Binary Trees Ernesto
|
|
|
- Elfreda King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
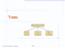
1 General Trees: Terminology (1) inary Trees Ernesto David hris Elsa nna EES2030: dvanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 HEN-WEI WNG Shirley Vanessa Peter root of tree : top element of the tree e.g., root of the above family tree: David parent of node v : node immediately above and connected to v e.g., parent of Vanessa: Elsa children of node v : nodes immediately below and connected to v e.g., children of Elsa: Shirley, Vanessa, and Peter e.g., children of Ernesto: 3 of 37 General Trees General Trees: Terminology (2) linear data structure is a sequence, where stored objects can be related via the before and after relationships. e.g., arrays, singly-linked lists, and doubly-linked lists tree is a non-linear collection of nodes. Each node stores some data object. Nodes stored in a tree is organized in a non-linear manner. In a tree, the relationships between stored objects are hierarchical : some objects are above others, and some are below others. The main terminology for the tree data structure comes from that of family trees: parents, siblings, children, ancestors, descendants. Ernesto David Elsa hris nna Shirley Vanessa Peter ancestors of node v : v + v s parent + v s grand parent +... e.g., ancestors of Vanessa: Vanessa, Elsa, hris, and David e.g., ancestors of David: David descendants of node v : v + v s children + v s grand children +... e.g., descendants of Vanessa: Vanessa e.g., descendants of David: the entire family tree 2 of 37 4 of 37
2 General Trees: Terminology (3) General Tree: Important haracteristics Ernesto David hris There is a single unique path along the edges from the root to any particular node. Elsa nna Shirley Vanessa Peter siblings of node v : nodes whose parents are the same as v s e.g., siblings of Vanessa: Shirley and Peter subtree rooted at v : a tree formed by all descendant of v external nodes (leaves) : nodes that have no children e.g., leaves of the above tree: Ernesto, nna, Shirley, Vanessa, Peter internal nodes : nodes that has at least one children e.g., non-leaves of the above tree: David, hris, Elsa 5 of 37 7 of 37 legal tree organization illegal tree organization (nontrees) Exercise: Identifying Subtrees How many subtrees are there? General Trees: Ordered Trees tree is ordered if there is a meaningful linear order among the children of each node. ook D E F G Preface Part Part References H I J K L M N O 15 subtrees [ i.e., subtrees rooted at each node ] 6 of 37 SIZE OF SUTREE ROOTS OF SUTREES 1 H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O 3 D, E, F, G 7, 15 8 of h. 1 h. 5 h. 6 h
3 General Trees: Unordered Trees tree is unordered if the order among the children of each node does not matter. cs016/ /user/rt/courses/ cs252/ inary Trees: Terminology (1) For an internal node n : Subtree rooted at its left child is called left subtree. n has no left child n s left subtree is empty Subtree rooted at its right child is called right subtree. n has no right child n s right subtree is empty grades homeworks/ programs/ projects/ grades hw1 hw2 hw3 pr1 pr2 pr3 papers/ demos/ D E F G H I J buylow sellhigh market s left subtree is rooted at and right subtree rooted at. 9 of 37 H s left subtree and right subtree are both empty. 11 of 37 inary Trees inary Trees: Recursive Definition binary tree is either: n empty tree; or nonempty tree with a root node r that binary tree is an ordered tree which satisfies the following properties: 1. Each node has at most two children. 2. Each child node is labeled as either a left child or a right child. 3. left child precedes a right child in the order of children of a node. 10 of 37 has a left binary subtree rooted at its left child has a right binary subtree rooted at its right child To solve problems recursively on a binary tree rooted at r : Do something with root r. Recur on r s left subtree. [ strictly smaller problem ] Recur on r s right subtree. [ strictly smaller problem ] Similar to how we recur on subarrays (by passing the from and to indices), we recur on subtrees by passing their roots (i.e., the current root s left child and right child). 12 of 37
4 inary Trees: pplication (1) decision tree is a binary tree used to to express the decision-making process: Each internal node has two children (yes and no). Each external node represents a decision. Do you attend classes regularly? yes You may pass with 30% confidence! no Do try out all code examples? yes no Tree Traversal lgorithms: Definition traversal of a tree T is a systematic way of visiting all the nodes of T. The visit of each node may be associated with an action: e.g., print the node element determine if the node element satisfies certain property accumulate the node element value to some global counter You may pass with another 30% confidence! Do you ask for help whenever getting stuck? yes no 13 of 37 You may pass with another 30% confidence! You may pass if there is a miracle! 15 of 37 inary Trees: pplication (2) n arithmetic expression can be represented using a binary tree: Each internal node denotes an operator (unary or binary). Each external node denotes an operand (i.e., a number). e.g., Use a binary tree to represent the arithmetic expression ( ((3 + 1) * 3) / ((9-5) + 2) ) - ( (3 * (7-4)) + 6 ) + 3 / To print, or to evaluate, the expression that is represented by a binary tree, certain traversal over the entire tree is required. 14 of Tree Traversal lgorithms: ommon Types Inorder: Visit left subtree, then parent, then right subtree. inorder (r): if(r!= null) {/*subtree with root r is not empty*/ inorder (r s left child) visit and act on the subtree rooted at r inorder (r s right child) Preorder: Visit parent, then left subtree, then right subtree. preorder (r): if(r!= null) {/*subtree with root r is not empty*/ visit and act on the subtree rooted at r preorder (r s left child) preorder (r s right child) Postorder: Visit left subtree, then right subtree, then parent. 16 of 37 postorder (r): if(r!= null) {/*subtree with root r is not empty*/ postorder (r s left child) postorder (r s right child) visit and act on the subtree rooted at r
5 Tree Traversal: Inorder Tree Traversal: Postorder D E F G D E F G H I J inorder traversal from the root : 17 of 37 H inorder(h) D I inorder(i) inorder(d) J inorder(j) E inordere inorder F inorder(f ) G inorder(g) inorder() inorder() H I J postorder traversal from the root : H I postorder(h) postorder(i) D postorder(d) J postorder(j) E postorder(e) postorder() F G postorder(f ) postorder(g) postorder() postorder() 19 of 37 Tree Traversal: Preorder Tree Traversal: Exercises / + D E F G H I J preorder traversal from the root : D H I preorder(h) preorder(i) preorder(d) E J preorder(j) preorder(e) preorder() F G preoder(f ) preoreder(g) preorder() preorder() 18 of inorder traversal from the root: 3+1*3/ *7-4+6 preorder traversal from the root: -/* *3-746 postorder traversal from the root: 31+3*95-2+/374-* of 37
6 inary Tree in Java: Linked Node public class TNode { private String element; private TNode left; private TNode right; TNode(String element) { this.element = element; public String getelement() { return element; public TNode getleft() { return left; public TNode getright() { return right; public void setelement(string element) { this.element = element; public void setleft(tnode left) { this.left = left; public void setright(tnode right) { this.right = right; 21 of 37 inary Tree in Java: dding Nodes (1) public class inarytree { private TNode root; public void addtoleft(tnode n, String element) { if(n.getleft()!= null) { throw new IllegalrgumentException("Left is already there"); n.setleft(new TNode(element)); public void addtoright(tnode n, String element) { if(n.getright()!= null) { throw new IllegalrgumentException("Right is already there"); n.setright(new TNode(element)); The way we implement the add methods is not recursive. These two add methods assume that the caller calls them by passing references of the parent nodes. 23 of 37 inary Tree in Java: Root Note public class inarytree { private TNode root; public inarytree() { /* Initialize an empty binary tree with root being null. */ public void setroot(tnode root) { this.root = root; of 37 inary Tree in Java: dding Nodes (2) Exercise: Write Java code to construct the following binary tree: left root left right D right left E G inarytree bt = new inarytree(); /* empty binary tree */ TNode root = new TNode("D"); /* node disconnected from T */ bt.setroot(root); /* node connected to T */ bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); 24 of 37 F right
7 inary Tree in Java: ounting Size (1) Size of a tree rooted at r is 1 (counting r itself) plus the size of r s left subtree and plus the size of r s right subtree. public class inarytree { private TNode root; public int size() { return sizehelper (root); private int sizehelper (TNode root) { if(root == null) { return 0; else { return 1 + sizehelper (root.getleft()) 25 of 37 + sizehelper (root.getright()); inary Tree in Java: Membership (1) n element e exists in a tree rooted at r if either r contains e, or r s left subtree contains e, or r s right subtree contains e. public class inarytree { private TNode root; public boolean has(string e) { return hashelper (root, e); private boolean hashelper (TNode root, String e) { if(root == null) { return false; else { return root.getelement().equals(e) hashelper (root.getleft(), e) 27 of 37 hashelper (root.getright(), e); inary Tree in Java: ounting Size public void testtsize() { inarytree bt = new inarytree(); assertequals(0, bt.size()); TNode root = new TNode("D"); bt.setroot(root); assertequals(1, bt.size()); bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); assertequals(7, bt.size()); 26 of 37 inary Tree in Java: Membership public void testtmembership() { inarytree bt = new inarytree(); assertfalse(bt.has("d")); TNode root = new TNode("D"); bt.setroot(root); asserttrue(bt.has("d")); assertfalse(bt.has("")); bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); asserttrue(bt.has("")); asserttrue(bt.has("")); asserttrue(bt.has("")); asserttrue(bt.has("d")); asserttrue(bt.has("e")); asserttrue(bt.has("f")); asserttrue(bt.has("g")); assertfalse(bt.has("h")); assertfalse(bt.has("i")); 28 of 37
8 inary Tree in Java: Inorder Traversal (1) inary Tree in Java: Preorder Traversal (1) public class inarytree { private TNode root; public rraylist<string> inroder() { rraylist<string> list = new rraylist<>(); inorderhelper (root, list); return list; private void inorderhelper (TNode root, rraylist<string> list) { if(root!= null) { inorderhelper (root.getleft(), list); list.add(root.getelement()); inorderhelper (root.getright(), list); public class inarytree { private TNode root; public rraylist<string> preorder() { rraylist<string> list = new rraylist<>(); preorderhelper (root, list); return list; private void preorderhelper (TNode root, rraylist<string> list) { if(root!= null) { list.add(root.getelement()); preorderhelper (root.getleft(), list); preorderhelper (root.getright(), list); 29 of of 37 inary Tree in Java: Inorder Traversal public void testt_inorder() { inarytree bt = new inarytree(); TNode root = new TNode("D"); bt.setroot(root); bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); rraylist<string> list = bt.inroder() ; assertequals(list.get(0), ""); assertequals(list.get(1), ""); assertequals(list.get(2), ""); assertequals(list.get(3), "D"); assertequals(list.get(4), "E"); assertequals(list.get(5), "F"); assertequals(list.get(6), "G"); 30 of 37 inary Tree in Java: Preorder Traversal public void testt_inorder() { inarytree bt = new inarytree(); TNode root = new TNode("D"); bt.setroot(root); bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); rraylist<string> list = bt.preorder() ; assertequals(list.get(0), "D"); assertequals(list.get(1), ""); assertequals(list.get(2), ""); assertequals(list.get(3), ""); assertequals(list.get(4), "F"); assertequals(list.get(5), "E"); assertequals(list.get(6), "G"); 32 of 37
9 inary Tree in Java: Postorder Traversal (1) public class inarytree { private TNode root; public rraylist<string> preorder() { rraylist<string> list = new rraylist<>(); postorderhelper (root, list); return list; private void postorderhelper (TNode root, rraylist<string> list) { if(root!= null) { list.add(root.getelement()); postorderhelper (root.getleft(), list); 33 of 37 postorderhelper (root.getright(), list); Index (1) General Trees General Trees: Terminology (1) General Trees: Terminology (2) General Trees: Terminology (3) Exercise: Identifying Subtrees General Tree: Important haracteristics General Trees: Ordered Trees General Trees: Unordered Trees inary Trees inary Trees: Terminology (1) inary Trees: Recursive Definition inary Trees: pplication (1) inary Trees: pplication (2) Tree Traversal lgorithms: Definition 35 of 37 inary Tree in Java: Postorder Traversal public void testt_inorder() { inarytree bt = new inarytree(); TNode root = new TNode("D"); bt.setroot(root); bt.addtoleft(root, ""); bt.addtoleft(root.getleft(), ""); bt.addtoright(root.getleft(), ""); rraylist<string> list = bt.postorder() ; assertequals(list.get(0), ""); assertequals(list.get(1), ""); assertequals(list.get(2), ""); assertequals(list.get(3), "E"); assertequals(list.get(4), "G"); assertequals(list.get(5), "F"); assertequals(list.get(6), "D"); 34 of 37 Index (2) Tree Traversal lgorithms: ommon Types Tree Traversal: Inorder Tree Traversal: Preorder Tree Traversal: Postorder Tree Traversal: Exercises inary Tree in Java: Linked Node inary Tree in Java: Root Node inary Tree in Java: dding Nodes (1) inary Tree in Java: dding Nodes (2) inary Tree in Java: ounting Size (1) inary Tree in Java: ounting Size (2) inary Tree in Java: Membership (1) inary Tree in Java: Membership (2) inary Tree in Java: Inorder Traversal (1) 36 of 37
10 Index (3) inary Tree in Java: Inorder Traversal (2) inary Tree in Java: Preorder Traversal (1) inary Tree in Java: Preorder Traversal (2) inary Tree in Java: Postorder Traversal (1) inary Tree in Java: Postorder Traversal (2) 37 of 37
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Binary trees. Binary trees. Binary trees
 Binary trees March 23, 2018 1 Binary trees A binary tree is a tree in which each internal node has at most two children. In a proper binary tree, each internal node has exactly two children. Children are
Binary trees March 23, 2018 1 Binary trees A binary tree is a tree in which each internal node has at most two children. In a proper binary tree, each internal node has exactly two children. Children are
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2017S-06 Binary Search Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 06-0: Ordered List ADT Operations: Insert an element in the list
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2017S-06 Binary Search Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 06-0: Ordered List ADT Operations: Insert an element in the list
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
a graph is a data structure made up of nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges
 1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
Binary Trees. Reading: Lewis & Chase 12.1, 12.3 Eck Programming Course CL I
 inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
Trees 3/19/14. Mammal. Dog Pig Cat
 Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
Trees. Trees. CSE 2011 Winter 2007
 Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
Topic 14. The BinaryTree ADT
 Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
CSC148 Week 6. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
BBM 201 Data structures
 BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
tree nonlinear Examples
 The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Binary Trees. Height 1
 Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Trees. Introduction & Terminology. February 05, 2018 Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
The tree data structure. Trees COL 106. Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal. Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo
 The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
Principles of Computer Science
 Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Trees. Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano Ronaldo Menezes, Florida Tech
 Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Garbage Collection: recycling unused memory
 Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Definition of a tree. A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children
 Trees Definition of a tree A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children Depending on the needs of the program, the children may or may not be ordered Like a binary tree,
Trees Definition of a tree A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children Depending on the needs of the program, the children may or may not be ordered Like a binary tree,
Introduction to Binary Trees
 Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
Trees 11/15/16. Chapter 11. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
BST Implementation. Data Structures. Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr University of Ain Shams
 Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Binary Trees Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree
 CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
Chapter 4 Trees. Theorem A graph G has a spanning tree if and only if G is connected.
 Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
What is a Tree. Trees. Tree ADT ( 6.1.2) Tree Terminology. subtree. In computer science, a tree is an abstract model
 What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
Lecture 26. Introduction to Trees. Trees
 Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
CS350: Data Structures Tree Traversal
 Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Data Structures. Trees. By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini. M.A. Eljinini, PhD
 Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Binary Trees reading: 17.1 17.3 2 Trees in computer science TreeMap and TreeSet implementations folders/files on a computer family genealogy; organizational charts AI: decision trees
Building Java Programs Binary Trees reading: 17.1 17.3 2 Trees in computer science TreeMap and TreeSet implementations folders/files on a computer family genealogy; organizational charts AI: decision trees
Tree Structures. A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node
 Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
CMPT 225. Binary Search Trees
 CMPT 225 Binary Search Trees Trees A set of nodes with a single starting point called the root Each node is connected by an edge to some other node A tree is a connected graph There is a path to every
CMPT 225 Binary Search Trees Trees A set of nodes with a single starting point called the root Each node is connected by an edge to some other node A tree is a connected graph There is a path to every
Tree. Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11. Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni. Sep 3,2010
 SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
Trees Chapter 19, 20. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Trees Chapter 19, 20 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Trees: Trees as data structures Tree terminology Tree implementations Analyzing tree efficiency Tree traversals
Trees Chapter 19, 20 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Trees: Trees as data structures Tree terminology Tree implementations Analyzing tree efficiency Tree traversals
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
OUTLINE. General Trees (Ch. 7.1) Binary Trees (Ch. 7.3) Tree Traversals (Ch. 7.2)
 CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
Successor/Predecessor Rules in Binary Trees
 Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data type. Topic 17. "A tree may grow a. its leaves will return to its roots." Properties of Trees
 Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
First Semester - Question Bank Department of Computer Science Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms...
 First Semester - Question Bank Department of Computer Science Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms.... Q1) What are some of the applications for the tree data structure? Q2) There are 8, 15, 13, and
First Semester - Question Bank Department of Computer Science Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms.... Q1) What are some of the applications for the tree data structure? Q2) There are 8, 15, 13, and
Topic 18 Binary Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb
 Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
If you took your exam home last time, I will still regrade it if you want.
 Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014
 TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014 Readings and Homework 2 Textbook, Chapter 23, 24 Homework: A thought problem (draw pictures!) Suppose you use trees to represent student schedules. For each student there
TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014 Readings and Homework 2 Textbook, Chapter 23, 24 Homework: A thought problem (draw pictures!) Suppose you use trees to represent student schedules. For each student there
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2
 CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Spring 2018
 TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Spring 2018 Important Announcements 2 A4 is out now and due two weeks from today. Have fun, and start early! Data Structures 3 There are different ways of storing data, called data
TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Spring 2018 Important Announcements 2 A4 is out now and due two weeks from today. Have fun, and start early! Data Structures 3 There are different ways of storing data, called data
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
Unit 9 Practice Test (AB27-30)
 Unit 9 Practice Test (AB27-30) Name 1. Consider the following method: public static int checktree(treenode root) return 0; int x = checktree(root.getleft()); if ( x >= 0 && checktree(root.getright()) ==
Unit 9 Practice Test (AB27-30) Name 1. Consider the following method: public static int checktree(treenode root) return 0; int x = checktree(root.getleft()); if ( x >= 0 && checktree(root.getright()) ==
CSCS-200 Data Structure and Algorithms. Lecture
 CSCS-200 Data Structure and Algorithms Lecture-13-14-15 Recursion What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem is by solving a smaller version of the exact same problem first Recursion
CSCS-200 Data Structure and Algorithms Lecture-13-14-15 Recursion What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem is by solving a smaller version of the exact same problem first Recursion
Trees: examples (Family trees)
 Ch 4: Trees it s a jungle out there... I think that I will never see a linked list useful as a tree; Linked lists are used by everybody, but it takes real smarts to do a tree Trees: examples (Family trees)
Ch 4: Trees it s a jungle out there... I think that I will never see a linked list useful as a tree; Linked lists are used by everybody, but it takes real smarts to do a tree Trees: examples (Family trees)
CSC 321: Data Structures. Fall 2012
 CSC 321: Data Structures Fall 2012 Proofs & trees proof techniques direct proof, proof by contradiction, proof by induction trees tree recursion BinaryTree class 1 Direct proofs the simplest kind of proof
CSC 321: Data Structures Fall 2012 Proofs & trees proof techniques direct proof, proof by contradiction, proof by induction trees tree recursion BinaryTree class 1 Direct proofs the simplest kind of proof
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
COSC 2011 Section N. Trees: Terminology and Basic Properties
 COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Binary Search Trees Lecture 23 October 29, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Binary Search Trees Lecture 23 October 29, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Ternary Operator Binary Search Tree Node based implementation Complexity 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Binary Search Trees Lecture 23 October 29, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Ternary Operator Binary Search Tree Node based implementation Complexity 2 Administrative
Data Structures - Binary Trees and Operations on Binary Trees
 ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
Trees. Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud. Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Trees Goodrich, Tamassia
 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Binary Tree. Binary tree terminology. Binary tree terminology Definition and Applications of Binary Trees
 Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson
 Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
CS 234. Module 5. October 18, CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25
 CS 234 Module 5 October 18, 2018 CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25 ADTs representing structure We have seen ADTs where: There is no relation among items. Items are orderable types
CS 234 Module 5 October 18, 2018 CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25 ADTs representing structure We have seen ADTs where: There is no relation among items. Items are orderable types
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections
 Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES WEEK - 6
 Ashish Jamuda Week 6 CS 331 DATA STRUCTURES & ALGORITHMS BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES OBJECTIVES: Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Tree
Ashish Jamuda Week 6 CS 331 DATA STRUCTURES & ALGORITHMS BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES OBJECTIVES: Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Tree
Terminology. The ADT Binary Tree. The ADT Binary Search Tree
 Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
Trees. T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
 Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
from inheritance onwards but no GUI programming expect to see an inheritance question, recursion questions, data structure questions
 Exam information in lab Tue, 18 Apr 2017, 9:00-noon programming part from inheritance onwards but no GUI programming expect to see an inheritance question, recursion questions, data structure questions
Exam information in lab Tue, 18 Apr 2017, 9:00-noon programming part from inheritance onwards but no GUI programming expect to see an inheritance question, recursion questions, data structure questions
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
References and Homework ABSTRACT DATA TYPES; LISTS & TREES. Abstract Data Type (ADT) 9/24/14. ADT example: Set (bunch of different values)
 9// References and Homework Text: Chapters, and ABSTRACT DATA TYPES; LISTS & TREES Homework: Learn these List methods, from http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/list.html add, addall, contains,
9// References and Homework Text: Chapters, and ABSTRACT DATA TYPES; LISTS & TREES Homework: Learn these List methods, from http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/list.html add, addall, contains,
About This Lecture. Trees. Outline. Recursive List Definition slide 1. Recursive Tree Definition. Recursive List Definition slide 2
 Revised 21-Mar-05 About This Lecture 2 Trees In this lecture we study a non-linear container called a Tree and a special kind of Tree called a Binary Tree. CMPUT 115 - Lecture 18 Department of Computing
Revised 21-Mar-05 About This Lecture 2 Trees In this lecture we study a non-linear container called a Tree and a special kind of Tree called a Binary Tree. CMPUT 115 - Lecture 18 Department of Computing
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Binary search tree (part I) Version of March 24, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Binary search tree (part I) Version of March 24, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
Data Structures. Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees
 Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
12 Abstract Data Types
 12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
Chapter Summary. Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees
 Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
