ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment
|
|
|
- Abel Marvin McKenzie
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dept of Electrical and Information Technology Jens A Andersson vers 3.1 ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment 1 Purpose and Goals This lab assignment will give a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and also how to set up routing protocols. You will prepare the lab session, perform the practical exercises, and write a lab report, which describes the whole lab, including planning, preparations, and results. You will work and hand in the report in groups of two students. The lab report will be assessed; grading is passed/failed. A grading bonus will be applied; check the course home page for details. 2 Overview The assignment is divided into preparation, execution, and documentation. The preparations are a crucial part of the lab assignment. Without them there is no possibility to fulfil the practical elements within the specified time; trial-and-error will not work. The carrying out of this lab is performed on the department s router lab. The lab is accessible from a computer of your choice via Internet. The only demands on your computer are that it has a ssh client and an Internet connection. You will practise on routers from Cisco and thus Cisco s router operation system IOS. As can be understood from the description of the router lab given in the Reference Guide the lab is fixed configured on the physical level. You change the outline of the lab networks by opening and closing individual router interfaces to build a network for your specific needs. When you are ready for the practical session you book the lab for a two-hour period; find more information on the course home page. This time should be enough to complete the practical elements and to gather information that goes into your lab report, but only if you have prepared yourself. You add the results from the practical session to your report and complete it. 3 Assignment Elements The assignment has these elements: Study the Router Lab documentation.
2 Plan the laboratory moments. Plan the outline of the report. Perform the practical elements. Add the results of the practical exercises to the report. Complete the report and hand it in. It might be the case that you have to revise it after the teacher s assessment. 4 Bug reports Please report any errors found in this manual or in the lab reference material to the author Jens_A.Andersson@eit.lth.se. 5 Preparations The preparations should be concluded before you book a practical session. In case you opt to not follow this advice you will unnecessarily block the lab for other students, without any time gain for you. You shall study the Router Lab Reference Guide. You shall make yourself familiar with the documentation that is given you as links on the Router Lab home page. You shall also study appropriate theory elements of the course textbook. The FAQ found on the Router Lab web site is also a good source of information. You must make notations on what steps you need to take to fulfil the specified tasks. These notes include configuration and control commands. 6 The Report This lab assignment finishes with a written report. The report shall consist of not less than 2 3 pages of your own text; any printouts from commands and such are not included in this amount. The report shall describe your planning and preparations as well as your findings during the practical elements. The report shall also present how long time in total you spent for the practical elements; that is the time you spent in the lab. A chapter with your own reflections and comments on the lab assignment concludes the report. 7 The Tasks The practical task is divided into three main sections: Hands on IOS CLI RIP OSPF
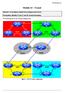
3 Figure 1: Lab Network Layout 7.1 Hands on Login to the lab You start this section with logging in to the front-end host. From there you connect to the different routers. Check that they are running the default configuration. If not, install the default configuration according to the Reference Guide. Also remember that it is a good advice to reload the routers so that the time marks in logs and debug printouts will be useful (see Reference Guide Section 6.5). Hint: It is possible to create several sessions to the front-end host and then use each session for a unique connection to a router. You thereby have one terminal window for each router Configuration Configure the lab according to Figure 1. Allocate appropriate network and host IP addresses. Remember that each router interface must have a unique IP address on the subnet the interface connects to. Make sure each subnet have a unique network identity. Hint 1: Use configuration command ip address <ip address> <mask> to configure the IP address of an interface. Hint 2: Read about serial interface configuration in section 6.4 in the Reference Guide to the Router Lab.
4 Hint3: You open interfaces with the interface configuration command no shutdown. Notice that the default state of interfaces varies. A good command to check status of interfaces is show ip interface brief CDP Use CDP and check your configuration. What information do you get with show cdp neighbor? Try this command on each router in the network. What information do you get with show cdp neighbour <interface> detail? Try this command on one of the routers rtr1 or rtr2. Copy examples of output of these commands into your report ping and traceroute Make yourself familiar with IOS ping and traceroute commands. Both commands come in two versions, normal and extended. We are only examining the normal version. Ping a neighbour using the command ping <host>. How many packets are sent? Explain the information you get from the output of this command? How long time does the router wait until a ping is declared lost? Which routers can you reach from which routers? Why is it so? Traceroute is not so meaningful as of yet but try it anyway. Add output of both ping and traceroute commands to your report. Note! Serial interfaces on the routers in the lab do not answer to ping if not both interfaces on the serial link are configured correctly. This is especially true for the IP addresses; both interfaces on the serial link must have IP addresses in the same subnet before any of them answers to ping requests Check routing table Check the routing table of one of the routers. What command do you use? Interpret the information given? Copy the output from the command to the report, and give a description of it Debug Check the debug command. Make sure that the output from the debug process is written to your terminal by issuing the command terminal monitor. Setup debug of all IP packets. What command do you use? Hint: The first word in the command string is debug. From one router ping one of its neighbours. Copy the output to your report, and give an interpretation of the information therein. Before you end this sub-section you should turn off debugging. Use the command no debug all to turn off all debugging.
5 7.2 RIP As you found in the first section you cannot send IP packets through the network, for example from rtr1 to rtr3. To do this routing has to be added to the network. In this section you will add RIP, a distance vector protocol, as routing protocol in your network. We are going to investigate RIP version 1. First discuss static routing versus using a routing protocol. Add the discussion to your report Start RIP The first task is to start the RIP routing process on the routers. The configuring command router rip does this. Note that when issuing this command you enter the router rip configuration sub-mode. Configure version Add interfaces to RIP Now you have to assign interfaces to the RIP process. For this you use the router rip submode command network <network id>. The network command takes an argument, the network id of the interface(s) that shall be assigned to the RIP process. The network id is classful, so you must make sure that you enter a network command for all interfaces. With the command show ip protocol you get information about parameters and current state of routing processes running on the router. You also get information about which networks that are included in the routing process. Perform this command. Does the network information given correspond to the networks you have configured? Explain. When you have configured all five routers, check the routing information in router rtr1. What command do you use? Hint: It is not show ip protocol but it starts with show ip. Copy the output of this command into the report and give an explanation to the output. Hint: The path cost is the number following the slash inside the squared brackets. For example, [120/3] means the cost is 3. There are two paths to the network between rtr4 and rtr5. Why is that? Why isn t the path over the Ethernet between rtr1 and rtr4, which has a capacity of 20 times that of the serial link between rtr1 and rtr5, preferred? Study RIP updates Turn on debugging of RIP. What command do you use? How often does this router receive updates from its neighbours? What information is sent to this router? How often does this router send updates to its neighbours? What information does this router send to its neighbours? Note that the information is not the same to all neighbours. Which information is suppressed? What is the name of this suppression technique? Copy an example of a sent update into your report and explain the findings. Turn off debugging again.
6 7.2.4 Check path Now that you have full routing running in your network you can check if packets are forwarded the expected paths. You shall compare the routing table of rtr1 and the result of a traceroute. From the routing table in router rtr1 find the path to interface serial 1 of router rtr3. Which path will packets take? Do a traceroute to this interface. Add the output from this command to the report. Did the packets take the expected path? Study convergence in error situation In the last exercise on RIP you will study routing convergence at failure. For this you need two active terminal sessions, one to router rtr1 and one to router rtr4. First traceroute interface serial 1, the target host in this exercise, on rtr3 from rtr1 and make sure that the connection is ok and that the path is over rtr4. Make a note of the target s network id that is the link between rtr3 and rtr4. Check the routing table, especially for the target network id. On router rtr1 turn on debugging of RIP. Make sure the output is displayed on your terminal. Now introduce an error by shutting down interface Ethernet 0 on rtr4. Note the time! Ping the target host. What was the result? Compare with the routing table and explain! Observe periodically on router rtr1 the changes in the routing table concerning the target network at the same time as you observe the debugging output. Look for information concerning the target network! Hint: It is possible to perform normal commands while you have debugging active. The displayed output on the terminal might be somewhat crumbled in cases, but just re-issue the last command. Which routers announce the target network? Which path does the routing table indicate? What changes in debug output and routing table information do you observe, and at what time from when you introduced the error. How long did it take before an alternative path is used? Which path is now taken? At last, restore the network by opening interface Ethernet 0 on rtr4. Observe routing table and debug output. How long is the convergence time in this case? Explain your findings in the report! Turn off debugging. 7.3 OSPF In this section you shall compare a distance vector based routing protocol with a link state based routing protocol, OSPF. You will use the same network layout as in the RIP exercises, so you do not have to reconfigure the links Remove RIP First you have to remove all configurations concerning RIP. Use the configuration command no router rip.
7 7.3.2 Start OSPF In OSPF every router has a unique identity. Cisco routers use the largest IP address assigned to any interface in the router as the router id. The method works well until that interface goes down in which case the router id has to change and the OSPF process has to recalculate and resend its information to its neighbours. It is an advantage if the router id could be fixed, and independent of interface status. Therefore Cisco IOS has given precedence to loop back interfaces in the selection of router id. If there is a loop back interface configured on the router, and the loop back interface has been assigned an IP address, this IP address will be used as the router id. A loop back interface has the good side that it is very stable; it never goes down unless the whole router is going down. The conclusion is that it is good practise to always configure a loop back interface in every Cisco router that is to run OSPF. Start with configuring loop back interface 0 on all routers. Give each loop back interface a unique IP host address. What commands will you use? Hint: A host address is assigned if you combine the IP address with a subnet mask with all ones, i.e Now you can initiate OSPF on the routers. What command will you use? Hint: The command is very similar to that you used when you started RIP. There is one difference: OSPF needs a process ID. Pick a number from 1 to of your choice Add interfaces to OSPF Adding interfaces to the OSPF routing process is similar to that of RIP in that you use a network sub-mode command. But in the case of OSPF you have to state the network address space with a combination of a network id and a so-called wildcard mask. The wildcard mask is the one s complement to that of a subnet mask. Any bit set in the wildcard mask indicates a position in the network id that has no significance. You also use the network command to assign in which area an interface shall reside. In our case we will only use one area, the backbone area, for all networks. We therefore can use the same network command in all routers. The general form of the network command is network address wildcard-mask area area-id What command will you use to assign all interfaces in one router to OSPF backbone area? When you have configured all five routers, check the routing information in router rtr1. What command do you use? Copy the output of this command into the report and give an explanation to the output. Compare this output with the findings in exercise In what way does the cost differ? Hint: The path cost is the number following the slash inside the squared brackets. For example, [110/3] means the cost is 3. Also use the command show ip ospf interface to find more information about costs Check path Repeat exercise 7.2.4, but this time using OSPF. You shall compare the routing table of rtr1 and the result of a traceroute. From the routing table in router rtr1 find the path to interface serial 1 of router rtr3. What path will packets take?
8 Do a traceroute to this interface. Add the output from this command to the report. Did the packets take the expected path? Study OSPF updates and convergence in error situation Go to router rtr1 and turn on OSPF debugging. In this case you shall study OSPF events. What command do you use? What events occur? How often? What is the purpose of the information sent and received? Turn off debugging of OSPF events, and instead turn on debugging of OSPF flooding. Also check the routing table of router rtr1, especially concerning the target network. This is the same as in exercise i.e. the link between routers rtr4 and rtr3. What kind of messages are flooded by OSPF? When, or how often, are these messages sent? Which is the best path to the target host, the interface s1 of router rtr3? Shut down interface Ethernet 0 on router rtr4, and observe the output of the debugging on router rtr1? What is now the best path to our target network? Check with traceroute that this path is used. Open the interface again, and observe. Estimate the time from the interface status change (note! both changes!) to arrival of first message and update of the routing table. Compare it to your findings concerning RIP in exercise Now you can turn off debugging in router rtr1. 8 Cleaning Up Before leaving the router lab, please clean up. If you want to save your configuration files, use tftp to copy the running configuration. If you have changed only the running configuration the cleaning up procedure is merely a matter of reloading the routers. Otherwise, you have to restore the start-up configuration with the default configurations stored on the tftp server. See the Router Lab Reference Guide for details. 9 Last assignment As the last assignment please give your personal comments on this lab. How did you experience the lab? What was good, what was not so good? Was it relevant for the course? 10 Documentation URL Reference Guide to the Router Lab (link on router lab web page) Course Textbook
ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment
 Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2009-04-28 Jens A Andersson vers 2.0.5 ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment 1 Purpose and Goals This lab assignment will give a hands-on experience
Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2009-04-28 Jens A Andersson vers 2.0.5 ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment 1 Purpose and Goals This lab assignment will give a hands-on experience
IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols
 IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly
IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly
ETSF05: Internet Protocol Routing Project Assignment
 Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2014-11-10 Jens A Andersson vers 7.0.5 ETSF05: Internet Protocol Routing Project Assignment 1 Introduction The goal of this project is to study two different
Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2014-11-10 Jens A Andersson vers 7.0.5 ETSF05: Internet Protocol Routing Project Assignment 1 Introduction The goal of this project is to study two different
The Assignment is divided into preparation, practical part, and documentation.
 EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB
 INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
ETSF Routing Project WILLIAM TÄRNEBERG
 ETSF10 2015 Routing Project WILLIAM TÄRNEBERG The project 19 tasks Explore two different routing protocols and observe how they deal with failures and changes in the network. First phase Getting familiar
ETSF10 2015 Routing Project WILLIAM TÄRNEBERG The project 19 tasks Explore two different routing protocols and observe how they deal with failures and changes in the network. First phase Getting familiar
The Project Study two different routing protocols for intra domain Internet routing Hands-on experience
 ETSF05 2013 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Project Study two different routing protocols for intra domain Internet routing Hands-on experience configuring and managing routers how to set up routing
ETSF05 2013 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Project Study two different routing protocols for intra domain Internet routing Hands-on experience configuring and managing routers how to set up routing
The Lab. The lab (cont ) 5 (6) routers ETSF05 + ETSF The routing lab. Jens A Andersson. Many links (vlans) Front-end server
 ETSF05 + ETSF10 2011 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Lab 2 The lab (cont ) 5 (6) routers Cisco 1841 IOS vers 15 Many links (vlans) Front-end server Access to router lab tftp and ftp server for the
ETSF05 + ETSF10 2011 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Lab 2 The lab (cont ) 5 (6) routers Cisco 1841 IOS vers 15 Many links (vlans) Front-end server Access to router lab tftp and ftp server for the
Static Routing. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Lab : OSPF Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Introduction to Networks: Case Study, Option 2
 Introduction to Networks: Case Study, Option 2 Name: Name: Name: Academy username: Academy username: Academy username: Topology Diagram Assessment Objectives For an acceptable Case Study, the student must
Introduction to Networks: Case Study, Option 2 Name: Name: Name: Academy username: Academy username: Academy username: Topology Diagram Assessment Objectives For an acceptable Case Study, the student must
KTH CSC, OSPF lab, rev: 1.15 KTH CSC. OSPF lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH CSC OSPF lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 OSPF in pairs...5 3.1Turn on OSPF...5 3.2 Monitor
KTH CSC OSPF lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 OSPF in pairs...5 3.1Turn on OSPF...5 3.2 Monitor
For this lab boot into windows XP. Choose other option in grub and then choose earlier version of Windows.
 IIIT Hyderabad Advanced Computer Networks Lab 5 - Routers Routers Basic router configuration For this lab boot into windows XP. Choose other option in grub and then choose earlier version of Windows. Create
IIIT Hyderabad Advanced Computer Networks Lab 5 - Routers Routers Basic router configuration For this lab boot into windows XP. Choose other option in grub and then choose earlier version of Windows. Create
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
KTH/CSC, RIP lab, rev: 1.13 KTH/CSC. RIP lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC RIP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 RIP in pairs...4 4 Simple policy-options...5 5 RIP
KTH/CSC RIP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 RIP in pairs...4 4 Simple policy-options...5 5 RIP
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
KTHNOC, OSPF lab, rev: OSPF-lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTHNOC OSPF-lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Lab report...3 3 Preparations...3 3.1Preparations for area part...4 4
KTHNOC OSPF-lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Lab report...3 3 Preparations...3 3.1Preparations for area part...4 4
Module 5 Policy Based Routing
 Module 5 Policy Based Routing Objective: Using interesting lab exercises, the student will implement some of the fundamental techniques of Policy Routing, as applied in Cisco IOS. Prerequisite: Module
Module 5 Policy Based Routing Objective: Using interesting lab exercises, the student will implement some of the fundamental techniques of Policy Routing, as applied in Cisco IOS. Prerequisite: Module
Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key)
 Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Name:. Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Develop the IPv4 Address Scheme (15 points, 0 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device IPv4 and Security
Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Name:. Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Develop the IPv4 Address Scheme (15 points, 0 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device IPv4 and Security
OSPF DR and BDR Elections
 OSPF DR and BDR Elections In Chapter 6, Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), of the Sybex CCNA Study Guide Standard and CCNA Study Guide Deluxe Editions, I discussed EIGRP and OSPF
OSPF DR and BDR Elections In Chapter 6, Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), of the Sybex CCNA Study Guide Standard and CCNA Study Guide Deluxe Editions, I discussed EIGRP and OSPF
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
CCNA Boot Camp. Course Description
 CCNA Boot Camp Course Description CCNA Boot Camp combines both the Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1 (ICND1) course and the Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 2 (ICND2) course into one
CCNA Boot Camp Course Description CCNA Boot Camp combines both the Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1 (ICND1) course and the Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 2 (ICND2) course into one
Lab Network Baseline Discovery
 Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
ETSF The routing lab. Jens A Andersson
 ETSF05 2014 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Project Study two different routing protocols for intra domain Internet routing in two error situations Hands-on experience configuring and managing routers
ETSF05 2014 The routing lab Jens A Andersson The Project Study two different routing protocols for intra domain Internet routing in two error situations Hands-on experience configuring and managing routers
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points
 Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
CCRI Networking Technology I CSCO-1850 Spring 2014
 CCRI Networking Technology I CSCO-1850 Spring 2014 Instructor John Mowry Telephone 401-825-2138 E-mail jmowry@ccri.edu Office Hours Room 2126 Class Sections 102 Monday & Wednesday 6:00PM-9:50PM, starts
CCRI Networking Technology I CSCO-1850 Spring 2014 Instructor John Mowry Telephone 401-825-2138 E-mail jmowry@ccri.edu Office Hours Room 2126 Class Sections 102 Monday & Wednesday 6:00PM-9:50PM, starts
Claim desired outcome
 Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
OHLONE COLLEGE Ohlone Community College District OFFICIAL COURSE OUTLINE
 OHLONE COLLEGE Ohlone Community College District OFFICIAL COURSE OUTLINE I. Description of Course: 1. Department/Course: CNET - 155A 2. Title: Introduction to Networks (CCNA1) 3. Cross Reference: 4. Units:
OHLONE COLLEGE Ohlone Community College District OFFICIAL COURSE OUTLINE I. Description of Course: 1. Department/Course: CNET - 155A 2. Title: Introduction to Networks (CCNA1) 3. Cross Reference: 4. Units:
Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge
 Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Create a logical topology given network requirements
Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Create a logical topology given network requirements
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45
 Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals. Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 7 Objectives: Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks The objective of this experiment
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 7 Objectives: Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks The objective of this experiment
Chapter 6 Reading Organizer
 Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Time: 20 minutes Given an IP address and mask of (address / mask), design an IP addressing scheme that satisfies the following requirements. Network address/mask
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Time: 20 minutes Given an IP address and mask of (address / mask), design an IP addressing scheme that satisfies the following requirements. Network address/mask
Lab Manual. ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Information Technology Solutions. Prepared by: Eng. Altaf Al Farhan.
 Kuwait University Information Technology Solutions College of Computing Sciences and Engineering Department of Information Science Lab Manual ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Prepared by: Eng.
Kuwait University Information Technology Solutions College of Computing Sciences and Engineering Department of Information Science Lab Manual ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Prepared by: Eng.
Module 18 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
Hands-On ROUTE Implementing Cisco IP Routing CCNP Course 1
 Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands
 Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
PT Activity 5.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Course Outline. Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND ) official cert guide.
 Course Outline Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND1 100-105) official 13 May 2018 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led
Course Outline Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND1 100-105) official 13 May 2018 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led
Lab Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical, Data Link, and Network Layers I
 Lab 5.2.1 Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical, Data Link, and Network Layers I Objective Complete the laboratory exercise by defining, isolating, and correcting the problems outlined in the scenario
Lab 5.2.1 Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical, Data Link, and Network Layers I Objective Complete the laboratory exercise by defining, isolating, and correcting the problems outlined in the scenario
Course Outline. Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND ) official cert guide.
 Course Outline Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND1 21 Apr 2018 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led Training
Course Outline Pearson CISCO: CCENT/CCNA (ICND1 21 Apr 2018 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led Training
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Lab Applying a Logical Layered Model to a Physical Network
 Lab 3.1.1 Applying a Logical Layered Model to a Physical Network Objective In this exercise, you will use various Cisco IOS commands and a protocol analyzer to map the layers in the OSI model to the encapsulated
Lab 3.1.1 Applying a Logical Layered Model to a Physical Network Objective In this exercise, you will use various Cisco IOS commands and a protocol analyzer to map the layers in the OSI model to the encapsulated
Lab05-Postlab-CSPF. Or: Opaque LSAs, administrative link colouring, and Constrained LSPs
 The following notes for the NET3012-IP Architectures and Solutions course are based on the Nokia MPLS (p/n 3HE02276AA) and Nokia Services Architecture (p/n 3HE02277AA) courses from the Nokia Service Routing
The following notes for the NET3012-IP Architectures and Solutions course are based on the Nokia MPLS (p/n 3HE02276AA) and Nokia Services Architecture (p/n 3HE02277AA) courses from the Nokia Service Routing
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Chapter 7. RIP Version 2 (RIPv2)
 Chapter 7 RIP Version 2 (RIPv2) CCNA2-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must
Chapter 7 RIP Version 2 (RIPv2) CCNA2-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must
Cisco 2: Routing Technologies
 Western Technical College 10150120 Cisco 2: Routing Technologies Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 Total Hours 90.00 The emphasis
Western Technical College 10150120 Cisco 2: Routing Technologies Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 Total Hours 90.00 The emphasis
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS
 CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS COMPARISON OF NEW CURRICULA WITH EXISTING CURRICULA Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Routing Protocols and Concepts Summary New CCNA
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS COMPARISON OF NEW CURRICULA WITH EXISTING CURRICULA Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Routing Protocols and Concepts Summary New CCNA
CCENT ICND Pearson ucertify. Course Outline. CCENT ICND Pearson ucertify. 26 Mar
 Course Outline CCENT ICND1 100-105 Pearson ucertify 26 Mar 2019 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led
Course Outline CCENT ICND1 100-105 Pearson ucertify 26 Mar 2019 Contents 1. Course Objective 2. Pre-Assessment 3. Exercises, Quizzes, Flashcards & Glossary Number of Questions 4. Expert Instructor-Led
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing
 CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
ETSF Routing Project JENS A ANDERSSON
 ETSF10 2017 Routing Project JENS A ANDERSSON The project Objective: compare routing protocols in different error conditions First phase Getting familiar with it all Configure the routers and the lab environment
ETSF10 2017 Routing Project JENS A ANDERSSON The project Objective: compare routing protocols in different error conditions First phase Getting familiar with it all Configure the routers and the lab environment
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals
 CCNA Exploration 4.0 1. Network Fundamentals The goal of this course is to introduce you to fundamental networking concepts and technologies. These online course materials will assist you in developing
CCNA Exploration 4.0 1. Network Fundamentals The goal of this course is to introduce you to fundamental networking concepts and technologies. These online course materials will assist you in developing
NET323 D: NETWORKS PROTOCOLS
 1 NET323 D: NETWORKS PROTOCOLS Networks and Communication Systems Department TA. Anfal AlHazzaa Lab # 6 : Dynamic Route (OSPF Single area) Lab Objectives 2 To connect small LANs using routers. To configure
1 NET323 D: NETWORKS PROTOCOLS Networks and Communication Systems Department TA. Anfal AlHazzaa Lab # 6 : Dynamic Route (OSPF Single area) Lab Objectives 2 To connect small LANs using routers. To configure
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
OSPF Complex Error Message Troubleshooting
 OSPF Complex Error Message Troubleshooting Document ID: 118880 Contributed by Mohammed Muddasir Khan, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 01, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
OSPF Complex Error Message Troubleshooting Document ID: 118880 Contributed by Mohammed Muddasir Khan, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 01, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Module 14 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
Lab 9.6.3: EIGRP Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 172.18.64.1 255.255.192.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.202.133 255.255.255.252
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 172.18.64.1 255.255.192.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.202.133 255.255.255.252
Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
Overview of the Cisco NCS Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE3080F tutor to get assigned to your routers.
 EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
Lab 2.8.2: Challenge Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab
 2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab
 Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp
 Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network
 APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
Static routing lab KTH/CSC. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name 1. Name 2. Name 3. Name 4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
EXAM - HP0-Y52. Applying HP FlexNetwork Fundamentals. Buy Full Product.
 HP EXAM - HP0-Y52 Applying HP FlexNetwork Fundamentals Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/hp0-y52.html Examskey HP HP0-Y52 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
HP EXAM - HP0-Y52 Applying HP FlexNetwork Fundamentals Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/hp0-y52.html Examskey HP HP0-Y52 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
Additional Scenarios A P P E N D I X
 A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Router Configuration. Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals
 Router Configuration Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals Router Fundamentals Here, we will examine two types of networks:
Router Configuration Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals Router Fundamentals Here, we will examine two types of networks:
Static routing KTHNOC/SUNET. January 18, 2004
 Static routing KTHNOC/SUNET January 18, 2004 The goal with this lab is to introduce you to configuring a Cisco router and your workstation. You will also learn how to set up the router for static routing.
Static routing KTHNOC/SUNET January 18, 2004 The goal with this lab is to introduce you to configuring a Cisco router and your workstation. You will also learn how to set up the router for static routing.
IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
Cisco CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test. Version
 Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
ECE 4110 Internetwork Programming Lab 7: Configuring a Network Using RIP Routing Protocol. Prelab Questions
 ECE 4110 Internetwork Programming Lab 7: Configuring a Network Using RIP Routing Protocol Group Number: Member Names: Date Issued: March 26, 2013 Date Due: April 3, 2013 Last Edited: January 31, 2013 This
ECE 4110 Internetwork Programming Lab 7: Configuring a Network Using RIP Routing Protocol Group Number: Member Names: Date Issued: March 26, 2013 Date Due: April 3, 2013 Last Edited: January 31, 2013 This
Lab Student Lab Orientation
 Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security
 Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security Device Designation Device Name VLAN 1 Address Subnet mask S1 FC-ASW-1 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 PC1 Host 1 10.0.0.254 255.255.255.0 PC2 Host 2 10.0.0.253 255.255.255.0
Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security Device Designation Device Name VLAN 1 Address Subnet mask S1 FC-ASW-1 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 PC1 Host 1 10.0.0.254 255.255.255.0 PC2 Host 2 10.0.0.253 255.255.255.0
ICND IOS CLI Study Guide (CCNA)
 ICND2-200-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCNA) SWITCH CONFIGURATION STP (Change Options): 2. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst [pvst] OR [mst] 3. Assign PortFast and/or BPDU Guard (sub-interface cmd): a. spanning-tree
ICND2-200-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCNA) SWITCH CONFIGURATION STP (Change Options): 2. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst [pvst] OR [mst] 3. Assign PortFast and/or BPDU Guard (sub-interface cmd): a. spanning-tree
Lab Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical and Data Link Layers
 Lab 4.2.1 Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical and Data Link Layers Objective Complete the lab exercise by defining, isolating, and correcting the problems outlined in the network support activity
Lab 4.2.1 Troubleshooting Problems at the Physical and Data Link Layers Objective Complete the lab exercise by defining, isolating, and correcting the problems outlined in the network support activity
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II. DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario. For CCIE Candidates
 Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 ICND1
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 ICND1 Course Length: 5 days Course Delivery: Traditional Classroom Online Live Course Overview Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 ICND1 Course Length: 5 days Course Delivery: Traditional Classroom Online Live Course Overview Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0
ISP Workshop Lab. Module 2 OSPF Areas
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp
 IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
