Chao Li Thomas Su Cheng Lu
|
|
|
- Beryl Wilkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMPT885 High-Performance Network Final Project Presentation Transport Protocols on IP Multicasting Chao Li Thomas Su Cheng Lu {clij, tmsu, School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University 4/20/01 1
2 Roadmap Introduction Implementation Details Centralized Approach Scalable Reliable Multicast Tree Based Reliable Multicast Discussion References 4/20/01 2
3 Introduction of Our Project Why we need multicast? Why we need multicast transport protocol? What we will do in our project? 4/20/01 3
4 Introduction of Multicast Unicast Vs Multicast Multiple copy Vs single copy Datalink Layer Support for Multicast Network Layer Support for Multicast Multicast routing Group membership management Group network addressing 4/20/01 4
5 Multicast Transport Protocols Why not just run TCP over Multicast? Multicast Transport Protocols Centralized Approach Unstructured Approach Scalable Reliable Multicast (SRM) Distributed Approach Tree-based Multicast Transport Protocols (TMTP) 4/20/01 5
6 Centralized Multicast Feature Rely on a central site Negative acknowledgment (NACK or NAK) Slotting Advantages Simplicity and ease of implemention Disadvantages 4/20/01 6
7 SRM- Scalable Reliable Multicast Requires only basic IP delivery model Every member is responsible for loss recovery Allow to a wide range of group size 4/20/01 7
8 SRM- Scalable Reliable Multicast Three types of messages Session message Request message Repair message Messages are multicast to the entire group 4/20/01 8
9 SRM- Scalable Reliable Multicast Session messages Report the highest sequence # received by every member Provide information for sender/receivers (status, # of participants, etc.) Estimate host-to-host distance (needed for repair) 4/20/01 9
10 SRM- Scalable Reliable Multicast Request messages loss detected when there is a gap in the sequence # A host wait a random time before multicast the request to the group Any host that has a copy of the requested data can answer 4/20/01 10
11 SRM- Scalable Reliable Multicast Repair messages Wait a random time before multicast the repair packet to the group 4/20/01 11
12 Simulation Environment Topology(from[8][9]) Source Campus Network Campus Network 3Mbit/s Link 1.5Mbit/s Link 4/20/01 12
13 Configuration Details Backgrou nd traffic HTTP Each campus network has one web server, other nodes are clients # of Sessions 800 # of page components 3 TCP/FTP page component size 12KB Senders/receivers spared all over Session interval 10s burst size 80,000 byte The credit goes to Velibor Markovski 4/20/01 13
14 More Configuration Details Multicast traffic CBR traffic (0.04s) 1 sender and 9 receivers 512 packet size Start at 10s for 200sec. Session message frequency 2s(SRM default) More experiment data will be collected on -Larger group size -Star war Trace 4/20/01 14
15 Snapshot(topology) 4/20/01 15
16 Snapshot(router) 4/20/01 16
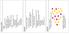
17 Simulation Results(Request delay) Comparision of Request Delay Centralized Multicast 1.4 SRM Average Request Delay /20/ Receiver Node
18 Simulation Results(Request duplicate) Camparision of Request Duplicate Average Request Duplicate Centralized Multicast SRM /20/01 Receiver Node 18
19 Tree-based Multicast Transport Protocol (TMTP) We are Implementing this protocol in ns2 using C++ and TCl
20 TMTP key features It exploits the IP multicast for packet routing and delivery. It dynamically organize the participants into hierarchical control tree. It achieves scalable reliable multicast via hierarchical control tree used for flow and error control.
21 TMTP hierarchical control tree It organizes the participants into a hierarchical domain. A domain manager(dm) acts as a representative of each domain. Every DM performs two roles for the responsibility for reliability inter-domain and intra-domain.
22 TMTP control tree management The control tree grows and shrinks dynamically in response to additions and deletions to and from the multicast group.
23 TMTP Join Tree A new DM executes an expanding ring search to join the control tree. The JoinTree algorithm Utilizes a time-to-live value (TTL). While (NotDone( NotDone){ Multicast a SEARCH-PARENT msg Collect respondses If (no responses) Increment TTL // try again Else select closet respondent as parent send JOIN-REQ to parent wait for JOIN-CONFIRM reply if (JOIN-CONFIRM received) NotDone = False Else //try again }
24 TMTP Leave Tree A DM only leave the tree after its last local member leaves the group. Internal managers is complicated. Leaf managers is straightforward. If ( I am a leaf manager) send LEAVE-TREE to parent receive LEAVE-CONFIRM terminate Else // I am an internal manager Fullfill all pending obligations send FIND-NEW-PARENT to children receive FIND-NEW-PARENT from all children send LEAVE-TREE to parent
25 TMTP error control(1) An important concept: - limited scope multicast messages It restricts the scope of a multicast message. It sets the TTL value in IP header: multicast radius.
26 TMTP error control(2) TMTP uses 2 error control techniques: sender initiated approach: Periodic positive ACK for receiver, Timeout, Retransmissions (limited scope multicast). receiver initiated approach: Negative ACK (NACK) to sender, NACk is restricted and suppressed, Retransmissions (limited scope multicast).
27 TMTP Flow control Window-based flow control T ack T ack Timer T ack 2 timers: T retrans retrans and T ack T retrans T retrans + T ack T retrans retrans +2 T ack T retrans =n*t ack, n=3 retrans =n*t
28 Test environment (2) We use standard IP multicast; We implement a sender-initiated reliable multicast transport agent using ns2; T ack = RTT, T retrans =3*T ack multicast traffic
29 Performance measure End-to-end delay Packet loss Bandwidth consuming
30 Some comments It is not flexible periodically JoinTree to change hierarchy
31 Reference [1] M. Banikazemi. IP Multicasting: Concepts, Algorithms, and Protocols, IGMP, RPM, CBT, DVMRP, MOSPF, PIM, MBONE, ; charly.kjist.ac..ac.kr/~dwlee/homepage/ipmulitcast.htm [2] B. Williamson. Developing IP Multicasting Networks Volume 1 - Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol and Multicast Open Shortest Path First, pp pp , Cisco Press, [3] E. C. Douglas, Internetworking with TCP/IP Volume 1 - Internet Multicasting (IGMP), pp , Prentice-Hall, Inc., [4] S. Deering,, D. Estrin,, D. Farinacci,, V. Jacobson, C. G. Liu, and L. Wei, An Architecture for Wide-Area Multicast Routing, ACM SIGCOMM '94,, vol. 24 no. 4, pp [5] S. Floyd, V. Jacobson, C.-G. Liu, S. McCanne.. and L. Zhang. A Reliable Mulitcast Framework for Light-weight Sessions and Application Level Framing, ACM SIGCOMM 95,, Aug. 1995, pp /20/01 31
32 [6] S. Armstrong, A. Freier,, K. Marzullo, RFC 1301: Multicast Transport Protocol, Feb. 1992, cis.ohio-state. -state.edu/cgi- bin/rfc rfc/rfc1301.html [7] B. Whetten,, G. Taskale. An Overview of Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol II, IEEE Network,, Jan/Feb 2000, pp ; komunikasi.org/.org/pdf/multicast/reliable-multicast-transport- protocol-ii.pdf pdf [8] M. T. Lucas, B. J. Dempsey, and A. C. Weaver. MESH: Distributed Error Recovery for Multimedia Streams in Wide-Area Multicast Networks, In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communication (ICC '97),, pp , June [9] M. T. Lucas. Efficient Data Distribution in Large-Scale Multicast Networks, Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Computer Science, University of Virginia, May [10] M. Goncalves and K. Niles, IP Multicasting, Concepts and Applications, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1998, pp , pp , pp /20/01 32
33 [11] ns-2 network simulator: isi.edu/nsnam/ns [12] Star Wars trace in ns format: att.com/~.com/~breslau/vint/trace.html [13] C. Hanle and M. Hofmann, Performance Comparison of Reliable Multicast Protocols using the Network Simulator ns- 2, Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN),, Boston, MA, USA, October 11-14, [14] V. Markovski, Simulation and Analysis of Loss in IP Networks Simulation scenarios, M. Sci.. Thesis, Department of Engineering Science, Simon Fraser University, Oct. 2000, pp [15] R. Yavatkar,, J. Griffioen,, and M. Suda. A A Reliable Dissemination Protocol for Interactive Collaborative Application, In Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia 95 Conference,, Nov /20/01 33
34 Individual contribution Chao Li: topology construction centralized approach Thomas Su: topology construction SRM background traffic Cheng Lu: building a TMTP agent into ns2 4/20/01 34
35 Thanks 4/20/01 35
Multicast EECS 122: Lecture 16
 Multicast EECS 1: Lecture 16 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Broadcasting to Groups Many applications are not one-one Broadcast Group collaboration
Multicast EECS 1: Lecture 16 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Broadcasting to Groups Many applications are not one-one Broadcast Group collaboration
Scalable Session Messages in SRM
 Scalable Session Messages in SRM Puneet Sharma Information Sciences Institute University of Southern California 4676 Admiralty Way Marina del Rey, CA 9291 Ph: 31-822-1511 ext. 742 Fax: 31-823-6714 puneet@isi.edu
Scalable Session Messages in SRM Puneet Sharma Information Sciences Institute University of Southern California 4676 Admiralty Way Marina del Rey, CA 9291 Ph: 31-822-1511 ext. 742 Fax: 31-823-6714 puneet@isi.edu
Contents. Overview Multicast = Send to a group of hosts. Overview. Overview. Implementation Issues. Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth
 EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
Reliable Multicast in Mobile Networks
 Reliable Multicast in Mobile Networks Pasi Tiihonen and Petri Hiirsalmi Lappeenranta University of Technology P.O. Box 20 FIN-53851 Lappeenranta, Finland, {Pasi Tiihonen, Petri Hiirsalmi}@lut.fi Key words:
Reliable Multicast in Mobile Networks Pasi Tiihonen and Petri Hiirsalmi Lappeenranta University of Technology P.O. Box 20 FIN-53851 Lappeenranta, Finland, {Pasi Tiihonen, Petri Hiirsalmi}@lut.fi Key words:
Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
 Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
Multicast Communications. Slide Set were original prepared by Dr. Tatsuya Susa
 Multicast Communications Slide Set were original prepared by Dr. Tatsuya Susa Outline 1. Advantages of multicast 2. Multicast addressing 3. Multicast Routing Protocols 4. Multicast in the Internet 5. IGMP
Multicast Communications Slide Set were original prepared by Dr. Tatsuya Susa Outline 1. Advantages of multicast 2. Multicast addressing 3. Multicast Routing Protocols 4. Multicast in the Internet 5. IGMP
A Reliable Multicast Framework for Light-weight Sessions. and Application Level Framing. Sally Floyd, Van Jacobson, Steve McCanne.
 A Reliable Multicast Framework for Light-weight Sessions and Application Level Framing Sally Floyd, Van Jacobson, Steve McCanne Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Ching-Gung Liu University of Southern
A Reliable Multicast Framework for Light-weight Sessions and Application Level Framing Sally Floyd, Van Jacobson, Steve McCanne Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Ching-Gung Liu University of Southern
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet
 ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2013, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Jens Andersson (Kaan Bür) Routing on the Internet Unicast routing protocols (part 2) [ed.5 ch.20.3] Multicast routing, IGMP [ed.5
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2013, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Jens Andersson (Kaan Bür) Routing on the Internet Unicast routing protocols (part 2) [ed.5 ch.20.3] Multicast routing, IGMP [ed.5
Flow Control in Reliable Multicast Protocol
 Flow Control in Reliable Multicast Protocol Flow Control in Reliable Multicast Protocol Ali M. Alsaih Department of Communication Technology and Networks University Putra Malaysia Abstract A Flow Control
Flow Control in Reliable Multicast Protocol Flow Control in Reliable Multicast Protocol Ali M. Alsaih Department of Communication Technology and Networks University Putra Malaysia Abstract A Flow Control
An analysis of retransmission strategies for reliable multicast protocols
 An analysis of retransmission strategies for reliable multicast protocols M. Schuba, P. Reichl Informatik 4, Aachen University of Technology 52056 Aachen, Germany email: marko peter@i4.informatik.rwth-aachen.de
An analysis of retransmission strategies for reliable multicast protocols M. Schuba, P. Reichl Informatik 4, Aachen University of Technology 52056 Aachen, Germany email: marko peter@i4.informatik.rwth-aachen.de
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol
 Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E-mail: sjkoh@pec.etri.re.kr Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple practical
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E-mail: sjkoh@pec.etri.re.kr Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple practical
Lecture 6: Multicast
 Lecture 6: Multicast Challenge: how do we efficiently send messages to a group of machines? Need to revisit all aspects of networking Last time outing This time eliable delivery Ordered delivery Congestion
Lecture 6: Multicast Challenge: how do we efficiently send messages to a group of machines? Need to revisit all aspects of networking Last time outing This time eliable delivery Ordered delivery Congestion
Implementation of a Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol (RMTP)
 Implementation of a Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol (RMTP) Greg Nilsen University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA nilsen@cs.pitt.edu April 22, 2003 Abstract While many network applications can be created
Implementation of a Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol (RMTP) Greg Nilsen University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA nilsen@cs.pitt.edu April 22, 2003 Abstract While many network applications can be created
Audio Streams Merging Over ALMI
 Audio Streams Merging Over ALMI Christopher J. Dunkle, Zhen Zhang, Sherlia Y. Shi, Zongming Fei Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 301 Rose Street, 2 nd floor Lexington, KY 40506-0495,
Audio Streams Merging Over ALMI Christopher J. Dunkle, Zhen Zhang, Sherlia Y. Shi, Zongming Fei Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 301 Rose Street, 2 nd floor Lexington, KY 40506-0495,
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet
 ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2012, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Kaan Bür, Jens Andersson Routing on the Internet Unicast routing protocols (part 2) [ed.4 ch.22.4] [ed.5 ch.20.3] Forwarding
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2012, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Kaan Bür, Jens Andersson Routing on the Internet Unicast routing protocols (part 2) [ed.4 ch.22.4] [ed.5 ch.20.3] Forwarding
CS 268: IP Multicast Routing
 Motivation CS 268: IP Multicast Routing Ion Stoica April 8, 2003 Many applications requires one-to-many communication - E.g., video/audio conferencing, news dissemination, file updates, etc. Using unicast
Motivation CS 268: IP Multicast Routing Ion Stoica April 8, 2003 Many applications requires one-to-many communication - E.g., video/audio conferencing, news dissemination, file updates, etc. Using unicast
Broadcast and Multicast Routing
 Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
Light-weight Reliable Multicast Protocol
 Light-weight Reliable Multicast Protocol Tie Liao INRIA, Rocquencourt, BP 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France Tie.Liao@inria.fr Abstract This paper describes the design and implementation of LRMP, the Light-weight
Light-weight Reliable Multicast Protocol Tie Liao INRIA, Rocquencourt, BP 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France Tie.Liao@inria.fr Abstract This paper describes the design and implementation of LRMP, the Light-weight
University of Delaware. Ucl London. Rutgers. ICSI, Berkeley. Purdue. Mannheim Germany. Wash U. T_ack T_ack T_ack T_ack T_ack. Time. Stage 1.
 Reliable Dissemination for Large-Scale Wide-Area Information Systems Rajendra Yavatkar James Grioen Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Abstract This paper describes a reliable multicast
Reliable Dissemination for Large-Scale Wide-Area Information Systems Rajendra Yavatkar James Grioen Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Abstract This paper describes a reliable multicast
Randomization. Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples:
 Randomization Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples: Ethernet multiple access protocol Router (de)synchronization Switch scheduling 1 Ethernet Single shared broadcast channel 2+ simultaneous
Randomization Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples: Ethernet multiple access protocol Router (de)synchronization Switch scheduling 1 Ethernet Single shared broadcast channel 2+ simultaneous
Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples: Ethernet multiple access protocol Router (de)synchronization Switch scheduling
 Randomization Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples: Ethernet multiple access protocol Router (de)synchronization Switch scheduling 1 Ethernet Single shared broadcast channel 2+ simultaneous
Randomization Randomization used in many protocols We ll study examples: Ethernet multiple access protocol Router (de)synchronization Switch scheduling 1 Ethernet Single shared broadcast channel 2+ simultaneous
Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast Routing Distance Vector Link State. Shared tree.
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 10 Internet Routing: Multicast Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast Routing Distance Vector
CSE 123A Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 10 Internet Routing: Multicast Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast Routing Distance Vector
CSE 123A Computer Networks
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 12 Internet Routing: Multicast Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast Routing Limiters
CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 12 Internet Routing: Multicast Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast Routing Limiters
Developing IP Muiticast Networks
 Developing IP Muiticast Networks Volume I Beau Williamson Cisco SYSTEMS CISCO PRESS Cisco Press 201 West 103rd Street Indianapolis, IN 46290 USA Table of Contents Introduction xviii Part I Fundamentals
Developing IP Muiticast Networks Volume I Beau Williamson Cisco SYSTEMS CISCO PRESS Cisco Press 201 West 103rd Street Indianapolis, IN 46290 USA Table of Contents Introduction xviii Part I Fundamentals
AN IMPROVED STEP IN MULTICAST CONGESTION CONTROL OF COMPUTER NETWORKS
 AN IMPROVED STEP IN MULTICAST CONGESTION CONTROL OF COMPUTER NETWORKS Shaikh Shariful Habib Assistant Professor, Computer Science & Engineering department International Islamic University Chittagong Bangladesh
AN IMPROVED STEP IN MULTICAST CONGESTION CONTROL OF COMPUTER NETWORKS Shaikh Shariful Habib Assistant Professor, Computer Science & Engineering department International Islamic University Chittagong Bangladesh
Broadcast Routing. Multicast. Flooding. In-network duplication. deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient:
 Broadcast Routing Multicast deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient: duplicate duplicate creation/transmission duplicate source duplication in-network duplication
Broadcast Routing Multicast deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient: duplicate duplicate creation/transmission duplicate source duplication in-network duplication
Different Layers Lecture 20
 Different Layers Lecture 20 10/15/2003 Jian Ren 1 The Network Layer 10/15/2003 Jian Ren 2 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every host,
Different Layers Lecture 20 10/15/2003 Jian Ren 1 The Network Layer 10/15/2003 Jian Ren 2 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every host,
Multicast Transport Protocol Analysis: Self-Similar Sources *
 Multicast Transport Protocol Analysis: Self-Similar Sources * Mine Çağlar 1 Öznur Özkasap 2 1 Koç University, Department of Mathematics, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Koç University, Department of Computer Engineering,
Multicast Transport Protocol Analysis: Self-Similar Sources * Mine Çağlar 1 Öznur Özkasap 2 1 Koç University, Department of Mathematics, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Koç University, Department of Computer Engineering,
A Randomized Error Recovery Algorithm for Reliable Multicast
 1 A Randomized Error Recovery Algorithm for Reliable Multicast Zhen Xiao, Kenneth P. Birman Abstract An efficient error recovery algorithm is essential for reliable multicast in large groups. Tree-based
1 A Randomized Error Recovery Algorithm for Reliable Multicast Zhen Xiao, Kenneth P. Birman Abstract An efficient error recovery algorithm is essential for reliable multicast in large groups. Tree-based
AMRIS: A Multicast Protocol for Ad hoc Wireless Networks
 of AMRIS: A Multicast Protocol for Ad hoc Wireless Networks C.W. Wu, Y.C. Tay National University of Singapore wuchunwei@alum.comp.nus.edu.sg,tay@acm.org Abstract This paper introduces AMRIS, a new multicast
of AMRIS: A Multicast Protocol for Ad hoc Wireless Networks C.W. Wu, Y.C. Tay National University of Singapore wuchunwei@alum.comp.nus.edu.sg,tay@acm.org Abstract This paper introduces AMRIS, a new multicast
Distributed Systems Multicast & Group Communication Services
 Distributed Systems 600.437 Multicast & Group Communication Services Department of Computer Science The Johns Hopkins University 1 Multicast & Group Communication Services Lecture 3 Guide to Reliable Distributed
Distributed Systems 600.437 Multicast & Group Communication Services Department of Computer Science The Johns Hopkins University 1 Multicast & Group Communication Services Lecture 3 Guide to Reliable Distributed
IP Multicast. Overview. Casts. Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 2001
 IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
How did IP Multicast get so complicated?
 How did IP Multicast get so complicated? Mark Handley ACIRI mjh@aciri.org Overview IP Multicast Service Model Multicast Addresses DVMRP (1988-1993) Broadcast and Prune PIM-DM (~1993) DVMRP for "real" routers
How did IP Multicast get so complicated? Mark Handley ACIRI mjh@aciri.org Overview IP Multicast Service Model Multicast Addresses DVMRP (1988-1993) Broadcast and Prune PIM-DM (~1993) DVMRP for "real" routers
Bridge-Node Selection and Loss Recovery in Island Multicast
 Bridge-Node Selection and Loss Recovery in Island Multicast W.-P. Ken Yiu K.-F. Simon Wong S.-H. Gary Chan Department of Computer Science The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Clear Water
Bridge-Node Selection and Loss Recovery in Island Multicast W.-P. Ken Yiu K.-F. Simon Wong S.-H. Gary Chan Department of Computer Science The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Clear Water
Advanced Networking. Multicast
 Advanced Networking Multicast Renato Lo Cigno Renato.LoCigno@dit.unitn.it Homepage: disi.unitn.it/locigno/index.php/teaching-duties/advanced-networking Multicasting Addresses that refer to group of hosts
Advanced Networking Multicast Renato Lo Cigno Renato.LoCigno@dit.unitn.it Homepage: disi.unitn.it/locigno/index.php/teaching-duties/advanced-networking Multicasting Addresses that refer to group of hosts
Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting
 Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting In this paper, we propose a simple and practical scheme for many-to-many IP multicasting. The proposed scheme is based on the core based tree
Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting In this paper, we propose a simple and practical scheme for many-to-many IP multicasting. The proposed scheme is based on the core based tree
Supporting IP Multicast for Mobile Hosts. Yu Wang Weidong Chen. Southern Methodist University. May 8, 1998.
 Supporting IP Multicast for Mobile Hosts Yu Wang Weidong Chen Southern Methodist University fwy,wcheng@seas.smu.edu May 8, 1998 Abstract IP Multicast is an ecient mechanism of delivering a large amount
Supporting IP Multicast for Mobile Hosts Yu Wang Weidong Chen Southern Methodist University fwy,wcheng@seas.smu.edu May 8, 1998 Abstract IP Multicast is an ecient mechanism of delivering a large amount
Multicast routing Draft
 Multicast routing Draft Lucia Tudose Nokia Research Center E-mail: tudose@research.nokia.com Abstract Multicast routing is establishing a tree which is routed from the source node and contains all the
Multicast routing Draft Lucia Tudose Nokia Research Center E-mail: tudose@research.nokia.com Abstract Multicast routing is establishing a tree which is routed from the source node and contains all the
Multicast Communications
 Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet
 ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2014, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Jens Andersson Internet Hierarchy 2014-11-10 ETSF05/ETSF05/ETSF10 - Internet Protocols 2 Hierarchical Routing aggregate routers
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Routing on the Internet 2014, Part 2, Lecture 1.2 Jens Andersson Internet Hierarchy 2014-11-10 ETSF05/ETSF05/ETSF10 - Internet Protocols 2 Hierarchical Routing aggregate routers
Category: Informational February Multicast Support for Nimrod : Requirements and Solution Approaches
 Network Working Group R. Ramanathan Request for Comments: 2102 BBN Systems and Technologies Category: Informational February 1997 Multicast Support for Nimrod : Requirements and Solution Approaches Status
Network Working Group R. Ramanathan Request for Comments: 2102 BBN Systems and Technologies Category: Informational February 1997 Multicast Support for Nimrod : Requirements and Solution Approaches Status
A Tree-Based Reliable Multicast Scheme Exploiting the Temporal Locality of Transmission Errors
 A Tree-Based Reliable Multicast Scheme Exploiting the Temporal Locality of Transmission Errors Jinsuk Baek 1 Jehan-François Pâris 1 Department of Computer Science University of Houston Houston, TX 77204-3010
A Tree-Based Reliable Multicast Scheme Exploiting the Temporal Locality of Transmission Errors Jinsuk Baek 1 Jehan-François Pâris 1 Department of Computer Science University of Houston Houston, TX 77204-3010
Page 1. This Week. CS 269: Lecture 11 Multicast A Tale of Two Failures. Multicast and QoS: the lost decade. Irony. History. Lectures.
 This Week CS 269: Lecture 11 Multicast A Tale of Two Failures Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
This Week CS 269: Lecture 11 Multicast A Tale of Two Failures Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
Analysis of Performance of Core Based Tree and Centralized Mode of Multicasting Routing Protocol
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 1 Analysis of Performance of Core Based Tree and Centralized Mode of Multicasting Routing Protocol Ijtaba Saleem
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 1 Analysis of Performance of Core Based Tree and Centralized Mode of Multicasting Routing Protocol Ijtaba Saleem
Multicast overview. Introduction to multicast. Information transmission techniques. Unicast
 Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
Sender. Local Domain. <= K nodes DM/GM. DM = Domain Manager GM = Group Member
 A Reliable Dissemination Protocol for Interactive Collaborative Applications Rajendra Yavatkar, James Grioen, and Madhu Sudan Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 fraj,gri,madhug@dcs.uky.edu
A Reliable Dissemination Protocol for Interactive Collaborative Applications Rajendra Yavatkar, James Grioen, and Madhu Sudan Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 fraj,gri,madhug@dcs.uky.edu
Exercises to Communication Systems
 Exercises to Communication Systems IP Multicast Additional Slides Dr.-Ing. Falko Dressler Department of Computer Science 7 University of Erlangen ÜKS, WS 05/06 1 IP Multicast Introduction Internet Group
Exercises to Communication Systems IP Multicast Additional Slides Dr.-Ing. Falko Dressler Department of Computer Science 7 University of Erlangen ÜKS, WS 05/06 1 IP Multicast Introduction Internet Group
Multicast overview. Introduction to multicast. Information transmission techniques. Unicast
 Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast benefits and applications 4 Multicast models
Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast benefits and applications 4 Multicast models
Advanced Networking. Multicast
 Advanced Networking Multicast Renato Lo Cigno Alessandro Russo LoCigno@disi.unitn.it - Russo@disi.unitn.it Homepage: disi.unitn.it/locigno/index.php/teaching-duties/advanced-networking The Multicast Tree
Advanced Networking Multicast Renato Lo Cigno Alessandro Russo LoCigno@disi.unitn.it - Russo@disi.unitn.it Homepage: disi.unitn.it/locigno/index.php/teaching-duties/advanced-networking The Multicast Tree
IMPLOSION CONTROL FOR MULTIPOINT APPLICATIONS 1
 Appeared in the proceedings of the Tenth Annual IEEE Workshop on Computer Communications, Sept. 1995 Page 1 IMPLOSION CONTROL FOR MULTIPOINT APPLICATIONS 1 ABSTRACT: Christos Papadopoulos christos@dworkin.wustl.edu
Appeared in the proceedings of the Tenth Annual IEEE Workshop on Computer Communications, Sept. 1995 Page 1 IMPLOSION CONTROL FOR MULTIPOINT APPLICATIONS 1 ABSTRACT: Christos Papadopoulos christos@dworkin.wustl.edu
IP Multicast. Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum Grundzüge der Datenkommunikation IP Multicast
 Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum falko.dressler@rrze.uni-erlangen.de 1 Agenda Basics Principles of IP multicast, addressing, TTL Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) IGMPv1, v2, v3 Layer-2
Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum falko.dressler@rrze.uni-erlangen.de 1 Agenda Basics Principles of IP multicast, addressing, TTL Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) IGMPv1, v2, v3 Layer-2
called OTERS for On-Tree Efficient Recovery using Subcasting. A Reliable Multicast Protocol
 OTERS (On-Tree Efficient Recovery using Subcasting): A Reliable Multicast Protocol Dan Li David R. Cheriton Department of Computer Science Stanford University fdli, cheritong@cs.stanford.edu Abstract This
OTERS (On-Tree Efficient Recovery using Subcasting): A Reliable Multicast Protocol Dan Li David R. Cheriton Department of Computer Science Stanford University fdli, cheritong@cs.stanford.edu Abstract This
Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees
 Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees Thesis by Junaid Haroon MSCS018 Supervised by Mr Shafiq ur Rahman Flow of Presentation Background Proposed
Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees Thesis by Junaid Haroon MSCS018 Supervised by Mr Shafiq ur Rahman Flow of Presentation Background Proposed
IP Multicast. What is multicast?
 IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
GMNF-DVMRP: AN ENHANCED VERSION OF DISTANCE VECTOR MULTICAST ROUTING PROTOCOL
 GMNF-DVMRP: AN ENHANCED VERSION OF DISTANCE VECTOR MULTICAST ROUTING PROTOCOL YUAN-CHENG LAI YING-DAR LIN AND WEI-CHE YU Department of Computer and Information Science, National Chiao Tung University,
GMNF-DVMRP: AN ENHANCED VERSION OF DISTANCE VECTOR MULTICAST ROUTING PROTOCOL YUAN-CHENG LAI YING-DAR LIN AND WEI-CHE YU Department of Computer and Information Science, National Chiao Tung University,
Revisiting IP Multicast
 Revisiting IP Multicast Juhoon Kim (kimjuhoon@gmail.com) Student Number: 312575 Seminar Internet Routing, Technische Universitaet Berlin WS 2006/2007 (January 17, 2008) Abstract This paper explains the
Revisiting IP Multicast Juhoon Kim (kimjuhoon@gmail.com) Student Number: 312575 Seminar Internet Routing, Technische Universitaet Berlin WS 2006/2007 (January 17, 2008) Abstract This paper explains the
Multiple LAN Internet Protocol Converter (MLIC) for Multimedia Conferencing
 Multiple LAN Internet Protocol Converter (MLIC) for Multimedia Conferencing Tat Chee Wan (tcwan@cs.usm.my) R. Sureswaran (sures@cs.usm.my) K. Saravanan (sara@network2.cs.usm.my) Network Research Group
Multiple LAN Internet Protocol Converter (MLIC) for Multimedia Conferencing Tat Chee Wan (tcwan@cs.usm.my) R. Sureswaran (sures@cs.usm.my) K. Saravanan (sara@network2.cs.usm.my) Network Research Group
TCP session analysis and modeling of hybrid satellite-terrestrial Internet traffic
 TCP session analysis and modeling of hybrid satellite-terrestrial Internet traffic Savio Lau saviol@cs.sfu.ca Communication Networks Laboratory http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/cnl School of Engineering Science
TCP session analysis and modeling of hybrid satellite-terrestrial Internet traffic Savio Lau saviol@cs.sfu.ca Communication Networks Laboratory http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/cnl School of Engineering Science
Enabling Group Communication in Global Networks
 Enabling Group Communication in Global Networks Markus Hofmann Institute of Telematics, University of Karlsruhe, Zirkel 2, 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany E-Mail: hofmann@acm.org WWW: http://www.telematik.informatik.uni-karlsruhe.de/~hofmann
Enabling Group Communication in Global Networks Markus Hofmann Institute of Telematics, University of Karlsruhe, Zirkel 2, 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany E-Mail: hofmann@acm.org WWW: http://www.telematik.informatik.uni-karlsruhe.de/~hofmann
Chapter 09 Network Protocols
 Chapter 09 Network Protocols Copyright 2011, Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal and Dr. Qing-An Zeng. All rights reserved. 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems
Chapter 09 Network Protocols Copyright 2011, Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal and Dr. Qing-An Zeng. All rights reserved. 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems
Reliable File Transfer in the Multicast Domain
 Reliable File Transfer in the Multicast Domain Winston Dang August 1993 Abstract This paper describes a broadcast file transfer protocol that is suitable for widespread distribution of files from several
Reliable File Transfer in the Multicast Domain Winston Dang August 1993 Abstract This paper describes a broadcast file transfer protocol that is suitable for widespread distribution of files from several
Multicast as an ISP service
 Multicast as an ISP service Lecture slides for S-38.3192 15.2.2007 Mika Ilvesmäki Networking laboratory Goals of this lecture After this lecture you will be able to Give an overall technical view of multicast
Multicast as an ISP service Lecture slides for S-38.3192 15.2.2007 Mika Ilvesmäki Networking laboratory Goals of this lecture After this lecture you will be able to Give an overall technical view of multicast
ICS 351: Today's plan. routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM
 ICS 351: Today's plan routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM what routing is not: Ethernet switching does not use IP addresses in any
ICS 351: Today's plan routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM what routing is not: Ethernet switching does not use IP addresses in any
EE122: Multicast. Kevin Lai October 7, 2002
 EE122: Multicast Kevin Lai October 7, 2002 Internet Radio www.digitallyimported.com (techno station) - sends out 128Kb/s MP3 music streams - peak usage ~9000 simultaneous streams only 5 unique streams
EE122: Multicast Kevin Lai October 7, 2002 Internet Radio www.digitallyimported.com (techno station) - sends out 128Kb/s MP3 music streams - peak usage ~9000 simultaneous streams only 5 unique streams
Failure Tolerance. Distributed Systems Santa Clara University
 Failure Tolerance Distributed Systems Santa Clara University Distributed Checkpointing Distributed Checkpointing Capture the global state of a distributed system Chandy and Lamport: Distributed snapshot
Failure Tolerance Distributed Systems Santa Clara University Distributed Checkpointing Distributed Checkpointing Capture the global state of a distributed system Chandy and Lamport: Distributed snapshot
EE122: Multicast. Internet Radio. Multicast Service Model 1. Motivation
 Internet Radio EE122: Multicast Kevin Lai October 7, 2002 wwwdigitallyimportedcom (techno station) - sends out 128Kb/s MP music streams - peak usage ~9000 simultaneous streams only 5 unique streams (trance,
Internet Radio EE122: Multicast Kevin Lai October 7, 2002 wwwdigitallyimportedcom (techno station) - sends out 128Kb/s MP music streams - peak usage ~9000 simultaneous streams only 5 unique streams (trance,
Chapter 12 Network Protocols
 Chapter 12 Network Protocols 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Transmission Control Protocol/Internetworking Protocol (TCP/IP)
Chapter 12 Network Protocols 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Transmission Control Protocol/Internetworking Protocol (TCP/IP)
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals. Unicast Transmission. Agenda. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals
 What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
Module 7 Implementing Multicast
 Module 7 Implementing Multicast Lesson 1 Explaining Multicast Why Multicast? Used when sending same data to multiple receivers Better bandwidth utilization Less host/router processing Used when addresses
Module 7 Implementing Multicast Lesson 1 Explaining Multicast Why Multicast? Used when sending same data to multiple receivers Better bandwidth utilization Less host/router processing Used when addresses
List of groups known at each router. Router gets those using IGMP. And where they are in use Where members are located. Enhancement to OSPF
 Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
UNIT IV -- TRANSPORT LAYER
 UNIT IV -- TRANSPORT LAYER TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1. Transport layer. 02 4.2. Reliable delivery service. 03 4.3. Congestion control. 05 4.4. Connection establishment.. 07 4.5. Flow control 09 4.6. Transmission
UNIT IV -- TRANSPORT LAYER TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1. Transport layer. 02 4.2. Reliable delivery service. 03 4.3. Congestion control. 05 4.4. Connection establishment.. 07 4.5. Flow control 09 4.6. Transmission
TCP Flavors Simulation Evaluations over Noisy Environment
 International Journal of Information Engineering and Applications 2018; 1(1): 11-17 http://www.aascit.org/journal/information TCP Flavors Simulation Evaluations over Noisy Environment Elsadig Gamaleldeen
International Journal of Information Engineering and Applications 2018; 1(1): 11-17 http://www.aascit.org/journal/information TCP Flavors Simulation Evaluations over Noisy Environment Elsadig Gamaleldeen
ASM. Engineering Workshops
 1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs
 Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
Different Layers Lecture 21
 Different Layers Lecture 21 10/17/2003 Jian Ren 1 The Transport Layer 10/17/2003 Jian Ren 2 Transport Services and Protocols Provide logical communication between app processes running on different hosts
Different Layers Lecture 21 10/17/2003 Jian Ren 1 The Transport Layer 10/17/2003 Jian Ren 2 Transport Services and Protocols Provide logical communication between app processes running on different hosts
Lecture 19: Multicast. CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage
 Lecture 19: Multicast CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast outing Limiters Distance Vector
Lecture 19: Multicast CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Today: Multicast routing Multicast service model Host interface Host-router interactions (IGMP) Multicast outing Limiters Distance Vector
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol
 Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E- mail: sj ko h @ pcc.c t ri.rc.k Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E- mail: sj ko h @ pcc.c t ri.rc.k Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple
The Multicast Dissemination Protocol (MDP) version 1 Framework
 Technical White Paper Joe Macker: Naval Research Laboratory Winston Dang: University of Hawaii Last Revision: April 1996 The Multicast Dissemination Protocol (MDP) version 1 Framework Abstract This white
Technical White Paper Joe Macker: Naval Research Laboratory Winston Dang: University of Hawaii Last Revision: April 1996 The Multicast Dissemination Protocol (MDP) version 1 Framework Abstract This white
Aggregated Multicast A Comparative Study UCLA CSD TR #
 Aggregated Multicast A Comparative Study 1 UCLA CSD TR # 211 Jun-Hong Cui, Jinkyu Kim Dario Maggiorini, Khaled Boussetta and Mario Gerla Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles,
Aggregated Multicast A Comparative Study 1 UCLA CSD TR # 211 Jun-Hong Cui, Jinkyu Kim Dario Maggiorini, Khaled Boussetta and Mario Gerla Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles,
BSMP - Broadcast Satellite Multimedia Protocol
 BSMP - Broadcast Satellite Multimedia Protocol Andreas ROTTMANN arott@cosy.sbg.ac.at Praxis-Project absolved at University of Salzburg, Austria Department of Computer Science Supervision: Hilmar Linder,
BSMP - Broadcast Satellite Multimedia Protocol Andreas ROTTMANN arott@cosy.sbg.ac.at Praxis-Project absolved at University of Salzburg, Austria Department of Computer Science Supervision: Hilmar Linder,
Review. Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and K. Ross
 Review The Internet (IP) Protocol Datagram format IP fragmentation ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol NAT: Network Address Translation Routing in the Internet Intra-AS routing: RIP and OSPF Inter-AS
Review The Internet (IP) Protocol Datagram format IP fragmentation ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol NAT: Network Address Translation Routing in the Internet Intra-AS routing: RIP and OSPF Inter-AS
Interaction of RSVP with ATM for the support of shortcut QoS VCs: extension to the multicast case
 Roberto Cocca, Stefano Salsano Interaction of RSVP with ATM for the support of shortcut QoS VCs: extension to the multicast case INFOCOM Department Report 004-004-1999 University of Rome La Sapienza Abstract
Roberto Cocca, Stefano Salsano Interaction of RSVP with ATM for the support of shortcut QoS VCs: extension to the multicast case INFOCOM Department Report 004-004-1999 University of Rome La Sapienza Abstract
A Timer-Based Mobile Multicast Routing Protocol in Mobile Networks
 A Timer-Based Mobile Multicast Routing Protocol in Mobile etworks Jin Park and oung-joo Suh Department of Computer Science & Engineering Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH) San 31 Hyoja-Dong
A Timer-Based Mobile Multicast Routing Protocol in Mobile etworks Jin Park and oung-joo Suh Department of Computer Science & Engineering Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH) San 31 Hyoja-Dong
TCP/IP Networking. Part 4: Network and Transport Layer Protocols
 TCP/IP Networking Part 4: Network and Transport Layer Protocols Orientation Application Application protocol Application TCP TCP protocol TCP IP IP protocol IP IP protocol IP IP protocol IP Network Access
TCP/IP Networking Part 4: Network and Transport Layer Protocols Orientation Application Application protocol Application TCP TCP protocol TCP IP IP protocol IP IP protocol IP IP protocol IP Network Access
14-740: Fundamentals of Computer and Telecommunication Networks
 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer and Telecommunication Networks Fall 2018 Quiz #2 Duration: 75 minutes ANSWER KEY Name: Andrew ID: Important: Each question is to be answered in the space provided. Material
14-740: Fundamentals of Computer and Telecommunication Networks Fall 2018 Quiz #2 Duration: 75 minutes ANSWER KEY Name: Andrew ID: Important: Each question is to be answered in the space provided. Material
Multicast Quick Start Configuration Guide
 Multicast Quick Start Configuration Guide Document ID: 9356 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dense Mode Sparse Mode with one RP Sparse Mode with Multiple RPs
Multicast Quick Start Configuration Guide Document ID: 9356 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dense Mode Sparse Mode with one RP Sparse Mode with Multiple RPs
CMSC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala. October 30, 2018
 CMSC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala October 30, 2018 Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment TCP router router IP IP packet
CMSC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala October 30, 2018 Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment TCP router router IP IP packet
Rate Based Pacing with Various TCP Variants
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Rate Based Pacing with Various TCP Variants Mr. Sreekanth Bandi 1, Mr.K.M.Rayudu 2 1 Asst.Professor, Dept of CSE,
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Rate Based Pacing with Various TCP Variants Mr. Sreekanth Bandi 1, Mr.K.M.Rayudu 2 1 Asst.Professor, Dept of CSE,
TM ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE OF OPTICAL BURST SWITCHING (OBS) NETWORKS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 232-7345 TM ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE OF OPTICAL BURST SWITCHING (OBS) NETWORKS Reza Poorzare 1 Young Researchers Club,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 232-7345 TM ALGORITHM TO IMPROVE PERFORMANCE OF OPTICAL BURST SWITCHING (OBS) NETWORKS Reza Poorzare 1 Young Researchers Club,
Staged Refresh Timers for RSVP
 Staged Refresh Timers for RSVP Ping Pan and Henning Schulzrinne Abstract The current resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) design has no reliability mechanism for the delivery of control messages. Instead,
Staged Refresh Timers for RSVP Ping Pan and Henning Schulzrinne Abstract The current resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) design has no reliability mechanism for the delivery of control messages. Instead,
CS610 Computer Network Final Term Papers Solved MCQs with reference by Virtualians Social Network
 CS610 Computer Network Final Term Papers Solved MCQs with reference by Virtualians Social Network Question No: 1( M a r k s: 1 ) A ---------- Relies on the hardware manufacturer to assign a unique physical
CS610 Computer Network Final Term Papers Solved MCQs with reference by Virtualians Social Network Question No: 1( M a r k s: 1 ) A ---------- Relies on the hardware manufacturer to assign a unique physical
Multicast Routing Protocols in a Satellite Environment*
 Multicast Routing Protocols in a Satellite Environment* Nikhil Ninan and Godred Fairhurst Electronics Research Group, Department Of Engineering Aberdeen University, Scotland, AB24 3UE Email: {nikhil, gorry}
Multicast Routing Protocols in a Satellite Environment* Nikhil Ninan and Godred Fairhurst Electronics Research Group, Department Of Engineering Aberdeen University, Scotland, AB24 3UE Email: {nikhil, gorry}
Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP
 Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP 1 Emil Farkas and 2 Iuliu Szekely 1 Wiener Strasse 27 Leopoldsdorf I. M., A-2285, Austria, farkas_emil@yahoo.com 2 Transilvania University of Brasov, Eroilor
Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP 1 Emil Farkas and 2 Iuliu Szekely 1 Wiener Strasse 27 Leopoldsdorf I. M., A-2285, Austria, farkas_emil@yahoo.com 2 Transilvania University of Brasov, Eroilor
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018
 CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
RELIABLE MULTICAST DATA DELIVERY for MILITARY NETWORKING
 RELIABLE MULTICAST DATA DELIVERY for MILITARY NETWORKING Joseph P. Macker J. Eric Klinker M. Scott Corson Naval Research Laboratory Naval Research Laboratory University of Maryland Washington, DC 20375
RELIABLE MULTICAST DATA DELIVERY for MILITARY NETWORKING Joseph P. Macker J. Eric Klinker M. Scott Corson Naval Research Laboratory Naval Research Laboratory University of Maryland Washington, DC 20375
Wenbo Liu. Supervistor : Seppo J Halme Instructor: Tapani Nieminen
 Traffic Measurement and Modeling in IP multicast Wenbo Liu Communication Laboratory, HUT Supervistor : Seppo J Halme Instructor: Tapani Nieminen Content Background Information Practical Task Mutlticast,
Traffic Measurement and Modeling in IP multicast Wenbo Liu Communication Laboratory, HUT Supervistor : Seppo J Halme Instructor: Tapani Nieminen Content Background Information Practical Task Mutlticast,
EVALUATING THE DIVERSE ALGORITHMS OF TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL UNDER THE ENVIRONMENT OF NS-2
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 6, June 2015, pg.157
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 6, June 2015, pg.157
Scaleable Round Trip Time Estimation for Layered Multicast Protocol
 Scaleable Round Trip Time Estimation for Layered Multicast Protocol Osman Ghazali and Suhaidi Hassan Department of Computer Sciences, Faculty of Information Technology Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010
Scaleable Round Trip Time Estimation for Layered Multicast Protocol Osman Ghazali and Suhaidi Hassan Department of Computer Sciences, Faculty of Information Technology Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks
 QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks Satyabrata Pradhan, Yi Li, and Muthucumaru Maheswaran Advanced Networking Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science University
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks Satyabrata Pradhan, Yi Li, and Muthucumaru Maheswaran Advanced Networking Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science University
Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s
 Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s M. Nagaratna Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE JNTUH, Hyderabad, India V. Kamakshi Prasad Prof & Additional Cont. of. Examinations
Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s M. Nagaratna Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE JNTUH, Hyderabad, India V. Kamakshi Prasad Prof & Additional Cont. of. Examinations
