Table of Contents. Cisco Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features
|
|
|
- Charity Lynette Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features...1 Document ID: Introduction...1 Feature Availability...1 Brief Summary of STP Port Roles...2 Feature Description: STP Loop Guard...2 Loop Guard Configuration Considerations...3 Loop Guard vs. Unidirectional Link Detection...5 Interoperability of Loop Guard with Other STP Features...5 Root Guard...5 Uplink Fast and Backbone Fast...6 PortFast and BPDU Guard and Dynamic VLAN...6 Shared Links...6 Multiple Spanning Tree (MST)...6 BPDU Skew Detection...6 Feature Description: BPDU Skew Detection...6 Configuring and Monitoring BPDU Skew Detection...7 Related Information...7 i
2 Spanning Tree Protocol Enhancements using Loop Guard and BPDU Skew Detection Features Document ID: Introduction Feature Availability Brief Summary of STP Port Roles Feature Description: STP Loop Guard Loop Guard Configuration Consideration Loop Guard vs. Unidirectional Link Detection Interoperability of Loop Guard with Other STP Features Root Guard Uplink Fast and Backbone Fast Portfast and BPDU Guard and Dynamic VLAN Shared Links Multiple Spanning Tree BPDU Skew Detection Feature Description: BPDU Skew Detection Configuring and Monitoring BPDU Skew Detection Related Information Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) resolves physically redundant topologies into loop free, tree like topologies. The biggest issue with STP is that some hardware failures can make it fail, thus creating forwarding loops (STP loops). Major network outages can be caused by STP loops. This document will discuss the loop guard STP feature intended to improve stability of the Layer 2 (L2) networks. Another feature covered in this document is BPDU skew detection. This diagnostic feature generates syslog messages when BPDUs are not received in due time. This document assumes familiarity with the STP operation and port roles, such as designated port, root port, and alternate port. For a description of STP operation, refer to the following document: Understanding How Spanning Tree Works Feature Availability The STP loop guard feature was introduced in CatOS version of the Catalyst software for Catalyst 4000 and Catalyst 5000 platforms, and in version for Catalyst 6000 platform. BPDU skew detection feature was introduced in CatOS version of the Catalyst software for Catalyst 4000 and Catalyst 5000 platforms and in version for Catalyst 6000 platform.
3 Brief Summary of STP Port Roles Internally, STP assigns a role to each port of a bridge (switch), depending on configuration, topology, relative position of the port in the topology, and other considerations. The port role defines the behavior of the port from the STP point of view. Depending on its role, the port will either send or receive STP Bridge Port Data Units (BPDUs), and will forward or block the data traffic. A brief summary of each STP port role is listed below. Designated: There is one designated port elected per link (segment). This is the port closest to the root bridge. The designated port is responsible for sending BPDUs on its link (segment) and for forwarding traffic towards the root bridge. In a STP converged network, each designated port is in the STP forwarding state. Root: The bridge can have only one root port. This is the port leading to the root bridge. In a STP converged network, root port is in the STP forwarding state. Alternate: The ports leading to the root bridge, but not root ports, are alternate. The alternate ports maintain the STP blocking state. Backup: This is a special case when two or more ports of the same bridge (switch) are connected together, directly or via shared media. In this case, one port will be designated and the rest will be blocking. This port's role is backup. Feature Description: STP Loop Guard The loop guard is intended to provide additional protection against L2 forwarding loops (STP loops). An STP loop is created when an STP blocking port in a redundant topology erroneously transitions to forwarding state. This usually happens because one of the ports of a physically redundant topology (not necessarily the STP blocking port) stopped receiving STP BPDUs. In its operation, STP relies on continuous reception or transmission of BPDUs, depending on the port role (designated port transmits, non designated port receives BPDUs). When one of the ports in a physically redundant topology stops receiving BPDUs, the STP conceives the topology as loop free. Eventually, the blocking port from the alternate or backup port becomes designated, and moves to forwarding state, thus creating a loop. With the loop guard, an additional check is made. If BPDUs are not received any more on a non designated port and the loop guard is enabled, that port will be moved into the STP loop inconsistent blocking state instead of moving to the listening / learning / forwarding state. Without the loop guard, the port would assume the designated port role. The port would move to STP forwarding state, and thus create a loop. When the loop guard blocks an inconsistent port, the following message is logged. SPANTREE 2 LOOPGUARDBLOCK: No BPDUs were received on port 3/2 in vlan 3. Moved to loop inconsiste Once the BPDU is received on a port in a loop inconsistent STP state, the port will transition into another STP state. According to the received BPDU, this means that the recovery is automatic, and no intervention is necessary. After the recovery, the following message is logged. SPANTREE 2 LOOPGUARDUNBLOCK: port 3/2 restored in vlan 3. To illustrate this behavior, consider the following example:
4 Switch A is the root switch. Due to unidirectional link failure on the link between switch B and switch C, switch C is not receiving BPDUs from B. Without the loop guard, STP blocking port on C will transition to STP listening upon max_age timer expiry, and then to forwarding in two times the forward_delay time. A loop will be created. With the loop guard enabled, the blocking port on switch C will transition into STP loop inconsistent state upon max_age timer expiry. A port in STP loop inconsistent state will not pass user traffic, so no loop is created (loop inconsistent state is effectively equal to blocking state). Loop Guard Configuration Considerations The loop guard is enabled on a per port basis. However, as long as it blocks the port on the STP level, it blocks inconsistent ports on a per VLAN basis (because of per VLAN STP). That is, if on the trunk port, BPDUs are not received for only one particular VLAN, only that VLAN will be blocked (moved to loop inconsistent STP state). For the same reason, if enabled on an EtherChannel interface, the entire channel will be blocked for a particular VLAN, not just one link (because EtherChannel is regarded as one logical port
5 from STP point of view). So, on which ports should the loop guard be enabled? The most obvious answer is on the blocking ports. However, this is not totally correct. The loop guard needs to be enabled on the non designated ports (more precisely, on root and alternate ports) for all possible combinations of active topologies. As long as the loop guard is not a per VLAN feature, the same (trunk) port might be designated for one VLAN and non designated for the other. The possible fail over scenarios should also be taken into account. Consider the following example: By default, the loop guard is disabled. The following command is used to enable the loop guard : set spantree guard loop <mod/port> Nelix> (enable) set spantree guard loop 3/13 Enable loopguard will disable rootguard if it's currently enabled on the port(s). Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y Loopguard on port 3/13 is enabled. Starting with version 7.1(1) of the Catalyst software, loop guard can be enabled globally on all ports. Effectively, loop guard will be enabled on all point to point links. The point to point link is detected by the duplex status of the link. If duplex is full, the link is considered point to point. It is still possible to configure, or override, global setting on per port basis. To enable loop guard globally, the following command is used: set spantree global default loopguard enable To disable the loop guard, the following command is used: set spantree guard none <mod/port> To globally disable loop guard, the following command is used: set spantree global default loopguard disable To verify the loop guard status, issue the following command: show spantree guard <mod/port> vlan Nelix> (enable) show spantree guard 3/13 Port VLAN Port State Guard Type
6 3/13 2 forwarding loop Nelix> (enable) Loop Guard vs. Unidirectional Link Detection The loop guard and Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) functionality are overlapping, partly in the sense that both protect against STP failures caused by unidirectional links. These two features are different in approach to the problem, and also in functionality. Consider the following table: As seen from the table above, depending on various design considerations, one can choose either UDLD or the loop guard. The most noticeable difference between the two features, in regards to STP, is the absence of protection in UDLD against STP failures caused by problems in software, resulting in the designated switch not sending BPDUs. It should be mentioned, however, that these types of failure are by orders of magnitude more rare than those caused by unidirectional links. In return, UDLD might be more flexible in the case of unidirectional links on EtherChannel. In this case, UDLD will only disable failed links, and the channel should remain functional with remaining links. The loop guard will block (by putting it into loop inconsistent state) the whole channel in such failure. Additionally, loop guard does not work on shared links or in situations where the link has been unidirectional since the link up. In this last case, the port never receives BPDU and becomes designated. This could be normal behavior, so this particular case is not covered by loop guard. UDLD does provide protection against such a scenario. As described, enabling both UDLD and loop guard provides the highest level of protection. Interoperability of Loop Guard with Other STP Features Root Guard The root guard is mutually exclusive with the loop guard, as it is to be used on designated ports and it does not allow the port to become non designated. The loop guard works on non designated ports and does not allow the port to become designated via max_age expiry. The root guard cannot be enabled on the same port as the loop guard. When the loop guard is being configured on the port, it will disable the root guard configured on the same port.
7 Uplink Fast and Backbone Fast Both uplink fast and backbone fast are transparent to the loop guard. When max_age is skipped by backbone fast during reconvergence, it is not triggering the loop guard. For more information on uplink fast and backbone fast, refer to the following documents: Understanding and Configuring the Cisco Uplink Fast Feature Understanding How Backbone Fast Works PortFast and BPDU Guard and Dynamic VLAN The loop guard cannot be enabled on a port with portfast enabled. Since BPDU guard is working on ports with portfast enabled, some restriction applies to BPDU guard. As dynamic VLAN ports have portfast enabled, the loop guard cannot be enabled on dynamic VLAN ports. Shared Links The loop guard should not be enabled on shared links; doing so may block the traffic from hosts connected to shared segment. Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) Loop guard will function correctly in the MST environment. BPDU Skew Detection Loop guard should interoperate correctly with BPDU skew detection. Feature Description: BPDU Skew Detection STP operation relies heavily on the timely reception of BPDUs. BPDUs are sent by the root bridge at every hello_time message (2 seconds by default). Non root bridges do not regenerate BPDUs for each hello_time message, but they receive relayed BPDUs from the root bridge. Therefore, every non root bridge is supposed to receive BPDUs on every VLAN for each hello_time message. In some cases BPDUs are lost or the bridge CPU is too busy to relay BPDU in a timely manner. These, and other issues, can cause BPDUs to arrive late, if at all. This potentially compromises the stability of the spanning tree topology. BPDU skew detection allows the switch to keep track of late arriving BPDUs and notify the administrator by means of syslog messages. For every port on which BPDU has ever arrived late (skewed), skew detection will report the most recent skewing and the duration of the skewing (latency). It also reports the longest BPDU delay on this particular port. To protect the bridge CPU from overloading, a syslog message is not generated every time BPDU skewing occurs. Messages are rate limited to one message every 60 seconds. However, should the delay of BPDU exceed max_age/2 (which makes 10 seconds by default), the message is always printed immediately. It is important to note that BPDU skewing detection is a diagnostic feature. Upon detection of BPDU skewing, it just sends a syslog message. BPDU skew detection takes no further corrective action. Below is an example of syslog message generated by BPDU skew detection:
8 %SPANTREE 2 BPDU_SKEWING: BPDU skewed with a delay of 10 secs (max_age/2) Configuring and Monitoring BPDU Skew Detection BPDU skew detection is configured on per switch basis. The default setting is disabled. To enable BPDU skew detection, the following command should be used: Cat6k> (enable) set spantree bpdu skewing enable Spantree bpdu skewing enabled on this switch. To see BPDU skewing information, use the sh spantree bpdu skewing <vlan> <mod/port> command as demonstrated below. Cat6k> (enable) sh spantree bpdu skewing 1 Bpdu skewing statistics for vlan 1 Port Last Skew (ms) Worst Skew (ms) Worst Skew Time 3/ Mon Nov , 16:36:04 Related Information Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Spanning Tree Portfast BPDU Guard Enhancement Understanding and Configuring the Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol (UDLD) Feature LAN Technologies Technical Tips LAN Technologies Top Issues All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement. Updated: May 10, 2005 Document ID: 10596
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement
 Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol Root Guard Enhancement Document ID: 10588 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Feature Description Availability Configuration CatOS Configuration
PrepKing. PrepKing
 PrepKing Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 180 min File Version: 9.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ PrepKing 350-001 Sections 1. Section 1.00 - Implement Layer 2 2. Section 2.00 - Implement IPv4
PrepKing Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 180 min File Version: 9.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ PrepKing 350-001 Sections 1. Section 1.00 - Implement Layer 2 2. Section 2.00 - Implement IPv4
Configuring STP Extensions
 Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan
 isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
isco Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Chan Table of Contents Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Changes...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Configuring STP Extensions Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) extensions on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About
This chapter describes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) extensions on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About
Configuring STP Extensions
 This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
 Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) Contents Introduction Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port Roles Port States Port Roles New BPDU Format Full View of the Cisco
Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) Contents Introduction Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port Roles Port States Port Roles New BPDU Format Full View of the Cisco
Table of Contents. Cisco Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
 Table of Contents Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)...1 Introduction...1 Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches...2 New Port States and Port Roles...2 Port States...2 Port Roles...3 New
Table of Contents Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)...1 Introduction...1 Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches...2 New Port States and Port Roles...2 Port States...2 Port Roles...3 New
Managing Network Spanning Trees
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
 CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
Configuring Spanning Tree
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
STP Optional Characteristic Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2
 Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Real4Test. Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps
 Real4Test http://www.real4test.com Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps Exam : 350-001 Title : CCIE Routing and Switching Written Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 13 Get Latest & Valid
Real4Test http://www.real4test.com Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps Exam : 350-001 Title : CCIE Routing and Switching Written Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 13 Get Latest & Valid
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
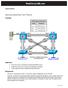 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]
![Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Cisco Exam Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ]](/thumbs/85/92420323.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 200-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 149 ] Topic break down Topic No. of Questions Topic 1: LAN Switching Technologies 18 Topic 2:
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Cisco - Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations
 Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)
 Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Exam Questions
 Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1
 Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
RSTP Configuration. RSTP Configuration
 RSTP Configuration Contents 16. STP Configuration...1 1.1 STP Overview...1 1.1.1 Function of STP... 1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP... 1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree Interface States...
RSTP Configuration Contents 16. STP Configuration...1 1.1 STP Overview...1 1.1.1 Function of STP... 1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP... 1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree Interface States...
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)
 Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
RSTP Configuration. Page 1 of 26
 RSTP Configuration Page 1 of 26 Content Chapter 1 STP Configuration... 1 1.1 STP Overview... 1 1.1.1 Function of STP...1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP...1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree
RSTP Configuration Page 1 of 26 Content Chapter 1 STP Configuration... 1 1.1 STP Overview... 1 1.1.1 Function of STP...1 1.1.2 Protocol Packets of STP...1 1.1.3 Basic Concepts in STP... 1 1.1.4 Spanning-Tree
Chapter 5: STP. * What is STP? How does STP work?
 Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
Describing the STP. IEEE Documents. Download this file. Enhancements to STP. Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt STP
 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands
 STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands...
STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Configuration Commands...
Configuring STP and Prestandard IEEE 802.1s MST
 20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
Document ID: Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used. Conventions. Background Information.
 Products & Services Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 72836 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Products & Services Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 72836 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging
 Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Configuring MST Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
Objectives. 1. Introduction:
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.5 Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Objectives 1. Explain the role of redundancy
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.5 Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Objectives 1. Explain the role of redundancy
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
DECUS IT-Symposium Spanning Tree Protocol Interoperability Cisco/HP ProCurve
 DECUS IT-Symposium 2006 Spanning Tree Protocol Interoperability Cisco/HP ProCurve Juergen Bruns Network Competency Center EMEA HP Services 2003 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
DECUS IT-Symposium 2006 Spanning Tree Protocol Interoperability Cisco/HP ProCurve Juergen Bruns Network Competency Center EMEA HP Services 2003 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
2.2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Catalyst 4500 Series Switches snmp ifindex clear. This command has no arguments or keywords.
 Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.
![2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords. 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.](/thumbs/72/66270180.jpg) 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones
 Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Cisco.Actualtests v by.Ciscothegr8.362q
 Cisco.Actualtests.350-001.v2013-10-21.by.Ciscothegr8.362q Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 16.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam Code: 350-001 Exam Name: Cisco CCIE Cisco
Cisco.Actualtests.350-001.v2013-10-21.by.Ciscothegr8.362q Number: 350-001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 16.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam Code: 350-001 Exam Name: Cisco CCIE Cisco
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
Improving network convergence with Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
 CEAI, Vol.15, No.1 pp. 79-87, 2013 Printed in Romania Improving network convergence with Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Roxana Stănică SC Civitas Systems S.R.L., Craiova, Romania (e-mail: roxana_batm@yahoo.com)
CEAI, Vol.15, No.1 pp. 79-87, 2013 Printed in Romania Improving network convergence with Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Roxana Stănică SC Civitas Systems S.R.L., Craiova, Romania (e-mail: roxana_batm@yahoo.com)
This chapter covers the following topics: Multilayer Campus Design Access Module Building Blocks Layer 2 Domain Layer 3 Domain
 This chapter covers the following topics: Multilayer Campus Design Access Module Building Blocks Layer 2 Domain Layer 3 Domain C H A P T E R 6 Access Module The access module is a network s interface to
This chapter covers the following topics: Multilayer Campus Design Access Module Building Blocks Layer 2 Domain Layer 3 Domain C H A P T E R 6 Access Module The access module is a network s interface to
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial
 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
Implementing MST in a Large Campus Environment
 Implementing MST in a Large Campus Environment February 13, 2007 Rich Ingram rni@umn.edu Overview Introduction Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Our Implementation Introduction U of M Twin Cities Campus
Implementing MST in a Large Campus Environment February 13, 2007 Rich Ingram rni@umn.edu Overview Introduction Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Our Implementation Introduction U of M Twin Cities Campus
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree
 Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN)
 Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Cisco EXAM Cisco ADVDESIGN. Buy Full Product.
 Cisco EXAM - 352-001 Cisco ADVDESIGN Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/352-001.html Examskey Cisco 352-001 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This Cisco 352-001
Cisco EXAM - 352-001 Cisco ADVDESIGN Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/352-001.html Examskey Cisco 352-001 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This Cisco 352-001
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols-PART-I LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Modified by Tony Chen 05/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you
MSTP Configuration. Configuration
 MSTP Configuration Contents 1. Configuring MSTP...2 1.1 Brief Introduction to MSTP... 2 1.2 BPDU... 2 1.2.1 Basic Concepts in MSTP...2 1.2.2 Roles of Ports...4 1.3 Algorithm Implementation... 7 1.3.1 MSTP
MSTP Configuration Contents 1. Configuring MSTP...2 1.1 Brief Introduction to MSTP... 2 1.2 BPDU... 2 1.2.1 Basic Concepts in MSTP...2 1.2.2 Roles of Ports...4 1.3 Algorithm Implementation... 7 1.3.1 MSTP
Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks
 10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Exam : Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert. Ver :
 Exam : 350-001 Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert Ver : 11-26-07 QUESTION 1: Under the OSPF process of your router's configuration, you type in "redistribute igrp 25 metric 35 subnets" in order
Exam : 350-001 Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert Ver : 11-26-07 QUESTION 1: Under the OSPF process of your router's configuration, you type in "redistribute igrp 25 metric 35 subnets" in order
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches
 Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Chapter 5. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I
 Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Campus Networking Workshop. Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs
 Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 Introduction to STP 1-1 Why STP 1-1 Protocol Packets of STP 1-1 Basic Concepts in STP 1-2 How STP works 1-3 Introduction to RSTP 1-9 Introduction
Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 Introduction to STP 1-1 Why STP 1-1 Protocol Packets of STP 1-1 Basic Concepts in STP 1-2 How STP works 1-3 Introduction to RSTP 1-9 Introduction
MSTP Configuration. Page 1 of 24
 MSTP Configuration Page 1 of 24 Contents Chapter1 Configuring MSTP... 3 1.1 Brief Introduction to MSTP...3 1.2 BPDU...3 1.2.1 Basic Concepts in MSTP... 4 1.2.2 Roles of Ports... 6 1.3 Algorithm Implementation...9
MSTP Configuration Page 1 of 24 Contents Chapter1 Configuring MSTP... 3 1.1 Brief Introduction to MSTP...3 1.2 BPDU...3 1.2.1 Basic Concepts in MSTP... 4 1.2.2 Roles of Ports... 6 1.3 Algorithm Implementation...9
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: June 27, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
Layer 2/3 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: June 27, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
Integrated Switch Technology
 CHAPTER 2 This section discusses the following topics: Cisco Intelligent Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the IBM BladeCenter Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the HP BladeSystem Cisco Intelligent
CHAPTER 2 This section discusses the following topics: Cisco Intelligent Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the IBM BladeCenter Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the HP BladeSystem Cisco Intelligent
Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Configuring MSTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 Configuring MSTP This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation
CHAPTER 16 Configuring MSTP This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation
The Spanning Tree 802.1D (2004) RSTP MSTP
 The Spanning Tree 802.1D (2004) RSTP MSTP (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 http://www.perihel.at 1 Problem Description We want redundant links in bridged networks But transparent bridging cannot deal with redundancy
The Spanning Tree 802.1D (2004) RSTP MSTP (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 http://www.perihel.at 1 Problem Description We want redundant links in bridged networks But transparent bridging cannot deal with redundancy
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
 Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Authorized CCNP. Student. LabManual SWITCH.
 Authorized CCNP SWITCH Student LabManual Web:www.networkershome.com Email:info@networkershome.com www.networkershome.com Authorized CCNPSWITCHWORKBOOK Module:01to20 CopyrightsNetworkersHome2007-2015 Website:htp:/www.networkershome.com;info@networkershome.com
Authorized CCNP SWITCH Student LabManual Web:www.networkershome.com Email:info@networkershome.com www.networkershome.com Authorized CCNPSWITCHWORKBOOK Module:01to20 CopyrightsNetworkersHome2007-2015 Website:htp:/www.networkershome.com;info@networkershome.com
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
Abstract. GAK; Reviewed: WCH 8/14/2003. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2003 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
CUDN PoP Switch Changes 2018
 CUDN PoP Switch Changes 2018 Agenda New PoP switch choices Port assignments Recommendations on connecting Spanning Tree now and changes How these will interact with your network DHCP Snooping & ARP Inspection
CUDN PoP Switch Changes 2018 Agenda New PoP switch choices Port assignments Recommendations on connecting Spanning Tree now and changes How these will interact with your network DHCP Snooping & ARP Inspection
Question No: 1 On the MSTP network as shown in the figure, what is the role of the switch in MSTI 1 according to the configuration?
 Volume: 629 Questions Question No: 1 On the MSTP network as shown in the figure, what is the role of the switch in MSTI 1 according to the configuration? A. Root switch B. Slave switch C. Non-root switch
Volume: 629 Questions Question No: 1 On the MSTP network as shown in the figure, what is the role of the switch in MSTI 1 according to the configuration? A. Root switch B. Slave switch C. Non-root switch
CCNP SWITCH (22 Hours)
 CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching
 CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 15 Objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 15 Objectives (con
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 1 & 15: Enhanced Switching Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 15 Objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 15 Objectives (con
Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH)
 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Switched Networks (SWITCH) v2.0 is a five-day instructor-led training course developed to help students prepare for
Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Switched Networks (SWITCH) v2.0 is a five-day instructor-led training course developed to help students prepare for
MSTP Technology White Paper
 MSTP Technology White Paper Key words: STP, RSTP, MSTP, rapid transition, multiple instances, redundancy loop, redundancy link, load sharing Abstract: This article introduces basic MSTP terms, MSTP algorithm
MSTP Technology White Paper Key words: STP, RSTP, MSTP, rapid transition, multiple instances, redundancy loop, redundancy link, load sharing Abstract: This article introduces basic MSTP terms, MSTP algorithm
62HConfiguring port role restriction 131H37. 63HConfiguring TC-BPDU transmission restriction 132H38. 64HEnabling TC-BPDU guard 133H38
 Contents Configuring spanning tree protocols 3 STP 3 STP protocol packets 3 Basic concepts in STP 4 Calculation process of the STP algorithm 5 RSTP 9 MSTP 10 MSTP features 10 MSTP basic concepts 10 How
Contents Configuring spanning tree protocols 3 STP 3 STP protocol packets 3 Basic concepts in STP 4 Calculation process of the STP algorithm 5 RSTP 9 MSTP 10 MSTP features 10 MSTP basic concepts 10 How
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) Course Overview
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) Course Overview This course will teach students about implementing scalable medium-sized networks, troubleshooting basic connectivity, implementing
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) Course Overview This course will teach students about implementing scalable medium-sized networks, troubleshooting basic connectivity, implementing
