A Classification Of analyzed Detection and Improvement OS Fingerprinting and Various finger stamping scanning ports
|
|
|
- Scot Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Classification Of analyzed Detection and Improvement OS Fingerprinting and Various finger stamping scanning ports Nitin Tiwari 1 1 Dept. of Information Technology, Swami Vivekananda University, Sagar, India Abstract: Finger stamping is an overview and analyzed operating system and detection methods using port scanning.o/s to specify based on stack finger stamping. Finger stamping to used various protocol and host such like as TCP/IP, FTP, TELNET, HTTP, DNS.O/S detection also used concern of system or safety admin using the port. Finger stamping method was working version different o/s version. Similar o/s to perform the various task. The main aim of finger stamping method to used trace to another receiver hand. Its tracer worked by the search that exists some TCP/IP protocol. More and more analyzed for the fingerprint to use some tools like inactive and active tools. Both tools are identifying remote o/s finger stamping. Active proceed work done by remote host analyzed and resisted. These are two methods to be recognized white-hat method and black hat method to implement by active way Ip packet sent to the host. And detection method is also used.many normal process used for fin investigation to checking is usually to transfer signal by the sender to receiver. Finger stamping is scanning method like as half scanning, full scanning, stealth scanning.to locate open, closed port on the server. All scan method to client level used on SYN and server level used of SYN/ACK.and after this process to client ask to connect to the full connection to remote host. Keywords: Finger Stamping, Host Detection, Port Scanning, Open Scanning, Half-Open Scanning, Stealth Scanning I. INTRODUCTION At the present time everyone is connected to the internet, so the need to secure him from the intrusions is essential. What happens if a bank data was hacked and taken down? This external threaten the organizations trigger them to use multiple security applications like firewalls/intrusion detection systems (IDSs) to insure themselves from the hackers. The operating system fingerprinting is a manner of remotely identifying and determining the identity of a scapegoat system by observing the TCP/IP packets that generated by that method[1]. The operating system detection can view from two parties. First, from the contrary point of view for the hackers needs. For example, the hackers detect OS to exploit. It's vulnerabilities for their hacking purposes to solved in the system. Another part of the network executives needs to access tool and mechanism. It is crucial for necessary data. Them to get as much information as probable about their networks. It is also wanted for the system administrator to have the specific summary about the peripherals that they have in connection with their network behind the situation. The network administrators to have full control of mainly for the vast network. For the system administrator, it's always important to be one step ahead of the attacker. This way, the attacker can make use of the latest vulnerabilities. It is also essential for the network manager to be sure that each OS in the network performs the concerned methods. For instance.when a user formats his Personal computer and rebooting a former version. Detecting such situation in an automated way is very important, uniquely for large networks.[2] Having the path to an up-to-date network list could allow a company to collect money by canceling the permit and support service for an OS that no longer used.the network executives also want to know which mobile devices, like Smartphone and tablets, are reaching his/her network. It may be further testing to respond to network attacks received by a wireless device. In some cases, the mobile users may not be granted and can cause network overload as network load evaluation might not have combined on-the-fly wireless users.[3] There is two principal method of performing O/S Fingerprinting. The active detection achieved by sending. A particular packet to the target device and get the response that can be analyzed to identify the OS type of the target device. The main weakness of active OS fingerprinting method is that it cannot do if the target system has firewall and intrusion detection systems (IDSs). On the other word, the passive approach of OS fingerprinting done by severe sniffing tool. The network packets remotely preferably by sending crafted packets to a target tool [4]. The idea of passive OS fingerprinting is to investigate the headers of TCP SYN packets (or other specific packets) to arrange the operating system. They equated with the predefined database that contains signatures of different operating systems. And discover this type of the O/S. It is vital for network executives to do.o/s fingerprinting passively to obtain the elimination of the active method due to Firewalls/IDSs[5][6]. 2609
2 A. Traditional Approach Port Scanning In this paper, we have to discuss port scanning. Port scanning to be used one or other network to be connected host. Port scanning is also known as network scanning method.we can many hosts for used scanning method[7].port scanning method is one of the most critical processes in computer networks. Port scanning is classified in many ways : 1) Network administrator and consultan 2) Monitoring application 3) Nontarget attackers 4) Target attackers 5) Application Sources Network administrator classified for port scanning depends on the local network. Port scan also performed an external scan and internal port scanning method. The monitoring application is standard detection process. It detects new peripheral devices. Nontarget attacker another means malware that uses port scanning in their search for the vulnerabilities.its full safe port scanning method to search host or targets need in their activities. Port scanning method to be scan huge of many hosts. Many application is used port scanning like online game application, peer to peer functionality, etc[8]. B. Types of port scanning Port scanning classified into four main groups:- 1) Vertical Scan:-This type of scan for purpose many hosts for the same port services. A vertical scan to be used search to attack entire network subnet 2) Horizontal Scan:-This type of scan to purpose one host for the accessibility of many ports such as likes TCP port and IP address 3) Strobe Scan: - This type of scan can use both types of scan method 4) Block scan: - this type of scan is a thorough scan in all ports on several hosts[9]. C. General Method At what time a talented person with partially an indication decides to attack your structure. They will primary attempt to identify the operating system. For the expert dissemination tester or hacker. O/S identification is an essential step in probing. So it is must understand the procedure used by most of the OS fingerprinting attempts before safeguarding from them General approach for any OS fingerprinting using stack fingerprinting is consisting of following three phases. 2610
3 D. Phase #1 host detection Host discovery is a term used to describe a particular phase of a perception test, where one tries to determine the convenient hosts on a network. Many times if a firewall rule set is written explicitly[10].it is difficult to decide on the number of hosts accurately. That is behind a firewall. Essential about this phase is to discover a reachable node. Finding out whether it's up or down. E. Phase # 2 Port Scanning It is one of the most general techniques used in the native to discover and map services. That is monitoring on a particularized port. This method used an attacker can then creates a list of potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities. In the proposed open port leading to exploitation and compromise of a remote host. Port scanning techniques take form in three specific and differentiated ways. 1) An open scanning 2) half-open scanning 3) stealth scanning 1) An Open Scan Method: This variety of scan method includes opening a complete attachment to a remote host connection using a typical three-way TCP/IP handshake. A standard transaction involves issuing the following flags to create an accepted connection: Client -> SYN Server -> SYN ACK Client -> ACK The above example gives a port acknowledging our initial connection request with an SYN ACK. This response means the port; packet was the target is in the open state. Its great handshake has observed an effect.[11] The connection will terminate by the client allowing a new socket created/called allowing the next port to checked until the maximum port threshold has reached. Reverse taking a look at a response from a closed port would expose the following: an client -> SYN a server -> RST ACK an client -> RST The RST ACK flags returned by the server is telling the client to tear down the connection attempt since the port is not in the LISTENING state thus is closed. This method is created through connect() system call, allowing almost instantaneous identification of an open or closed port. If the connect() call returns true, the port is open; else the port is closed. Since this technique issues a three-way handshake to connect to an arbitrary host, a The spoofed connection is impossible, that is to say, a client can not manipulate the correct source IP, as a spoofed connection attempt involves sending an exact sequence number as well as setting the right return flags to set up for data transaction. Apparently, this technique is easily identifiable on any inbound traffic because it opens a full connection. Thus all IDS and firewalls can detect and block against this scan. However, because the connect() method uses the three-way handshake, results of this scan are about as accurate as you could get to determine open/closed ports. 2611
4 2) Half Open Scan Methods Or (Syn Scanning): The term half-open refers to the way the client terminates. The connection before the three-way handshake is completed. This scanning technique will often go unlogged by relationship-based IDS' and will return reasonably accurate results (reliability of open/closed port recognition. The implementation of this scan method is similar to a full TCP connect () three-way handshake except rather by sending ACK responses we promptly split feathers the connection. A presentation of this routine is necessary to confirm a half-open transaction: An client -> SYN A server -> SYN ACK An client -> RST This precedent has given that the target port was open because the server responded including SYN ACK flags. The RST bit is kernel oriented. That means the client demand does not send another packet. This bit like the kernel's TCP/IP stack code automates its. Opposite, a closed port will return with RST ACK. An client -> SYN An server -> RST ACK As is represented, this combination of flags is symbolic of a non- listening port. Although, this method has become rather simple to identify by many IDS because a paramount of Denial of Service (DoS)[12] utilities base their Attacks by sending excess SYN packets. 3) Stealth Scanning: The definition of a "stealth" scan has varied over recent years. The term was used to define a procedure. That avoided IDS and logging, as half-open scanning method. Though, nowadays stealth is considered to be any scan that is concerned with a few of the following: setting individual flags (ACK, FIN, RST) NULL flags set All flags set bypassing filters, firewalls, routers preparing as casual network traffic varied packet dispersal rates Broadly this scan is called TCP Fragmenting, where the different flags and another offset of TCP packet are targeted to scan the port from the response. TCP fragmenting is not a scan method so to speak, although it employs an approach to complex scanning implementations by splitting the TCP header into smaller fragments. IP reassembly on the server-side can often lead to unpredictable and abnormal results (IP headers carrying data can be fragmented). Many hosts are unable to parse and reassemble the tiny packets and thus may cause crashes, reboots, or even network device monitoring dumps. Alternatively,[13] these small packets may be potentially blocked by IP fragmentation queues in the kernel or caught by a stately firewall rule set. Since much intrusion detection systems use signature-based mechanisms to signify scanning attempts based on IP and the TCP header, fragmentation is often able to defeat this type of packet filtering and detection, and naturally, the scan will go undiscovered. A minimally allowable 2612
5 fragmented TCP header must contain a destination and source port for the first packet (8 octets, 64 bit), typically the initialized flags in the next, allowing the remote host to reassemble the package upon arrival. The actual reassembly is established through an IPM (internet protocol module) that identifies the fragmented packets by the field similar values of Source,Destination, Protocol, identification. F. Phase #3 os Detection It is the process of actively determining a targeted network node's underlying operating system by probing the targeted system with several packets and examining the response(s) received. Once, the classical techniques of OS fingerprinting met with stronger countermeasure form both the vendors and users new modern methods have surfaced. Eventually, more advanced technologies based on stack querying came about it. Stack querying means to actively packets to send the network. Stack on the remote host and examine the acknowledgments. This idea takes advantage of each OS vendor's network stack implementation. The first approach to use stack querying was aimed at the TCP stack. It includes sending standard and non-standard TCP packets to the remote host and examining the acknowledgments. The next process was identified as ISN (Initial Sequence Number) analysis. This determines the variations in the random number generators found in the TCP stack. Up until that point, the entire stack querying methods was found by looking at the TCP protocol. Later, researchers found a new approach that used the ICMP protocol.[14] The technique is known as ICMP response analysis. It involves sending ICMP messages to the remote host and analyzing the responses.tcp/ip stacks behavior of a targeted network element when probed with several legitimate and malformed packets. The received results would then be compared to a signature database to find an appropriate match. TCP fingerprinting works by sending TCP packets to a port and noticing how the TCP stack responds[15]. Many of the specifications for TCP/IP are left open to interpretation, so each vendor implements the TCP/IP stack a little differently, creating a unique identifier or fingerprint. Typically, seven packets are sent to a destination port using different flag variants including SYN, SYN/ACK, FIN, FIN/ACK, SYN/FIN, PSH, and SYN+ Reserved. Based on the data returned,[17] the results can be mapped to a particular operating system and version, decoding the OS for users of the tools. II. CONCLUSION In this paper, we presented o/s determine to check security and protection analyzed various port. Everyone is connected to the internet, so the need to secure him from the intrusions is essential. The hackers detect OS to exploit. It's vulnerabilities for their 2613
6 hacking purposes to solve in the system. Another part of the network administrators needs to access tool and mechanism. It is also essential for the network administrator to be sure that each OS in the network performs the concerned methods. Operating OS Detecting such situation in an automated way is necessary, especially for large networks. And discover this type of the O/S. It is vital for network administrators to do O/S fingerprinting passively to succeed the suppression of the active method due to IDSs. And we have to discuss port scanning. Port scanning to be used one or other network to be connected host. Port scanning is also known as network scanning method.we can many hosts for used scanning method. Host detection method is to discover a reachable node. Finding out whether it's up or down. Port scanning is one of the most famous techniques used in the wild to identify and map services. That is listening on a particularized port. This process, an attacker can then create a list of potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Open scan method involves opening a full connection to a remote host using a typical three-way TCP/IP handshake. The term half-open scan method applies to the way the client terminates the connection before the three-way handshake is completed. The definition of a "stealth" scan has varied over recent years, and initially, the term was used to define a procedure that avoided IDS and logging. it s Called half-open scanning method. Os detection is the process of actively determining a targeted network node's underlying operating system by probing the targeted system with several packets and examining the response(s) received. Once, the classical techniques of OS fingerprinting met with stronger countermeasure form both the vendors and users new modern methods have surfaced. Eventually, more advanced technologies based on stack querying came about it. Stack querying means to actively send packets to the network stack on the remote host and analyze the responses. REFERENCES [1] L. Spitzner, Passive fingerprinting, vol. 3, pp. 1 4, May 2003 [2] L. G. Greenwald and T. J. Thomas, Understanding and preventingnetwork device fingerprinting, Bell Lab. Tech. J., vol. 3, pp ,2007 [3] G. Taleck, Ambiguity resolution via passive OS fingerprinting, inproc. the 6th International Symposium on Recent Advances inintrusion Detection, 2003, pp [4] NitinTiwari entitle topics Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) Technology- Network Behavior Analysis System (NBAS),ISCA Vol. 1(1), 51-56, July (201 [5] aher Al-Shehari and FarrukhShahzad Improving Operating System Fingerprinting using Machine Learning Techniques International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 1,pp57-pp62 February 201 [6] P. B. Falch, Investigating passive operating system detection, M.S.thesis, University of Oslo, May 24, 2011 [7] G. Lyon, Remote OS detection via TCP/IP Stack Finger-Printing, Phrack Magazine, vol. 8, no. 54, December 1998 [8] Barnett, R. J. & Irwin, B Towards a taxonomy of network scanning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2008 annual research conference of the South African Institute of Computer Scientists and Information Technologists on IT research in developing countries: riding the wave of technology,saicsit 08, 1 7, New York, NY, USA. ACM [9] Larsen, R. Fast-flux Service Networks in botnet malware. Visited: , November 2010 [10] Wolthusen, S. IMT 4651 Applied Information Security. Class Lectures. Presentations. Gjøvik University College, 2010 [11] S. Kalia and M. Singh, Masking approach to secure systems fromoperating system fingerprinting, TENCON 2005 IEEE Region10, vol. 1, no. 6, pp , Nov [12] NitinTiwari An Overview & Analysis Safety Proposal and Policies of Internet Network Safety IJARCET b [13] NitinTiwari An overview & comparison of internet protocol TCP/IP protocol V/S OSI Reference Modal.IJARCET ISSN code vol-1 issue 7 pp sep 201 [14] NitinTiwari an Overview & Comparison of Inactive and Active Finger Stamping IJSER by ISSN code [15] NitinTiwari entitle topics on an overview An Overview of Techniques for Framework of Finger Stamping.IJRCSEE June 2012 [16] NitinTiwari entitle topics on An Overview & Analysis for Computer System s Remote Analysis (RACS) by ISSN code by ISSN code vol-1 issue 7 pp sep
Scanning. Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III. Reading Assignment. Unit Lesson UNIT III STUDY GUIDE
 UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Recall the terms port scanning, network scanning, and vulnerability scanning. 2.
UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Recall the terms port scanning, network scanning, and vulnerability scanning. 2.
INF5290 Ethical Hacking. Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning. Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi
 INF5290 Ethical Hacking Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi Lecture Overview Identifying hosts in a network Identifying services on a host What are the typical
INF5290 Ethical Hacking Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi Lecture Overview Identifying hosts in a network Identifying services on a host What are the typical
Configuring attack detection and prevention 1
 Contents Configuring attack detection and prevention 1 Overview 1 Attacks that the device can prevent 1 Single-packet attacks 1 Scanning attacks 2 Flood attacks 3 TCP fragment attack 4 Login DoS attack
Contents Configuring attack detection and prevention 1 Overview 1 Attacks that the device can prevent 1 Single-packet attacks 1 Scanning attacks 2 Flood attacks 3 TCP fragment attack 4 Login DoS attack
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems
 CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting CIT 480: Securing Computer
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting CIT 480: Securing Computer
Configuring attack detection and prevention 1
 Contents Configuring attack detection and prevention 1 Overview 1 Attacks that the device can prevent 1 Single-packet attacks 1 Scanning attacks 2 Flood attacks 3 TCP fragment attack 4 Login DoS attack
Contents Configuring attack detection and prevention 1 Overview 1 Attacks that the device can prevent 1 Single-packet attacks 1 Scanning attacks 2 Flood attacks 3 TCP fragment attack 4 Login DoS attack
CSC 574 Computer and Network Security. TCP/IP Security
 CSC 574 Computer and Network Security TCP/IP Security Alexandros Kapravelos kapravelos@ncsu.edu (Derived from slides by Will Enck and Micah Sherr) Network Stack, yet again Application Transport Network
CSC 574 Computer and Network Security TCP/IP Security Alexandros Kapravelos kapravelos@ncsu.edu (Derived from slides by Will Enck and Micah Sherr) Network Stack, yet again Application Transport Network
Denial of Service and Distributed Denial of Service Attacks
 Denial of Service and Distributed Denial of Service Attacks Objectives: 1. To understand denial of service and distributed denial of service. 2. To take a glance about DoS techniques. Distributed denial
Denial of Service and Distributed Denial of Service Attacks Objectives: 1. To understand denial of service and distributed denial of service. 2. To take a glance about DoS techniques. Distributed denial
Single Network: applications, client and server hosts, switches, access links, trunk links, frames, path. Review of TCP/IP Internetworking
 1 Review of TCP/IP working Single Network: applications, client and server hosts, switches, access links, trunk links, frames, path Frame Path Chapter 3 Client Host Trunk Link Server Host Panko, Corporate
1 Review of TCP/IP working Single Network: applications, client and server hosts, switches, access links, trunk links, frames, path Frame Path Chapter 3 Client Host Trunk Link Server Host Panko, Corporate
Computer Security and Privacy
 CSE P 590 / CSE M 590 (Spring 2010) Computer Security and Privacy Tadayoshi Kohno Thanks to Dan Boneh, Dieter Gollmann, John Manferdelli, John Mitchell, Vitaly Shmatikov, Bennet Yee, and many others for
CSE P 590 / CSE M 590 (Spring 2010) Computer Security and Privacy Tadayoshi Kohno Thanks to Dan Boneh, Dieter Gollmann, John Manferdelli, John Mitchell, Vitaly Shmatikov, Bennet Yee, and many others for
Attack Prevention Technology White Paper
 Attack Prevention Technology White Paper Keywords: Attack prevention, denial of service Abstract: This document introduces the common network attacks and the corresponding prevention measures, and describes
Attack Prevention Technology White Paper Keywords: Attack prevention, denial of service Abstract: This document introduces the common network attacks and the corresponding prevention measures, and describes
Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable?
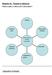 Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable? Sharing Unknown path Many points of attack What makes a network vulnerable? Unknown perimeter Anonymity Complexity of system Categories of
Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable? Sharing Unknown path Many points of attack What makes a network vulnerable? Unknown perimeter Anonymity Complexity of system Categories of
ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. No matter what medium connects computers on a network copper wires, fiber-optic cables, or a wireless setup the same protocol must be
ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. No matter what medium connects computers on a network copper wires, fiber-optic cables, or a wireless setup the same protocol must be
Network Security. Evil ICMP, Careless TCP & Boring Security Analyses. Mohamed Sabt Univ Rennes, CNRS, IRISA Thursday, October 4th, 2018
 Network Security Evil ICMP, Careless TCP & Boring Security Analyses Mohamed Sabt Univ Rennes, CNRS, IRISA Thursday, October 4th, 2018 Part I Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Why ICMP No method
Network Security Evil ICMP, Careless TCP & Boring Security Analyses Mohamed Sabt Univ Rennes, CNRS, IRISA Thursday, October 4th, 2018 Part I Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Why ICMP No method
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and countermeasures
 Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Roma La Sapienza Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and countermeasures Definitions of DoS and DDoS attacks Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and countermeasures A
Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Roma La Sapienza Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and countermeasures Definitions of DoS and DDoS attacks Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and countermeasures A
A quick theorical introduction to network scanning. 23rd November 2005
 A quick theorical introduction to network ASBL CSRRT-LU (Computer Security Research and Response Team Luxembourg) http://www.csrrt.org/ 23rd November 2005 IP protocol ACK Network is not exact science When
A quick theorical introduction to network ASBL CSRRT-LU (Computer Security Research and Response Team Luxembourg) http://www.csrrt.org/ 23rd November 2005 IP protocol ACK Network is not exact science When
A Study on Intrusion Detection Techniques in a TCP/IP Environment
 A Study on Intrusion Detection Techniques in a TCP/IP Environment C. A. Voglis and S. A. Paschos Department of Computer Science University of Ioannina GREECE Abstract: The TCP/IP protocol suite is the
A Study on Intrusion Detection Techniques in a TCP/IP Environment C. A. Voglis and S. A. Paschos Department of Computer Science University of Ioannina GREECE Abstract: The TCP/IP protocol suite is the
What this talk is about?
 On the Current State of Remote Active OS Fingerprinting Tools Ofir Arkin CTO ofir.arkin@insightix.com Defcon 13 1 What this talk is about? This talk examines different aspects of remote active operating
On the Current State of Remote Active OS Fingerprinting Tools Ofir Arkin CTO ofir.arkin@insightix.com Defcon 13 1 What this talk is about? This talk examines different aspects of remote active operating
Introduction to TCP/IP networking
 Introduction to TCP/IP networking TCP/IP protocol family IP : Internet Protocol UDP : User Datagram Protocol RTP, traceroute TCP : Transmission Control Protocol HTTP, FTP, ssh What is an internet? A set
Introduction to TCP/IP networking TCP/IP protocol family IP : Internet Protocol UDP : User Datagram Protocol RTP, traceroute TCP : Transmission Control Protocol HTTP, FTP, ssh What is an internet? A set
Network Forensics Prefix Hijacking Theory Prefix Hijacking Forensics Concluding Remarks. Network Forensics:
 Network Forensics: Network OS Fingerprinting Prefix Hijacking Analysis Scott Hand September 30 th, 2011 Outline 1 Network Forensics Introduction OS Fingerprinting 2 Prefix Hijacking Theory BGP Background
Network Forensics: Network OS Fingerprinting Prefix Hijacking Analysis Scott Hand September 30 th, 2011 Outline 1 Network Forensics Introduction OS Fingerprinting 2 Prefix Hijacking Theory BGP Background
Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key
 Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key DAY CLASS Dr. William M. Farmer DURATION OF EXAMINATION: 2 Hours MCMASTER UNIVERSITY FINAL EXAMINATION April 2002 (1) [2 pts.] Conventional encryption cannot be used
Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key DAY CLASS Dr. William M. Farmer DURATION OF EXAMINATION: 2 Hours MCMASTER UNIVERSITY FINAL EXAMINATION April 2002 (1) [2 pts.] Conventional encryption cannot be used
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET SPOOFING
 CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET SPOOFING Last month, we started this series to cover the important cyber attacks that impact critical IT infrastructure in organisations. The first was the denial-of-service
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: PACKET SPOOFING Last month, we started this series to cover the important cyber attacks that impact critical IT infrastructure in organisations. The first was the denial-of-service
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 19: Intrusion Detection Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline Intruders Intrusion detection host-based network-based
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 19: Intrusion Detection Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline Intruders Intrusion detection host-based network-based
Network Security. Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation)
 1 Network Security Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation) A Brief History of the World 2 OSI Model vs TCP/IP suite 3 TFTP & SMTP 4 ICMP 5 NAT/PAT 6 ARP/RARP 7 DHCP 8
1 Network Security Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation) A Brief History of the World 2 OSI Model vs TCP/IP suite 3 TFTP & SMTP 4 ICMP 5 NAT/PAT 6 ARP/RARP 7 DHCP 8
Exam Questions CEH-001
 Exam Questions CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/ceh-001/ 1. A company is legally liable for the content of email that is sent from its systems, regardless of whether
Exam Questions CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/ceh-001/ 1. A company is legally liable for the content of email that is sent from its systems, regardless of whether
Outline. What is TCP protocol? How the TCP Protocol Works SYN Flooding Attack TCP Reset Attack TCP Session Hijacking Attack
 Attacks on TCP Outline What is TCP protocol? How the TCP Protocol Works SYN Flooding Attack TCP Reset Attack TCP Session Hijacking Attack TCP Protocol Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a core protocol
Attacks on TCP Outline What is TCP protocol? How the TCP Protocol Works SYN Flooding Attack TCP Reset Attack TCP Session Hijacking Attack TCP Protocol Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a core protocol
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense
 Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 2 TCP/IP Concepts Review Last modified 1-11-17 Objectives Describe the TCP/IP protocol stack Explain the basic concepts of IP addressing Explain the
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 2 TCP/IP Concepts Review Last modified 1-11-17 Objectives Describe the TCP/IP protocol stack Explain the basic concepts of IP addressing Explain the
HP High-End Firewalls
 HP High-End Firewalls Attack Protection Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2650 Software version: F1000-A-EI&F1000-S-EI: R3721 F5000: F3210 F1000-E: F3171 Firewall module: F3171 Document version: 6PW101-20120719
HP High-End Firewalls Attack Protection Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2650 Software version: F1000-A-EI&F1000-S-EI: R3721 F5000: F3210 F1000-E: F3171 Firewall module: F3171 Document version: 6PW101-20120719
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Department of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle. Network Security. Chapter 8
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Department of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle Network Security Chapter 8 System Vulnerabilities and Denial of Service Attacks System Vulnerabilities and
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Department of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle Network Security Chapter 8 System Vulnerabilities and Denial of Service Attacks System Vulnerabilities and
TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu
 TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu OSI Model and TCP/IP Model Comparison TCP / IP Protocols (Application Layer) The TCP/IP subprotocols listed in this layer are services that support a number of network functions:
TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu OSI Model and TCP/IP Model Comparison TCP / IP Protocols (Application Layer) The TCP/IP subprotocols listed in this layer are services that support a number of network functions:
Lecture 33. Firewalls. Firewall Locations in the Network. Castle and Moat Analogy. Firewall Types. Firewall: Illustration. Security April 15, 2005
 Firewalls Lecture 33 Security April 15, 2005 Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Intranet Firewall DMZ Router Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks
Firewalls Lecture 33 Security April 15, 2005 Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Intranet Firewall DMZ Router Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning
 Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning Last revised 10-4-17 KonBoot Get into any account without the password Works on Windows and Linux No longer free Link Ch 5r From the
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning Last revised 10-4-17 KonBoot Get into any account without the password Works on Windows and Linux No longer free Link Ch 5r From the
Detecting Specific Threats
 The following topics explain how to use preprocessors in a network analysis policy to detect specific threats: Introduction to Specific Threat Detection, page 1 Back Orifice Detection, page 1 Portscan
The following topics explain how to use preprocessors in a network analysis policy to detect specific threats: Introduction to Specific Threat Detection, page 1 Back Orifice Detection, page 1 Portscan
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning
 Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning Last revised 1-11-17 KonBoot Get into any account without the password Works on Windows and Linux No longer free Link Ch 5r From the
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 5 Port Scanning Last revised 1-11-17 KonBoot Get into any account without the password Works on Windows and Linux No longer free Link Ch 5r From the
UDP and TCP. Introduction. So far we have studied some data link layer protocols such as PPP which are responsible for getting data
 ELEX 4550 : Wide Area Networks 2015 Winter Session UDP and TCP is lecture describes the two most common transport-layer protocols used by IP networks: the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and the Transmission
ELEX 4550 : Wide Area Networks 2015 Winter Session UDP and TCP is lecture describes the two most common transport-layer protocols used by IP networks: the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and the Transmission
20-CS Cyber Defense Overview Fall, Network Basics
 20-CS-5155 6055 Cyber Defense Overview Fall, 2017 Network Basics Who Are The Attackers? Hackers: do it for fun or to alert a sysadmin Criminals: do it for monetary gain Malicious insiders: ignores perimeter
20-CS-5155 6055 Cyber Defense Overview Fall, 2017 Network Basics Who Are The Attackers? Hackers: do it for fun or to alert a sysadmin Criminals: do it for monetary gain Malicious insiders: ignores perimeter
CSCI-GA Operating Systems. Networking. Hubertus Franke
 CSCI-GA.2250-001 Operating Systems Networking Hubertus Franke frankeh@cs.nyu.edu Source: Ganesh Sittampalam NYU TCP/IP protocol family IP : Internet Protocol UDP : User Datagram Protocol RTP, traceroute
CSCI-GA.2250-001 Operating Systems Networking Hubertus Franke frankeh@cs.nyu.edu Source: Ganesh Sittampalam NYU TCP/IP protocol family IP : Internet Protocol UDP : User Datagram Protocol RTP, traceroute
OSI Transport Layer. objectives
 LECTURE 5 OSI Transport Layer objectives 1. Roles of the Transport Layer 1. segmentation of data 2. error detection 3. Multiplexing of upper layer application using port numbers 2. The TCP protocol Communicating
LECTURE 5 OSI Transport Layer objectives 1. Roles of the Transport Layer 1. segmentation of data 2. error detection 3. Multiplexing of upper layer application using port numbers 2. The TCP protocol Communicating
Authors: Mark Handley, Vern Paxson, Christian Kreibich
 Network Intrusion Detection: Evasion, Traffic Normalization, and End-to-End Protocol Semantics Authors: Mark Handley, Vern Paxson, Christian Kreibich Exploitable Ambiguities NIDS does not have full range
Network Intrusion Detection: Evasion, Traffic Normalization, and End-to-End Protocol Semantics Authors: Mark Handley, Vern Paxson, Christian Kreibich Exploitable Ambiguities NIDS does not have full range
Strengthening and Securing the TCP/IP Stack against SYN Attacks
 Strengthening and Securing the TCP/IP Stack against SYN Attacks A.Baes Mohamed Arab Academy for Science and Technology baithmm@hotmail.com Abstract. This paper analyzes a (DoS) Denial of Service attack
Strengthening and Securing the TCP/IP Stack against SYN Attacks A.Baes Mohamed Arab Academy for Science and Technology baithmm@hotmail.com Abstract. This paper analyzes a (DoS) Denial of Service attack
Firewalls, Tunnels, and Network Intrusion Detection
 Firewalls, Tunnels, and Network Intrusion Detection 1 Intrusion Detection Systems Intrusion Actions aimed at compromising the security of the target (confidentiality, integrity, availability of computing/networking
Firewalls, Tunnels, and Network Intrusion Detection 1 Intrusion Detection Systems Intrusion Actions aimed at compromising the security of the target (confidentiality, integrity, availability of computing/networking
ELEC5616 COMPUTER & NETWORK SECURITY
 ELEC5616 COMPUTER & NETWORK SECURITY Lecture 17: Network Protocols I IP The Internet Protocol (IP) is a stateless protocol that is used to send packets from one machine to another using 32- bit addresses
ELEC5616 COMPUTER & NETWORK SECURITY Lecture 17: Network Protocols I IP The Internet Protocol (IP) is a stateless protocol that is used to send packets from one machine to another using 32- bit addresses
ERT Threat Alert New Risks Revealed by Mirai Botnet November 2, 2016
 Abstract The Mirai botnet struck the security industry in three massive attacks that shook traditional DDoS protection paradigms, proving that the Internet of Things (IoT) threat is real and the grounds
Abstract The Mirai botnet struck the security industry in three massive attacks that shook traditional DDoS protection paradigms, proving that the Internet of Things (IoT) threat is real and the grounds
EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities
 EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities Objective: After this experiment, the students should be able to: i. Understand the format of standard frames and packet headers. Overview: The Open Systems
EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities Objective: After this experiment, the students should be able to: i. Understand the format of standard frames and packet headers. Overview: The Open Systems
AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM
 1 AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM 2 Introduction (1/2) TCP provides a full duplex reliable stream connection between two end points A connection is uniquely defined by the quadruple
1 AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM 2 Introduction (1/2) TCP provides a full duplex reliable stream connection between two end points A connection is uniquely defined by the quadruple
Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cybercrime, 2nd Edition. Chapter 2 Investigating Network Traffic
 Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cybercrime, 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Investigating Network Traffic Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Understand network
Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cybercrime, 2nd Edition Chapter 2 Investigating Network Traffic Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Understand network
Denial of Service (DoS)
 Flood Denial of Service (DoS) Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline Flood 1 2 3 4 5 Flood 6 7 8 Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack Flood The NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide defines a DoS attack as:
Flood Denial of Service (DoS) Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline Flood 1 2 3 4 5 Flood 6 7 8 Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack Flood The NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide defines a DoS attack as:
Table of Contents. 1 Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1 Overview 1-1 Displaying Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1 Overview 1-1 Displaying Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1 i 1 Intrusion Detection Statistics Overview Intrusion detection is an important network
Table of Contents 1 Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1 Overview 1-1 Displaying Intrusion Detection Statistics 1-1 i 1 Intrusion Detection Statistics Overview Intrusion detection is an important network
Ping of death Land attack Teardrop Syn flood Smurf attack. DOS Attack Methods
 Ping of death Land attack Teardrop Syn flood Smurf attack DOS Attack Methods Ping of Death A type of buffer overflow attack that exploits a design flaw in certain ICMP implementations where the assumption
Ping of death Land attack Teardrop Syn flood Smurf attack DOS Attack Methods Ping of Death A type of buffer overflow attack that exploits a design flaw in certain ICMP implementations where the assumption
Configuring Flood Protection
 Configuring Flood Protection NOTE: Control Plane flood protection is located on the Firewall Settings > Advanced Settings page. TIP: You must click Accept to activate any settings you select. The Firewall
Configuring Flood Protection NOTE: Control Plane flood protection is located on the Firewall Settings > Advanced Settings page. TIP: You must click Accept to activate any settings you select. The Firewall
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering. Spring 2018
 ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Networking Transport Layer Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) TCP/IP Model 2 Transport Layer Problem solved:
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Networking Transport Layer Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) TCP/IP Model 2 Transport Layer Problem solved:
User Datagram Protocol
 Topics Transport Layer TCP s three-way handshake TCP s connection termination sequence TCP s TIME_WAIT state TCP and UDP buffering by the socket layer 2 Introduction UDP is a simple, unreliable datagram
Topics Transport Layer TCP s three-way handshake TCP s connection termination sequence TCP s TIME_WAIT state TCP and UDP buffering by the socket layer 2 Introduction UDP is a simple, unreliable datagram
WEB APPLICATION AND WEB SERVER FOOTPRINT MAKER AND ANALYZER
 Volume 119 No. 15 2018, 1499-1504 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ WEB APPLICATION AND WEB SERVER FOOTPRINT MAKER AND ANALYZER U. Sarath kumar
Volume 119 No. 15 2018, 1499-1504 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ WEB APPLICATION AND WEB SERVER FOOTPRINT MAKER AND ANALYZER U. Sarath kumar
Network Security. Thierry Sans
 Network Security Thierry Sans HTTP SMTP DNS BGP The Protocol Stack Application TCP UDP Transport IPv4 IPv6 ICMP Network ARP Link Ethernet WiFi The attacker is capable of confidentiality integrity availability
Network Security Thierry Sans HTTP SMTP DNS BGP The Protocol Stack Application TCP UDP Transport IPv4 IPv6 ICMP Network ARP Link Ethernet WiFi The attacker is capable of confidentiality integrity availability
8/19/2010. Computer Forensics Network forensics. Data sources. Monitoring
 Computer Forensics Network forensics Thomas Mundt thm@informatik.uni-rostock.de Data sources Assessment Monitoring Monitoring Software Logs and Log Analysis Incident Analysis External Assessment Hackers
Computer Forensics Network forensics Thomas Mundt thm@informatik.uni-rostock.de Data sources Assessment Monitoring Monitoring Software Logs and Log Analysis Incident Analysis External Assessment Hackers
CS155 Firewalls. Why Firewalls? Why Firewalls? Bugs, Bugs, Bugs
 CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something useful with your computer Drawbacks;
CS155 - Firewalls Simon Cooper Why Firewalls? Need for the exchange of information; education, business, recreation, social and political Need to do something useful with your computer Drawbacks;
Network Working Group. Updates: 1858 June 2001 Category: Informational. Protection Against a Variant of the Tiny Fragment Attack
 Network Working Group I. Miller Request for Comments: 3128 Singularis Ltd Updates: 1858 June 2001 Category: Informational Protection Against a Variant of the Tiny Fragment Attack Status of this Memo This
Network Working Group I. Miller Request for Comments: 3128 Singularis Ltd Updates: 1858 June 2001 Category: Informational Protection Against a Variant of the Tiny Fragment Attack Status of this Memo This
firewalls perimeter firewall systems firewalls security gateways secure Internet gateways
 Firewalls 1 Overview In old days, brick walls (called firewalls ) built between buildings to prevent fire spreading from building to another Today, when private network (i.e., intranet) connected to public
Firewalls 1 Overview In old days, brick walls (called firewalls ) built between buildings to prevent fire spreading from building to another Today, when private network (i.e., intranet) connected to public
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Defending against Flooding-Based DDoS Attacks: A Tutorial Rocky K. C. Chang Presented by Adwait Belsare (adwait@wpi.edu) Suvesh Pratapa (suveshp@wpi.edu) Modified by
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Defending against Flooding-Based DDoS Attacks: A Tutorial Rocky K. C. Chang Presented by Adwait Belsare (adwait@wpi.edu) Suvesh Pratapa (suveshp@wpi.edu) Modified by
Chapter 8 roadmap. Network Security
 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7 Securing
Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7 Securing
ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF DISTRIBUTED DENIAL OF SERVICE ATTACKS IDENTIFICATION METHODS
 ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF DISTRIBUTED DENIAL OF SERVICE ATTACKS IDENTIFICATION METHODS Saulius Grusnys, Ingrida Lagzdinyte Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Computer Networks, Studentu 50,
ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF DISTRIBUTED DENIAL OF SERVICE ATTACKS IDENTIFICATION METHODS Saulius Grusnys, Ingrida Lagzdinyte Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Computer Networks, Studentu 50,
Chapter 2 Advanced TCP/IP
 Tactical Perimeter Defense 2-1 Chapter 2 Advanced TCP/IP At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional
Tactical Perimeter Defense 2-1 Chapter 2 Advanced TCP/IP At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional
On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure
 2018 On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure Dr Mahdi Aiash 4/24/2018 1. Introduction A port scan is a method for determining which ports on a network are open. As ports
2018 On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure Dr Mahdi Aiash 4/24/2018 1. Introduction A port scan is a method for determining which ports on a network are open. As ports
Introduction to Network. Topics
 Introduction to Network Security Chapter 7 Transport Layer Protocols 1 TCP Layer Topics Responsible for reliable end-to-end transfer of application data. TCP vulnerabilities UDP UDP vulnerabilities DNS
Introduction to Network Security Chapter 7 Transport Layer Protocols 1 TCP Layer Topics Responsible for reliable end-to-end transfer of application data. TCP vulnerabilities UDP UDP vulnerabilities DNS
CSC Network Security
 CSC 474 -- Security Topic 9. Firewalls CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 1 Outline Overview of Firewalls Filtering Firewalls Proxy Servers CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 2 Overview of Firewalls CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 3 1 Internet
CSC 474 -- Security Topic 9. Firewalls CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 1 Outline Overview of Firewalls Filtering Firewalls Proxy Servers CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 2 Overview of Firewalls CSC 474 Dr. Peng Ning 3 1 Internet
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 20: Intrusion Prevention Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Overview Firewalls purpose types locations Network perimeter
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 20: Intrusion Prevention Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Overview Firewalls purpose types locations Network perimeter
Introduction to Computer Networks. CS 166: Introduction to Computer Systems Security
 Introduction to Computer Networks CS 166: Introduction to Computer Systems Security Network Communication Communication in modern networks is characterized by the following fundamental principles Packet
Introduction to Computer Networks CS 166: Introduction to Computer Systems Security Network Communication Communication in modern networks is characterized by the following fundamental principles Packet
Internet Layers. Physical Layer. Application. Application. Transport. Transport. Network. Network. Network. Network. Link. Link. Link.
 Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Chapter 2 - Part 1. The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet
 Chapter 2 - Part 1 The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet Protocols A protocol is a language or set of rules that two or more computers use to communicate 2 Protocol Analogy: Phone Call Parties
Chapter 2 - Part 1 The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet Protocols A protocol is a language or set of rules that two or more computers use to communicate 2 Protocol Analogy: Phone Call Parties
9. Security. Safeguard Engine. Safeguard Engine Settings
 9. Security Safeguard Engine Traffic Segmentation Settings Storm Control DoS Attack Prevention Settings Zone Defense Settings SSL Safeguard Engine D-Link s Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology
9. Security Safeguard Engine Traffic Segmentation Settings Storm Control DoS Attack Prevention Settings Zone Defense Settings SSL Safeguard Engine D-Link s Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology
CS 457 Lecture 11 More IP Networking. Fall 2011
 CS 457 Lecture 11 More IP Networking Fall 2011 IP datagram format IP protocol version number header length (bytes) type of data max number remaining hops (decremented at each router) upper layer protocol
CS 457 Lecture 11 More IP Networking Fall 2011 IP datagram format IP protocol version number header length (bytes) type of data max number remaining hops (decremented at each router) upper layer protocol
Exit from Hell? Reducing the Impact of Amplification DDoS Attacks Marc Kührer, Thomas Hupperich, Christian Rossow, and Thorsten Holz
 Exit from Hell? Reducing the Impact of Amplification DDoS Attacks Marc Kührer, Thomas Hupperich, Christian Rossow, and Thorsten Holz Presented By : Richie Noble Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
Exit from Hell? Reducing the Impact of Amplification DDoS Attacks Marc Kührer, Thomas Hupperich, Christian Rossow, and Thorsten Holz Presented By : Richie Noble Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
Network Security and Cryptography. 2 September Marking Scheme
 Network Security and Cryptography 2 September 2015 Marking Scheme This marking scheme has been prepared as a guide only to markers. This is not a set of model answers, or the exclusive answers to the questions,
Network Security and Cryptography 2 September 2015 Marking Scheme This marking scheme has been prepared as a guide only to markers. This is not a set of model answers, or the exclusive answers to the questions,
CSCI 680: Computer & Network Security
 CSCI 680: Computer & Network Security Lecture 15 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Fall 2017 Derived from slides by William Enck and Micah Sherr 1 Grading Class Participat ion and Quizzes 10% Grade Breakdown Homewo
CSCI 680: Computer & Network Security Lecture 15 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Fall 2017 Derived from slides by William Enck and Micah Sherr 1 Grading Class Participat ion and Quizzes 10% Grade Breakdown Homewo
Internet Security: Firewall
 Internet Security: Firewall What is a Firewall firewall = wall to protect against fire propagation More like a moat around a medieval castle restricts entry to carefully controlled points restricts exits
Internet Security: Firewall What is a Firewall firewall = wall to protect against fire propagation More like a moat around a medieval castle restricts entry to carefully controlled points restricts exits
Storage Efficient Capturing of Port Scanning Attack Traffic
 Storage Efficient Capturing of Port Scanning Attack Traffic Rajni Ranjan Singh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India Orcid Id:
Storage Efficient Capturing of Port Scanning Attack Traffic Rajni Ranjan Singh Department of Computer Science and Engineering Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India Orcid Id:
Kent State University
 CS 4/54201 Computer Communication Network Kent State University Dept. of Computer Science www.mcs.kent.edu/~javed/class-net06f/ 1 A Course on Networking and Computer Communication LECT-10, S-2 IP- Internet
CS 4/54201 Computer Communication Network Kent State University Dept. of Computer Science www.mcs.kent.edu/~javed/class-net06f/ 1 A Course on Networking and Computer Communication LECT-10, S-2 IP- Internet
IDS: Signature Detection
 IDS: Signature Detection Idea: What is bad, is known What is not bad, is good Determines whether a sequence of instructions being executed is known to violate the site security policy Signatures: Descriptions
IDS: Signature Detection Idea: What is bad, is known What is not bad, is good Determines whether a sequence of instructions being executed is known to violate the site security policy Signatures: Descriptions
TCP TCP/IP: TCP. TCP segment. TCP segment. TCP encapsulation. TCP encapsulation 1/25/2012. Network Security Lecture 6
 TCP TCP/IP: TCP Network Security Lecture 6 Based on IP Provides connection-oriented, reliable stream delivery service (handles loss, duplication, transmission errors, reordering) Provides port abstraction
TCP TCP/IP: TCP Network Security Lecture 6 Based on IP Provides connection-oriented, reliable stream delivery service (handles loss, duplication, transmission errors, reordering) Provides port abstraction
The following topics describe how to configure correlation policies and rules.
 The following topics describe how to configure correlation policies and rules. Introduction to and Rules, page 1 Configuring, page 2 Configuring Correlation Rules, page 5 Configuring Correlation Response
The following topics describe how to configure correlation policies and rules. Introduction to and Rules, page 1 Configuring, page 2 Configuring Correlation Rules, page 5 Configuring Correlation Response
inside: THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE April 2002 Volume 27 Number 2 SECURITY A Remote Active OS Fingerprinting Tool Using ICMP BY OFIR ARKIN
 THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE April 2002 Volume 27 Number 2 inside: SECURITY A Remote Active OS Fingerprinting Tool Using ICMP BY OFIR ARKIN & The Advanced Computing Systems Association & The System Administrators
THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE April 2002 Volume 27 Number 2 inside: SECURITY A Remote Active OS Fingerprinting Tool Using ICMP BY OFIR ARKIN & The Advanced Computing Systems Association & The System Administrators
HP High-End Firewalls
 HP High-End Firewalls Attack Protection Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2630 Software version: F1000-E/Firewall module: R3166 F5000-A5: R3206 Document version: 6PW101-20120706 Legal and notice information
HP High-End Firewalls Attack Protection Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2630 Software version: F1000-E/Firewall module: R3166 F5000-A5: R3206 Document version: 6PW101-20120706 Legal and notice information
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 13 Connections and Fragmentation. TCP Connection Management
 CSE/EE 461 Lecture 13 Connections and Fragmentation Tom Anderson tom@cs.washington.edu Peterson, Chapter 5.2 TCP Connection Management Setup assymetric 3-way handshake Transfer sliding window; data and
CSE/EE 461 Lecture 13 Connections and Fragmentation Tom Anderson tom@cs.washington.edu Peterson, Chapter 5.2 TCP Connection Management Setup assymetric 3-way handshake Transfer sliding window; data and
EE 122: Network Security
 Motivation EE 122: Network Security Kevin Lai December 2, 2002 Internet currently used for important services - financial transactions, medical records Could be used in the future for critical services
Motivation EE 122: Network Security Kevin Lai December 2, 2002 Internet currently used for important services - financial transactions, medical records Could be used in the future for critical services
Chapter 7. Denial of Service Attacks
 Chapter 7 Denial of Service Attacks DoS attack: An action that prevents or impairs the authorized use of networks, systems, or applications by exhausting resources such as central processing units (CPU),
Chapter 7 Denial of Service Attacks DoS attack: An action that prevents or impairs the authorized use of networks, systems, or applications by exhausting resources such as central processing units (CPU),
ASA Access Control. Section 3
 [ 39 ] CCNP Security Firewall 642-617 Quick Reference Section 3 ASA Access Control Now that you have connectivity to the ASA and have configured basic networking settings on the ASA, you can start to look
[ 39 ] CCNP Security Firewall 642-617 Quick Reference Section 3 ASA Access Control Now that you have connectivity to the ASA and have configured basic networking settings on the ASA, you can start to look
Analysis of TCP Segment Header Based Attack Using Proposed Model
 Chapter 4 Analysis of TCP Segment Header Based Attack Using Proposed Model 4.0 Introduction Though TCP has been extensively used for the wired network but is being used for mobile Adhoc network in the
Chapter 4 Analysis of TCP Segment Header Based Attack Using Proposed Model 4.0 Introduction Though TCP has been extensively used for the wired network but is being used for mobile Adhoc network in the
IJSER. Virtualization Intrusion Detection System in Cloud Environment Ku.Rupali D. Wankhade. Department of Computer Science and Technology
 ISSN 2229-5518 321 Virtualization Intrusion Detection System in Cloud Environment Ku.Rupali D. Wankhade. Department of Computer Science and Technology Abstract - Nowadays all are working with cloud Environment(cloud
ISSN 2229-5518 321 Virtualization Intrusion Detection System in Cloud Environment Ku.Rupali D. Wankhade. Department of Computer Science and Technology Abstract - Nowadays all are working with cloud Environment(cloud
Overview Intrusion Detection Systems and Practices
 Overview Intrusion Detection Systems and Practices Chapter 13 Lecturer: Pei-yih Ting Intrusion Detection Concepts Dealing with Intruders Detecting Intruders Principles of Intrusions and IDS The IDS Taxonomy
Overview Intrusion Detection Systems and Practices Chapter 13 Lecturer: Pei-yih Ting Intrusion Detection Concepts Dealing with Intruders Detecting Intruders Principles of Intrusions and IDS The IDS Taxonomy
4.0.1 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION
 4.0.1 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION Data networks and the Internet support the human network by supplying seamless, reliable communication between people - both locally and around the globe. On a single device,
4.0.1 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION Data networks and the Internet support the human network by supplying seamless, reliable communication between people - both locally and around the globe. On a single device,
Usage of Honeypot to Secure datacenter in Infrastructure as a Service data
 Usage of Honeypot to Secure datacenter in Infrastructure as a Service data Ms. Priyanka Paliwal M. Tech. Student 2 nd yr.(comp. Science& Eng.) Government Engineering College Ajmer Ajmer, India (Erpriyanka_paliwal06@rediffmail.com)
Usage of Honeypot to Secure datacenter in Infrastructure as a Service data Ms. Priyanka Paliwal M. Tech. Student 2 nd yr.(comp. Science& Eng.) Government Engineering College Ajmer Ajmer, India (Erpriyanka_paliwal06@rediffmail.com)
CCNA 1 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the
CCNA 1 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the
User Datagram Protocol (UDP):
 SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security Feb 2-5 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 13-15 User Datagram Protocol (UDP): UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol: each output operation
SFWR 4C03: Computer Networks and Computer Security Feb 2-5 2004 Lecturer: Kartik Krishnan Lectures 13-15 User Datagram Protocol (UDP): UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol: each output operation
Information Systems Security
 Information Systems Security Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport Firewalls ISS Dr. Ayman Abdel Hamid 1 Outline
Information Systems Security Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport Firewalls ISS Dr. Ayman Abdel Hamid 1 Outline
GAQM Exam CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 878 ]
![GAQM Exam CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 878 ] GAQM Exam CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 878 ]](/thumbs/93/111879210.jpg) s@lm@n GAQM Exam CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 878 ] Topic 1, Volume A GAQM CEH-001 : Practice Test Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which of the following countermeasure
s@lm@n GAQM Exam CEH-001 Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 878 ] Topic 1, Volume A GAQM CEH-001 : Practice Test Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which of the following countermeasure
Firewalls, IDS and IPS. MIS5214 Midterm Study Support Materials
 Firewalls, IDS and IPS MIS5214 Midterm Study Support Materials Agenda Firewalls Intrusion Detection Systems Intrusion Prevention Systems Firewalls are used to Implement Network Security Policy Firewalls
Firewalls, IDS and IPS MIS5214 Midterm Study Support Materials Agenda Firewalls Intrusion Detection Systems Intrusion Prevention Systems Firewalls are used to Implement Network Security Policy Firewalls
Nsauditor White Paper. Abstract
 Nsauditor White Paper NSASOFT LLC. http://www.nsauditor.com E-mail: info@nsauditor.com Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples herein
Nsauditor White Paper NSASOFT LLC. http://www.nsauditor.com E-mail: info@nsauditor.com Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples herein
Detecting Denial of Service Intrusion Detection Aamir Islam Dept. of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan.
 Detecting Denial of Service Intrusion Detection Aamir Islam Dept. of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan. aamir.islam@pcit.ucp.edu.pk Abstract Denial of Service (DoS) attack
Detecting Denial of Service Intrusion Detection Aamir Islam Dept. of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan. aamir.islam@pcit.ucp.edu.pk Abstract Denial of Service (DoS) attack
Specialized Security Services, Inc. REDUCE RISK WITH CONFIDENCE. s3security.com
 Specialized Security Services, Inc. REDUCE RISK WITH CONFIDENCE s3security.com Security Professional Services S3 offers security services through its Security Professional Services (SPS) group, the security-consulting
Specialized Security Services, Inc. REDUCE RISK WITH CONFIDENCE s3security.com Security Professional Services S3 offers security services through its Security Professional Services (SPS) group, the security-consulting
Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures V7
 EC-Council EC1-350 Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures V7 Version: 4.4 Topic 1, Volume A QUESTION NO: 1 Which of the following countermeasure can specifically protect against both the MAC Flood and MAC
EC-Council EC1-350 Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures V7 Version: 4.4 Topic 1, Volume A QUESTION NO: 1 Which of the following countermeasure can specifically protect against both the MAC Flood and MAC
Introduction to Internet. Ass. Prof. J.Y. Tigli University of Nice Sophia Antipolis
 Introduction to Internet Ass. Prof. J.Y. Tigli University of Nice Sophia Antipolis What about inter-networks communications? Between LANs? Ethernet?? Ethernet Example Similarities and Differences between
Introduction to Internet Ass. Prof. J.Y. Tigli University of Nice Sophia Antipolis What about inter-networks communications? Between LANs? Ethernet?? Ethernet Example Similarities and Differences between
