Setting Up a Multihomed System
|
|
|
- Juniper Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 4 By default, the installation of the Cisco Configuration Engine software offers a single-homed system setup. If you require a multihomed system setup, you must manually customize the network parameters of the Cisco Configuration Engine server. This chapter provides instructions for manually customizing these network parameters. It contains the following sections: Setup Restrictions, page 4-1 Typical Deployment of the Multihomed System, page 4-2 Understanding the Routing Table, page 4-4 Manually Updating the Routing Table, page 4-5 Reloading the Routing Table, page 4-9 Information About the /etc/hosts File, page 4-9 Setup Restrictions Two network interfaces are installed in the Cisco Configuration Engine server: eth0 (Ethernet 0) and eth1 (Ethernet 1). Both interfaces can be configured and connected to networks. Cisco Configuration Engine setup has the following restrictions: 1. The hostname and domain name that are input at setup make up the identity for eth0. 2. There are no hostname and domain name assignments for eth1. 3. For both eth0 and eth1 interfaces, the default gateway must be configured on the same network as eth0. 4. Ethernet0 is used to connect to the management network. The customer premises equipment () resides in the management network. 5. There are no setup prompts that allow you to add additional routes into the routing table. 6. The Cisco Configuration Engine user interface does not allow you to manipulate the routing table. 7. The routing table changes are not automatically backed up and saved. 4-1
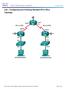
2 Typical Deployment of the Multihomed System Chapter 4 Typical Deployment of the Multihomed System Figure 4-1 shows a typical deployment of Cisco Configuration Engine server with the Cisco Configuration Engine software in a two-network environment: private network and public network. Private Network The private network contains the Network Operation Center (NOC), where the provisioning applications connect to the Cisco Configuration Engine through the CNS Event Bus. Public Network The public network is the entry to the management network where connects to the Cisco Configuration Engine through TCP connections. This deployment provides security to network management because it physically isolates provisioning applications from external traffic. 4-2
3 Chapter 4 Typical Deployment of the Multihomed System Figure 4-1 Typical Deployment of a Multihomed System NOC /24 Private network /24 eth1 eth Cisco Configuration Engine software installed on a Cisco Configuration Engine server Public network / Gateway / / /27 See Figure 4-1 on page 4-3 and Setup Restrictions, page 4-1, and note the following: Ethernet0 is used for connecting to the in the public (management) network (restriction 4) and eth1 is used for connecting to the provisioning applications in the private network. Gateway is the default gateway because setup restricts the location of the default gateway (restriction 3). In effect, this restriction requires all routes going to the private network to be explicitly declared (or controlled) in the Cisco Configuration Engine server s routing table. 4-3
4 Understanding the Routing Table Chapter 4 The CNS Event Bus Network Parameter prompt in the Cisco Configuration Engine setup controls the location of the CNS Event Bus. By default, the CNS Event Bus is set to eth0, which means that the event bus is started on the public network. If you choose to start the event bus on the private network, you must set the CNS Event Bus Network Parameter to the eth1 IP address. By default, Cisco Configuration Engine setup automatically creates direct and default routes in the routing table. The network administrator must manually add the indirect routes to the routing table (restriction 5). For details, see Adding Indirect Routes to the Routing Table, page 4-6. In the public network, the routes leading to networks /27, /16, and /27 could be defined either in the default gateway or in the Cisco Configuration Engine server. Defining the routes in the default gateway is preferable because it reduces management burden on the Cisco Configuration Engine server. In this chapter, however, we defined the routes in the Cisco Configuration Engine server to illustrate the routing table management tasks that you can perform on the server. Understanding the Routing Table The routing table in the Cisco Configuration Engine server plays a major role in maintaining the two network topologies. The Cisco Configuration Engine server is not a gateway for passing traffic between the public and private network, and it should be controlled and restrained from network access. Thus, the number of routes to be maintained in the routing table must be small. The current approach for maintaining the routing table is static routing. Each route in the routing table describes a path from the network interface to the reachable network for directing outbound traffic. There are three types of routes required in the routing table: direct, indirect, and default. Understanding Direct Routes Direct routes specify the networks that are directly connected to the network interfaces. For example, the two directly connected networks in Figure 4-1 are networks /24 and /27. The two direct routes are: eth1 > /24 eth0 > /27 Understanding Indirect Routes Indirect routes describe the paths from the directly connected gateways to the indirectly connected networks. See Figure 4-1, and note the following information. The indirectly connected networks in the public network are: / / / /27 4-4
5 Chapter 4 Manually Updating the Routing Table The indirect routes in the public network are: > / > / > /27 A packet destined for network /27 is first forwarded to gateway , which sends it to gateway ; therefore, the route > /27 is required in the Cisco Configuration Engine server s routing table. The indirect route in the private network is: > /24 Understanding Default Route The default route specifies the default gateway for sending outgoing packets that have no matching routes. The default route in Figure 4-1 is > /0. Network /0 is a wildcard notation that matches any network address. Manually Updating the Routing Table By default, Cisco Configuration Engine setup automatically creates the direct and default routes in the routing table. The network administrator must manually add the indirect routes to the routing table. The following sections provide the steps for manually adding indirect routes and changing the default route: Indirect Routes, page 4-5 Default Route, page 4-7 Direct Routes, page 4-8 When modifying the routing table, we recommend that you log in through the serial port console connection. Indirect Routes Use variations of the route command to display, add, or delete routes from the routing table. The following sections provide more information: Displaying the Routing Table, page 4-6 Adding Indirect Routes to the Routing Table, page 4-6 Deleting a Route from the Routing Table, page 4-7 Persistent Update Indirect Routes, page
6 Manually Updating the Routing Table Chapter 4 Displaying the Routing Table Use the route n command to display the routing table: Router# route -n The n part of the command allows numerical addresses to be displayed instead of symbolic hostnames, thus avoiding DNS for hostname lookup. This prevents the command from hanging if the DNS is not ready or reachable. Example of the Routing Table Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface U eth U eth U lo UG eth0 The first two lines are direct routes (eth0 > and eth1 > ). The last line is the default route ( > ). This default route was configured during Cisco Configuration Engine setup. The third line is the route for using the loopback interface (lo > ). This is the interface with a special IP address: This loopback interface is configured by default during setup. Adding Indirect Routes to the Routing Table Use the route add command to add indirect routes to the routing table. You must specify the network address, network mask, gateway address, and network interface identifier in the command: route add -net netmask gw dev eth1 route add -net netmask gw dev eth0 route add -net netmask gw dev eth0 route add -net netmask gw dev eth0 In the example, the first line adds the indirect route for the private network: > /24. The next three lines add the indirect routes for the public network: > / > / > /27 After you add the indirect routes, use the route n command to display the updated routing table: Router# route -n 4-6
7 Chapter 4 Manually Updating the Routing Table Example of the Updated Routing Table Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface UG eth U eth UG eth UG eth U lo UG eth U eth UG eth0 Deleting a Route from the Routing Table Use the route del command to delete a route from the routing table. For example, to delete the route to network , enter the following command: route del -net netmask gw dev eth1 Persistent Update Indirect Routes Modifying the routing table with the route command provides only a temporary solution that is in effect until the machine reboots. For a persistent update, add the indirect routes into the file /etc/sysconfig/static-routes, in the following format: any <type destination-address> netmask <netmask-address> gw <gateway-address> dev <interface number> Example any net netmask gw dev eth1 any net netmask gw dev eth0 any net netmask gw dev eth0 any net netmask gw dev eth0 When the server reboots, the network startup script, /etc/rc.d/init.d/network, executes the following route add command for each line in the static routes table, beginning with the keyword any (as shown in the example above): route add <type destination-address> netmask <netmask-address> gw <gateway-address> dev <interface number> If the routes are no longer required, you must physically remove them from the /etc/sysconfig/static-routes file. Default Route Use the route command to change the default route on the routing table. The following sections provide more information: Changing the Default Route, page 4-8 Persistent Update Default Routes, page
8 Manually Updating the Routing Table Chapter 4 Changing the Default Route To change the default route, you must first delete the existing default route and then add the new default route to the routing table. For example, to change the default route in Figure 4-1 so that it points to the default gateway that is connected to eth0 on the public network, follow these steps: Step 1 Step 2 Delete the default route. To delete the default route , enter the following command: route del default gw Add the default route. To add the default route , enter the following command: route add default gw Example of the Routing Table with the Default Gateway Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface UG eth U eth UG eth UG eth U lo UG eth U eth UG eth1 The last line displays the new default route. Persistent Update Default Routes The /etc/sysconfig/network file stores the following network parameters: NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=rain106.cisco.com DOMAINNAME=cisco.com GATEWAY= GATEWAYDEV=eth0 For a persistent default route update, you must substitute the GATEWAY parameter and the GATEWAYDEV parameter with the new desired values; for example, and eth1. The Setup program updates the file with the gateway parameters, but your manual changes are lost when you rerun the Setup program. Direct Routes Because the direct routes are already defined at setup, you do not need to manually define them. 4-8
9 Chapter 4 Reloading the Routing Table Persistent Update Direct Routes The files ifcfg-eth0 and ifcfg-eth1 in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory store the network parameters for eth0 and eth1. These files are used to configure the network interface and to create direct routes after each reboot. Reloading the Routing Table You can reload the routing table in one of the following ways: Use the route command to update temporary changes, modify the associated file, and then reboot the machine for persistent changes. Enter the following command directly at the command line: /etc/rc.d/init.d/network restart. This updates the routing table with all persistent changes without rebooting your machine. Information About the /etc/hosts File The hostname and domain name that you added during the Cisco Configuration Engine Setup program defined the identity of the system and of eth0. This information is stored in the /etc/hosts file. If a name is required for eth1, you can add it to the /etc/hosts file. However, the setup script removes eth0 and eth1 entries from the /etc/hosts file at setup and regenerates the eth0 entry only. Therefore, you must re-add the eth1 entry after each setup. Other entries are not affected. 4-9
10 Information About the /etc/hosts File Chapter
Addressing and Routing
 Addressing and Routing Andrew Scott a.scott@lancaster.ac.uk Physical/ Hardware Addresses Aka MAC* or link(-layer) address Can only talk to things on same link Unique ID given to every network interface
Addressing and Routing Andrew Scott a.scott@lancaster.ac.uk Physical/ Hardware Addresses Aka MAC* or link(-layer) address Can only talk to things on same link Unique ID given to every network interface
Static and source based routing
 Static and source based routing Lab setup For this lab students have to work in teams of two. Two team of two students (that is overall four students) should form a group and perform lab tasks together.
Static and source based routing Lab setup For this lab students have to work in teams of two. Two team of two students (that is overall four students) should form a group and perform lab tasks together.
Manually Change Default Gateway Centos Command Line Windows
 Manually Change Default Gateway Centos Command Line Windows Learn how to add a defaull gateway on Redhat Linux. Linux command line tutorial Bash scripting tutorial Vim tutorial Perl programming tutorial
Manually Change Default Gateway Centos Command Line Windows Learn how to add a defaull gateway on Redhat Linux. Linux command line tutorial Bash scripting tutorial Vim tutorial Perl programming tutorial
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Best Practices VMware VMotion with HyperIP
 Best Practices VMware VMotion with HyperIP 6420 Sycamore Lane N. Maple Grove, MN 55369 http://www.netex.com March 30, 2010 Page 1 of 10 Adding HyperIP into your network HyperIP improves the performance
Best Practices VMware VMotion with HyperIP 6420 Sycamore Lane N. Maple Grove, MN 55369 http://www.netex.com March 30, 2010 Page 1 of 10 Adding HyperIP into your network HyperIP improves the performance
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Linux. Computer networks - Administration 1DV202. fredag 30 mars 12
 Linux Computer networks - Administration 1DV202 Configuration files /etc/hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/network/interfaces /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost 127.0.1.1 lokal.kalmar.se lokal
Linux Computer networks - Administration 1DV202 Configuration files /etc/hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/network/interfaces /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost 127.0.1.1 lokal.kalmar.se lokal
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
LAN Setup Reflection
 LAN Setup Reflection After the LAN setup, ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other
LAN Setup Reflection After the LAN setup, ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other
TCP/IP Network Essentials
 TCP/IP Network Essentials Linux System Administration and IP Services AfNOG 2012 Layers Complex problems can be solved using the common divide and conquer principle. In this case the internals of the Internet
TCP/IP Network Essentials Linux System Administration and IP Services AfNOG 2012 Layers Complex problems can be solved using the common divide and conquer principle. In this case the internals of the Internet
Experimenting Internetworking using Linux Virtual Machines Part I
 Experimenting Internetworking using Linux Virtual Machines Part I Hui Chen Previous Release on October 27, 2014 Lastly revised on November 4, 2015 Revision: Copyright c 2016. Hui Chen
Experimenting Internetworking using Linux Virtual Machines Part I Hui Chen Previous Release on October 27, 2014 Lastly revised on November 4, 2015 Revision: Copyright c 2016. Hui Chen
IP Basics Unix/IP Preparation Course June 29, 2010 Pago Pago, American Samoa
 IP Basics Unix/IP Preparation Course June 29, 2010 Layers Complex problems can be solved using the common divide and conquer principle. In this case the internals of the Internet are divided into separate
IP Basics Unix/IP Preparation Course June 29, 2010 Layers Complex problems can be solved using the common divide and conquer principle. In this case the internals of the Internet are divided into separate
Network Administra0on
 Network Administra0on (Introduc0on) Administración en Red 1 Index Introduc0on (TCP/IP) Network Interface Link Layer Network Layer Monitoring/Test Administración en Red 2 Introduc0on (TCP/IP) Protocol Suite,
Network Administra0on (Introduc0on) Administración en Red 1 Index Introduc0on (TCP/IP) Network Interface Link Layer Network Layer Monitoring/Test Administración en Red 2 Introduc0on (TCP/IP) Protocol Suite,
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab 2.8.2: Challenge Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
IP over IB Protocol. Introduction CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 The following sections appear in this chapter: Introduction, page 3-1 Manually Configure IPoIB for Default IB Partition, page 3-2 Subinterfaces, page 3-2 Verify IPoIB Functionality, page 3-5
CHAPTER 3 The following sections appear in this chapter: Introduction, page 3-1 Manually Configure IPoIB for Default IB Partition, page 3-2 Subinterfaces, page 3-2 Verify IPoIB Functionality, page 3-5
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
LAN Setup Reflection. Ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external?
 LAN Setup Reflection Ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other VMs in the classroom?
LAN Setup Reflection Ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other VMs in the classroom?
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Quick guide for configuring a system with multiple IP-LINKs
 Quick guide for configuring a system with multiple IP-LINKs October 4 th 2005, KK. This guide will show an example configurations for a system with multiple IP-LINKs. Example 1, three devices connected
Quick guide for configuring a system with multiple IP-LINKs October 4 th 2005, KK. This guide will show an example configurations for a system with multiple IP-LINKs. Example 1, three devices connected
THE INTERNET PROTOCOL/1
 THE INTERNET PROTOCOL a (connectionless) network layer protocol designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks (store-and-forward paradigm) provides for transmitting
THE INTERNET PROTOCOL a (connectionless) network layer protocol designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks (store-and-forward paradigm) provides for transmitting
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45
 Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
THE INTERNET PROTOCOL INTERFACES
 THE INTERNET PROTOCOL The Internet Protocol Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 A (connectionless) network protocol Designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks
THE INTERNET PROTOCOL The Internet Protocol Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 A (connectionless) network protocol Designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks
Network Configuration for Cisco UCS Director Baremetal Agent
 Network Configuration for Cisco UCS Director Baremetal Agent This chapter contains the following sections: About the Network Configuration Options, page 1 Single Network for Management and PXE, page 1
Network Configuration for Cisco UCS Director Baremetal Agent This chapter contains the following sections: About the Network Configuration Options, page 1 Single Network for Management and PXE, page 1
The Internet Protocol
 The Internet Protocol Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 THE INTERNET PROTOCOL A (connectionless) network layer protocol Designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks
The Internet Protocol Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 THE INTERNET PROTOCOL A (connectionless) network layer protocol Designed for use in interconnected systems of packet-switched computer communication networks
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
GSS Administration and Troubleshooting
 CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
Certification. Securing Networks
 Certification Securing Networks UNIT 9 Securing Networks 1 Objectives Explain packet filtering architecture Explain primary filtering command syntax Explain Network Address Translation Provide examples
Certification Securing Networks UNIT 9 Securing Networks 1 Objectives Explain packet filtering architecture Explain primary filtering command syntax Explain Network Address Translation Provide examples
Setting Up Initial System Configuration
 Default System Configuration on the Cisco ENCS, page 2 Default System Configuration on the Cisco UCS C220 M4 Server, page 3 Default System Configuration on the Cisco UCS E-Series Servers, page 4 Changing
Default System Configuration on the Cisco ENCS, page 2 Default System Configuration on the Cisco UCS C220 M4 Server, page 3 Default System Configuration on the Cisco UCS E-Series Servers, page 4 Changing
For personnal use only
 Network Namespaces in RHEL7 Finnbarr P. Murphy (fpm@fpmurphy.com) Linux namespaces are somewhat like Solaris zones in many ways from a user perspective but have significant differences under the hood.
Network Namespaces in RHEL7 Finnbarr P. Murphy (fpm@fpmurphy.com) Linux namespaces are somewhat like Solaris zones in many ways from a user perspective but have significant differences under the hood.
lab rip experiences with RIPv2 distance vector protocol
 lab rip experiences with RIPv2 distance vector protocol hosts need routing each host with a network stack performs some elementary routing ip layer nic eth0? lo the network stack may be used to access
lab rip experiences with RIPv2 distance vector protocol hosts need routing each host with a network stack performs some elementary routing ip layer nic eth0? lo the network stack may be used to access
Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Datagram. Source IP address. Destination IP address. Options. Data
 Datagram Version H. len Service Datagram length Datagram identifier FR-FR FR-FR-FR-FR Time-to-live Transp. prot. H. Checksum Source IP address Destination IP address Options Data Each line represents a
Datagram Version H. len Service Datagram length Datagram identifier FR-FR FR-FR-FR-FR Time-to-live Transp. prot. H. Checksum Source IP address Destination IP address Options Data Each line represents a
Inspection of Inter-Subnet traffic in AWS VPC using CloudGuard
 Inspection of Inter-Subnet traffic in AWS VPC using CloudGuard I've been asked an interesting and, seemingly, trivial question: "How would you protect the hosts in AWS VPC located in a different subnets
Inspection of Inter-Subnet traffic in AWS VPC using CloudGuard I've been asked an interesting and, seemingly, trivial question: "How would you protect the hosts in AWS VPC located in a different subnets
Virtual Lab for CIS 192 & 196 Rich Simms May 27, 2006
 Virtual Lab for CIS 192 & 196 Rich Simms May 27, 2006 Overview Microsoft s virtualization technology has been available as a product called Virtual Server. Microsoft recently announced two major changes
Virtual Lab for CIS 192 & 196 Rich Simms May 27, 2006 Overview Microsoft s virtualization technology has been available as a product called Virtual Server. Microsoft recently announced two major changes
Configuring Cisco IOS CNS Agents
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco IOS CNS agents on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete configuration information for the Cisco Configuration Engine, see this URL on Cisco.com
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco IOS CNS agents on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete configuration information for the Cisco Configuration Engine, see this URL on Cisco.com
BEAWebLogic SIP Server. Configuring Network Resources
 BEAWebLogic SIP Server Configuring Network Resources Version 3.0 Revised: December 13, 2006 Copyright Copyright 1995-2006 BEA Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Restricted Rights Legend This software is
BEAWebLogic SIP Server Configuring Network Resources Version 3.0 Revised: December 13, 2006 Copyright Copyright 1995-2006 BEA Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Restricted Rights Legend This software is
Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs)
 Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs) This chapter describes software-based ACLs, which are ACLs that processed traffic in software or CPU. (This type of ACL was also referred to as flow-based
Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs) This chapter describes software-based ACLs, which are ACLs that processed traffic in software or CPU. (This type of ACL was also referred to as flow-based
MiPDF.COM. 3. Which procedure is used to access a Cisco 2960 switch when performing an initial configuration in a secure environment?
 CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
How to Deploy Axon on VMware vcenter
 How to Deploy Axon on VMware vcenter Copyright Informatica LLC 2017. Informatica, the Informatica logo, Intelligent Data Lake, Big Data Mangement, and Live Data Map are trademarks or registered trademarks
How to Deploy Axon on VMware vcenter Copyright Informatica LLC 2017. Informatica, the Informatica logo, Intelligent Data Lake, Big Data Mangement, and Live Data Map are trademarks or registered trademarks
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
 First Published: June 19, 2006 Last Updated: June 19, 2006 The Cisco Networking Services () feature is a collection of services that can provide remote event-driven configuring of Cisco IOS networking
First Published: June 19, 2006 Last Updated: June 19, 2006 The Cisco Networking Services () feature is a collection of services that can provide remote event-driven configuring of Cisco IOS networking
IOS and Configuration Basics
 APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
ROUTING INTRODUCTION TO IP, IP ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND PROXY ARP
 IP ROUTING INTRODUCTION TO IP, IP ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND PROXY ARP Peter R. Egli 1/37 Contents 1. IP Routing 2. Routing Protocols 3. Fragmentation in the IP Layer 4. Proxy ARP 5. Routing and IP forwarding
IP ROUTING INTRODUCTION TO IP, IP ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND PROXY ARP Peter R. Egli 1/37 Contents 1. IP Routing 2. Routing Protocols 3. Fragmentation in the IP Layer 4. Proxy ARP 5. Routing and IP forwarding
Lab : OSPF Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Appliance Quick Start Guide. v7.5
 Appliance Quick Start Guide v7.5 rev. 1.0.8 Copyright 2002 2014 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. Table of Contents Loadbalancer.org Terminology... 4 What is a Virtual IP Address?... 4 What is a Floating IP Address?...
Appliance Quick Start Guide v7.5 rev. 1.0.8 Copyright 2002 2014 Loadbalancer.org, Inc. Table of Contents Loadbalancer.org Terminology... 4 What is a Virtual IP Address?... 4 What is a Floating IP Address?...
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
Scenario: V114 Configuration on Vyatta
 Scenario: V114 Configuration on Vyatta This section steps you through initial system configuration tasks. These are tasks that are required for almost any scenario in which you might use the V114 on the
Scenario: V114 Configuration on Vyatta This section steps you through initial system configuration tasks. These are tasks that are required for almost any scenario in which you might use the V114 on the
Configuring the Fabric Interconnects
 Configuring the Fabric Interconnects This chapter includes the following sections: Initial System Setup, page 1 Performing an Initial System Setup for a Standalone Configuration, page 3 Initial System
Configuring the Fabric Interconnects This chapter includes the following sections: Initial System Setup, page 1 Performing an Initial System Setup for a Standalone Configuration, page 3 Initial System
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
IM and Presence Service Network Setup
 Configuration changes and service restart notifications, page 1 DNS Domain Configuration, page 2 IM and Presence Service Default Domain Configuration, page 6 IM Address Configuration, page 7 Domain Management
Configuration changes and service restart notifications, page 1 DNS Domain Configuration, page 2 IM and Presence Service Default Domain Configuration, page 6 IM Address Configuration, page 7 Domain Management
Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter. Deployment Guide v Copyright Loadbalancer.org
 Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter Deployment Guide v1.3.5 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org Software Versions
Load Balancing Bloxx Web Filter Deployment Guide v1.3.5 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org Software Versions
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Network Address Translation
 Network Services Network Address Translation Network address translation (NAT) Defined in RFC 3022 Describes methods for connecting private (internal) IP addresses to the Internet NAT uses a one-to-one
Network Services Network Address Translation Network address translation (NAT) Defined in RFC 3022 Describes methods for connecting private (internal) IP addresses to the Internet NAT uses a one-to-one
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2
 Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Networking Fundamentals
 Networking Fundamentals Network Startup Resource Center www.nsrc.org These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Networking Fundamentals Network Startup Resource Center www.nsrc.org These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Appliance Quick Start Guide v8.0
 Appliance Quick Start Guide v8.0 rev. 1.0.6 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc Table of Contents About this Guide... 5 About the Appliance... 5 Appliance Configuration Overview... 5 Appliance Security...
Appliance Quick Start Guide v8.0 rev. 1.0.6 Copyright 2002 2015 Loadbalancer.org, Inc Table of Contents About this Guide... 5 About the Appliance... 5 Appliance Configuration Overview... 5 Appliance Security...
Cisco Modeling Labs OVA Installation
 Prepare for an OVA File Installation, page 1 Download the Cisco Modeling Labs OVA File, page 2 Configure Security and Network Settings, page 2 Deploy the Cisco Modeling Labs OVA, page 12 Edit the Virtual
Prepare for an OVA File Installation, page 1 Download the Cisco Modeling Labs OVA File, page 2 Configure Security and Network Settings, page 2 Deploy the Cisco Modeling Labs OVA, page 12 Edit the Virtual
Load Balancing Web Proxies / Filters / Gateways. Deployment Guide v Copyright Loadbalancer.org
 Load Balancing Web Proxies / Filters / Gateways Deployment Guide v1.6.5 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org
Load Balancing Web Proxies / Filters / Gateways Deployment Guide v1.6.5 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
CIS Lesson 3. Instructor: Rich Simms Dial-in: Passcode:
 Instructor: Rich Simms Dial-in: 888-450-4821 Passcode: 761867 Solomon Sean C. Chris Corey Bryan Sean F. Tony David Donna Dave Evan Gabriel Elia Tajvia Carlos Adam Ben Laura Email me (risimms@cabrillo.edu)
Instructor: Rich Simms Dial-in: 888-450-4821 Passcode: 761867 Solomon Sean C. Chris Corey Bryan Sean F. Tony David Donna Dave Evan Gabriel Elia Tajvia Carlos Adam Ben Laura Email me (risimms@cabrillo.edu)
Routers use access lists to control incoming or outgoing traffic. You should know the following characteristics of an access list.
 8.1. Access List Routers use access lists to control incoming or outgoing traffic. You should know the following characteristics of an access list. Access lists describe the traffic type that will be controlled.
8.1. Access List Routers use access lists to control incoming or outgoing traffic. You should know the following characteristics of an access list. Access lists describe the traffic type that will be controlled.
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
EdgeConnect for Amazon Web Services (AWS)
 Silver Peak Systems EdgeConnect for Amazon Web Services (AWS) Dinesh Fernando 2-22-2018 Contents EdgeConnect for Amazon Web Services (AWS) Overview... 1 Deploying EC-V Router Mode... 2 Topology... 2 Assumptions
Silver Peak Systems EdgeConnect for Amazon Web Services (AWS) Dinesh Fernando 2-22-2018 Contents EdgeConnect for Amazon Web Services (AWS) Overview... 1 Deploying EC-V Router Mode... 2 Topology... 2 Assumptions
Antonio Cianfrani. Access Control List (ACL) Part I
 Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
hpinsmh.cup.hp.com NAME routing - system support for local network packet routing
 NAME routing - system support for local network packet routing DESCRIPTION The network facilities for HP-UX provide general packet routing support. Routing table maintenance is handled by application processes.
NAME routing - system support for local network packet routing DESCRIPTION The network facilities for HP-UX provide general packet routing support. Routing table maintenance is handled by application processes.
Ref: A. Leon Garcia and I. Widjaja, Communication Networks, 2 nd Ed. McGraw Hill, 2006 Latest update of this lecture was on
 IP Routing Routing is the process performed by routers to transfer packets from the source machine to the destination. Unlike switches, routers are configured by a network administrator. Routers share
IP Routing Routing is the process performed by routers to transfer packets from the source machine to the destination. Unlike switches, routers are configured by a network administrator. Routers share
Cluster Computing Spring 2004 Paul A. Farrell
 Configuring & Tuning Cluster Networks Node connectivity Node visibility Networking Services Security Performance Enhancement Internet Protocol Stack and Parameters NIC/OS Driver Maximum Amount of Data
Configuring & Tuning Cluster Networks Node connectivity Node visibility Networking Services Security Performance Enhancement Internet Protocol Stack and Parameters NIC/OS Driver Maximum Amount of Data
NETWORK CONFIGURATION AND SERVICES. route add default gw /etc/init.d/apache restart
 NETWORK CONFIGURATION AND SERVICES route add default gw 192.168.0.1 /etc/init.d/apache restart NETWORK CONFIGURATION There are two main approaches to configuring a machine for network access: Static configuration
NETWORK CONFIGURATION AND SERVICES route add default gw 192.168.0.1 /etc/init.d/apache restart NETWORK CONFIGURATION There are two main approaches to configuring a machine for network access: Static configuration
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Supplies VLab pod 192 VMs shown above. Forum
 Lab 4: Dynamic routing In this lab we will be using the Quagga package to implement dynamic routing across the three routers shown in the diagram below. Supplies VLab pod 192 VMs shown above Forum Use
Lab 4: Dynamic routing In this lab we will be using the Quagga package to implement dynamic routing across the three routers shown in the diagram below. Supplies VLab pod 192 VMs shown above Forum Use
Networks Lab Pod Diagram
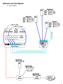 (Console cable) Networks Lab Pod Diagram (x = pod number) 190.111.50.x 190.111.x.254 PodxLinux Addr: 190.111.x.3 Mask: 255.255.255.0 GW: 190.111.x.254 DNS: 190.111.x.1 PodxServer Addr: 190.111.x.1 Mask:
(Console cable) Networks Lab Pod Diagram (x = pod number) 190.111.50.x 190.111.x.254 PodxLinux Addr: 190.111.x.3 Mask: 255.255.255.0 GW: 190.111.x.254 DNS: 190.111.x.1 PodxServer Addr: 190.111.x.1 Mask:
The Assignment is divided into preparation, practical part, and documentation.
 EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
Maintaining the System Software
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter covers the tasks required for maintaining a Content Engine. Upgrading the System Software, page 2-1 Recovering the System Software, page 2-2 Maintaining the Hard Disk Storage, page
CHAPTER 2 This chapter covers the tasks required for maintaining a Content Engine. Upgrading the System Software, page 2-1 Recovering the System Software, page 2-2 Maintaining the Hard Disk Storage, page
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Translation
 This chapter includes the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, on page 1 Information About Static NAT, on page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, on page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, on page 3 NAT Inside
This chapter includes the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, on page 1 Information About Static NAT, on page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, on page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, on page 3 NAT Inside
Configuring a LAN Interface
 Version: 3312 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Router Installation and Configuration Manual/Configuring a LAN Interface...1 Understanding
Version: 3312 Copyright 2007-2010 ImageStream Internet Solutions, Inc., All rights Reserved. Table of Contents Router Installation and Configuration Manual/Configuring a LAN Interface...1 Understanding
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
This document guides the user through: 1. Setting up and configuring networking for the BeagleBone black or green with the host.
 Networking Guide for BeagleBone (Black or Green) by Brian Fraser Last update: Nov 17, 2017 This document guides the user through: 1. Setting up and configuring networking for the BeagleBone black or green
Networking Guide for BeagleBone (Black or Green) by Brian Fraser Last update: Nov 17, 2017 This document guides the user through: 1. Setting up and configuring networking for the BeagleBone black or green
ITexamGuide. High-quality IT Cert Exam study guide
 ITexamGuide High-quality IT Cert Exam study guide Exam : 310-302 Title : Sun Certified Network Administrator for Solaris 10 OS Vendors : SUN Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 310-302 Exam's Question and
ITexamGuide High-quality IT Cert Exam study guide Exam : 310-302 Title : Sun Certified Network Administrator for Solaris 10 OS Vendors : SUN Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 310-302 Exam's Question and
Pexip Infinity and Amazon Web Services Deployment Guide
 Pexip Infinity and Amazon Web Services Deployment Guide Contents Introduction 1 Deployment guidelines 2 Configuring AWS security groups 4 Deploying a Management Node in AWS 6 Deploying a Conferencing Node
Pexip Infinity and Amazon Web Services Deployment Guide Contents Introduction 1 Deployment guidelines 2 Configuring AWS security groups 4 Deploying a Management Node in AWS 6 Deploying a Conferencing Node
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
NGX (R60) Link Selection VPN Deployments August 30, 2005
 NGX (R60) Link Selection VPN Deployments August 30, 2005 Introduction In This Document Introduction page 1 Link Selection in NGX R60 page 1 Configuration Scenarios page 7 This document provides general
NGX (R60) Link Selection VPN Deployments August 30, 2005 Introduction In This Document Introduction page 1 Link Selection in NGX R60 page 1 Configuration Scenarios page 7 This document provides general
Load Balancing Microsoft IIS. Deployment Guide v Copyright Loadbalancer.org
 Load Balancing Microsoft IIS Deployment Guide v1.6.4 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org Software Versions
Load Balancing Microsoft IIS Deployment Guide v1.6.4 Copyright Loadbalancer.org Table of Contents 1. About this Guide...4 2. Loadbalancer.org Appliances Supported...4 3. Loadbalancer.org Software Versions
Exercise 1 INTERNET. x.x.x.254. net /24. net /24. x.x.x.33. x.x.x.254. x.x.x.52. x.x.x.254. x.x.x.254. x.x.x.
 Exercise 1 Given the IP network below: Assign feasible IP addresses to the interfaces and write down a feasible routing table for routers A and B guaranteeing full connectivity x.x.x.33 x.x.x.254 net 131.175.16.0/24
Exercise 1 Given the IP network below: Assign feasible IP addresses to the interfaces and write down a feasible routing table for routers A and B guaranteeing full connectivity x.x.x.33 x.x.x.254 net 131.175.16.0/24
Configuring High Availability (HA)
 4 CHAPTER This chapter covers the following topics: Adding High Availability Cisco NAC Appliance To Your Network, page 4-1 Installing a Clean Access Manager High Availability Pair, page 4-3 Installing
4 CHAPTER This chapter covers the following topics: Adding High Availability Cisco NAC Appliance To Your Network, page 4-1 Installing a Clean Access Manager High Availability Pair, page 4-3 Installing
ACSLS SUPPORT FOR DUAL TCP/IP CONNECTIONS
 ACSLS SUPPORT FOR DUAL TCP/IP CONNECTIONS TO THE SL8500 MODULAR LIBRARY SYSTEM Overview 17 August 2006 Dual TCP/IP is an option that can be purchased for the SL8500. It provides two TCP/IP connections
ACSLS SUPPORT FOR DUAL TCP/IP CONNECTIONS TO THE SL8500 MODULAR LIBRARY SYSTEM Overview 17 August 2006 Dual TCP/IP is an option that can be purchased for the SL8500. It provides two TCP/IP connections
Configuring MWTM to Run with Various Networking Options
 APPENDIXH Configuring MWTM to Run with Various Networking Options In addition to running on standard IP-connected networks, the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager (MWTM) has the flexibility to adapt
APPENDIXH Configuring MWTM to Run with Various Networking Options In addition to running on standard IP-connected networks, the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager (MWTM) has the flexibility to adapt
Configure Segment Routing for IS-IS Protocol
 Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
My problem was not understanding that each tunnel had to be on it's own network. I took subnet as; I could assign each tunnel to an address like
 {Network & Hardware layout} First I'll describe my network setup and platform. We have 9 private networks on the 192.168.x.x network, connected via a core router and 1 Mandrake Linux 9.2 server with 2
{Network & Hardware layout} First I'll describe my network setup and platform. We have 9 private networks on the 192.168.x.x network, connected via a core router and 1 Mandrake Linux 9.2 server with 2
SE 4C03 Winter Sample Midterm Test. Instructor: Kartik Krishnan
 Name Student number SE 4C03 Winter 2004 Sample Midterm Test Instructor: Kartik Krishnan You have 50 minutes to complete this test consisting of 6 pages and 18 questions. The test is open book and class
Name Student number SE 4C03 Winter 2004 Sample Midterm Test Instructor: Kartik Krishnan You have 50 minutes to complete this test consisting of 6 pages and 18 questions. The test is open book and class
