Using a Cache Simulator on Big Data Applications
|
|
|
- Maude Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
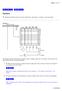
1 1 Using a Cache Simulator on Big Data Applications Liliane Ntaganda Spelman College lntagand@scmail.spelman.edu Hyesoon Kim Georgia Institute of Technology hyesoon@cc.gatech.edu ABSTRACT From the computer architect's perspective, Big Data benchmark is considered none other than a heavily memory-intensive application as opposed to a more normal application. Then again, due to its overwhelmingly huge amount of data access, it is actually more than a simple heavily memory-intensive application. Therefore people are trying to come up with a new system that can handle those applications more efficiently, in terms of both energy and performance. In this research project, an efficient cache simulator is needed to help study and analyze new memory architectures that might help improve performance for those big data applications, while not sacrificing energy consumption. To benefit more from all the functionalities of an efficient cache simulator, various cache features such as N-way set associativity, appropriate replacement policy, appropriate write and read policy, and different levels of closeness and accessibility to the microprocessor have to be considered. By using a multicore-multilevel cache simulator, and running several simulations, results show that the cache performance can be improved when cache parameters are varied efficiently. The results also show that in order to increase the overall system performance, it is necessary to greatly reduce the cache miss rate. This research presents the results obtained by running some application traces on the implemented cache simulator. Keywords Big Data Benchmark, Cache Simulator, DineroIV cache simulator, Data Cache, Traces, Cache Hit Rate, Cache Miss Rate, N-way Set Associativity, Write Through policy, Write Allocate policy, LRU (Least Recently Used) replacement policy, SRAM, DRAM, CPU (Central Processing Unit), C OBJECTIVES The goal of this research is to explore a new memory architecture that is capable of processing huge amount of data, generally represented by the term Big Data. To this end, the first stage of this research is to understand important characteristics of those applications for which Big Data Benchmarks are going to be collected. In addition, a cache simulator has to be implemented, with which those interesting new memory architectures that might help improve performance for those Big Data applications are studied and analyzed. Understanding how cache works is necessary to design and implement accurate and efficient cache simulator. In this project, a CPU cache simulator program is written in C++. Then, various simulations are performed to draw observations and conclusions. Observations from program testing are used to analyze how the cache miss rate is reduced and to take appropriate measures in order to significantly improve the cache simulator performance. 2. CACHE ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION 2.1 Overview of Cache Figure 1: Basic Cache Model Figure 1 shows a simplified diagram of a system with cache. In this system, every time the CPU performs a read or write, the cache may intercept the bus transaction, allowing the cache to decrease the response time of the system [1]. Thus, a cache memory is a memory that a computer microprocessor, CPU, can access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. A Cache is a small high speed memory usually a SRAM that contains the most recently accessed pieces of main memory [1].It is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. Hence, the greater the number of requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the overall system performance becomes. One may want to know the reason why this high speed memory is necessary or beneficial. In today s systems, the time it takes to bring an instruction or piece of data into the processor is very long when compared to the time to execute the instruction [1]. Therefore a bottle neck forms at the input to the processor. Cache memory helps by decreasing the time it takes to move information to and from the processor. One may again want to know how such a small piece of high speed memory can improve the system performance. The theory that explains this performance is called Locality of Reference [2]. The concept is that at any given time the processor will be accessing memory in a small or localized region of memory. The cache loads this region allowing the processor to access the memory region faster.
2 2 2.2 Features Implemented in the Cache Simulator Features implemented in the cache simulator program are as follow: - Multicore-multilevel cache: the simulator program supports many levels of cache memory. Program users state the number of levels they prefer the cache simulator to have. Each level can have more than one cache. Each cache on the first level, the level that is the closest to the CPU, is private to their core. - N-way set associativity: the cache simulator supports more than one degree of freedom. With N-way set associative, cache slots are grouped into sets. When locating a cache block, you find the appropriate set for a given address, and within the set you find the appropriate slot. This scheme has fewer collisions because you have more slots to pick from, even when cache lines map to the same set. - Write through policy: when there is a write hit, the information is written to both the block in the cache and to the block in the lower-level memory [1]. - Write allocate policy: when there is a write miss, a block containing missed data is allocated and loaded from memory to cache, and data is written into that cache block [1]. - LRU replacement policy: the least recently used policy is used to select what to remove from the cache. 3. METHODOLOGY 3.1 Language The cache simulator program is written in C++ programming language. C++ is built off of the C language with less dependency on the functions for basic tasks, such as input and output, and also adds object-oriented features [6]. 3.2 Multilevel Cache Simulator Cache memory is sometimes described in levels of closeness and accessibility to the microprocessor [3]. An L1 (level one) cache is on the same chip as the microprocessor. L2 (level two) cache is usually a separate static RAM chip. In order to maintain the multilevel characteristic of the cache in our program, some rules of how caches on different levels would be placed and communicate to each other are set. The program can support any number of cache levels and any number of caches on the first level. The numbers of caches on other levels are computed and set by the program according to the implemented rules. These are the implemented rules in the program of how the cache simulator is structured: - The program prompts the user to input the number of cache levels, and the number of caches on the first level. The program does the rest of the work by itself, which is to compute the number of caches that must go on other cache levels according to the user input. - An equal number of caches are distributed to corresponding parent caches in the lower/precedent level. [4] - The number of L1 cache must be divisible by the number of L2 cache with no remainder. - If the number of the lowest level cache is odd, the number of the next highest level cache must equal 1, meaning having just one cache on this level. 3.3 Program Validation To verify the effectiveness of our cache simulator program, the DineroIV cache simulator program was used. Output results from our program had to be compared to the output results from the DineroIV cache simulator. Dinero is a trace-driven uniprocessor CPU cache simulator for memory reference traces, written by Dr. Jan Edler and Prof. Mark D. Hill from the University of Wisconsin Madison [4]. Since the Dinero cache simulator is a uni-core simulator [4], in simulations from our program that had to be compared with the Dinero results, only one cache was used on the first level, leading to have one cache on each of the higher levels as well. 3.4 Application Traces Simulation results are determined by the input trace and the cache parameters. A trace is a finite sequence of memory references usually obtained by the interpretive execution of a program or set of programs. Traces used in our simulation experiments are: - A C compiler trace that has both read and write addresses - A trace called trace_4664_2_0.raw that has only read addresses Some testing simulation results from our program that involved both reading and writing addresses slightly differed from the Dinero results. Thus, we decided to use traces with only read addresses in our further experiments to ensure that the data obtained and observations made are correct. All the following simulation results are obtained using traces with only read addresses. 3.5 Cache Performance and System Performance The time of a program execution is one of the most reliable performance measure [5]. CPUtime = IC*(CPIexecution +Memory accesses/instruction *Miss rate * Miss penalty) * Clock cycle With IC being the instruction count, CPI, clocks per instruction, and Miss Penalty, the extra delay caused by a cache miss. From the above CPU time formula, it is well observed that if Miss Rate is reduced, CPU time would reduce as well which can improve the overall system performance. Therefore, various experimental simulations have been conducted to figure out what needs to be done to reduce the cache Miss Rate. Using larger block size and higher cache associativity have shown to reduce the cache Miss Rate since the number of cache collisions clearly reduce. Even though the goal of implementing the cache simulator is to only obtain the cache miss rate and hit rate information, it is a good
3 3 practice to also consider the effect of the cache simulator design on the overall system performance. Since CPU time and cache Miss Rate are interrelated, reducing cache Miss Rate will reduce the CPU time which will be beneficial for big data applications because of their huge amount of data access and computation. - Level 1 cache miss rate = Level 2 cache miss rate = Figure 3: DineroIV Sample Simulation Output 2 levels cache simulator with 1 data cache on each level 4. RESULTS Running sample simulations in both the implemented cache simulator program and the DineroIV cache simulator has shown to provide similar output results. Comparing both results is the assurance that all the cache features are well implemented in the program. Figure 2: Sample Simulation Output 2 levels cache simulator with 1 cache on each level Figure 3 depicts the output result that comes from running the same simulation in the DineroIV cache simulator program. The Dinero cache simulator has both instruction cache and data cache, but in this case, data cache is used since it is the cache that matches with our implemented cache simulator program. - l1-cache miss rate = l2-cache miss rate = Figure 2 depicts the output result that comes from running a simulation in our implemented cache simulator program. The cache simulator is composed of two levels and one cache on each level. Both screenshot figures display how the output while running simulations on two different cache simulators produces the same result. In both cases, cache miss rates are similar. To ensure that the comparison is accurate, cache parameters such as cache size, cache block size, and cache associativity, must the same in both programs. Implementation policies such as replacement policy, and allocation policy must be similar as well. Those criteria were maintained in comparing our sample simulations. In addition, similar traces had to be used in both simulator programs. In these sample simulations, there is only one cache on each level. The only reason behind that is because the DineroIV is a uni-core cache simulator. It can only have one cache on a level. Having only one cache on a level in our implemented program was an easy way
4 4 to be able to compare our results with the DineroIV simulator results. Other than that, our implemented simulator program can have more than one cache on a level. Figure 6: Reducing Cache Misses via Higher Associativity 5. DISCUSSION After running simulations in two different cache simulator programs and confirming that the output results do match, it was safe to proceed with other analysis tests on our implemented cache simulator program. By varying cache parameters such as cache size, cache block size, and the number of associativity, different simulations helped in the study and analysis of various ways that can be used to improve cache performance. Using larger block size and higher associativity have shown to improve cache performance since they reduce the cache miss rate. Since CPU performance is highly connected to cache miss rate, a reduced cache miss rate would greatly increase the system performance. Figure 4: Reducing Cache Misses via Larger Block Size 6. CONCLUSION This research project has shown that the performance of a cache simulator program depends on a combination of the effectiveness of the algorithm used in the program, and the effectiveness of the cache design options chosen to implement the simulator. The better the cache simulator works efficiently, the easier it will be to use it on big data applications which will accelerate the process of understanding how well new memory architectures for big data applications have to be constructed. It is the hope that computer scientists continue exploring memory architectures that are capable of handling Big Data applications more efficiently. - Cache associativity is 4 in each of the above cases Figure 5: Corresponding Graph to the above tables 7. FUTURE PLANS The future work will be to eliminate all of the malfunctions encountered in cache simulations since for instance write addresses had some issues in the cache simulator program. That will require to fix writing addresses by choosing an efficient write policy to use and implement it in the program correctly. More importantly in order to accomplish the goal of the project, traces from big data applications will have to be used in simulations since at this point simulations have been done using traces of simple, general applications. Another aspect that is of interest will be to verify and improve multicore cache programmability in the simulator program as well as take into account better cache design options such as knowing which policies are better to combine or not in the cache simulator program. The first step in improving multicore cache programmability will be to find another already built cache simulator that can support more than one cache on a level such as an advanced or improved version of DineroIV. Such cache simulator would help in validating output results from our cache simulator program in case more than one cache are used on a cache simulator level. 8. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This research was funded by the Computing Research Association's Distributed Mentoring Program under the mentorship of Dr.Hyesoon Kim at Georgia Institute of Technology, College of Computing.
5 5 References [1] A. S. Tanenbaum, Structured Computer Organization, Prentice Hall, 1993, pp ; [2] P. J. Denning, Communication Networks and Computer Systems, Imperial College Press, 2006, pp [3] M. A. Ismail, T. Altaf and S. H. Mirza, "A new parallel Multilevel Cache Simulator For multi-core processors," in Electronics, Communications and Photonics Conference (SIECPC), Riyadh, [4] J. Edler and M. D. Hill, "Dinero IV Trace-Driven Uniprocessor Cache Simulator," [Online]. Available: [5] D. A. Patterson and J. L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design, San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2013, pp [6] B. Stroustrup, The C++ Programming Language, Ann Arbor: Addison-Wesley Professional, 2013.
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Finding Optimal L1 Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems
 Finding Optimal L1 Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems Andhi Janapsatya, Aleksandar Ignjatovic, Sri Parameswaran School of Computer Science and Engineering Outline Motivation and Goal Existing Work
Finding Optimal L1 Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems Andhi Janapsatya, Aleksandar Ignjatovic, Sri Parameswaran School of Computer Science and Engineering Outline Motivation and Goal Existing Work
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy. Caching Chapter 7. Locality. Program Characteristics. What does that mean?!? Exploiting Spatial & Temporal Locality
 Caching Chapter 7 Basics (7.,7.2) Cache Writes (7.2 - p 483-485) configurations (7.2 p 487-49) Performance (7.3) Associative caches (7.3 p 496-54) Multilevel caches (7.3 p 55-5) Tech SRAM (logic) SRAM
Caching Chapter 7 Basics (7.,7.2) Cache Writes (7.2 - p 483-485) configurations (7.2 p 487-49) Performance (7.3) Associative caches (7.3 p 496-54) Multilevel caches (7.3 p 55-5) Tech SRAM (logic) SRAM
ECE 485/585 Microprocessor System Design
 Microprocessor System Design Lecture 8: Principle of Locality Cache Architecture Cache Replacement Policies Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer
Microprocessor System Design Lecture 8: Principle of Locality Cache Architecture Cache Replacement Policies Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis
 Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis Bruce R. Childers, Jack W. Davidson Computer Science Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia 22901 {brc2m, jwd}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract The
Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis Bruce R. Childers, Jack W. Davidson Computer Science Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia 22901 {brc2m, jwd}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract The
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
The Cache Write Problem
 Cache Coherency A multiprocessor and a multicomputer each comprise a number of independent processors connected by a communications medium, either a bus or more advanced switching system, such as a crossbar
Cache Coherency A multiprocessor and a multicomputer each comprise a number of independent processors connected by a communications medium, either a bus or more advanced switching system, such as a crossbar
The Impact of Write Back on Cache Performance
 The Impact of Write Back on Cache Performance Daniel Kroening and Silvia M. Mueller Computer Science Department Universitaet des Saarlandes, 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany email: kroening@handshake.de, smueller@cs.uni-sb.de,
The Impact of Write Back on Cache Performance Daniel Kroening and Silvia M. Mueller Computer Science Department Universitaet des Saarlandes, 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany email: kroening@handshake.de, smueller@cs.uni-sb.de,
SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm
 SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm Jaafar Alghazo, Adil Akaaboune, Nazeih Botros Southern Illinois University at Carbondale Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carbondale, IL 6291 alghazo@siu.edu,
SF-LRU Cache Replacement Algorithm Jaafar Alghazo, Adil Akaaboune, Nazeih Botros Southern Illinois University at Carbondale Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carbondale, IL 6291 alghazo@siu.edu,
Locality. Cache. Direct Mapped Cache. Direct Mapped Cache
 Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Cache Memory and Performance
 Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" Why it s important " Fundamental lesson(s)" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter
 Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting.
 Page 1 of 17 Caches indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. The diagram above illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache for a computer that uses
Page 1 of 17 Caches indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. The diagram above illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache for a computer that uses
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 25: Multilevel Caches & Data Access Strategies Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 25: Multilevel Caches & Data Access Strategies Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM. Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections )
 Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
12 Cache-Organization 1
 12 Cache-Organization 1 Caches Memory, 64M, 500 cycles L1 cache 64K, 1 cycles 1-5% misses L2 cache 4M, 10 cycles 10-20% misses L3 cache 16M, 20 cycles Memory, 256MB, 500 cycles 2 Improving Miss Penalty
12 Cache-Organization 1 Caches Memory, 64M, 500 cycles L1 cache 64K, 1 cycles 1-5% misses L2 cache 4M, 10 cycles 10-20% misses L3 cache 16M, 20 cycles Memory, 256MB, 500 cycles 2 Improving Miss Penalty
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
CS 136: Advanced Architecture. Review of Caches
 1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Question?! Processor comparison!
 1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
Cache Optimization. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Cache Optimization Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Cache Misses On cache hit CPU proceeds normally On cache miss Stall the CPU pipeline
Cache Optimization Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Cache Misses On cache hit CPU proceeds normally On cache miss Stall the CPU pipeline
COMP 3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
 COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
Cache memory. Lecture 4. Principles, structure, mapping
 Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Memory Organization Part II
 ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design. In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST
 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Cache Memory and Performance
 Cache Memory and Performance Cache Organization 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Cache Memory and Performance Cache Organization 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier
 Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science CPUtime = IC CPI Execution + Memory accesses Instruction
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science CPUtime = IC CPI Execution + Memory accesses Instruction
A Framework for the Performance Evaluation of Operating System Emulators. Joshua H. Shaffer. A Proposal Submitted to the Honors Council
 A Framework for the Performance Evaluation of Operating System Emulators by Joshua H. Shaffer A Proposal Submitted to the Honors Council For Honors in Computer Science 15 October 2003 Approved By: Luiz
A Framework for the Performance Evaluation of Operating System Emulators by Joshua H. Shaffer A Proposal Submitted to the Honors Council For Honors in Computer Science 15 October 2003 Approved By: Luiz
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Slide Set 5. for ENCM 501 in Winter Term, Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 5 for ENCM 501 in Winter Term, 2017 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2017 ENCM 501 W17 Lectures: Slide
Slide Set 5 for ENCM 501 in Winter Term, 2017 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2017 ENCM 501 W17 Lectures: Slide
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Architectural Issues for the 1990s. David A. Patterson. Computer Science Division EECS Department University of California Berkeley, CA 94720
 Microprocessor Forum 10/90 1 Architectural Issues for the 1990s David A. Patterson Computer Science Division EECS Department University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 1990 (presented at Microprocessor
Microprocessor Forum 10/90 1 Architectural Issues for the 1990s David A. Patterson Computer Science Division EECS Department University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 1990 (presented at Microprocessor
Memory Systems IRAM. Principle of IRAM
 Memory Systems 165 other devices of the module will be in the Standby state (which is the primary state of all RDRAM devices) or another state with low-power consumption. The RDRAM devices provide several
Memory Systems 165 other devices of the module will be in the Standby state (which is the primary state of all RDRAM devices) or another state with low-power consumption. The RDRAM devices provide several
Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors
 Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors G. Chen 1, M. Kandemir 1, I. Kolcu 2, and A. Choudhary 3 1 Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA 2 UMIST,
Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors G. Chen 1, M. Kandemir 1, I. Kolcu 2, and A. Choudhary 3 1 Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA 2 UMIST,
5. Memory Hierarchy Computer Architecture COMP SCI 2GA3 / SFWR ENG 2GA3. Emil Sekerinski, McMaster University, Fall Term 2015/16
 5. Memory Hierarchy Computer Architecture COMP SCI 2GA3 / SFWR ENG 2GA3 Emil Sekerinski, McMaster University, Fall Term 2015/16 Movie Rental Store You have a huge warehouse with every movie ever made.
5. Memory Hierarchy Computer Architecture COMP SCI 2GA3 / SFWR ENG 2GA3 Emil Sekerinski, McMaster University, Fall Term 2015/16 Movie Rental Store You have a huge warehouse with every movie ever made.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-201 971 Comparative Performance Analysis Of Sorting Algorithms Abhinav Yadav, Dr. Sanjeev Bansal Abstract Sorting Algorithms
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-201 971 Comparative Performance Analysis Of Sorting Algorithms Abhinav Yadav, Dr. Sanjeev Bansal Abstract Sorting Algorithms
Let!s go back to a course goal... Let!s go back to a course goal... Question? Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies
 1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1]
![2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1] 2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1]](/thumbs/73/69207197.jpg) EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #7 Processor Architecture Stanford University Tuesday, June 6, 2000 Memory Systems and Memory Latency Lecture #7: Wednesday, April 19, 2000 Lecturer: Brian
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #7 Processor Architecture Stanford University Tuesday, June 6, 2000 Memory Systems and Memory Latency Lecture #7: Wednesday, April 19, 2000 Lecturer: Brian
ELE 375 / COS 471 Final Exam Fall, 2001 Prof. Martonosi
 ELE 375 / COS 471 Final Exam Fall, 2001 Prof. Martonosi Question Score 1 /10 2 /20 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /20 7 /20 8 /25 9 /30 10 /30 11 /30 12 /15 13 /10 Total / 250 Please write your answers clearly in
ELE 375 / COS 471 Final Exam Fall, 2001 Prof. Martonosi Question Score 1 /10 2 /20 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /20 7 /20 8 /25 9 /30 10 /30 11 /30 12 /15 13 /10 Total / 250 Please write your answers clearly in
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 4: Memory Organization Our goal: understand the basic types of memory in computer understand memory hierarchy and the general process to access memory
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 4: Memory Organization Our goal: understand the basic types of memory in computer understand memory hierarchy and the general process to access memory
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Q3: Block Replacement. Replacement Algorithms. ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
1/19/2009. Data Locality. Exploiting Locality: Caches
 Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology CACHE MEMORY. Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy.
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
MIPS) ( MUX
 Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Computer Architecture. Fall Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Computer Architecture Fall 2018 1 Syllabus Instructors: Dongkun Shin Office : Room 85470 E-mail : dongkun@skku.edu Office Hours: Wed. 15:00-17:30 or by appointment Lecture notes nyx.skku.ac.kr Courses
Computer Architecture Fall 2018 1 Syllabus Instructors: Dongkun Shin Office : Room 85470 E-mail : dongkun@skku.edu Office Hours: Wed. 15:00-17:30 or by appointment Lecture notes nyx.skku.ac.kr Courses
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Main Memory Supporting Caches
 Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Pipelined MIPS processor with cache controller using VHDL implementation for educational purpose
 Journal From the SelectedWorks of Kirat Pal Singh Winter December 28, 203 Pipelined MIPS processor with cache controller using VHDL implementation for educational purpose Hadeel Sh. Mahmood, College of
Journal From the SelectedWorks of Kirat Pal Singh Winter December 28, 203 Pipelined MIPS processor with cache controller using VHDL implementation for educational purpose Hadeel Sh. Mahmood, College of
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Topics. Digital Systems Architecture EECE EECE Need More Cache?
 Digital Systems Architecture EECE 33-0 EECE 9-0 Need More Cache? Dr. William H. Robinson March, 00 http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/eece33/ Topics Cache: a safe place for hiding or storing things. Webster
Digital Systems Architecture EECE 33-0 EECE 9-0 Need More Cache? Dr. William H. Robinson March, 00 http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/eece33/ Topics Cache: a safe place for hiding or storing things. Webster
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
High Performance Memory Read Using Cross-Coupled Pull-up Circuitry
 High Performance Memory Read Using Cross-Coupled Pull-up Circuitry Katie Blomster and José G. Delgado-Frias School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Pullman, WA
High Performance Memory Read Using Cross-Coupled Pull-up Circuitry Katie Blomster and José G. Delgado-Frias School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Pullman, WA
DESIGN RAM MEMORIES BY USING FLIP-FLOP CIRCUITS
 DESIGN RAM MEMORIES BY USING FLIP-FLOP CIRCUITS Saed Soliman Alasttal Computer Department, Faculty of Science, Al Asmarya Islamic University-Zliten E-mail :saedelasttal@gmail.com Abdalla Mohamed Alasoud
DESIGN RAM MEMORIES BY USING FLIP-FLOP CIRCUITS Saed Soliman Alasttal Computer Department, Faculty of Science, Al Asmarya Islamic University-Zliten E-mail :saedelasttal@gmail.com Abdalla Mohamed Alasoud
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
CISC 360. Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 2009
 Topics ν CISC 36 Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 29 Review of cache memory mapping Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. ν Hold frequently
Topics ν CISC 36 Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 29 Review of cache memory mapping Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. ν Hold frequently
Chapter 6 Memory 11/3/2015. Chapter 6 Objectives. 6.2 Types of Memory. 6.1 Introduction
 Chapter 6 Objectives Chapter 6 Memory Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Chapter 6 Objectives Chapter 6 Memory Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Memory
 Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Start with (Very) Basic Block Diagram CPU (Actual work done here) (Starting and ending data stored here, along with program) Organization of : Designer s choice 1 Problem
Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Start with (Very) Basic Block Diagram CPU (Actual work done here) (Starting and ending data stored here, along with program) Organization of : Designer s choice 1 Problem
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Solutions for Chapter 7 Exercises
 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 1 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 7.1 There are several reasons why you may not want to build large memories out of RAM. RAMs require more transistors to build than DRAMs
olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 1 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 7.1 There are several reasons why you may not want to build large memories out of RAM. RAMs require more transistors to build than DRAMs
How What When Why CSC3501 FALL07 CSC3501 FALL07. Louisiana State University 1- Introduction - 1. Louisiana State University 1- Introduction - 2
 Computer Organization and Design Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70803 durresi@csc.lsu.edu d These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc3501_07/ Louisiana
Computer Organization and Design Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70803 durresi@csc.lsu.edu d These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc3501_07/ Louisiana
Managing Multiple Record Entries Part II
 1 Managing Multiple Record Entries Part II Lincoln Stoller, Ph.D. Braided Matrix, Inc. Contents of Part I I. Introduction to multiple record entries II. Techniques A. Global transaction B. Hierarchical
1 Managing Multiple Record Entries Part II Lincoln Stoller, Ph.D. Braided Matrix, Inc. Contents of Part I I. Introduction to multiple record entries II. Techniques A. Global transaction B. Hierarchical
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 24 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 29, 2010 04/29/2010 Lecture 24 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 24 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 29, 2010 04/29/2010 Lecture 24 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Finding Optimal L1 Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems
 Finding Optimal L Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems Andhi Janapsatya, Aleksandar Ignjatović, Sri Parameswaran School of Computer Science and Engineering, The University of New South Wales Sydney,
Finding Optimal L Cache Configuration for Embedded Systems Andhi Janapsatya, Aleksandar Ignjatović, Sri Parameswaran School of Computer Science and Engineering, The University of New South Wales Sydney,
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory System Design Part II. Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore.
 Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
AMD actual programming and testing on a system board. We will take a simple design example and go through the various stages of this design process.
 actual programming and testing on a system board. We will take a simple design example and go through the various stages of this design process. Conceptualize A Design Problem Select Device Implement Design
actual programming and testing on a system board. We will take a simple design example and go through the various stages of this design process. Conceptualize A Design Problem Select Device Implement Design
Memory Hierarchy: The motivation
 Memory Hierarchy: The motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
Memory Hierarchy: The motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
Chapter Seven. Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Agenda. EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Memory. Naive Register File. Agenda. Memory Arrays: SRAM. Memory Arrays: Register File
 EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
CS 31: Intro to Systems Caching. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 2015
 CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
 Dr. Michael Manzke :: CS7031 :: 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three :: October 20, 2010 p. 1/17 [CS7031] Graphics and Console Hardware and Real-time Rendering 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
Dr. Michael Manzke :: CS7031 :: 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three :: October 20, 2010 p. 1/17 [CS7031] Graphics and Console Hardware and Real-time Rendering 6 th Lecture :: The Cache - Part Three
