Table of Contents. Cisco Catalyst Switch GigaStack Configuration and Implications
|
|
|
- Sophie Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents Switch GigaStack Configuration and Implications...1 Document ID: Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...3 Conventions...3 Cabling Configuration...3 Point to Point Connection...4 Cascaded Stack Connections...4 Cascaded Stack Connections with a Redundant Link...5 Using the Cross Tack Uplink Fast Feature...5 Troubleshooting...8 NetPro Discussion Forums Featured Conversations...10 Related Information...10 i
2 Switch GigaStack Configuration and Implications Document ID: Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cabling Configuration Point to Point Connection Cascaded Stack Connections Cascaded Stack Connections with a Redundant Link Using the Cross Tack Uplink Fast Feature Troubleshooting NetPro Discussion Forums Featured Conversations Related Information Introduction The GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) is a Cisco proprietary GBIC. The GigaStack GBIC provides low cost, high bandwidth connections between supported devices. Gigabit connections can be configured in a point to point or cascaded stack configuration, with or without redundancy. The GigaStack GBIC allows you to stack up to nine switches to form an independent backbone that can be managed with a single IP address. This stack gives the appearance of a single large switch for network management purposes. You can also form a point to point link between two switches. The GigaStack GBIC supports one full duplex link (in a point to point link), or up to eight half duplex links (in a stack configuration) to other Gigabit Ethernet devices. This document outlines the necessary steps to insure a working configuration and possible issues related to a misconfiguration. Prerequisites Requirements The following table shows the list of Cisco switches that support the GigaStack GBIC, along with the IOS that supports redundant loop configuration. Redundant loop configuration is not supported in any prior release. The GigaStack GBIC is not supported in the 4000, 5000, and 6000 product line. Model Minimum Release Minimum Required to Release Minimum support Required for Recommend GigaStack Loop Release 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU Detection 12.0(5)WC3b
3 2912MF XL 2924M XL 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 2924M XL DC 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b WS X2931 XL 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 3508G XL 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 3512 XL 3524 XL 3524 PWR XL 3548 XL 2950G 12 EI 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 11.2(8)SA6 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 12.0(5)XP 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC3b 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2c 2950G 24 EI 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2c 2950G 24 EI DC 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2c 2950G 48 EI 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2 12.1(6)EA2c G 12.1(6)EA1 12.1(6)EA1 12.1(8)EA1c T SMI EMI SMI DC SMI EMI 12.1(4)EA1c 12.1(4)EA1c 12.1(8)EA1c 12.1(6)EA1a 12.1(6)EA1a 12.1(8)EA1c 12.1(6)EA1b 12.1(6)EA1b 12.1(8)EA1c 12.1(8)EA1b 12.1(8)EA1b 12.1(8)EA1c Note: Upgrade all the switches in a series to the same software version. Otherwise, the loop breaking algorithm might never resolve itself. For example, if the stack includes only 2900 series XL and 3500 series XL switches, they must run Release 12.0(5)XU or later. If the stack includes a mixture of 2900 series XL, 3500 series XL, 2950, and 3550 switches, all the 2900 XL and 3500 XL switches must run Release 12.0(5)XW or later, all 2950 switches must run 12.1(6)EA2 or later, and all the 3550 switches must run Release at least 12.1(4)EA1 or later, depending on model.
4 Components Used The GigaStack GBIC is an adapter that can only be installed into the GBIC modules slot of any supported switch. The maximum distance for a GBIC to GBIC connection is one meter. The GigaStack GBIC requires Cisco proprietary signaling and cabling. Each GigaStack GBIC consists of two ports, port 1 and port 2. One or both ports can be used, depending on cabling configuration. GBIC: WS X3500 XL (Cisco GigaStack GBIC and 50 centimeter cable for GigaStack GBIC) Cable: CAB GS 1M (one meter cable/ inches) Cable: CAB GS 50CM (50 centimeter cable/ inches) Caution: Do not use standard IEEE 1394 cables with the GigaStack GBIC. You must use one of the Cisco proprietary cables (CAB GS 50CM or CAB GS 1M). If you use any other cable, you will not have connectivity. Caution: Do not use the GigaStack GBIC with standard IEEE 1394 equipment. You might damage the equipment or lose data. Conventions For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions. Cabling Configuration It is extremely important to understand how to physically connect the GigaStack GBICs and what mode of operation will occur. Each physical configuration is is cabled somewhat differently and may require the use of more than one GigaStack per switch. Failure to comply may result in a loss of connectivity. The GigaStack GBIC can be cabled in one of the following three ways: Point to point Cascaded stack Cascaded stack with a redundant link The GigaStack GBIC will auto negotiate to either full duplex or half duplex. The software determines the mode of operation by the way the cables are connected and the number of switches in the stack. Note that although duplex can be forced, it is not supported. The only supported option for duplex is to leave it to auto negotiate.
5 Point to Point Connection Point to point connections consist of one GigaStack GBIC per switch and only one connection exists between these modules. The additional available port on the Gigastack is not used and should not be connected to any other device. In this configuration, the GigaStack interface will automatically negotiate to full duplex. One switch can have multiple point to point connections with neighbors as long as you are only using one per port on separate GigaStacks to neighboring switches. In point to point operations, it does not matter what port is connected to the neighbor's port. For example, GigaStack port 1 on switch A can be connected to GigaStack port 2 on switch B. Cascaded Stack Connections Cascaded stack configurations consist of one GigaStack GBIC per switch. Multiple connections exist between these modules. By using one module per switch, you are able to interconnect between three and nine switches using only one GigaStack module per switch. The cable is daisy chained between switches by connecting opposite port numbers between switches. Port 1 to neighboring switch port 2 and so on. There is no physical redundancy. In this configuration, all GigaStack interfaces will automatically negotiate to half duplex. All GigaStack ports will act as a repeater and share the one Gbps channel. The shared Gigabit connection between all switches is called a multidrop backbone.
6 Caution: GBICs are sensitive to power spikes. It is advised to regulate the power to the devices to avoid GBIC failures. Cascaded Stack Connections with a Redundant Link Cascaded stack configuration with a redundant link consists of one GigaStack GBIC per switch. Multiple connections exist between these modules. By using one module per switch, you are able to interconnect between three and nine switches using only one GigaStack module per switch. The cable is daisy chained between switches by connecting opposite port numbers between switches. Port 1 to neighboring switch port 2 and so on. Physical redundancy occurs when you complete the connection between the first and last switch. Every port in all GigaStack modules will have a connection in use. In this configuration, all GigaStack interfaces will automatically negotiate to half duplex. All GigaStack ports will act as a repeater and share the one Gbps channel. A loop configuration will be detected by a loop detection algorithm and one of the links on a GigaStack module will be used as the redundant link. The redundant link in the stack is disabled for data transmission while all other links in the stack are up. When another link in the stack goes down, the redundant link will be enabled for data transmission. No user intervention is required. Note: This configuration is only supported if all switches in the stack run software that supports the loop detection mechanism. Using the Cross Tack Uplink Fast Feature Cross stack UplinkFast (CSUF) provides a fast spanning tree transition (fast convergence in less than one second under normal network conditions) across a stack of switches that use the GigaStack GBICs connected
7 in a shared cascaded configuration (multidrop backbone). During the fast transition, an alternate redundant link on the stack of switches is placed in the forwarding state without causing temporary spanning tree loops or loss of connectivity to the backbone. With this feature, you can have a redundant and resilient network in some configurations. On the catalyst 2900/3500XL, 2950, and 3550 series switches you enable CSUF by first entering the spanning tree uplinkfast command in global configuration mode, and then using the spanning tree stack port interface configuration command on the Gigastack interface desired. On catalyst switches 3750 CSUF is automatically enabled when you enable the UplinkFast feature by using the spanning tree uplinkfast global configuration command. The CSUF feature is supported only when the switch is running PVST. Note: The 2900xl and 3500xl switches require code version 12.0(5)XW or higher to support the Cross stack uplinkfast feature. How CSUF Works CSUF ensures that one link in the stack is elected as the path to the root. As shown in the figure below, Switches A, B, and C are cascaded through the GigaStack GBIC to form a multidrop backbone, which communicates control and data traffic across the switches at the access layer. The switches in the stack use their stack ports to communicate with each other and to connect to the stack backbone; stack ports are always in the spanning tree forwarding state. The stack root port on Switch A provides the path to the root of the spanning tree; the alternate stack root ports on Switches B and C can provide an alternate path to the spanning tree root if the current stack root switch fails or if its link to the spanning tree root fails. Link A, the root link, is in the spanning tree forwarding state; Links B and C are alternate redundant links that are in the spanning tree blocking state. If Link A, Switch A or its stack root port fails, CSUF selects either the Switch B or Switch C alternate stack root port and puts it into the forwarding state in less than one second. Cross Stack UplinkFast Topology CSUF uses the Stack Membership Discovery Protocol to build a neighbor list of stack members through the receipt of discovery hello packets. When certain link loss or spanning tree events occur (described in the
8 Events that Cause Fast Convergence section of this document), the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol uses the neighbor list to send fast transition requests on the stack port to stack members. The switch sending the fast transition request needs to do a fast transition to the forwarding state of a port that it has chosen as the root port, and it must obtain an acknowledgement from each stack switch before performing the fast transition. Each switch in the stack determines if the sending switch is a better choice than itself to be the stack root of this spanning tree instance by comparing the root, cost, and bridge ID. If the sending switch is the best choice as the stack root, each switch in the stack returns an acknowledgement; otherwise, it does not respond to the sending switch (drops the packet). The sending switch then has not received acknowledgements from all stack switches. When acknowledgements are received from all stack switches, the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol on the sending switch immediately transitions its alternate stack root port to the forwarding state. If acknowledgements from all stack switches are not obtained by the sending switch, the normal spanning tree transitions (blocking, listening, learning, and forwarding) take place, and the spanning tree topology converges at its normal rate (2 * forward delay time + max age time). The Fast Uplink Transition Protocol is implemented on a per VLAN basis and affects only one spanning tree instance at a time. Events that Cause Fast Convergence Depending on the network event or failure, the CSUF fast convergence may or may not occur. Fast convergence (less than one second under normal network conditions) occurs under these circumstances: The stack root port link fails. If two switches in the stack have alternate paths to the root, only one of the switches performs the fast transition. The failed link, which connects the stack root to the spanning tree root, recovers. A network reconfiguration causes a new stack root switch to be selected. A network reconfiguration causes a new port on the current stack root switch to be chosen as the stack root port. Note: The fast transition might not occur if multiple events occur simultaneously. For example, if a stack member switch is powered off while the link connecting the stack root to the spanning tree root comes back up, the normal spanning tree convergence occurs. Normal spanning tree convergence (30 to 40 seconds) occurs under the following conditions: The stack root switch is powered off, or the software failed. The stack root switch, which was powered off or failed, is powered on. A new switch, which might become the stack root, is added to the stack. A switch other than the stack root is powered off or failed. A link fails between stack ports on the multidrop backbone. Limitations These limitations apply to CSUF:
9 CSUF uses the GigaStack GBIC and runs on all 3550 switches, all 3500 XL switches, 2950 switches with GBIC module slots, and only on modular 2900 XL switches that have the 1000BASE X module installed. Up to nine stack switches can be connected through their stack ports to the multidrop backbone. Only one stack port per switch is supported. Each stack switch can be connected to the spanning tree backbone through one uplink. If the stack consists of a mixture of 3550, 3500 XL, 2950, and 2900 XL switches, up to 64 VLANs with spanning tree enabled are supported. If the stack consists of only 3550 switches, up to 128 VLANs with spanning tree enabled are supported. The CSUF feature is supported only when the switch is running PVST. If a stack that has 2955, 2950, or 2940 switches also has 2900 XL or 3500 XL switches, cross stack UplinkFast (CSUF) does not function if the management VLAN on the 2900 XL or 3500 XL switches is changed to a VLAN other than VLAN 1 (the default). The workaround is to make sure that the management VLANs of all 2900 XL or 3500 XL switches in the stack are set to VLAN 1. (CSCdv82224) Troubleshooting The following are troubleshooting steps to take on a case by case scenario: For common problems and their solutions, refer to the following document: Common Problems and Their Solutions For an explanation of GigaStack LEDS, refer to the following document: GigaStack GBIC LEDs Error Message: NO_LOOP_DETECT NO_LOOP_DETECT, GIGASTACK, LOG_ALERT, 0, The link neighbor of link %d of GigaStack This error message indicates that there is no acknowledgment for GigaStack loop detection request received from one of the links on a GigaStack GBIC. Either the neighboring switch does not support the GigaStack loop breaking algorithm, or the link between the two GigaStack GBICs is broken. Under this condition, a GigaStack loop topology is not be automatically detected, and the connectivity between switches in the stack could be lost. If loop topology is used in the GigaStack, make sure the latest software is running on all switches in the stack. Check the GigaStack GBICs involved to make sure they are functioning. If no loop exists in the GigaStack GBIC stack, as a workaround, you can disable the loop breaking algorithm by issuing the no gigastack loop breaking [interface id] global configuration command. This is meant as a workaround until you can upgrade all switches to support loop breaking. One Way Traffic Flow When using the GigaStack GBIC with a 3500 XL switch or 2900 XL modular switch and IOS Release 11.2(8.1)SA6, you may experience a problem with traffic flow in one direction when you insert or remove a cable. This is resolved in 11.2(8.2) SA6 and greater. Link Flaps and Never Stabilizes
10 When two switches are connected by a GigaStack GBIC and duplex is forced to full on both ends, the link may flap and never stabilize. When reconfigured to auto duplex on both ends, the link still will not stabilize. After reinserting one of the razors, the link finally stabilizes. This is also seen when link negotiation is shut off. Duplex must always be auto negotiated when a GigaStack GBIC is inserted. Configure the GigaStack ports to auto negotiate duplex by issuing the interface command duplex auto. Configure the GigaStack port to negotiate the link by issuing the interface command negotiation auto. Once complete, remove and reinsert the GigaStack GBIC. The show interface command will show the negotiated state for the GigaStack. Check for the following values in the show interface command output: Auto duplex (Half), 1000Mb/s, media type is CX_GIGASTACK Note: Link and duplex auto negotiation are the default configuration for the GigaStack interfaces. Message: %GIGASTACK 6 LOOP_DETECTED In a redundant loop configuration, an election of which GigaStack link is to be blocked occurs, also known as master loop breaker. All the LEDs on all GigaStacks will flash amber. Once the master loop breaker has been elected, all GigaStack LEDs will be solid green with the exception of the blocked master loop breaker. This link will be solid amber. The following message is displayed on the elected master loop breaker switch: %GIGASTACK 6 LOOP_DETECTED: Gigastack GBIC in is selected as Master Loop Breaker. Link 2 of the master loop breaker GigaStack GBIC is disabled to break the loop. Issuing the show interface command on the master loop breaker port will display the following: GigaStack module(0.1) in GBIC slot. link1 is up, link2 is redundant link. This is normal operation and the message is for informational purposes only. During this time, you may see the links go up/down multiple times. This is normal behavior. ] The loop breaking algorithm occurs between the GigaStack GBICs by exchanging MAC addresses using their A and B ports. The winner of the election, the one with the lowest byte order reversed MAC address, will become the master loop breaker and disable its port 2. For example, if a gig port has the MAC address 00:d0:79:6b:ee:01 (00d0.796b.ee01), the byte order reversed MAC address is ee:01:79:6b:00:d0 (ee01.796b.00d0). To determine the Master Loop Breaker, the reversed MAC addresses are broken into seven data bit chunks, with the first chunk having the highest significance as Master Loop Breaker. The loop breaker will be the seven data bit chunk with the lowest value. If the first seven data bit chunks are identical, then compare the next seven bits until there is a loop breaker. To find out which switch will disable its B port, issue the sh int gig x/y command on each switch and make note of the MAC address in parentheses (the one that says bia and then a MAC address). With this information, perform the byte order reversing operation and then compare the first seven data bit chunks to find the lowest value. The reversed MAC address with the lowest value in its first seven data bit chunk will be the master loop breaker and will disable its port 2. If the first seven data bit chunks are identical, compare the next group until a non identical comparison value can be found.
11 NetPro Discussion Forums Featured Conversations Networking Professionals Connection is a forum for networking professionals to share questions, suggestions, and information about networking solutions, products, and technologies. The featured links are some of the most recent conversations available in this technology. NetPro Discussion Forums Featured Conversations for LAN Network Infrastructure: LAN Routing and Switching Network Infrastructure: Getting Started with LANs Related Information GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) Technical Support Cisco Systems All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement. Updated: Sep 01, 2005 Document ID: 22360
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)
 Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
 CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
4 PWR XL: Catalyst 3524 PWR XL Stackable 10/100 Ethernet
 4 PWR XL: Catalyst 3524 PWR XL Stackable 10/100 Ethernet Table of Contents...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Ordering Information...1 Key Features/Benefits...2 Flexible and Scalable Switch Clustering Architecture...3
4 PWR XL: Catalyst 3524 PWR XL Stackable 10/100 Ethernet Table of Contents...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Ordering Information...1 Key Features/Benefits...2 Flexible and Scalable Switch Clustering Architecture...3
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Overview. Switch Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview The 2900 XL series switches are workgroup Ethernet switches that supply autosensing 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections on all ports. Expansion slots on Catalyst 2912MF XL and 2924M XL switches
CHAPTER 1 Overview The 2900 XL series switches are workgroup Ethernet switches that supply autosensing 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections on all ports. Expansion slots on Catalyst 2912MF XL and 2924M XL switches
Managing Your Switches
 CHAPTER 3 Managing Your Switches You can use the IOS Release 12.0(5)XP software to manage a single switch, a stack of switches that are managed individually, or a cluster of switches that is managed through
CHAPTER 3 Managing Your Switches You can use the IOS Release 12.0(5)XP software to manage a single switch, a stack of switches that are managed individually, or a cluster of switches that is managed through
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]
![Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]](/thumbs/85/92420323.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
Managing Switch Stacks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 2 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 14 Troubleshooting
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 2 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 14 Troubleshooting
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
Managing Network Spanning Trees
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
Configuring STP and Prestandard IEEE 802.1s MST
 20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior
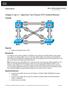 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Managing Switch Stacks
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to manage Catalyst 3750 switch stacks. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the command reference for this release.
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to manage Catalyst 3750 switch stacks. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the command reference for this release.
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
 13 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 How Spanning Tree Operates.................................
13 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 How Spanning Tree Operates.................................
Configuring EtherChannels
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
New Product: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Fast Ethernet Desktop Switches
 New Product: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Fast Ethernet Desktop Switches Product Overview The Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series of fixed configuration, wire-speed Fast Ethernet desktop switches delivers premium
New Product: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Fast Ethernet Desktop Switches Product Overview The Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series of fixed configuration, wire-speed Fast Ethernet desktop switches delivers premium
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial
 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement
 Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
Table of Contents. Cisco Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
 Table of Contents Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)...1 Introduction...1 Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches...2 New Port States and Port Roles...2 Port States...2 Port Roles...3 New
Table of Contents Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)...1 Introduction...1 Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches...2 New Port States and Port Roles...2 Port States...2 Port Roles...3 New
Configuring Spanning Tree
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
Configuring Flex Links
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring MST Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter
 Text Part Number: 78-6494-0 Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter July 6, 999 These release notes describe the features and caveats for the GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter
Text Part Number: 78-6494-0 Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter July 6, 999 These release notes describe the features and caveats for the GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
Cisco - Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations
 Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2
 Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Product Overview. Switch Features. Catalyst 4503 Switch Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER This chapter provides an overview of the features and components of the Catalyst 4500 series switches. The Catalyst 4500 series switches are the Catalyst 4503 switch, the Catalyst 4506 switch,
CHAPTER This chapter provides an overview of the features and components of the Catalyst 4500 series switches. The Catalyst 4500 series switches are the Catalyst 4503 switch, the Catalyst 4506 switch,
Aironet and WLAN Controller Product Power Options
 Aironet and WLAN Controller Product Power Options Document ID: 21480 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cisco Discovery Protocol Power Options Aironet 350 Series
Aironet and WLAN Controller Product Power Options Document ID: 21480 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cisco Discovery Protocol Power Options Aironet 350 Series
Configuring MSTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 Configuring MSTP This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation
CHAPTER 16 Configuring MSTP This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation
Product Overview. Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides these topics that describe the Catalyst 2900 series XL switches, hereafter referred to as the switches. Switch features, including management options Descriptions of the
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides these topics that describe the Catalyst 2900 series XL switches, hereafter referred to as the switches. Switch features, including management options Descriptions of the
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging
 Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP)
 3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
Application Guide. Stacking XGS / XGS HP / XGS / XGS HP
 Application Guide Stacking XGS3700-24 / XGS3700-24HP / XGS3700-48 / XGS3700-48HP Index 1. Purpose of this Document.... 2 2. Scenario One: Stack two Switches... 3 2.1 Topology... 3 2.2 Application Scenario...
Application Guide Stacking XGS3700-24 / XGS3700-24HP / XGS3700-48 / XGS3700-48HP Index 1. Purpose of this Document.... 2 2. Scenario One: Stack two Switches... 3 2.1 Topology... 3 2.2 Application Scenario...
Multicast Does Not Work in the Same VLAN in Catalyst Switches
 Multicast Does Not Work in the Same VLAN in Catalyst Switches Document ID: 68131 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Problem Revisit Some Key Multicast
Multicast Does Not Work in the Same VLAN in Catalyst Switches Document ID: 68131 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Problem Revisit Some Key Multicast
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)
 Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
Product Overview. Switch Model
 Switch Models The Catalyst 3850 family of switches are Ethernet switches to which you can connect devices such as Cisco IP Phones, Cisco Wireless Access Points, workstations, and other network devices
Switch Models The Catalyst 3850 family of switches are Ethernet switches to which you can connect devices such as Cisco IP Phones, Cisco Wireless Access Points, workstations, and other network devices
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Exam Questions
 Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1
 Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Smart Install Concepts
 CHAPTER 1 Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and image-management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. This means that a customer can ship a switch to a location, place
CHAPTER 1 Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and image-management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. This means that a customer can ship a switch to a location, place
material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments
 CHAPTER Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Transparent bridges were first developed at Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital) in the early 1980s and are now very popular in Ethernet/IEEE
CHAPTER Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Transparent bridges were first developed at Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital) in the early 1980s and are now very popular in Ethernet/IEEE
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
 Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) Contents Introduction Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port Roles Port States Port Roles New BPDU Format Full View of the Cisco
Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) Contents Introduction Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port Roles Port States Port Roles New BPDU Format Full View of the Cisco
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
Product Overview. Switch Models CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 The Cisco CGS 2520 switches, also referred to as the switch, are Ethernet switches that you can connect devices such as Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), distributed controllers, substation
CHAPTER 1 The Cisco CGS 2520 switches, also referred to as the switch, are Ethernet switches that you can connect devices such as Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), distributed controllers, substation
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Box to Box Redundancy on the CSS 11xxx Configuration Example
 Box to Box Redundancy on the CSS 11xxx Configuration Example Document ID: 50405 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Box to Box Redundancy on the CSS 11xxx Configuration Example Document ID: 50405 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Describing the STP. IEEE Documents. Download this file. Enhancements to STP. Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt STP
 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
Table of Contents. Cisco Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features
 Table of Contents Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features...1 Document ID: 10596...1 Introduction...1 Feature Availability...1 Brief Summary of STP Port Roles...2
Table of Contents Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features...1 Document ID: 10596...1 Introduction...1 Feature Availability...1 Brief Summary of STP Port Roles...2
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
This chapter describes the power management feature in the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches.
 28 CHAPTER This chapter describes the power management feature in the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this chapter, refer to
28 CHAPTER This chapter describes the power management feature in the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this chapter, refer to
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree
 Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Financial Services Design for High Availability
 Financial Services Design for High Availability Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 March 28, 2003 This document was created. This document describes the best practice for building a multicast
Financial Services Design for High Availability Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 March 28, 2003 This document was created. This document describes the best practice for building a multicast
Table of Contents. Cisco Buffer Tuning for all Cisco Routers
 Table of Contents Buffer Tuning for all Cisco Routers...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1
Table of Contents Buffer Tuning for all Cisco Routers...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1
Table of Contents. Cisco Troubleshooting the Catalyst VMPS Switch
 Table of Contents Troubleshooting the Catalyst VMPS Switch...1 Document ID: 23797...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...2 Troubleshooting DVLAN Membership...2
Table of Contents Troubleshooting the Catalyst VMPS Switch...1 Document ID: 23797...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...2 Troubleshooting DVLAN Membership...2
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Catalyst 2960-X and 2960-XR Switch Hardware Guide
 2960-X and 2960-XR Switch Hardware Guide The 2960-X and 2960-XRfamily of switches are Ethernet switches to which you can connect devices such as Cisco IP Phones, Cisco Wireless Access Points, workstations,
2960-X and 2960-XR Switch Hardware Guide The 2960-X and 2960-XRfamily of switches are Ethernet switches to which you can connect devices such as Cisco IP Phones, Cisco Wireless Access Points, workstations,
Document ID: Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used. Conventions. Background Information.
 Products & Services Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 72836 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Products & Services Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 72836 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Linksys Stackable Switches
 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Linksys Stackable Switches How to Build Stacks and Understand Their Operation This document describes how to stack Linksys switches and covers advanced stacking information, as well
TECHNICAL BULLETIN Linksys Stackable Switches How to Build Stacks and Understand Their Operation This document describes how to stack Linksys switches and covers advanced stacking information, as well
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Communication Redundancy User s Manual
 User s Manual Fifth Edition, June 2015 www.moxa.com/product 2015 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
User s Manual Fifth Edition, June 2015 www.moxa.com/product 2015 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
New Products: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Intelligent Ethernet Switches
 New Products: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Intelligent Ethernet Switches Product Overview Cisco extends its Catalyst 2950 Series Intelligent Ethernet Switches with new fixed-configuration, stackable models
New Products: Cisco Catalyst 2950 Series Intelligent Ethernet Switches Product Overview Cisco extends its Catalyst 2950 Series Intelligent Ethernet Switches with new fixed-configuration, stackable models
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching
 Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Clustering Switches. Understanding Switch Clusters CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides the concepts and procedures to create and manage Catalyst 2975 switch clusters. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack.
CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides the concepts and procedures to create and manage Catalyst 2975 switch clusters. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack.
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
2.2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Catalyst 4500 Series Switches snmp ifindex clear. This command has no arguments or keywords.
 Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan
 isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Exam Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH)
 Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Abstract. GAK; Reviewed: WCH 8/14/2003. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2003 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Overview. About the Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 Switches CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
RSTP Configuration. Page 1 of 26
 RSTP Configuration Page 1 of 26 Content Chapter 1 STP Configuration... 1 1.1 STP Overview... 1 1.1.1 Function of STP...1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP...1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree
RSTP Configuration Page 1 of 26 Content Chapter 1 STP Configuration... 1 1.1 STP Overview... 1 1.1.1 Function of STP...1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP...1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter
 Text Part Number: 78-6494-04 Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter February 4, 2000 These release notes describe the features and caveats for the GigaStack Gigabit Interface
Text Part Number: 78-6494-04 Release Notes for Catalyst GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter February 4, 2000 These release notes describe the features and caveats for the GigaStack Gigabit Interface
Managing Switch Stacks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 1 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 17 Troubleshooting
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 1 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 17 Troubleshooting
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: June 27, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: June 27, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
