Avoiding Sorting and Grouping In Processing Queries
|
|
|
- Chester Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Avoiding Sorting and Grouping In Processing Queries
2 Outline Motivation Simple Example Order Properties Grouping followed by ordering Order Property Optimization Performance Results Conclusion
3 Motivation Previous presentation: Fundamental Techniques for Order Optimization Using FDs and selection predicates Determining order propagation from input to output Infer from ordering Current presentation: Aside from orderings, we also infer how relations are grouped (i.e., how records in relations are clustered according to value of certain attributes) Infer from grouping Infer from secondary ordering
4 Motivation(cont.) Inferred orderings Make it possible to avoid ing when preprocessing ORDER BY clauses of SQL query Inferred groupings Avoid ing or hashing prior to computing aggregates for GROUP BY clauses Reduce the cost of projection with duplicate elimination Complete projection and duplicate elimination in a single pass Reduce the cost of evaluating selection queries in the form σ A=k (R) in the absence of indexes or an ordering on A Inference of secondary ordering and grouping Avoid unnecessary ing or grouping over multiple attributes Infer new primary orderings or groupings (example follows)
5 Simple Example Benefits of inferring grouping and secondary ordering TPC-H Query SELECT c_custkey, COUNT (*) FROM Customer, Supplier WHERE c_nationkey = s_nationkey GROUPBY c_custkey How many suppliers could supply each costumer directly without having to go through customs
6 Simple Example (cont.) -merge join result is ed (and hence grouped) on c_nationkey and the output tuples are in the same group with respect to c_nationkey, they are themselves grouped on the key of outer relation (c_custkey) But one-pass aggregation requires data only to be grouped and not ed! group c_custkey, count(*) c_custkey merge-join c_nationkey = s_nationkey c_nationkey G c_custkey G =>no Postgres Plan first s the join result to on the grouping attribute c_custkey so as to be able to aggregate over groups in a single pass. TPC-H Query c_nationkey table scan customer s_nationkey table scan supplier SELECT c_custkey, COUNT (*) FROM Customer, Supplier WHERE c_nationkey = s_nationkey GROUPBY c_custkey Postgres QEP of the Query
7 Order Properties order properties have the form: each A i is an attribute, each α i either specifies an ordering (α i = O) or a grouping (α i =G) A 1 α 1 primary ordering or grouping and A2 α 2 secondary Signatures for ordering constructs
8 Order Properties (cont.) The general properties have the form: Shorthand: Also, given and Shorthand: o 1 o 2 (concatenation of OP):
9 Order Properties (cont.) Identities for any order property that holds of a physical relation, all prefixes of that order property also hold of R an ordering on any attribute implies a grouping on that attribute If X functionally determines B, and an order property that includes all attributes in X (ordered or grouped) appearing before B α, then B α is superfluous.
10 Order Properties (cont.) Identities (cont.) special case of identity #3, covering the case where X consists of a single attribute the grouping of an attribute that is functionally determined by the attribute that follows it in the order property is superfluous
11 Grouping followed by ordering Suppose that R=(A,B) consists of 10 tuples, t 1,,t 10, and its physical representation satisfies the order property, A o B G is illustrated on the next slide
12 Grouping followed by ordering (cont.) The primary ordering (A O ) says that the group of tuples with A=1 precedes the group of tuples with A=2 which precedes the group with A=3 A=1 B=1 B=2 t 1 t 2 t 3 A=3 B=3 B=2 t 7 t 6 B=1 t 5 t 4 The secondary ordering (B G ) says that within each group of tuples with like values of A, tuples are clustered together if they have the same value for B t 1 can precede t2 or t2 can precede t1 but the must be adjacent < B=1 t 8 A=2 < B=2 t 9 t 10 Two Example permutations that satisfies the order property : t 2, t 1, t 3, t 10, t 8, t 9, t 6, t 7, t 4, t 5 An illustration of A O B G t 1, t 2, t 3, t 9, t 8, t 10, t 4, t 5, t 6, t 7
13 Order Property Optimization Postgres Plan Operators Summarized The data structures for all plan nodes in postgres include the following fields: inp1, inp n : the fields contained in all input tuples to the node left: the left subtree of the node (set to Null for leaf nodes and Append) right: the right subtree of the node (set to Null for leaf nodes, unary operators and Append).
14 Order Property Optimization Postgres Plan Operators Summarized(cont.) Additional operator-specific fields provided by Postgres and used by our refinement algorithm
15 Order Property Optimization Postgres Plan Operators Summarized (cont.) Group performs two passes over its input: 1. insert Null values between pairs of consecutive tuples with different values for attributes, att 1,,att k, 2. apply functions F k+1,, F n to the collection of values of attributes att k+1,,att n respectively, for each set of tuples separated by Nulls. Hash: builds a hash table over its input using a predetermined hash function over attribute att.
16 Order Property Optimization HJoin: performs a (non-order-preserving) simple hash equijoin (att 1 = att 2 ) with the relation produced by left as the probe relation, and the relation produced by right as the build relation. Merge: performs a merge equijoin (att 1 = att 2 ) with the relation produced by left as the outer relation, and the relation produced by right as the inner relation. NOP: we have added as a dummy plan operator that we temporarily make the root of a Postgres plan prior to its refinement.
17 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm Input: query plan tree generated by Postgres Output: an equivalent plan tree with unnecessary Sort operators (used either to order or group) removed Requires: 4 new attributes associated with every node in a query plan tree
18 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm(cont.) New Attributes keys: a set of attribute sets that are guaranteed to be keys of inputs to n fds: a set of functional dependencies (attribute sets attribute) that are guaranteed to hold of inputs to n req: a single order property that is required to hold of inputs either to n or some ancestor node of n for that node to execute sat: a set of order properties that are guaranteed to be satisfied by outputs of n
19 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) Idea: decorate the input plan with the attributes above remove any Sort operator n whose child node produces a result that is guaranteed to satisfy an order property required by its parent node Accomplished in 3 passes
20 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) Refinement of the query plan NOP group c_custkey, count(*) c_custkey merge-join c_nationkey = s_nationkey c_nationkey table scan customer s_nationkey table scan supplier
21 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) Pass 1:Functional Dependencies and Keys A bottom-up pass, FDs and keys are propagated upwards when inferred to hold intermediate query result Pass 2:Required Order Properties Top-down pass requires order properties (req) which are propagated downwards from the root of the tree Operations pseudocode captured in SetReq New required operators are generated by: NOP: Node Order Property (called on the root of the plan to trigger the top-down pass) Group and Unique Join operator All other nodes pass the required order properties they inherit from parent nodes to their child nodes, except for Hash and Append which propagate the empty order property to their child nodes
22 Order Property Optimization
23 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) Pass 3:Sort Elimination A bottom-up pass of the query plan tree that determines what order properties are guaranteed to be satisfied by outputs of each node (sat), and that concurrently removes any Sort operator, n for which n.left.sat Є n.req Algorithm: InferSat!
24 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) InferSat
25 Order Property Optimization A Plan Refinement Algorithm (cont.) InferSat (cont.)
26 Example:TPC-D(now TPC-H) Query 3 TPC-D Query 3 select l_orderkey, sum (l _extendedprice*( 1- l_discount)) as rev, o_orderdate, o_shippriority from customer, order, lineitem where o_orderkey = l_orderkey and c_custkey = o_custkey and c_mktsegment = building and o_orderdate < date( ) and l_shipdate > date( ) group by l_orderkey, o_orderdate, o_shippriority order by rev desc, o_orderdate
27 Example:TPC-D(now TPC-H) Query 3 Previous presentation: We showed that the optimized plan outperformed the original plan by a factor of 2 Now: Improve using our approach to plan refinement reasons about groupings and secondary orderings
28 Example:TPC-D(now TPC-H) Query 3 NLJ R=> O o_orderkey G(U) Identitiy#5 => O o_orderkey G(T) Identitiy#4 =>O o_custkey G O o_orderkey G(T) rev, o_orderdate group by o_orderkey MJ Rule =>O c_custkey G c_custkey G o_custkey G o_orderkey G(T) and c_custkey = o_custkey => O o_custkey G o_custkey G o_custkey G o_orderkey G(T) merge-join c_custkey = o_custkey nested-loops o_orderkey = l_orderkey o_orderkey Index scan lineitem Identitiy#5 => O c_custkey G o_orderkey G(S) O c_custkey o(r)=> O c_custkey G(R) c_custkey o_custkey O o_custkey o(s)=> O o_custkey G(S) table scan customer table scan order
29 Performance Results TPC-D (now TPC-H) Results Database: PC: Customer table: 150,000 rows Supplier table: 10,000 rows Order table: 1,500,000 rows LineItem table: 6,000,000 rows 1 GHz Pentium III Linux, with 512 MB RAM, 120 GB HDD
30 Performance Results Experiment #1 our example Postgres Plan sec Refined sec Ratio group c_custkey, count(*) c_custkey merge-join c_nationkey = s_nationkey c_nationkey s_nationkey table scan customer table scan supplier
31 Performance Results Experiment #2 TPC-H Query 3 rev, o_orderdate Postgres Plan Refined Ratio group by o_orderkey sec Same value of o_orderkey were consecutive tuples thereby increased likelihood of finding joining tuples from lineitem in the cache sec 0.05 merge-join c_custkey = o_custkey nested-loops o_orderkey = l_orderkey o_orderkey Index scan lineitem c_custkey o_custkey table scan customer table scan order
32 Performance Results Experiment #2 TPC-H Query 3 With table scan on lineitem Postgres Plan Refined Ratio rev, o_orderdate group by o_orderkey sec sec 1.07 nested-loops o_orderkey = l_orderkey o_orderkey Table scan lineitem merge-join c_custkey = o_custkey c_custkey o_custkey table scan customer table scan order
33 Conclusion we present a formal approach to order optimization that integrates both orderings and groupings within the same comprehensive framework We also consider secondary orderings and groupings By inferring secondary orderings and groupings, it is possible to avoid unnecessary ing or grouping over multiple attributes we can use secondary orderings known of an operator's input to infer primary orderings of its output
34 Any Questions?
Midterm Review. March 27, 2017
 Midterm Review March 27, 2017 1 Overview Relational Algebra & Query Evaluation Relational Algebra Rewrites Index Design / Selection Physical Layouts 2 Relational Algebra & Query Evaluation 3 Relational
Midterm Review March 27, 2017 1 Overview Relational Algebra & Query Evaluation Relational Algebra Rewrites Index Design / Selection Physical Layouts 2 Relational Algebra & Query Evaluation 3 Relational
On-Disk Bitmap Index Performance in Bizgres 0.9
 On-Disk Bitmap Index Performance in Bizgres 0.9 A Greenplum Whitepaper April 2, 2006 Author: Ayush Parashar Performance Engineering Lab Table of Contents 1.0 Summary...1 2.0 Introduction...1 3.0 Performance
On-Disk Bitmap Index Performance in Bizgres 0.9 A Greenplum Whitepaper April 2, 2006 Author: Ayush Parashar Performance Engineering Lab Table of Contents 1.0 Summary...1 2.0 Introduction...1 3.0 Performance
6.830 Problem Set 2 (2017)
 6.830 Problem Set 2 1 Assigned: Monday, Sep 25, 2017 6.830 Problem Set 2 (2017) Due: Monday, Oct 16, 2017, 11:59 PM Submit to Gradescope: https://gradescope.com/courses/10498 The purpose of this problem
6.830 Problem Set 2 1 Assigned: Monday, Sep 25, 2017 6.830 Problem Set 2 (2017) Due: Monday, Oct 16, 2017, 11:59 PM Submit to Gradescope: https://gradescope.com/courses/10498 The purpose of this problem
Introduction to Query Processing and Query Optimization Techniques. Copyright 2011 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant Navathe
 Introduction to Query Processing and Query Optimization Techniques Outline Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra Algorithms for External Sorting Algorithms for SELECT and JOIN Operations Algorithms
Introduction to Query Processing and Query Optimization Techniques Outline Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra Algorithms for External Sorting Algorithms for SELECT and JOIN Operations Algorithms
Beyond EXPLAIN. Query Optimization From Theory To Code. Yuto Hayamizu Ryoji Kawamichi. 2016/5/20 PGCon Ottawa
 Beyond EXPLAIN Query Optimization From Theory To Code Yuto Hayamizu Ryoji Kawamichi 2016/5/20 PGCon 2016 @ Ottawa Historically Before Relational Querying was physical Need to understand physical organization
Beyond EXPLAIN Query Optimization From Theory To Code Yuto Hayamizu Ryoji Kawamichi 2016/5/20 PGCon 2016 @ Ottawa Historically Before Relational Querying was physical Need to understand physical organization
Advanced Database Systems
 Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Chapter 12: Query Processing. Chapter 12: Query Processing
 Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Querying Data with Transact SQL
 Course 20761A: Querying Data with Transact SQL Course details Course Outline Module 1: Introduction to Microsoft SQL Server 2016 This module introduces SQL Server, the versions of SQL Server, including
Course 20761A: Querying Data with Transact SQL Course details Course Outline Module 1: Introduction to Microsoft SQL Server 2016 This module introduces SQL Server, the versions of SQL Server, including
Chapter 13: Query Processing
 Chapter 13: Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 13.1 Basic Steps in Query Processing 1. Parsing
Chapter 13: Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 13.1 Basic Steps in Query Processing 1. Parsing
Database System Concepts
 Chapter 13: Query Processing s Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 st Semester 2008/2009 Slides (fortemente) baseados nos slides oficiais do livro c Silberschatz, Korth
Chapter 13: Query Processing s Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 st Semester 2008/2009 Slides (fortemente) baseados nos slides oficiais do livro c Silberschatz, Korth
Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization. 0. Introduction to Query Processing (1)
 Chapter 19 Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization 0. Introduction to Query Processing (1) Query optimization: The process of choosing a suitable execution strategy for processing a query. Two
Chapter 19 Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization 0. Introduction to Query Processing (1) Query optimization: The process of choosing a suitable execution strategy for processing a query. Two
Chapter 12: Query Processing
 Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Overview Chapter 12: Query Processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Overview Chapter 12: Query Processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Histogram Support in MySQL 8.0
 Histogram Support in MySQL 8.0 Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer MySQL Optimizer Team, Oracle February 2018 Program Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 Motivating example Quick start guide How are histograms
Histogram Support in MySQL 8.0 Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer MySQL Optimizer Team, Oracle February 2018 Program Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 Motivating example Quick start guide How are histograms
! A relational algebra expression may have many equivalent. ! Cost is generally measured as total elapsed time for
 Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing
 Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Towards Comprehensive Testing Tools
 Towards Comprehensive Testing Tools Redefining testing mechanisms! Kuntal Ghosh (Software Engineer) PGCon 2017 26.05.2017 1 Contents Motivation Picasso Visualizer Picasso Art Gallery for PostgreSQL 10
Towards Comprehensive Testing Tools Redefining testing mechanisms! Kuntal Ghosh (Software Engineer) PGCon 2017 26.05.2017 1 Contents Motivation Picasso Visualizer Picasso Art Gallery for PostgreSQL 10
MOIRA A Goal-Oriented Incremental Machine Learning Approach to Dynamic Resource Cost Estimation in Distributed Stream Processing Systems
 MOIRA A Goal-Oriented Incremental Machine Learning Approach to Dynamic Resource Cost Estimation in Distributed Stream Processing Systems Daniele Foroni, C. Axenie, S. Bortoli, M. Al Hajj Hassan, R. Acker,
MOIRA A Goal-Oriented Incremental Machine Learning Approach to Dynamic Resource Cost Estimation in Distributed Stream Processing Systems Daniele Foroni, C. Axenie, S. Bortoli, M. Al Hajj Hassan, R. Acker,
Query Processing. Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016
 Query Processing Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016 Slides re-used with some modification from www.db-book.com Reference: Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. By Silberschatz,
Query Processing Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016 Slides re-used with some modification from www.db-book.com Reference: Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. By Silberschatz,
Efficient in-memory query execution using JIT compiling. Han-Gyu Park
 Efficient in-memory query execution using JIT compiling Han-Gyu Park 2012-11-16 CONTENTS Introduction How DCX works Experiment(purpose(at the beginning of this slide), environment, result, analysis & conclusion)
Efficient in-memory query execution using JIT compiling Han-Gyu Park 2012-11-16 CONTENTS Introduction How DCX works Experiment(purpose(at the beginning of this slide), environment, result, analysis & conclusion)
Chapter 3. Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization
 Chapter 3 Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization Chapter Outline 1. Introduction to Query Processing 2. Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra 3. Algorithms for External Sorting 4. Algorithms
Chapter 3 Algorithms for Query Processing and Optimization Chapter Outline 1. Introduction to Query Processing 2. Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra 3. Algorithms for External Sorting 4. Algorithms
Optimizing Queries Using Materialized Views
 Optimizing Queries Using Materialized Views Paul Larson & Jonathan Goldstein Microsoft Research 3/22/2001 Paul Larson, View matching 1 Materialized views Precomputed, stored result defined by a view expression
Optimizing Queries Using Materialized Views Paul Larson & Jonathan Goldstein Microsoft Research 3/22/2001 Paul Larson, View matching 1 Materialized views Precomputed, stored result defined by a view expression
Orri Erling (Program Manager, OpenLink Virtuoso), Ivan Mikhailov (Lead Developer, OpenLink Virtuoso).
 Orri Erling (Program Manager, OpenLink Virtuoso), Ivan Mikhailov (Lead Developer, OpenLink Virtuoso). Business Intelligence Extensions for SPARQL Orri Erling and Ivan Mikhailov OpenLink Software, 10 Burlington
Orri Erling (Program Manager, OpenLink Virtuoso), Ivan Mikhailov (Lead Developer, OpenLink Virtuoso). Business Intelligence Extensions for SPARQL Orri Erling and Ivan Mikhailov OpenLink Software, 10 Burlington
A Compression Framework for Query Results
 A Compression Framework for Query Results Zhiyuan Chen and Praveen Seshadri Cornell University zhychen, praveen@cs.cornell.edu, contact: (607)255-1045, fax:(607)255-4428 Decision-support applications in
A Compression Framework for Query Results Zhiyuan Chen and Praveen Seshadri Cornell University zhychen, praveen@cs.cornell.edu, contact: (607)255-1045, fax:(607)255-4428 Decision-support applications in
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 6 Outline. Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and
 Chapter 6 The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 6 Outline Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and PROJECT Relational
Chapter 6 The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 6 Outline Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and PROJECT Relational
Evaluation of Relational Operations
 Evaluation of Relational Operations Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst March 13 and 15, 2006 Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Relational Operations We will consider how to implement: Selection
Evaluation of Relational Operations Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst March 13 and 15, 2006 Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Relational Operations We will consider how to implement: Selection
Optimizer Standof. MySQL 5.6 vs MariaDB 5.5. Peter Zaitsev, Ovais Tariq Percona Inc April 18, 2012
 Optimizer Standof MySQL 5.6 vs MariaDB 5.5 Peter Zaitsev, Ovais Tariq Percona Inc April 18, 2012 Thank you Ovais Tariq Ovais Did a lot of heavy lifing for this presentation He could not come to talk together
Optimizer Standof MySQL 5.6 vs MariaDB 5.5 Peter Zaitsev, Ovais Tariq Percona Inc April 18, 2012 Thank you Ovais Tariq Ovais Did a lot of heavy lifing for this presentation He could not come to talk together
Materialized Views. March 28, 2018
 Materialized Views March 28, 2018 1 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth AS SELECT l.* FROM lineitem l, orders o WHERE l.orderkey = o.orderkey AND o.orderdate > DATE( 2015-03-31 ) 2 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth
Materialized Views March 28, 2018 1 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth AS SELECT l.* FROM lineitem l, orders o WHERE l.orderkey = o.orderkey AND o.orderdate > DATE( 2015-03-31 ) 2 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth
Two-Phase Optimization for Selecting Materialized Views in a Data Warehouse
 Two-Phase Optimization for Selecting Materialized Views in a Data Warehouse Jiratta Phuboon-ob, and Raweewan Auepanwiriyakul Abstract A data warehouse (DW) is a system which has value and role for decision-making
Two-Phase Optimization for Selecting Materialized Views in a Data Warehouse Jiratta Phuboon-ob, and Raweewan Auepanwiriyakul Abstract A data warehouse (DW) is a system which has value and role for decision-making
1.1 - Basics of Query Processing in SQL Server
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2013/2014 Database Administration and Tuning Lab 3 2nd semester In this lab class, we will address query processing. For students with a particular interest
Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2013/2014 Database Administration and Tuning Lab 3 2nd semester In this lab class, we will address query processing. For students with a particular interest
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 CHAPTER 19 Query Optimization Introduction Query optimization Conducted by a query optimizer in a DBMS Goal: select best available strategy for executing query Based on information available Most RDBMSs
CHAPTER 19 Query Optimization Introduction Query optimization Conducted by a query optimizer in a DBMS Goal: select best available strategy for executing query Based on information available Most RDBMSs
Lazy Maintenance of Materialized Views
 Lazy Maintenance of Materialized Views Jingren Zhou, Microsoft Research, USA Paul Larson, Microsoft Research, USA Hicham G. Elmongui, Purdue University, USA Introduction 2 Materialized views Speed up query
Lazy Maintenance of Materialized Views Jingren Zhou, Microsoft Research, USA Paul Larson, Microsoft Research, USA Hicham G. Elmongui, Purdue University, USA Introduction 2 Materialized views Speed up query
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques
 Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques Chapter 12, Part B Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke 1 Using an Index for Selections v Cost depends on #qualifying
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques Chapter 12, Part B Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke 1 Using an Index for Selections v Cost depends on #qualifying
CMSC424: Database Design. Instructor: Amol Deshpande
 CMSC424: Database Design Instructor: Amol Deshpande amol@cs.umd.edu Databases Data Models Conceptual representa1on of the data Data Retrieval How to ask ques1ons of the database How to answer those ques1ons
CMSC424: Database Design Instructor: Amol Deshpande amol@cs.umd.edu Databases Data Models Conceptual representa1on of the data Data Retrieval How to ask ques1ons of the database How to answer those ques1ons
Spark-GPU: An Accelerated In-Memory Data Processing Engine on Clusters
 1 Spark-GPU: An Accelerated In-Memory Data Processing Engine on Clusters Yuan Yuan, Meisam Fathi Salmi, Yin Huai, Kaibo Wang, Rubao Lee and Xiaodong Zhang The Ohio State University Paypal Inc. Databricks
1 Spark-GPU: An Accelerated In-Memory Data Processing Engine on Clusters Yuan Yuan, Meisam Fathi Salmi, Yin Huai, Kaibo Wang, Rubao Lee and Xiaodong Zhang The Ohio State University Paypal Inc. Databricks
When and How to Take Advantage of New Optimizer Features in MySQL 5.6. Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer, MySQL Oracle
 When and How to Take Advantage of New Optimizer Features in MySQL 5.6 Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer, MySQL Oracle Program Agenda Improvements for disk-bound queries Subquery improvements
When and How to Take Advantage of New Optimizer Features in MySQL 5.6 Øystein Grøvlen Senior Principal Software Engineer, MySQL Oracle Program Agenda Improvements for disk-bound queries Subquery improvements
Database Applications (15-415)
 Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VI Lecture 14, March 12, 2014 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: DBMS Internals- Part V Hash-based indexes (Cont d) and External Sorting Today s Session:
Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VI Lecture 14, March 12, 2014 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: DBMS Internals- Part V Hash-based indexes (Cont d) and External Sorting Today s Session:
Chapter 12: Query Processing
 Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Catalog Information for Cost Estimation $ Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join Operation Other Operations Evaluation of Expressions Transformation
Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Catalog Information for Cost Estimation $ Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join Operation Other Operations Evaluation of Expressions Transformation
CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems
 CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems L10: Query Processing Other Operations, Pipelining and Materialization Dr. Kenneth LEUNG Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science
CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems L10: Query Processing Other Operations, Pipelining and Materialization Dr. Kenneth LEUNG Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques
 Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques [R&G] Chapter 14, Part B CS4320 1 Using an Index for Selections Cost depends on #qualifying tuples, and clustering. Cost of finding qualifying data
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques [R&G] Chapter 14, Part B CS4320 1 Using an Index for Selections Cost depends on #qualifying tuples, and clustering. Cost of finding qualifying data
Advances in Data Management Query Processing and Query Optimisation A.Poulovassilis
 1 Advances in Data Management Query Processing and Query Optimisation A.Poulovassilis 1 General approach to the implementation of Query Processing and Query Optimisation functionalities in DBMSs 1. Parse
1 Advances in Data Management Query Processing and Query Optimisation A.Poulovassilis 1 General approach to the implementation of Query Processing and Query Optimisation functionalities in DBMSs 1. Parse
DBMS Query evaluation
 Data Management for Data Science DBMS Maurizio Lenzerini, Riccardo Rosati Corso di laurea magistrale in Data Science Sapienza Università di Roma Academic Year 2016/2017 http://www.dis.uniroma1.it/~rosati/dmds/
Data Management for Data Science DBMS Maurizio Lenzerini, Riccardo Rosati Corso di laurea magistrale in Data Science Sapienza Università di Roma Academic Year 2016/2017 http://www.dis.uniroma1.it/~rosati/dmds/
Chapter 18 Indexing Structures for Files
 Chapter 18 Indexing Structures for Files Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Disk I/O for Read/ Write Unit for Disk I/O for Read/ Write: Chapter 18 One Buffer for
Chapter 18 Indexing Structures for Files Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Disk I/O for Read/ Write Unit for Disk I/O for Read/ Write: Chapter 18 One Buffer for
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques
 Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques Chapter 14, Part B Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke 1 Using an Index for Selections Cost depends on #qualifying
Evaluation of Relational Operations: Other Techniques Chapter 14, Part B Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke 1 Using an Index for Selections Cost depends on #qualifying
arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 22 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 22 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 22 Sep 2014](/thumbs/95/125062301.jpg) Enabling Incremental Query Re-Optimization Mengmeng Liu University of Pennsylvania 333 Walnut Street Philadelphia, PA 1914 mengmeng@cis.upenn.edu Zachary G. Ives University of Pennsylvania 333 Walnut Street
Enabling Incremental Query Re-Optimization Mengmeng Liu University of Pennsylvania 333 Walnut Street Philadelphia, PA 1914 mengmeng@cis.upenn.edu Zachary G. Ives University of Pennsylvania 333 Walnut Street
Implementation of Relational Operations: Other Operations
 Implementation of Relational Operations: Other Operations Module 4, Lecture 2 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan 1 Simple Selections SELECT * FROM Reserves R WHERE R.rname < C% Of the form σ
Implementation of Relational Operations: Other Operations Module 4, Lecture 2 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan 1 Simple Selections SELECT * FROM Reserves R WHERE R.rname < C% Of the form σ
Faloutsos 1. Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science Database Applications. Outline
 Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science 15-415 - Database Applications Lecture #14: Implementation of Relational Operations (R&G ch. 12 and 14) 15-415 Faloutsos 1 introduction selection projection
Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science 15-415 - Database Applications Lecture #14: Implementation of Relational Operations (R&G ch. 12 and 14) 15-415 Faloutsos 1 introduction selection projection
Leveraging Query Parallelism In PostgreSQL
 Leveraging Query Parallelism In PostgreSQL Get the most from intra-query parallelism! Dilip Kumar (Principle Software Engineer) Rafia Sabih (Software Engineer) 2013 EDB All rights reserved. 1 Overview
Leveraging Query Parallelism In PostgreSQL Get the most from intra-query parallelism! Dilip Kumar (Principle Software Engineer) Rafia Sabih (Software Engineer) 2013 EDB All rights reserved. 1 Overview
Materialized Views. March 26, 2018
 Materialized Views March 26, 2018 1 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth AS SELECT l.* FROM lineitem l, orders o WHERE l.orderkey = o.orderkey AND o.orderdate > DATE( 2015-03-31 ) SELECT partkey FROM salessincelastmonth
Materialized Views March 26, 2018 1 CREATE VIEW salessincelastmonth AS SELECT l.* FROM lineitem l, orders o WHERE l.orderkey = o.orderkey AND o.orderdate > DATE( 2015-03-31 ) SELECT partkey FROM salessincelastmonth
What happens. 376a. Database Design. Execution strategy. Query conversion. Next. Two types of techniques
 376a. Database Design Dept. of Computer Science Vassar College http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~cs376 Class 16 Query optimization What happens Database is given a query Query is scanned - scanner creates a list
376a. Database Design Dept. of Computer Science Vassar College http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~cs376 Class 16 Query optimization What happens Database is given a query Query is scanned - scanner creates a list
Advanced Query Optimization
 Advanced Query Optimization Andreas Meister Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg Summer Term 2018 Why do we need query optimization? Andreas Meister Advanced Query Optimization Last Change: April 23,
Advanced Query Optimization Andreas Meister Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg Summer Term 2018 Why do we need query optimization? Andreas Meister Advanced Query Optimization Last Change: April 23,
TPC-H Benchmark Set. TPC-H Benchmark. DDL for TPC-H datasets
 TPC-H Benchmark Set TPC-H Benchmark TPC-H is an ad-hoc and decision support benchmark. Some of queries are available in the current Tajo. You can download the TPC-H data generator here. DDL for TPC-H datasets
TPC-H Benchmark Set TPC-H Benchmark TPC-H is an ad-hoc and decision support benchmark. Some of queries are available in the current Tajo. You can download the TPC-H data generator here. DDL for TPC-H datasets
Hash table example. B+ Tree Index by Example Recall binary trees from CSE 143! Clustered vs Unclustered. Example
 Student Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Hash table example Index Student_ID on Student.ID Data File Student 10 Tom Hanks 10 20 20 Amy Hanks ID fname lname 10 Tom Hanks 20 Amy Hanks Lecture 26:
Student Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Hash table example Index Student_ID on Student.ID Data File Student 10 Tom Hanks 10 20 20 Amy Hanks ID fname lname 10 Tom Hanks 20 Amy Hanks Lecture 26:
Fundamentals of Database Systems
 Fundamentals of Database Systems Assignment: 4 September 21, 2015 Instructions 1. This question paper contains 10 questions in 5 pages. Q1: Calculate branching factor in case for B- tree index structure,
Fundamentals of Database Systems Assignment: 4 September 21, 2015 Instructions 1. This question paper contains 10 questions in 5 pages. Q1: Calculate branching factor in case for B- tree index structure,
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Stop-and-Resume Style Execution for Long Running Decision Support Queries
 Stop-and-Resume Style Execution for Long Running Decision Support Queries Surajit Chaudhuri Raghav Kaushik Abhijit Pol Ravi Ramamurthy Microsoft Research Microsoft Research University of Florida Microsoft
Stop-and-Resume Style Execution for Long Running Decision Support Queries Surajit Chaudhuri Raghav Kaushik Abhijit Pol Ravi Ramamurthy Microsoft Research Microsoft Research University of Florida Microsoft
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems. B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #10: Query Processing
 CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #10: Query Processing Outline introduction selection projection join set & aggregate operations Prakash 2018 VT CS 4604 2
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #10: Query Processing Outline introduction selection projection join set & aggregate operations Prakash 2018 VT CS 4604 2
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414. Lecture 26: More Indexes and Operator Costs
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 26: More Indexes and Operator Costs CSE 414 - Spring 2018 1 Student ID fname lname Hash table example 10 Tom Hanks Index Student_ID on Student.ID Data File
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 26: More Indexes and Operator Costs CSE 414 - Spring 2018 1 Student ID fname lname Hash table example 10 Tom Hanks Index Student_ID on Student.ID Data File
Outline. Database Management and Tuning. Outline. Join Strategies Running Example. Index Tuning. Johann Gamper. Unit 6 April 12, 2012
 Outline Database Management and Tuning Johann Gamper Free University of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Science IDSE Unit 6 April 12, 2012 1 Acknowledgements: The slides are provided by Nikolaus Augsten
Outline Database Management and Tuning Johann Gamper Free University of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Science IDSE Unit 6 April 12, 2012 1 Acknowledgements: The slides are provided by Nikolaus Augsten
Database Management
 Database Management - 2011 Model Answers 1. a. A data model should comprise a structural part, an integrity part and a manipulative part. The relational model provides standard definitions for all three
Database Management - 2011 Model Answers 1. a. A data model should comprise a structural part, an integrity part and a manipulative part. The relational model provides standard definitions for all three
SELECT Product.name, Purchase.store FROM Product JOIN Purchase ON Product.name = Purchase.prodName
 Announcements Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lectures 5: More SQL aggregates Homework 2 has been released Web quiz 2 is also open Both due next week 1 2 Outline Outer joins (6.3.8, review) More
Announcements Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lectures 5: More SQL aggregates Homework 2 has been released Web quiz 2 is also open Both due next week 1 2 Outline Outer joins (6.3.8, review) More
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems. Query Processing: The Basics. Textbook: Chapter 10. (first edition: Chapter 13) University of Alberta 1
 CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems Query Processing: The Basics Textbook: Chapter 10 (first edition: Chapter 13) Based on slides by Lewis, Bernstein and Kifer University of Alberta 1 External Sorting
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems Query Processing: The Basics Textbook: Chapter 10 (first edition: Chapter 13) Based on slides by Lewis, Bernstein and Kifer University of Alberta 1 External Sorting
Querying Data with Transact-SQL
 Course 20761A: Querying Data with Transact-SQL Page 1 of 5 Querying Data with Transact-SQL Course 20761A: 2 days; Instructor-Led Introduction The main purpose of this 2 day instructor led course is to
Course 20761A: Querying Data with Transact-SQL Page 1 of 5 Querying Data with Transact-SQL Course 20761A: 2 days; Instructor-Led Introduction The main purpose of this 2 day instructor led course is to
Chapter 18: Parallel Databases
 Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery
Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery
Chapter 18: Parallel Databases. Chapter 18: Parallel Databases. Parallelism in Databases. Introduction
 Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery Parallelism Intraoperation Parallelism Interoperation Parallelism Design of
Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Chapter 18: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery Parallelism Intraoperation Parallelism Interoperation Parallelism Design of
Evaluation of relational operations
 Evaluation of relational operations Iztok Savnik, FAMNIT Slides & Textbook Textbook: Raghu Ramakrishnan, Johannes Gehrke, Database Management Systems, McGraw-Hill, 3 rd ed., 2007. Slides: From Cow Book
Evaluation of relational operations Iztok Savnik, FAMNIT Slides & Textbook Textbook: Raghu Ramakrishnan, Johannes Gehrke, Database Management Systems, McGraw-Hill, 3 rd ed., 2007. Slides: From Cow Book
Evaluation of Relational Operations
 Evaluation of Relational Operations Chapter 14 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2010 1 Relational Operations We will consider in more detail how to implement: Selection ( ) Selects a subset of rows from
Evaluation of Relational Operations Chapter 14 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2010 1 Relational Operations We will consider in more detail how to implement: Selection ( ) Selects a subset of rows from
Query Optimization. Query Optimization. Optimization considerations. Example. Interaction of algorithm choice and tree arrangement.
 COS 597: Principles of Database and Information Systems Query Optimization Query Optimization Query as expression over relational algebraic operations Get evaluation (parse) tree Leaves: base relations
COS 597: Principles of Database and Information Systems Query Optimization Query Optimization Query as expression over relational algebraic operations Get evaluation (parse) tree Leaves: base relations
CAS CS 460/660 Introduction to Database Systems. Query Evaluation II 1.1
 CAS CS 460/660 Introduction to Database Systems Query Evaluation II 1.1 Cost-based Query Sub-System Queries Select * From Blah B Where B.blah = blah Query Parser Query Optimizer Plan Generator Plan Cost
CAS CS 460/660 Introduction to Database Systems Query Evaluation II 1.1 Cost-based Query Sub-System Queries Select * From Blah B Where B.blah = blah Query Parser Query Optimizer Plan Generator Plan Cost
CSC317/MCS9317. Database Performance Tuning. Class test
 CSC317/MCS9317 Database Performance Tuning Class test 7 October 2015 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. The test time is approximately 120 minutes. The test is close book and close
CSC317/MCS9317 Database Performance Tuning Class test 7 October 2015 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. The test time is approximately 120 minutes. The test is close book and close
PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it?
 6.830 Lecture 7 9/25/2017 PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it? Project Teams Due Wednesday Those of you who don't have groups -- send us email, or hand in a sheet with just your
6.830 Lecture 7 9/25/2017 PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it? Project Teams Due Wednesday Those of you who don't have groups -- send us email, or hand in a sheet with just your
Technical Report - Distributed Database Victor FERNANDES - Université de Strasbourg /2000 TECHNICAL REPORT
 TECHNICAL REPORT Distributed Databases And Implementation of the TPC-H Benchmark Victor FERNANDES DESS Informatique Promotion : 1999 / 2000 Page 1 / 29 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... 3 INTRODUCTION... 3
TECHNICAL REPORT Distributed Databases And Implementation of the TPC-H Benchmark Victor FERNANDES DESS Informatique Promotion : 1999 / 2000 Page 1 / 29 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... 3 INTRODUCTION... 3
Join (SQL) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 페이지 1 / 7 Sample tables All subsequent explanations on join types in this article make use of the following two tables. The rows in these tables serve to illustrate the effect of different types of joins
페이지 1 / 7 Sample tables All subsequent explanations on join types in this article make use of the following two tables. The rows in these tables serve to illustrate the effect of different types of joins
! Parallel machines are becoming quite common and affordable. ! Databases are growing increasingly large
 Chapter 20: Parallel Databases Introduction! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems!
Chapter 20: Parallel Databases Introduction! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems!
Chapter 20: Parallel Databases
 Chapter 20: Parallel Databases! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems 20.1 Introduction!
Chapter 20: Parallel Databases! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems 20.1 Introduction!
Chapter 20: Parallel Databases. Introduction
 Chapter 20: Parallel Databases! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems 20.1 Introduction!
Chapter 20: Parallel Databases! Introduction! I/O Parallelism! Interquery Parallelism! Intraquery Parallelism! Intraoperation Parallelism! Interoperation Parallelism! Design of Parallel Systems 20.1 Introduction!
Querying Data with Transact SQL Microsoft Official Curriculum (MOC 20761)
 Querying Data with Transact SQL Microsoft Official Curriculum (MOC 20761) Course Length: 3 days Course Delivery: Traditional Classroom Online Live MOC on Demand Course Overview The main purpose of this
Querying Data with Transact SQL Microsoft Official Curriculum (MOC 20761) Course Length: 3 days Course Delivery: Traditional Classroom Online Live MOC on Demand Course Overview The main purpose of this
Database Applications (15-415)
 Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VII Lecture 15, March 17, 2014 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: DBMS Internals- Part VI Algorithms for Relational Operations Today s Session: DBMS
Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VII Lecture 15, March 17, 2014 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: DBMS Internals- Part VI Algorithms for Relational Operations Today s Session: DBMS
Evaluation of Relational Operations
 Evaluation of Relational Operations Chapter 12, Part A Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Relational Operations We will consider how to implement: Selection ( ) Selects a subset
Evaluation of Relational Operations Chapter 12, Part A Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Relational Operations We will consider how to implement: Selection ( ) Selects a subset
Chapter 17: Parallel Databases
 Chapter 17: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery Parallelism Intraoperation Parallelism Interoperation Parallelism Design of Parallel Systems Database Systems
Chapter 17: Parallel Databases Introduction I/O Parallelism Interquery Parallelism Intraquery Parallelism Intraoperation Parallelism Interoperation Parallelism Design of Parallel Systems Database Systems
Administriva. CS 133: Databases. General Themes. Goals for Today. Fall 2018 Lec 11 10/11 Query Evaluation Prof. Beth Trushkowsky
 Administriva Lab 2 Final version due next Wednesday CS 133: Databases Fall 2018 Lec 11 10/11 Query Evaluation Prof. Beth Trushkowsky Problem sets PSet 5 due today No PSet out this week optional practice
Administriva Lab 2 Final version due next Wednesday CS 133: Databases Fall 2018 Lec 11 10/11 Query Evaluation Prof. Beth Trushkowsky Problem sets PSet 5 due today No PSet out this week optional practice
CSE 530A. B+ Trees. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
Chapter 18 Strategies for Query Processing. We focus this discussion w.r.t RDBMS, however, they are applicable to OODBS.
 Chapter 18 Strategies for Query Processing We focus this discussion w.r.t RDBMS, however, they are applicable to OODBS. 1 1. Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra and Other Operators - SQL is
Chapter 18 Strategies for Query Processing We focus this discussion w.r.t RDBMS, however, they are applicable to OODBS. 1 1. Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra and Other Operators - SQL is
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing. Basic Concepts
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
Announcement. Reading Material. Overview of Query Evaluation. Overview of Query Evaluation. Overview of Query Evaluation 9/26/17
 Announcement CompSci 516 Database Systems Lecture 10 Query Evaluation and Join Algorithms Project proposal pdf due on sakai by 5 pm, tomorrow, Thursday 09/27 One per group by any member Instructor: Sudeepa
Announcement CompSci 516 Database Systems Lecture 10 Query Evaluation and Join Algorithms Project proposal pdf due on sakai by 5 pm, tomorrow, Thursday 09/27 One per group by any member Instructor: Sudeepa
Query Processing & Optimization
 Query Processing & Optimization 1 Roadmap of This Lecture Overview of query processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join Operation Other Operations Evaluation of Expressions Introduction
Query Processing & Optimization 1 Roadmap of This Lecture Overview of query processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join Operation Other Operations Evaluation of Expressions Introduction
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan See for conditions on re-use
 Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files Static
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files Static
SQL QUERY EVALUATION. CS121: Relational Databases Fall 2017 Lecture 12
 SQL QUERY EVALUATION CS121: Relational Databases Fall 2017 Lecture 12 Query Evaluation 2 Last time: Began looking at database implementation details How data is stored and accessed by the database Using
SQL QUERY EVALUATION CS121: Relational Databases Fall 2017 Lecture 12 Query Evaluation 2 Last time: Began looking at database implementation details How data is stored and accessed by the database Using
CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems. Magdalena Balazinska Fall 2007 Lecture 7 - Query execution
 CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems Magdalena Balazinska Fall 2007 Lecture 7 - Query execution References Generalized Search Trees for Database Systems. J. M. Hellerstein, J. F. Naughton
CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems Magdalena Balazinska Fall 2007 Lecture 7 - Query execution References Generalized Search Trees for Database Systems. J. M. Hellerstein, J. F. Naughton
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 5th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Database System Concepts, 5th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree
Dtb Database Systems. Announcement
 Dtb Database Systems ( 資料庫系統 ) December 10, 2008 Lecture #11 1 Announcement Assignment #5 will be out on the course webpage today. 2 1 External Sorting Chapter 13 3 Why learn sorting again? O (n*n): bubble,
Dtb Database Systems ( 資料庫系統 ) December 10, 2008 Lecture #11 1 Announcement Assignment #5 will be out on the course webpage today. 2 1 External Sorting Chapter 13 3 Why learn sorting again? O (n*n): bubble,
Query Processing. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2017
 Query Processing Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2017 2 Announcements (Tue., Nov. 14) Homework #3 sample solution posted in Sakai Homework #4 assigned today; due on 12/05 Project milestone #2
Query Processing Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2017 2 Announcements (Tue., Nov. 14) Homework #3 sample solution posted in Sakai Homework #4 assigned today; due on 12/05 Project milestone #2
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Chapter 11: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B + -Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Toward a Progress Indicator for Database Queries
 Toward a Progress Indicator for Database Queries Gang Luo Jeffrey F. Naughton Curt J. Ellmann Michael W. Watzke University of Wisconsin-Madison NCR Advance Development Lab {gangluo, naughton}@cs.wisc.edu
Toward a Progress Indicator for Database Queries Gang Luo Jeffrey F. Naughton Curt J. Ellmann Michael W. Watzke University of Wisconsin-Madison NCR Advance Development Lab {gangluo, naughton}@cs.wisc.edu
Query processing of pre-partitioned data using Sandwich Operators
 Query processing of pre-partitioned data using Sandwich Operators Stephan Baumann 1, Peter Boncz 2, and Kai-Uwe Sattler 1 1 Ilmenau University of Technology, Ilmenau, Germany, first.last@tu-ilmenau.de,
Query processing of pre-partitioned data using Sandwich Operators Stephan Baumann 1, Peter Boncz 2, and Kai-Uwe Sattler 1 1 Ilmenau University of Technology, Ilmenau, Germany, first.last@tu-ilmenau.de,
University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Sample Solution
 1. (4 total marks) University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Sample Solution Winter, 2012 Suppose that a relational database contains the following large relation: Track(ReleaseID, TrackNum, Title, Length,
1. (4 total marks) University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Sample Solution Winter, 2012 Suppose that a relational database contains the following large relation: Track(ReleaseID, TrackNum, Title, Length,
Indexing and Hashing
 C H A P T E R 1 Indexing and Hashing This chapter covers indexing techniques ranging from the most basic one to highly specialized ones. Due to the extensive use of indices in database systems, this chapter
C H A P T E R 1 Indexing and Hashing This chapter covers indexing techniques ranging from the most basic one to highly specialized ones. Due to the extensive use of indices in database systems, this chapter
Database Applications (15-415)
 Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VI Lecture 17, March 24, 2015 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Two Sessions: DBMS Internals- Part V External Sorting How to Start a Company in Five (maybe
Database Applications (15-415) DBMS Internals- Part VI Lecture 17, March 24, 2015 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Two Sessions: DBMS Internals- Part V External Sorting How to Start a Company in Five (maybe
Question 1 (a) 10 marks
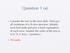 Question 1 (a) Consider the tree in the next slide. Find any/ all violations of a B+tree structure. Identify each bad node and give a brief explanation of each error. Assume the order of the tree is 4
Question 1 (a) Consider the tree in the next slide. Find any/ all violations of a B+tree structure. Identify each bad node and give a brief explanation of each error. Assume the order of the tree is 4
