Certificates, Trust & PKI. Certificates, Trust & PKI. Brian A. LaMacchia.
|
|
|
- Corey Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Certificates, Trust & PKI Certificates, Trust & PKI Brian A. LaMacchia Portions , Brian A. LaMacchia. This material is provided without warranty of any kind including, without limitation, warranty of non-infringement or suitability for any purpose. This material is not guaranteed to be error free and is intended for instructional use only.
2 Certificates
3 Why do I trust the server key?! How do I know I m really talking to Amazon.com?! What defeats a man-in in-the the-middle attack? HTTP with SSL/TLS Client Mallet HTTP with SSL/TLS Web Server February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 3
4 SSL/TLS You (client) Merchant (server) Let s talk securely. Here are the protocols and ciphers I understand. I choose this protocol and ciphers. Here is my public key and some other stuff that will make you trust this key is mine. Here is a fresh key encrypted with your key. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 4
5 What s the some other stuff How can we convince Alice that some key belongs to Bob?! Alice and Bob could have met previously & exchanged keys directly. " Jeff Bezos isn t going to shake hands with everyone he d like to sell to...! Someone Alice trusts could vouch to her for Bob and Bob s key " A third party can certify Bob s key in a way that convinces Alice. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 5
6 What is a certificate?! A certificate is a digitally-signed statement that binds a public key to some identifying information. " The signer of the certificate is called its issuer. " The entity talked about in the certificate is the subject of the certificate.! That s all a certificate is, at the 30,000 level. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 6
7 Certificates are Like Marriage By the power vested in me I now declare this text and this bit string name and key. What RSA has joined, let no man put asunder. --Bob Blakley February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 7
8 Certs in the real world! A driver s license is like a certificate " It is a signed document (sealed, tamper-resistant) resistant) " It is created and signed by an issuing authority (the WA Dept. of Licensing) " It binds together various pieces of identifying information " Name " License number " Driving restrictions (must wear glasses, etc.) February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 8
9 More certs certs in the real world Many physical objects are like certificates: " Any type of license! Many physical objects are like Any type of license vehicle tabs, restaurant liquor license, amateur radio license, etc. " Government Government-issued IDs (passports, green cards) " Membership cards (e.g. Costco, discount cards)! All of these examples bind an identity and certain rights, privileges or other identifiers " BAL ==N1TJT signed FCC February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 9
10 Why do we believe what certs say?! In the physical world, why do we trust the statements contained on a physical cert? " We believe it s hard to forge the cert " We trust the entity that signed the cert! In the digital world we need those same two properties " We need to believe it s hard to forge the digital signature on a signed document " We need to trust the issuer/signer not to lie to us February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 10
11 Defeating Mallet Bob can convince Alice that his key really does belong to him if he can also send along a digital certificate Alice will believe & trust Let s talk securely. Here are the protocols and ciphers I understand. Cert Cert Alice I choose this protocol and ciphers. Here is my public key and a certificate to convince you that the key really belongs to me. Bob February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 11
12 Getting a certificate! How does Bob get a certificate for his key?! He goes to a Certificate Authority (CA) that issues certificates and asks for one...! The CA issues Bob a certificate for his public key. " CA is the issuer " Bob is the subject February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 12
13 Using Certificates! Now that Bob has a certificate, is it useful?! Alice will believe Bob s key belongs to Bob if Alice believes the certificate Bob gives her for his key.! Alice will believe Bob s key belongs to Bob if Alice trusts the issuer of Bob s certificate to make key-name binding statements! Have we made the situation any better? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 13
14 Does Alice Trust Bob s CA? How can we convince Alice to trust Bob s CA?! Alice and Bob s CA could have met previously & exchanged keys directly. " Bob s CA isn t going to shake hands with Bob s CA isn t going to shake hands with everyone he s certified, let alone everyone whom Bob wants to talk to. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 14
15 Does Alice Trust Bob s CA? How can we convince Alice to trust Bob s CA?! Alice and Bob s CA could have met previously & exchanged keys directly. " Bob s CA isn t going to shake hands with Bob s CA isn t going to shake hands with everyone he s certified, let alone everyone whom Bob wants to talk to.! Someone Alice trusts could vouch to her for Bob s CA and Bob s CA s key " Infinite Loop: See Loop, Infinite. " Actually, it s just a bounded recursion... February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 15
16 What s Alice s Trust Model! Alice has to implicitly trust some set of keys " Once she does that, those keys can introduce others to her.! In the model used by SSL/TLS, CAs are arranged in a hierarchy " Alice, and everyone else, trusts one or more root CA that live at the top of the tree! Other models work differently February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 16
17 Public Key Infrastructure Public Key Infrastructure
18 Certificate Authorities! A certificate authority (CA) guarantees the connection between a key and another CA or an end entity.! An end entity is: " A person " A role ( VP of sales ) " An organization " A pseudonym " A piece of hardware or software " An account Some CA s only allow a subset of these types.! Some CA s only allow a subset of these February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 18
19 CA Hierarchies! CAs can certify other CAs or end entities! Certificates are links in a tree of EEs & CAs Root CA CA CA EE CA EE EE February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 19
20 BAL s No-Frills Certs! Certificates can contain all sorts of information inside them " We ll talk about the details in a little bit! In the abstract, though, they re just statements by an issuer about a subject: Issuer Subject February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 20
21 Does Alice trust Bob s Key?! Alice trusts Bob s key if there is a chain of certificates from Bob s key to a root CA that Alice implicitly trusts Root CA CA EE Root CA Root CA Root CA CA CA EE February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 21
22 Chain Building & Validation! Given an end-entity entity certificate, does there exist a cryptographically valid chain of certificates linking it to a trusted root certificate? Root CA CA EE Root CA Root CA Root CA CA CA EE February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 22
23 Chaining Certificates! In theory, building chains of certificates should be easy " Just link them together like dominos! In practice, it s a lot more complicated... February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 23
24 Chain Building Details (1) Root CA Root CA CA1 Root CA CA2 CA1 CA2 CA1 EE1 CA1 EE2 CA2 EE3 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 24
25 Chain Building Details (2) Root CA1 Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 25
26 Chain Building Details (3) Root CA1 Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 26
27 Chain Building Details (3) Root CA1 Bridge CA Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 27
28 Chain Building Details (3) Root CA1 Bridge CA Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 28
29 Chain Building Details (3) Root CA1 Bridge CA Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 29
30 Chain Building Details (3) Root CA1 Bridge CA Root CA2 CA1 CA2 EE1 EE2 EE3 February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 30
31 Chaining Certificates! How do we determine whether two certificates chain together? " You d think this was an easy problem... " But it s actually a question with religious significance in the security community " Are you a believer in names,, or in keys?! In order to understand the schism, we need to digress for a bit and talk about names and some history February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 31
32 PKI Alphabet Soup! X.509v3 - standard content of a certificate! PKIX IETF Working Group on PKI interoperability " PKIX == Public Key Infrastructure using X.509v3 certificates! ASN.1 - Abstract Syntax Notation, exact description of a certificate format! DER - Distinguished Encoding Rules, how to physically package a certificate February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 32
33 The X.500 Directory Model! The model SSL/TLS uses, the X.509 certificate model, is based on names " Names as principles! Specifically, X.509 is based on the X.500 directory model! X.500 defined a global, all- encompassing directory, to be run by the telcos " One directory to rule them all, one directory to define them... February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 33
34 X.500 Distinguished Names! In the X.500 model, everything has a single, unique, global, assigned name " There is a worldwide hierarchy, and you re in it! Country C=US SP = OR State or Province SP = WA SP = CA Locality L=Redmond L=Seattle Organization O=Microsoft O=Univ. of Washington February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 34
35 DNs in Practice! Name is unique within the scope of the CA s name! Public CAs (e.g. Verisign) ) typically set " C = CA Country " O = CA Name " OU = Certificate type/class " CN = User name " E= address February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 35
36 Private-label DNs! If you own the CA, you get to decide what fields go in the DN " Really varies on what the software supports! Can get really strange as people try to guess values for fields that are required by software " Software requires an OU, we don t have OUs,, so I better make something up! February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 36
37 DNs in X.509 Certificates! The X.509 certificate standard began as a way to associate a certificate with a node in the directory.! How is the subject of a cert identified? " By its DN.! How is the issuer of a cert identified? " By its DN.! How are certificates linked together? " By DNs. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 37
38 Key fields in a certificate! The core fields of an X.509 certificate are " The subject public key " The subject Distinguished Name " The issuer Distinguished Name! What s missing here? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 38
39 Key fields in a certificate! The core fields of an X.509 certificate are " The subject public key " The subject Distinguished Name " The issuer Distinguished Name! What s missing here? " The issuer s public key is not present in the certificate. " You can t verify the signature on the cert without finding a parent cert! February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 39
40 Back to Chain Building! OK, assume we re a relying party application -- something that received an end-entity entity certificate and wants to verify it. " Our task is to build a cert chain from that end-entity entity cert to one of our trusted roots! How do we do that? " We start with our EE cert, and using the information contained within we look for possible parent certificates. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 40
41 Parent certs! What s a valid parent certificate? " In the raw X.509 model, parent-child relationships are determined solely by matching Issuer DN in the child to Subject DN in the parent " Recall that there s an assumption that you have a big directory handy to find certs.! If you don t have a directory handy, you need to do the matching yourself " This is not as easy as you might think February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 41
42 Name matching Issuer Name Subject Name Issuer Name Subject Name February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 42
43 Matching Names! How do we determine if two DNs match? " Use directory name matching rules! " Try to be mildly smart about it " Remove spaces, case-fold, etc. " Disaster " Try to be really dumb about it " Exact binary match " Less of a disaster, but there are still problems we can t work around February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 43
44 Unicode Names! Are these two character equal? é é! They look equal February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 44
45 Unicode Names! Are these two character equal? é é! They look equal! but may not be! In Unicode, you can compose characters, so:! Ick! " é as one character " é as two characters e followed by non- spacing accent " é as two characters non-spacing accent followed by e February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 45
46 Even More Chain Building! Name matching is just the beginning of the chain-building process It is necessary that subject and issuer DNs " It is exactly match for two certs not always sufficient certs to chain, but! The chain building process is also influenced dynamically by other information contained within the certs themselves " What other information is there in certs? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 46
47 Trusted Root Certificates! Who do I trust to be roots at the top of the cert chain?! In theory, anyone you want! In practice, trusted roots come from two sources " They re baked into your web browser or operating system " They re pushed onto your enterprise managed desktop February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 47
48 Trusted Root Certificates February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 48
49 Certificate Extensions Certificate Extensions
50 Exploring inside an X.509 Cert February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 50
51 Exploring inside an X.509 Cert February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 51
52 Exploring inside an X.509 Cert February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 52
53 Inside an X.509v3 Certificate Version Serial Number Signing Algorithm Issuer Distinguished Name Validity Period Subject Distinguished Name Subject Public Key Extensions Extension 1 Extension 2 Extension n February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 53
54 Certificate Extensions! An extension consists of three things: " A critical flag (boolean ( boolean) " A type identifier " A value " Format of the value depends on the type identifier February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 54
55 Certificate Extensions Extensions Key Usage Subject Key ID Authority Key ID CRL Distribution Points Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Critical? Authority Info Access Extended Key Usage Subject Alt Name Certificate Policies Proprietary Extension 1 Critical? Proprietary Extension n February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 55
56 Critical Flags! The critical flag on an extension is used to protect the issuing CA from assumptions made by software that doesn t understand (implement support for) a particular extension " If the flag is set, relying parties must process the extension if they recognize it, or reject the certificate " If the flag is not set, the extension may be ignored February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 56
57 Critical Flags (2)! Some questions you might be asking yourself right now...! What does must process the extension if they recognize it mean? " What does recognize mean? " What does process mean? " You ve got me... " The IETF standards folks didn t know either... February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 57
58 Critical Flags (3) Actual definitions of flag usage are vague:! Actual definitions of flag usage are " X.509: Non-critical extension is an advisory field and does not imply that usage of the key is restricted to the purpose indicated " PKIX: CA s are required to support constrain extensions but support is never defined. " S/MIME: Implementations should correctly handle certain extensions " Verisign Verisign: : All persons shall process the extension...or else ignore the extension February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 58
59 Types of Extensions! There are two flavors of extensions " Usage/informational extensions, which provide additional info about the subject of the certificate " Constraint extensions, which place restrictions on one or more of: " Use of the certificate " The user of the certificate " The keys associated with the certificate February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 59
60 Some common extensions! Key Usage " digitalsignature " Sign things that don t look like certs " keyencipherment " Exchange encrypted session keys " keyagreement " Diffie-Hellman " keycertsign/keycrlsign " Sign things that look like certs " nonrepidiation February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 60
61 NonRepudiation The nonrepudiation bit is the black hole of PKIX " It absorbs infinite amounts of argument! The time on the mailing list without making any progress toward understanding what any progress toward understanding what it means " What does it mean? How do you enforce What does it mean? How do you enforce that? " No one knows...! Nonrepudiation is anything which fails to go away when you stop believing in it February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 61
62 More Extensions! Subject Key ID " Short identifier for the subject public key! Authority Key ID " Short identifier for the issuer s public key useful for locating possible parent certs! CRL Distribution Points " List of URLs pointing to revocation information servers! Authority Info Access " Pointer to issuer cert publication location February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 62
63 Even More Extensions! Basic constraints " Is the cert a CA cert? " Limits on path length beneath this cert! Name constraints " Limits on types of certs this key can issue! Policy mappings " Convert one policy ID into another! Policy constraints " Anti-matter for policy mappings February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 63
64 Still More Extensions! Extended Key Usage " Because Key Usage wasn t confusing enough!! Private Key Usage Period " CA attempt to limit key validity period! Subject Alternative names " Everything which doesn t fit in a DN " RFC822 names, DNS names, URIs " IP addresses, X.400 names, EDI, etc. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 64
65 Yet Still More Extensions! Certificate policies " Information identifying the CA policy that was in effect when the cert was issued " Policy identifier " Policy qualifier " Explicit text " Hash reference (hash + URI) to a document! X.509 defers cert semantics to the CA s issuing policy! Most CA policies disclaim liability February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 65
66 Extensions and Chain Building! When you build a cert chain, you start with the EE cert and discover possible parent certificates by matching DNs " Build the chain from the bottom up.! However, to verify a cert chain, you have to start and the root and interpret all the extensions that may constrain subordinate CAs (and EEs) " Build the chain from the top down. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 66
67 Certificate Lifecycle Management
68 Lifecycle Management! Certificate Enrollment " Initial acquisition of a certificate based on other authentication information! Renewal " Acquiring a new certificate for a key when the existing certificate expires! Revocation " Undoing a certificate February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 68
69 Certificate Enrollment! Enrollment is the process of obtaining a certificate from a CA. 1. Alice generates a key pair, creates a message containing a copy of the public key and her identifying information, and signs the message with the private key (PKCS#10). Signing the message provided proof-of of- " Signing the message provided proof possession (POP) of the private key as well as message integrity 2. CA verifies Alice s signature on the message February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 69
70 Certificate Enrollment (2) 3. (Optional) CA verifies Alice s ID through out-of of-band means. 4. CA creates a certificate containing the ID and public key, and signs it with the CA s own key " CA has certified the binding between key and ID 5. Alice verifies the key, ID & CA signature 6. Alice and/or the CA publish the certificate February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 70
71 Certificate Enrollment Flow Cert Client Certificate Request and Installation CA Publish Certificate? Directory February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 71
72 More PKI Alphabet Soup! PKCS #10 (old) standard message format for certificate requests! PKCS #7 (old) standard message format for encrypted/signed data " Also used for certificate request responses " Replaced by IETF CMS syntax! CMC Certificate Management with CMS " Replacement for PKCS #10/PKCS#7 in a certificate management context! CMP Certificate Management Protocols " Alternative to CMC February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 72
73 Revocation
74 Expiration & Revocation! Certificates (at least, all the ones we re concerned with) contain explicit validity periods valid from & expires on Expiration dates help bound the risk associated with issuing a certificate! Sometimes, though, it becomes " Expiration dates help bound the risk necessary to undo a certificate while it is still valid " Key compromise Cert was issued under false pretenses! This is called revoking a certificate " Cert was issued under false pretenses February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 74
75 Status Info for Certificates! Two standards within PKIX: " X.509v2/PKIX Part 1 Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs ( CRLs) " Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)! Both methods state: " Whether a cert has been revoked " A revocation code indicating why the cert was revoked " The time at which the cert was revoked February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 75
76 Certificate Revocation! A CA revokes a certificate by placing the cert on its Certificate Revocation List (CRL) " Every CA issues CRLs to cancel out issued certs " A CRL is like anti-matter when it comes into contact with a certificate it lists it cancels out the certificate " Think 1970s-style style credit-card card blacklist! Relying parties are expected to check CRLs before they rely on a certificate The cert is valid unless you hear something telling you otherwise " The cert is valid unless you hear February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 76
77 The Problem with CRLs! Blacklists have numerous problems " Not issued frequently enough to be effective against a serious attack " Expensive to distribute (size & bandwidth) " Vulnerable to simple DOS attacks " If you block on lack of CRL access, why have off-line support in the first place? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 77
78 The Problem with CRLs (2)! CRL design made it worse " CLRs can contain retroactive invalidity dates " A CRL issued today can say a cert was invalid as of last week. " Checking that something was valid at time t wasn t sufficient! " Back-dated CRLs can appear at any time in the future " If you rely on certs & CRLs you re screwed because the CA can change the rules out from under you later. February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 78
79 The Problem with CRLs (3)! Revoking a CA cert is more problematic than revoking an end-entity entity cert " When you revoke a CA cert, you potentially take out the entire subordinate structure, depending on what chaining logic you use! How do you revoke a self-signed signed cert? " The cert revokes itself. " Huh? " Do I accept the CRL as valid & bounce the cert? " Do I reject the CRL because the cert associated with the CRL signing key was revoked? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 79
80 The Problem with CRLs (4)! You can t revoke a CRL " Once you commit to a CRL, it s a valid state for the entirety of its validity period! What happens if you have to update the CRL while the CRL you just issued is still valid? " You can update it, but clients aren t required to fetch it since the one they have is still valid!! Bottom line: yikes! " We need something else February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 80
81 CRLs vs. OCSP Responses! Aggregation vs. Freshness CRLs combine revocation information for " CRLs many certs certs into one long-lived lived object " OCSP Responses designed for real-time responses to queries about the status of a single certificate! Both CRLs & OCSP Responses are generated by the issuing CA or its designate. (Generally this is not relying party.) not the February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 81
82 Online Status Checking! OCSP: Online Certificate Status Protocol " A way to ask is this certificate good right now? " Get back a signed response from the OCSP server saying, Yes, cert C is good at time t " Response is like a freshness certificate! OCSP response is like a selective CRL " Client indicates the certs for which he wants status information " OCSP responder dynamically creates a lightweight CRL-like response for those certs February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 82
83 OCSP in Action CA OCSP Response Cert Request Cert OCSP Request OCSP For Cert End-entity Transaction + Cert Transaction Response Relying Party February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 83
84 Final thoughts on Revocation! From a financial standpoint, it s the revocation data that is valuable, not the issued certificate itself " For high-valued financial transactions, seller wants to know your cert is good right now " Same situation as with credit cards, where the merchant wants the card authorized right now at the point-of of-sale! Card authorizations transfer risk from merchant to bank thus they re worth $$$ " Same with cert status checks February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 84
85 Using Certificates! Most certificate uses do not require any sort of directory " Only needed to locate someone else s certificate for encryption! Authentication protocols have the client present their certificate (or chain) to the server " Ex: SSL, TLS, Smart card logon " Rules for mapping a certificate to user account vary widely " Cert fields, name forms, binary compare! Signing operations embed the certificates with the signature " How else would you know who signed it? February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 85
86 Using Certificates (2)! X.509 and PKIX define the basic structure of certificates " If you understand X.509, you can parse any certificate you re presented! However, every protocol defines a certificate profile for certificate use in that particular protocol " Ex: TLS, S/MIME, IPSEC, WPA/WPA2! CAs/organizations define profiles too " Ex: US DoD Common Access Card certs February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 86
87 Additional Implementation Considerations! Publishing certificates " How? Where? What format?! Key escrow / data recovery for encryption keys/certs! Auto-enrollment (users & machines)! Establishing trusts / hierarchies! Protecting private keys! Disseminating root certificates February 21, 2006 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 87
Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography
 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography Lecture 6: Certificates & Trust Part II -- X.509 vs PGP Josh Benaloh & Brian LaMacchia Last time on CSE 590... Certificates Certificate Authorities Certificate
Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography Lecture 6: Certificates & Trust Part II -- X.509 vs PGP Josh Benaloh & Brian LaMacchia Last time on CSE 590... Certificates Certificate Authorities Certificate
Chapter 9: Key Management
 Chapter 9: Key Management Session and Interchange Keys Key Exchange Cryptographic Key Infrastructure Storing and Revoking Keys Digital Signatures Slide #9-1 Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange
Chapter 9: Key Management Session and Interchange Keys Key Exchange Cryptographic Key Infrastructure Storing and Revoking Keys Digital Signatures Slide #9-1 Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange
Public-Key Infrastructure NETS E2008
 Public-Key Infrastructure NETS E2008 Many slides from Vitaly Shmatikov, UT Austin slide 1 Authenticity of Public Keys? private key Alice Bob public key Problem: How does Alice know that the public key
Public-Key Infrastructure NETS E2008 Many slides from Vitaly Shmatikov, UT Austin slide 1 Authenticity of Public Keys? private key Alice Bob public key Problem: How does Alice know that the public key
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 11: Public Key Infrastructure Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline Public key infrastructure Certificates Trust
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 11: Public Key Infrastructure Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline Public key infrastructure Certificates Trust
Crypto meets Web Security: Certificates and SSL/TLS
 CSE 484 / CSE M 584: Computer Security and Privacy Crypto meets Web Security: Certificates and SSL/TLS Spring 2016 Franziska (Franzi) Roesner franzi@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Dan Boneh, Dieter Gollmann,
CSE 484 / CSE M 584: Computer Security and Privacy Crypto meets Web Security: Certificates and SSL/TLS Spring 2016 Franziska (Franzi) Roesner franzi@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Dan Boneh, Dieter Gollmann,
Digital Certificates Demystified
 Digital Certificates Demystified Ross Cooper, CISSP IBM Corporation RACF/PKI Development Poughkeepsie, NY Email: rdc@us.ibm.com August 9 th, 2012 Session 11622 Agenda Cryptography What are Digital Certificates
Digital Certificates Demystified Ross Cooper, CISSP IBM Corporation RACF/PKI Development Poughkeepsie, NY Email: rdc@us.ibm.com August 9 th, 2012 Session 11622 Agenda Cryptography What are Digital Certificates
Background. Network Security - Certificates, Keys and Signatures - Digital Signatures. Digital Signatures. Dr. John Keeney 3BA33
 Background Network Security - Certificates, Keys and Signatures - Dr. John Keeney 3BA33 Slides Sources: Karl Quinn, Donal O Mahoney, Henric Johnson, Charlie Kaufman, Wikipedia, Google, Brian Raiter. Recommended
Background Network Security - Certificates, Keys and Signatures - Dr. John Keeney 3BA33 Slides Sources: Karl Quinn, Donal O Mahoney, Henric Johnson, Charlie Kaufman, Wikipedia, Google, Brian Raiter. Recommended
Key Management and Distribution
 Key Management and Distribution Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-14/
Key Management and Distribution Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-14/
Lecture 13. Public Key Distribution (certification) PK-based Needham-Schroeder TTP. 3. [N a, A] PKb 6. [N a, N b ] PKa. 7.
![Lecture 13. Public Key Distribution (certification) PK-based Needham-Schroeder TTP. 3. [N a, A] PKb 6. [N a, N b ] PKa. 7. Lecture 13. Public Key Distribution (certification) PK-based Needham-Schroeder TTP. 3. [N a, A] PKb 6. [N a, N b ] PKa. 7.](/thumbs/84/91191448.jpg) Lecture 13 Public Key Distribution (certification) 1 PK-based Needham-Schroeder TTP 1. A, B 4. B, A 2. {PKb, B}SKT B}SKs 5. {PK a, A} SKT SKs A 3. [N a, A] PKb 6. [N a, N b ] PKa B 7. [N b ] PKb Here,
Lecture 13 Public Key Distribution (certification) 1 PK-based Needham-Schroeder TTP 1. A, B 4. B, A 2. {PKb, B}SKT B}SKs 5. {PK a, A} SKT SKs A 3. [N a, A] PKb 6. [N a, N b ] PKa B 7. [N b ] PKb Here,
Certificates, Certification Authorities and Public-Key Infrastructures
 (Digital) Certificates Certificates, Certification Authorities and Public-Key Infrastructures We need to be sure that the public key used to encrypt a message indeed belongs to the destination of the message
(Digital) Certificates Certificates, Certification Authorities and Public-Key Infrastructures We need to be sure that the public key used to encrypt a message indeed belongs to the destination of the message
Cryptography and Network Security
 Cryptography and Network Security Spring 2012 http://users.abo.fi/ipetre/crypto/ Lecture 8: Protocols for public-key management Ion Petre Department of IT, Åbo Akademi University 1 Key management two problems
Cryptography and Network Security Spring 2012 http://users.abo.fi/ipetre/crypto/ Lecture 8: Protocols for public-key management Ion Petre Department of IT, Åbo Akademi University 1 Key management two problems
Public Key Establishment
 Public Key Establishment Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven February 2007 Thanks to Paul van Oorschot How to establish public keys? point-to-point on a trusted channel mail business card, phone
Public Key Establishment Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven February 2007 Thanks to Paul van Oorschot How to establish public keys? point-to-point on a trusted channel mail business card, phone
Outline Key Management CS 239 Computer Security February 9, 2004
 Outline Key Management CS 239 Computer Security February 9, 2004 Properties of keys Key management Key servers Certificates Page 1 Page 2 Introduction Properties of Keys It doesn t matter how strong your
Outline Key Management CS 239 Computer Security February 9, 2004 Properties of keys Key management Key servers Certificates Page 1 Page 2 Introduction Properties of Keys It doesn t matter how strong your
PROVING WHO YOU ARE TLS & THE PKI
 PROVING WHO YOU ARE TLS & THE PKI CMSC 414 MAR 29 2018 RECALL OUR PROBLEM WITH DIFFIE-HELLMAN The two communicating parties thought, but did not confirm, that they were talking to one another. Therefore,
PROVING WHO YOU ARE TLS & THE PKI CMSC 414 MAR 29 2018 RECALL OUR PROBLEM WITH DIFFIE-HELLMAN The two communicating parties thought, but did not confirm, that they were talking to one another. Therefore,
Security Protocols and Infrastructures. Winter Term 2015/2016
 Security Protocols and Infrastructures Winter Term 2015/2016 Nicolas Buchmann (Harald Baier) Chapter 5: Standards for Security Infrastructures Contents Introduction and naming scheme X.509 and its core
Security Protocols and Infrastructures Winter Term 2015/2016 Nicolas Buchmann (Harald Baier) Chapter 5: Standards for Security Infrastructures Contents Introduction and naming scheme X.509 and its core
Cristina Nita-Rotaru. CS355: Cryptography. Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment.
 CS355: Cryptography Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment. Public Keys and Trust Public Key:P A Secret key: S A Public Key:P B Secret key: S B How are public keys stored How
CS355: Cryptography Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment. Public Keys and Trust Public Key:P A Secret key: S A Public Key:P B Secret key: S B How are public keys stored How
Public Key Infrastructures. Using PKC to solve network security problems
 Public Key Infrastructures Using PKC to solve network security problems Distributing public keys P keys allow parties to share secrets over unprotected channels Extremely useful in an open network: Parties
Public Key Infrastructures Using PKC to solve network security problems Distributing public keys P keys allow parties to share secrets over unprotected channels Extremely useful in an open network: Parties
Certification Practice Statement of the Federal Reserve Banks Services Public Key Infrastructure
 Certification Practice Statement of the Federal Reserve Banks Services Public Key Infrastructure 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Overview The Federal Reserve Banks operate a public key infrastructure (PKI) that manages
Certification Practice Statement of the Federal Reserve Banks Services Public Key Infrastructure 1.0 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Overview The Federal Reserve Banks operate a public key infrastructure (PKI) that manages
X.509 CERTIFICATE X.509 CERTIFICATE PUBLIC-KEY CERTIFICATES THE CERTIFICATE TRIANGLE CERTIFICATE TRUST. INFS 766 Internet Security Protocols
 INFS 766 Internet Security Protocols X.509 CERTIFICATE Lecture 6 Digital Certificates VERSION SERIAL NUMBER SIGNATURE ALGORITHM ISSUER VALIDITY Prof. Ravi SUBJECT SUBJECT PUBLIC KEY INFO SIGNATURE 4 PUBLIC-KEY
INFS 766 Internet Security Protocols X.509 CERTIFICATE Lecture 6 Digital Certificates VERSION SERIAL NUMBER SIGNATURE ALGORITHM ISSUER VALIDITY Prof. Ravi SUBJECT SUBJECT PUBLIC KEY INFO SIGNATURE 4 PUBLIC-KEY
Public Key Infrastructures
 Foundations for secure e-commerce (bmevihim219) Dr. Levente Buttyán associate professor BME Hálózati Rendszerek és Szolgáltatások Tanszék Lab of Cryptography and System Security (CrySyS) buttyan@hit.bme.hu,
Foundations for secure e-commerce (bmevihim219) Dr. Levente Buttyán associate professor BME Hálózati Rendszerek és Szolgáltatások Tanszék Lab of Cryptography and System Security (CrySyS) buttyan@hit.bme.hu,
Introduction to SSL. Copyright 2005 by Sericon Technology Inc.
 Introduction to SSL The cornerstone of e-commerce is a Web site s ability to prevent eavesdropping on data transmitted to and from its site. Without this, consumers would justifiably be afraid to enter
Introduction to SSL The cornerstone of e-commerce is a Web site s ability to prevent eavesdropping on data transmitted to and from its site. Without this, consumers would justifiably be afraid to enter
Managing Certificates
 CHAPTER 12 The Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) relies on public key infrastructure (PKI) to provide secure communication for the following: Client and server authentication for Transport Layer
CHAPTER 12 The Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) relies on public key infrastructure (PKI) to provide secure communication for the following: Client and server authentication for Transport Layer
PUBLIC-KEY CERTIFICATES
 INFS 766 Internet Security Protocols Lecture 6 Digital Certificates Prof. Ravi Sandhu PUBLIC-KEY CERTIFICATES reliable distribution of public-keys public-key encryption sender needs public key of receiver
INFS 766 Internet Security Protocols Lecture 6 Digital Certificates Prof. Ravi Sandhu PUBLIC-KEY CERTIFICATES reliable distribution of public-keys public-key encryption sender needs public key of receiver
Diffie-Hellman. Part 1 Cryptography 136
 Diffie-Hellman Part 1 Cryptography 136 Diffie-Hellman Invented by Williamson (GCHQ) and, independently, by D and H (Stanford) A key exchange algorithm o Used to establish a shared symmetric key Not for
Diffie-Hellman Part 1 Cryptography 136 Diffie-Hellman Invented by Williamson (GCHQ) and, independently, by D and H (Stanford) A key exchange algorithm o Used to establish a shared symmetric key Not for
SSH Communications Tectia SSH
 Secured by RSA Implementation Guide for 3rd Party PKI Applications Last Modified: December 8, 2014 Partner Information Product Information Partner Name Web Site Product Name Version & Platform Product
Secured by RSA Implementation Guide for 3rd Party PKI Applications Last Modified: December 8, 2014 Partner Information Product Information Partner Name Web Site Product Name Version & Platform Product
Security Protocols and Infrastructures
 Security Protocols and Infrastructures Dr. Michael Schneider michael.schneider@h-da.de Chapter 5: Standards for Security Infrastructures November 13, 2017 h_da WS2017/18 Dr. Michael Schneider 1 1 Introduction
Security Protocols and Infrastructures Dr. Michael Schneider michael.schneider@h-da.de Chapter 5: Standards for Security Infrastructures November 13, 2017 h_da WS2017/18 Dr. Michael Schneider 1 1 Introduction
Key Management. Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange. Handwritten Signature
 Key Management Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange 1 Handwritten Signature Used everyday in a letter, on a check, sign a contract A signature on a signed paper
Key Management Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange 1 Handwritten Signature Used everyday in a letter, on a check, sign a contract A signature on a signed paper
Certificateless Public Key Cryptography
 Certificateless Public Key Cryptography Mohsen Toorani Department of Informatics University of Bergen Norsk Kryptoseminar November 9, 2011 1 Public Key Cryptography (PKC) Also known as asymmetric cryptography.
Certificateless Public Key Cryptography Mohsen Toorani Department of Informatics University of Bergen Norsk Kryptoseminar November 9, 2011 1 Public Key Cryptography (PKC) Also known as asymmetric cryptography.
Lecture 15 Public Key Distribution (certification)
 0 < i < 2 n = N X i,y i random secret keys index i = random (secret) value Merkle s Puzzles (1974) Puzzle P i = {index i,x i,s} Y i S fixed string, e.g., " Alice to Bob" { P 0 < i < 2 i n } Pick random
0 < i < 2 n = N X i,y i random secret keys index i = random (secret) value Merkle s Puzzles (1974) Puzzle P i = {index i,x i,s} Y i S fixed string, e.g., " Alice to Bob" { P 0 < i < 2 i n } Pick random
Lecture Notes 14 : Public-Key Infrastructure
 6.857 Computer and Network Security October 24, 2002 Lecture Notes 14 : Public-Key Infrastructure Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Armour/Johann-Berkel/Owsley/Quealy [These notes come from Fall 2001. These
6.857 Computer and Network Security October 24, 2002 Lecture Notes 14 : Public-Key Infrastructure Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Armour/Johann-Berkel/Owsley/Quealy [These notes come from Fall 2001. These
Spring 2010: CS419 Computer Security
 Spring 2010: CS419 Computer Security Vinod Ganapathy Lecture 7 Topic: Key exchange protocols Material: Class handout (lecture7_handout.pdf) Chapter 2 in Anderson's book. Today s agenda Key exchange basics
Spring 2010: CS419 Computer Security Vinod Ganapathy Lecture 7 Topic: Key exchange protocols Material: Class handout (lecture7_handout.pdf) Chapter 2 in Anderson's book. Today s agenda Key exchange basics
X.509. CPSC 457/557 10/17/13 Jeffrey Zhu
 X.509 CPSC 457/557 10/17/13 Jeffrey Zhu 2 3 X.509 Outline X.509 Overview Certificate Lifecycle Alternative Certification Models 4 What is X.509? The most commonly used Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) on
X.509 CPSC 457/557 10/17/13 Jeffrey Zhu 2 3 X.509 Outline X.509 Overview Certificate Lifecycle Alternative Certification Models 4 What is X.509? The most commonly used Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) on
IBM. Security Digital Certificate Manager. IBM i 7.1
 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read the information in
IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read the information in
SSL Certificates Certificate Policy (CP)
 SSL Certificates Last Revision Date: February 26, 2015 Version 1.0 Revisions Version Date Description of changes Author s Name Draft 17 Jan 2011 Initial Release (Draft) Ivo Vitorino 1.0 26 Feb 2015 Full
SSL Certificates Last Revision Date: February 26, 2015 Version 1.0 Revisions Version Date Description of changes Author s Name Draft 17 Jan 2011 Initial Release (Draft) Ivo Vitorino 1.0 26 Feb 2015 Full
ICS 180 May 4th, Guest Lecturer: Einar Mykletun
 ICS 180 May 4th, 2004 Guest Lecturer: Einar Mykletun 1 Symmetric Key Crypto 2 Symmetric Key Two users who wish to communicate share a secret key Properties High encryption speed Limited applications: encryption
ICS 180 May 4th, 2004 Guest Lecturer: Einar Mykletun 1 Symmetric Key Crypto 2 Symmetric Key Two users who wish to communicate share a secret key Properties High encryption speed Limited applications: encryption
Information Security. message M. fingerprint f = H(M) one-way hash. 4/19/2006 Information Security 1
 Information Security message M one-way hash fingerprint f = H(M) 4/19/2006 Information Security 1 Outline and Reading Digital signatures Definition RSA signature and verification One-way hash functions
Information Security message M one-way hash fingerprint f = H(M) 4/19/2006 Information Security 1 Outline and Reading Digital signatures Definition RSA signature and verification One-way hash functions
Topics. Dramatis Personae Cathy, the Computer, trusted 3 rd party. Cryptographic Protocols
 Cryptographic Protocols Topics 1. Dramatis Personae and Notation 2. Session and Interchange Keys 3. Key Exchange 4. Key Generation 5. Cryptographic Key Infrastructure 6. Storing and Revoking Keys 7. Digital
Cryptographic Protocols Topics 1. Dramatis Personae and Notation 2. Session and Interchange Keys 3. Key Exchange 4. Key Generation 5. Cryptographic Key Infrastructure 6. Storing and Revoking Keys 7. Digital
Security Digital Certificate Manager
 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure
System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure
Send documentation comments to
 CHAPTER 6 Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates This chapter includes the following topics: Information About Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates, page 6-1 Default Settings,
CHAPTER 6 Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates This chapter includes the following topics: Information About Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates, page 6-1 Default Settings,
IBM i Version 7.2. Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM
 IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
Bugzilla ID: Bugzilla Summary:
 Bugzilla ID: Bugzilla Summary: CAs wishing to have their certificates included in Mozilla products must 1) Comply with the requirements of the Mozilla CA certificate policy (http://www.mozilla.org/projects/security/certs/policy/)
Bugzilla ID: Bugzilla Summary: CAs wishing to have their certificates included in Mozilla products must 1) Comply with the requirements of the Mozilla CA certificate policy (http://www.mozilla.org/projects/security/certs/policy/)
Overview of SSL/TLS. Luke Anderson. 12 th May University Of Sydney.
 Overview of SSL/TLS Luke Anderson luke@lukeanderson.com.au 12 th May 2017 University Of Sydney Overview 1. Introduction 1.1 Raw HTTP 1.2 Introducing SSL/TLS 2. Certificates 3. Attacks Introduction Raw
Overview of SSL/TLS Luke Anderson luke@lukeanderson.com.au 12 th May 2017 University Of Sydney Overview 1. Introduction 1.1 Raw HTTP 1.2 Introducing SSL/TLS 2. Certificates 3. Attacks Introduction Raw
Lecture 15 PKI & Authenticated Key Exchange. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 15 PKI & Authenticated Key Exchange COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Today We will see how signatures are used to create public-key infrastructures
Lecture 15 PKI & Authenticated Key Exchange COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Today We will see how signatures are used to create public-key infrastructures
Securing Internet Communication: TLS
 Securing Internet Communication: TLS CS 161: Computer Security Prof. David Wagner March 11, 2016 Today s Lecture Applying crypto technology in practice Two simple abstractions cover 80% of the use cases
Securing Internet Communication: TLS CS 161: Computer Security Prof. David Wagner March 11, 2016 Today s Lecture Applying crypto technology in practice Two simple abstractions cover 80% of the use cases
Distributed Systems. 25. Authentication Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Fall 2018
 Distributed Systems 25. Authentication Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2018 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Authentication For a user (or process): Establish & verify identity Then decide whether to
Distributed Systems 25. Authentication Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2018 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Authentication For a user (or process): Establish & verify identity Then decide whether to
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
 CHAPTER 43 Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) support provides the means for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches to obtain and use digital certificates
CHAPTER 43 Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) support provides the means for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches to obtain and use digital certificates
SSL/TLS & 3D Secure. CS 470 Introduction to Applied Cryptography. Ali Aydın Selçuk. CS470, A.A.Selçuk SSL/TLS & 3DSec 1
 SSL/TLS & 3D Secure CS 470 Introduction to Applied Cryptography Ali Aydın Selçuk CS470, A.A.Selçuk SSL/TLS & 3DSec 1 SSLv2 Brief History of SSL/TLS Released in 1995 with Netscape 1.1 Key generation algorithm
SSL/TLS & 3D Secure CS 470 Introduction to Applied Cryptography Ali Aydın Selçuk CS470, A.A.Selçuk SSL/TLS & 3DSec 1 SSLv2 Brief History of SSL/TLS Released in 1995 with Netscape 1.1 Key generation algorithm
Server-based Certificate Validation Protocol
 Server-based Certificate Validation Protocol Digital Certificate and PKI a public-key certificate is a digital certificate that binds a system entity's identity to a public key value, and possibly to additional
Server-based Certificate Validation Protocol Digital Certificate and PKI a public-key certificate is a digital certificate that binds a system entity's identity to a public key value, and possibly to additional
Overview. Cryptographic key infrastructure Certificates. May 13, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #1. Notation
 Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange keys Classical, public key methods Key generation Cryptographic key infrastructure Certificates Key storage Key escrow Key revocation Digital signatures May
Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange keys Classical, public key methods Key generation Cryptographic key infrastructure Certificates Key storage Key escrow Key revocation Digital signatures May
Configuring SSL. SSL Overview CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This topic describes the steps required to configure your ACE appliance as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination. The topics included in this section are:
7 CHAPTER This topic describes the steps required to configure your ACE appliance as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination. The topics included in this section are:
CT30A8800 Secured communications
 CT30A8800 Secured communications Pekka Jäppinen October 31, 2007 Pekka Jäppinen, Lappeenranta University of Technology: October 31, 2007 Secured Communications: Key exchange Schneier, Applied Cryptography:
CT30A8800 Secured communications Pekka Jäppinen October 31, 2007 Pekka Jäppinen, Lappeenranta University of Technology: October 31, 2007 Secured Communications: Key exchange Schneier, Applied Cryptography:
Introduction to Network Security Missouri S&T University CPE 5420 Key Management and Distribution
 Introduction to Network Security Missouri S&T University CPE 5420 Key Management and Distribution Egemen K. Çetinkaya Egemen K. Çetinkaya Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University
Introduction to Network Security Missouri S&T University CPE 5420 Key Management and Distribution Egemen K. Çetinkaya Egemen K. Çetinkaya Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University
Configuring SSL CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes the steps required to configure your ACE appliance as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination. The topics included in this section
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes the steps required to configure your ACE appliance as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination. The topics included in this section
ECE 646 Lecture 3. Key management
 ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution Using the same key for multiple
ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution Using the same key for multiple
Key Management and Distribution
 2 and Distribution : Security and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 20 December 2015 css441y15s2l10, Steve/Courses/2015/s2/css441/lectures/key-management-and-distribution.tex,
2 and Distribution : Security and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 20 December 2015 css441y15s2l10, Steve/Courses/2015/s2/css441/lectures/key-management-and-distribution.tex,
Sensitive Information in a Wired World
 Sensitive Information in a Wired World CPSC 457/557, Fall 2013 Lecture 11, October 3, 2013 1:00-2:15 pm; AKW 400 http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs457/fall13/ Brian A. LaMacchia, used with permission 1
Sensitive Information in a Wired World CPSC 457/557, Fall 2013 Lecture 11, October 3, 2013 1:00-2:15 pm; AKW 400 http://zoo.cs.yale.edu/classes/cs457/fall13/ Brian A. LaMacchia, used with permission 1
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture
CS November 2018
 Authentication Distributed Systems 25. Authentication For a user (or process): Establish & verify identity Then decide whether to allow access to resources (= authorization) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University
Authentication Distributed Systems 25. Authentication For a user (or process): Establish & verify identity Then decide whether to allow access to resources (= authorization) Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University
Expires in 6 months September Internet Public Key Infrastructure Online Certificate Status Protocol - OCSP <draft-ietf-pkix-ocsp-00.
 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 09 Apr 2002 06:26:11 GMT Server: Apache/1.3.20 (Unix) Last-Modified: Thu, 23 Oct 1997 15:29:00 GMT ETag: "304c31-471a-344f6d3c" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 18202 Connection:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 09 Apr 2002 06:26:11 GMT Server: Apache/1.3.20 (Unix) Last-Modified: Thu, 23 Oct 1997 15:29:00 GMT ETag: "304c31-471a-344f6d3c" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 18202 Connection:
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement
 Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Apple Application Integration Sub-CA Apple Application Integration 2 Sub-CA Apple Application Integration - G3 Sub-CA Version 6.2 Effective
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Apple Application Integration Sub-CA Apple Application Integration 2 Sub-CA Apple Application Integration - G3 Sub-CA Version 6.2 Effective
Ten Risks of PKI : What You re not Being Told about Public Key Infrastructure By Carl Ellison and Bruce Schneier
 Presented by Joshua Schiffman & Archana Viswanath Ten Risks of PKI : What You re not Being Told about Public Key Infrastructure By Carl Ellison and Bruce Schneier Trust Models Rooted Trust Model! In a
Presented by Joshua Schiffman & Archana Viswanath Ten Risks of PKI : What You re not Being Told about Public Key Infrastructure By Carl Ellison and Bruce Schneier Trust Models Rooted Trust Model! In a
A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification
 A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification AUSCERT 2006 Geoff Huston Research Scientist APNIC If You wanted to be Bad on the Internet And you wanted to: Hijack a site Inspect
A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification AUSCERT 2006 Geoff Huston Research Scientist APNIC If You wanted to be Bad on the Internet And you wanted to: Hijack a site Inspect
Technical Trust Policy
 Technical Trust Policy Version 1.2 Last Updated: May 20, 2016 Introduction Carequality creates a community of trusted exchange partners who rely on each organization s adherence to the terms of the Carequality
Technical Trust Policy Version 1.2 Last Updated: May 20, 2016 Introduction Carequality creates a community of trusted exchange partners who rely on each organization s adherence to the terms of the Carequality
Issues. Separation of. Distributed system security. Security services. Security policies. Security mechanism
 Module 9 - Security Issues Separation of Security policies Precise definition of which entities in the system can take what actions Security mechanism Means of enforcing that policy Distributed system
Module 9 - Security Issues Separation of Security policies Precise definition of which entities in the system can take what actions Security mechanism Means of enforcing that policy Distributed system
Public. Atos Trustcenter. Server Certificates + Codesigning Certificates. Version 1.2
 Atos Trustcenter Server Certificates + Codesigning Certificates Version 1.2 20.11.2015 Content 1 Introduction... 3 2 The Atos Trustcenter Portfolio... 3 3 TrustedRoot PKI... 4 3.1 TrustedRoot Hierarchy...
Atos Trustcenter Server Certificates + Codesigning Certificates Version 1.2 20.11.2015 Content 1 Introduction... 3 2 The Atos Trustcenter Portfolio... 3 3 TrustedRoot PKI... 4 3.1 TrustedRoot Hierarchy...
Lecture 2 Applied Cryptography (Part 2)
 Lecture 2 Applied Cryptography (Part 2) Patrick P. C. Lee Tsinghua Summer Course 2010 2-1 Roadmap Number theory Public key cryptography RSA Diffie-Hellman DSA Certificates Tsinghua Summer Course 2010 2-2
Lecture 2 Applied Cryptography (Part 2) Patrick P. C. Lee Tsinghua Summer Course 2010 2-1 Roadmap Number theory Public key cryptography RSA Diffie-Hellman DSA Certificates Tsinghua Summer Course 2010 2-2
Computer Security. 08r. Pre-exam 2 Last-minute Review Cryptography. Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Spring 2018
 Computer Security 08r. Pre-exam 2 Last-minute Review Cryptography Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2018 March 26, 2018 CS 419 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Cryptographic Systems March 26, 2018 CS
Computer Security 08r. Pre-exam 2 Last-minute Review Cryptography Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2018 March 26, 2018 CS 419 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Cryptographic Systems March 26, 2018 CS
What is a Digital Certificate? Basic Problem. Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure. Sections
 Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure Sections 14.3-14.5 Basic Problem What does a public-key signature verification tell you? Verification parameters include public
Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure Sections 14.3-14.5 Basic Problem What does a public-key signature verification tell you? Verification parameters include public
Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure. Sections
 Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure Sections 14.3-14.5 Basic Problem What does a public-key signature verification tell you? Verification parameters include public
Digital Certificates, Certification Authorities, and Public Key Infrastructure Sections 14.3-14.5 Basic Problem What does a public-key signature verification tell you? Verification parameters include public
Module: Authentication. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Authentication Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Kerberos History: from UNIX to Networks (late 80s) Solves: password eavesdropping Also mutual authentication
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Authentication Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Kerberos History: from UNIX to Networks (late 80s) Solves: password eavesdropping Also mutual authentication
Module: Authentication. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Authentication Professor Trent Jaeger CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security 1 Kerberos History: from UNIX to Networks (late
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Authentication Professor Trent Jaeger CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security 1 Kerberos History: from UNIX to Networks (late
Certificate implementation The good, the bad, and the ugly
 Certificate implementation The good, the bad, and the ugly DOE Security Training Workshop James A. Rome Oak Ridge National Laboratory April 29, 1998 A wealth of riches? I decided to use certificates for
Certificate implementation The good, the bad, and the ugly DOE Security Training Workshop James A. Rome Oak Ridge National Laboratory April 29, 1998 A wealth of riches? I decided to use certificates for
6 Public Key Infrastructure 6.1 Certificates Structure of an X.509 certificate X.500 Distinguished Name and X.509v3 subjectalternativename
 6 Public Key Infrastructure 6.1 Certificates Structure of an X.509 certificate X.500 Distinguished Name and X.509v3 subjectalternativename Certificate formats (DER, PEM, PKCS #12) 6.2 Certificate Authorities
6 Public Key Infrastructure 6.1 Certificates Structure of an X.509 certificate X.500 Distinguished Name and X.509v3 subjectalternativename Certificate formats (DER, PEM, PKCS #12) 6.2 Certificate Authorities
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS)
 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 20 th November 2017 What Problems Do SSL/TLS Solve? Two parties, client and server, not previously
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 20 th November 2017 What Problems Do SSL/TLS Solve? Two parties, client and server, not previously
Cryptography (Overview)
 Cryptography (Overview) Some history Caesar cipher, rot13 substitution ciphers, etc. Enigma (Turing) Modern secret key cryptography DES, AES Public key cryptography RSA, digital signatures Cryptography
Cryptography (Overview) Some history Caesar cipher, rot13 substitution ciphers, etc. Enigma (Turing) Modern secret key cryptography DES, AES Public key cryptography RSA, digital signatures Cryptography
draft-ietf-smime-cert-06.txt December 14, 1998 Expires in six months S/MIME Version 3 Certificate Handling Status of this memo
 Internet Draft draft-ietf-smime-cert-06.txt December 14, 1998 Expires in six months Editor: Blake Ramsdell, Worldtalk Status of this memo S/MIME Version 3 Certificate Handling This document is an Internet-Draft.
Internet Draft draft-ietf-smime-cert-06.txt December 14, 1998 Expires in six months Editor: Blake Ramsdell, Worldtalk Status of this memo S/MIME Version 3 Certificate Handling This document is an Internet-Draft.
Configuring SSL. SSL Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 8 Date: 4/23/09 This topic describes the steps required to configure your ACE (both the ACE module and the ACE appliance) as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination.
CHAPTER 8 Date: 4/23/09 This topic describes the steps required to configure your ACE (both the ACE module and the ACE appliance) as a virtual Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) server for SSL initiation or termination.
Bart Preneel PKI. February Public Key Establishment. PKI Overview. Keys and Lifecycle Management. How to establish public keys?
 art Preneel How to establish public keys? Public Key Establishment art Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven Thanks to Paul van Oorschot point-to-point on a trusted channel mail business card, phone direct
art Preneel How to establish public keys? Public Key Establishment art Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven Thanks to Paul van Oorschot point-to-point on a trusted channel mail business card, phone direct
SEEM4540 Open Systems for E-Commerce Lecture 03 Internet Security
 SEEM4540 Open Systems for E-Commerce Lecture 03 Internet Security Consider 2. Based on DNS, identified the IP address of www.cuhk.edu.hk is 137.189.11.73. 1. Go to http://www.cuhk.edu.hk 3. Forward the
SEEM4540 Open Systems for E-Commerce Lecture 03 Internet Security Consider 2. Based on DNS, identified the IP address of www.cuhk.edu.hk is 137.189.11.73. 1. Go to http://www.cuhk.edu.hk 3. Forward the
CS Computer Networks 1: Authentication
 CS 3251- Computer Networks 1: Authentication Professor Patrick Traynor 4/14/11 Lecture 25 Announcements Homework 3 is due next class. Submit via T-Square or in person. Project 3 has been graded. Scores
CS 3251- Computer Networks 1: Authentication Professor Patrick Traynor 4/14/11 Lecture 25 Announcements Homework 3 is due next class. Submit via T-Square or in person. Project 3 has been graded. Scores
Manage Certificates. Certificates Overview
 Certificates Overview, page 1 Show Certificates, page 3 Download Certificates, page 4 Install Intermediate Certificates, page 4 Delete a Trust Certificate, page 5 Regenerate a Certificate, page 6 Upload
Certificates Overview, page 1 Show Certificates, page 3 Download Certificates, page 4 Install Intermediate Certificates, page 4 Delete a Trust Certificate, page 5 Regenerate a Certificate, page 6 Upload
Cryptographic Checksums
 Cryptographic Checksums Mathematical function to generate a set of k bits from a set of n bits (where k n). k is smaller then n except in unusual circumstances Example: ASCII parity bit ASCII has 7 bits;
Cryptographic Checksums Mathematical function to generate a set of k bits from a set of n bits (where k n). k is smaller then n except in unusual circumstances Example: ASCII parity bit ASCII has 7 bits;
Next Generation Physical Access Control Systems A Smart Card Alliance Educational Institute Workshop
 Next Generation Physical Access Control Systems A Smart Card Alliance Educational Institute Workshop PACS Integration into the Identity Infrastructure Salvatore D Agostino CEO, IDmachines LLC 8 th Annual
Next Generation Physical Access Control Systems A Smart Card Alliance Educational Institute Workshop PACS Integration into the Identity Infrastructure Salvatore D Agostino CEO, IDmachines LLC 8 th Annual
Network Security Essentials
 Network Security Essentials Fifth Edition by William Stallings Chapter 4 Key Distribution and User Authentication No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture out of the house without a bunch of
Network Security Essentials Fifth Edition by William Stallings Chapter 4 Key Distribution and User Authentication No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture out of the house without a bunch of
Key management. Pretty Good Privacy
 ECE 646 - Lecture 4 Key management Pretty Good Privacy Using the same key for multiple messages M 1 M 2 M 3 M 4 M 5 time E K time C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 1 Using Session Keys & Key Encryption Keys K 1 K 2
ECE 646 - Lecture 4 Key management Pretty Good Privacy Using the same key for multiple messages M 1 M 2 M 3 M 4 M 5 time E K time C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 1 Using Session Keys & Key Encryption Keys K 1 K 2
ECE 646 Lecture 3. Key management. Required Reading. Using the same key for multiple messages
 ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution Using the same key for multiple
ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution Using the same key for multiple
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement
 Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Apple Application Integration Sub-CA Apple Application Integration 2 Sub-CA Apple Application Integration - G3 Sub-CA Version 6.3 Effective
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Apple Application Integration Sub-CA Apple Application Integration 2 Sub-CA Apple Application Integration - G3 Sub-CA Version 6.3 Effective
Apple Corporate Certificates Certificate Policy and Certification Practice Statement. Apple Inc.
 Apple Inc. Certificate Policy and Certification Practice Statement Version 1.0 Effective Date: March 12, 2015 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 4 1.1. Trademarks... 4 1.2. Table of acronyms... 4 1.3.
Apple Inc. Certificate Policy and Certification Practice Statement Version 1.0 Effective Date: March 12, 2015 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 4 1.1. Trademarks... 4 1.2. Table of acronyms... 4 1.3.
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Worldwide Developer Relations
 Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Worldwide Developer Relations Version 1.18 Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 5 1.1. Trademarks...
Apple Inc. Certification Authority Certification Practice Statement Worldwide Developer Relations Version 1.18 Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 5 1.1. Trademarks...
Public Key Infrastructure
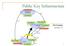 Public Key Infrastructure Ed Crowley Summer 11 1 Topics Public Key Infrastructure Defined PKI Overview PKI Architecture Trust Models Components X.509 Certificates X.500 LDAP 2 Public Key Infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure Ed Crowley Summer 11 1 Topics Public Key Infrastructure Defined PKI Overview PKI Architecture Trust Models Components X.509 Certificates X.500 LDAP 2 Public Key Infrastructure
CSC 482/582: Computer Security. Security Protocols
 Security Protocols Topics 1. Basic Concepts of Cryptography 2. Security Protocols 3. Authentication Protocols 4. Key Exchange Protocols 5. Kerberos 6. Public Key Infrastructure Encryption and Decryption
Security Protocols Topics 1. Basic Concepts of Cryptography 2. Security Protocols 3. Authentication Protocols 4. Key Exchange Protocols 5. Kerberos 6. Public Key Infrastructure Encryption and Decryption
Data Security and Privacy. Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment
 Data Security and Privacy Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment 1 Announcements Mid-term Exam Tuesday March 6, during class 2 Need for Key Establishment Encrypt K (M) C = Encrypt K (M) M = Decrypt
Data Security and Privacy Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment 1 Announcements Mid-term Exam Tuesday March 6, during class 2 Need for Key Establishment Encrypt K (M) C = Encrypt K (M) M = Decrypt
Key management. Required Reading. Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E
 ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution 1 Using the same key for multiple
ECE 646 Lecture 3 Key management Required Reading Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5/E or 6/E Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution 1 Using the same key for multiple
Public Key Infrastructure PKI. National Digital Certification Center Information Technology Authority Sultanate of Oman
 Public Key Infrastructure PKI National Digital Certification Center Information Technology Authority Sultanate of Oman Agenda Objectives PKI Features etrust Components Government eservices Oman National
Public Key Infrastructure PKI National Digital Certification Center Information Technology Authority Sultanate of Oman Agenda Objectives PKI Features etrust Components Government eservices Oman National
L7: Key Distributions. Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806
 L7: Key Distributions Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 9/16/2015 CSCI 451 - Fall 2015 1 Acknowledgement Many slides are from or are
L7: Key Distributions Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 9/16/2015 CSCI 451 - Fall 2015 1 Acknowledgement Many slides are from or are
Electronic Seal Administrator Guide Published:December 27, 2017
 Electronic Seal Administrator Guide Published:December 27, 2017 Copyright Version 4.25.2.3 Copyright 2003-2018 DocuSign, Inc. All rights reserved. For information about DocuSign trademarks, copyrights
Electronic Seal Administrator Guide Published:December 27, 2017 Copyright Version 4.25.2.3 Copyright 2003-2018 DocuSign, Inc. All rights reserved. For information about DocuSign trademarks, copyrights
Version 3 X.509 Certificates
 Entrust Technologies White Paper Author: Ian Curry Date: July 1996 Version: 1.0 Entrust Technologies, 1997. All rights reserved. 1 1. Introduction This document provides a description of the version 3
Entrust Technologies White Paper Author: Ian Curry Date: July 1996 Version: 1.0 Entrust Technologies, 1997. All rights reserved. 1 1. Introduction This document provides a description of the version 3
Using Cryptography CMSC 414. October 16, 2017
 Using Cryptography CMSC 414 October 16, 2017 Digital Certificates Recall: K pub = (n, e) This is an RSA public key How do we know who this is for? Need to bind identity to a public key We can do this using
Using Cryptography CMSC 414 October 16, 2017 Digital Certificates Recall: K pub = (n, e) This is an RSA public key How do we know who this is for? Need to bind identity to a public key We can do this using
PKI-An Operational Perspective. NANOG 38 ARIN XVIII October 10, 2006
 PKI-An Operational Perspective NANOG 38 ARIN XVIII October 10, 2006 Briefing Contents PKI Usage Benefits Constituency Acceptance Specific Discussion of Requirements Certificate Policy Certificate Policy
PKI-An Operational Perspective NANOG 38 ARIN XVIII October 10, 2006 Briefing Contents PKI Usage Benefits Constituency Acceptance Specific Discussion of Requirements Certificate Policy Certificate Policy
Authentication and Key Distribution
 1 Alice and Bob share a key How do they determine that they do? Challenge-response protocols 2 How do they establish the shared secret in the first place? Key distribution PKI, Kerberos, Other key distribution
1 Alice and Bob share a key How do they determine that they do? Challenge-response protocols 2 How do they establish the shared secret in the first place? Key distribution PKI, Kerberos, Other key distribution
