Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 15 Prof. Patrick Crowley
|
|
|
- Joleen Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 15 Prof. Patrick Crowley
2 Plan for Today Announcements PM2 due today Design presentations due Nov 4 Questions Today s discussion: Memory Hierarchy Basics
3 Design Presentations, Nov 4 Your presentation should clearly describe your processor and the design choices you made in PM1 & 2 Presentation logistics Limit your presentation to 10 minutes, and expect 5 mins of questions. Be sure that all group members contribute to the presentation. Send a copy of your PPT presentation to Shakir before class You are free to use your own laptop for the presentation. If you prefer to use Prof. Crowley s laptop, you must submit your slides via by 3pm or bring a copy on a USB memory stick. Also, before class, upload 10-minute screencast version (see next)
4 Project Design Screencast For at least two reasons, you will create 10 min screencasts of your design presentations 1. Use SnagIt (or another tool). My demo: 2. Upload the video to youtube.com 3. Post the link on the course discussion page
5 Project Logistics Groups of three Project Timeline Task Due Description Three major deadlines Design due Oct 19 Project Demo Nov 23 Project Milestone 1 Project Milestone 2 Oct 19 Nov 2 Processor Design Detailed Design & VHDL Report due Dec 7 Design Presentations Nov 4 Presentation of detailed design This week: PM2 due, design presentations Project Demo Final Report Nov 23 Dec 7 Demo working VHDL model Final report due
6 Project Groups Group 1 David Lu Michael Schultz Austin Abrams 2 Yong Fu Greg Galloway Christopher Thomas 3 Timothy York Haowei Yuan Stephen Schuh 4 Yu-Ying Liang Abu Sayeed Saifullah Raphael Njuguna 5 Cory Flanagin Jessica Schupp
7 Importance of Memory Performance
8 Memory Hierarchy Registers: visible to ISA and renamed by hardware (Hierarchy of) Caches: plus their enhancements Write buffers, victim caches, prefetch/stream buffers, etc. TLBs and their management Virtual memory system (O.S. level) and hardware assists Main memory Disks Remote memory Based on principle of locality
9 Illustrated Hierarchy
10 Questions that arise at each level What is the unit of information transferred from level to level? word, block, page table entry, page Where is that unit of info placed? directed by ISA, restricted mapping, general mapping How do we find if that unit of info is present? depends on the mapping What happens if there is no room for it? structural hazard, replacement algorithm What happens when we change the contents of the info unit? i.e., what happens on a write?
11 Caches (on-chip, off-chip) Caches consist of a set of entries where each entry has A block (or line) of data: some subset of memory content A tag: allows us to recognize if the desired block is present Status bits: valid, dirty, status for multiprocessors, etc. Capacity (or size) of a cache Number of blocks * block size
12 Cache Organization Most restricted mapping Direct-mapped cache. A given memory location (block) can only be mapped in a single place in the cache. Generally this place is given by: (block address) mod (number of blocks in the cache) Number of blocks usually a power of two Most general mapping Fully-associative cache. A given memory location (block) can be mapped anywhere in the cache. No cache of decent size is implemented this way but this is the (general) mapping for pages (disk to main memory) and for small TLBs.
13 Cache Organization (cont d) Less restricted mapping Set-associative cache. Blocks in the cache are grouped into sets and a given memory location (block) maps into a set. Within the set the block can be placed anywhere. Sets with 2 (2-way set associative), 4, 8 and 16 blocks have been implemented. Set usually chosen with (block address) mod (number of sets in cache) Direct-mapped = 1-way set associative Fully associative with m entries is m-way set associative Capacity Capacity = number of sets * set-associativity * block size
14 Organization Illustrated
15 Cache hit or miss? How to detect if a memory address (a byte address) has a valid image in the cache Address is decomposed into 3 fields Block offset (depends on block size) Index (depends on number of sets) Tag (the remainder of the address) The index determines the set, and the tag can be used to check for a match Also need to check status bits for validity
16 Detecting a Cache Hit 32 bit addresses 2 blocks per set 2K sets
17 Why Set-Associative Caches? Pros Better hit ratio Great improvement from 1 to 2, less from 2 to 4, minimal after that (according to conventional wisdom) Cons The higher the associativity the larger the number of comparisons to be made in parallel for high-performance can have an impact on cycle time for on-chip caches Higher associativity requires a wider tag array
18 Replacement Algorithm None for direct-mapped Random or LRU or pseudo-lru for setassociative caches Not a very important factor for performance
19 Write Policies Write-through On a write hit, write both in cache and in memory Pro: consistent view of memory (better for I/O & coherence) Con: more memory traffic Write-back On a write hit, write only in cache (requires a dirty bit) Only update memory when evicted block is dirty Pro-con: reverse of write-through Write miss: Write allocate Usually used with write-back No-write allocate (non-allocate, write-around) Usually used with write-through
20 Classifying misses: The 3 C s Compulsory (cold start) The first time you touch a block. Reduced (for a given cache capacity and associativity) by having large blocks Capacity The working set is too big for the ideal cache of same capacity and block size (i.e., fully associative with optimal replacement algorithm). Only remedy: larger cache. Conflict (interference) Mapping of two or more hot blocks to the same location. Increasing associativity decreases this type of miss. There is a fourth C: coherence misses (for multiprocessors)
21 Example Cache Hierarchies AMD Athlon Intel P3 Intel P4 IBM PPC 405CR App Desktop Desktop,server Desktop Embedded ICache(L1) 64KB,2-way 16KB, 2-way 12K uop 16KB,2-way trace cache DCache(L1) 64KB,2-way 16KB,2-way 8KB,4-way 8KB,2-way L2(on-chip) 256KB, 16-way KB, 8-way 256KB,8-way None
22 Assignment Readings For Wednesday None For Monday H&P: Read C.3-C.4, 5.2 For Wednesday (Nov 11) H&P: sections
Performance metrics for caches
 Performance metrics for caches Basic performance metric: hit ratio h h = Number of memory references that hit in the cache / total number of memory references Typically h = 0.90 to 0.97 Equivalent metric:
Performance metrics for caches Basic performance metric: hit ratio h h = Number of memory references that hit in the cache / total number of memory references Typically h = 0.90 to 0.97 Equivalent metric:
Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements No class meeting on Monday, meet in project groups Project demos < 2 weeks, Nov 23 rd Questions
Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements No class meeting on Monday, meet in project groups Project demos < 2 weeks, Nov 23 rd Questions
Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements and Reminders Project demos in three weeks (Nov. 23 rd ) Questions Today s discussion: Improving
Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements and Reminders Project demos in three weeks (Nov. 23 rd ) Questions Today s discussion: Improving
Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 19 Prof. Patrick Crowley
 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 19 Prof. Patrick Crowley Plan for Today Announcement No lecture next Wednesday (Thanksgiving holiday) Take Home Final Exam Available Dec 7 Due via email
Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 19 Prof. Patrick Crowley Plan for Today Announcement No lecture next Wednesday (Thanksgiving holiday) Take Home Final Exam Available Dec 7 Due via email
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
Lecture 13: Cache Hierarchies. Today: cache access basics and innovations (Sections )
 Lecture 13: Cache Hierarchies Today: cache access basics and innovations (Sections 5.1-5.2) 1 The Cache Hierarchy Core L1 L2 L3 Off-chip memory 2 Accessing the Cache Byte address 101000 Offset 8-byte words
Lecture 13: Cache Hierarchies Today: cache access basics and innovations (Sections 5.1-5.2) 1 The Cache Hierarchy Core L1 L2 L3 Off-chip memory 2 Accessing the Cache Byte address 101000 Offset 8-byte words
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 1, 2012! Prashanth Mohan!! Slides from Anthony Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Caching!
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 1, 2012! Prashanth Mohan!! Slides from Anthony Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Caching!
Q3: Block Replacement. Replacement Algorithms. ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring Lectures 17 Virtual Memory. Announcements Office Hour
 CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures 7 Virtual Memory Pramod V. Argade May 25, 25 Announcements Office Hour Monday, June 6th: 6:3-8 PM, AP&M 528 Instead of regular Monday office hour 5-6 PM Reading
CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures 7 Virtual Memory Pramod V. Argade May 25, 25 Announcements Office Hour Monday, June 6th: 6:3-8 PM, AP&M 528 Instead of regular Monday office hour 5-6 PM Reading
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Virtual Memory. CS61, Lecture 15. Prof. Stephen Chong October 20, 2011
 Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
 Dr. Michael Manzke :: CS7031 :: 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three :: October 20, 2010 p. 1/17 [CS7031] Graphics and Console Hardware and Real-time Rendering 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
Dr. Michael Manzke :: CS7031 :: 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three :: October 20, 2010 p. 1/17 [CS7031] Graphics and Console Hardware and Real-time Rendering 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng
 Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Paging! 2/22! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica CS162 UCB Fall 2012! " (0xE0)" " " " (0x70)" " (0x50)"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 4pm
 Announcements Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 19) @ 4pm Next week: no classes Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2017-2018 1 The Memory Gap 1.2x-1.5x 1.07x H&P 5/e, Fig. 2.2 Memory subsystem design increasingly important!
Announcements Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 19) @ 4pm Next week: no classes Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2017-2018 1 The Memory Gap 1.2x-1.5x 1.07x H&P 5/e, Fig. 2.2 Memory subsystem design increasingly important!
TDT 4260 lecture 3 spring semester 2015
 1 TDT 4260 lecture 3 spring semester 2015 Lasse Natvig, The CARD group Dept. of computer & information science NTNU http://research.idi.ntnu.no/multicore 2 Lecture overview Repetition Chap.1: Performance,
1 TDT 4260 lecture 3 spring semester 2015 Lasse Natvig, The CARD group Dept. of computer & information science NTNU http://research.idi.ntnu.no/multicore 2 Lecture overview Repetition Chap.1: Performance,
Reducing Hit Times. Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI. small is always faster and can be put on chip
 Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
Advanced Computer Architecture
 ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Module 2: Virtual Memory and Caches Lecture 3: Virtual Memory and Caches. The Lecture Contains:
 The Lecture Contains: Program Optimization for Multi-core: Hardware Side of It Contents RECAP: VIRTUAL MEMORY AND CACHE Why Virtual Memory? Virtual Memory Addressing VM VA to PA Translation Page Fault
The Lecture Contains: Program Optimization for Multi-core: Hardware Side of It Contents RECAP: VIRTUAL MEMORY AND CACHE Why Virtual Memory? Virtual Memory Addressing VM VA to PA Translation Page Fault
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
Page 1. Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation "
 Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS. B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming
 MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
EECS 470. Lecture 14 Advanced Caches. DEC Alpha. Fall Jon Beaumont
 Lecture 14 Advanced Caches DEC Alpha Fall 2018 Instruction Cache BIU Jon Beaumont www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470/ Data Cache Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti,
Lecture 14 Advanced Caches DEC Alpha Fall 2018 Instruction Cache BIU Jon Beaumont www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470/ Data Cache Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti,
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Virtual Memory. Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University
 Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Portland State University ECE 587/687. Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism
 Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
10/7/13! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny CS162 UCB Fall 2013! " (0xE0)" " " " (0x70)" " (0x50)"
 Goals for Todayʼs Lecture" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 7, 2013! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Paging- and
Goals for Todayʼs Lecture" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 7, 2013! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Paging- and
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB
 ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 submission deadline: Nov.
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 submission deadline: Nov.
data block 0, word 0 block 0, word 1 block 1, word 0 block 1, word 1 block 2, word 0 block 2, word 1 block 3, word 0 block 3, word 1 Word index cache
 Taking advantage of spatial locality Use block size larger than one word Example: two words Block index tag () () Alternate representations Word index tag block, word block, word block, word block, word
Taking advantage of spatial locality Use block size larger than one word Example: two words Block index tag () () Alternate representations Word index tag block, word block, word block, word block, word
Memory hierarchy review. ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches. Marco Paolieri Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook
 CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" Why it s important " Fundamental lesson(s)" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter
 Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Spring 2018 :: CSE 502. Cache Design Basics. Nima Honarmand
 Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 13. Caches and TLBs. Page 1
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 13 Caches and TLBs March 12, 2008 Prof. Anthony D. Joseph http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review Multi-level Translation What about a tree of
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 13 Caches and TLBs March 12, 2008 Prof. Anthony D. Joseph http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review Multi-level Translation What about a tree of
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
Question?! Processor comparison!
 1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
Virtual Memory Review. Page faults. Paging system summary (so far)
 Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 28: More Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications from
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 28: More Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications from
COMP 3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
 COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 16 - Cache and virtual memory review
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Memory hier ar hier ch ar y ch rev re i v e i w e ECE 154B Dmitri Struko Struk v o
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
Virtual Memory. Motivation:
 Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design. In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST
 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Improving Cache Performance. Administrative. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. Review: Principle of Locality
 Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
Computer Systems C S Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College
 Computer Systems C S 0 7 Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College 2 Today s Topics TODAY S LECTURE: Caching ANNOUNCEMENTS: Assign6 & Assign7 due Friday! 6 & 7 NO late
Computer Systems C S 0 7 Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College 2 Today s Topics TODAY S LECTURE: Caching ANNOUNCEMENTS: Assign6 & Assign7 due Friday! 6 & 7 NO late
Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size. Lecture #22 Caches II Block Size Tradeoff (3/3) Block Size Tradeoff (2/3)
 CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB
 ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 submission deadline: Mar.
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 submission deadline: Mar.
Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden of managing overlays.
 CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
10/19/17. You Are Here! Review: Direct-Mapped Cache. Typical Memory Hierarchy
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture ( ) Timothy Roscoe
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 09: Memory Hierarchy. Instructor: Rob Bergen Applied Computer Science University of Winnipeg
 Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 09: Memory Hierarchy Instructor: Rob Bergen Applied Computer Science University of Winnipeg Announcements Midterm returned + solutions in class today SSD
Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 09: Memory Hierarchy Instructor: Rob Bergen Applied Computer Science University of Winnipeg Announcements Midterm returned + solutions in class today SSD
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache performance 4 Cache
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache performance 4 Cache
5DV118 Computer Organization and Architecture Umeå University Department of Computing Science Stephen J. Hegner
 5DV8 Computer Organization and Architecture Umeå University Department of Computing Science Stephen J. Hegner Topic 5: The Memory Hierarchy Part B: Address Translation These slides are mostly taken verbatim,
5DV8 Computer Organization and Architecture Umeå University Department of Computing Science Stephen J. Hegner Topic 5: The Memory Hierarchy Part B: Address Translation These slides are mostly taken verbatim,
lecture 18 cache 2 TLB miss TLB - TLB (hit and miss) - instruction or data cache - cache (hit and miss)
 lecture 18 2 virtual physical virtual physical - TLB ( and ) - instruction or data - ( and ) Wed. March 16, 2016 Last lecture I discussed the TLB and how virtual es are translated to physical es. I only
lecture 18 2 virtual physical virtual physical - TLB ( and ) - instruction or data - ( and ) Wed. March 16, 2016 Last lecture I discussed the TLB and how virtual es are translated to physical es. I only
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
Introduction to OpenMP. Lecture 10: Caches
 Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Chapter 6 Caches. Computer System. Alpha Chip Photo. Topics. Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM Caches Direct Mapped Associative
 Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14. Caching and Demand Paging
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14 Caching and Demand Paging October 17, 2007 Prof. John Kubiatowicz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review: Hierarchy of a Modern Computer
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14 Caching and Demand Paging October 17, 2007 Prof. John Kubiatowicz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review: Hierarchy of a Modern Computer
Agenda. Cache-Memory Consistency? (1/2) 7/14/2011. New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!)
 7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
Fall 2007 Prof. Thomas Wenisch
 Basic Caches Fall 2007 Prof. Thomas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, and Vijaykumar
Basic Caches Fall 2007 Prof. Thomas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, and Vijaykumar
Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 Lecture 5a Caching Review Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 Lecture 5a Caching Review Marten van Dijk Syed Kamran Haider, Chenglu Jin, Phuong Ha Nguyen Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming ( )
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
Chapter 5 (Part II) Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
15-740/ Computer Architecture
 15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 19: Caching II Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Fall 2011, 10/31/2011 Announcements Milestone II Due November 4, Friday Please talk with us if you
15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 19: Caching II Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Fall 2011, 10/31/2011 Announcements Milestone II Due November 4, Friday Please talk with us if you
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM. Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections )
 Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6)
 Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
CS61C Review of Cache/VM/TLB. Lecture 26. April 30, 1999 Dave Patterson (http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson)
 CS6C Review of Cache/VM/TLB Lecture 26 April 3, 999 Dave Patterson (http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/schedule.html Outline Review Pipelining Review Cache/VM/TLB Review
CS6C Review of Cache/VM/TLB Lecture 26 April 3, 999 Dave Patterson (http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/schedule.html Outline Review Pipelining Review Cache/VM/TLB Review
Page 1. CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14. Caching and Demand Paging
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14 Caching and Demand Paging March 4, 2010 Ion Stoica http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review: Hierarchy of a Modern Computer System Take advantage
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 14 Caching and Demand Paging March 4, 2010 Ion Stoica http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162 Review: Hierarchy of a Modern Computer System Take advantage
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Caches. Cache Memory. memory hierarchy. CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first
 Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
Logical Diagram of a Set-associative Cache Accessing a Cache
 Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
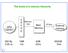 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CSE Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 07 Memory Hierarchies Assigned: November 8, 2011, Due: November 22, 2011, Total Points: 100
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 07 Memory Hierarchies Assigned: November 8, 2011, Due: November 22, 2011, Total Points: 100 Problem 1: (30 points) Background: One possible organization
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 07 Memory Hierarchies Assigned: November 8, 2011, Due: November 22, 2011, Total Points: 100 Problem 1: (30 points) Background: One possible organization
10/16/17. Outline. Outline. Typical Memory Hierarchy. Adding Cache to Computer. Key Cache Concepts
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
Let!s go back to a course goal... Let!s go back to a course goal... Question? Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies
 1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Lecture 11: SMT and Caching Basics. Today: SMT, cache access basics (Sections 3.5, 5.1)
 Lecture 11: SMT and Caching Basics Today: SMT, cache access basics (Sections 3.5, 5.1) 1 Thread-Level Parallelism Motivation: a single thread leaves a processor under-utilized for most of the time by doubling
Lecture 11: SMT and Caching Basics Today: SMT, cache access basics (Sections 3.5, 5.1) 1 Thread-Level Parallelism Motivation: a single thread leaves a processor under-utilized for most of the time by doubling
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
