KTHNOC, OSPF lab, rev: OSPF-lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
|
|
|
- Corey Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KTHNOC OSPF-lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature
2 Table of Contents 1 Goals Lab report Preparations Preparations for area part OSPF in pairs Turn on OSPF Monitor OSPF Redistributing static routes Redundant paths square...7 7Load balancing Shared network cross Backbone Areas Areas in the world Stub areas Totally stub areas NSSA Cleanup References
3 1 Goals The goal with this lab is to introduce you to the link-state OSPF routing protocol and to understand how to configure OSPF for a variety of networks. The lab is relatively long and will take two days. As previous labs, the scenario is an ISP where the workstations act as customers together with four virtual customer networks. You will start with single-area configurations, and will later proceed with multi-area networks. You will also connect all other groups into one OSPF network. 2 Preparations Before you begin this lab, please consult documents [1] and [2]. Ensure that you have the network map of topology 1 [3]. You should also have read the lecture notes and RFC pages about OSPF[4]. Extra material from vendors published on the web are also useful. Before you begin the lab, answer the following questions. Which OSPF message types are there? Describe LSA types 1 to 7. What is an advertising router with respect to LSAs? What is the role of a Designated Router? What is the role of a Backup Designated Router? How do you do the following in JunOS? 1. Check OSPF neighbours 2. Check the OSPF database 3. Check the OSPF (internal) routing table (NOTE: not the same as the global RIB). 4. Check which OSPF routes are installed in the (global) routing table 2.1 Preparations for area part These questions need to be answered before you start the area (Section 9) part of the lab. Normally, you do not start with areas until the second lab. What is the benefit of a regular area? Describe the differences between a (regular) area, a stub area, an NSSA and a totally stub area? Explain the differences in terms of how LSA:s are filtered or mapped. How do you do the following in JunOS? 3
4 1. Create an area 2. Create a stub area with a default route 3. Create a totally stub area 4. Create an NSSA 3 OSPF in pairs First start working in pairs, RTX1 with RTX4 and RTX2 with RTX3. Connect and bring up the network between the workstation and the router and configure the workstation with an IP address and static routes according to the topology map. Do not configure any more router interfaces than required for a pair. You can re-use an old configuration from earlier labs. Ensure that you can ping the router from the workstation, and between routers. Investigate the state of the router. In particular note all routes and be sure that you have understood which routes exists in the routing table. 3.1 Turn on OSPF Start with setting the router-id to X.Y. Assign this address to the loopback interface (By default, however, OSPF will use the first lo0 address as router-id). Turn on OSPF on the interfaces connecting you to your neighbour using area 0, the backbone. Also turn on OSPF on the interface to the work-station (fe-0/0/0). But since we do not expect an OSPF router to appear on the customer network declare it as passive. That is, do not run the OSPF protocol, but announce it as an internal OSPF network. Try to ping between your workstations. Also try to ping all the routers addresses, including the loopback addresses. Check OSPF neighbours and interfaces to verify that OSPF runs correctly. 4
5 Check the OSPF database using the detailed (or extensive) option. Explain the entries and fields in the entries in the database. In particular, which different types of LSA:s exist? Which links? Who is advertising router? Explain the sequence and age values. What does the asterisk in front of some LSAs indicate? Examine the OSPF internal routing table. For example, what does path type mean? Check the routing table. Do you see any OSPF routes? Why/ why not? Try disabling the interface between a work-station and a router and see how this influences the database and routing table. What happens (note that this will disconnect any ssh connections from that workstation)? Try configuring the interface down between the two routers. Study how the neighbour adjacency is reformed after the break. How long does it take before it is re-established? Also examine which router is DR, and which is BDR. Does this change when you disconnect? Milestone 1: Show a working pair in OSPF. 3.2 Monitor OSPF For debugging purposes, it might be useful to monitor the OSPF messages. Therefore, turn on traceoptions for hello, error and lsaupdates, and either monitor the results, or check the log now and then. If you monitor the log, it is recommended to do this in a separate ssh connection. 4 More routes To create a more realistic scenario, you shall now add more routes to your network. These routes represent more customer networks, Consult the topology map[3] and create the two first of the 10.X.Y.0/24 networks as secondary subnetworks on the host network 5
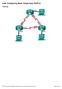
6 fe-0/0/0. Assign the.1 address of each of those networks to the interface. Then create the remaining two routes as static routes and redistribute them into OSPF using a policy. Set the.1 address of these two networks on the loopback (so that you can ping them later). How do these new routes appear in the OSPF database? Ensure that these networks appear also in the neighbour. After this has been done, you should be able to ping the four.1 addresses from the other routers. Can you also ping them from the workstations? If not, try adding a new static route to the /8 network on the workstation. Examine the ospf neighbours, database, routing table, etc. How have they changed? Try also restarting the routing processes and monitor with the show neighbour command the re-establishment. Which states does it go through and how long does it take to form adjacency? 5 Redundant paths square Now connect all four routers in a quad a square network as shown in the Figure. Do not connect the shared network /24. Examine the OSPF database and routing table and verify that you can ping from all routers and workstations to all other routers and workstations. In particular, ensure that you can reach the diagonal neighbour and workstation. 6
7 Now ping and traceroute diagonally (eg, RTX1 to RTX3) both to the other workstation and to the local addresses on the 10/8 network. Examine if all packets follow the same path or of they choose different paths. In particular, ping the four different loopback addresses on the diagonal router with the record-route option. Explain the result. Now examine how long OSPF takes to make failover by pinging to a neighbouring workstation (eg wsx1 to wsx2) and disabling the inteface between the closest routers (eg RTX1 and RTX2). How long does it take before the ping resumes. Which path does the traffic now take? Study how the LSAs are affected by the change. In particular, you should be able to examine all entries in the linkstate database (show ospf database), and explain all OSPF routes (show route protocol ospf). Milestone 2: Show a working square in OSPF. 6 Load balancing Use the same square configuration as in the previous part of the lab. Try now to the load balance traffic to the same address on a diagonal workstation or router. In order to achieve load-balancing you need to create a per-packet policy and export this policy into the forwarding-table. This will cause layer-3 load-balancing which causes address-pairs (and pings) to take separate paths. See [3] for details. Milestone 3: Load balancing. 7 Shared network cross 7
8 The fe-2/0/0 interface is connected to a hub shared by all your routers. It can be used to study OSPF over a transit network with more than two routers. Use the addresses assigned in the topology map. For this exercise, you shall use the monitor traffic command on the router to show the traffic in real time. When you configure OSPF on the routers' interfaces study (and list in report) the output of the monitor. Describe the messages being transferred. Describe which states the routers go through before they reach a stable state. Disable the interface connecting the DR to the net. Which machine becomes the next DR? How long does it take for the new DR to be assigned? Reconnect the old DR to the net. Does the old DR become DR again? If yes, how long does it take? Otherwise, why does it not become DR again? Illustrate with monitor output. Milestone 4: Transit link. 8 Backbone In this part, you will continue the previous section by connecting your square to the ``world'' by connecting the switches into one shared network 1. The goal is that everyone should be able to ping every other workstation and loopback address. A helpful attitude helps in this part of the lab. :-) 1 Depends on the progress on the other groups. 8
9 Study the database, routing tables, and the DR election on the shared network: What happens when two shared medium networks (with two DRs) are connected to each other? You are expected to get at least this far on the first lab. Milestone 5: Backbone 9 Areas Disconnect the hub and configure a square again (see Section 6). Keep the secondary, and static routes and loopback addresses. It is recommended that you restart your routers, or at least restart the routing process, so that you do not inherit old OSPF state. Disable the interface between RTX1 and RTX2 so that your topology looks like a U (lying down). Define two areas per group: RTX1 and RTX4 shares one area and RTX2 and RTX3 another. Call the areas 0.0.X.1 and 0.0.X.2, respectively, where X is 1 for group A, 2 for group B, etc. Let RTX4 and RTX3 communicate over the backbone area. Ensure now that your network works by pinging between all workstations and routers including the loopback interfaces. Examine your OSPF database to see if you can detect the new LSAs. Which new LSAs do you see? In particular, study the OSPF link-state database on RTX3 and RTX4. Explain the LSAs in the different area databases. Why do some seem to appear in both areas? What are their differences? Milestone 6: Areas in OSPF. 10 Areas in the world 1 Connect RTX4 to the world, that is, the Ethernet switch, and declare the interface (fe-2/0/0) as area 0. 1 Depends on the progress of other groups 9
10 The goal is to try to create one large OSPF network using areas. Try to ping all other groups. You can here also use monitor to see what is going on. 11 Stub areas Continue with the configuration from the section 9. But declare your sub-areas as stub areas, and inject a default route into the areas. Ensure now that your network works by pinging between all workstations and routers. Do this especially for the networks that are treated as external by OSPF. Examine the OSPF database and routes. What happens to the static routes inserted by RTX1 and RTX2? Why? Notice the default summary route in the stub-areas. As in the previous section, study the states of the routers. What are the differences between the regular areas? 11.1 Totally stub areas Make your two stub areas totally stub, that is, filter LSA-3's as well. What is the difference? Milestone 7: Stub areas. 12 NSSA In this part, you shall create Not-so-stubby areas. That is, you should be able to distribute the static routes from RTX1 and RTX2 again. Redefine your sub-areas as nssa areas. Again, go through the state of the routers, list the output in the report, and describe what happens. What new LSAs appear inside the sub-areas? How do the external routes appear outside of your area. What LSA are they? Milestone 8: NSSAs. 10
11 13 Cleanup To reset the machines to their initial state, follow the following steps for all routers. Reset the configuration by loading (using override) the /root/labconf configuration. Also do not forget to log out from your workstations. 14 References [1] KTHNOC Router lab Introduction - Juniper version [2] KTHNOC Router lab Reference - Juniper version [3] KTHNOC Router lab Netmap - Topology 1 [4] IETF RFC 2328, OSPF version 2 11
KTH CSC, OSPF lab, rev: 1.15 KTH CSC. OSPF lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH CSC OSPF lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 OSPF in pairs...5 3.1Turn on OSPF...5 3.2 Monitor
KTH CSC OSPF lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 OSPF in pairs...5 3.1Turn on OSPF...5 3.2 Monitor
KTH/CSC, RIP lab, rev: 1.13 KTH/CSC. RIP lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC RIP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 RIP in pairs...4 4 Simple policy-options...5 5 RIP
KTH/CSC RIP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 RIP in pairs...4 4 Simple policy-options...5 5 RIP
KTHNOC, MPLS/RSVP lab, rev: 1.7 KTHNOC. MPLS/RSVP lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTHNOC MPLS/RSVP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 2.1RSVP concepts...3 3 Initial configuration...4
KTHNOC MPLS/RSVP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 2.1RSVP concepts...3 3 Initial configuration...4
KTHNOC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.7. PIM-SM lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTHNOC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.7 KTHNOC PIM-SM lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Install multicast application...3
KTHNOC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.7 KTHNOC PIM-SM lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Install multicast application...3
MPLS/RSVP/BGP lab KTH CSC. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Name5. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH CSC MPLS/RSVP/BGP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Name5 Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Initial configuration...5 4 RSVP-signalled
KTH CSC MPLS/RSVP/BGP lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Name5 Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Initial configuration...5 4 RSVP-signalled
Introduction to Routing
 KTHNOC Introduction to Routing Introduction laboration to JunOS and dynamic routing protocols Table of contents 1 Goals, background and overview...3 2 Preparation Questions...3 2Preparation questions...3
KTHNOC Introduction to Routing Introduction laboration to JunOS and dynamic routing protocols Table of contents 1 Goals, background and overview...3 2 Preparation Questions...3 2Preparation questions...3
Static routing lab KTH/CSC. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name 1. Name 2. Name 3. Name 4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
KTH/CSC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.13 KTH/CSC. PIM-SM lab. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name1. Name2. Name3. Name4. Name5. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC PIM-SM lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Name5 Grade Instructor s Signature KTH/CSC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.12 Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Install the multicast
KTH/CSC PIM-SM lab Juniper version Group Nr Name1 Name2 Name3 Name4 Name5 Grade Instructor s Signature KTH/CSC, PIM-SM lab, rev: 1.12 Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparations...3 3 Install the multicast
Module 5 Advanced OSPF
 Module 5 Advanced OSPF ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement different types of OSPF areas and use advanced OSPF Features in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module 1 and OSPF presentation
Module 5 Advanced OSPF ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To implement different types of OSPF areas and use advanced OSPF Features in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module 1 and OSPF presentation
Router Lab Reference
 KTHNOC Router Lab Reference Juniper version Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Reference: Workstation...3 2.1 Configuring network access...3 2.2 Connecting to your router...4 3 Reference: Basic commands...4
KTHNOC Router Lab Reference Juniper version Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Reference: Workstation...3 2.1 Configuring network access...3 2.2 Connecting to your router...4 3 Reference: Basic commands...4
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
MikroTik RouterOS Training. Routing. Schedule. Instructors. Housekeeping. Introduce Yourself. Course Objective 7/4/ :00 10:30 Morning Session I
 MikroTik RouterOS Training Routing Schedule 09:00 10:30 Morning Session I 10:30 11:00 Morning Break 11:00 12:30 Morning Session II 12:30 13:30 Lunch Break 13:30 15:00 Afternoon Session I 15:00 15:30 Afternoon
MikroTik RouterOS Training Routing Schedule 09:00 10:30 Morning Session I 10:30 11:00 Morning Break 11:00 12:30 Morning Session II 12:30 13:30 Lunch Break 13:30 15:00 Afternoon Session I 15:00 15:30 Afternoon
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
OSPF. OSPF processs can be enabled on 2 levels
 OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
Introduction to OSPF OSPF. Link State Routing. Link State. Fast Convergence. Low Bandwidth Utilisation
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
Module 1b IS-IS. Prerequisites: The setup section of Module 1. The following will be the common topology used for the first series of labs.
 Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
DD2490 p Link-state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
OSPF Protocol Overview on page 187. OSPF Standards on page 188. OSPF Area Terminology on page 188. OSPF Routing Algorithm on page 190
 Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Question: 3 Which LSA type describes the router ID of ASBR routers located in remote areas?
 Volume: 65 Questions Question: 1 Which two statements describe aggregate routes? (Choose two.) A. Invalid routing prefixes are not advertised to external peers. B. Internal routing instabilities can be
Volume: 65 Questions Question: 1 Which two statements describe aggregate routes? (Choose two.) A. Invalid routing prefixes are not advertised to external peers. B. Internal routing instabilities can be
Configuring OSPF with CLI
 OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature
 OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability. Buy Full Product.
 Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco Exam Preparation Materials:
 2016 NEW Cisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-101: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Exam Questions and Answers RELEASED in Braindump2go.com Online IT Study Website Today! 2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco
2016 NEW Cisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-101: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Exam Questions and Answers RELEASED in Braindump2go.com Online IT Study Website Today! 2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Introduction to routing
 DD2490 p4 2010 Introduction to routing Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Network example: KTH Intranet Levels of abstraction The Internet is huge Necessary to divide the routing problem into sub-problems. There are
DD2490 p4 2010 Introduction to routing Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Network example: KTH Intranet Levels of abstraction The Internet is huge Necessary to divide the routing problem into sub-problems. There are
IT-Operation (2) OSPF. Who am I
 IT-Operation (2) OSPF yasu@wide.ad.jp Who am I Name: Yasuhiro Ohara 3rd grade of doctoral course in KEIO Univ. Author of Zebra ospf6d One of WIDE 6Bone operators developer or researcher rather than operator
IT-Operation (2) OSPF yasu@wide.ad.jp Who am I Name: Yasuhiro Ohara 3rd grade of doctoral course in KEIO Univ. Author of Zebra ospf6d One of WIDE 6Bone operators developer or researcher rather than operator
Any individual involved in implementation and verification of routing protocols in the enterprise networks
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING Information Length: 5 Days Courseware : Course code: Delivery Type Included CIS_ROUTE Classroom Description Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v1.0 is a five-day course
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING Information Length: 5 Days Courseware : Course code: Delivery Type Included CIS_ROUTE Classroom Description Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v1.0 is a five-day course
ROUTING CONSORTIUM. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) NSSA Option Test Suite. Technical Document. Revision 1.9
 ROUTING CONSORTIUM Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) NSSA Option Test Suite Technical Document Revision 1.9 University of New Hampshire 121 Technology Drive, Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824-3525 Routing Consortium
ROUTING CONSORTIUM Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) NSSA Option Test Suite Technical Document Revision 1.9 University of New Hampshire 121 Technology Drive, Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824-3525 Routing Consortium
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
DD2490 p Lecture 4: OSPF. Link-state routing and Open Shortest Path First. Olof Hagsand KTH CSC
 DD2490 p4 20 Lecture 4: OSPF Link-state routing and Open Shortest Path First Olof Hagsand KTH CSC OSPF is the routing protocol that we deal with in most detail in this course. OSPF is a complex protocol,
DD2490 p4 20 Lecture 4: OSPF Link-state routing and Open Shortest Path First Olof Hagsand KTH CSC OSPF is the routing protocol that we deal with in most detail in this course. OSPF is a complex protocol,
ISP Workshop Lab. Module 2 OSPF Areas
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
ISP Workshop Lab Module 2 SPF Areas bjective: To migrate from one flat SPF topology to SPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite: Module
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
GuideTorrent. The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider
 GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT)
GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT)
DD2490 p Link state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD490 p4 00 Link state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 3: Section except.. Section 3 (areas), but only last two paragraphs of 3.5 Link state routing Each router spreads information
DD490 p4 00 Link state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 3: Section except.. Section 3 (areas), but only last two paragraphs of 3.5 Link state routing Each router spreads information
DD2490 p Link-state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2490 p4 2009 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex)
DD2490 p4 2009 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex)
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
IPv6 Module 2 OSPF Areas
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 2 OSPF Areas Objective: To migrate from one flat OSPF topology to OSPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 2 OSPF Areas Objective: To migrate from one flat OSPF topology to OSPF areas, plus introduce neighbour authentication and area summarisation in the lab network. Prerequisite:
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
CCNP 1: Advanced Routing
 Scope and Sequence CCNP 1: Advanced Routing Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 3.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CCNP 1: ADVANCED ROUTING...1 TARGET AUDIENCE...3 PREREQUISITES...3 COURSE DESCRIPTION...3 COURSE
Scope and Sequence CCNP 1: Advanced Routing Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 3.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CCNP 1: ADVANCED ROUTING...1 TARGET AUDIENCE...3 PREREQUISITES...3 COURSE DESCRIPTION...3 COURSE
OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2)
 OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Abstract from RFC 3101 Section 2.5 Abstract
OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Abstract from RFC 3101 Section 2.5 Abstract
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network
 APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Routing Protocols. Technology Description BGP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for routing protocols, as follows: Technology Description, page 11-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 11-3 Vendor-Specific
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for routing protocols, as follows: Technology Description, page 11-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 11-3 Vendor-Specific
ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment
 Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2010-10-13 Jens A Andersson vers 3.1 ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment 1 Purpose and Goals This lab assignment will give a hands-on experience
Dept of Electrical and Information Technology 2010-10-13 Jens A Andersson vers 3.1 ETS110: Internet Protocol Routing Lab Assignment 1 Purpose and Goals This lab assignment will give a hands-on experience
OSPF Commands: A through Z
 OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
Lab 2 Postlab: Multi-area OSPF Or: Simple multi-area, ASBR, Stub, Totally stubby, NSSA
 The following notes for the NET3012-IP Architectures and Solutions course are based on the Nokia MPLS (p/n 3HE02276AA) and Nokia Services Architecture (p/n 3HE02277AA) courses from the Nokia Service Routing
The following notes for the NET3012-IP Architectures and Solutions course are based on the Nokia MPLS (p/n 3HE02276AA) and Nokia Services Architecture (p/n 3HE02277AA) courses from the Nokia Service Routing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols
 IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly
IP Routing Lab Assignment Configuring Basic Aspects of IP IGP Routing Protocols 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly
Standard Areas OSPF AREA TYPES:
 OSPF AREA TYPES: OSPF relies on several types of Link State Advertisements (LSAs) to communicate link state information between neighbors. A brief review of the most applicable LSA types: Type 1 - Represents
OSPF AREA TYPES: OSPF relies on several types of Link State Advertisements (LSAs) to communicate link state information between neighbors. A brief review of the most applicable LSA types: Type 1 - Represents
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ]
![Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ]](/thumbs/85/92097848.jpg) s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which connection method do OSPF
s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which connection method do OSPF
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
 OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
4A Alcatel-Lucent. Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
 Alcatel-Lucent 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/4a0-101 QUESTION: 297 Click on the exhibit. In
Alcatel-Lucent 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/4a0-101 QUESTION: 297 Click on the exhibit. In
Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of opaque LSAs 40 Configuring OSPF to
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3
 Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Hands-On ROUTE Implementing Cisco IP Routing CCNP Course 1
 Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability
 OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
OSPF Commands. adjacency stagger, page 7. authentication-key (OSPF), page 14
 OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
The Assignment is divided into preparation, practical part, and documentation.
 EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
EINTE LAB EXERCISES LAB EXERCISE #4 IGP ROUTING PURPOSE AND GOALS This lab assignment will give you a hands-on experience in configuring and managing routers and particularly in setting up IP routing protocols.
OSPFv2 deep dive. Михайловский Василий Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015
 OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs
 Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto two different upstream ISPs. Prerequisites: Module 12 and Multihoming
Module 13 Multihoming to Different ISPs ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto two different upstream ISPs. Prerequisites: Module 12 and Multihoming
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Module 18 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 18 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Veryx ATTEST TM. Sample Test cases Overview. Conformance Test Suite. Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2)
 Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) Sample Test cases Overview Part Number: T / TCLS OSPFv2 1.0-1110/1.0 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction
Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) Sample Test cases Overview Part Number: T / TCLS OSPFv2 1.0-1110/1.0 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1
 IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
Exam Questions 4A0-101
 Exam Questions 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/4a0-101/ 1.When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match in the routing
Exam Questions 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/4a0-101/ 1.When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match in the routing
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://
 IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.How
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.How
OSPF. Unless otherwise noted, OSPF refers to OSPFv2 throughout this document.
 Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
Network Working Group. Category: Standards Track Stanford University March 1994
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
Introduction to IS-IS
 Introduction to IS-IS ISP Workshops Last updated 28 November 2013 1 IS-IS p Intermediate System to Intermediate System p ISO 10589 specifies OSI IS-IS routing protocol for CLNS traffic n A Link State protocol
Introduction to IS-IS ISP Workshops Last updated 28 November 2013 1 IS-IS p Intermediate System to Intermediate System p ISO 10589 specifies OSI IS-IS routing protocol for CLNS traffic n A Link State protocol
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
INTERNET LABORATORY PROJECT. EIGRP Routing Protocol. Abhay Tambe Aniruddha Deshmukh Sahil Jaya
 INTERNET LABORATORY PROJECT on EIGRP Routing Protocol by Abhay Tambe Aniruddha Deshmukh Sahil Jaya INTRODUCTION TO EIGRP SETUP FOR LAB: This lab uses two different network topologies. The first network
INTERNET LABORATORY PROJECT on EIGRP Routing Protocol by Abhay Tambe Aniruddha Deshmukh Sahil Jaya INTRODUCTION TO EIGRP SETUP FOR LAB: This lab uses two different network topologies. The first network
Logging neighbor state changes 38 Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point
 IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
