Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
|
|
|
- Claribel Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01
2 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2. Inter-domain routing 3. BGP 2
3 We have studied Intra-Domain Routing Domain 1 (e.g., UCL) host host DNS host host... DNS / router router router /24 Internet Domain: single organization, typically owning 100s routers 3
4 We now look at Inter-Domain Routing Domain 1 (e.g., UCL) Domain 2 (e.g., JANET) Domain 3 (e.g., Cambridge) 4
5 in the Big Internet Domain 10 (e.g., GEANT) Domain 172 (e.g., Internet2) Domain 2 (e.g., JANET) Domain 1 (e.g., UCL) Domain 3 (e.g., Cambridge) Domain 564 (e.g., CENIC) Domain 1771 (e.g., Berkeley) 5
6 in the Big Internet Domain 10 (e.g., GEANT) Domain 172 (e.g., Internet2) About Domain 60,000 2 Ases on (e.g., Dec JANET) 5 th, 2017 (see cidr-report.org) Domain 1 (e.g., UCL) Domain 3 (e.g., Cambridge) Domain 564 (e.g., CENIC) Domain 1771 (e.g., Berkeley) 6
7 Domains == Autonomous Systems In inter-domain routing, a domain is also called Autonomous System (AS) Each AS known by unique 32-bit number used to be 16 bits, but expanded in 2006 AS owns one or a handful of address prefixes assigned by Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) RIPE, ARIN, LACNIC, APNIC, AFRINIC overseen by IANA 7
8 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2. Inter-domain routing 3. BGP 8
9
10 Global Internet Routing: Naïve View Shared, densely connected infrastructure ASes cooperate to find globally optimal paths e.g., globally shortest and lightly loaded paths No correspondence to reality! 10
11 Global Internet Routing: Socialist Style Multiple, interconnected Internet Service Providers (ISPs) ISPs all equal: in connectivity and network extent Little correspondence to reality! 11
12 Global Internet Routing: Capitalist Style Tiers of ISPs: Tier 3: local ISPs Tier 2: regional ISPs Tier 1: worldwide ISPs Some relation to reality! ISPs are business entities Routing follows money, per-as policies 12
13 AS Relationships Basic connectivity model: customer-provider Customer: smaller AS paying for connectivity (e.g., corporations, universities) Provider: larger AS being paid for connectivity (e.g., regional ISPs) Alternative: peering Two ASes mutually forward their own traffic, but there is no exchange of money 13
14 AS Relationship: Customer-Provider Provider allow customer to route to (nearly) all destinations in its routing tables It provides transit to customer s traffic Transit nearly always involves payment from customer to provider 14
15 AS Relationship: Peering Two ASes mutually allow one another to route to some destinations usually, ISPs peer for customers destinations Contractual agreement, but usually no money changes hands as long as traffic ratio is narrower than, e.g., 4:1 15
16 Incentives to Peer Typically, two ISPs notice their own direct customers originate a lot of traffic for the other Peering ISPs avoids paying transit costs to providers for this traffic; shunt it directly to one another Often better performance (shorter latency, lower loss rate) as avoid transit via another provider Easier than attracting one another s customers Note: Tier 1s must typically peer with one another to build complete, global routing tables 16
17 Disincentives to Peer Yet, ISPs compete with each other Peering doesn t let ISPs charge anybody Transit traffic enables to charge customers Peering contracts must be renegotiated often Peers need to agree on how to handle asymmetric traffic loads between them Nobody really knows if and how traffic patterns will change after peering 17
18 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context 2. Inter-domain routing Goals Basic scheme 3. BGP 18
19 Inter-Domain Routing: Goals Scalability Each Internet host must have unique IP address Internet hosts are millions (potentially, trillions?) Onerous / impractical to consult central authority for each new host 19
20 Internet Address Allocation is Hierarchical Routers keep track IP prefixes Divide 32-bit IP address hierarchically e.g., is a host at UCL e.g., /24 prefix is UCL CS dept e.g., /16 prefix is all of UCL 20
21 Hierarchical Addressing: Pros Reduction of number of destinations in global Internet routing system Outside UCL, single prefix /16 can represent thousands of hosts on UCL network Decentralized allocation of unique addresses Inside UCL, local authority can allocate low-order 16 bits of host IP addresses under prefix Based on the intuition that centralized address allocation is easier for smaller user/host population 21
22 Hierarchical Addressing: Cons Inherent loss of information from global routing protocol; implies less optimal routes External ASes know nothing about UCL s addresses: all traffic via London if UCL has host in Antarctica Host addresses indicate both host identity and network attachment point Suppose I move my UCL laptop to Berkeley: IP address must change, so it aggregates under Berkeley IP prefix! 22
23 Inter-Domain Routing: Goals Scalability in number of ASes and prefixes Yet, 60k ASes and 700k announced prefixes 23
24 Inter-Domain Routing: Goals Scalability in number of ASes and prefixes Yet, 60k ASes and 700k announced prefixes Enforcing policies, not optimality! ASes are competitors, and routing must reflect commercial agreements We need cooperation under competitive pressure BGP designed to run on successor to NSFnet, the former single, government-run backbone 24
25 Intra-Domain Protocols aren t appropriate Insufficient scalability DV and LS cannot scale to Internet routing prohibitive message complexity for LS flooding loops and slow convergence for DV No support for policies DV and LS compute shortest paths How to reflect commercial agreements? 25
26 Hence, BGP... New goals raise the need for a new protocol BGP is the de-facto inter-domain routing protocol It allows to route between ASes, with policies BGP is complementary to LS and DV protocols BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), as it runs between ASes LS and DV are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs), since they run among subnets inside a single AS 26
27 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context 2. Inter-domain routing Goals Basic scheme 3. BGP 27
28 Inter-domain Routing Principles ASes exchange coarse-grained information At a per-as level rather than at a per-router one Scalable, support Internet business model competition à information hiding Each AS implements autonomous routing choices Custom route selection Custom route filtering 28
29 Routes are Offers to Carry Traffic AS A can offer to forward traffic from AS B to a destination D A advertises to B a route for destination D Forwarding traffic has a cost bandwidth, network resources, etc. Routes reflect economic agreement between ASes e.g., B pays A for the forwarded traffic 29
30 ASes Autonomously Select Routes Each AS selects one among the many routes received for the same destination e.g., routers may hear a different route from each neighbouring AS In route selection, the identity of advertiser is key ASes are profit-driven Customer traffic is remunerative, peering traffic is neutral and provider traffic is a cost Customer routes > peer routes > provider routes 30
31 ASes Filter Routes ASes import only some routes from neighbours Strongly motivated to control which routes to avoid e.g., don t carry traffic for a provider (for free) But also export only some routes to neighbours e.g., only let peering AS send to specific customer destinations enumerated peering contract Note: only selected routes are exported! 31
32 Routes Heard from Customers An ISP is motivated to advertise routes to reach its own customers to everybody Customers pay to be reachable from global Internet More traffic à customer will buy a faster link If an ISP hears route for its own customer from multiple neighbours, it should favour advertisement from its own customer 32
33 Routes Heard from Providers If ISP hears routes from its provider (via a transit relationship), it passes them to customers only Customers pay to reach global Internet Not to peers or providers: they don t pay, so no motivation to provide transit service for them! 33
34 Example: Routes Heard from Providers ISP P announces route to C P, own customer, to X X doesn t announce C P to Y or Z; no revenue from peering X announces C P to C i ; they re paying to be able to reach everywhere 34
35 Routes Advertised to Peers Which routes should an ISP advertise to ASes with whom it has peering relationships? Routes to ISP s own addresses Routes for all own downstream customers Not routes heard from upstream transit providers, which don t pay Not routes heard from other peerings: don t pay 35
36 Example: Routes Advertised to Peers ISP X announces C i to Y and Z ISP X doesn t announce routes heard from ISP P to Y or Z ISP X doesn t announce routes heard from ISP Y to ISP Z, or vice-versa 36
37 Route Filtering: Summary ISPs typically provide selective transit Full transit (export of all routes) for own customers in both directions Some transit (export of routes between mutual customers) across peering relationship Customer-only transit (export of routes to customers) for providers Route advertisements are based on policies (money), not optimality (e.g., shortest paths) 37
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 3035/GZ01 4 th December 2014 Outline Context: Inter-Domain Routing
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 3035/GZ01 4 th December 2014 Outline Context: Inter-Domain Routing
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2.
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2.
Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing. CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage
 Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Overview Autonomous Systems Each network on the Internet has its own goals Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed route selection
Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Overview Autonomous Systems Each network on the Internet has its own goals Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed route selection
Routing on the Internet. Routing on the Internet. Hierarchical Routing. Computer Networks. Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP
 Routing on the Internet Computer Networks Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP In the beginning there was the ARPANET: route using GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol), a distance vector routing protocol
Routing on the Internet Computer Networks Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP In the beginning there was the ARPANET: route using GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol), a distance vector routing protocol
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II Mark Handley UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 BGP Protocol (cont d) BGP doesn t chiefly aim to compute shortest paths (or minimize other metric, as do DV, LS) Chief purpose
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II Mark Handley UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 BGP Protocol (cont d) BGP doesn t chiefly aim to compute shortest paths (or minimize other metric, as do DV, LS) Chief purpose
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 05/GZ01 4 th December 2014 BGP Protocol (cont d) BGP doesn t
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP II Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 05/GZ01 4 th December 2014 BGP Protocol (cont d) BGP doesn t
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017
 CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 11. Inter-domain Routing. This Lecture. Structure of the Internet. Focus How do we make routing scale?
 CSE/EE 461 Lecture 11 Inter-domain Routing This Lecture Focus How do we make routing scale? Inter-domain routing ASes and BGP Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical sdg //
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 11 Inter-domain Routing This Lecture Focus How do we make routing scale? Inter-domain routing ASes and BGP Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical sdg //
CS 43: Computer Networks. 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol
 Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 3 due Wednesday Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman & Craig Labovitz Lecture 18 Overview Path-vector Routing Allows scalable,
Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 3 due Wednesday Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman & Craig Labovitz Lecture 18 Overview Path-vector Routing Allows scalable,
CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks. Intra-domain routing. Inter-domain Routing: Hierarchy. Aditya Akella
 CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks Aditya Akella Lecture 11 - Inter-Domain Routing - BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Intra-domain routing The Story So Far Routing protocols generate the forwarding
CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks Aditya Akella Lecture 11 - Inter-Domain Routing - BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Intra-domain routing The Story So Far Routing protocols generate the forwarding
Inter-domain Routing. Outline. Border Gateway Protocol
 Inter-domain Routing Outline Border Gateway Protocol Internet Structure Original idea CS 640 2 Internet Structure Today CS 640 3 Route Propagation in the Internet Autonomous System (AS) corresponds to
Inter-domain Routing Outline Border Gateway Protocol Internet Structure Original idea CS 640 2 Internet Structure Today CS 640 3 Route Propagation in the Internet Autonomous System (AS) corresponds to
CS 457 Networking and the Internet. The Global Internet (Then) The Global Internet (And Now) 10/4/16. Fall 2016
 CS 457 Networking and the Internet Fall 2016 The Global Internet (Then) The tree structure of the Internet in 1990 The Global Internet (And Now) A simple multi-provider Internet 1 The Global Internet Some
CS 457 Networking and the Internet Fall 2016 The Global Internet (Then) The tree structure of the Internet in 1990 The Global Internet (And Now) A simple multi-provider Internet 1 The Global Internet Some
Routing Concepts. IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols
 Routing Basics 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 Addresses are 32 bits long Range from 1.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
Routing Basics 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 Addresses are 32 bits long Range from 1.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Chair for Network Architectures and
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Chair for Network Architectures and
CS BGP v4. Fall 2014
 CS 457 - BGP v4 Fall 2014 Autonomous Systems What is an AS? a set of routers under a single technical administration uses an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and common metrics to route packets within the
CS 457 - BGP v4 Fall 2014 Autonomous Systems What is an AS? a set of routers under a single technical administration uses an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and common metrics to route packets within the
IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing. Next Topic
 IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing Next Topic IP Addressing Hierarchy (prefixes, class A, B, C, subnets) Interdomain routing Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Scalability
IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing Next Topic IP Addressing Hierarchy (prefixes, class A, B, C, subnets) Interdomain routing Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Scalability
CSE 461 Interdomain routing. David Wetherall
 CSE 461 Interdomain routing David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Interdomain routing Focus: Routing across internetworks made up of different parties Route scaling Application Route policy Transport The
CSE 461 Interdomain routing David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Interdomain routing Focus: Routing across internetworks made up of different parties Route scaling Application Route policy Transport The
Internet Routing : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Internet Routing 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Looking Ahead Lab #2 just due Quiz #2
Internet Routing 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Looking Ahead Lab #2 just due Quiz #2
Important Lessons From Last Lecture Computer Networking. Outline. Routing Review. Routing hierarchy. Internet structure. External BGP (E-BGP)
 Important Lessons From Last Lecture 15-441 Computer Networking Inter-Domain outing BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Every router needs to be able to forward towards any destination Forwarding table must be
Important Lessons From Last Lecture 15-441 Computer Networking Inter-Domain outing BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Every router needs to be able to forward towards any destination Forwarding table must be
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 3103: Compute Networks and Protocols Inter-Domain Routing Internet is a network of networks Hierarchy
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 3103: Compute Networks and Protocols Inter-Domain Routing Internet is a network of networks Hierarchy
Lecture 17: Border Gateway Protocol
 Lecture 17: Border Gateway Protocol CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 18 Overview Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) The canonical path vector protocol How
Lecture 17: Border Gateway Protocol CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 18 Overview Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) The canonical path vector protocol How
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 01 & 02
 Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 01 & 02 Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2010 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Internet Routing Outline Lecture 1 : Inter-domain routing architecture, the
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 01 & 02 Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2010 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Internet Routing Outline Lecture 1 : Inter-domain routing architecture, the
TELE 301 Network Management
 TELE 301 Network Management Lecture 24: Exterior Routing and BGP Haibo Zhang Computer Science, University of Otago TELE301 Lecture 16: Remote Terminal Services 1 Today s Focus How routing between different
TELE 301 Network Management Lecture 24: Exterior Routing and BGP Haibo Zhang Computer Science, University of Otago TELE301 Lecture 16: Remote Terminal Services 1 Today s Focus How routing between different
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Routing Basics. ISP Workshops. Last updated 10 th December 2015
 Routing Basics ISP Workshops Last updated 10 th December 2015 1 Routing Concepts p IPv4 & IPv6 p Routing p Forwarding p Some definitions p Policy options p Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 p Internet still uses
Routing Basics ISP Workshops Last updated 10 th December 2015 1 Routing Concepts p IPv4 & IPv6 p Routing p Forwarding p Some definitions p Policy options p Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 p Internet still uses
Outline Computer Networking. Inter and Intra-Domain Routing. Internet s Area Hierarchy Routing hierarchy. Internet structure
 Outline 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 10: Inter-Domain outing Border Gateway Protocol -BGP Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 outing hierarchy Internet structure
Outline 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 10: Inter-Domain outing Border Gateway Protocol -BGP Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 outing hierarchy Internet structure
BGP. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
CS 204: BGP. Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences
 CS 204: BGP Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Overview AS relationships Inter-AS routing BGP Example Paper discussion
CS 204: BGP Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Overview AS relationships Inter-AS routing BGP Example Paper discussion
COMP/ELEC 429 Introduction to Computer Networks
 COMP/ELEC 429 Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture 11: Inter-domain routing Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang T. S. Eugene Ng eugeneng at
COMP/ELEC 429 Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture 11: Inter-domain routing Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang T. S. Eugene Ng eugeneng at
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks
 CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Lecture 12: Inter-domain routing Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove at ccs.neu.edu
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Lecture 12: Inter-domain routing Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove at ccs.neu.edu
CS519: Computer Networks. Lecture 4, Part 5: Mar 1, 2004 Internet Routing:
 : Computer Networks Lecture 4, Part 5: Mar 1, 2004 Internet Routing: AS s, igp, and BGP As we said earlier, the Internet is composed of Autonomous Systems (ASs) Where each AS is a set of routers, links,
: Computer Networks Lecture 4, Part 5: Mar 1, 2004 Internet Routing: AS s, igp, and BGP As we said earlier, the Internet is composed of Autonomous Systems (ASs) Where each AS is a set of routers, links,
CMSC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala October 9, 2018 (a) October 18 October 9,
 CMSC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala October 9, 2018 (a) October 18 October 9, 2018 1 host Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment
CMSC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala October 9, 2018 (a) October 18 October 9, 2018 1 host Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment
EECS 122, Lecture 17. The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) Optimization Criteria. DUAL Data Structures. Selecting Among Neighbors.
 EECS 122, Lecture 17 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) J.J. Garcia-Luna Luna-Aceves [SIGCOMM 89] Aims at removing transient loops in both DV and LS routing protocols
EECS 122, Lecture 17 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) J.J. Garcia-Luna Luna-Aceves [SIGCOMM 89] Aims at removing transient loops in both DV and LS routing protocols
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops
 Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer)
 Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
Inter-AS routing. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley
 Inter-AS routing Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley Some materials copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Chapter 4:
Inter-AS routing Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley Some materials copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Chapter 4:
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013
 CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013 1 Reading Quiz Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 14, 2013 1 Reading Quiz Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat
How the Internet works? The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
 Chair of Network Architectures and Services - Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science Technical University of Munich How the Internet works? The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Edwin Cordeiro ilab2 Lecture
Chair of Network Architectures and Services - Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science Technical University of Munich How the Internet works? The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Edwin Cordeiro ilab2 Lecture
Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing
 Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing CS640, 2015-02-26 Announcements Assignment #2 is due Tuesday Overview Link state routing Internet structure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Path vector routing Inter
Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing CS640, 2015-02-26 Announcements Assignment #2 is due Tuesday Overview Link state routing Internet structure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Path vector routing Inter
CS4450. Computer Networks: Architecture and Protocols. Lecture 15 BGP. Spring 2018 Rachit Agarwal
 CS4450 Computer Networks: Architecture and Protocols Lecture 15 BGP Spring 2018 Rachit Agarwal Autonomous System (AS) or Domain Region of a network under a single administrative entity Border Routers Interior
CS4450 Computer Networks: Architecture and Protocols Lecture 15 BGP Spring 2018 Rachit Agarwal Autonomous System (AS) or Domain Region of a network under a single administrative entity Border Routers Interior
Routing Basics. Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop
 Routing Basics Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Routing Basics Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Routing Basics. Routing Concepts. IPv4. IPv4 address format. A day in a life of a router. What does a router do? IPv4 Routing
 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 1 2 IPv4 IPv4 address format Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range
Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 1 2 IPv4 IPv4 address format Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing
 Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Autonomous Routing Domains A collection of physical networks
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Autonomous Routing Domains A collection of physical networks
Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011
 Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Overview Business relationships between ASes Interdomain routing using BGP Advertisements Routing policy Integration with intradomain routing
Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Overview Business relationships between ASes Interdomain routing using BGP Advertisements Routing policy Integration with intradomain routing
CSC458 Lecture 6. Administrivia. Inter-domain Routing IP Addressing. Midterm will Cover Following Topics (2) Midterm will Cover Following Topics
 CSC458 Lecture 6 Inter-domain Routing IP Addressing Administrivia Homework: #2 due today #3 out today, due in two weeks (same date as midterm) No lecture next week Reading Week Midterm in two weeks 60
CSC458 Lecture 6 Inter-domain Routing IP Addressing Administrivia Homework: #2 due today #3 out today, due in two weeks (same date as midterm) No lecture next week Reading Week Midterm in two weeks 60
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops
 Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet
 Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F
Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F
Introduction to The Internet
 Introduction to The Internet ITU/APNIC/MICT IPv6 Security Workshop 23 rd 27 th May 2016 Bangkok Last updated 5 th May 2015 1 Introduction to the Internet p Topologies and Definitions p IP Addressing p
Introduction to The Internet ITU/APNIC/MICT IPv6 Security Workshop 23 rd 27 th May 2016 Bangkok Last updated 5 th May 2015 1 Introduction to the Internet p Topologies and Definitions p IP Addressing p
Routing Basics. ISP Workshops
 Routing Basics ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated 26
Routing Basics ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated 26
Introduction to The Internet
 Introduction to The Internet ITU/APNIC/MOIC IPv6 Workshop 19 th 21 st June 2017 Thimphu These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Introduction to The Internet ITU/APNIC/MOIC IPv6 Workshop 19 th 21 st June 2017 Thimphu These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
CSE 561 Lecture 6, Spring David Wetherall
 Inter-domain Routing CSE 561 Lecture 6, Spring 2002. David Wetherall Overview Inter-domain routing BGP mechanics of route selection ISP policy considerations Traffic engineering Intra-ISP: ARPANET dynamic
Inter-domain Routing CSE 561 Lecture 6, Spring 2002. David Wetherall Overview Inter-domain routing BGP mechanics of route selection ISP policy considerations Traffic engineering Intra-ISP: ARPANET dynamic
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing.! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway Protocol! Route aggregation
 ! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
BGP Case Studies. ISP Workshops
 BGP Case Studies ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
BGP Case Studies ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
Introduction to exterior routing. Autonomous Systems
 Introduction to exterior routing CIDR1 Autonomous Systems An Autonomous System (AS) is a part of the Internet owned by a single organization. In an AS, usually one interior routing protocol is used e.g.
Introduction to exterior routing CIDR1 Autonomous Systems An Autonomous System (AS) is a part of the Internet owned by a single organization. In an AS, usually one interior routing protocol is used e.g.
Last time. Transitioning to IPv6. Routing. Tunneling. Gateways. Graph abstraction. Link-state routing. Distance-vector routing. Dijkstra's Algorithm
 Last time Transitioning to IPv6 Tunneling Gateways Routing Graph abstraction Link-state routing Dijkstra's Algorithm Distance-vector routing Bellman-Ford Equation 10-1 This time Distance vector link cost
Last time Transitioning to IPv6 Tunneling Gateways Routing Graph abstraction Link-state routing Dijkstra's Algorithm Distance-vector routing Bellman-Ford Equation 10-1 This time Distance vector link cost
Network Layer (Routing)
 Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing
 Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing Nick Feamster, Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs -- Research The state of interdomain
Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing Nick Feamster, Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs -- Research The state of interdomain
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing
 Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline Continued from previous lecture on: Distance vector routing Link state routing IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol, Exterior
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline Continued from previous lecture on: Distance vector routing Link state routing IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol, Exterior
BGP Protocol & Configuration. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008
 BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
Lecture 4: Intradomain Routing. CS 598: Advanced Internetworking Matthew Caesar February 1, 2011
 Lecture 4: Intradomain Routing CS 598: Advanced Internetworking Matthew Caesar February 1, 011 1 Robert. How can routers find paths? Robert s local DNS server 10.1.8.7 A 10.1.0.0/16 10.1.0.1 Routing Table
Lecture 4: Intradomain Routing CS 598: Advanced Internetworking Matthew Caesar February 1, 011 1 Robert. How can routers find paths? Robert s local DNS server 10.1.8.7 A 10.1.0.0/16 10.1.0.1 Routing Table
Introduction to Networking. Topologies and Definitions. Network Topology and Definitions. Some Icons. Network Topologies. Network Topologies
 Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Introduction to Networking Interconnections and s ISP/ IP Addressing Gluing it all together 1 2 Some Icons Router
Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Introduction to Networking Interconnections and s ISP/ IP Addressing Gluing it all together 1 2 Some Icons Router
Basic Idea. Routing. Example. Routing by the Network
 Basic Idea Routing Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Basic Idea Routing Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing
 Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Continued from previous lecture on:! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol,
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Continued from previous lecture on:! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol,
Back to basics J. Addressing is the key! Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Transport. Transport (TCP/UDP) Internet (IPv4/IPv6)
 Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
Dynamic Routing. The Protocols
 Dynamic Routing The Protocols Desirable Characteristics of Dynamic Routing Automatically detect and adapt to topology changes Provide optimal routing Scalability Robustness Simplicity Rapid convergence
Dynamic Routing The Protocols Desirable Characteristics of Dynamic Routing Automatically detect and adapt to topology changes Provide optimal routing Scalability Robustness Simplicity Rapid convergence
Routing by the Network
 Routing Basic Idea Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Routing Basic Idea Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing
 Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol!
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol!
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan. Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri
 Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Internet structure: network of networks local ISP Tier
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Internet structure: network of networks local ISP Tier
Internet Routing Protocols, DHCP, and NAT
 Internet Routing Protocols, DHCP, and NAT Hwajung Lee Modified from Slides Courtesy of Cisco Networking Academy and the book titled Communication Networks by Leon-Garcia Contents Basic Routing Single Area
Internet Routing Protocols, DHCP, and NAT Hwajung Lee Modified from Slides Courtesy of Cisco Networking Academy and the book titled Communication Networks by Leon-Garcia Contents Basic Routing Single Area
Routing in the Internet
 Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops
 BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure, carrier failure)
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure, carrier failure)
BGP101. Howard C. Berkowitz. (703)
 BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
CS 268: Computer Networking. Next Lecture: Interdomain Routing
 CS 268: Computer Networking L-3 BGP Next Lecture: Interdomain Routing BGP Assigned Reading MIT BGP Class Notes [Gao00] On Inferring Autonomous System Relationships in the Internet 2 Outline Need for hierarchical
CS 268: Computer Networking L-3 BGP Next Lecture: Interdomain Routing BGP Assigned Reading MIT BGP Class Notes [Gao00] On Inferring Autonomous System Relationships in the Internet 2 Outline Need for hierarchical
BGP Multihoming. ISP/IXP Workshops
 BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
Introduction to IP Routing. Geoff Huston
 Introduction to IP Routing Geoff Huston Routing How do packets get from A to B in the Internet? A Internet B Connectionless Forwarding Each router (switch) makes a LOCAL decision to forward the packet
Introduction to IP Routing Geoff Huston Routing How do packets get from A to B in the Internet? A Internet B Connectionless Forwarding Each router (switch) makes a LOCAL decision to forward the packet
What is an Internet exchange Point (IXP)?
 What is an IXP? What is an Internet exchange Point (IXP)? The Internet is an interconnection of networks Each controlled by separate entities Generally called Internet Service Providers (ISPs) Grouped
What is an IXP? What is an Internet exchange Point (IXP)? The Internet is an interconnection of networks Each controlled by separate entities Generally called Internet Service Providers (ISPs) Grouped
Module 14 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
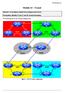 ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
Internetworking: Global Internet and MPLS. Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806
 Internetworking: Global Internet and MPLS Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 10/19/2016 CSCI 445 Fall 2016 1 Acknowledgements Some pictures
Internetworking: Global Internet and MPLS Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 10/19/2016 CSCI 445 Fall 2016 1 Acknowledgements Some pictures
Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation:
 IPv6 Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation: header format helps speed processing/forwarding header changes to facilitate QoS IPv6 datagram format:
IPv6 Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation: header format helps speed processing/forwarding header changes to facilitate QoS IPv6 datagram format:
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016 Lecture 13 Router Algorithms and Design Chapter 5 1 Topics Router Algorithms Routing in General Hierarchical routing Interior Gateway Protocols OSPF mention of
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networks Spring 2016 Lecture 13 Router Algorithms and Design Chapter 5 1 Topics Router Algorithms Routing in General Hierarchical routing Interior Gateway Protocols OSPF mention of
Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections P&D 4.3.{3,4}
 Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections P&D 4.3.{3,4} EE122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2006 (MW 4:00-5:30 in Donner 155) Vern Paxson TAs: Dilip Antony Joseph and Sukun Kim http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/
Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections P&D 4.3.{3,4} EE122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2006 (MW 4:00-5:30 in Donner 155) Vern Paxson TAs: Dilip Antony Joseph and Sukun Kim http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/
3/10/2011. Copyright Link Technologies, Inc.
 Mikrotik Certified Trainer / Engineer MikroTik Certified Dude Consultant Consulting Since 1997 Enterprise Class Networks WAN Connectivity Certifications Cisco, Microsoft, MikroTik BGP/OSPF Experience Deployed
Mikrotik Certified Trainer / Engineer MikroTik Certified Dude Consultant Consulting Since 1997 Enterprise Class Networks WAN Connectivity Certifications Cisco, Microsoft, MikroTik BGP/OSPF Experience Deployed
EECS 122, Lecture 16. Link Costs and Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Static Cost Metrics.
 EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
PART III. Implementing Inter-Network Relationships with BGP
 PART III Implementing Inter-Network Relationships with BGP ICNP 2002 Routing Protocols Autonomous System BGP-4 BGP = Border Gateway Protocol Is a Policy-Based routing protocol Is the de facto EGP of today
PART III Implementing Inter-Network Relationships with BGP ICNP 2002 Routing Protocols Autonomous System BGP-4 BGP = Border Gateway Protocol Is a Policy-Based routing protocol Is the de facto EGP of today
Networking 101 ISP/IXP Workshops
 Networking 101 ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Interconnections and IXPs IP Addressing Gluing it all together 2 Topologies and
Networking 101 ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Interconnections and IXPs IP Addressing Gluing it all together 2 Topologies and
Route Filtering. Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes. Downstream customers Internet prefixes
 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
Chapter IV: Network Layer
 Chapter IV: Network Layer UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Myungjin Lee myungjin.lee@ed.ac.uk Slides copyright of Kurose and Ross Hierarchical routing our routing study thus far - idealization
Chapter IV: Network Layer UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Myungjin Lee myungjin.lee@ed.ac.uk Slides copyright of Kurose and Ross Hierarchical routing our routing study thus far - idealization
EE 122: Inter-domain routing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
 EE 122: Inter-domain routing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Ion Stoica October 2, 2002 (* this presentation is based on Lakshmi Subramanian s slides) Big Picture Large ISP Large ISP St u b D i al - U p
EE 122: Inter-domain routing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Ion Stoica October 2, 2002 (* this presentation is based on Lakshmi Subramanian s slides) Big Picture Large ISP Large ISP St u b D i al - U p
Service Provider Multihoming
 BGP Traffic Engineering Previous examples dealt with loadsharing inbound traffic Of primary concern at Internet edge What about outbound traffic? Transit ISPs strive to balance traffic flows in both directions
BGP Traffic Engineering Previous examples dealt with loadsharing inbound traffic Of primary concern at Internet edge What about outbound traffic? Transit ISPs strive to balance traffic flows in both directions
Route Filtering. Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes. Downstream customers Internet prefixes
 1 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes 2 Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
1 Types of prefixes in IP core network: Internal Prefixes External prefixes Downstream customers Internet prefixes 2 Internal prefixes originated in IP core network Loopback Transport Connect inter-regional
Routing Basics. SANOG July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA
 Routing Basics SANOG 30 14-18 July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E
Routing Basics SANOG 30 14-18 July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E
Inter-AS routing and BGP. Network Layer 4-1
 Inter-AS routing and BGP Network Layer 4-1 Review: intra-as routing v Also known as interior gateway protocols (IGP) v Most common intra-as routing protocols: RIP: Routing Information Protocol, distance
Inter-AS routing and BGP Network Layer 4-1 Review: intra-as routing v Also known as interior gateway protocols (IGP) v Most common intra-as routing protocols: RIP: Routing Information Protocol, distance
Unicast Routing. TCP/IP class
 Unicast Routing TCP/IP class Routing Protocols intro RIP and son of RIP OSPF BGP odd bodkins NAT TCP/IP Internetworking Protocols 2 divide routing world into 3 parts topology IETF ISO/OSI same link or
Unicast Routing TCP/IP class Routing Protocols intro RIP and son of RIP OSPF BGP odd bodkins NAT TCP/IP Internetworking Protocols 2 divide routing world into 3 parts topology IETF ISO/OSI same link or
Internet Measurements. Motivation
 Internet Measurements Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2004 Motivation Types of measurements Understand the topology of the Internet Measure performance characteristics Tools: BGP Tables Traceroute measurements
Internet Measurements Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2004 Motivation Types of measurements Understand the topology of the Internet Measure performance characteristics Tools: BGP Tables Traceroute measurements
Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections K&R EE122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2007 (WF 4:00-5:30 in Cory 277)
 Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections K&R 4.6.3 EE122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2007 (WF 4:00-5:30 in Cory 277) Guest Lecture by Brighten Godfrey Instructor: Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel
Interdomain Routing Reading: Sections K&R 4.6.3 EE122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2007 (WF 4:00-5:30 in Cory 277) Guest Lecture by Brighten Godfrey Instructor: Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel
6.829 BGP Recitation. Rob Beverly September 29, Addressing and Assignment
 6.829 BGP Recitation Rob Beverly September 29, 2006 Addressing and Assignment 1 Area-Routing Review Why does Internet Scale? Hierarchical Addressing How are addresses assigned? Classfull
6.829 BGP Recitation Rob Beverly September 29, 2006 Addressing and Assignment 1 Area-Routing Review Why does Internet Scale? Hierarchical Addressing How are addresses assigned? Classfull
Routing. Jens A Andersson Communication Systems
 Routing Jens A Andersson Communication Systems R1 Choosing an Optimal Path R4 5 R7 5 10 40 R6 6 5 B R2 15 A 20 4 10 10 R8 R3 5 R5 10 Router A router is a type of internetworking device that passes data
Routing Jens A Andersson Communication Systems R1 Choosing an Optimal Path R4 5 R7 5 10 40 R6 6 5 B R2 15 A 20 4 10 10 R8 R3 5 R5 10 Router A router is a type of internetworking device that passes data
Life After IPv4 Depletion
 1 Life After IPv4 Depletion Jon Worley Analyst Securing Core Internet Functions Resource Certification, RPKI Mark Kosters Chief Technology Officer 2 Core Internet Functions: Routing & DNS The Internet
1 Life After IPv4 Depletion Jon Worley Analyst Securing Core Internet Functions Resource Certification, RPKI Mark Kosters Chief Technology Officer 2 Core Internet Functions: Routing & DNS The Internet
