Operation Manual Login and User Interface. Table of Contents
|
|
|
- Amos Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Switch Login Setting Up Configuration Environment Through the Console Port Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Telnet Connecting a PC to the Switch Through Telnet Accessing a Switch Through Another Switch via Telnet Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Modem Dial-up User Interface Overview User Interface Configuration Entering User Interface View Defining the Login Header Configuring Asynchronous Port Attributes Configuring Terminal Attributes Managing Users Configuring Telnet Configuring Modem Attributes Configuring Redirection Displaying and Debugging User Interface Chapter 3 Management Port Configuration Management Port Overview Management Port Configuration IP Isolation Overview i
2 Chapter 1 Switch Login Chapter 1 Switch Login When configuring switch login, go to these sections for information you are interested in: Setting Up Configuration Environment Through the Console Port Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Telnet Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Modem Dial-up 1.1 Setting Up Configuration Environment Through the Console Port Step 1: As shown in the figure below, to set up the local configuration environment, connect the serial port of a PC (or a terminal) to the console port of the switch with the console cable. Figure 1-1 Set up the local configuration environment through the console port Step 2: Run a terminal emulator (such as Terminal of Windows 2000 or HyperTerminal of Windows XP) on the computer. Set the terminal communication parameters as follows: Set Bits per second to 9600, Data bits to 8, Parity to none, Stop bits to 1, and Flow control to none, and select the VT100 as the terminal type.. Figure 1-2 Set up new connection 1-1
3 Chapter 1 Switch Login Figure 1-3 Configure the port for connection Figure 1-4 Set communication parameters Step 3: The switch is powered on. Display self-test information of the switch and prompt you to press Enter to show the command line prompt such as <H3C>. Step 4: Input a command to configure the switch or view the operation state. Input a? for help. For details of specific commands, refer to the following chapters. 1.2 Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Telnet Connecting a PC to the Switch Through Telnet To telnet to the Ethernet Switch, ensure that the following conditions are satisfied: Assign an IP address to the management VLAN interface correctly in the Ethernet Switch (use the ip address command in VLAN interface view). 1-2
4 Chapter 1 Switch Login Specify the Ethernet port connected with the PC to belong to the management VLAN (use the port command in VLAN view) If the PC and the switch s port connected with the PC reside in the same LAN, their IP addresses must be configured to reside in the same network segment. Otherwise, the PC and the Switch must be reachable to each other. Then, you can telnet to the Ethernet Switch to configure it. Follow the given steps below: Step 1: Before logging into the switch through telnet, you need to configure the Telnet user name and password on the switch through the console port. Note: By default, the password is required for authenticating the Telnet user to log into the switch. If a user tries to log in through Telnet without a password, the system will prompt that the login fails because no password is set. <H3C> system-view System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z. [H3C] user-interface vty 0 [H3C-ui-vty0] set authentication password simple xxxx (xxxx is the login password of Telnet user) Step 2: To set up the configuration environment, connect the Ethernet port of the PC to that of the switch via the LAN, as shown in Figure 1-5. Workstation Switch Ethernet M- Ethernet Server Workstation PC (for the switch via configuring telnet ) Figure 1-5 Set up configuration environment through telnet Step 3: Run Telnet on the PC and input the IP address of the VLAN connected to the PC port, as shown in Figure
5 Chapter 1 Switch Login Figure 1-6 Run Telnet Step 4: The terminal displays Login authentication! and prompts the user to input the logon password. After you input the correct password, it displays the command line prompt (such as <H3C>). If the prompt All user interfaces are used, please try later! The connection was closed by the remote host! appears, it indicates that the maximum number of Telnet users that can be accessed to the switch is reached at this moment. In this case, please reconnect later. At most 5 Telnet users are allowed to log on to the H3C series switches simultaneously. Step 5: Use the corresponding commands to configure the switch or to monitor the running state. Enter? to get the immediate help. For details of specific commands, refer to the following chapters. Note: When configuring the switch via Telnet, do not modify the IP address of it unless necessary, for the modification might cut the Telnet connection. By default, when a Telnet user passes the password authentication to log on to the switch, he can access the commands at Level Accessing a Switch Through Another Switch via Telnet After a user has logged into a switch, he or she can configure another switch through the switch via Telnet. The local switch serves as Telnet client and the peer switch serves as Telnet server. If the ports connecting the two switches are on the same local network, the IP addresses of the two switches must be in the same network segment. Otherwise, a route must be available between the two switches. As shown in the figure below, after you telnet to a switch, you can run telnet command to log in and configure another switch. 1-4
6 Chapter 1 Switch Login PC Telnet Client Telnet Server Figure 1-7 Provide Telnet Client service Step 1: Configure the Telnet user name and password on the Telnet Server through the console port. Note: By default, the password is required for authenticating the Telnet user to log into the switch. If a user logs in via the Telnet without password, he will see the prompt Login password has not been set!. <H3C> system-view System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z. [H3C] user-interface vty 0 [H3C-ui-vty0] set authentication password simple xxxx Step 2: The user logs in the Telnet Client (switch). For the login process, refer to the section describing Connecting a PC to the Switch through Telnet. Step 3: Perform the following operations on the Telnet Client: <H3C> telnet xxxx xxxx is the hostname or IP address of the Telnet Server. If hostname is used, it must be the one configured with the ip host command or the DNS domain name of the Telnet Server. Step 4: Enter the preset login password and you will see the prompt such <H3C>. If the prompt All user interfaces are used, please try later! The connection was closed by the remote host! appears, it indicates that the maximum number of Telnet users that can be accessed to the switch is reached at this moment. In this case, please connect later. Step 5: Use the corresponding commands to configure the switch or view it running state. Enter? to get the immediate help. For details of specific commands, refer to the following chapters. 1-5
7 Chapter 1 Switch Login 1.3 Setting Up Configuration Environment Through Modem Dial-up Step 1: Perform authentication configuration for the modem user via the console port of the switch before the user logs into the switch through a dial-up modem. Note: By default, the modem user is authenticated against password when logging into the switch. If no password is set, the prompt Login password has not been set!. will be displayed when the modem user logs in. <H3C> system-view System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.. [H3C] user-interface aux 0 [H3C-ui-aux0] set authentication password simple xxxx Step 2: As shown in the figure below, to set up the remote configuration environment, connect the Modems to a PC (or a terminal) serial port and the switch AUX port respectively. Figure 1-8 Set up remote configuration environment Step 3: Dial for connection to the switch, using the terminal emulator and Modem on the remote end. The number dialed shall be the telephone number of the Modem connected to the switch. See the two figures below. 1-6
8 Chapter 1 Switch Login Figure 1-9 Set the dialed number Figure 1-10 Dial on the remote PC Step 4: Enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt such as <H3C>. Then you can configure and manage the switch. Enter? to get the immediate help. For details of specific commands, refer to the following chapters. Note: By default, when a Modem user logs in, he can access the commands at Level
9 When configuring user interface, go to these sections for information you are interested in: User Interface Overview User Interface Configuration Displaying and Debugging User Interface 2.1 User Interface Overview To facilitate system management, the switches support user interface based configuration for the configuration and management of port attributes. Presently, the S9500 series switches support the following user interface based configuration methods: Local configuration via the console port and AUX port Local and remote configuration through Telnet on Ethernet port Remote configuration through dialing with modem via the AUX port. According to the above-mentioned configuration methods, there are three types of user interfaces: Console user interface Console user interface is used to log into the switch via the console port. A switch can only have one console user interface. AUX user interface AUX user interface is used to log into the switch locally or remotely with a modem via the AUX port. A switch can only have one AUX user interface. The local configuration for it is similar to that for the console user interface. VTY user interface VTY user interface is used to telnet the switch. A switch can have up to five VTY user interface. User interface is numbered in the following two ways: absolute number and relative number. I. Absolute number The user interfaces of the S9500 routing switch include three types, which are sequenced as follows: console interface (CON), auxiliary interface (AUX) and virtual interface (VTY). A switch has one CON, one AUX and multiple VTYs. The first absolute number is designated as 0; the second one is designated as 1; and so on. This method can specify a unique user interface or a group of interfaces. 2-1
10 It follows the rules below. Console user interface is numbered as the first interface designated as user interface 0. AUX user interface is numbered as the second interface designated as user interface 1. VTY is numbered after AUX user interface. The absolute number of the first VTY is incremented by 1 than the AUX user interface number. II. Relative number The relative number is in the format of user interface type + number. The number refers to the internal number for each user interface type. With this numbering method, when performing a configuration operation for user interfaces, you can only specify a same type of user interfaces instead of specifying different types of user interfaces. It follows the rules below: Number of console user interface: console 0. Number of AUX user interface: AUX 0. Number of VTY: The first VTY interface is designated as VTY 0; the second one is designated as VTY 1, and so on. 2.2 User Interface Configuration The following sections describe the user interface configuration tasks. Entering User Interface View Defining the Login Header Configuring Asynchronous Port Attributes Configuring Terminal Attributes Managing Users Configuring Telnet Configuring Modem Attributes Configuring Redirection Entering User Interface View The following command is used for entering a user interface view. You can enter a single user interface view or multi user interface view to configure one or more user interfaces respectively. Perform the following configuration in system view. 2-2
11 Follow these steps to enter user interface view: Enter a single user interface view or multi user interface views user-interface [ type ] first-number [ last-number ] Defining the Login Header The following command is used for configuring the displayed header when user login. When the users log into the switch, if a connection is activated, the login header will be displayed. After the user successfully logs in the switch, the shell header will be displayed. Perform the following configuration in system view. Follow these steps to configure the login header: Configure the login header Remove the login header configured header [ shell incoming login ] text undo header [ shell incoming login ] Note that if you press <Enter> after typing any of the three keywords shell, login and incoming in the command, then what you type after the word header is the contents of the login information, instead of identifying header type Configuring Asynchronous Port Attributes The following commands can be used for configuring the attributes of the asynchronous port in asynchronous interactive mode, including speed, flow control, parity, stop bit and data bit. Perform the following configurations in user interface (Console and AUX user interface only) view. I. Configuring the transmission speed Follow these steps to configure the transmission speed: Configure the transmission speed Restore the default transmission speed speed speed-value undo speed By default, the transmission speed on an asynchronous port is 9600 bps. 2-3
12 II. Configuring flow control Follow these steps to configure flow control: Configure the flow control Restore the default flow control mode flow-control { hardware none software } undo flow-control By default, the flow control on an asynchronous port is none, that is, no flow control will be performed. III. Configuring parity Follow these steps to configure parity: Configure parity mode Restore the default parity mode parity { even mark none odd space } undo parity By default, the parity on an asynchronous port is none, that is, no parity bit. IV. Configuring the stop bit Follow these steps to configure the stop bit: Configure the stop bit stopbits { } Restore the default stop bit undo stopbits By default, an asynchronous port supports 1 stop bit. Note that setting 1.5 stop bits is not available on S9500 series at present. V. Configuring the data bit Follow these steps to configure the data bit: Configure the data bit databits { 7 8 } Restore the default data bit undo databits By default, an asynchronous port supports 8 data bits. 2-4
13 2.2.4 Configuring Terminal Attributes The following commands can be used for configuring the terminal attributes, including enabling/disabling terminal service, disconnection upon timeout, lockable user interface, configuring terminal screen length and history command buffer size. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Perform lock command in user view. I. Enabling/disabling terminal service After the terminal service is disabled on a user interface, you cannot log into the switch through the user interface. However, the user logged in through the user interface before disabling the terminal service can continue his operation. After such user logs out, he cannot log in again. In this case, a user can log into the switch through the user interface only when the terminal service is enabled again. Follow these steps to enable/disable terminal service: Enable terminal service Disable terminal service shell undo shell By default, terminal service is enabled on all the user interfaces. Note the following points: For the sake of security, the undo shell command can only be used on the user interfaces other than console user interface. You cannot use this command on the user interface via which you log in. You will be asked to confirm before using undo shell on any legal user interface. II. Configuring idle-timeout Follow these steps to configure idle-timeout: Configure idle-timeout idle-timeout minutes [ seconds ] Restore the default idle-timeout undo idle-timeout By default, idle-timeout is enabled and set to 10 minutes on all the user interfaces. That is, the user interface will be disconnected automatically after 10 minutes without any operation. idle-timeout 0 means disabling idle-timeout. 2-5
14 III. Locking user interface This configuration is to lock the current user interface and prompt the user to enter the password. This makes it impossible for others to operate in the interface after the user leaves. Follow these steps to lock user interface: Lock user interface lock IV. Setting the screen length If a command displays more than one screen of information, you can use the following command to set how many lines to be displayed in a screen, so that the information can be separated in different screens and you can view it more conveniently. Follow these steps to set the screen length: Configure the maximum number of lines of information on one screen of the terminal Restore the default screen-length screen-length undo screen-length Note that the number of lines that can be displayed in each screen remains the same when screen-length is set to 1 or 2. By default, 24 lines (including the multi-screen identifier lines) are displayed in one screen when the multi-screen display function is enabled. Use screen-length 0 to disable the multi-screen display function. V. Setting the history command buffer size Follow these steps to set the history command buffer size: Set the history command buffer size Restore the default history command buffer size history-command max-size value undo history-command max-size By default, the size of the history command buffer is 10, that is, 10 history commands can be saved. 2-6
15 2.2.5 Managing Users The management of users includes the setting of user logon authentication method, level of command which a user can use after logging on, level of command which a user can use after logging on from the specifically user interface, and command level. I. Configuring the authentication method The following command is used for configuring the user login authentication method to deny the access of an unauthorized user. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Follow these steps to configure the authentication method: Configure the authentication method authentication-mode { password scheme [ command-authorization ] none } By default, terminal authentication is not required for local users log in via the console port. However, password authentication is required for local users and remote Modem users to log in via the AUX port, and for Telnet users and the VTY users to log in through Ethernet port. Note: If the console port is configured for local password authentication, the user can directly log into the system even without a password configured; if other user interfaces, such as the AUX port and VTY interface, are configured for local password authentication, users cannot log into the system without a password. 1) Perform local password authentication to the user interface Using authentication-mode password command, you can perform local password authentication. That is, you need use the command below to configure a login password in order to login successfully. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Follow these steps to configure the local authentication password: Configure the local authentication password Remove the local authentication password set authentication password { cipher simple } password undo set authentication password # Configure for password authentication when a user logs in through a VTY 0 user interface and set the password to test <H3C>system-view 2-7
16 System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z. [H3C] user-interface vty 0 [H3C-ui-vty0] authentication-mode password [H3C-ui-vty0] set authentication password simple test 2) Perform authentication using the AAA scheme specified for an ISP domain. Using authentication-mode scheme [ command-authorization ] command, you can perform authentication using the AAA scheme specified for an ISP domain.. An ISP domain is selected based on the following rules: If the username input at login does not contain character, the default ISP domain is selected; If the username input at login contains character: For the local scheme, the character string before the is used as the username, and the character string after the is used as the ISP domain name; for the RADIUS and HWTACACS schemes, the character string before the is used as the username, and the character string after the is used as the ISP domain name. If the command-authorization keyword is provided, it indicates that authorization is needed for the command that the user executes. The authorization mode depends on the AAA scheme configured for an ISP domain. If multiple AAA schemes are configured for an ISP domain, the scheme used at user login is adopted. Among all the AAA schemes: HWTACACS: Command lines are authorized based on the rules configured on the HWTACACS server; Local: Command lines are authorized by the command levels configured by local users; None: All command lines are trusted and authorized; RADIUS: No command lines are authorized. In the following example, local username and password authentication are configured. # Perform username and password authentication when a user logs in through VTY 0 user interface and set the username and password to zbr and test respectively. [H3C-ui-vty0] authentication-mode scheme [H3C-ui-vty0] quit [H3C] local-user zbr [H3C-luser-zbr] password simple test [H3C-luser-zbr] service-type telnet 3) No authentication [H3C-ui-vty0] authentication-mode none 2-8
17 Note: By default, password is required to be set for authenticating local users and remote Modem users log in via the AUX port, and Telnet users log in through Ethernet port. If no password has been set, the following prompt will be displayed Login password has not been set!. If the authentication-mode none command is used, the local and Modem users via the AUX port and Telnet users will not be required to input password. II. Setting the command level used after a user logging in The following command is used for setting the command level used after a user logging in. Perform the following configuration in local-user view. Follow these steps to set the command level used after a user logging in: Set command level used after a user logging in Restore the default command level used after a user logging in service-type telnet [ level level ] undo service-type telnet By default, the specified logon user can access the commands at Level 2. III. Setting the command level used after a user logs in from a user interface You can use the following command to set the command level after a user logs in from a specific user interface, so that a user is able to execute the commands at such command level. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Follow these steps to set the command level used after a user logging in from a user interface: Set command level used after a user logging in from a user interface Restore the default command level used after a user logging in from a user interface user privilege level level undo user privilege level 2-9
18 By default, you can access the commands at Level 3 after logging in through the console user interface, and the commands at Level 0 after logging in through the AUX or VTY user interface. Note: When a user logs in the switch, the command level that it can access depends on two points. One is the command level that the user itself can access, the other is the set command level of this user interface. If the two levels are different, the former will be taken. For example, the command level of VTY 0 user interface is 1, however, you have the right to access commands of level 3; if you log in from VTY 0 user interface, you can access commands of level 3 and lower. IV. Setting the command priority The following command is used for setting the priority of a specified command in a certain view. The command levels include visit, monitoring, configuration, and management, which are identified with 0 through 3 respectively. An administrator assigns authorities as per user requirements. Perform the following configuration in system view. Follow these steps to set the command priority: Set the command priority in a specified view. Restore the default command level in a specified view. command-privilege level level view view command undo command-privilege view view command V. Setting input protocol for a user terminal You can use the following command to set input protocol for a user terminal. The input protocol type can be TELNET, SSH or all. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Follow these steps to set input protocol for a user terminal: Set input protocol for a user terminal protocol inbound { all telnet ssh } By default, the input protocol type for a user terminal is all. 2-10
19 VI. Enabling command line accounting After command line accounting is enabled, every time you execute a command, the system sends an accounting packet containing the command information to the TACACS server. At present, only the TACACS protocol supports the command line accounting function. After this function is enabled, the system sends accounting packets to the TACACS server when the following two conditions are satisfied: Command line authorization is not enabled, or command line authorization is enabled and the command line is successfully authorized; You have passed the TACACS authorization. Follow these steps to enable command line accounting: Remarks Enter user interface view Enable command line accounting user-interface [ type ] first-number [ last-number ] accounting commands scheme Disabled by default Note: After you have configured the TACACS command line accounting function, if the accounting packets cannot reach the TACACS server due to some reason, you can still execute the commands, but the commands are not accounted. For this kind of situation, the system does not give any prompt, nor record anything. For command line authorization, see the authentication-mode { password scheme [ command-authorization ] none } command Configuring Telnet You can configure Telnet so as to log into other switches from the current switch for remote management. Perform the following configuration in user view. Follow these steps to configure Telnet : Configure Telnet telnet [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] { hostname ip-address } [ service-port ] [ source { ip ip-address interface interface-type interface-number } ] 2-11
20 You can press <Ctrl+k> to terminate a Telnet operation. The default Telnet port number is 23. If you specify the source address or source interface, then the specified IP address of the main IP address of the specified interface is taken as the source address Configuring Modem Attributes When logging in the switch via the Modem, you can use the following commands to configure these parameters. Perform the following configuration in AUX user interface view. Follow these steps to configure Modem attributes: Set the interval since the system receives the RING until CD_UP Restore the default interval since the system receives the RING until CD_UP Configure auto answer Configure manual answer Configure to allow call-in Configure to bar call-in Configure to permit call-in and call-out. Configure to disable call-in and call-out modem timer answer seconds undo modem timer answer modem auto-answer undo modem auto-answer modem call-in undo modem call-in modem both undo modem both Configuring Redirection I. Send command The following command can be used for sending messages between user interfaces. Perform the following configuration in user view. Follow these steps to configure to send messages between different user interfaces: Configure to send messages between different user interfaces. send { all number type number } 2-12
21 II. Auto-execute command The following command is used to automatically run a command after you log in. After a command is configured to be run automatically, it will be automatically executed when you log in again. This command is usually used to automatically execute telnet command on the terminal, which will connect the user to a designated device automatically. Perform the following configuration in user interface view. Follow these steps to configure to automatically run the command: Configure to automatically run the command Configure not to automatically run the command auto-execute command text undo auto-execute command Note the following points: After executing this command, the user interface can no longer be used to carry out the routine configurations for the local system. Use this command with caution. Make sure that you will be able to log into the system in some other way and cancel the configuration, before you use the auto-execute command command and save the configuration. # Telnet after the user logs in through VTY0 automatically. [H3C-ui-vty0] auto-execute command telnet Displaying and Debugging User Interface Remarks Release a specified user interface connection Display the user application information of the user interface Display the physical attributes and some configurations of the user interface Query history commands selectively free user-interface [ type ] number display users [ all ] display user-interface [ type number number ] [ summary ] display history-command [ Command-Number ] [ { begin include exclude } Match-string ] Available in user view Available in any view Available in any view Available in any view 2-13
22 Remarks Enable debugging for the Modem debugging modem Available in user view 2-14
23 Chapter 3 Management Port Configuration Chapter 3 Management Port Configuration When configuring management port, go to these sections for information you are interested in: Management Port Overview Management Port Configuration IP Isolation Overview 3.1 Management Port Overview S9500 series provide a 10/100Base-TX management port on their SRPU board. The port can be used for the following purposes: Connecting to a background PC for software loading and system debugging Connecting to a remote network management station for remote system management 3.2 Management Port Configuration The following sections describe management port configuration tasks. Configuring an IP address for the port Enabling/disabling the port Setting port description Displaying current system information Testing network connectivity (ping, tracert) Enabling IP isolation Refer to the Ethernet Port part and System Maintenance part of this manual for details. Caution: Only the management port configured with an IP address can be used to manage a switch. 3.3 IP Isolation Overview The main function of IP isolation is to isolate packets between the network management port and the service ports to enhance the security of the network management port. When this feature is enabled, there is no route between network 3-1
24 Chapter 3 Management Port Configuration management port and service ports and packets are not forwarded between them. You can use the network management port dedicatedly to manage the switch, and enabling IP isolation on the management port will not affect data communication service of the switch. If this feature is enabled, the network management port and the service ports cannot communicate with each other and the switch will drop the packets to be forwarded between the network management port and the service ports. Otherwise, the switch can forward packets between the network management port and the service ports. Use the following commands to enable IP isolation between the network management port and the service ports. Follow these steps to configure IP isolation: Remarks Enter system view system-view Enter network management port view Enable IP isolation between the network management port and the service ports. interface M-Ethernet m-ethernet ip isolation Optional This feature is disabled by default. 3-2
Table of Contents 1 Commands for Access Controller Switch Interface Board 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Commands for Access Controller Switch Interface Board 1-1 Commands for Access Controller and Access Controller Switch Interface Board 1-1 acl (user interface view) 1-1 activation-key
Table of Contents 1 Commands for Access Controller Switch Interface Board 1-1 Commands for Access Controller and Access Controller Switch Interface Board 1-1 acl (user interface view) 1-1 activation-key
Login management commands
 Contents Login management commands 1 CLI login configuration commands 1 display telnet client configuration 1 telnet 1 telnet ipv6 2 telnet server enable 3 User interface configuration commands 3 acl (user
Contents Login management commands 1 CLI login configuration commands 1 display telnet client configuration 1 telnet 1 telnet ipv6 2 telnet server enable 3 User interface configuration commands 3 acl (user
Logging in to the CLI
 Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console port 2 Introduction 2 Configuration procedure 2 Logging in through the AUX port 5 Configuration prerequisites 5 Configuration
Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console port 2 Introduction 2 Configuration procedure 2 Logging in through the AUX port 5 Configuration prerequisites 5 Configuration
Logging in through SNMP from an NMS 22 Overview 22 Configuring SNMP agent 22 NMS login example 24
 Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console or AUX port 2 Introduction 2 Configuration procedure 2 Logging in through Telnet 6 Introduction 6 Logging in to the switch
Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console or AUX port 2 Introduction 2 Configuration procedure 2 Logging in through Telnet 6 Introduction 6 Logging in to the switch
User authentication configuration example 11 Command authorization configuration example 13 Command accounting configuration example 14
 Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console or AUX port 2 Logging in through Telnet 5 Telnetting to the switch 5 Telnetting from the switch to another device 7 Logging
Contents Logging in to the CLI 1 Login methods 1 Logging in through the console or AUX port 2 Logging in through Telnet 5 Telnetting to the switch 5 Telnetting from the switch to another device 7 Logging
Operation Manual Security. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1x Configuration... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 802.1x Standard Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 802.1x System Architecture... 1-1 1.1.3 802.1x Authentication
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1x Configuration... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 802.1x Standard Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 802.1x System Architecture... 1-1 1.1.3 802.1x Authentication
HP Load Balancing Module
 HP Load Balancing Module System Management Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4216 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP Load Balancing Module System Management Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4216 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
Privilege Level Switching Authentication Technology White Paper
 Privilege Level Switching Authentication Technology White Paper Keywords: Privilege level switching authentication, RADIUS, HWTACACS Abstract: This document briefly describes the background and implementation
Privilege Level Switching Authentication Technology White Paper Keywords: Privilege level switching authentication, RADIUS, HWTACACS Abstract: This document briefly describes the background and implementation
Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview AAA Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview 1-1 Introduction to AAA 1-1 Authentication 1-1 Authorization 1-1 Accounting 1-2 Introduction to ISP Domain 1-2 Introduction to AAA Services 1-3 Introduction to RADIUS 1-3
Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview 1-1 Introduction to AAA 1-1 Authentication 1-1 Authorization 1-1 Accounting 1-2 Introduction to ISP Domain 1-2 Introduction to AAA Services 1-3 Introduction to RADIUS 1-3
H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points. Fundamentals Command Reference
 H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Fundamentals Command Reference Abstract This document details the commands for the WA series WLAN access points. Intended audience includes network planners, field technical
H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Fundamentals Command Reference Abstract This document details the commands for the WA series WLAN access points. Intended audience includes network planners, field technical
HP A3100 v2 Switch Series
 HP A3100 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference HP A3100-8 v2 SI Switch (JG221A) HP A3100-16 v2 SI Switch (JG222A) HP A3100-24 v2 SI Switch (JG223A) HP A3100-8 v2 EI Switch (JD318B) HP A3100-16
HP A3100 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference HP A3100-8 v2 SI Switch (JG221A) HP A3100-16 v2 SI Switch (JG222A) HP A3100-24 v2 SI Switch (JG223A) HP A3100-8 v2 EI Switch (JD318B) HP A3100-16
Operation Manual AAA RADIUS HWTACACS H3C S5500-EI Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 AAA/RADIUS/HWTACACS Over... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to AAA... 1-1 1.1.2 Introduction to RADIUS... 1-3 1.1.3 Introduction to HWTACACS... 1-9 1.1.4 Protocols
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 AAA/RADIUS/HWTACACS Over... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to AAA... 1-1 1.1.2 Introduction to RADIUS... 1-3 1.1.3 Introduction to HWTACACS... 1-9 1.1.4 Protocols
Part number: Published: March Com Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide
 http://www.3com.com/ Part number: 10015003 Published: March 2006 3Com Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064 Copyright 2006, 3Com Corporation.
http://www.3com.com/ Part number: 10015003 Published: March 2006 3Com Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064 Copyright 2006, 3Com Corporation.
Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview AAA Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview 1-1 Introduction to AAA 1-1 Authentication 1-1 Authorization 1-1 Accounting 1-2 Introduction to ISP Domain 1-2 Introduction to AAA Services 1-2 Introduction to RADIUS 1-2
Table of Contents 1 AAA Overview 1-1 Introduction to AAA 1-1 Authentication 1-1 Authorization 1-1 Accounting 1-2 Introduction to ISP Domain 1-2 Introduction to AAA Services 1-2 Introduction to RADIUS 1-2
HP 3600 v2 Switch Series
 HP 3600 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-7608 Software version: Release 2110P02 Document version: 6W100-20150305 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
HP 3600 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-7608 Software version: Release 2110P02 Document version: 6W100-20150305 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
H3C S9500 Series Routing Switches
 Operation Manual Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Manual Version: T2-08165E-20081225-C-1.24 Product Version: S9500-CMW310-R1648 Copyright 2007-2008, Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co.,
Operation Manual Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Manual Version: T2-08165E-20081225-C-1.24 Product Version: S9500-CMW310-R1648 Copyright 2007-2008, Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co.,
HP 3600 v2 Switch Series
 HP 3600 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-2359 Software version: Release 2101 Document version: 6W101-20130930 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP 3600 v2 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-2359 Software version: Release 2101 Document version: 6W101-20130930 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
FSOS Getting Started Operation
 FSOS Getting Started Operation Contents Contents...2 Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch...3 1.1 Set up Configuration Environment via Console Port...3 1.2 Set up Configuration Environment through Telnet...
FSOS Getting Started Operation Contents Contents...2 Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch...3 1.1 Set up Configuration Environment via Console Port...3 1.2 Set up Configuration Environment through Telnet...
Part number: DUA1756-1CAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Command Reference Guide Version 3.1.
 http://www.3com.com/ Part number: DUA1756-1CAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Command Reference Guide Version 3.1.x 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064
http://www.3com.com/ Part number: DUA1756-1CAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Command Reference Guide Version 3.1.x 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064
HPE FlexFabric 5700 Switch Series
 HPE FlexFabric 5700 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-5600R Software version: Release 2422P01 and later Document version: 6W100-20160331 Copyright 2016 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
HPE FlexFabric 5700 Switch Series Fundamentals Command Reference Part number: 5998-5600R Software version: Release 2422P01 and later Document version: 6W100-20160331 Copyright 2016 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Configuring the Management Interface and Security
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Management Interface and Security Revised: February 15, 2011, Introduction This module describes how to configure the physical management interfaces (ports) as well as the various
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Management Interface and Security Revised: February 15, 2011, Introduction This module describes how to configure the physical management interfaces (ports) as well as the various
Operation Manual Security. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Network Security Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to the Network Security Features Provided by CMW... 1-1 1.2 Hierarchical Line Protection... 1-2 1.3 RADIUS-Based
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Network Security Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to the Network Security Features Provided by CMW... 1-1 1.2 Hierarchical Line Protection... 1-2 1.3 RADIUS-Based
Part number: DUA1756-1BAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide
 http://www.3com.com/ Part number: DUA1756-1BAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064 Copyright
http://www.3com.com/ Part number: DUA1756-1BAA01 Published: September 2005 SuperStack 3 Switch 4500 Family Configuration Guide 3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA 01752-3064 Copyright
Examples of Cisco APE Scenarios
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes three example scenarios with which to use Cisco APE: Access to Asynchronous Lines, page 5-1 Cisco IOS Shell, page 5-3 Command Authorization, page 5-5 Note For intructions
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes three example scenarios with which to use Cisco APE: Access to Asynchronous Lines, page 5-1 Cisco IOS Shell, page 5-3 Command Authorization, page 5-5 Note For intructions
HP High-End Firewalls
 HP High-End Firewalls Getting Started Guide Part number: 5998-2646 Software version: F1000-A-EI&F1000-S-EI: R3721 F5000: F3210 F1000-E: F3171 Firewall module: F3171 Document version: 6PW101-20120719 Legal
HP High-End Firewalls Getting Started Guide Part number: 5998-2646 Software version: F1000-A-EI&F1000-S-EI: R3721 F5000: F3210 F1000-E: F3171 Firewall module: F3171 Document version: 6PW101-20120719 Legal
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server
 Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
Table of Contents 1 FTP and SFTP Configuration TFTP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 FTP and SFTP Configuration 1-1 Introduction to FTP and SFTP 1-1 Introduction to FTP 1-1 Introduction to SFTP 1-1 FTP Configuration 1-2 FTP Configuration: A Switch Operating as an FTP
Table of Contents 1 FTP and SFTP Configuration 1-1 Introduction to FTP and SFTP 1-1 Introduction to FTP 1-1 Introduction to SFTP 1-1 FTP Configuration 1-2 FTP Configuration: A Switch Operating as an FTP
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide. Figure 9-1 Port Security Global Settings window
 9. Security DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide Port Security 802.1X AAA RADIUS TACACS IMPB DHCP Server Screening ARP Spoofing Prevention MAC Authentication Web-based
9. Security DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide Port Security 802.1X AAA RADIUS TACACS IMPB DHCP Server Screening ARP Spoofing Prevention MAC Authentication Web-based
Table of Contents 1 SSH Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 SSH Configuration 1-1 SSH Overview 1-1 Introduction to SSH 1-1 Algorithm and Key 1-1 Asymmetric Key Algorithm 1-2 SSH Operating Process 1-2 Configuring the SSH Server 1-4 SSH Server
Table of Contents 1 SSH Configuration 1-1 SSH Overview 1-1 Introduction to SSH 1-1 Algorithm and Key 1-1 Asymmetric Key Algorithm 1-2 SSH Operating Process 1-2 Configuring the SSH Server 1-4 SSH Server
H3C S5830V2 & S5820V2 Switch Series
 H3C S5830V2 & S5820V2 Switch Series Security Command Reference Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: Release2108 Document version: 6W101-20120531 Copyright 2012, Hangzhou
H3C S5830V2 & S5820V2 Switch Series Security Command Reference Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: Release2108 Document version: 6W101-20120531 Copyright 2012, Hangzhou
Operation Manual System Management. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 File System Management... 1-1 1.1 File System Configuration... 1-1 1.1.1 File System Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Directory... 1-1 1.1.3 File... 1-2 1.1.4 Storage
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 File System Management... 1-1 1.1 File System Configuration... 1-1 1.1.1 File System Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Directory... 1-1 1.1.3 File... 1-2 1.1.4 Storage
Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands PPPoE Configuration Commands 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1-1 link-protocol ppp 1-2 mtu 1-2 ppp account-statistics enable 1-3 ppp authentication-mode 1-3
Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1-1 link-protocol ppp 1-2 mtu 1-2 ppp account-statistics enable 1-3 ppp authentication-mode 1-3
Using Cisco IOS XE Software
 This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
Operation Manual 802.1x. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Architecture of 802.1x... 1-1 1.1.2 Operation of 802.1x... 1-3 1.1.3 EAP Encapsulation over LANs... 1-4 1.1.4 EAP Encapsulation
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Architecture of 802.1x... 1-1 1.1.2 Operation of 802.1x... 1-3 1.1.3 EAP Encapsulation over LANs... 1-4 1.1.4 EAP Encapsulation
PPP configuration commands
 Contents PPP configuration commands 1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1 ip pool 1 link-protocol ppp 2 ppp authentication-mode 2 ppp chap password 4 ppp chap user 5 ppp ipcp remote-address forced 5 ppp pap local-user
Contents PPP configuration commands 1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1 ip pool 1 link-protocol ppp 2 ppp authentication-mode 2 ppp chap password 4 ppp chap user 5 ppp ipcp remote-address forced 5 ppp pap local-user
Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
HWTACACS Technology White Paper
 S Series Switches HWTACACS Technology White Paper Issue 1.0 Date 2015-08-08 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2015. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
S Series Switches HWTACACS Technology White Paper Issue 1.0 Date 2015-08-08 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2015. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
Table of Contents 1 CLI Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 CLI Configuration 1-1 Introduction to the CLI 1-1 Command Hierarchy 1-1 Switching User Levels 1-2 Setting the Level of a Command in a Specific View 1-3 CLI Views 1-4 CLI Features 1-6
Table of Contents 1 CLI Configuration 1-1 Introduction to the CLI 1-1 Command Hierarchy 1-1 Switching User Levels 1-2 Setting the Level of a Command in a Specific View 1-3 CLI Views 1-4 CLI Features 1-6
L2TP Configuration. L2TP Overview. Introduction. Typical L2TP Networking Application
 Table of Contents L2TP Configuration 1 L2TP Overview 1 Introduction 1 Typical L2TP Networking Application 1 Basic Concepts of L2TP 2 L2TP Tunneling Modes and Tunnel Establishment Process 4 L2TP Features
Table of Contents L2TP Configuration 1 L2TP Overview 1 Introduction 1 Typical L2TP Networking Application 1 Basic Concepts of L2TP 2 L2TP Tunneling Modes and Tunnel Establishment Process 4 L2TP Features
Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server The authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) feature verifies the identity of, grants access to, and tracks the actions of users
CHAPTER 3 Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server The authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) feature verifies the identity of, grants access to, and tracks the actions of users
ZyWALL 10W. Internet Security Gateway. Quick Start Guide Version 3.62 December 2003
 Internet Security Gateway Quick Start Guide Version 3.62 December 2003 Introducing the ZyWALL The is the ideal secure gateway for all data passing between the Internet and the LAN. By integrating NAT,
Internet Security Gateway Quick Start Guide Version 3.62 December 2003 Introducing the ZyWALL The is the ideal secure gateway for all data passing between the Internet and the LAN. By integrating NAT,
Configuring TACACS+ Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for TACACS+
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-2 clock summer-time repeating 1-3 clock timezone 1-4 configure-user
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-2 clock summer-time repeating 1-3 clock timezone 1-4 configure-user
Table of Contents X Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-1 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-2 EAP over LAN 1-3 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-1 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-2 EAP over LAN 1-3 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
802.1x Configuration Examples H3C S7500 Series Ethernet Switches Release Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1X Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to 802.1X... 1-1 1.2 Features Configuration... 1-1 1.2.1 Global Configuration... 1-1 1.2.2 Configuration in Port View...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1X Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to 802.1X... 1-1 1.2 Features Configuration... 1-1 1.2.1 Global Configuration... 1-1 1.2.2 Configuration in Port View...
H3C S12500 Series Routing Switches
 H3C S12500 Series Routing Switches Security Command Reference Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: S12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Copyright 2012,
H3C S12500 Series Routing Switches Security Command Reference Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: S12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Copyright 2012,
Passwords and Privileges Commands
 Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series
 HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Security Command Reference Part number: 5998-2887 Software version: Release2208 Document version: 6W100-20130228 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Security Command Reference Part number: 5998-2887 Software version: Release2208 Document version: 6W100-20130228 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
Table of Contents. 4 System Guard Configuration 4-1 System Guard Overview 4-1 Guard Against IP Attacks 4-1 Guard Against TCN Attacks 4-1
 Table of Contents 1 802.1x Configuration 1-1 Introduction to 802.1x 1-1 Architecture of 802.1x Authentication 1-1 The Mechanism of an 802.1x Authentication System 1-3 Encapsulation of EAPoL Messages 1-3
Table of Contents 1 802.1x Configuration 1-1 Introduction to 802.1x 1-1 Architecture of 802.1x Authentication 1-1 The Mechanism of an 802.1x Authentication System 1-3 Encapsulation of EAPoL Messages 1-3
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
TECHNICAL NOTE UWW & CLEARPASS HOW-TO: CONFIGURE UNIFIED WIRELESS WITH CLEARPASS. Version 2
 HOW-TO: CONFIGURE UNIFIED WIRELESS WITH CLEARPASS Version 2 CONTENTS Introduction... 7 Background information... 7 Requirements... 7 Network diagram... 7 VLANs... 8 Switch configuration... 8 Initial setup...
HOW-TO: CONFIGURE UNIFIED WIRELESS WITH CLEARPASS Version 2 CONTENTS Introduction... 7 Background information... 7 Requirements... 7 Network diagram... 7 VLANs... 8 Switch configuration... 8 Initial setup...
Lab AAA Authorization and Accounting
 Lab 11.3.2 AAA Authorization and Accounting Objective Scenario Step 1 In this lab, the student will use the exec-timeout command to control the amount of time before an idle telnet or console session is
Lab 11.3.2 AAA Authorization and Accounting Objective Scenario Step 1 In this lab, the student will use the exec-timeout command to control the amount of time before an idle telnet or console session is
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE3080F tutor to get assigned to your routers.
 EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
Management Software AT-S79. User s Guide. For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches. Version Rev.
 Management Software AT-S79 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches Version 1.0.0 613-000207 Rev. A Copyright 2005 Allied Telesyn, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
Management Software AT-S79 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches Version 1.0.0 613-000207 Rev. A Copyright 2005 Allied Telesyn, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
Controlled/uncontrolled port and port authorization status
 Contents 802.1X fundamentals 1 802.1X architecture 1 Controlled/uncontrolled port and port authorization status 1 802.1X-related protocols 2 Packet formats 2 EAP over RADIUS 4 Initiating 802.1X authentication
Contents 802.1X fundamentals 1 802.1X architecture 1 Controlled/uncontrolled port and port authorization status 1 802.1X-related protocols 2 Packet formats 2 EAP over RADIUS 4 Initiating 802.1X authentication
RADIUS Configuration. Overview. Introduction to RADIUS. Client/Server Model
 Table of Contents RADIUS Configuration 1 Overview 1 Introduction to RADIUS 1 Client/Server Model 1 Security and Authentication Mechanisms 2 Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS 2 RADIUS Packet Format
Table of Contents RADIUS Configuration 1 Overview 1 Introduction to RADIUS 1 Client/Server Model 1 Security and Authentication Mechanisms 2 Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS 2 RADIUS Packet Format
Operation Manual SSH H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 SSH Overview... 1-1 1.2 Configuring the SSH Server... 1-5 1.2.1 Enabling SSH Server... 1-5 1.2.2 Configuring the Protocols for the SSH Client User Interface
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 SSH Overview... 1-1 1.2 Configuring the SSH Server... 1-5 1.2.1 Enabling SSH Server... 1-5 1.2.2 Configuring the Protocols for the SSH Client User Interface
Configuring Terminal Settings and Sessions
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Terminal Settings and Sessions, page 1 Configuring the Console Port, page 3 Configuring the COM1 Port, page 5 Configuring Virtual Terminals,
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Terminal Settings and Sessions, page 1 Configuring the Console Port, page 3 Configuring the COM1 Port, page 5 Configuring Virtual Terminals,
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-2 clock summer-time repeating 1-3 clock timezone 1-4 command-privilege
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-2 clock summer-time repeating 1-3 clock timezone 1-4 command-privilege
Configuring Authorization
 Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-1 clock summer-time repeating 1-2 clock timezone 1-4 command-privilege
Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 Basic Configuration Commands 1-1 clock datetime 1-1 clock summer-time one-off 1-1 clock summer-time repeating 1-2 clock timezone 1-4 command-privilege
HP 5500 EI & 5500 SI Switch Series
 HP 5500 EI & 5500 SI Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-1707 Software version: Release 2220 Document version: 6W100-20130810 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP 5500 EI & 5500 SI Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-1707 Software version: Release 2220 Document version: 6W100-20130810 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
Firewall Authentication Proxy for FTP and Telnet Sessions
 Firewall Authentication Proxy for FTP and Telnet Sessions Last Updated: January 18, 2012 Before the introduction of the Firewall Authentication Proxy for FTP and Telnet Sessions feature, users could enable
Firewall Authentication Proxy for FTP and Telnet Sessions Last Updated: January 18, 2012 Before the introduction of the Firewall Authentication Proxy for FTP and Telnet Sessions feature, users could enable
Configuring Security for the ML-Series Card
 19 CHAPTER Configuring Security for the ML-Series Card This chapter describes the security features of the ML-Series card. This chapter includes the following major sections: Understanding Security, page
19 CHAPTER Configuring Security for the ML-Series Card This chapter describes the security features of the ML-Series card. This chapter includes the following major sections: Understanding Security, page
HP 6125 Blade Switch Series
 HP 6125 Blade Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3153 Software version: Release 2103 Document version: 6W100-20120907 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
HP 6125 Blade Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3153 Software version: Release 2103 Document version: 6W100-20120907 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Cisco - Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable
 1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
Table of Contents X Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-2 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-3 EAP over LAN 1-4 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-2 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-3 EAP over LAN 1-4 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
PT Activity: Configure AAA Authentication on Cisco Routers
 PT Activity: Configure AAA Authentication on Cisco Routers Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 10.1.1.2
PT Activity: Configure AAA Authentication on Cisco Routers Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 10.1.1.2
HP A5830 Switch Series Fundamentals. Configuration Guide. Abstract
 HP A5830 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures.
HP A5830 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures.
HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches
 HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3153a Software version: Release 2103 and later Document version: 6W102-20141218 Legal and notice information Copyright
HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3153a Software version: Release 2103 and later Document version: 6W102-20141218 Legal and notice information Copyright
Software Update C.09.xx Release Notes for the HP Procurve Switches 1600M, 2400M, 2424M, 4000M, and 8000M
 Software Update C.09.xx Release Notes for the HP Procurve Switches 1600M, 2400M, 2424M, 4000M, and 8000M Topics: TACACS+ Authentication for Centralized Control of Switch Access Security (page 7) CDP (page
Software Update C.09.xx Release Notes for the HP Procurve Switches 1600M, 2400M, 2424M, 4000M, and 8000M Topics: TACACS+ Authentication for Centralized Control of Switch Access Security (page 7) CDP (page
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
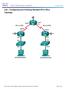 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Operation Manual User Access. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 PPP Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to PPP... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to PPP... 1-1 1.2 Configuring PPP... 1-2 1.2.1 Configuring PPP Encapsulation on
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 PPP Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to PPP... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to PPP... 1-1 1.2 Configuring PPP... 1-2 1.2.1 Configuring PPP Encapsulation on
Appendix A Command Index A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
 The command index includes all the commands in the Comware Command Manual, which are arranged alphabetically. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A access-limit accounting accounting optional
The command index includes all the commands in the Comware Command Manual, which are arranged alphabetically. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A access-limit accounting accounting optional
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
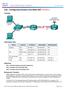 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy
 Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature. It includes information on the benefits of the feature, supported platforms, configuration
Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature. It includes information on the benefits of the feature, supported platforms, configuration
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against industry standard TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication protocols.
The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against industry standard TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication protocols.
Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands
 CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Configuring the WMIC for the First Time
 Configuring the WMIC for the First Time This document describes how to configure basic settings on a Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) for the first time. Before You Start Before you install
Configuring the WMIC for the First Time This document describes how to configure basic settings on a Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) for the first time. Before You Start Before you install
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
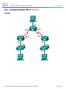 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+), page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+), page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode
 How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 7, 2013 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 7, 2013 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Using the Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) and how to use it to configure your Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It contains these sections: Understanding Command Modes,
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) and how to use it to configure your Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It contains these sections: Understanding Command Modes,
Configure a Cisco Router with TACACS+ Authentication
 Configure a Cisco Router with TACACS+ Authentication Document ID: 13865 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Authentication Add Authorization Add Accounting Test
Configure a Cisco Router with TACACS+ Authentication Document ID: 13865 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Authentication Add Authorization Add Accounting Test
Configuring Terminal Settings and Sessions
 This chapter describes how to manage the terminal settings and sessions on a Cisco NX-OS device. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Terminal Settings and Sessions, page 1 Licensing
This chapter describes how to manage the terminal settings and sessions on a Cisco NX-OS device. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Terminal Settings and Sessions, page 1 Licensing
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts
 Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
AAA and the Local Database
 This chapter describes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA, pronounced triple A ). AAA is a a set of services for controlling access to computer resources, enforcing policies, assessing
This chapter describes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA, pronounced triple A ). AAA is a a set of services for controlling access to computer resources, enforcing policies, assessing
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE
 CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
CISCO SWITCH BEST PRACTICES GUIDE Table of Contents (After Clicking Link Hit HOME to Return to TOC) 1) Add Hostname... 2 2) Add Username and Password... 2 3) Create Secret Password... 2 4) Encrypt Password...
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example
 Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
aaa max-sessions maximum-number-of-sessions The default value for aaa max-sessions command is platform dependent. Release 15.0(1)M.
 aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
HP Unified Wired-WLAN Products
 HP Unified Wired-WLAN Products Security Command Reference HP 830 Unified Wired-WLAN PoE+ Switch Series HP 850 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance HP 870 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance HP 11900/10500/7500 20G Unified
HP Unified Wired-WLAN Products Security Command Reference HP 830 Unified Wired-WLAN PoE+ Switch Series HP 850 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance HP 870 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance HP 11900/10500/7500 20G Unified
