ComparisonamongDifferentRoutingProtocolsofVehicularAdHocNetworks
|
|
|
- Willis Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 17 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: & Print ISSN: Comparison among Different Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks By Ahmed Shoeb Al Hasan, Md. Hasan Tareque & Fatema Tuz Zohra Bangladesh University of Business & Technology, Bangladesh Abstract- To improve highway transport security, VANET (Vehicular Ad Hoc Network) is used which is a developing technology incorporating ad hoc network, cellular technology and wireless LAN. VANETs are different from other type ad hoc networks by their cross network constructions, node association features and new application setups. The approach of an effective routing protocol for VANETs is vital as VANETs show various distinctive networking research challenges. In this paper, we discuss the research challenges of routing in VANETs and compare recent routing protocols of VANETs. Keywords: MANET, VANET, wlan, routing. GJCST-E Classification : C.2.2 ComparisonamongDifferentRoutingProtocolsofVehicularAdHocNetworks Strictly as per the compliance and regulations of: Ahmed Shoeb Al Hasan, Md. Hasan Tareque & Fatema Tuz Zohra. This is a research/review paper, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported License permitting all non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction inany medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
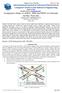
2 Comparison among Different Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Ahmed Shoeb Al Hasan α, Md. Hasan Tareque σ & Fatema Tuz Zohra ρ Abstract- To improve highway transport security, VANET (Vehicular Ad Hoc Network) is used which is a developing technology incorporating ad hoc network, cellular technology and wireless LAN. VANETs are different from other type ad hoc networks by their cross network constructions, node association features and new application setups. The approach of an effective routing protocol for VANETs is vital as VANETs show various distinctive networking research challenges. In this paper, we discuss the research challenges of routing in VANETs and compare recent routing protocols of VANETs. Keywords: MANET, VANET, wlan, routing. I. Introduction Vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) is a special type of Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) which is designed to facilitate vehicle to vehicle (V2V) and vehicle to roadside communications. It is a promising new technology to achieve intelligent inter-vehicle communications and flawless internet connectivity by integrating the capabilities of new generation wireless networks to vehicles. Analogous to MANET it is autonomous, self-organizing and self-managing wireless communication network. Nodes in VANET involve themselves as servers and/or clients for exchanging & sharing information via shared radio transmission. Three possible network architectures for VANET are: pure cellular/wlan, pure ad hoc, and hybrid. A simple scenario of vehicular ad-hoc network is shown in figure 1. VANET introduces Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) which includes a variety of applications such as co-operative traffic monitoring, control of traffic flows, blind crossing, prevention of collisions, nearby information services and real-time detour routes computation. It can be also used for providing Internet connectivity to vehicular nodes while on the move. The unique characteristics of VANET are the high nodes mobility and unreliable channel conditions which poses the problems of frequent change in network topology. So finding and maintaining routes is a very challenging task in VANETs. The existing routing protocols for MANET shows poor performance when directly applied to Authors α ρ: Department of CSE, Bangladesh University of Business & Technology, Bangladesh. shoeb.al.hasan@gmail.com, kaniz_csemist@yahoo.com Author σ: Department of CSE, IBAIS University, Bangladesh. hasantareque07@gmail.com Figure 1 : Vehicular Ad Hoc Network. VANET environment due to the fast vehicles movement and dynamic information exchange. Thus design of a suitable routing protocol to deal with the highly dynamic nature of VANET has taken significant attention. In this literature we will review the key characteristics in VANET and some of the existing routing protocols for VANET which can be used for better understanding of the routing protocols and future improvement can be made. II. Characteristics of Vanet VANET has some unique characteristics which make it different from other kinds of Ad hoc networks as well as challenging for designing VANET routing protocols. a) High Dynamic topology The topology of VANET is always changing due to the high speed and choice of path of vehicles. If we assume two vehicles moving away from each other with a speed of 60 mph (25m/sec) and the transmission range is about 250m, then the link between these two vehicles will last only for at most10 seconds. b) Frequent disconnected Network Due to the same reason, the nodes needed another link with nearby vehicle in about 10 seconds to maintain seamless connectivity. But in case of such failure, particularly in case of low vehicle density zone, Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( D E ) Volume XIII Issue XVII Version I Year
3 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( E ) Volume D XIII Issue XVII Version I Year frequent disruption of network connectivity will occur. One possible solution of such problems is addressed by road-side deployment of relay nodes. c) Mobility Modeling and Prediction Besides the highly mobile node movement and dynamic topology, vehicular nodes are usually constrained by prebuilt highways, roads and streets. So mobility model and node prediction based on study of predefined roadways model and vehicle speed is of paramount importance for effective network protocol design for VANET. d) Communication Environment VANET are typically operated on two communication environments: highway traffic scenario and city environment. The node prediction design and routing algorithm also therefore need to adapt for these two environments. Highway mobility model is rather simple and easy to predict than the city mobility model. Street structure, variable node density, presence of buildings and trees that behave as obstacles to even small distance communication make the city model very complex and difficult. e) Hard Delay Constraints Overcoming the issues of hard delay constraints are of great importance in VANET than the high data rate. For example safety aspect such as accidents or brake event the message should be transferred and arrived in a certain time to avoid car crash. f) Interaction with onboard sensors It is assumed that the nodes are equipped with on-board sensors such as GPS receivers. This sensors helps in providing node location and their movement nature that are used for effective communication link and routing purposes. g) Battery Power and Storage capacity Modern vehicles have enough computing power because of unlimited battery power and storage which is unavailable in MANET. It is helpful for effective communication & making routing decisions. III. Routing Protocols for Vanet Routing in VANET can be classified in many dimensions. In this literature we classify them into five categories as follows: ad hoc, position-based, clusterbased, broadcast, and geo-cast routing protocols. These protocols are characterized on the basis of area / application where they are most suitable. In this section we have discussed about these protocols. a) Adhoc Routing Most of the characteristics of Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) are analogous to that of Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET). Therefore most of existing MANET routing protocols can be directly applied to VANET. Reactive routing protocols such as AODV (Ad Hoc on demand distance vector) and DSR (Dynamic source routing) are also called on-demand routing protocols as they periodically update the routing table. Reactive routing consists of route discovery phase which causes more routing overhead and also suffer from the initial route discovery process. Moreover route maintenance process in DSR does not locally repair a broken link. Simulation of these algorithms in VANET brought out frequent communication break because of the highly dynamic nodes. Therefore it becomes obligatory to suitably modify the existing protocols of MANET to meet the challenges in VANET. i. PRAODV/PRAODV-M: Namboodiri et al. proposed some modifications in [1]. A highly partitioned highway scenario is used for the network model. Therefore most path segments are relatively small. To reduce the ill-effects of frequent route breakages in case of AODV two new predictions-based AODV algorithms are introduced. First one is referred as PR-AODV and it uses node position and their speed information in AODV to predict link life time. It constructs a new alternate link before the end of estimated link lifetime. Where in AODV, the link created only after the failure of connectivity occurs. In contrast to selecting shortest path as in PRAODV or AODV the second modified algorithm (PRAOVD- M) computes the maximum predicted life time among various route options. The simulation on both showed slight improvement in packet driving ratio. However, the success of this algorithm largely depends on the prediction of node position and mobility. ii. AODV-bis: Another modification is proposed in [2]. AODV is modified to forward the route request within a zone of relevance (ZOR) from the point of event occurrence. ZOR can be rectangular or circular specified by the particular application. b) Position Based Routing Routing strategies that employs geographical information in their routing decision have been identified as more promising routing paradigm for VANET environment. These protocols use location information to select the next forwarding hops so no global route between source and destination needs to be created and maintained. Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR): GPSR (Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing) [3] is one of the best known position based routing. It takes greedy forwarding decision based on the location information of immediate neighbors. Where greedy forwarding fails it
4 uses perimeter mode or face routing on a planarized graph of the network to find the next forwarding hop. Figure 2 shows greedy Figure 2 : (a) greedy forwarding and (b) perimeter mode forwarding. forwarding and forwarding in perimeter mode. It works best in highway scenario with evenly distributed nodes. GPSR generally shows better performance when applied to highway scenario than that of DSR because of fewer obstacles compared with city scenario. GPSR has to face some challenges when applied to city scenario: Greedy forwarding sometimes fails in case where direct communication between nodes does not exist due to the obstacles such as buildings and trees. In perimeter mode a planarized network graph is traversed when greedy fails which create longer path resulting in higher delays and also degrade the performance Due to the highly dynamic nature of nodes in VANET routing loops can be induced by the righthand rule used in face routing Moreover Packet can be forwarded in wrong direction resulting higher delays Geographic Source Routing (GSR): Lochert et al [4] proposed GSR routing for vehicular ad hoc networks in city environments. It combines. Figure 3 shows some examples of GPSR failures. To solve the above constraints certain improvements are made in the GPSR algorithm positionbased routing with topological knowledge. This street awareness in GSR is provided by static street map and it uses Reactive Location Service (RLS) to get the destination position. GSR uses greedy forwarding along a pre-selected shortest path and this path is computed by Dijkstra shortest path algorithm. GSR shows better average delivery rate, smaller total bandwidth consumption and similar latency as with DSR or AODV. The protocol overlook the situation where the traffic density is low it is difficult to find end to end connection along a preselected path. Greedy Perimeter Coordinator Routing (GPCR): Greedy Perimeter Coordinator Routing (GPCR) is proposed in [5] and it consists of two parts: a restricted greedy forwarding and a repair strategy. Unlike GSR this algorithm is based on the topology of real world streets and junctions which form a natural planar graph. Therefore it does not require a graph planarization process as GPSR or does not use any global topology information like GSR. The restrictive greedy algorithm is applied when nodes are in street and an actual routing decision is taken only at the junction of streets. So packets are forwarded to a junction node (coordinator) rather sending it across the junction. When stuck into a local minimum GPCR adopt a repair strategy. (1) Coordinator node decides using right-hand rule which street the packets should follow. (2) In between junctions greedy forwarding is applied to reach the next junction. In figure 4 restricted greedy routing and repair strategy in GPCR is shown. There are two different approaches to detect junction nodes: (1) by analyzing node position and the position and presence of the neighbor s neighbors from beacon messages (2) by calculating the correlation coefficient with respect to the position of its neighbors. The simulation results using NS-2 simulator in a real city scenario shows higher delivery rate than that of GPSR with large average number of hops. But it introduces slight increase in latency. GPCR fails to work efficiently in city scenario with high rise building, uneven concentration of vehicles on roads. Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( D E ) Volume XIII Issue XVII Version I Year
5 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( E ) Volume D XIII Issue XVII Version I Year (a) Network Disconnection: link uv is removed by planarization. However, due to obstacles (such as buildings), there is no direct link ua or ub. (b) Longer path in perimeter mode. (c) Routing loop introduced by right-hand rule in face routing. There are problems in junction detection approaches. First approach fails in case of curve streets and second one fails for sparse streets. (a) (b) (a) Using restricted greedy forwarding packet is forwarded to C1 (coordinator node) from S instead of N1 (regular greedy forwarding). (b) Repair Strategy: In node S (local minimum) algorithm switched to repair strategy. Packets forwarded to C1 (coordinator node) and it decides which road to follow. Figure 4 : GPCR routing strategy Anchor based street and traffic aware Routing (A-STAR): Anchor-Based Street and Traffic Aware Routing [6] (A-STAR) is a position based routing protocol which is specially design for city scenarios for inter vehicle communication system. But unlike GSR, A- STAR takes into account both street and traffic awareness in computing the anchor paths. A-STAR integrates traffic awareness by using vehicular traffic city bus information to identify an anchor path with high connectivity for packet delivery. An anchor path can be computed using Dijkstra's least-weight path algorithm. Traffic awareness can be incorporated by using either statistically rated maps or dynamically rated maps. A- STAR employs a new local recovery strategy for packets that stuck into a local minimum which is more suitable for a city environment than the recovery strategies used in GPSR and GSR. A new anchor path is computed from the point of local minimum and the packet is routed through this new anchor path. The street at which local minimum is occurred is marked as out of service temporarily. Figure 3 : Examples of GPSR failures A-STAR shows the best performance compared to GSR and GPSR, because it can select paths with higher connectivity for packet delivery. As much as 40% more packets are delivered by A-STAR compared to GSR. A-STAR guarantees for finding an end-to-end connection in case of low traffic density. The subscript for the permeability of vacuum 0, and other common scientific constants, is zero with subscript formatting, not a lowercase letter o. c) Geocast Routing Geocast routing protocols follow the standard of routing data packets from a single source vehicle to all vehicles fitting to the destination area called zone of relevance ZOR. This multicast routing protocol can be implemented by simply defining the multicast group within the ZOR. Geocast routing follows a directed flooding strategy within a defined forwarding area, zone of forwarding ZOF so that it can limit the message overhead and network congestion of simple flooding. Figure 5 illustrates the ZOR in Geocast routing. The message is first forwarded from the sender to the geographic area via unicast. It is then simply broadcasted to all vehicles inside the target region. So identify the zone of relevance is important in Geocast routing. IVG, Cached Geocast, Abiding Geocast, DRG, ROVER, DG-CastoR, Mobicast, DTSG, Constrained Geocast, and Geocache are some existing Geocast routing protocols in VANETs. In this literature IVG, ROVER and Abiding Geocast are discussed. Alert area (ZOR) Accident Figure 5 : Geocast routing. Inter Vehicles Geocast Protocol (IVG): Bachir and Benslimane in [7] proposed a Geocast protocol named Inter-Vehicles Geocast (IVG).
6 IVG works by informing the vehicles located in a risk area, which formed a multicast group about any danger on the highway. A message alert is broadcasted to the multicast group by the damaged vehicle. The precise obstacle location and the driving directions are taken into account in determining the risk area. Neighbors inside the risk area calculate a differ time backoff that helps the furthest node to relay rebroadcasting the message. Figure 6 shows an example of relay selection in IVG. RObust Vehicular Routing (ROVER): ROVER [8] proposed by M. Kihl and al. is a protocol which is similar to AODV. It broadcasts only the control packets & data packets are unicasted. ROVER assumptions are: Each vehicle has an Identification Number, Each vehicle should have a GPS receiver, Vehicles must have access to a digital map, ZOR is a rectangle area and within ZOR reactive route discovery process are used, ZOF includes the sender and the ZOR. The goal of ROVER is to deliver an application generated message to all vehicles those are located into the specified ZOR. A lot of redundant messages is created by this protocol which caused in network congestion and high delay in data transfer. Figure 6 : IVG Relay selection: x is more distant to z then y. x is a relay. x permits to reach w while y not Abiding Geocast: Abiding Geocast [9] was proposed by Maihöfer and Eberhardt. It allows a continuous delivery of a Geocast message in Ad Hoc Networks. Three solutions are provided for Abiding Geocast: 1. Using a server that stores Geocast message. Main objective of this server is to use a Geocast protocol that periodically delivers the Geocast message to the destination zone. 2. A node is nominated in the appropriate destination area in order to store the Geocast message and periodically or by notification retransmit it. 3. The neighbour approach allows all nodes to store the Geocast message. Uses of abiding Geocast: Advertising or informing drivers about the state of the road. (slippery surface, ice storm, etc.) Elected node approach and neighbour approach are more improved for safety applications to inform drivers about an accident on their way. d) Cluster Based Routing In cluster-based routing scalability is provided by creating a virtual network infrastructure through the clustering of nodes. Figure 7 illustrates a cluster-based routing. Cluster is represented by a cluster head. Intercommunication between different clusters is carried through cluster heads. Intra-communication within each cluster is made through direct link. The current clusterbased protocols in MANET are not stable in vehicular ad-hoc network because of their short-life. Figure 7 : Vehicles form multiple clusters in clusterbased routing. Some Cluster-Based Routing protocols in VANETs are: COIN, LORA_CBF. COIN: Clustering for Open IVC Networks (COIN) algorithm is proposed by Blum et al. [10]. Cluster head election is constructed on vehicular dynamics and driver purposes, instead of ID or relative mobility. This algorithm shows the oscillatory nature of inter-vehicle distances. COIN increases the average cluster lifetime by at least 192% and reduces number of cluster membership changes by 46%. LORA_CBF: LORA_CBF is a reactive location based routing algorithm proposed by Santos et al. [11]. It uses cluster-based flooding for VANETs. Any node can be the cluster- head, gateway or cluster member. Every cluster has exactly one cluster-head. A node connected to more than one cluster is called a gateway. The cluster-head preserves information about its members and gateways. Packets are forwarded using greedy routing. If the location of the destination is not available, only the Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( D E ) Volume XIII Issue XVII Version I Year
7 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( E ) Volume D XIII Issue XVII Version I Year cluster-heads and gateways will propagate the LREQ (Location Request) and LREP (Location Reply) messages. The performances of LORA_CBF, AODV and DSR are evaluated in typical urban and highway traffic scenarios. The results show that network mobility and size affect the performance of AODV and DSR more ominously than LORA_CBF. Cluster-based routing protocols can achieve good scalability for large networks. A major obstacle for the protocols is fastchanging VANET systems, the delay and overhead involved in creating and preserving these clusters. e) Broadcast Routing Regularly used routing scheme in VANETs is Broadcast. Broadcast is used for sharing information about crisis, street situations, advertisements etc. Efficient route exploration in unicast protocol is another usage of Broadcast routing. Easiest technique to apply broadcast is flooding. Flooding enables every node to forward the incoming message to its entire neighbours except its parent node. Flooding works efficiently in small networks. But efficiency decreases for larger networks. BROADCOMM: The freeway is separated into virtual cells in BROACOMM [12]. In BROADCOMM, movement of virtual cells are based on the movement of vehicles. All the vehicles of freeway are classified in two groups. Figure 7. Vehicles form multiple clusters in cluster-based routing. 1. All the vehicles in a cell 2. Small number of vehicles situated closely to the centre of the cell, called cell reflectors. BROADCOMM works better than analogous flooding based protocols for message broadcasting delay and routing overhead. The drawback is, it is only applicable for simple freeway networks. Urban Multi-Hop Broadcast protocol (UMB): Urban Multi-Hop Broadcast protocol (UMB) [13] is proposed to transmit messages in urban areas. There are some issues related to urban area such as interference, packet collisions and hidden nodes problems due to multihop broadcast. There are two steps in UMB: 1. Directional Broadcast: Transmitting node picks the furthest node in broadcast direction without any Table 1 : Comparisons of Routing Protocols In Vanets topology information. Selected node has the responsibility of next forwarding. 2. Intersection Broadcast: Repeaters are installed in every intersection point. Repeaters re-broadcast the packets to all road segments except the receiving direction. Figure 8 : UMB protocol For dense networks and high packet loads, UMB protocol has higher success rate than distance and random protocols. Vector-based TRAcking DEtection (V-TRADE): V-TRADE [14] is a GPS based message broadcasting protocol which is similar to the unicast routing protocol Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP) [15]. Neighbours are classified into different forwarding groups based on position and movement information. Border vehicles which are small subset of vehicles from each group are selected to forward the message. V-TRADE selects small number of vehicles to forward the messages. This feature utilizes bandwidth. Reachability decreases slightly due to small number of forwarding vehicles. f) Comparison of routing protocol in VANET Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of routing protocols in VANET. Routing Protocols Routing Type Position Information? (How to use) Hierarchical structure Network Simulator Simulation Scenario AODV Unicast No No DSR Unicast No No GPSR Unicast Packet Forwarding No PRAODV/ PRAODV-M Unicast Route Selection (lifetime prediction) No NS2 Simple highway model (20km segment only) AODV-bis Unicast Route-Req Forwarding No GSR Unicast Packet Forwarding No NS2 Real city model (from map)
8 IV. GPCR Unicast Packet Forwarding No NS2 Real city model (from map) A-STAR Unicast Packet Forwarding No NS2 Grid city model COIN Unicast Cluster Formation Yes Own Real highway model LORA CBF Unicast Packet Forwarding Yes Opnet Simple circle and square road Flooding Broadcast No No UMB Broadcast Packet Forwarding No Own Simple intersection road V-TRADE/ Broadcast Classify forwarding No Own Simple intersection HV-TRADE Group BROADCOMM Broadcast Formation of Cells Yes Own Simple highway model (15 Msg Dis Protcl Geocast Packet Forwarding No Own Simple highway d model ) (10 km ) IVG Geocast Packet Forwarding No Glomosin Simple highway model (10 km long, 100/200 nodes) Cached Geocast Geocast Packet Forwarding No NS2 Quadratic network (size from 1 km Abiding Geocast Geocast Packet Forwarding No Limitations and Future Perspectives There are some observations after surveying the existing protocols for VANET. Most of the routing protocols in VANET perform better for a specific street condition or environment. But to provide an efficient routing, scalability should be considered which is very difficult in VANET environment. An efficient routing protocol for VANET must be able to communicate under low network density. The network density is usually low in off-peak hour in the city scenario or in the highway; however, the broadcast message is still necessarily need to disseminate to all vehicles in a network. Most of the protocols in VANET do not consider the direction of the vehicles in the road. But due to the high speed and choice of path of vehicles sometimes packets may get forwarded to the wrong direction leading higher delays or even network partitions. Moreover there is no agreed-upon standard or mobility model to validate their performance. For example GPSR is a widely known position based routing protocol. But the position-based routing keeps advancing into many subareas in VANETs. So evaluation of the protocols using GPSR is no longer a reasonable comparison. Security is also an important issue for routing in VANETs, because many applications will affect lifeor-death decisions and illegal tampering can have devastating consequences. The characteristics of VANETs make the secure routing problem more challenging and novel. A possible future work is to design an efficient routing protocol for comfort and safety applications with delay-constraint and delay-tolerant capabilities and low bandwidth utilization. V. Conclusion Vehicular Ad Hoc network exhibits very different characteristics from MANETs. So the existing routing protocols for MANET shows poor performance when directly applied to VANET environment. In this literature, we survey on several routing protocols proposed for VANETs. From the survey it is clear that the positionbased routing and Geocast routing property. The performance of a routing protocol in VANETs perform better than other routing protocols because they support geographical property. The performance of a routing protocol in VANETs depends on various facts like mobility model, driving environment, vehicular density & many other issues. There are still lots of area where VANET can be improved or more research can be done. References Références Referencias 1. V. Namboodiri, M. Agarwal, and L. Gao, A study on the feasibility of mobile gateways for vehicular adhoc networks, in Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, pp , C.-C. Ooi and N. Fisal, Implementation of geocastenhanced AODV-bis routing protocol in MANET, in Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference, vol. 2, pp , B. Karp and H.T. Kung, GPSR: Greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks, in Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom), C. Lochert, H. Hartenstein, J. Tian, D. Herrmann, H. Füßler, and M. Mauve, A routing strategy for vehicular ad hoc networks in city environments, in Proceedings of IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2003), pp , June C. Lochert, M. Mauve, H. Füßler, and H. Hartenstein, Geographic routing in city scenarios, ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communi- Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( D E ) Volume XIII Issue XVII Version I Year
9 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology ( E ) Volume D XIII Issue XVII Version I Year cations Review (MC2R), vol. 9, no. 1, pp , Jan G. Liu, B.-S. Lee, B.-C. Seet, C.H. Foh, K.J. Wong, and K.-K. Lee, A routing strategy for metropolis vehicular communications, in International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), pp , Bachir and A. Benslimane, A multicast protocol in ad hoc networks intervehicle geocast, in Proceedings of the 57th IEEE Semiannual Vehicular Technology Conference, vol. 4, pp , M. Kihl, M. Sichitiu, T. Ekeroth and M. Rozenberg, Reliable Geographical Multicast Routing in Vehicular Adhoc Networks, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4517 LNCS[C], pp , C. Maihöfer, T. Leinmüller, and E. Schoch, Abiding geocast: time-stable Geocast for ad hoc networks, in Proceedings of the 2 nd ACM international workshop on Vehicular ad hoc networks (VANET 05), pp , J. Blum, A. Eskandarian, and L. Hoffman, Mobility management in IVC networks, in IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, R.A. Santos, A. Edwards, R. Edwards, and L. Seed, Performance evaluation of routing protocols in vehicular adhoc networks, The International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, vol. 1, no. 1/2, pp , [12] M. Durresi, A. Durresi, and L. Barolli, Emergency broadcast protocol for intervehicle communications, in ICPADS 05: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems Workshops (ICPADS 05), M. Durresi, A. Durresi, and L. Barolli, Emergency broadcast protocol for intervehicle communications, in ICPADS 05: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems Workshops (ICPADS 05), M. Sun, W. Feng, T.-H. Lai, K. Yamada, H. Okada, and K. Fujimura, GPS-based message broadcasting for inter-vehicle communication, in ICPP 00: Proceedings of the 2000 International Conference on Parallel Processing, Z.J. Haas and M.R. Pearlman, The zone routing protocol (ZRP) for ad hoc networks, in Internet draft Mobile Ad hoc NET working (MANET), Working Group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), Nov
Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V2 PP 06-14 www.iosrjen.org Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V2 PP 06-14 www.iosrjen.org Research Challenges of Position Based Routing Protocol in
Impact of routing protocol on performance of wireless ad hoc vehicular network
 1 v.p.patil, 2 b.p.saoji 1,2 Smt Indira Gandhi college of Engineering Navi Mumbai, INDIA Email: 1 bkvpp@rediffmail.com, 2 bpsaoji@rediffmail.com Abstract: Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) is an emerging
1 v.p.patil, 2 b.p.saoji 1,2 Smt Indira Gandhi college of Engineering Navi Mumbai, INDIA Email: 1 bkvpp@rediffmail.com, 2 bpsaoji@rediffmail.com Abstract: Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) is an emerging
Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 7, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol Stavan Karia
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 7, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Understanding Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks and Use of Greedy Routing Protocol Stavan Karia
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads
 Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network
 Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network 1 Mr.Nikhil D.Karande, Assistant Professor & Head of CSE, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College Of Engineering,Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India 2 Ms.Kushal K.Kulkarni,
Efficient Routing Protocols For Vehicular Adhoc Network 1 Mr.Nikhil D.Karande, Assistant Professor & Head of CSE, Bharati Vidyapeeth s College Of Engineering,Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India 2 Ms.Kushal K.Kulkarni,
MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS. Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang
 Master's Programme in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang Embedded and Intelligent Systems,
Master's Programme in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS SIMULATION-BASED PERFORMANCE COMPARISONS OF GEOCAST ROUTING PROTOCOLS Hequn Zhang, Rui Wang Embedded and Intelligent Systems,
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET
 Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET R. Nirmala 1, R. Sudha 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, K.S.R College of Arts & Science (Autonomous),
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET R. Nirmala 1, R. Sudha 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, K.S.R College of Arts & Science (Autonomous),
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET
 Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET K. Lakshmi 1, K.Thilagam 2, K. Rama 3, A.Jeevarathinam 4, S.Manju Priya 5. 1,3&4 Lecturer, Dept. of Computer Applications,
Comparison of Three Greedy Routing Algorithms for Efficient Packet Forwarding in VANET K. Lakshmi 1, K.Thilagam 2, K. Rama 3, A.Jeevarathinam 4, S.Manju Priya 5. 1,3&4 Lecturer, Dept. of Computer Applications,
A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network
 A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Arshdeep Kaur 1, Shilpa Sharma 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
A Review on Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Arshdeep Kaur 1, Shilpa Sharma 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
Routing Convenant For Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks based on Pragmatic Cluster
 Routing Convenant For Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks based on Pragmatic Cluster Archana Nagelli, Dept of CSE Christu Jyothi Institute of Technology & Science, Warangal M. Divya Dept of CSIT Christu Jyothi Institute
Routing Convenant For Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks based on Pragmatic Cluster Archana Nagelli, Dept of CSE Christu Jyothi Institute of Technology & Science, Warangal M. Divya Dept of CSIT Christu Jyothi Institute
A Survey of Vehicular Ad hoc Networks Routing Protocols
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS
 130 CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS 5.1 INTRODUCTION The feasibility of direct and wireless multi-hop V2V communication based on WLAN technologies, and the importance of position based
130 CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE EXTENSIONS 5.1 INTRODUCTION The feasibility of direct and wireless multi-hop V2V communication based on WLAN technologies, and the importance of position based
A Review on Position Based Routing Protocol in Vehicular Adhoc Network
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2013 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-02, pp-07-13 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2013 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-02, pp-07-13 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking. Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT
 Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
Keywords: Adhoc Network, Vehicular Adhoc Network, VANET, position-based routing protocols. I. INTRODUCTION
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com A Review: Position based Routing Protocols in VANET Rathod Kirit R 1st PhD Scholar, Rai University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com A Review: Position based Routing Protocols in VANET Rathod Kirit R 1st PhD Scholar, Rai University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 AN OVERVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF VARIOUS ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET PARUL GUPTA* *Dept. Of Computer Science, P.I.G.G.C.W. Jind (Haryan), India ABSTRACT Vehicular connectivity is most important for an Intelligent
AN OVERVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF VARIOUS ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET PARUL GUPTA* *Dept. Of Computer Science, P.I.G.G.C.W. Jind (Haryan), India ABSTRACT Vehicular connectivity is most important for an Intelligent
Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Raj K. Shrestha, Sangman Moh, Ilyong Chung, and Dongmin Choi Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chosun University 375 Seoseok-dong,
Vertex-Based Multihop Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Routing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Raj K. Shrestha, Sangman Moh, Ilyong Chung, and Dongmin Choi Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chosun University 375 Seoseok-dong,
Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2
 An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
Literature Review on Characteristic Analysis of Efficient and Reliable Broadcast in Vehicular Networks
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 205-210 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Literature Review
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 3 (2013), pp. 205-210 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Literature Review
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security
 The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET Sanjay Batish, Manisha Chahal and Sanjeev Sofat CSE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India E-Mail: sbatish@pec.ac.in
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET Sanjay Batish, Manisha Chahal and Sanjeev Sofat CSE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India E-Mail: sbatish@pec.ac.in
ASurveyonTopologybasedReactiveRoutingProtocolsinVanets
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: E Network, Web & Security Volume 18 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Online
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: E Network, Web & Security Volume 18 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Online
ROUTING TECHNIQUES ON INTERVEHICULAR COMMMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 ROUTING TECHNIQUES ON INTERVEHICULAR COMMMMUNICATION SYSTEM Smita Rani Sahu 1, Uriti Archana 2 1,2 Computer Science & Engineering Department, Sri Venkateswara college of Engineering & Technology, (India)
ROUTING TECHNIQUES ON INTERVEHICULAR COMMMMUNICATION SYSTEM Smita Rani Sahu 1, Uriti Archana 2 1,2 Computer Science & Engineering Department, Sri Venkateswara college of Engineering & Technology, (India)
Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using p and g
 Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using 802.11p and 802.11g Rasha Kaiss Aswed and Mohammed Ahmed Abdala Network Engineering Department, College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University
Analyzing Routing Protocols Performance in VANET Using 802.11p and 802.11g Rasha Kaiss Aswed and Mohammed Ahmed Abdala Network Engineering Department, College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University
A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs)
 A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) Sarvesh Kr. Soni 1, B.P Chaurasia 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of CSE, KNIT- Sultanpur, U.P, India 2
A Qualitative Survey on Position Based Unicast Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) Sarvesh Kr. Soni 1, B.P Chaurasia 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of CSE, KNIT- Sultanpur, U.P, India 2
will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes.
 IJEEE, Vol. 1, Issue 4 (August, 2014) e-issn: 1694-2310 p-issn: 1694-2426 SURVEY OVER VANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR VEHICLE COMMUNICATION 1 Amanpreet Kaur, 2 Dr. Dinesh Arora 1,2 Gurukul Vidyapeeth Institute
IJEEE, Vol. 1, Issue 4 (August, 2014) e-issn: 1694-2310 p-issn: 1694-2426 SURVEY OVER VANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR VEHICLE COMMUNICATION 1 Amanpreet Kaur, 2 Dr. Dinesh Arora 1,2 Gurukul Vidyapeeth Institute
EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM
 EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM D.Yamini 1, J. Jayavel 2 1 III-M.tech(IT), Department of Information technology,
EFFICIENT DATA TRANSMISSION AND SECURE COMMUNICATION IN VANETS USING NODE-PRIORITY AND CERTIFICATE REVOCATION MECHANISM D.Yamini 1, J. Jayavel 2 1 III-M.tech(IT), Department of Information technology,
Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET
 Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET Vinod Kumar*, Meenakshi Bansal Mtech Student YCOE,Talwandi Sabo(india), A.P. YCOE, Talwandi Sabo(india) Vinod_Sharma85@rediffmail.com,
Reliable and Efficient flooding Algorithm for Broadcasting in VANET Vinod Kumar*, Meenakshi Bansal Mtech Student YCOE,Talwandi Sabo(india), A.P. YCOE, Talwandi Sabo(india) Vinod_Sharma85@rediffmail.com,
Keywords-MANETs, Multicast mode, Clustering, Inter-domain routing.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Multicast
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Multicast
Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs)
 Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) 1 Overview of Ad hoc Network Communication between various devices makes it possible to provide unique and innovative services. Although this inter-device
Introduction to Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) 1 Overview of Ad hoc Network Communication between various devices makes it possible to provide unique and innovative services. Although this inter-device
Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks: Characteristics and Comparisons
 International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Volume 2016, Article ID 1605734, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1605734 Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks:
International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Volume 2016, Article ID 1605734, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1605734 Review Article Road-Aware Routing Strategies for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks:
Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET
 208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario
 Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
Distributed Robust Geocast
 Distributed Robust Geocast Multicast Routing for Inter-Vehicle Communication Harshvardhan P. Joshi 1, Mihail L. Sichitiu 1, and Maria Kihl 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina
Distributed Robust Geocast Multicast Routing for Inter-Vehicle Communication Harshvardhan P. Joshi 1, Mihail L. Sichitiu 1, and Maria Kihl 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina
Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment
 Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment Rab Nawaz Jadoon, Mehtab Afzal, and Jawad Shafi Abstract Vehicular ad hoc networks are more helpful in providing road safety and many other commercial
Reliable Routing Scheme for VANETs in City Environment Rab Nawaz Jadoon, Mehtab Afzal, and Jawad Shafi Abstract Vehicular ad hoc networks are more helpful in providing road safety and many other commercial
An Improved Vehicular Ad Hoc Routing Protocol for City Environments
 An Improved Vehicular Ad Hoc Routing Protocol for City Environments Moez Jerbi*, Sidi-Mohammed Senouci*, Rabah Meraihi* and Yacine Ghamri-Doudane** *France Telecom R&D, Core Network Laboratories, Lannion,
An Improved Vehicular Ad Hoc Routing Protocol for City Environments Moez Jerbi*, Sidi-Mohammed Senouci*, Rabah Meraihi* and Yacine Ghamri-Doudane** *France Telecom R&D, Core Network Laboratories, Lannion,
Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET
 Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET Mrs. Uma Nagaraj Department of Computer Engg. MAE, Alandi Pune, India Ms. Poonam P. Dhamal Department of Computer Engg.
Performance Comparision of AODV, AOMDV, OLSR, DSR and GSR Routing Protocols in VANET Mrs. Uma Nagaraj Department of Computer Engg. MAE, Alandi Pune, India Ms. Poonam P. Dhamal Department of Computer Engg.
BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications
 BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications Kai-Juan Wong, Bu-Sung Lee, Boon-Chong Seet, Genping Liu, Lijuan Zhu School of Computer
BUSNet: Model and Usage of Regular Traffic Patterns in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks for Inter-Vehicular Communications Kai-Juan Wong, Bu-Sung Lee, Boon-Chong Seet, Genping Liu, Lijuan Zhu School of Computer
DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL P. Kalaivani 1, G. Sathya 2, N.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL P. Kalaivani 1, G. Sathya 2, N.
Content. 1. Introduction. 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm. 3. Simulation and Results. 4. Future Work. 5.
 Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks
 23 IEEE Military Communications Conference PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks Baber Aslam, Faisal Amjad and Cliff C. Zou National University
23 IEEE Military Communications Conference PMTR: Privacy-enhancing Multilayer Trajectory-based Routing Protocol for Vehicular ad hoc Networks Baber Aslam, Faisal Amjad and Cliff C. Zou National University
Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1
 Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1 Hsin-Ya Pan, Rong-Hong Jan 2, Andy An-Kai Jeng, and Chien Chen Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan {hypan,
Mobile-Gateway Routing for Vehicular Networks 1 Hsin-Ya Pan, Rong-Hong Jan 2, Andy An-Kai Jeng, and Chien Chen Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan {hypan,
Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks
 Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks Lijuan Ai Wenyu Wang Yi Zhou 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing, Fall 2001 1 PART I INTRODUCTION TO MANET & LOCATION-AWARE COMPONENTS 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing,
Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks Lijuan Ai Wenyu Wang Yi Zhou 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing, Fall 2001 1 PART I INTRODUCTION TO MANET & LOCATION-AWARE COMPONENTS 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing,
Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
 Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks E. Priyanka 1, M.Vijaya Kanth 2 M.Tech, Department of CSE, JNTUACE, Ananthapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 Lecturer, Department
Routing Protocol with Quality Optimization for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks E. Priyanka 1, M.Vijaya Kanth 2 M.Tech, Department of CSE, JNTUACE, Ananthapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 Lecturer, Department
(General article) Position Based Routing Technique: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing for Wireless Networks
 ijesm www.ijesm.com International Journal of Engineering, Science and Metallurgy (General article) Position Based Routing Technique: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing for Wireless Networks Niyati Bansal
ijesm www.ijesm.com International Journal of Engineering, Science and Metallurgy (General article) Position Based Routing Technique: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing for Wireless Networks Niyati Bansal
Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs
 POSTER 2018, PRAGUE MAY 10 1 Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs Tibor PETROV Dept. of Multimedia and Information-Communication Technologies, University
POSTER 2018, PRAGUE MAY 10 1 Simulation of Routing Protocols for Emergency Vehicle Warning Application in VANETs Tibor PETROV Dept. of Multimedia and Information-Communication Technologies, University
Keywords VANET, Routing protocols, AODV, DSR, DSDV.
 Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach
 Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach 1 Mr. Bhagirath Patel, 2 Ms. Khushbu Shah 1 Department of Computer engineering, 1 LJ Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad, India 1 er.bhagirath@gmail.com,
Reliable Routing In VANET Using Cross Layer Approach 1 Mr. Bhagirath Patel, 2 Ms. Khushbu Shah 1 Department of Computer engineering, 1 LJ Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad, India 1 er.bhagirath@gmail.com,
Routing Protocols in MANET: Comparative Study
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Enhanced Junction Selection Mechanism for Routing Protocol in VANETs
 422 The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 8, No. 4, October 2011 Enhanced Junction Selection Mechanism for Routing Protocol in VANETs Sardar Bilal, Sajjad Madani, and Imran Khan
422 The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 8, No. 4, October 2011 Enhanced Junction Selection Mechanism for Routing Protocol in VANETs Sardar Bilal, Sajjad Madani, and Imran Khan
Figure 1: Ad-Hoc routing protocols.
 Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
ComparisonofPacketDeliveryforblackholeattackinadhocnetwork. Comparison of Packet Delivery for Black Hole Attack in ad hoc Network
 Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and electronics engineering Volume 12 Issue 3 Version 1.0 March 2012 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and electronics engineering Volume 12 Issue 3 Version 1.0 March 2012 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development COMPARISON OF POSITION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 2, February -2015 COMPARISON
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 2, February -2015 COMPARISON
Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation
 Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation Kashif Naseer Qureshi 1, Abdul Hanan Abdullah 1, Rohana Yusof 2 1 Faculty of Computing, Universiti
Position-based Routing Protocols of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks & Applicability in Typical Road Situation Kashif Naseer Qureshi 1, Abdul Hanan Abdullah 1, Rohana Yusof 2 1 Faculty of Computing, Universiti
Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing
 Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs
 Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs A Viswanath, Dept of CSE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, AP, India. N Papanna, M.Tech, Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering
Survey on Multicast Routing Protocols in MANETs A Viswanath, Dept of CSE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, AP, India. N Papanna, M.Tech, Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering
Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet
 Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-323-328 ISSN: 2249-6645 Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet Jaya Jacob*, V.Seethalakshmi** *II MECS, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and
Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-323-328 ISSN: 2249-6645 Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet Jaya Jacob*, V.Seethalakshmi** *II MECS, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs
 Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
Enhanced Approach to Reduce Routing Overhead on VANET
 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 Special Issue SIEICON-2017,April -2017 e-issn : 2348-4470 p-issn : 2348-6406 Enhanced
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 Special Issue SIEICON-2017,April -2017 e-issn : 2348-4470 p-issn : 2348-6406 Enhanced
Enabling IP geomulticast services for vehicular networks
 Enabling IP geomulticast services for vehicular networks Alberto Gordillo, Maria Calderon, Carlos J. Bernardos E-mail: {alberto.gordillo, maria.calderon, carlosjesus.bernardos}@uc3m.es Universidad Carlos
Enabling IP geomulticast services for vehicular networks Alberto Gordillo, Maria Calderon, Carlos J. Bernardos E-mail: {alberto.gordillo, maria.calderon, carlosjesus.bernardos}@uc3m.es Universidad Carlos
Challenges in Geographic Routing: Sparse Networks, Obstacles, and Traffic Provisioning
 Challenges in Geographic Routing: Sparse Networks, Obstacles, and Traffic Provisioning Brad Karp Berkeley, CA bkarp@icsi.berkeley.edu DIMACS Pervasive Networking Workshop 2 May, 2 Motivating Examples Vast
Challenges in Geographic Routing: Sparse Networks, Obstacles, and Traffic Provisioning Brad Karp Berkeley, CA bkarp@icsi.berkeley.edu DIMACS Pervasive Networking Workshop 2 May, 2 Motivating Examples Vast
6367(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March April (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS
 COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS Deepa B 1 and Dr. S A Kulkarni 2 1 IV Sem M. Tech, Dept of CSE, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi deepa.bangarshetru@gmail.com
COOPERATIVE DATA SHARING WITH SECURITY IN VEHICULAR AD-HOC NETWORKS Deepa B 1 and Dr. S A Kulkarni 2 1 IV Sem M. Tech, Dept of CSE, KLS Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi deepa.bangarshetru@gmail.com
Efficient Hybrid Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks
 Efficient Hybrid Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Jayanta Biswas and Mukti Barai and S. K. Nandy CAD Lab, Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, 56, India {jayanta@cadl, mbarai@cadl,
Efficient Hybrid Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Jayanta Biswas and Mukti Barai and S. K. Nandy CAD Lab, Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, 56, India {jayanta@cadl, mbarai@cadl,
[Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675
![[Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675 [Shilpa R et al., 3(6): June, 2016] ISSN Impact Factor 2.675](/thumbs/82/86597446.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES A SURVEY ON ROUTING PERFORMANCE IN VANET Shilpa R*, Dr. B R Prasad Babu, Mr. Ravi Kumar M * M. Tech Student Dept. of CSE, R&D Centre EPCET,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES AND SCIENCES A SURVEY ON ROUTING PERFORMANCE IN VANET Shilpa R*, Dr. B R Prasad Babu, Mr. Ravi Kumar M * M. Tech Student Dept. of CSE, R&D Centre EPCET,
Performance of Various Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks-A Survey
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(22): 4181-4185, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: January 26, 2013 Accepted: March
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(22): 4181-4185, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: January 26, 2013 Accepted: March
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development. Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET Ravi Shrimali
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 Improved OLSR Protocol for VANET Ravi Shrimali
Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization
 Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization Dhanveer Kaur 1, Harwant Singh Arri 2 1 M.Tech, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
Enhancement of Routing in Urban Scenario using Link State Routing Protocol and Firefly Optimization Dhanveer Kaur 1, Harwant Singh Arri 2 1 M.Tech, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
15-441: Computer Networking. Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks
 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
Receiver Based Multicasting Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks
 Receiver Based Multicasting Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks Madesha M Assistant Professor, Department of CSE Sahyadri College of Engineering and Management Chaya D Lecturer, Department of CSE H.M.S
Receiver Based Multicasting Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks Madesha M Assistant Professor, Department of CSE Sahyadri College of Engineering and Management Chaya D Lecturer, Department of CSE H.M.S
A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET
 A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET Jeng-Wei Lee*, Chun-Chih Lo*, Shih-Pu Tang*, Mong-Fong Horng** and Yau-Hwang Kuo* * Department of Computer
A Hybrid Traffic Geographic Routing with Cooperative Traffic Information Collection Scheme in VANET Jeng-Wei Lee*, Chun-Chih Lo*, Shih-Pu Tang*, Mong-Fong Horng** and Yau-Hwang Kuo* * Department of Computer
Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets
 Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets Ms.Priyanka.G 1, Mr.Sundareswari.K 2 PG Scholar, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, Karpagam University,
Back-Bone Assisted Hop Greedy Routing in Vanets Ms.Priyanka.G 1, Mr.Sundareswari.K 2 PG Scholar, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, Karpagam University,
Avoiding Traffic Congestion Using Position Based Routing Protocol in VANET
 Avoiding Traffic Congestion Using Position Based Routing Protocol in VANET Ms. D. Jeya 1, Mr P. Ranjith Kumar 2, Mr G. Naresh kumar 3 (M.E) PG-Scholar, Department of Computer Science And Engineering, Sri
Avoiding Traffic Congestion Using Position Based Routing Protocol in VANET Ms. D. Jeya 1, Mr P. Ranjith Kumar 2, Mr G. Naresh kumar 3 (M.E) PG-Scholar, Department of Computer Science And Engineering, Sri
Performance Evaluation of Proactive and Reactive Protocols in VANET
 Performance Evaluation of Proactive and Reactive Protocols in VANET Uma Nagaraj and Poonam P. Dhamal Abstract VANET (Vehicular adhoc network) research field is growing very fast. It has to serves a wide
Performance Evaluation of Proactive and Reactive Protocols in VANET Uma Nagaraj and Poonam P. Dhamal Abstract VANET (Vehicular adhoc network) research field is growing very fast. It has to serves a wide
A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR
 A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR Shiva Prakash 1, Rajeev Kumar 2, Brijesh Nayak 3, Manindar Kumar Yadav 4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan Mohan
A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR Shiva Prakash 1, Rajeev Kumar 2, Brijesh Nayak 3, Manindar Kumar Yadav 4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan Mohan
2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Performance Evaluation of Ad Hoc Networking Protocol with QoS (Quality of Service)
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Dr. Ashikur Rahman CSE 6811: Wireless Ad hoc Networks
 Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
AParametericEstimationApproachtoforEffectiveClusterSelectioninWPAN
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: E Network, Web & Security Volume 14 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology: E Network, Web & Security Volume 14 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
International Journal of Information Movement. Website: ISSN: (online) Pages
 REVIEW: VANET ARCHITECTURES AND DESIGN Chetna Research Scholar Department Of Electronic & Communication Engg. Galaxy Global Group of Institutions, Dinarpur Saranjeet Singh Faculty Department of Electronic
REVIEW: VANET ARCHITECTURES AND DESIGN Chetna Research Scholar Department Of Electronic & Communication Engg. Galaxy Global Group of Institutions, Dinarpur Saranjeet Singh Faculty Department of Electronic
A Comparative study on Traditional Transport System and Intelligent Transport System
 A Comparative study on Traditional Transport and Intelligent Transport Irfan Ali Khan #1, Rizwan Khan *2, Ravi Shankar Shukla #3 # Department of Computer Science & Engineering, # Department of CS/IT Prem
A Comparative study on Traditional Transport and Intelligent Transport Irfan Ali Khan #1, Rizwan Khan *2, Ravi Shankar Shukla #3 # Department of Computer Science & Engineering, # Department of CS/IT Prem
An Efficient Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication protocol to avoid the congestion in VANETs.
 An Efficient Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication protocol to avoid the congestion in VANETs. kaveri G 1, Sujata M 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, GECW, Kalaburagi, India 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of ISE,
An Efficient Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication protocol to avoid the congestion in VANETs. kaveri G 1, Sujata M 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, GECW, Kalaburagi, India 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of ISE,
EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS
 EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS Nandhini P. 1 and Ravi G. 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Communication Systems, Sona College of
EFFICIENT TRAJECTORY PROTOCOL FOR MULTICASTING IN VEHICULAR AD HOC NETWORKS Nandhini P. 1 and Ravi G. 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Communication Systems, Sona College of
A Location-based Predictive Route Caching Scheme for Pure Reactive Zone-based Routing Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Abstract Introduction
 A Location-based Predictive Route Caching Scheme for Pure Reactive Zone-based Routing Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Weibo Chen 1, Kun Yang 1 and Xueqi Cheng 2 1. University of Essex, School of Computer
A Location-based Predictive Route Caching Scheme for Pure Reactive Zone-based Routing Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Weibo Chen 1, Kun Yang 1 and Xueqi Cheng 2 1. University of Essex, School of Computer
UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 TOPIC 8. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Routing TOPIC 8 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) Introduction
Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Routing TOPIC 8 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) Introduction
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET
 Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Abstract Keywords:
 Volume-9 Number-1 Jan -June 2017 pp. 16-21 available online at www.csjournalss.com Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Sachin Lalar, Arun Kumar Yadav
Volume-9 Number-1 Jan -June 2017 pp. 16-21 available online at www.csjournalss.com Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Sachin Lalar, Arun Kumar Yadav
A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks
 Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-4, February 10, 2012 A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks Padmavathi K Asst. Professor, Department
Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-4, February 10, 2012 A Surveying on Road Safety Using Vehicular Communication Networks Padmavathi K Asst. Professor, Department
Routing Protocols in MANETs
 Chapter 4 Routing Protocols in MANETs 4.1 Introduction The main aim of any Ad Hoc network routing protocol is to meet the challenges of the dynamically changing topology and establish a correct and an
Chapter 4 Routing Protocols in MANETs 4.1 Introduction The main aim of any Ad Hoc network routing protocol is to meet the challenges of the dynamically changing topology and establish a correct and an
Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 09 March 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET S.Bavani V.Aiswariya
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 09 March 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Packet Routing using Optimal Flooding Protocol in Cluster based MANET S.Bavani V.Aiswariya
Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OLSR Routing Protocol for VANET
 Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OL Routing Protocol for VANET Suhaib sheikh 1, Bhawna Sharma 2, Sunil Panjeta 3 1,2 Mtech scholar in electronics and communication engineering, YIET,
Performance Analysis of Optimization Techniques for OL Routing Protocol for VANET Suhaib sheikh 1, Bhawna Sharma 2, Sunil Panjeta 3 1,2 Mtech scholar in electronics and communication engineering, YIET,
Survey on Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast Routing Techniques in Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks Present and Future
 British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science 13(4): 1-26, 2016, Article no.bjmcs.22007 ISSN: 2231-0851 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Survey on Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science 13(4): 1-26, 2016, Article no.bjmcs.22007 ISSN: 2231-0851 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Survey on Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
icarii: Intersection-based Connectivity Aware Routing in Vehicular Networks
 icarii: Intersection-based Connectivity Aware Routing in Vehicular Networks Nizar Alsharif* and Xuemin (Sherman) Shen* *Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo
icarii: Intersection-based Connectivity Aware Routing in Vehicular Networks Nizar Alsharif* and Xuemin (Sherman) Shen* *Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo
Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths
 Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas
 Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas Shen Wan, Jian Tang and Richard S. Wolff Abstract The demands for vehicular Internet access are proliferating. Access Points (APs)
Reliable Routing for Roadside to Vehicle Communications in Rural Areas Shen Wan, Jian Tang and Richard S. Wolff Abstract The demands for vehicular Internet access are proliferating. Access Points (APs)
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh
 A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
MANET TECHNOLOGY. Keywords: MANET, Wireless Nodes, Ad-Hoc Network, Mobile Nodes, Routes Protocols.
 MANET TECHNOLOGY Dharna 1, Varsha Saroha 2, R. B. Dubey 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Hindu College of Engineering, Sonepat, Haryana,(India) ABSTRACT Wireless technology
MANET TECHNOLOGY Dharna 1, Varsha Saroha 2, R. B. Dubey 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Hindu College of Engineering, Sonepat, Haryana,(India) ABSTRACT Wireless technology
GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS
 GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS A.Robertsingh 1, Suganya A 2 1 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University, Krishnankoil, India 2 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University,
GLOBAL FRONTRUNNER ROUTING ALGORITHM (GFRA) FOR V2V COMMUNICATION IN VANETS A.Robertsingh 1, Suganya A 2 1 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University, Krishnankoil, India 2 Asst.Prof, CSE, Kalasalingam University,
Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks & Routing Algorithms
 Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks & Routing Algorithms EMMANOUIL G. SPANAKIS, PhD. spanakis@csd.uoc.gr COLLABORATING RESEARCHER, COMPUTATIONAL BIOMEDICINE LABORATORY, FORTH-ICS VISITING LECTURER, COMPUTER SCIENCE
Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks & Routing Algorithms EMMANOUIL G. SPANAKIS, PhD. spanakis@csd.uoc.gr COLLABORATING RESEARCHER, COMPUTATIONAL BIOMEDICINE LABORATORY, FORTH-ICS VISITING LECTURER, COMPUTER SCIENCE
