ROUTING TECHNIQUES ON INTERVEHICULAR COMMMMUNICATION SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Kathleen Cook
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROUTING TECHNIQUES ON INTERVEHICULAR COMMMMUNICATION SYSTEM Smita Rani Sahu 1, Uriti Archana 2 1,2 Computer Science & Engineering Department, Sri Venkateswara college of Engineering & Technology, (India) ABSTRACT In past few years, VANET (Vehicular Ad-hoc Network) has become a remarkable area for research analysis and development. VANET is a subgroup of MANET (Mobile Ad-hoc Network). VANET and MANET both are wireless networks which are characterized as self-configured and autonomous ad-hoc networks. VANETs differ from MANETs in terms of dynamic topology and high mobility. Due to unstable connectivity, high mobility and network partitioning, information routing in VANETs becomes difficult and challenging, thus creating a need for efficient VANET routing protocols. This work aims to develop and evaluate routing protocols which focus on vehicle to vehicle i.e. V2V communication. Keywords: Ad-hoc Network, MANET, VANET I. INTRODUCTION 1.1VANET Vehicular Ad hoc networks (VANETs) are a special type of mobile ad hoc networks; where vehicles are simulated as mobile nodes. VANET contains two entities: access points and vehicles, the access points are fixed and usually connected to the internet, and they could participate as a distribution point for vehicles. VANET addresses the wireless communication between vehicles (V2V), and between vehicles and infrastructure access point (V2I). Vehicle to vehicle communication (V2V) has two types of communication: one hop communication (direct vehicle to vehicle communication), and multi hop communication (vehicle relies on other vehicles to retransmit) [1]. VANET implements intelligent transportation system (ITS) and aims to optimize traffic flow, improve road safety and reduce congestion. The communication depends on routing. The sporadic connectivity and sudden changes in network topology are the characteristics of VANET that make routing a challenging task. This paper gives a brief overview of routing protocols in VANET, their issues which are under research. VANET also has special characteristics that distinguish it from other mobile ad hoc networks; the most important characteristics are: high mobility, self-organization, distributed communication, road pattern restrictions, and no restrictions of network size, all these characteristics made VANETs environment a challenging for developing efficient routing protocols. Recent improvements in mobile ad-hoc network 485 P a g e
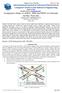
2 (MANET) technology and ever-increasing safety requirements as well as consumer interest in Internet access have made VANETs an important research topic. Vehicle to vehicle and vehicle to roadside communications have become important components of vehicle infrastructure integration. Most of the VANET research has focused on urban and suburban roadway conditions, where the numbers of vehicles are large, the inter-vehicle spacing is small, terrain is not a significant factor and fixed communication infrastructure is available. In rural and sparse areas, the conditions and constraints are significantly different. Node densities are low, inter-vehicle spacing can be large, terrain effects may be significant and there is very little or no fixed communication infrastructure available. Vehicular ad-hoc networks are responsible for the communication between moving vehicles in a certain environment. A vehicle can communicate with another vehicle directly which is called Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) communication, or a vehicle can communicate to an infrastructure such as a Road Side Unit (RSU), known as Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I). Figure 1 shows a typical VANET scenario. Fig 1. Ad-hoc Network using Vehicles (VANETs) [1] VANET is a subclass of mobile ad-hoc networks (MANETs). It is a self-organizing network without any physical infrastructure. VANET allows the fast moving vehicles to exchange real-time information that can assist the drivers to avoid any situation like-accidents, traffic jams, etc. With the rapid increase in the vehicular traffic on roads, the corresponding increase in accidents created a security issue that drew the attention of 486 P a g e
3 researchers towards VANET. Dedicated short range communication (DSRC) facilitates the wireless communication in VANET. DSRC is IEEE p standard and is a MAC protocol operating at 5.9 GHz [2]. IEEE has standardized the whole communication stack that is referred to as wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE). VANET provides a wide variety of applications for both safety and non-safety purposes. The major application of VANET is ITS [3]. In addition several value added services such as enhanced navigation; automated toll payment, internet access, and location based services are also provided. In VANET, each vehicle is equipped with devices that allow it to send, receive and exchange information with other vehicles or road side units.[4] Facilitating communication among the vehicles and developing an efficient routing protocol in VANET is a challenging task due to the following reasons: signal fading due to the presence of obstacles (buildings etc.), bandwidth constraints, high mobility of the vehicles and the speed depends on the traffic signs and signals. High mobility results in frequent fragmentation in the network [5]. 1.2 Importance of Routing in VANET Wireless communication, particularly real-time communication is highly unreliable. In addition, VANET has certain unique issues that make it different from other wireless networks. Because no central coordination can be assumed, a sole shared control channel is required at the MAC layer (the so-called one channel paradigm). Mobility movements of vehicular networks are also very specific, e.g. vehicles move along the roads, in predefined directions, and this requires new specific mobility models to be devised. Normal mobility models could not address the requirements of VANET. Moreover, now a day s cars are having very high mobility rates and so change the topology in an in-deterministic fashion that makes wireless transmission very challenging. The applications of vehicular networks should also fulfil a number of non-functional requirements, such as potentially very high reliability, but also security to ensure that safety-critical applications cannot be tempered with. Vehicles range over very large geographical areas (cities or countries), and therefore require potentially large-scale networks, and especially a very extensive deployment of equipment if infrastructure-based networks are used. Many VANET applications have either delay constraints or other QoS requirements. Efficient broadcasting of safety messages for getting full coverage and low latency to provide QoS and reliability in VANET routing is still a challenging problem[6]. Since mobility of VANETs cannot be captured by general mobility models. Traffic flow (both in time and space) need to be studied and integrated in the design of reliable and high-performance mobility models. Cooperation among inter-vehicular networks and sensor networks placed within the vehicles or along the road need to be further investigated and analyzed. As the number of vehicles grows the trust between them should also be maintained for the smooth communication. In addition to technical challenges, socio-economic challenges have to be solved. The benefits of V2V communication only become significant when there are a sufficiently large number of vehicles using the technology. Vehicular applications must therefore be able to operate and be useful despite initial low penetration. 487 P a g e
4 II. LITERATURE SURVEY Routing is a process of sending data packets from source node to destination node, therefore routing in ad-hoc networks is a critical issue. There are a number of routing protocols existing in various networks; this paper focuses on the routing protocols of VANETs between vehicle to vehicle communication, the routing protocol classification and the related research open issues in VANET routing. III.ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET In V2V communication, each vehicle is designed by using sensors, network devices, Global positioning System (GPS), computing devices and digital map which has the road segment information. The communication between V2V can be either unicast or multicast packet forwarding techniques from source vehicle to destination vehicles. The routing protocols of VANET can be classified into five categories: 1) Topology based Routing Protocol 2) Position based Routing Protocol 3) Cluster based Routing Protocol 4) Geocast based Routing Protocol 5) Broadcast based Routing Protocol 1 ) Topology Based Routing Protocol Topology based routing protocol use the link information that is available in the existing networks to perform packet forwarding [7]. This protocol is further classified into three main protocols. a)proactive Routing Protocols/Table-Driven routing protocol : Proactive routing protocol will store and maintain the routing information about the paths that are currently in use and also not in use [8].The main advantage is that the packets are transmitted constantly among the nodes therefore no discovery of route is required since they maintain the route information at the background. The main disadvantage is that it also maintains unused path information that will occupy the significant part of available bandwidth and causes reduction of bandwidth in the network topology. b)routing Protocol/On-Demand routing protocol : The routes are discovered to the destinations on-demand [9]. The routing table is maintained only for the routes that are used currently which reduces the traffic in the network. This protocol consumes less bandwidth when compared to proactive routing protocol but it takes more time to discover a route that results delay in the network. The disadvantage is that, though the routing table is maintained with currently used routes, due to changes in the network topology it will result in significant 488 P a g e
5 amount of network traffic. This will also result in loss of packets to the destination. Another disadvantage is dislocation of communication nodes in the network due to excessive flooding. c)hybrid Routing Protocol/Zone Routing Protocol: In this routing protocol, the characteristics of both Proactive and Reactive Routing protocol is combined to make the routing process more efficient and scalable [10].This protocol is to overcome the drawbacks of Proactive and Reactive routing protocols and also it solves on-demand routing by using limited number of routes. The network overhead caused by Proactive routing and network delay caused by Reacting routing are reduced by discovering the routes efficiently. The main drawback is that, this protocol cannot withstand in some environment like VANET where the node s behaviour is highly dynamic and changes rapidly. 2) Position Based Routing Protocol By using the property of geographic positioning information like GPS, the position based protocol will selectthe next forwarding hops. Therefore it is not necessary to create and maintain routing table or to exchange routing information with neighbour nodes. The disadvantage of position based routing protocol is, it requires position determining services. The position based routing protocol is broadly classified into the following protocols. a) Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR): Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing [11], each node finds the neighbouring nodes by using beacon signal or HELLO messages and the position of the destination with the use of location service. In GPSR, each node should be capable of finding its current position..the advantage of GPSR is the packet forwarding decision is made dynamically and a node needs to know only one hop neighbour location to forward the packet. The disadvantage is destination node will send the information through packet header of intermediate node but it is not updated in the routing table of that node. b)greedy Perimeter Coordinator Routing (GPCR): Greedy Perimeter Coordinator Routing will forward packets to the path that are selected previously by using greedy algorithms [12].in this protocol, the decisions are made at the junction in the road that helps to communicate by providing more number of alternate paths. The advantage is it does not require any global or external information like static maps. The disadvantage is since this protocol uses junction nodes, the first approach will fail on curve road and the second approach will fail on sparse road. c) Connectivity-Aware Routing (CAR): CAR is designed by combining the characteristics of both Geographic routing and Ad-hoc routing protocols [13]. In this protocol, path discovery is done by using AODV and data dissemination is done by using PGB. CAR follows four main phases like path discovery, data forwarding, guard concept and error recovery. The advantage of Connectivity-Aware Routing is it does not require any digital maps and no local maximum problem. The disadvantage will be selecting unnecessary node as head node and when there is any changes in the network traffic due to environment problems, it is very difficult to adapt with the sub-paths. 489 P a g e
6 d)geographic Source Routing (GSR): GSR protocol consists of topological knowledge with the combination of position-based routing protocol. Like GPCR [14], the shortest path is preselected by using Greedy forwarding algorithm and the same path is calculated with the help of Dijkstra algorithm. The advantage of this GSR protocol, exceeds them in packet delivery ratio and average delay time. The disadvantage is it fails to have enough packets for forwarding, when there is low traffic density in sparse network. e) Anchor-Based Street and Traffic Aware Routing (A-STAR): A-STAR [15] is designed for the purpose of inter vehicle communication system especially for city environment. For an end-to-end communication, high connectivity in packet delivery is assured with the help of city bus traffic information. This is the advantage of this routing protocol even in low traffic density. The disadvantage of A-STAR will be connectivity problem for finding a path from source to destination. 3) Cluster Based Routing Protocol In Cluster Based Routing, a Cluster is made with group of nodes or vehicles. Every cluster has one Cluster head which will be responsible for all inter-cluster and intra cluster communication. Each node in the cluster will describe them as a part of the cluster. There are different types of Cluster based routing protocol. a)hierarchical Cluster Based Routing (HCB): The HCB routing protocol is designed for MANET with the help of clustering techniques [16]. HCB have two layers communication architecture. In Layer I, the nodes will communicate with each other through multihop path and they have single radio interface whereas in Layer II, the nodes will communicate with each other through base station. Due to large number of packet loss, the number of retransmission is high. b) Cluster-Based Directional Routing Protocol (CBDRP): This protocol [17] is designed especially for the vehicles that will move in same direction. Here, the source node will forward its packet to the cluster head and it is transmitted in the same cluster by cluster head. The advantage of this protocol is reliability and rapid data transfer. It also solves link stability problem. The disadvantage is that the number of retransmission is high and it has average control packet overhead. c)cluster Based Location Routing (CBLR): Though CBLR protocol is cluster based protocol, it also possess the properties of Reactive and On- Demand routing protocols [18]. Every cluster head maintains a routing table which has the information like address and location of each cluster members. The main advantage is CBLR protocol will suit for all high mobility networks and it makes use of digital maps. Here, it has low control packet overhead. Like CBDRP, it has the disadvantage of large number of retransmission. d)cluster Based Routing (CBR): CBR protocol is based on position and cluster protocols in which the geographic area is divided into square grids [19]. That geographic information will help to forward data packets 490 P a g e
7 from every node to its neighbour node. The CBR will not find route discovery is an advantage of this protocol which results in less routing overhead. The important parameters like velocity and direction is not considered in CBR protocol is the main disadvantage. e)location Routing Algorithm with Cluster-Based Flooding (LORA-CBF): This protocol is similar to greedy routing protocol. The information about each and every node is maintained by the cluster head [20]. It has the advantage of packet forwarding technique. The disadvantage is it results in heterogeneous performance. 4) Broadcast Based Routing Protocol Broadcast routing protocol is used in VANET to broadcast the information for maximum number of nodes when an unexpected event like accident, traffic jam occurs. When these packets are broadcast into the network it leads to collision, utilization of high bandwidth consumption, and reduce the overall performance. This Broadcast routing protocol is suitable for smaller network where less number of nodes are connected. There is large number of broadcasting protocols available and they are as follows: a)broadcomm: BROADCOMM [21] is designed specifically for highway network and this protocol is mainly based on hierarchical structure. The advantage is it has better outperformance for a highway network that has less number of nodes. The only disadvantage is the position information is entirely based on cell formations. b)edge-aware Epidemic Protocol (EAEP): The main function of this EAEP is to transmit messages over all the vehicles [22]. This special kind of protocol will allow each vehicle to possess its own geographical position. The advantage of EAEP is, it will overcome even simple flooding problem and by rejecting hello packets, this protocol will decrease control packet overhead. The main disadvantage is it results in large number of data transmission with high delay and also the issues that caused by intermittent connectivity is not handled in this protocol. c) Secure Ring Broadcasting (SRB): Based on the receiving power, the secure Ring Broadcasting divides the nodes into three groups such as Inner node, Outer node and Secure Ring nodes [23].The advantage of SRB is by reducing number of retransmission messages, more stable routes are gained. The disadvantage is it has more control packet overhead. d) Preferred Group Broadcast: This protocol is specially designed to prevent the problem that is caused due to broadcast storm from transmitting route request [24]. It has the advantage of decreasing RREQ broadcasting. This PGB protocol is not a reliable broadcasting protocol. e)urban Multihop Broadcasting (UMB): During message transmission in multi hop broadcasting it will come across lot of problems like Collision and hidden node problem, this UMB protocol is designed to overcome this 491 P a g e
8 issues [25]. The advantages are the performance is good in case of high packet loads and vehicle traffic density. It also solves collision and hidden node problems. The only disadvantage is this protocol has unused bandwidth. 5) Geocast Based Routing Protocol The message will be sent to all vehicles in the predefined geographical area since this protocol depends on location based multicast routing protocol. The Zone of Relevance or ZOR is the place selected for the purpose of transmission. This protocol has different routing protocols as follows: a) Inter-Vehicle Geocast (IVG): When the vehicles are moving on highways [26], this protocol will broadcast messages to those vehicles. b) Robust Vehicular Routing (ROVER): The ROVER protocol is especially designed for sending messages to all the vehicles that are present in a specific Zone of relevance [27]. The advantage is it depends on geographical multicast protocol. Due to redundant message, the data transfer will result in more delay is the main disadvantage of ROVER. Another disadvantage is it has more number of retransmissions and control packet overhead. c)dynamic Time-Stable Geocast Routing (DTSG): The DTSG protocol is used for sparse density networks and it is designed with two phases [28].The advantage of this protocol helps to align the network density and speed of the vehicles dynamically that result in better performance. IV.CHALLENGES IN DESIGNING OF PROTOCOLS IN VANET Various issues and challenges are defined as follows: (a) Quality of Service (QoS): Provision of certain quality of service levels in VANET is an important task. A network with minimum delay for data delivery, less retransmissions, and high connectivity time can provide certain QoS guaranteed to the users. Promising this kind of QoS with different user applications and dynamic network environment is an interesting and challenging task in VANET design. (b) Efficient Routing Algorithms Design: In order to timely and properly sending data packets from one node to another node an efficient routing algorithm is required. In VANET, efficient routing algorithm means a routing scheme with minimum delay, maximum system capacity and less computational complexity. Design such an algorithm which can be implemented in multiple topologies of the network and satisfies all of the above mentioned properties is an active area of research in VANET. (c) Scalability and Robustness: Designing a scalable and robust network remains an open area of research in VANET because of its challenging characteristics. Many design approaches fall short when VANETs transform 492 P a g e
9 from sparse to high dense mode, or from high mobility to slow traffic scenarios. A complete VANET framework that is scalable to different network scales and robust to the topological changes is required. This is an emerging area of research for VANET environment. (d) Co-operative Communication: A key challenge in VANET is establishing the communication among different nodes. Different concepts of co-operative communication from wireless network theory may not be directly applied to VANET. This co-operative communication, such as up to which extent nodes should exchange information among themselves, is one of the key research areas in the VANET design. (e) Security and confidentiality: Keeping a reasonable balance between the security and privacy is one of the main challenges in VANET; the receipt of trustworthy information from its source is important for the receiver. However, this trusted information can violate the privacy needs of the sender [29]. (f)connectivity: Owing to the high mobility and rapid changes of topology, which lead to a frequent fragmentation in networks, the time duration required to elongate the life of the link communication should be as long as possible. This task can be accomplished by increasing the transmission power; however, that may lead to throughput degradation. Accordingly, connectivity is considered to be an important issue in VANET. (g)signal fading and distortions: Objects placed as obstacles between two communicating vehicles are one of the challenges that can affect the efficiency of VANET; these obstacles can be other vehicles or buildings distributed along single road in the villages. Their impact is placed on preventing the signal from reaching its destination and increasing the fading in the transmitted signal. (h) Bandwidth limitations: Another key issue in the VANET is the absence of a central coordinator that controls the communications between nodes, and which has the responsibility of managing the bandwidth and contention operation. Therefore it is necessary to utilize the availability of bandwidth efficiently. There is a high probability that channel congestion can occur, Owing to the limited range of bandwidth frequency (10 20 MHz) for VANET applications, particularly in a rural environment. The fair use of bandwidth has its impact on reducing the time delay for disseminating messages; if a vehicle needs to send a message and finds there are no opportunities for transmission, it must wait for a time. V. PROBLEM STATEMENT Motivated by the need of routing protocols in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, the protocols used for routing techniques and keeping the research directions in view, it has been realized that there exists enough scope to improve the routing protocol. This work aims to analyse the routing protocols on Inter Vehicular Communication. 493 P a g e
10 VI. CONCLUSION In this work an attempt will be made to address the research issues in designing energy efficient routing protocols for VANETs i.e. vehicular ad hoc networks. A literature survey will be made on various protocols used for communication in VANET. The communication in VANET takes place in two different ways Vehicle- To-Vehicle (V2V) communication and Vehicle-To-Infrastructure (V2I) communication. The existing routing algorithms used for communication between vehicle to vehicle will be analyzed individually with their advantages and disadvantages. All these approaches tend to focus on V2V and require GPS. REFERENCES [1] Survey of Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks," Kevin C. Lee, Uichin Lee, Mario Gerla, Advances in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks: Developments and Challenges, IGI Global, Oct, Border Node-based Routing Protocols for VANETS in Sparse and Rural Areas, Zhang and Wolff: Auto net Workshop, IEEE Globe COM, Washington DC, November [2] Yousef-Awwad Daraghmi, Chih-Wei Yi, Forwarding Methods in Data Dissemination and Routing Protocols for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, IEEE Network [3] Fan Li, Yu Wang, Routing in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks: A Survey, IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine,2007 [4] M. Durresi, "Emergency broadcast protocol for intervehicle communications," [5] Amandeep Kaur, Issues and Challenges of Routing Protocols in VANET-Survey, National Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IEIT-2014), March [6] Routing Protocols for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks in Rural Areas, Zhang and Wolff IEEE Communications Magazine, November, 2008, pp [7] DongreManoj M, Bawane N G, JawadeNilima R, Routing Protocols for V2V communications used in Urban VANET to improve ITS, National Conference on Innovative Paradigms in Engineering & Technology (NCIPET-2012), International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA) 19. [8] Bernsen, J. Manivannan, D., Routing Protocols for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks That Ensure Quality of Service, In the fourth international conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications., pp.1-6, Aug [9] C. Lochert, H. Hartenstein, J. Tian, D. Herrmann, H. Füßler, and M. Mauve, A routing strategy for vehicular ad hoc networks in city environments, in Proceedings of IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2003), pp , June [10] Tarik Taleb,, EhssanSakhaee, Student Member,, Abbas Jamalipour, Kazuo Hashimoto, Nei Kato,, and Yoshiaki Nemoto, A Stable Routing Protocol to Support ITS Services in VANET Networks IEEE TRANSACTIONSON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 56, NO. 6, NOVEMBER [11] Karp, B. and Kung, H. T (2000), GPSR: greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks. In Mobile Computing and Networking, pages , P a g e
11 [12] Lochert, C., Mauve, M., F ussler, H., and Hartenstein, H., Geographic routing in city scenarios, SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput.Commun.Rev., vol. 9, no. 1, pp , 2005 [13] Naumov, V., Gross, T.R. (2007), "Connectivity-Aware Routing (CAR) in Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks," INFOCOM th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications.IEEE, vol., no., pp , 6-12 May, [14] Lochert, C., Hartenstein, H., Tian, J., Fussler, H., Hermann, D., Mauve, M. (2003), A routing strategy for vehicular ad-hoc networks in city environments, Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Proceedings. IEEE, vol., no., pp , 9-11 June [15] Seet, B.-C., Liu, G., Lee, B.-S., Foh, C. H., Wong, K. J., Lee, K.-K. (2004), A-STAR: A Mobile Ad Hoc Routing Strategy for Metropolis Vehicular Communications. NETWORKING 2004, [16] Yang Xia, Hierarchical Cluster Based Routing for Highly Mobile Heterogeneous MANET, [17] Tao Song, Wei Xia, Tiecheng Song, LianfengShen, A Cluster-Based Directional Routing Protocol in VANET, International Conference on Communication and Mobile Computing, [18] R. A. Santns, R. M. Edwards, A. Edwards and D. Belis, A novel cluster-based location routing algorithm for intervehicular communication, Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, IEEE proceedings of the 15th Annual Symposium, [19] Yuyi Luo, Wei Zhang, YangqingHu, A New Cluster Based Routing Protocol for VANET, IEEE Wireless Communications and Trusted Computing, [20] R. A. Santos, "Performance evaluation of routing protocols in vehicular ad hoc networks," [21] M. Durresi, "Emergency broadcast protocol for intervehicle communications," [22] M. Nekovee, B. BjamiBogason, Reliable and efficient information dissemination in intermittently connected vehicular ad hoc networks, IEEE the 65th VTC 07 spring, Dublin, Ireland, (2007). [23] V. Naumov, R. Baumann, and T. Gross, An evaluation of inter-vehicle ad hoc networks based on realistic vehicular traces, Proc. ACM the 7th ACM MohiHoc 06, Florence, Italy, May (2006). [24] G. Korkmaz, Urban multihop broadcast protocol for inter-vehicle communication systems. [25] A. Bachir, "A Multicast Protocol", in Ad hoc Networks Inter-Vehicle Geocast. April [26] M. Kihl, Reliable Geographical Multicast Routing in Vehicular Adhoc Networks, [27] HamidrezaRahbar, KshirasagarNaik, AmiyaNayak, DTSG: Dynamic Time-Stable Geocast Routing in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, [28] Routing Protocols for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks in Rural Areas, Zhang and Wolff IEEE Communications Magazine, November, 2008, pp [29] Rainer Baumann, Vehicular Ad hoc Networks, Master s Thesis in Computer Science, ETH Zurich (2004). 495 P a g e
Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 7, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol Stavan Karia
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 7, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol Stavan Karia
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads
 Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs)
 A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) Sarvesh Kr. Soni 1, B.P Chaurasia 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of CSE, KNIT- Sultanpur, U.P, India 2
A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) Sarvesh Kr. Soni 1, B.P Chaurasia 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of CSE, KNIT- Sultanpur, U.P, India 2
will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes.
 IJEEE, Vol. 1, Issue 4 (August, 2014) e-issn: 1694-2310 p-issn: 1694-2426 SURVEY OVER VANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR VEHICLE COMMUNICATION 1 Amanpreet Kaur, 2 Dr. Dinesh Arora 1,2 Gurukul Vidyapeeth Institute
IJEEE, Vol. 1, Issue 4 (August, 2014) e-issn: 1694-2310 p-issn: 1694-2426 SURVEY OVER VANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR VEHICLE COMMUNICATION 1 Amanpreet Kaur, 2 Dr. Dinesh Arora 1,2 Gurukul Vidyapeeth Institute
Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach
 Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach 1 Mr. Bhagirath Patel, 2 Ms. Khushbu Shah 1 Department of Computer engineering, 1 LJ Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad, India 1 er.bhagirath@gmail.com,
Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach 1 Mr. Bhagirath Patel, 2 Ms. Khushbu Shah 1 Department of Computer engineering, 1 LJ Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad, India 1 er.bhagirath@gmail.com,
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS
 130 CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS 5.1 INTRODUCTION The feasibility of direct and wireless multi-hop V2V communication based on WLAN technologies, and the importance of position based
130 CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS 5.1 INTRODUCTION The feasibility of direct and wireless multi-hop V2V communication based on WLAN technologies, and the importance of position based
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security
 The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2
 An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
Literature Review on Characteristic Analysis of Efficient and Reliable Broadcast in Vehicular Networks
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 205-210 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Literature Review
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 205-210 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Literature Review
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET
 Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET R. Nirmala 1, R. Sudha 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, K.S.R College of Arts & Science (Autonomous),
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET R. Nirmala 1, R. Sudha 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, K.S.R College of Arts & Science (Autonomous),
Keywords: Adhoc Network, Vehicular Adhoc Network, VANET, position-based routing protocols. I. INTRODUCTION
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com A Review: Position based Routing Protocols in VANET Rathod Kirit R 1st PhD Scholar, Rai University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com A Review: Position based Routing Protocols in VANET Rathod Kirit R 1st PhD Scholar, Rai University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Broadcasting Routing Protocols in VANET
 Broadcasting Routing Protocols in VANET Uma Nagaraj, Poonam Dhamal Pune University, Alandi, Pune India E-mail: umanagaraj67@gmail.com Abstract Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANET) is a subclass of Mobile
Broadcasting Routing Protocols in VANET Uma Nagaraj, Poonam Dhamal Pune University, Alandi, Pune India E-mail: umanagaraj67@gmail.com Abstract Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANET) is a subclass of Mobile
Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Raj K. Shrestha, Sangman Moh, Ilyong Chung, and Dongmin Choi Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chosun University 375 Seoseok-dong,
Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Raj K. Shrestha, Sangman Moh, Ilyong Chung, and Dongmin Choi Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chosun University 375 Seoseok-dong,
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET
 Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET K. Lakshmi 1, K.Thilagam 2, K. Rama 3, A.Jeevarathinam 4, S.Manju Priya 5. 1,3&4 Lecturer, Dept. of Computer Applications,
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET K. Lakshmi 1, K.Thilagam 2, K. Rama 3, A.Jeevarathinam 4, S.Manju Priya 5. 1,3&4 Lecturer, Dept. of Computer Applications,
ComparisonamongDifferentRoutingProtocolsofVehicularAdHocNetworks
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 17 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 17 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Overview of Challenges in VANET
 Overview of Challenges in VANET Er.Gurpreet Singh Department of Computer Science, Baba Farid College, Bathinda(Punjab), India ABSTRACT VANET are becoming active area of research and development because
Overview of Challenges in VANET Er.Gurpreet Singh Department of Computer Science, Baba Farid College, Bathinda(Punjab), India ABSTRACT VANET are becoming active area of research and development because
Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs)
 Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) 1 Overview of Ad hoc Network Communication between various devices makes it possible to provide unique and innovative services. Although this inter-device
Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) 1 Overview of Ad hoc Network Communication between various devices makes it possible to provide unique and innovative services. Although this inter-device
A Survey of Vehicular Ad hoc Networks Routing Protocols
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using p and g
 Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using 802.11p and 802.11g Rasha Kaiss Aswed and Mohammed Ahmed Abdala Network Engineering Department, College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University
Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using 802.11p and 802.11g Rasha Kaiss Aswed and Mohammed Ahmed Abdala Network Engineering Department, College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University
Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V2 PP 06-14 www.iosrjen.org Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V2 PP 06-14 www.iosrjen.org Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in
MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS. Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang
 Master's Programme in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang Embedded and Intelligent Systems,
Master's Programme in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang Embedded and Intelligent Systems,
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET Sanjay Batish, Manisha Chahal and Sanjeev Sofat CSE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India E-Mail: sbatish@pec.ac.in
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET Sanjay Batish, Manisha Chahal and Sanjeev Sofat CSE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India E-Mail: sbatish@pec.ac.in
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario
 Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS
 EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS Nandhini P. 1 and Ravi G. 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Communication Systems, Sona College of
EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS Nandhini P. 1 and Ravi G. 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Communication Systems, Sona College of
Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 09 March 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET S.Bavani V.Aiswariya
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 09 March 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET S.Bavani V.Aiswariya
Keywords VANET, Routing protocols, AODV, DSR, DSDV.
 Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network
 A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Arshdeep Kaur 1, Shilpa Sharma 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Arshdeep Kaur 1, Shilpa Sharma 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS
 GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS A.Robertsingh 1, Suganya A 2 1 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University, Krishnankoil, India 2 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University,
GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS A.Robertsingh 1, Suganya A 2 1 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University, Krishnankoil, India 2 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University,
Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET
 Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET Vinod Kumar*, Meenakshi Bansal Mtech Student YCOE,Talwandi Sabo(india), A.P. YCOE, Talwandi Sabo(india) Vinod_Sharma85@rediffmail.com,
Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET Vinod Kumar*, Meenakshi Bansal Mtech Student YCOE,Talwandi Sabo(india), A.P. YCOE, Talwandi Sabo(india) Vinod_Sharma85@rediffmail.com,
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development COMPARISON OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 2, February -2015 COMPARISON
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 2, February -2015 COMPARISON
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development. Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET Ravi Shrimali
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET Ravi Shrimali
A Review on Position Based Routing Protocol in Vehicular Adhoc Network
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2013 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-02, pp-07-13 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2013 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-02, pp-07-13 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access
Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation
 Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation Kashif Naseer Qureshi 1, Abdul Hanan Abdullah 1, Rohana Yusof 2 1 Faculty of Computing, Universiti
Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation Kashif Naseer Qureshi 1, Abdul Hanan Abdullah 1, Rohana Yusof 2 1 Faculty of Computing, Universiti
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 AN OVERVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF VARIOUS ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET PARUL GUPTA* *Dept. Of Computer Science, P.I.G.G.C.W. Jind (Haryan), India ABSTRACT Vehicular connectivity is most important for an Intelligent
AN OVERVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF VARIOUS ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET PARUL GUPTA* *Dept. Of Computer Science, P.I.G.G.C.W. Jind (Haryan), India ABSTRACT Vehicular connectivity is most important for an Intelligent
Efficient Working of Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network with Carry Forward Technique
 Efficient Working of Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network with Carry Forward Technique Govind Sood 1, Dr. Tanu Preet Singh 2 ergovind.sood333@gmail.com, tanupreet.singh@gmail.com Abstract Vehicular Ad-Hoc network
Efficient Working of Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network with Carry Forward Technique Govind Sood 1, Dr. Tanu Preet Singh 2 ergovind.sood333@gmail.com, tanupreet.singh@gmail.com Abstract Vehicular Ad-Hoc network
2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Performance Evaluation of Ad Hoc Networking Protocol with QoS (Quality of Service)
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 9, September ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2013 831 Performance Analysis of Reactive and Proactive Routing Protocols for Vehicular Adhoc Network Ms. Monika
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2013 831 Performance Analysis of Reactive and Proactive Routing Protocols for Vehicular Adhoc Network Ms. Monika
Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization
 Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization Dhanveer Kaur 1, Harwant Singh Arri 2 1 M.Tech, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization Dhanveer Kaur 1, Harwant Singh Arri 2 1 M.Tech, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model
 Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Research Topics: QoS in VANETs
 Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Research Topics: QoS in VANETs Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Research Topics: QoS in VANETs Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
Integrated Resource Adaptive On Demand Geographic Routing (IRA-ODGR) for MANET
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 6, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Integrated Demand (IRA-ODGR) for MANET M J.Kalaiselvi 1 K.Sathishkumar 2 1 M.E. Student,
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 6, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Integrated Demand (IRA-ODGR) for MANET M J.Kalaiselvi 1 K.Sathishkumar 2 1 M.E. Student,
Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets
 Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets Ms.Priyanka.G 1, Mr.Sundareswari.K 2 PG Scholar, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, Karpagam University,
Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets Ms.Priyanka.G 1, Mr.Sundareswari.K 2 PG Scholar, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, Karpagam University,
EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM
 EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM D.Yamini 1, J. Jayavel 2 1 III-M.tech(IT), Department of Information technology,
EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM D.Yamini 1, J. Jayavel 2 1 III-M.tech(IT), Department of Information technology,
EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet
 EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet Bency Wilson 1, Geethu Bastian 2, Vinitha Ann Regi 3, Arun Soman 4 Department of Information Technology, Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology, Rajagiri
EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet Bency Wilson 1, Geethu Bastian 2, Vinitha Ann Regi 3, Arun Soman 4 Department of Information Technology, Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology, Rajagiri
STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF VELOCITY ON END-TO- END DELAY FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN ITS
 STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF VELOCITY ON END-TO- END DELAY FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN ITS Prof. Bhagat Sunilkumar Madhusudan 1# Prof (Dr.) Wadhai V.M 2 1 Research Scholar (Amravati University), Dept. of Information
STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF VELOCITY ON END-TO- END DELAY FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN ITS Prof. Bhagat Sunilkumar Madhusudan 1# Prof (Dr.) Wadhai V.M 2 1 Research Scholar (Amravati University), Dept. of Information
Performance Analysis of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols For Vehicular Ad Hoc - Networks
 Performance Analysis of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols For Vehicular Ad Hoc - Networks Sunil Shukla¹, Namrata Dixit² 1 Fourth Semester M.Tech, Acropolis institute of Technology & Research, Indore. ²Asst. Prof.Dept
Performance Analysis of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols For Vehicular Ad Hoc - Networks Sunil Shukla¹, Namrata Dixit² 1 Fourth Semester M.Tech, Acropolis institute of Technology & Research, Indore. ²Asst. Prof.Dept
Chapter 2: Routing Protocols on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs) Chapter 2: Routing Protocols on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Goals
Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs) Chapter 2: Routing Protocols on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Goals
Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network
 Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network 1 Mr.Nikhil D.Karande, Assistant Professor & Head of CSE, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College Of Engineering,Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India 2 Ms.Kushal K.Kulkarni,
Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network 1 Mr.Nikhil D.Karande, Assistant Professor & Head of CSE, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College Of Engineering,Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India 2 Ms.Kushal K.Kulkarni,
Keywords Mobile Ad hoc Networks, Multi-hop Routing, Infrastructure less, Multicast Routing, Routing.
 Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Study on Various
Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Study on Various
Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Protocol
 Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Nisha Bhanushali Priyanka Thakkar Prasanna Shete ABSTRACT The multi-hop ad hoc networks are self organizing networks with dynamic topology. The reactive
Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Nisha Bhanushali Priyanka Thakkar Prasanna Shete ABSTRACT The multi-hop ad hoc networks are self organizing networks with dynamic topology. The reactive
A Dynamic Time Scalable Hybrid Location based Ad hoc Routing Protocol
 A Dynamic Time Scalable Hybrid Location based Ad hoc Routing Protocol Priyanka P Jadhav 1, Manoj M. Dongre 2 1, 2 Electronics and Telecommunication Department, Ramrao Adik Institute of Technology, Navi
A Dynamic Time Scalable Hybrid Location based Ad hoc Routing Protocol Priyanka P Jadhav 1, Manoj M. Dongre 2 1, 2 Electronics and Telecommunication Department, Ramrao Adik Institute of Technology, Navi
Presenting a multicast routing protocol for enhanced efficiency in mobile ad-hoc networks
 Presenting a multicast routing protocol for enhanced efficiency in mobile ad-hoc networks Mehdi Jalili, Islamic Azad University, Shabestar Branch, Shabestar, Iran mehdijalili2000@gmail.com Mohammad Ali
Presenting a multicast routing protocol for enhanced efficiency in mobile ad-hoc networks Mehdi Jalili, Islamic Azad University, Shabestar Branch, Shabestar, Iran mehdijalili2000@gmail.com Mohammad Ali
Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs
 POSTER 2018, PRAGUE MAY 10 1 Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs Tibor PETROV Dept. of Multimedia and Information-Communication Technologies, University
POSTER 2018, PRAGUE MAY 10 1 Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs Tibor PETROV Dept. of Multimedia and Information-Communication Technologies, University
A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET
 A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET Jeng-Wei Lee*, Chun-Chih Lo*, Shih-Pu Tang*, Mong-Fong Horng** and Yau-Hwang Kuo* * Department of Computer
A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET Jeng-Wei Lee*, Chun-Chih Lo*, Shih-Pu Tang*, Mong-Fong Horng** and Yau-Hwang Kuo* * Department of Computer
Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks E. Priyanka 1, M.Vijaya Kanth 2 M.Tech, Department of CSE, JNTUACE, Ananthapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 Lecturer, Department
Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks E. Priyanka 1, M.Vijaya Kanth 2 M.Tech, Department of CSE, JNTUACE, Ananthapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 Lecturer, Department
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking. Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT
 Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
A Survey on Routing Protocols and its Issues in VANET
 A Survey on Routing Protocols and its Issues in VANET Jagadeesh Kakarla 1, S Siva Sathya 1, B Govinda Laxmi 2, Ramesh Babu B 3 1 School of Engineering and Technology, Department of Computer Science, Pondicherry
A Survey on Routing Protocols and its Issues in VANET Jagadeesh Kakarla 1, S Siva Sathya 1, B Govinda Laxmi 2, Ramesh Babu B 3 1 School of Engineering and Technology, Department of Computer Science, Pondicherry
An Efficient Data Transmission in VANET Using Clustering Method
 INTL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS, 2017, VOL. 63, NO. 3, PP. 309-313 Manuscript received April 29, 2016; revised July, 2017. DOI: 10.1515/eletel-2017-0045 An Efficient Data Transmission
INTL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS, 2017, VOL. 63, NO. 3, PP. 309-313 Manuscript received April 29, 2016; revised July, 2017. DOI: 10.1515/eletel-2017-0045 An Efficient Data Transmission
A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET
 A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET Nidhishkumar P. Modi 1, Krunal J. Panchal 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, LJIET, Gujarat, India 2 Asst.Professor,
A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET Nidhishkumar P. Modi 1, Krunal J. Panchal 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, LJIET, Gujarat, India 2 Asst.Professor,
Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs
 Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs A Viswanath, Dept of CSE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, AP, India. N Papanna, M.Tech, Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering
Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs A Viswanath, Dept of CSE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, AP, India. N Papanna, M.Tech, Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model
 Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model Deepak Agrawal, Brajesh Patel Department of CSE Shri Ram Institute of Technology Jabalpur,
Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model Deepak Agrawal, Brajesh Patel Department of CSE Shri Ram Institute of Technology Jabalpur,
PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks
 23 IEEE Military Communications Conference PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks Baber Aslam, Faisal Amjad and Cliff C. Zou National University
23 IEEE Military Communications Conference PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks Baber Aslam, Faisal Amjad and Cliff C. Zou National University
A Protocol for Reducing Routing Overhead in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 A Protocol for Reducing Routing Overhead in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Radhu.R.Nair #1 T. K Parani *2 # Student, M.E Communication Systems engineering, Anna University DSCE Coimbatore, India *Assistant professor,
A Protocol for Reducing Routing Overhead in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Radhu.R.Nair #1 T. K Parani *2 # Student, M.E Communication Systems engineering, Anna University DSCE Coimbatore, India *Assistant professor,
BRAVE: Beacon-less Routing Algorithm for Vehicular Environments
 : Beacon-less Routing Algorithm for Vehicular Environments Pedro M. Ruiz, Victor Cabrera, Juan A. Martinez, Francisco J. Ros Dept. of Information and Communications Engineering University of Murcia, Spain
: Beacon-less Routing Algorithm for Vehicular Environments Pedro M. Ruiz, Victor Cabrera, Juan A. Martinez, Francisco J. Ros Dept. of Information and Communications Engineering University of Murcia, Spain
[Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675
![[Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675 [Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675](/thumbs/82/86597446.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES A SURVEY ON ROUTING PERFORMANCE IN VANET Shilpa R*, Dr. B R Prasad Babu, Mr. Ravi Kumar M * M. Tech Student Dept. of CSE, R&D Centre EPCET,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES A SURVEY ON ROUTING PERFORMANCE IN VANET Shilpa R*, Dr. B R Prasad Babu, Mr. Ravi Kumar M * M. Tech Student Dept. of CSE, R&D Centre EPCET,
Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET
 208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh
 A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
Impact of routing protocol on performance of wireless ad hoc vehicular network
 1 v.p.patil, 2 b.p.saoji 1,2 Smt Indira Gandhi college of Engineering Navi Mumbai, INDIA Email: 1 bkvpp@rediffmail.com, 2 bpsaoji@rediffmail.com Abstract: Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) is an emerging
1 v.p.patil, 2 b.p.saoji 1,2 Smt Indira Gandhi college of Engineering Navi Mumbai, INDIA Email: 1 bkvpp@rediffmail.com, 2 bpsaoji@rediffmail.com Abstract: Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) is an emerging
6367(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March April (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks: Characteristics and Comparisons
 International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Volume 2016, Article ID 1605734, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1605734 Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks:
International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Volume 2016, Article ID 1605734, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1605734 Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks:
Performance Evaluation of MANET through NS2 Simulation
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique
 Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique Vijay J Parmar Department of Computer Engineering,Sarvajanic College of Engineering and Technology Surat, Gujrat (India),E-mail
Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique Vijay J Parmar Department of Computer Engineering,Sarvajanic College of Engineering and Technology Surat, Gujrat (India),E-mail
Figure 1: Ad-Hoc routing protocols.
 Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
Angle-Aware Greedy Forwarding Algorithm for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Angle-Aware Greedy Forwarding Algorithm for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Aye Zarchi Minn 1 and May Zin Oo 2 Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University,
Angle-Aware Greedy Forwarding Algorithm for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Aye Zarchi Minn 1 and May Zin Oo 2 Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University,
Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OLSR Routing Protocol for VANET
 Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OL Routing Protocol for VANET Suhaib sheikh 1, Bhawna Sharma 2, Sunil Panjeta 3 1,2 Mtech scholar in electronics and communication engineering, YIET,
Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OL Routing Protocol for VANET Suhaib sheikh 1, Bhawna Sharma 2, Sunil Panjeta 3 1,2 Mtech scholar in electronics and communication engineering, YIET,
A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Humayun Bakht Research Fellow, London School of Commerce, United Kingdom humayunbakht@yahoo.co.uk
A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Humayun Bakht Research Fellow, London School of Commerce, United Kingdom humayunbakht@yahoo.co.uk
Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1
 Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1 Hsin-Ya Pan, Rong-Hong Jan 2, Andy An-Kai Jeng, and Chien Chen Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan {hypan,
Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1 Hsin-Ya Pan, Rong-Hong Jan 2, Andy An-Kai Jeng, and Chien Chen Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan {hypan,
POSITION BASED ADAPTIVE ROUTING FOR VANETS
 POSITION BASED ADAPTIVE ROUTING FOR VANETS Ajay Guleria 1 and Kuldeep Singh 2 1 Computer Centre, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India 2 Computer Science & Application Department, Panjab University, Chandigarh,
POSITION BASED ADAPTIVE ROUTING FOR VANETS Ajay Guleria 1 and Kuldeep Singh 2 1 Computer Centre, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India 2 Computer Science & Application Department, Panjab University, Chandigarh,
PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP
 Realistic Mobility Model And Co-Operative Peer To Peer Data Transmission For VANET s Using SUMO And MOVE Nataraj B, Dr. T. Kantharaju 1,2 Electronics and Communication, JNTUA, BITIT, Hindupur, Andhra Pradesh,
Realistic Mobility Model And Co-Operative Peer To Peer Data Transmission For VANET s Using SUMO And MOVE Nataraj B, Dr. T. Kantharaju 1,2 Electronics and Communication, JNTUA, BITIT, Hindupur, Andhra Pradesh,
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET
 Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications
 BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications Kai-Juan Wong, Bu-Sung Lee, Boon-Chong Seet, Genping Liu, Lijuan Zhu School of Computer
BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications Kai-Juan Wong, Bu-Sung Lee, Boon-Chong Seet, Genping Liu, Lijuan Zhu School of Computer
A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks
 Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-4, February 10, 2012 A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks Padmavathi K Asst. Professor, Department
Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-4, February 10, 2012 A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks Padmavathi K Asst. Professor, Department
Various Issues in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks : A Survey
 International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Vol. 1, No. 2, July-December 2010, pp. 399-403 Various Issues in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks : A Survey Shinde S. S. 1 & Patil S. P 2 1,2 Annasaheb
International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Vol. 1, No. 2, July-December 2010, pp. 399-403 Various Issues in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks : A Survey Shinde S. S. 1 & Patil S. P 2 1,2 Annasaheb
Keywords-MANETs, Multicast mode, Clustering, Inter-domain routing.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Multicast
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Multicast
International Journal of Information Movement. Website: ISSN: (online) Pages
 REVIEW: VANET ARCHITECTURES AND DESIGN Chetna Research Scholar Department Of Electronic & Communication Engg. Galaxy Global Group of Institutions, Dinarpur Saranjeet Singh Faculty Department of Electronic
REVIEW: VANET ARCHITECTURES AND DESIGN Chetna Research Scholar Department Of Electronic & Communication Engg. Galaxy Global Group of Institutions, Dinarpur Saranjeet Singh Faculty Department of Electronic
COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS
 COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS Deepa B 1 and Dr. S A Kulkarni 2 1 IV Sem M. Tech, Dept of CSE, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi deepa.bangarshetru@gmail.com
COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS Deepa B 1 and Dr. S A Kulkarni 2 1 IV Sem M. Tech, Dept of CSE, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi deepa.bangarshetru@gmail.com
VANETs. Marc Torrent-Moreno, Prof. Hannes Hartenstein Decentralized Systems and Network Services Institute for Telematics, University of Karlsruhe
 VANETs Marc Torrent-Moreno, Prof. Hannes Hartenstein Decentralized Systems and Network Services Institute for Telematics, University of Karlsruhe April 15 th 2005 Marc Torrent Moreno 1 Main Motivation
VANETs Marc Torrent-Moreno, Prof. Hannes Hartenstein Decentralized Systems and Network Services Institute for Telematics, University of Karlsruhe April 15 th 2005 Marc Torrent Moreno 1 Main Motivation
Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment
 Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment Rab Nawaz Jadoon, Mehtab Afzal, and Jawad Shafi Abstract Vehicular ad hoc networks are more helpful in providing road safety and many other commercial
Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment Rab Nawaz Jadoon, Mehtab Afzal, and Jawad Shafi Abstract Vehicular ad hoc networks are more helpful in providing road safety and many other commercial
SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
 Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Performance Analysis of Broadcast Based Mobile Adhoc Routing Protocols AODV and DSDV
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND MOBILE APPLICATIONS IJCSMA Performance Analysis of Broadcast Based Mobile Adhoc Routing Protocols AODV and DSDV Er. Sandeep Singh Khehra 1, Er. Abhinash Singla
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND MOBILE APPLICATIONS IJCSMA Performance Analysis of Broadcast Based Mobile Adhoc Routing Protocols AODV and DSDV Er. Sandeep Singh Khehra 1, Er. Abhinash Singla
Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator C4R and MOVE using Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR)
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V1 PP 25-29 www.iosrjen.org Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator and MOVE using
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V1 PP 25-29 www.iosrjen.org Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator and MOVE using
Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas
 Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas Shen Wan, Jian Tang and Richard S. Wolff Abstract The demands for vehicular Internet access are proliferating. Access Points (APs)
Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas Shen Wan, Jian Tang and Richard S. Wolff Abstract The demands for vehicular Internet access are proliferating. Access Points (APs)
Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET
 Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET Mrs. Uma Nagaraj Department of Computer Engg. MAE, Alandi Pune, India Ms. Poonam P. Dhamal Department of Computer Engg.
Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET Mrs. Uma Nagaraj Department of Computer Engg. MAE, Alandi Pune, India Ms. Poonam P. Dhamal Department of Computer Engg.
The Challenges of Robust Inter-Vehicle Communications
 The Challenges of Robust Inter-Vehicle Communications IEEE VTC2005-Fall Marc Torrent-Moreno, Moritz Killat and Hannes Hartenstein DSN Research Group Institute of Telematics University of Karlsruhe Marc
The Challenges of Robust Inter-Vehicle Communications IEEE VTC2005-Fall Marc Torrent-Moreno, Moritz Killat and Hannes Hartenstein DSN Research Group Institute of Telematics University of Karlsruhe Marc
A Comparative study on Traditional Transport System and Intelligent Transport System
 A Comparative study on Traditional Transport and Intelligent Transport Irfan Ali Khan #1, Rizwan Khan *2, Ravi Shankar Shukla #3 # Department of Computer Science & Engineering, # Department of CS/IT Prem
A Comparative study on Traditional Transport and Intelligent Transport Irfan Ali Khan #1, Rizwan Khan *2, Ravi Shankar Shukla #3 # Department of Computer Science & Engineering, # Department of CS/IT Prem
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Dr. Ashikur Rahman CSE 6811: Wireless Ad hoc Networks
 Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
Intelligent Route Discovery through DSP Algorithm in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Intelligent
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Intelligent
