Segment ID for LDP Prefixes. Make sure CE10 is reachable from CE12 and vice versa Configure XR_PE6 to prefer SR label over LDP label LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 40
41 Mapping Server Like a proxy for nodes without SR capability Responsible for propagating Segment ID mapping for LDP Prefixes in SR domain. Transported through IGP to all SR capable nodes ISIS uses SID/Label Binding TLV (149) OSPFv2 uses Extended Prefix Opaque LSA (type 7) OSPFv2 Extended Prefix TLV (1) Prefix SID Sub-TLV (2) Location independent LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 41
42 Configuring Mapping Server On XR nodes XR_PE1: segment-routing mapping-server prefix-sid-map address-family ipv / /32 9 router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast segment-routing prefix-sid-map advertise-local Assigns manual prefix to SID mapping for LDP Prefixes Activates IGP (ISIS) to advertise Prefix SID mapping Verification Check isis database for mapping advertisements Check the labels in the forwarding table (show mpls forwarding labels 18009) Check the border boxes for label merge operation Check end to end ping between CE10 and CE12 loopback IPs LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 42
43 Verifying prefix-to-sid mappings RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show segment-routing mapping-server prefix-sid-map ipv4 Fri Jan 13 04:06: UTC Prefix SID Index Range Flags / / On Mapping server RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show isis database verbose XR_PE1 Fri Jan 13 03:59: UTC <deleted> Prefix-SID Index: 1, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 SID Binding: /32 F:0 M:0 S:0 D:0 A:0 Weight:0 Range:1 SID: Start:8, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:0 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 SID Binding: /32 F:0 M:0 S:0 D:0 A:0 Weight:0 Range:1 SID: Start:9, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:0 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 On any ISIS router RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show isis segment-routing prefix-sid-map active-policy Fri Jan 13 04:05: UTC IS-IS 1 active policy Prefix SID Index Range Flags / / Mapping On other SR routers LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 43
44 Verifying SR-LDP Border node programming SR label translated/merged to LDP label 16 on the border router RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show mpls forwarding labels Fri Jan 13 04:06: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched SR Pfx (idx 9) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show mpls ldp bind /32 Thu Feb 9 20:49: UTC /32, rev 27 Local binding: label: Remote bindings: (1 peers) Peer Label :0 16 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 44
45 SR-LDP Preference Relevant to Ingress SR nodes which have to choose between SR and LDP when they impose the label stack. By default LDP label will be preferred over SR. Configure XR_PE6 to override the behavior. (**Artificial scenario created by injecting LDP label from PE3) On XR_PE6 router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast segment-routing mpls sr-prefer Default value After changing default RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show mpls forwarding i /32 Thu Jan 5 13:10: UTC SR Pfx (idx 1) Gi0/0/0/ << SR label /32 Gi0/0/0/ <<LDP label RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show cef /32 Mon Jan 9 17:11: UTC /32, version 213, internal 0x x1 (ptr 0xa141acf4) [1], 0x0 ( <SNIP> next hop /32 local adjacency local label labels imposed {24020} RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show cef /32 Mon Jan 9 17:11: UTC /32, version 454, internal 0x x83 (ptr 0xa141acf4) [1], 0x0 <SNIP> next hop /32 local adjacency local label labels imposed {18001} LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 45
46 Segment ID Conflict With Mapping Server, conflicts may be seen due to human error Prefix Conflict Same Prefix advertised with different Segment ID by different nodes. Segment ID Conflict Different Prefix advertised with same Segment ID by different nodes. There are efforts underway to standardize the behavior. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 46
47 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
48 Basic Segment Routing Verification Control plane Verification Forwarding plane Verification Path Validation using LSP Ping LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 48
49 Control Plane Verification - XR RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls label table detail Table Label Owner State Rewrite LSD(A) LSD(A) InUse InUse Yes Yes LSD(A) LSD(A) InUse InUse Yes Yes SRGB block associated with ISIS instance 1 (Label range = to 19999) ISIS(A):1 InUse No (Lbl-blk SRGB, vers:0, (start_label=18000, size=2000) BGP-VPNv4(A):bgp-default InUse No (IPv4, vers:0, 'live':4u, /32) ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=1, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/0, nh= ) ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes List of locally assigned Adjacency (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=3, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/0, nh= ) Segment ID ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=1, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/1, nh= ) ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=3, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/1, nh= ) ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=1, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/2, nh= ) ISIS(A):1 InUse Yes (SR Adj Segment IPv4, vers:0, index=3, type=0, intf=gi0/0/0/2, nh= ) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 49
50 Control Plane Verification XR SID mapping Shows Prefix to SID mapping (hidden command) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show isis segment-routing label table Thu Jan 5 13:34: UTC IS-IS 1 IS Label Table Label Prefix/Interface / / / / / Loopback /32 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 50
51 Control Plane Verification - XR RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show isis database XR_PE1 verbose Thu Jan 5 00:56: UTC IS-IS 1 (Level-1) Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL XR_PE * 0x000006be 0xe /0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xcc Hostname: XR_PE1 IP Address: Router Cap: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 Total Level-1 LSP count: 1 Local Level-1 LSP count: 1 IS-IS 1 (Level-2) Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL XR_PE * 0x000006c5 0x /0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xcc Hostname: XR_PE1 IP Address: Router Cap: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 Metric: 1 IS-Extended XE_PE2.00 Interface IP Address: Neighbor IP Address: ADJ-SID: F:0 B:1 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24001 ADJ-SID: F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24002 Metric: 1 IS-Extended XR_P3.00 Interface IP Address: Neighbor IP Address: ADJ-SID: F:0 B:1 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24003 ADJ-SID: F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24004 Metric: 1 IS-Extended XR_PCE5.00 Interface IP Address: Neighbor IP Address: ADJ-SID: F:0 B:1 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24005 ADJ-SID: F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24006 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /30 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /30 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /30 Metric: 0 IP-Extended /32 S:0, don t propagate TLV to other level D:0, TLV not propagated L2 L1 SRGB: Start: 18,000, Size: 2000 [18,000 19,999] I:1 IPv4 support V:0, No IPv6 support Locally assigned Adjacency Segment ID LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 51
52 Control Plane Verification - XE XE_PE2#show mpls label range Downstream Generic label region: Min/Max label: 16/ Range for Reserved labels: 1. Range ID: 0 Owner: SR-APP Min/Max label: 18000/19999 Clients Permitted: ISIS OSPF Clients In Use: ISIS Checkpoint Labels Unclaimed: FALSE SRGB block associated with ISIS instance 1 (Label range = to 19999) XE_PE2# XE_P4#show isis segment-routing connected-sid Tag 1: Prefix to SID map IS-IS Level-1 connected prefix-sids: Host Prefix SID Index Range Flags XE_P4 * / Tag 1: IS-IS Level-2 connected prefix-sids: Host Prefix SID Index Range Flags XR_P / XR_PE / XR_PCE / XR_PE / XR_P / XE_PE / LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 52
53 Control Plane Verification - XE XE_PE2#show isis database XE_PE verbose Tag 1: IS-IS Level-1 LSP XE_PE LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL XE_PE * 0x000006BB 0x69ED 478/* 0/0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xCC Router CAP: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 Hostname: XE_PE2 IP Address: Metric: 10 IP /32 Prefix-attr: X:0 R:0 N:1 Prefix-SID Index: 2, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 S:0, don t propagate TLV to other level D:0, TLV not propagated L2 L1 SRGB: Start: 18,000, Size: 2000 [18,000 19,999] I:1 IPv4 support V:0, No IPv6 support IS-IS Level-2 LSP XE_PE LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL XE_PE * 0x000006C3 0xC /* 0/0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xCC Router CAP: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 Hostname: XE_PE2 Metric: 1 IS-Extended XE_P4.00 Adjacency SID Value:18 F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 Weight:0 Metric: 1 IS-Extended XR_PE1.00 Adjacency SID Value:17 F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 Weight:0 IP Address: Metric: 10 IP /32 Prefix-attr: X:0 R:0 N:1 Prefix-SID Index: 2, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 Metric: 1 IP /30 Prefix-attr: X:0 R:0 N:0 Metric: 1 IP /30 Prefix-attr: X:0 R:0 N:0 XE_PE2# Locally assigned Adjacency Segment ID LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 53
54 Path Validation LSP Ping On all XR nodes XR_PE1, XR_P3, XR_PE6, XR_PCE5, XR_P7 Conf t mpls oam! XR nodes are required to be enabled with MPLS OAM. No specific commands required on XE nodes. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 54
55 Path Validation LSP Ping RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#ping mpls ipv /32 Thu Jan 5 01:11: UTC Sending 5, 100-byte MPLS Echos to /32, timeout is 2 seconds, send interval is 0 msec: Codes: '!' - success, 'Q' - request not sent, '.' - timeout, 'L' - labeled output interface, 'B' - unlabeled output interface, 'D' - DS Map mismatch, 'F' - no FEC mapping, 'f' - FEC mismatch, 'M' - malformed request, 'm' - unsupported tlvs, 'N' - no rx label, 'P' - no rx intf label prot, 'p' - premature termination of LSP, 'R' - transit router, 'I' - unknown upstream index, 'X' - unknown return code, 'x' - return code 0 Type escape sequence to abort. QQQQQ Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# It could be noted that PE1 does not send any request out. By default, it tries to use LDP as FEC-type (which is not enabled) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 55
56 Path Validation LSP Ping RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#ping mpls ipv /32 fec-type generic Thu Jan 5 01:11: UTC Sending 5, 100-byte MPLS Echos to /32, timeout is 2 seconds, send interval is 0 msec: Codes: '!' - success, 'Q' - request not sent, '.' - timeout, 'L' - labeled output interface, 'B' - unlabeled output interface, 'D' - DS Map mismatch, 'F' - no FEC mapping, 'f' - FEC mismatch, 'M' - malformed request, 'm' - unsupported tlvs, 'N' - no rx label, 'P' - no rx intf label prot, 'p' - premature termination of LSP, 'R' - transit router, 'I' - unknown upstream index, 'X' - unknown return code, 'x' - return code 0 Type escape sequence to abort.!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/10 ms RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# Use FEC-type as generic. FEC type for Segment routing is work under progress (draft-ietf-mplsspring-lsp-ping) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 56
57 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
58 Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) Enable SR core routers to support MPLS TE Enable IGP to support MPLS TE extensions Configure SR-TE Dynamic tunnel number 1 from XR_PE1 to XR_PE6 Configure an Explicit SR-TE tunnel number 2 from XE_PE2 to XR_PE6 using path (PE2-PE1-PCE5-P3-P4-P7-PE6). To reach P4 from P3 use the adjacency SID of G0/0/0/0 link instead of the P4 node SID. Verify Functionality of both the tunnels by directing L3VPN traffic onto these tunnels LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 58
59 SR TE enabling core Activate MPLS traffic engineering (On All routers) XR_PE1, XR_PE3_XR_PCE5, XR_PE6, XR_P7!!!Enable MPLS traffic engineering globally. Interface need not be configured under it mpls traffic-eng configure TE extension for IGP (On All routers) XE_P2 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi2 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi3 mpls traffic-eng tunnels XE_P4 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi2 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi3 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi4 mpls traffic-eng tunnels! int gi5 mpls traffic-eng tunnels XR router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast mpls traffic-eng level-2! mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0! XE router isis 1 mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0 mpls traffic-eng level-2! LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 59
60 SR TE Dynamic tunnel configuration XR_PE1 SR dynamic tunnels (on Headend) interface tunnel-te1 ipv4 unnumbered Loopback0 destination autoroute destination path-option 1 dynamic segment-routing! LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 60
61 SR TE Explicit tunnel configuration G0/0/0/0 G0/0/0/3 On XE_PE2 Ip explicit-path name PE2-PE1-PE5-P3-P4-P7-PE6 index 1 next-label index 2 next-label index 3 next-label index 4 next-label <adj label of P3-P4 link> index 5 next-label index 6 next-label 18006! interface tunnel2 ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel destination tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute destination tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name PE2-PE1-PE5-P3-P4-P7- PE6 segment-routing RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show isis adjacency G0/0/0/0 detail level 2 Fri Feb 10 15:06: UTC IS-IS 1 Level-2 adjacencies: System Id Interface SNPA State Hold Changed NSF IPv4 IPv6 BFD BFD XE_P4 Gi0/0/0/0 *PtoP* Up 28 2w3d Yes None None Area Address: 49 Neighbor IPv4 Address: * Adjacency SID: Non-FRR Adjacency SID: Topology: IPv4 Unicast Total adjacency count: 1 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 61
62 SR TE dynamic verification Verify ISIS database and check SR, TE extensions (show isis database verbose XR_P ) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show isis database verbose XR_PE Wed Jan 11 10:39: UTC <SNIP> IS-IS 1 (Level-2) Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL XR_PE x f 0x2d4b 858 0/0/0 Area Address: 49 NLPID: 0xcc Hostname: XR_PE6 IP Address: Router ID: Router Cap: , D:0, S:0 Segment Routing: I:1 V:0, SRGB Base: Range: 2000 <SNIP..continued> <SNIP continued> Metric: 1 IS-Extended XR_P7.00 Affinity: 0x Interface IP Address: Neighbor IP Address: Physical BW: kbits/sec Reservable Global pool BW: 0 kbits/sec Global Pool BW Unreserved: [0]: 0 kbits/sec [1]: 0 kbits/sec [2]: 0 kbits/sec [3]: 0 kbits/sec [4]: 0 kbits/sec [5]: 0 kbits/sec [6]: 0 kbits/sec [7]: 0 kbits/sec Admin. Weight: 1 Ext Admin Group: Length: 32 0x x x x x x x x ADJ-SID: F:0 B:1 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24023 ADJ-SID: F:0 B:0 V:1 L:1 S:0 weight:0 Adjacency-sid:24024 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /24 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /24 Metric: 1 IP-Extended /24 Metric: 0 IP-Extended /32 Prefix-SID Index: 6, Algorithm:0, R:0 N:1 P:0 E:0 V:0 L:0 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 62
63 SR TE dynamic verification MPLS Segment Routing TE topology RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing Wed Jan 11 05:47: UTC IGP[0]:: IS-IS 1 level 2, Strict SPF Disabled Nodes: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Segment-Routing: TE Node-SID Index: 6i SRGB Info: Start 18000, Size 2000 Link[1]:Point-to-Point, Nbr IGP Id: , Nbr Node Id:3, gen:18110 Frag Id:0, Intf Address: , Intf Id:0 Segment-Routing Adjacency-SIDs: 2 Adjacency-SID[0]: 24022, Flags: V, L to Nbr:: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Adjacency-SID[1]: 24021, Flags: B, V, L to Nbr:: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Nbr Intf Address: , Nbr Intf Id:0 TE Metric:1, IGP Metric:1 Ext Admin Group: Length: 256 bits Value : 0x:: Attribute Names: <SNIP. Other links deleted. Check actual output on router> Prefixes: /32, SID index: 6, flags: N Adv. router(s) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 63
64 SR TE dynamic verification Verify MPLS TE for SID info (show mpls traffic-eng tunnel <number>) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels 1 Wed Jan 11 05:37: UTC Name: tunnel-te1 Destination: Ifhandle:0xd0 Signalled-Name: XR_PE1_t1 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, (Segment-Routing) type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 2) <SNIP.some detaild deleted> Segment-Routing Path Info (IS-IS 1 level-2) Segment0[Link]: , Label: Segment1[Link]: , Label: Displayed 1 (of 1) heads, 0 (of 0) midpoints, 0 (of 0) tails RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls forwarding labels Wed Feb 8 21:33: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Adj (idx 1) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls forwarding labels Wed Feb 8 21:34: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Adj (idx 1) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 64
65 SR TE explicit verification Shut XR_PE1-CE10 link. XE_PE2#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel2 Name: XE_PE2_t2 (Tunnel2) Destination: Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, (SEGMENT-ROUTING) type explicit PE2-PE1-P3-P4- P7-PE6 (Basis for Setup) <SNIP> Tun_Instance: 9 Segment-Routing Path Info (isis level-2) Segment0[ - ]: Label: Segment1[ - ]: Label: Segment2[ - ]: Label: Segment3[ - ]: Label: Segment4[ - ]: Label: XE_PE2# CE10#traceroute source lo0 num prob 1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) msec [MPLS: Labels 18003/24000/18007/18006/24018 Exp 0] 16 msec [MPLS: Labels 24000/18007/18006/24018 Exp 0] 15 msec [MPLS: Labels 18007/18006/24018 Exp 0] 13 msec [MPLS: Labels 0/18006/24018 Exp 0] 13 msec [MPLS: Label Exp 0] 12 msec msec CE10# Repeat the verification steps as SR-TE dynamic case. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 65
66 SR TE verification Shut XE_PE2-CE10 link. Trace from CE10 to CE11 and check what is the path followed (trace source lo0) Verify labels from trace CE10#trace source lo 0 numeric probe 1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) msec [MPLS: Labels 24005/24018 Exp 0] 15 msec [MPLS: Label Exp 0] 11 msec msec CE10# Verify MPLS TE and forwarding table that no additional LSPs are created in the transit routers with SR-TE. on XR_P3 (show mpls traffic-eng tunnels role middle, show mpls forwarding table) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels role middle Wed Jan 11 05:20: UTC RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls forwarding i tt Wed Jan 11 05:30: UTC RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 66
67 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
68 SR TE PCE controller based Configure tunnel number 100 on XR_PE1 destined to XR_PE6. For tunnel setup, request path information from PCE. Configure XR_PCE5 as SR PCE controller Configure XR_PE1 as SR PCC stateful client agent and authorize controller to instantiate LSPs Configure BGP-LS session with XR_PCE5 and XR_P3 Configure IGP on XR_P3 to distribute IGP database to BGP-LS BGP LS LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 68
69 PCE BGP-LS configurations XR_PCE5 - PCE!PCEP PCE configuration router bgp 1! address-family link-state link-state exit! neighbor > BGP LS peer loopback IP remote-as 1 update-source loopback 0 address-family link-state link-state XR_P3 For topology information transport to PCE using BGP-LS!BGP LS config router bgp 1! address-family link-state link-state exit! neighbor remote-as 1 update-source loopback 0 address-family link-state link-state!igp to LS distribution config router isis 1 distribute bgp-ls instance-id 32 throttle 10 BGP Link State is a new address-family with AFI and SAFI 71 Used to exchange link-state information of Segment Routing domain to PCE server LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 69
70 SR TE PCE based configuration XR_PE1 - PCC!PCEP session configuration with controller mpls traffic-eng pce peer ipv > ip address of PCE! segment-routing stateful-client instantiation!!tunnel configuration interface tunnel-te100 ipv4 unnumbered Loopback0 destination path-option 1 dynamic pce segment-routing autoroute destination ! XR_PCE5 - PCE!PCEP PCE configuration pce address ipv > PCE local loopback IP PCEP and tunnel configurations LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 70
71 PCE based SR TE verification Check PCEP sessions are up between PCE (show pce ipv4 peer) and PCC (show mpls traffic-eng pce peer). Check BGP LS table for prefixes learnt.(show bgp link-state link-state) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show pce ipv4 peer Wed Jan 11 11:22: UTC PCE's peer database: Peer address: State: Up Capabilities: Stateful, Segment-Routing, Update, Instantiation RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls traffic-eng pce peer Wed Jan 11 11:23: UTC Address Precedence State Learned From Up Static config RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show bgp link-state link-state <SNIP> Prefix codes: E link, V node, T IP reacheable route, u/u unknown I Identifier, N local node, R remote node, L link, P prefix L1/L2 ISIS level-1/level-2, O OSPF, D direct, S static/peer-node a area-id, l link-id, t topology-id, s ISO-ID, c confed-id/asn, b bgp-identifier, r router-id, i if-address, n nbr-address, o OSPF Route-type, p IP-prefix d designated router address Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i[v][l1][i0x20][n[c1][b ][s ]]/ i RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show bgp link-state link-state summary <SNIP> Neighbor Spk AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down St/PfxRcd :02:33 73 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 71
72 Link state BGP Node Information : V type route RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show bgp link-state link-state [V][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b192.1$ Wed Jan 11 12:43: UTC BGP routing table entry for [V][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b ][s ]]/328 <SNIP> Local (metric 1) from ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 0, version 17 Link-state: Node-name: XR_PE6, ISIS area: 49, Local TE Router-ID: SRGB: 18000:2000 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5# Prefix Info, prefix SID: T type RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show bgp link-state link-state [T][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b192.1$ Wed Jan 11 12:40: UTC BGP routing table entry for [T][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b ][s ]][P[p /32]]/400 <SNIP> Local (metric 1) from ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 0, version 18 Link-state: Metric: 0, PFX-SID: 6(40/0) Link info: E type Adj SID info TE attributes Link attributes RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show bgp link-state link-state [E][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b192.1$ Wed Jan 11 12:27: UTC BGP routing table entry for [E][L2][I0x20][N[c1][b ][s ]][R[c1][b ][s ]][L[i ][n ]]/696 <SNIP> Local (metric 1) from ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 0, version 10 Link-state: Local TE Router-ID: , Remote TE Router-ID: admin-group: 0x , max-link-bw (kbits/sec): max-reserv-link-bw (kbits/sec): 0, max-unreserv-link-bw (kbits/sec): TE-default-metric: 1, metric: 1, ADJ-SID: 24023(70) ADJ-SID: 24024(30) LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 72
73 PCE based SR TE verification Shut XE_PE2-CE10 link and tunnel 1 on XR_PE1. Trace from CE10 to CE11 and check what is the path followed (trace source lo0) Verify labels from trace Verify MPLS TE for SID info (show mpls traffic-eng tunnel <number>) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels 100 Wed Jan 11 13:18: UTC Name: tunnel-te100 Destination: Ifhandle:0xf0 Signalled-Name: XR_PE1_t100 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, (Segment-Routing) type dynamic pce (Basis for Setup, path weight 2) G-PID: 0x0800 (derived from egress interface properties) Bandwidth Requested: 0 kbps CT0 <SNIP> Segment-Routing Path Info (PCE computed path) Segment0[Node]: , Label: Displayed 1 (of 2) heads, 0 (of 0) midpoints, 0 (of 0) tails Displayed 1 up, 0 down, 0 recovering, 0 recovered heads RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# CE10#trace source lo0 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) msec 1 msec 1 msec [MPLS: Labels 18006/24018 Exp 0] 15 msec 13 msec 14 msec [MPLS: Label Exp 0] 12 msec 11 msec 11 msec msec * 14 msec CE10# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 73
74 PCE based SR TE verification Verify MPLS TE topology database (show mpls traffic-eng topology , show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing ) Verify PCE TE database (show pce ipv4 topology) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show pce ipv4 topology Wed Jan 11 13:34: UTC PCE's topology database: Node 3 TE router ID: Host name: XR_PE6 ISIS system ID: level-2 domain ID: 32 Prefix SID: Prefix , label (regular) Link[0]: local address , remote address Local node: ISIS system ID: level-2 domain ID: 32 Remote node: Host name: XR_P3 ISIS system ID: level-2 Metric: IGP 1, TE 1 Bandwidth: Total link , Reservable 0 Adj SID: (protected) (unprotected) <SNIP..check on router for details> RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PCE5#show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing Wed Jan 11 13:43: UTC IGP[0]:: IS-IS 1 level 2, Strict SPF Disabled Nodes: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Segment-Routing: TE Node-SID Index: 6i SRGB Info: Start 18000, Size 2000 Link[0]:Point-to-Point, Nbr IGP Id: , Nbr Node Id:17, gen:29170 Frag Id:0, Intf Address: , Intf Id:0 Segment-Routing Adjacency-SIDs: 2 Adjacency-SID[0]: 24020, Flags: V, L to Nbr:: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Adjacency-SID[1]: 24019, Flags: B, V, L to Nbr:: IGP Id: , MPLS TE Id: Nbr Intf Address: , Nbr Intf Id:0 TE Metric:1, IGP Metric:1 Ext Admin Group: Length: 256 bits Value : 0x:: Attribute Names: <SNIP..check on router for details> LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 74
75 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
76 Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Seamless BFD configuration TI-LFA Configuration LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 76
77 S-BFD Configuration On SR-TE head end node interface tunnel-te1 bfd multiplier 3 fast-detect sbfd minimum-interval 150 Enables Seamless BFD on SR-TE tunnel. Currently supported only for ASR9k platforms as SR-TE headend. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 77
78 TI LFA (FRR) Configuration Task Protect the XE_P4 to XR_P7 link so that traffic on this link is Fast rerouted incase of failure. Verify the mpls forwarding table behavior Verify CEF label imposition Shut down the protected link and verify traffic protection. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 78
79 Fast Reroute Loop Free Alternate Path Metric=1 Z XR_PCE XR_PE Metric=1 XR_P Metric=2 XR_PE LFA Scenario XR_P XE_PE2 Metric=1 XE_P4 Calculates P and Q Space Scenario P space: set of nodes reachable from Source ( or PLR) without using protected link Q space: set of nodes that can reach destination D without using protected link P R-LFA PQ LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 79
80 TI-LFA P and Q node are not the same node. Post Convergence Path Prefix SID (P) Prefix SID (Q) Prefix SID(Z) Packet to Z Metric=1 XR_PE XE_PE Metric=3 Metric=1 Metric=1 Enforcing loop-freeness on post-convergence path Where can I release the packet? At the intersection between the post-convergence shortest path and the Q space How do I reach the release point? By chaining intermediate segments that are assessed to be loop-free P R-LFA Scenario XR_P XE_P Metric=2 Q Z LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 80
81 TI-LFA selection preference 1. Prefer 0-segment (directly connected) TI-LFA candidate 2. Prefer 1-segment (PQ node) TI-LFA candidate 3. Prefer 2-segment (P and Q nodes) TI-LFA candidate 4. Fallback to other non-sr or non-epc* LFA candidate * non-epc: not Explicit Post-Convergence, i.e. not located on post-convergence path LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 81
82 TI-LFA Configuration Example Protects traffic on specified link failure On XR generic example router isis 1 interface < > address-family ipv4 unicast fast-reroute per-prefix fast-reroute per-prefix ti-lfa level-2 Enables pre-prefix FRR On XE_P4 router isis 1 fast-reroute per-prefix level-2 all fast-reroute ti-lfa level-2 Enables pre-prefix FRR Uses TI-LFA to compute the backup path Uses TI-LFA to compute the backup path TI-LFA uses Prefix and Adjacency Segment ID to compute the backup path. Topology Independent and can compute path even in scenarios where rlfa cannot help. Identifies and uses the stack of segment ID for backup path. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 82
83 TI-LFA Verification Example On XR_P3 increase P3_PE6 link metric to 20 router isis 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/4 address-family ipv4 unicast metric 20 On XE_P4 router isis 1 fast-reroute per-prefix level-2 all fast-reroute ti-lfa level-2 Backup Path PLR PQ XR_P4 LFIB Table XR_P7 Primary Path Primary Path Push XR_P3 Backup Path = TILFA tunnel label Primary Path from XE_PE2 to XR_PE6 is XE_P4->XR_P7->XR_PE6. In our example, XE_P4 acts as Point of Local Repair (PLR) and XR_PE6 as PQ node. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 83
84 Verifying TI-LFA Backup Path On XE_P4 XE_P4#show ip cef /32 nexthop GigabitEthernet4 label [18006 implicit-null]-(local:18006) repair: attached-nexthop MPLS-SR-Tunnel3 XE_P4# Backup Path Tunnel PQ node XE_P4#show isis fast-reroute ti-lfa tunnel Tag 1: Fast-Reroute TI-LFA Tunnels: Tunnel Interface Next Hop End Point Label End Point Host MP1 Gi XR_PE1 MP3 Gi XR_PE6 XE_P4# Backup label is 24009, PQ node is XR_PE6, Next hop is LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 84
85 Verifying TI-LFA ISIS RIB table (XR) On XR_P3 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show isis ipv4 fast-reroute /32 Tue Jan 24 16:36: UTC L /32 [1/115] via , GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1, XR_PE1, SRGB Base: 18000, Weight: 0 FRR backup via , GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2, XR_PCE5, SRGB Base: 18000, Weight: 0, Metric: 2 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# Backup Path imposed incase of link failure LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 85
86 Verifying TI-LFA Label Forwarding table (XR) On XR_P3 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls forwarding labels detail Tue Jan 24 16:38: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Pfx (idx 1) Gi0/0/0/ Updated: Jan 24 16:33: Path Flags: 0x400 [ BKUP-IDX:1 (0xa0e532ec) ] Version: 599, Priority: 1 Label Stack (Top -> Bottom): { Imp-Null } NHID: 0x0, Encap-ID: N/A, Path idx: 0, Backup path idx: 1, Weight: 0 MAC/Encaps: 14/14, MTU: 1500 Packets Switched: SR Pfx (idx 1) Gi0/0/0/ (!) Updated: Jan 24 16:33: Path Flags: 0x300 [ IDX:1 BKUP, NoFwd ] Version: 599, Priority: 1 Label Stack (Top -> Bottom): { } NHID: 0x0, Encap-ID: N/A, Path idx: 1, Backup path idx: 0, Weight: 0 MAC/Encaps: 14/18, MTU: 1500 Packets Switched: 0 (!): FRR pure backup Primary Path Backup label imposed incase of link failure Traffic-Matrix Packets/Bytes Switched: 0/0 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 86
87 TI-LFA Functionality Verification Trigger Ping from XR_PE2 to (ICMP or LSP Ping) XE_PE2#ping rep Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 1000, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Below stats shows that there were no traffic received with Adjacency SID on XR_P3. RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls for labels Tue Jan 24 17:52: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Adj (idx 3) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# Now Shut G4 interface (Primary Path) on XE_P4. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 87
88 TI-LFA Functionality Verification No Ping drop should be observed. Check if the forwarding stats counter increased for Adjacency label on XR_P3 to XR_PE6. RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls for labels Tue Jan 24 17:52: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Adj (idx 3) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 88
89 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
90 L3VPN - XR L3 VPN PE (VRF, RD, RT, BGP VPNv4) configuration is same as in LDP case (Preconfigured) In place of LDP following Segment-routing configurations needed which is already done in previous tasks (listed here for reference). 1. [optional] configure Segment routing Global Block 2. Ensure that segment routing is enabled on an IGP instance, addressfamily, or interface. 3. Configure prefix/node SID router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast segment-routing mpls! interface Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-sid index <sid index>! LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 90
91 L3VPN - XE L3 VPN PE (VRF, RD, RT, BGP VPNv4) configuration is same as in LDP case (Preconfigured) In place of LDP following Segment-routing configurations needed which is already done in previous tasks (listed here for reference). 1. Enable segment routing globally 2. [optional] configure Segment routing Global Block 3. Ensure that segment routing is enabled on IGP 4. Configure prefix/node SID segment-routing mpls global-block ! connected-prefix-sid-map address-family ipv4 <prefix>/32 index <sid index> range 1 exit-address-family! router isis 1 address-family ipv4 unicast segment-routing mpls LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 91
92 L3VPN verification Check VPNv4 labels in bgp vrf live. (show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf live {labels} ) Check ISIS Prefix SID database for top SID label (show isis segment-routing label table) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf live Wed Jan 11 15:04: UTC BGP routing table entry for /32, Route Distinguisher: 1:1 <SNIP> (metric 2) from ( ) Received Label Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best, import-candidate, imported <SNIP> Wed Jan 11 15:07: UTCRP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show isis segment-routing label table i "Label IS-IS 1 IS Label Table Label Prefix/Interface /32 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 92
93 L3VPN verification Check mpls forwarding table (show mpls forwarding prefix /32) Check vrf live CEF for label programming(show cef vrf live /32 ) RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls forwarding prefix /32 Wed Jan 11 15:14: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched SR Pfx (idx 6) Gi0/0/0/ RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show cef vrf live /32 Wed Jan 11 15:14: UTC /32, version 16, internal 0x x0 (ptr 0xa14578f4) [1], 0x0 (0x0), 0x208 (0xa159d140) Updated Jan 10 05:11: Prefix Len 32, traffic index 0, precedence n/a, priority 3 via /32, 3 dependencies, recursive [flags 0x6000] path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0xa16057f4 0x0] recursion-via-/32 next hop VRF - 'default', table - 0xe next hop /32 via 18006/0/21 next hop /32 Gi0/0/0/1 labels imposed { } RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 93
94 L3VPN verification All TE tunnels can be shut to see plain SR operation Check end to end ping and trace from CE10 to CE11, CE12 (loopback IPs) Change path and check effect on label values. Note top label never changes thought the path (unlike LDP) CE10#trace source lo0 numeric Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) msec 1 msec 1 msec [MPLS: Labels 18006/24018 Exp 0] 14 msec 13 msec 12 msec [MPLS: Label Exp 0] 10 msec 11 msec 10 msec msec * 13 msec CE10# CE10#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. CE10(config)#int g0/1 CE10(config-if)#shut CE10(config-if)#^Z CE10# CE10#trace source lo0 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) msec 1 msec 1 msec [MPLS: Labels 18006/24018 Exp 0] 14 msec 11 msec 11 msec [MPLS: Labels 18006/24018 Exp 0] 12 msec 11 msec 9 msec [MPLS: Label Exp 0] 9 msec 12 msec 20 msec msec * 11 msec CE10# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 94
95 L2VPN XR L2VPN configuration on SR is not different from what it would have been on an LDP core (with BGP signaling). Here are the detailed steps to follow. Ensure that SR is enabled in the domain Activate L2VPN between CE10 ge1/0.123 and CE11 ge0/ L2 encapsulation mode is vlan Use BGP signaling and BGP auto discovery Enable l2vpn address-family with auto RD assignemnt, VPN ID 100 and RT 1:123 Use ce-id 1 on XR_PE1 and ce-id 2 on XR_PE6 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 95
96 L2VPN-XR configuration On XR_PE1 and XR_PE6 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3.123 l2transport encapsulation dot1q 123!!!enable BGP vpls address family and peer router bgp 1! address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws! neighbor address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws!!configure the L2VPN l2vpn xconnect group TEST mp2mp TEST_SR vpn-id 100 <- should match with remote PE l2-encapsulation vlan autodiscovery bgp rd auto route-target 1:123 <- should match with remote PE signaling-protocol bgp!local ce-id should match with remote ce id and vice versa ce-id 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3.123 remote-ce-id 2 On RR: XR_PCE5 router bgp 1! address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws! neighbor address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws route-reflector-client! neighbor address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws route-reflector-client! LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 96
97 Verify L2VPN XR Check the PW ID between the PE s (show l2vpn xconnect detail) Verify the signaling, top and bottom labels Check the PW ID s, bgp l2vpn table, transport labels The PW should be up but CE to CE data flow will not work due to no dataplane support on XRv. This configuration should work on real routers. LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 97
98 L2VPN verification RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show l2vpn xconnect detail Wed Jan 11 16:48: UTC Group TEST, XC TEST_SR.1:2, state is up; Interworking none Local CE ID: 1, Remote CE ID: 2, Discovery State: Advertised AC: GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3.123, state is up Type VLAN; Num Ranges: 1 VLAN ranges: [123, 123] MTU 1504; XC ID 0x1; interworking none <SNIP> PW: neighbor , PW ID 65538, state is up ( established ) PW class not set, XC ID 0xfff80001 Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP Source address PW type Ethernet VLAN, control word enabled, interworking none PW backup disable delay 0 sec Sequencing not set MPLS Local Remote Label MTU Control word enabled enabled PW type Ethernet VLAN Ethernet VLAN CE-ID MIB cpwvcindex: <SNIP> RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 98
99 L2VPN verification RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show cef Wed Jan 11 18:46: UTC /32, version 216, internal 0x x81 (ptr 0xa1456af4) [1], 0x0 (0xa143c0e8), 0xa28 (0xa159d348) Updated Jan 11 16:48: local adjacency Prefix Len 32, traffic index 0, precedence n/a, priority 1 via /32, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1, 10 dependencies, weight 0, class 0 [flags 0x0] path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0xa10f7168 0x0] next hop /32 local adjacency local label labels imposed {18006} CEF programming to highlight the transport label imposed to reach remote PE LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 99
100 Agenda Introduction to Segment routing Basic Segment Routing Configuration SR-LDP Interoperability Basic Segment Routing Verification Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) PCE based SR-TE Fast Failure Detection and Fast Reroute (FRR) Enabling MPLS Services End-to-End Service Verification
101 End-to-End Service Verification We have L3VPN and MPLS SR TE dynamic tunnel implemented Verifying Control plane Verifying Forwarding plane Path Validation LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 101
102 End-to-End Validation On CE10 CE10#show ip cef /32 nexthop GigabitEthernet0/1 CE10# On CE, show ip cef <remote-ce-address> LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 102
103 End-to-End Validation On XR_PE1 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf live /32 Thu Jan 12 14:16: UTC BGP routing table entry for /32, Route Distinguisher: 1:1 Versions: Process brib/rib SendTblVer Speaker Last Modified: Jan 11 16:48: for 21:28:43 Paths: (1 available, best #1) Not advertised to any peer Path #1: Received by speaker 0 Not advertised to any peer (metric 2) from ( ) Received Label Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best, group-best, import-candidate, imported Received Path ID 0, Local Path ID 0, version 48 Extended community: RT:1:1 Originator: , Cluster list: Source AFI: VPNv4 Unicast, Source VRF: live, Source Route Distinguisher: 1:1 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# VPN label advertised by egress PE On XR_PE1, show bgp vpnv4 vrf <> <Prefix> - Highlight the label LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 103
104 End-to-End Validation On XR_PE1 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show cef vrf live /32 Thu Jan 12 14:20: UTC /32, version 57, internal 0x x0 (ptr 0xa14578f4) [1], 0x0 (0x0), 0x208 (0xa159d140) Updated Jan 11 16:48: Prefix Len 32, traffic index 0, precedence n/a, priority 3 via /32, 6 dependencies, recursive [flags 0x6000] path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0xa16057f4 0x0] recursion-via-/32 next hop VRF - 'default', table - 0xe next hop /32 via 18006/0/21 next hop /32 tt1 labels imposed {ImplNull 24018} RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show cef /32 Thu Jan 12 14:21: UTC /32, version 218, attached, internal 0x x0 (ptr 0xa1456af4) [1], 0x0 (0xa143c034), 0xa20 (0xa159d410) Updated Jan 11 19:52: Prefix Len 32, traffic index 0, precedence n/a, priority 3 via tunnel-te1, 5 dependencies, weight 0, class 0 [flags 0x8] path-idx 0 NHID 0x0 [0xa10f74b0 0xa10f7408] local adjacency local label labels imposed {ImplNull} RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# VPN label advertised by egress PE Egress interface is SR- TE tunnel 1 On XR_PE1, show cef vrf <name> <remote-ce-address> - Dataplane programming LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 104
105 End-to-End Validation On XR_PE1 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1#show mpls traffic tunnel 1 Name: tunnel-te1 Destination: Ifhandle:0xd0 Signalled-Name: XR_PE1_t1 Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, (Segment-Routing) type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 2) <Removed> Segment-Routing Path Info (IS-IS 1 level-2) Segment0[Link]: , Label: Segment1[Link]: , Label: Displayed 1 (of 2) heads, 0 (of 0) midpoints, 0 (of 0) tails Displayed 1 up, 0 down, 0 recovering, 0 recovered heads RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE1# Transport label imposed Egress interface is SR- TE tunnel 1 On XR_PE1, show mpls traffic tunnel <> - Transport label programming LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 105
106 End-to-End Validation XR_PE1 Table Push Tunnel-te1 XR_PE1 Table Tunnel-te 1 Push LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 106
107 End-to-End Validation XR_PE1 Table Push Tunnel-te1 XR_PE1 Table Tunnel-te 1 Push IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 107
108 End-to-End Validation XR_PE1 Table Push Tunnel-te1 XR_PE1 Table Tunnel-te 1 Push IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 108
109 End-to-End Validation XR_PE1 Table Push Tunnel-te1 XR_PE1 Table Tunnel-te 1 Push IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 109
110 End-to-End Validation On XR_P3 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3#show mpls forwarding labels detail Thu Jan 12 14:37: UTC Local Outgoing Prefix Outgoing Next Hop Bytes Label Label or ID Interface Switched Pop SR Adj (idx 3) Gi0/0/0/ Updated: Jan 10 15:15: Version: 30, Priority: 1 Label Stack (Top -> Bottom): { Imp-Null } NHID: 0x0, Encap-ID: N/A, Path idx: 0, Backup path idx: 0, Weight: 0 MAC/Encaps: 14/14, MTU: 1500 Packets Switched: 113 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_P3# On XR_P3, show mpls forwarding labels <> - Label action LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 110
111 End-to-End Validation XR_P3 Table POP G00/0/4 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 111
112 End-to-End Validation XR_P3 Table POP G00/0/ IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 112
113 End-to-End Validation XR_P3 Table POP G00/0/4 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 113
114 End-to-End Validation XR_P3 Table POP G00/0/ IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 114
115 End-to-End Validation On XR_PE6 RP/0/0/CPU0:XR_PE6#show mpls forwarding detail beg Thu Jan 12 14:53: UTC Unlabelled /32[V] Gi0/0/0/ Updated: Jan 10 05:11: Path Flags: 0x6020 [ EXT ] Version: 13, Priority: 3 Label Stack (Top -> Bottom): { Unlabelled } NHID: 0x0, Encap-ID: N/A, Path idx: 0, Backup path idx: 0, Weight: 0 MAC/Encaps: 14/14, MTU: 1500 Packets Switched: 390 On XR_PE6, show mpls forwarding labels <> - Label action LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 115
116 End-to-End Validation XR_PE6 Table VRF live XR_PE6 VRF Table G0/0/0/3 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 116
117 End-to-End Validation XR_PE6 Table VRF live XR_PE6 VRF Table G0/0/0/ IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 117
118 End-to-End Validation XR_PE6 Table VRF live XR_PE6 VRF Table G0/0/0/3 LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 118
119 End-to-End Validation XR_PE6 Table VRF live XR_PE6 VRF Table G0/0/0/ IP LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 119
120 Troubleshooting commands Show isis databse verbose - Shows ISIS LSP database Show isis database <LSP name> verbose - verify SID mapping and SR related information exchange [XE] Show isis segmet-routing connected-sid - shows SID to prefix mapping Show isis segment-routing label table (hidden command) - shows SID to prefix mapping Show isis segment-routing label summary - Summary of the SR label usages show isis segment-routing prefix-sid-map active-policy - shows SID to prefix advertisements form MAPPING server Show isis adjacency detail - to verify Adjacency SID assignment Show mpls forwarding verifying SID programming to MPLS forwarding table Show mpls label range shows the label space Show mpls label table detail shows detailed information of every label allocated by the router Show cef <prefix> - verify SID, prefix programming to CEF LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 120
121 Troubleshooting commands Show mpls traffic-eng tunnel <tu number> - tunnel status, SID assignment and other TE related information Show mpls traffic-eng topology incase of tunnel does not come up verify TE database Show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing topology SR TE database Show pce ipv4 peer - on PCE verify PCEP sessions Show mpls traffic-eng pce peer on PCC verify PCEP sessions Show pce ipv4 topology shows PCE TE database Show isis fast-reroute <prefix> - TILFA outputs related to the prefix Show cef <prefix> - label programming to cef LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 121
122 Conclusion SR-based MPLS Classic MPLS Basic MPLS transport IGP IGP + LDP Traffic black hole, IGP / LDP synchronization No Problem to manage 50ms Fast Reroute IGP IGP + RSP + TE TE states for FRR No additional state Extra states to mange TE states on Transit device No. Only at headend Yes. On all transit nodes ECMP for TE Yes No Seamless interworking Compatible with classic MPLS Engineered for SDN Yes No N/A LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 122
123 Stay Informed More details are available in below links: LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 123
124 Complete Your Online Session Evaluation Please complete your Online Session Evaluations after each session Complete 4 Session Evaluations & the Overall Conference Evaluation (available from Thursday) to receive your Cisco Live T-shirt All surveys can be completed via the Cisco Live Mobile App or the Communication Stations Don t forget: Cisco Live sessions will be available for viewing on-demand after the event at CiscoLive.com/Online LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 124
125 Cisco Spark Ask Questions, Get Answers, Continue the Experience Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the Speaker and fellow participants after the session Download the Cisco Spark app from itunes or Google Play 1. Go to the Cisco events Mobile app 2. Find this session 3. Click the Spark button under Speakers in the session description 4. Enter the room, room name = LTRRST Join the conversation! The Spark Room will be open for 2 weeks after Cisco Live LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 125
126 Continue Your Education Demos in the Cisco campus Walk-in Self-Paced Labs Lunch & Learn Meet the Engineer 1:1 meetings Related sessions LTRRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 126
127 Q & A
128 Thank You
129
130 Appendix
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing Configuration 3 Configuration
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing Configuration 3 Configuration
You cannot configure prefix-sids on transit links at this time. Support for this feature may be introduced in later code versions.
 8.1 Segment Routing Segment Routing (SR) is a relatively new technology pioneered by Cisco that is meant to reduce state in MPLS core networks. One can use SR to replace LDP and RSVP-TE wholesale provided
8.1 Segment Routing Segment Routing (SR) is a relatively new technology pioneered by Cisco that is meant to reduce state in MPLS core networks. One can use SR to replace LDP and RSVP-TE wholesale provided
Configure IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC)
 IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC) provides stateful path computation element (PCE) functionality by exting the existing IOS-XR PCE functionality with additional capabilities. The current IOS-XR PCE function
IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC) provides stateful path computation element (PCE) functionality by exting the existing IOS-XR PCE functionality with additional capabilities. The current IOS-XR PCE function
Segment Routing Commands
 Segment Routing Commands address ipv4 (PCE), page 4 adjacency-sid, page 5 apply-weight ecmp-only bandwidth, page 7 attribute-set, page 8 autoroute announce, page 10 autoroute destination, page 12 clear
Segment Routing Commands address ipv4 (PCE), page 4 adjacency-sid, page 5 apply-weight ecmp-only bandwidth, page 7 attribute-set, page 8 autoroute announce, page 10 autoroute destination, page 12 clear
Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x
 Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x First Published: 2015-09-01 Last Modified: 2016-11-21 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x First Published: 2015-09-01 Last Modified: 2016-11-21 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
Configure Segment Routing for IS-IS Protocol
 Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 2 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco NCS 5500 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x
 Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco NCS 5500 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x First Published: 2016-11-01 Last Modified: 2017-05-25 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
Segment Routing Configuration Guide for Cisco NCS 5500 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.1.x First Published: 2016-11-01 Last Modified: 2017-05-25 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN
 Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
Configure SR-TE Policies
 This module provides information about segment routing for traffic engineering (SR-TE) policies, how to configure SR-TE policies, and how to steer traffic into an SR-TE policy. About SR-TE Policies, page
This module provides information about segment routing for traffic engineering (SR-TE) policies, how to configure SR-TE policies, and how to steer traffic into an SR-TE policy. About SR-TE Policies, page
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 1 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Introduction to Segment Routing Santiago Álvarez, Distinguished Technical Marketing Engineer BRKRST-2124
 Introduction to Segment Routing Santiago Álvarez, Distinguished Technical Marketing Engineer BRKRST-2124 Agenda Technology Overview Use Cases A Closer Look to Control and Data Plane Traffic Protection
Introduction to Segment Routing Santiago Álvarez, Distinguished Technical Marketing Engineer BRKRST-2124 Agenda Technology Overview Use Cases A Closer Look to Control and Data Plane Traffic Protection
Configure Segment Routing for BGP
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free inter-domain routing between autonomous systems. An autonomous system is a set of routers under a
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free inter-domain routing between autonomous systems. An autonomous system is a set of routers under a
Segment Routing MPLS OAM Support
 Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Introduction to Segment Routing
 Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Segment Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.7.x
 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Segment Routing Configuration Guide
 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Overview In a nutshell Motivations Introduction
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Overview In a nutshell Motivations Introduction
OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict SPF
 The OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict Shortest Path First (SPF) feature provides information about the strict SPF segment identifiers (SIDs). Restrictions for, on page 1 Information About, on page 1 Enabling
The OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict Shortest Path First (SPF) feature provides information about the strict SPF segment identifiers (SIDs). Restrictions for, on page 1 Information About, on page 1 Enabling
Introduction to MPLS APNIC
 Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Segment Routing With IS-IS v4 Node SID
 This chapter describes how Segment Routing (SR) works with IS-IS. Restrictions for, page 1 Information About Segment Routing IS-IS v4 Node SID, page 1 How to Configure Segment Routing IS-IS v4 Node SID,
This chapter describes how Segment Routing (SR) works with IS-IS. Restrictions for, page 1 Information About Segment Routing IS-IS v4 Node SID, page 1 How to Configure Segment Routing IS-IS v4 Node SID,
Dynamic PCC. Information About Dynamic PCC. Path Computation Element Protocol Functions
 The Stateful Path Computation Element Protocol(PCEP) enables a router to report and optionally delegate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) which is established using either Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
The Stateful Path Computation Element Protocol(PCEP) enables a router to report and optionally delegate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) which is established using either Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
Segment Routing MPLS data plane. Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen
 Segment Routing MPLS data plane Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen Segment Routing MPLS data plane Segment Routing leverages existing MPLS data plane How to verify Segment Routing MPLS forwarding 2 Segment
Segment Routing MPLS data plane Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen Segment Routing MPLS data plane Segment Routing leverages existing MPLS data plane How to verify Segment Routing MPLS forwarding 2 Segment
Using Segment Routing OAM
 Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
MPLS Ping and Traceroute for BGP and IGP Prefix-SID
 MPLS Ping and Traceroute for BGP and IGP Prefix-SID MPLS Ping and Traceroute operations for Prefix SID are supported for various BGP and IGP scenarios, for example: Within an IS-IS level or OSPF area Across
MPLS Ping and Traceroute for BGP and IGP Prefix-SID MPLS Ping and Traceroute operations for Prefix SID are supported for various BGP and IGP scenarios, for example: Within an IS-IS level or OSPF area Across
MENOG 18. Segment Routing. Vahid Tavajjohi. From HAMIM Corporation
 Segment Routing MENOG 18 Rasoul Mesghali Vahid Tavajjohi CCIE#34938 From HAMIM Corporation 1 Agenda Introduction Technology Overview Use Cases Closer look at the Control and Data Plane Traffic Protection
Segment Routing MENOG 18 Rasoul Mesghali Vahid Tavajjohi CCIE#34938 From HAMIM Corporation 1 Agenda Introduction Technology Overview Use Cases Closer look at the Control and Data Plane Traffic Protection
MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates
 MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:
![Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision: Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:](/thumbs/79/79964001.jpg) Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Overview In a nutshell Introduction to
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Overview In a nutshell Introduction to
Segment Routing SR/LDP interworking. Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen
 Segment Routing SR/ interworking Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen Segment Routing SR/ interworking Simple, automatic and seamless interworking with Role of Mapping Server Data plane interworking functionality
Segment Routing SR/ interworking Clarence Filsfils Kris Michielsen Segment Routing SR/ interworking Simple, automatic and seamless interworking with Role of Mapping Server Data plane interworking functionality
MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering Support for Static Pseudowires
 MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering Support for Static Pseudowires The MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering: Support for Static Pseudowires feature allows you to configure a point-to-multipoint
MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering Support for Static Pseudowires The MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering: Support for Static Pseudowires feature allows you to configure a point-to-multipoint
SR-TE On Demand LSP. The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the
 The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the destination. The static route is mapped to an explicit path and that will trigger an on demand
The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the destination. The static route is mapped to an explicit path and that will trigger an on demand
CONTENTS. Introduction
 CONTENTS Introduction MP-1 Multiprotocol Label Switching Commands MP-3 address-family MP-4 affinity (LSP Attributes) MP-6 append-after MP-8 auto-bw (LSP Attributes) MP-9 bandwidth (LSP Attributes) MP-11
CONTENTS Introduction MP-1 Multiprotocol Label Switching Commands MP-3 address-family MP-4 affinity (LSP Attributes) MP-6 append-after MP-8 auto-bw (LSP Attributes) MP-9 bandwidth (LSP Attributes) MP-11
Configure Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA)
 Configure Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) uses segment routing to provide link protection in topologies where other fast reroute techniques
Configure Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) uses segment routing to provide link protection in topologies where other fast reroute techniques
A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial. R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017
 A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017 AKA: SPRING IETF Standardization Source Packet Routing In Networking (SPRING) WG ISIS, OSPF, IDR and MPLS WGs What is SR? A tunneling technology
A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017 AKA: SPRING IETF Standardization Source Packet Routing In Networking (SPRING) WG ISIS, OSPF, IDR and MPLS WGs What is SR? A tunneling technology
Segment Routing MPLS OAM Support
 Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
BGP Link-State. Finding Feature Information. Overview of Link-State Information in BGP
 (LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
(LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
IOS-XR EVPN Distributed Anycast IRB Gateway, L2/L3VPN Service with MPLS Data Plane
 IOS-XR EVPN Distributed Anycast IRB Gateway, L2/L3VPN Service with MPLS Data Plane Table of Content: 1. Overview... 2 2. Transport... 3 3. Services EVPN IRB L2/l3VPN Multipoint... 4 3.1. VRF/IRB Configuration...
IOS-XR EVPN Distributed Anycast IRB Gateway, L2/L3VPN Service with MPLS Data Plane Table of Content: 1. Overview... 2 2. Transport... 3 3. Services EVPN IRB L2/l3VPN Multipoint... 4 3.1. VRF/IRB Configuration...
Segment Routing On Demand for L2VPN/VPWS
 On-Demand Next Hop (ODN) for Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) creates a segment routing (SR) traffic-engineering (TE) auto-tunnel and uses the auto-tunnel for pseudowire dataplane. Restrictions
On-Demand Next Hop (ODN) for Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) creates a segment routing (SR) traffic-engineering (TE) auto-tunnel and uses the auto-tunnel for pseudowire dataplane. Restrictions
Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS
 CHAPTER 43 Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Cisco ME 3800X and ME 3600X
CHAPTER 43 Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Cisco ME 3800X and ME 3600X
Bit Indexed Explicit Replication A Stateless Multicast Architecture. Nagendra Kumar Nainar NANOG72
 Bit Indexed Explicit Replication A Stateless Multicast Architecture Nagendra Kumar Nainar NANOG72 Agenda Multicast Architecture Challenges Introduction to BIER BIER Control plane behavior BIER Data plane
Bit Indexed Explicit Replication A Stateless Multicast Architecture Nagendra Kumar Nainar NANOG72 Agenda Multicast Architecture Challenges Introduction to BIER BIER Control plane behavior BIER Data plane
Configure Segment Routing Mapping Server
 The mapping server is a key component of the interworking between LDP and segment routing. It enables SR-capable nodes to interwork with LDP nodes. The mapping server advertises Prefix-to-SID mappings
The mapping server is a key component of the interworking between LDP and segment routing. It enables SR-capable nodes to interwork with LDP nodes. The mapping server advertises Prefix-to-SID mappings
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN
 Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Next Generation MULTICAST In-band Signaling (VRF MLDP: Profile 6)
 Next Generation MULTICAST In-band Signaling (VRF MLDP: Profile 6) Contents Introduction Background Information MLDP Signaling In-Band Signaling Overlay or Out-Of-Band Signaling Label Distribution Protocol
Next Generation MULTICAST In-band Signaling (VRF MLDP: Profile 6) Contents Introduction Background Information MLDP Signaling In-Band Signaling Overlay or Out-Of-Band Signaling Label Distribution Protocol
Introduction to Segment Routing
 Introduction to Segment Routing Michael Kowal, Vertical Solutions Architect @ciscomk Abstract Introduction to Segment Routing This session provides an overview of the segment routing technology and its
Introduction to Segment Routing Michael Kowal, Vertical Solutions Architect @ciscomk Abstract Introduction to Segment Routing This session provides an overview of the segment routing technology and its
Troubleshooting End-to-End MPLS
 Troubleshooting End-to-End MPLS Vinit Jain - CCIE# 22854 Twitter - @vinugenie BRKMPL-3124 Coming this year BRKMPL-3124 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 3 Agenda Fundamentals
Troubleshooting End-to-End MPLS Vinit Jain - CCIE# 22854 Twitter - @vinugenie BRKMPL-3124 Coming this year BRKMPL-3124 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 3 Agenda Fundamentals
Introduction to Segment Routing
 BRKRST-2124 Introduction to Segment Routing Alberto Donzelli, Solution Architect Service Provider Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1. Find this
BRKRST-2124 Introduction to Segment Routing Alberto Donzelli, Solution Architect Service Provider Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1. Find this
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
MPLS LDP. Agenda. LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 9/27/16. Nurul Islam Roman
 MPLS LDP Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) 1 Agenda LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 1 Label Distribution Protocol Overview MPLS nodes need to exchange label information
MPLS LDP Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) 1 Agenda LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 1 Label Distribution Protocol Overview MPLS nodes need to exchange label information
MPLS Forwarding Commands
 Note All commands applicable for the Cisco NCS 5500 Series Router are also supported on the Cisco NCS 540 Series Router that is introduced from Cisco IOS XR 6.3.2. References to earlier releases in Command
Note All commands applicable for the Cisco NCS 5500 Series Router are also supported on the Cisco NCS 540 Series Router that is introduced from Cisco IOS XR 6.3.2. References to earlier releases in Command
MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone TEST. 26 April 2016 AN. Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC PBB-TE VPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS GMPLS SR RSVP-TE OSPF-TE PCEP
 Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
ECMP Load Balancing. MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) 1
 Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 Overview of MPLS TE 3 Why MPLS Traffic Engineering? Handling
Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 Overview of MPLS TE 3 Why MPLS Traffic Engineering? Handling
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS
 CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
MVPN: Inter-AS Option B
 MVPN: Inter-AS Option B In This Chapter This section provides information about MVPN: Inter-AS Option B configurations. Topics in this section include: Applicability on page 802 Overview on page 803 Configuration
MVPN: Inter-AS Option B In This Chapter This section provides information about MVPN: Inter-AS Option B configurations. Topics in this section include: Applicability on page 802 Overview on page 803 Configuration
CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook. Copyright Information. Copyright Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2012 Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All
Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2012 Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
MPLS Forwarding Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software
 MPLS Forwarding Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software This chapter describes the commands that you will use to configure and use Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) forwarding. For detailed information about
MPLS Forwarding Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software This chapter describes the commands that you will use to configure and use Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) forwarding. For detailed information about
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Segment Routing. Clarence Filsfils Distinguished Engineer
 Segment Routing Clarence Filsfils Distinguished Engineer cf@cisco.com Segment Routing Unified DC + WAN + Aggregation from server in the DC, through WAN and to the service edge Policy-aware DC: disjoint
Segment Routing Clarence Filsfils Distinguished Engineer cf@cisco.com Segment Routing Unified DC + WAN + Aggregation from server in the DC, through WAN and to the service edge Policy-aware DC: disjoint
Segment Routing On Demand SR Next Hop. Bertrand Duvivier Principal Engineer CKN, March 29 th 2016
 Segment Routing On Demand SR Next Hop Bertrand Duvivier Principal Engineer CKN, March 29 th 2016 (from next slide) 2 Network Bandwidth demand in SP s Network demand double every 18 months Compute demand
Segment Routing On Demand SR Next Hop Bertrand Duvivier Principal Engineer CKN, March 29 th 2016 (from next slide) 2 Network Bandwidth demand in SP s Network demand double every 18 months Compute demand
AS 100 AS 300. Lab -1 Private Communities - II .1 S1/2. Task 1. On R1: / / /24. Configure the above topology.
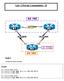 Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network
 Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Advanced Topics and Future Directions in MPLS
 Toronto, Canada May 30, 2013 Advanced Topics and Future Directions in MPLS Matt Gillies Customer Solutions Architect 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Connect 1 Agenda IETF
Toronto, Canada May 30, 2013 Advanced Topics and Future Directions in MPLS Matt Gillies Customer Solutions Architect 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Connect 1 Agenda IETF
What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following:
 What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following: What static MPLS labels are and how they can be used The difference between static MPLS bindings and
What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following: What static MPLS labels are and how they can be used The difference between static MPLS bindings and
Segment Routing on Cisco Nexus 9500, 9300, 9200, 3200, and 3100 Platform Switches
 White Paper Segment Routing on Cisco Nexus 9500, 9300, 9200, 3200, and 3100 Platform Switches Authors Ambrish Mehta, Cisco Systems Inc. Haider Salman, Cisco Systems Inc. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates.
White Paper Segment Routing on Cisco Nexus 9500, 9300, 9200, 3200, and 3100 Platform Switches Authors Ambrish Mehta, Cisco Systems Inc. Haider Salman, Cisco Systems Inc. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates.
Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote
 Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote Table of contents Executive Summary....................................................................2 Overview of Segment Routing..............................................................2
Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote Table of contents Executive Summary....................................................................2 Overview of Segment Routing..............................................................2
Implementing DCI VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway
 This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
Configuring MLPPP. Finding Feature Information
 The Multilink Point-to-Point (MLPPP) feature provides load balancing functionality over multiple WAN links, while providing multivendor interoperability, packet fragmentation and proper sequencing, and
The Multilink Point-to-Point (MLPPP) feature provides load balancing functionality over multiple WAN links, while providing multivendor interoperability, packet fragmentation and proper sequencing, and
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Contents. BGP commands 1
 Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Cisco. Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM)
 Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies For OSPFv3
 Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies For OSPFv3
 Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Signaling Methods and Object Association for Flex LSPs
 Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
MPLS LSP Ping, Traceroute, and AToM VCCV
 As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate MPLS
As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate MPLS
IPv6 Routing Protocols Update
 IPv6 Routing Protocols Update Wim Verrydt Solutions Architect BRKRST-2022 Abstract and Pre-requisite The proposed session provides a comprehensive overview of the main IPv6 routing protocols: IS-IS, OSPFv3,
IPv6 Routing Protocols Update Wim Verrydt Solutions Architect BRKRST-2022 Abstract and Pre-requisite The proposed session provides a comprehensive overview of the main IPv6 routing protocols: IS-IS, OSPFv3,
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection Contents Introduction Background Information Network Diagram Theory IOS-XR Implementation Configure Configuration Example MPLS Traffic-Engineering
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection Contents Introduction Background Information Network Diagram Theory IOS-XR Implementation Configure Configuration Example MPLS Traffic-Engineering
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF
 LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
Implementing MPLS Label Distribution Protocol
 , on page 1 Prerequisites for, on page 2 Overview of Label Distribution Protocol, on page 2 Label Distribution Protocol Discovery Parameters, on page 2 Enable Label Distribution Protocol Over an Interface,
, on page 1 Prerequisites for, on page 2 Overview of Label Distribution Protocol, on page 2 Label Distribution Protocol Discovery Parameters, on page 2 Enable Label Distribution Protocol Over an Interface,
IPv6 Routing: IS-IS Support for IPv6
 This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that advertises link-state information throughout
This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that advertises link-state information throughout
Implementing MPLS Label Distribution Protocol
 The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-based solution driven by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that was devised to convert the Internet and IP backbones from best-effort networks
The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-based solution driven by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that was devised to convert the Internet and IP backbones from best-effort networks
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA 4A Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching
 Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
 A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Signaling Methods and Object Association for Flex LSPs
 Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV
 MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
High Availability for 2547 VPN Service
 Fast Service Restoration High Availability for 2547 VPN Service Emil Gągała JNCIE PLNOG, Kraków, 21.10.2012 ACKLOWLEDGEMENTS Many thanks to Yakov Rekhter, Hannes Gredler for their contributions to the
Fast Service Restoration High Availability for 2547 VPN Service Emil Gągała JNCIE PLNOG, Kraków, 21.10.2012 ACKLOWLEDGEMENTS Many thanks to Yakov Rekhter, Hannes Gredler for their contributions to the
MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute
 MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute The MPLS Traffic Engineering: BFD-triggered Fast Reroute feature allows you to obtain link and node protection by using the Bidirectional Forwarding
MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute The MPLS Traffic Engineering: BFD-triggered Fast Reroute feature allows you to obtain link and node protection by using the Bidirectional Forwarding
Implementing IS-IS for IPv6
 Implementing IS-IS for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol
Implementing IS-IS for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol
IS-IS IPv6 Administrative Tag
 The feature allows you to assign a tag to IPv6 prefixes that you can use to apply administrative policies with a route map. For example, you can control routes redistributed between area and domain boundaries
The feature allows you to assign a tag to IPv6 prefixes that you can use to apply administrative policies with a route map. For example, you can control routes redistributed between area and domain boundaries
MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE
 MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE Last Updated: November 22, 2011 The MPLS Traffic Engineering: Inter-AS TE feature provides Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) node protection, loose path reoptimization,
MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE Last Updated: November 22, 2011 The MPLS Traffic Engineering: Inter-AS TE feature provides Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) node protection, loose path reoptimization,
