OPTIMIZING ANDROID UI PRO TIPS FOR CREATING SMOOTH AND RESPONSIVE APPS
|
|
|
- Beverley Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPTIMIZING ANDROID UI PRO TIPS FOR CREATING SMOOTH AND RESPONSIVE APPS
2 @CYRILMOTTIER
3 GET TO KNOW JAVA
4 DON T USE BOXED TYPES UNNECESSARILY
5 HashMap<Integer, String> hashmap = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); hashmap.put(665, "Android"); hashmap.put(666, "rocks"); hashmap.get(666);
6 HashMap< Integer, String> hashmap = new HashMap< Integer, String>(); hashmap.put(665, "Android"); hashmap.put(666, Integer is "rocks"); not int hashmap.get(666);
7 BECOMES DREAMS new Integer(666) REALITY
8 QUESTION Would the result have been the same if we had been trying to add Android with 42 as key?
9 QUESTION Would the result have been the same if we had been trying to add Android with 42 as key? ANSWER Yes 42 is the answer to the Java universe
10 QUESTION Would the result have been the same if we had been trying to add Android with 42 as key? ANSWER Yes 42 is the anwser to the Java universe I AM JOKING
11 QUESTION Would the result have been the same if we had been trying to add Android with 42 as key? ANSWER No Integer has an internal cache for [-128, 127]
12 SparseArray: SparseArrays map integers to Objects. Unlike a normal array of Objects, there can be gaps in the indices. It is intended to be more efficient than using a HashMap to map Integers to Objects.
13 SparseArray<String> sparsearray = new SparseArray<String>(); sparsearray.put(665, "Android"); sparsearray.put(666, "rocks"); sparsearray.get(666);
14 SparseArray<String> sparsearray = new SparseArray<String>(); sparsearray.put(665, "Android"); sparsearray.put(666, "rocks"); ints as keys, Strings as values sparsearray.get(666);
15 SparseArray<String> sparsearray = new SparseArray<String>(); sparsearray.put(665, "Android"); sparsearray.put(666, no autoboxing, "rocks"); at all ints as keys, Strings as values sparsearray.get(666);
16 REUSE AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE
17 NEVER DO public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { final View itemview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, false); // parent // attach ((TextView) itemview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) itemview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); return itemview;
18 NEVER DO public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { final View itemview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, // parent false); // attach inflate a new View at every getview call ((TextView) itemview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) itemview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); return itemview;
19 convertview: The old view to reuse, if possible. Note: You should check that this view is non-null and of an appropriate type before using. If it is not possible to convert this view to display the correct data, this method can create a new view.
20 (RE)USE THE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, // parent false); // attach ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); return convertview;
21 (RE)USE THE check for a convertview public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, // parent false); // attach ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); return convertview;
22 (RE)USE THE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( check for a convertview android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, // parent false); // attach ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); create a view only when necessary return convertview;
23 PREFER STATIC FACTORY METHODS TO CONSTRUCTORS
24 private static final int MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME = 0xcafe; public void sendmessage(handler handler, Object userinfo) { final Message message = new Message(); message.what = MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME; message.obj = userinfo; handler.sendmessage(message);
25 private static final int MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME = 0xcafe; public void sendmessage(handler handler, Object userinfo) { final Message message = new Message(); message.what = MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME; message.obj = userinfo; creation of a new Message instance handler.sendmessage(message);
26 private static final int MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME = 0xcafe; public void sendmessage(handler handler, Object userinfo) { final Message message = Message.obtain(); message.what = MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME; message.obj = userinfo; handler.sendmessage(message);
27 private static final int MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME = 0xcafe; public void sendmessage(handler handler, Object userinfo) { final Message message = Message.obtain(); message.what = MSG_ANIMATION_FRAME; message.obj = userinfo; try to reuse Message instances handler.sendmessage(message); Message.obtain(): Gets an object from a pool or create a new one
28 Want this in your app? Go to github.com/android/platform_frameworks_base Find android.util Copy PoolableManager, Pool, Poolable, Pools, FinitePool, etc. Paste in your project Enjoy the easy-to-use object pooling mechanism
29 PREFER STATIC VARIABLES TO TEMPORARY VARIABLES
30 @Override public boolean onintercepttouchevent(motionevent event) { final int x = (int) event.getx(); final int y = (int) event.gety(); final Rect frame = new Rect(); // Are we touching mhost? mhost.gethitrect(frame); if (!frame.contains(x, y)) { return false; return true;
31 @Override public boolean onintercepttouchevent(motionevent event) { final int x = (int) event.getx(); final int y = (int) event.gety(); final Rect frame = new Rect(); // Are we touching mhost creation? of a new Rect instance mhost.gethitrect(frame); if (!frame.contains(x, y)) { return false; return true;
32 private final Rect mframerect = new public boolean onintercepttouchevent(motionevent event) { final int x = (int) event.getx(); final int y = (int) event.gety(); final Rect frame = mframerect; // Are we touching mhost? mhost.gethitrect(frame); if (!frame.contains(x, y)) { return false; return true;
33 private final Rect mframerect = new create a single Rect public boolean onintercepttouchevent(motionevent event) { final int x = (int) event.getx(); final int y = (int) event.gety(); final Rect frame = mframerect; // Are we touching mhost? mhost.gethitrect(frame); if (!frame.contains(x, y)) { return false; return true;
34 private final Rect mframerect = new create a single Rect public boolean onintercepttouchevent(motionevent event) { final int x = (int) event.getx(); final int y = (int) event.gety(); final Rect frame = mframerect; always use the same instance of Rect // Are we touching mhost? mhost.gethitrect(frame); if (!frame.contains(x, y)) { return false; return true;
35 REMEMBER STRINGS ARE ELLIGIBLE TO GARBAGE COLLECTION
36 public class CharArrayBufferAdapter extends CursorAdapter { private interface DataQuery { int TITLE = 0; int SUBTITLE = 1; public CharArrayBufferAdapter(Context context, Cursor c) { super(context, public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; item.gettext1().settext(cursor.getstring(dataquery.title)); public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { return LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false);
37 public class CharArrayBufferAdapter extends CursorAdapter { private interface DataQuery { int TITLE = 0; int SUBTITLE = 1; public CharArrayBufferAdapter(Context context, Cursor c) { super(context, public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; item.gettext1().settext( cursor.getstring(dataquery.title) ); item.gettext2().settext( cursor.getstring(dataquery.subtitle) public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { return LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( getstring means new String android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false);
38 private static class ViewHolder { CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128); CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = new public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; final ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) view.gettag(); final CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.title, titlebuffer); item.gettext1().settext(titlebuffer.data, 0, titlebuffer.sizecopied); final CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.subtitle, subtitlebuffer); item.gettext2().settext(subtitlebuffer.data, 0, public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { final View v = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); v.settag(new ViewHolder()); return v;
39 private static class ViewHolder { CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128); CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = new public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; final ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) view.gettag(); final CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.title, titlebuffer); item.gettext1().settext(titlebuffer.data, 0, titlebuffer.sizecopied); final CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.subtitle, subtitlebuffer); item.gettext2().settext(subtitlebuffer.data, 0, public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { attach buffers to the itemview final View v = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); v.settag(new ViewHolder()); return v;
40 private static class ViewHolder { CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128); CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = new public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; final ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) view.gettag(); final CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.title, titlebuffer); get the buffers item.gettext1().settext(titlebuffer.data, 0, titlebuffer.sizecopied); final CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.subtitle, subtitlebuffer); item.gettext2().settext(subtitlebuffer.data, 0, public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { attach buffers to the itemview final View v = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); v.settag(new ViewHolder()); return v;
41 private static class ViewHolder { CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128); CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = new public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; copy column content to buffer final ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) view.gettag(); final CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.title, titlebuffer); get the buffers item.gettext1().settext(titlebuffer.data, 0, titlebuffer.sizecopied); final CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.subtitle, subtitlebuffer); item.gettext2().settext(subtitlebuffer.data, 0, public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { attach buffers to the itemview final View v = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); v.settag(new ViewHolder()); return v;
42 private static class ViewHolder { CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128); CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = new public void bindview(view view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { final TwoLineListItem item = (TwoLineListItem) view; copy column content to buffer final ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) view.gettag(); final CharArrayBuffer titlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.title, titlebuffer); get the buffers item.gettext1().settext(titlebuffer.data, 0, titlebuffer.sizecopied); set the buffer to the TextView final CharArrayBuffer subtitlebuffer = holder.titlebuffer; cursor.copystringtobuffer(dataquery.subtitle, subtitlebuffer); item.gettext2().settext(subtitlebuffer.data, 0, public View newview(context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { attach buffers to the itemview final View v = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); v.settag(new ViewHolder()); return v;
43 FLATTEN VIEW HIERARCHIES
44 PERFECTLY MASTER THE ANDROID UI TOOLKIT
45 1 GridLayout 2 RelativeLayout 3 <merge />
46 1 GridLayout A Layout that places its children in a rectangular grid
47 1 GridLayout 12 VIEWS
48 1 GridLayout 12 VIEWS 9 VIEWS
49 A Layout where the positions of the children can be described in relation to each other or to the parent. 2 RelativeLayout
50 A Layout where the positions of the children can be described in relation to each other or to the parent. 2 RelativeLayout Flatten hierarchy
51 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ImageView xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 3 <merge />
52 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ImageView xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> INVALID XML DOCUMENT 3 <merge />
53 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </FrameLayout> 3 <merge />
54 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android=" android:layout_width="fill_parent" useless ViewGroup android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </FrameLayout> 3 <merge />
55 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <merge xmlns:android=" <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </merge> 3 <merge />
56 COOK YOUR OWN VIEWS WHENEVER NECESSARY
57 AVélov goo.gl/8lddz
58
59
60
61
62 ListView s padding
63 QUESTION What are the available techniques to create such a a great ListView header?
64 public class UnderlinedTextView extends TextView { private final Paint mpaint = new Paint(); private int munderlineheight; public UnderlinedTextView(Context context) { super(context); public UnderlinedTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); public UnderlinedTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defstyle) { super(context, attrs, defstyle);
65 public class UnderlinedTextView extends TextView { private final Paint mpaint = new Paint(); private int munderlineheight; public UnderlinedTextView(Context context) { super(context); public UnderlinedTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); extends TextView public UnderlinedTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defstyle) { super(context, attrs, defstyle);
66 @Override public void setpadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { super.setpadding(left, top, right, munderlineheight + bottom); public void setunderlineheight(int underlineheight) { if (underlineheight < 0) underlineheight = 0; if (underlineheight!= munderlineheight) { munderlineheight = underlineheight; super.setpadding(getpaddingleft(), getpaddingtop(), getpaddingright(), getpaddingbottom() + munderlineheight); public void setunderlinecolor(int underlinecolor) { if (mpaint.getcolor()!= underlinecolor) { mpaint.setcolor(underlinecolor); protected void ondraw(canvas canvas) { super.ondraw(canvas); canvas.drawrect(0, getheight() - munderlineheight, getwidth(), getheight(), mpaint);
67 @Override public void setpadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { super.setpadding(left, top, right, munderlineheight + bottom); public void setunderlineheight(int underlineheight) { if (underlineheight < 0) underlineheight = 0; if (underlineheight!= munderlineheight) { munderlineheight = underlineheight; super.setpadding(getpaddingleft(), getpaddingtop(), getpaddingright(), getpaddingbottom() + munderlineheight); public void setunderlinecolor(int underlinecolor) { if (mpaint.getcolor()!= underlinecolor) { mpaint.setcolor(underlinecolor); invalidate(); use padding to avoid measurements use padding to avoid protected void ondraw(canvas canvas) { super.ondraw(canvas); canvas.drawrect(0, getheight() - munderlineheight, getwidth(), getheight(), mpaint);
68 @Override public void setpadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { super.setpadding(left, top, right, munderlineheight + bottom); public void setunderlineheight(int underlineheight) { if (underlineheight < 0) underlineheight = 0; if (underlineheight!= munderlineheight) { munderlineheight = underlineheight; super.setpadding(getpaddingleft(), getpaddingtop(), getpaddingright(), getpaddingbottom() + munderlineheight); public void setunderlinecolor(int underlinecolor) { if (mpaint.getcolor()!= underlinecolor) { mpaint.setcolor(underlinecolor); invalidate(); use padding to avoid measurements extend TextView default behavior use padding to avoid protected void ondraw(canvas canvas) { super.ondraw(canvas); canvas.drawrect(0, getheight() - munderlineheight, getwidth(), getheight(), mpaint);
69 ASSERTION DEVELOPERS TEND TO BE «NEVER SATISFIED» PEOPLE THAT ARE ALWAYS ASKING FOR MORE Yep, this is the exact same definition of «being French»
70 VIEW & VIEWGROUP have been designed to be easily extended via inheritance
71 GET OFF THE MAIN THREAD
72 DON T BLOCK THE MAIN THREAD
73 TRUE FACT THE MAIN THREAD IS WHERE ALL EVENTS ARE DISPATCHED
74 EVENT QUEUE EVENT LOOP
75 BE MINDFUL WITH CRITICAL METHODS onmeasure onlayout ondraw ontouchevent
76 3 MAIN OPERATIONS to perform in background disc network hardware
77 MOVE WORK OFF THE MAIN THREAD
78 THE JAVA WAY... Plain old Java java.util.concurrent
79 THE JAVA WAY... Plain old Java FOR BEARDED MEN ONLY java.util.concurrent
80 YOU ARE MORE THIS KIND OF GUY?
81 THE ANDROID WAY... Handler AsyncTask Loader IntentService
82 DO LESS AND APPROPRIATELY
83 CACHE VALUES NOT TO OVER COMPUTE THEM
84 DO YOU REMEMBER public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, // resource parent, false); // parent // attach ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1)).settext(titles.get(position)); ((TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2)).settext(subtitles.get(position)); return convertview;
85 QUESTION How to avoid having findviewbyid executed at every call to getview?
86 QUESTION How to avoid having findviewbyid executed at every call to getview? ANSWER Caching it!
87 VIEW HOLDER static class ViewHolder { TextView text1; TextView text2;
88 AVOID REPETITIVE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder holder; if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); holder = new ViewHolder(); holder.text1 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1); holder.text2 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2); convertview.settag(holder); else { holder = (ViewHolder) convertview.gettag(); holder.text1.settext(strings.get(position)); holder.text2.settext(strings.get(position)); return convertview;
89 AVOID REPETITIVE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder holder; if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); holder = new ViewHolder(); holder.text1 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1); holder.text2 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2); convertview.settag(holder); else { holder = (ViewHolder) convertview.gettag(); cache refs to the children holder.text1.settext(strings.get(position)); holder.text2.settext(strings.get(position)); return convertview;
90 AVOID REPETITIVE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder holder; if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); holder = new ViewHolder(); holder.text1 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1); holder.text2 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2); convertview.settag(holder); else { holder = (ViewHolder) convertview.gettag(); cache refs to the children holder.text1.settext(strings.get(position)); holder.text2.settext(strings.get(position)); retrieve cached refs return convertview;
91 AVOID REPETITIVE public View getview(int position, View convertview, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder holder; if (convertview == null) { convertview = minflater.inflate( android.r.layout.two_line_list_item, parent, false); holder = new ViewHolder(); holder.text1 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text1); holder.text2 = (TextView) convertview.findviewbyid(android.r.id.text2); convertview.settag(holder); else { holder = (ViewHolder) convertview.gettag(); cache refs to the children holder.text1.settext(strings.get(position)); holder.text2.settext(strings.get(position)); retrieve cached refs return convertview; use cached refs
92 GIVE PRORITITY TO YOUR THREADS
93 private static final int MSG_LOAD = 0xbeef; private Handler mhandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()); public void loadurl(final String url) { new Thread(new Runnable() public void run() { Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); InputStream i = null; Bitmap b = null; try { i = new URL(url).openStream(); b = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(i); catch (Exception e) { finally { if (i!= null) try { i.close(); catch (IOException e) { ).start(); Message.obtain(mHandler, MSG_LOAD, b).sendtotarget();
94 private static final int MSG_LOAD = 0xbeef; private Handler mhandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()); public void loadurl(final String url) { new Thread(new Runnable() { set a low public void run() { Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); InputStream i = null; Bitmap b = null; try { i = new URL(url).openStream(); b = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(i); catch (Exception e) { finally { if (i!= null) try { i.close(); catch (IOException e) { ).start(); Message.obtain(mHandler, MSG_LOAD, b).sendtotarget();
95 private static final int MSG_LOAD = 0xbeef; private Handler mhandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()); public void loadurl(final String url) { new Thread(new Runnable() { set a low public void run() { Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); InputStream i = null; Bitmap b = null; try { i = new URL(url).openStream(); b = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(i); catch (Exception e) { finally { if (i!= null) try { i.close(); catch (IOException e) { ).start(); Message.obtain(mHandler, MSG_LOAD, b).sendtotarget(); post a Message to callback the UI Thread
96 FAVOR UI TO BACKGROUND COMPUTATIONS
97 ListView can have 3 SCROLL STATES The current ListView s scroll state can be obtained using an OnScrollListener
98 1 2 3 IDLE TOUCH SCROLL FLING
99 1IDLE The view is not scrolling
100 2TOUCH SCROLL The user is scrolling using touch, and their finger is still on the screen
101 The user had previously been scrolling using touch and had performed a fling. The animation is now coasting to a stop Avoid blocking the animation pause worker Threads 3FLING
102 getlistview().setonscrolllistener(mscrolllistener); private OnScrollListener mscrolllistener = new OnScrollListener() public void onscrollstatechanged(abslistview view, int scrollstate) { ImageLoader imageloader = ImageLoader.get(getContext()); imageloader.setpaused(scrollstate == OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING); public void onscroll(abslistview view, int firstvisibleitem, int visibleitemcount, int totalitemcount) { // Nothing to do
103 getlistview().setonscrolllistener(mscrolllistener); set the listener private OnScrollListener mscrolllistener = new OnScrollListener() public void onscrollstatechanged(abslistview view, int scrollstate) { ImageLoader imageloader = ImageLoader.get(getContext()); imageloader.setpaused(scrollstate == OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING); public void onscroll(abslistview view, int firstvisibleitem, int visibleitemcount, int totalitemcount) { // Nothing to do
104 getlistview().setonscrolllistener(mscrolllistener); set the listener private OnScrollListener mscrolllistener = new OnScrollListener() { public void onscrollstatechanged(abslistview view, int scrollstate) { ImageLoader imageloader = ImageLoader.get(getContext()); imageloader.setpaused(scrollstate == public void onscroll(abslistview view, int firstvisibleitem, int visibleitemcount, int totalitemcount) { // Nothing to do (un)pause ImageLoader
105 CONCLUSION
106 DO NOT BLOCK THE MAIN THREAD
107 FLATTEN YOUR VIEW HIERARCHY
108 LAZY LOAD AND REUSE WHENEVER POSSIBLE
109 PRIORITIZE TASKS: UI ALWAYS COMES FIRST
110 CYRIL android.cyrilmottier.com
The World of List View. Romain Guy and Adam Powell May 19, 2010
 The World of List View Romain Guy and Adam Powell May 19, 2010 View live notes and ask questions about this session on Wave http://bit.ly/9zozbr Agenda Virtualization and adapters Item properties Headers
The World of List View Romain Guy and Adam Powell May 19, 2010 View live notes and ask questions about this session on Wave http://bit.ly/9zozbr Agenda Virtualization and adapters Item properties Headers
Creating a Custom ListView
 Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001
 Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 9 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 9 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
INTRODUCTION COS MOBILE DEVELOPMENT WHAT IS ANDROID CORE OS. 6-Android Basics.key - February 21, Linux-based.
 1 COS 470 - MOBILE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION 2 WHAT IS ANDROID Linux-based Java/Kotlin Android Runtime (ART) System Apps SMS, Calendar, etc. Platform Architecture 3 CORE OS Linux (64 bit) Each app is a
1 COS 470 - MOBILE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION 2 WHAT IS ANDROID Linux-based Java/Kotlin Android Runtime (ART) System Apps SMS, Calendar, etc. Platform Architecture 3 CORE OS Linux (64 bit) Each app is a
Adapter.
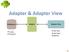 1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
Custom Views in Android Tutorial
 Custom Views in Android Tutorial The Android platform provides an extensive range of user interface items that are sufficient for the needs of most apps. However, there may be occasions on which you feel
Custom Views in Android Tutorial The Android platform provides an extensive range of user interface items that are sufficient for the needs of most apps. However, there may be occasions on which you feel
Spring Lecture 7 Lecturer: Omid Jafarinezhad
 Mobile Programming Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 - Lecture 7 Lecturer: Omid Jafarinezhad Grid View GridView is a ViewGroup that displays items in a two-dimensional, scrollable grid. The grid
Mobile Programming Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 - Lecture 7 Lecturer: Omid Jafarinezhad Grid View GridView is a ViewGroup that displays items in a two-dimensional, scrollable grid. The grid
Mastering Android Drawables
 Cyril Mottier Mastering Android Drawables Drawable are powerful so use them! Global note 2 Introduction Drawables 101 3 Introduction What s a Drawable? 4 Introduction What s a Drawable? Entity that can
Cyril Mottier Mastering Android Drawables Drawable are powerful so use them! Global note 2 Introduction Drawables 101 3 Introduction What s a Drawable? 4 Introduction What s a Drawable? Entity that can
Diving into Android. By Jeroen Tietema. Jeroen Tietema,
 Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
Responsive mobile design in practice. Kirill Grouchnikov Android, Google Inc.
 Responsive mobile design in practice Kirill Grouchnikov Android, Google Inc. this talk is about minimizing the pain of developing for multiple form factors device variety Experia Pro 3.7 Flyer 7 Sony Tablet
Responsive mobile design in practice Kirill Grouchnikov Android, Google Inc. this talk is about minimizing the pain of developing for multiple form factors device variety Experia Pro 3.7 Flyer 7 Sony Tablet
Practical 1.ListView example
 Practical 1.ListView example In this example, we show you how to display a list of fruit name via ListView. Android Layout file File : res/layout/list_fruit.xml
Practical 1.ListView example In this example, we show you how to display a list of fruit name via ListView. Android Layout file File : res/layout/list_fruit.xml
Programming of Mobile Services, Spring 2012
 Programming of Mobile Services, Spring 2012 HI1017 Lecturer: Anders Lindström, anders.lindstrom@sth.kth.se Lecture 6 Today s topics Android graphics - Views, Canvas, Drawables, Paint - Double buffering,
Programming of Mobile Services, Spring 2012 HI1017 Lecturer: Anders Lindström, anders.lindstrom@sth.kth.se Lecture 6 Today s topics Android graphics - Views, Canvas, Drawables, Paint - Double buffering,
Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall Updated 1st November 2015
 Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2015 Updated 1st November 2015 Android Lab 3 & Midterm Additional Concepts No Class Assignment 2 Class Plan Android : Additional
Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2015 Updated 1st November 2015 Android Lab 3 & Midterm Additional Concepts No Class Assignment 2 Class Plan Android : Additional
Android UI: Overview
 1 Android UI: Overview An Activity is the front end component and it can contain screens. Android screens are composed of components or screen containers and components within the containers Screen containers
1 Android UI: Overview An Activity is the front end component and it can contain screens. Android screens are composed of components or screen containers and components within the containers Screen containers
User Interface: Layout. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 User Interface: Layout Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://twitter.com/krunapon Agenda User Interface Declaring Layout Common Layouts User Interface
User Interface: Layout Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://twitter.com/krunapon Agenda User Interface Declaring Layout Common Layouts User Interface
Stanislav Rost CSAIL, MIT
 Session 2: Lifecycles, GUI Stanislav Rost CSAIL, MIT The Plan 1 Activity lifecycle Service lifecycle 2 Selected GUI elements UI Layouts 3 Hands on assignment: RoboChat Application GUI Design Birth, death,
Session 2: Lifecycles, GUI Stanislav Rost CSAIL, MIT The Plan 1 Activity lifecycle Service lifecycle 2 Selected GUI elements UI Layouts 3 Hands on assignment: RoboChat Application GUI Design Birth, death,
Developing Android Applications
 Developing Android Applications SEG2105 - Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2016 Presented by: Felipe M. Modesto TA & PhD Candidate Faculty of Engineering Faculté de Génie uottawa.ca Additional
Developing Android Applications SEG2105 - Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2016 Presented by: Felipe M. Modesto TA & PhD Candidate Faculty of Engineering Faculté de Génie uottawa.ca Additional
Agenda. Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen
 Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID
 INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID 1 Niv Voskoboynik Ben-Gurion University Electrical and Computer Engineering Advanced computer lab 2015 2 Contents Introduction Prior learning Download and install Thread Android
INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID 1 Niv Voskoboynik Ben-Gurion University Electrical and Computer Engineering Advanced computer lab 2015 2 Contents Introduction Prior learning Download and install Thread Android
Android Specifics. Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9)
 Android Specifics Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9) Android Specifics ArrayAdapter Preferences Widgets Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs 2 ArrayAdapter Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs
Android Specifics Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9) Android Specifics ArrayAdapter Preferences Widgets Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs 2 ArrayAdapter Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University. Overview (Review)
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
When programming in groups of people, it s essential to version the code. One of the most popular versioning tools is git. Some benefits of git are:
 ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
Charlie Collins Michael Galpin Matthias Käppler IN PRACTICE. Includes 91 Techniques SAMPLE CHAPTER MANNING
 Charlie Collins Michael Galpin Matthias Käppler IN PRACTICE Includes 91 Techniques MANNING SAMPLE CHAPTER Android in Practice by Charlie Collins, Michael D. Galpin, and Matthias Käppler Chapter 4 Copyright
Charlie Collins Michael Galpin Matthias Käppler IN PRACTICE Includes 91 Techniques MANNING SAMPLE CHAPTER Android in Practice by Charlie Collins, Michael D. Galpin, and Matthias Käppler Chapter 4 Copyright
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
Chapter 5 Flashing Neon FrameLayout
 5.1 Case Overview This case mainly introduced the usages of FrameLayout; we can use FrameLayout to realize the effect, the superposition of multiple widgets. This example is combined with Timer and Handler
5.1 Case Overview This case mainly introduced the usages of FrameLayout; we can use FrameLayout to realize the effect, the superposition of multiple widgets. This example is combined with Timer and Handler
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
User Interface Development. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr.
 User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
Introductory Mobile App Development
 Introductory Mobile App Development 152-160 Quick Links & Text References Overview Pages ListView Pages ArrayAdaper Pages Filling a ListView Pages Sensing Click Pages Selected Item Info Pages Configuring
Introductory Mobile App Development 152-160 Quick Links & Text References Overview Pages ListView Pages ArrayAdaper Pages Filling a ListView Pages Sensing Click Pages Selected Item Info Pages Configuring
Programming with Android: Introduction. Layouts. Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and
Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and
ListView (link) An ordered collection of selectable choices. key attributes in XML:
 CS 193A Lists This document is copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stanford Computer Science. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. ListView (link) An ordered collection
CS 193A Lists This document is copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stanford Computer Science. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. ListView (link) An ordered collection
Solving an Android Threading Problem
 Home Java News Brief Archive OCI Educational Services Solving an Android Threading Problem Introduction by Eric M. Burke, Principal Software Engineer Object Computing, Inc. (OCI) By now, you probably know
Home Java News Brief Archive OCI Educational Services Solving an Android Threading Problem Introduction by Eric M. Burke, Principal Software Engineer Object Computing, Inc. (OCI) By now, you probably know
GATAV 5. Animations Using a Game Loop
 GATAV 5. Animations Using a Game Loop TOC 1. The basic principle. 2. Creating bubbles. 3. Making the bubbles more look alive. 4. The appearent look. 5. Making the audiance impressed. 6. Now it up to you:
GATAV 5. Animations Using a Game Loop TOC 1. The basic principle. 2. Creating bubbles. 3. Making the bubbles more look alive. 4. The appearent look. 5. Making the audiance impressed. 6. Now it up to you:
package import import import import import import import public class extends public void super new this class extends public super public void new
 Android 2-D Drawing Android uses a Canvas object to host its 2-D drawing methods. The program below draws a blue circle on a white canvas. It does not make use of the main.xml layout but draws directly
Android 2-D Drawing Android uses a Canvas object to host its 2-D drawing methods. The program below draws a blue circle on a white canvas. It does not make use of the main.xml layout but draws directly
ListView Containers. Resources. Creating a ListView
 ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE)
 PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
Upon completion of the second part of the lab the students will have:
 ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 2.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of lab 2 is to introduce students to the basics of Android development and help them to create a starting
ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 2.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of lab 2 is to introduce students to the basics of Android development and help them to create a starting
Thread. A Thread is a concurrent unit of execution. The thread has its own call stack for methods being invoked, their arguments and local variables.
 1 Thread A Thread is a concurrent unit of execution. The thread has its own call stack for methods being invoked, their arguments and local variables. Each virtual machine instance has at least one main
1 Thread A Thread is a concurrent unit of execution. The thread has its own call stack for methods being invoked, their arguments and local variables. Each virtual machine instance has at least one main
Hello World. Lesson 1. Android Developer Fundamentals. Android Developer Fundamentals. Layouts, and. NonCommercial
 Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
ANDROID USER INTERFACE
 1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform
 Enterprise Application Development using J2EE Shmulik London Lecture #2 A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform Enterprise Application Development Using J2EE / Shmulik London 2004 Interdisciplinary Center
Enterprise Application Development using J2EE Shmulik London Lecture #2 A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform Enterprise Application Development Using J2EE / Shmulik London 2004 Interdisciplinary Center
Android Development Tutorial
 Android Development Tutorial Part II Human-Computer Interaction (COMP 4020) Winter 2013 2 Canvas Example public class CanvasApp extends Activity @Override protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate)
Android Development Tutorial Part II Human-Computer Interaction (COMP 4020) Winter 2013 2 Canvas Example public class CanvasApp extends Activity @Override protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate)
GUI Widget. Lecture6
 GUI Widget Lecture6 AnalogClock/Digital Clock Button CheckBox DatePicker EditText Gallery ImageView/Button MapView ProgressBar RadioButton Spinner TextView TimePicker WebView Android Widgets Designing
GUI Widget Lecture6 AnalogClock/Digital Clock Button CheckBox DatePicker EditText Gallery ImageView/Button MapView ProgressBar RadioButton Spinner TextView TimePicker WebView Android Widgets Designing
Android Exam AND-401 Android Application Development Version: 7.0 [ Total Questions: 129 ]
![Android Exam AND-401 Android Application Development Version: 7.0 [ Total Questions: 129 ] Android Exam AND-401 Android Application Development Version: 7.0 [ Total Questions: 129 ]](/thumbs/93/114127695.jpg) s@lm@n Android Exam AND-401 Android Application Development Version: 7.0 [ Total Questions: 129 ] Android AND-401 : Practice Test Question No : 1 Which of the following is required to allow the Android
s@lm@n Android Exam AND-401 Android Application Development Version: 7.0 [ Total Questions: 129 ] Android AND-401 : Practice Test Question No : 1 Which of the following is required to allow the Android
Mobile Computing Fragments
 Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Mobile Computing Practice # 2a Android Applications - Interface
 Mobile Computing Practice # 2a Android Applications - Interface 1. Create an Android Lunch Places List application that allows the user to take note of restaurant characteristics like its name, address
Mobile Computing Practice # 2a Android Applications - Interface 1. Create an Android Lunch Places List application that allows the user to take note of restaurant characteristics like its name, address
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. David Drohan Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology
 Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie User Interface Design" & Development -
Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie User Interface Design" & Development -
05. RecyclerView and Styles
 05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. David Drohan Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology
 Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie The image cannot be displayed. Your computer
Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie The image cannot be displayed. Your computer
CMSC434. Introduction to Human-Computer Interaction. Week 10 Lecture 17 Mar 31, 2016 Engineering Interfaces III. Jon
 CMSC434 Introduction to Human-Computer Interaction Week 10 Lecture 17 Mar 31, 2016 Engineering Interfaces III Jon Froehlich @jonfroehlich Human Computer Interaction Laboratory COMPUTER SCIENCE UNIVERSITY
CMSC434 Introduction to Human-Computer Interaction Week 10 Lecture 17 Mar 31, 2016 Engineering Interfaces III Jon Froehlich @jonfroehlich Human Computer Interaction Laboratory COMPUTER SCIENCE UNIVERSITY
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I)
 CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2015 Winter 2015 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2015 Winter 2015 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
Android Application Model I
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Android development. Outline. Android Studio. Setting up Android Studio. 1. Set up Android Studio. Tiberiu Vilcu. 2.
 Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I)
 CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2018 Winter 2018 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2018 Winter 2018 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events. Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna Outline Components of an Activity ViewGroup: definition
Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna Outline Components of an Activity ViewGroup: definition
Chapter 7: Reveal! Displaying Pictures in a Gallery
 Chapter 7: Reveal! Displaying Pictures in a Gallery Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Create an Android project using a Gallery control Add a Gallery to display a horizontal list of images Reference
Chapter 7: Reveal! Displaying Pictures in a Gallery Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Create an Android project using a Gallery control Add a Gallery to display a horizontal list of images Reference
Programming with Android: Introduction. Layouts. Luca Bedogni. Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
MotionEvents Touch Handling Gestures
 MotionEvents Touch Handling Gestures Represents a movement in an input device reading pen, trackball, mouse, finger Action Code State change that occurred Action Values Position and movement properties,
MotionEvents Touch Handling Gestures Represents a movement in an input device reading pen, trackball, mouse, finger Action Code State change that occurred Action Values Position and movement properties,
Android Application Model I. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr.
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
Android Basics. Android UI Architecture. Android UI 1
 Android Basics Android UI Architecture Android UI 1 Android Design Constraints Limited resources like memory, processing, battery à Android stops your app when not in use Primarily touch interaction à
Android Basics Android UI Architecture Android UI 1 Android Design Constraints Limited resources like memory, processing, battery à Android stops your app when not in use Primarily touch interaction à
Database Development In Android Applications
 ITU- FAO- DOA- TRCSL Training on Innovation & Application Development for E- Agriculture Database Development In Android Applications 11 th - 15 th December 2017 Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Shahryar Khan & Imran
ITU- FAO- DOA- TRCSL Training on Innovation & Application Development for E- Agriculture Database Development In Android Applications 11 th - 15 th December 2017 Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Shahryar Khan & Imran
Mobile Application (Design and) Development
 Mobile Application (Design and) Development 7 th class Prof. Stephen Intille s.intille@neu.edu Northeastern University 1 Q&A Workspace setup in lab. Anyone try it? Anyone looking for a partner? Boggle
Mobile Application (Design and) Development 7 th class Prof. Stephen Intille s.intille@neu.edu Northeastern University 1 Q&A Workspace setup in lab. Anyone try it? Anyone looking for a partner? Boggle
Basic UI elements: Android Buttons (Basics) Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento
 Basic UI elements: Android Buttons (Basics) Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento Let s work with the listener Button button = ; button.setonclicklistener(new.onclicklistener() { public void
Basic UI elements: Android Buttons (Basics) Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento Let s work with the listener Button button = ; button.setonclicklistener(new.onclicklistener() { public void
Overview. What are layouts Creating and using layouts Common layouts and examples Layout parameters Types of views Event listeners
 Layouts and Views http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/view.html Repo: https://github.com/karlmorris/viewsandlayouts Overview
Layouts and Views http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/view.html Repo: https://github.com/karlmorris/viewsandlayouts Overview
Android App Development. Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology
 Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
ELET4133: Embedded Systems. Topic 15 Sensors
 ELET4133: Embedded Systems Topic 15 Sensors Agenda What is a sensor? Different types of sensors Detecting sensors Example application of the accelerometer 2 What is a sensor? Piece of hardware that collects
ELET4133: Embedded Systems Topic 15 Sensors Agenda What is a sensor? Different types of sensors Detecting sensors Example application of the accelerometer 2 What is a sensor? Piece of hardware that collects
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I)
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Programming
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Programming
Contents. Orientation SearchBar and Gallery List Advanced Multiple Form Multi Touch Animations Layout Designing UI using UI Builder
 Advanced UI Contents Orientation SearchBar and Gallery List Advanced Multiple Form Multi Touch Animations Layout Designing UI using UI Builder Introduction Advanced UI Concepts A detailed view of controls
Advanced UI Contents Orientation SearchBar and Gallery List Advanced Multiple Form Multi Touch Animations Layout Designing UI using UI Builder Introduction Advanced UI Concepts A detailed view of controls
Programming Mobile Applications with Android Lab2
 Programming Mobile Applications Lab2 22-26 September, Albacete, Spain Jesus Martínez-Gómez .- Create, compile and execute an Android application to understand the Android life cycle Follow the instructions
Programming Mobile Applications Lab2 22-26 September, Albacete, Spain Jesus Martínez-Gómez .- Create, compile and execute an Android application to understand the Android life cycle Follow the instructions
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Saving State
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II
 Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II Mobile App Development 1 MVC 2 MVC 1 MVC 2 MVC Android redraw View invalidate Controller tap, key pressed update Model MVC MVC in Android View
Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II Mobile App Development 1 MVC 2 MVC 1 MVC 2 MVC Android redraw View invalidate Controller tap, key pressed update Model MVC MVC in Android View
CS378 -Mobile Computing. User Interface Basics
 CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
Graphical User Interfaces
 Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
CS371m - Mobile Computing. Responsiveness
 CS371m - Mobile Computing Responsiveness An App Idea From Nifty Assignments Draw a picture use randomness Pick an equation at random Operators in the equation have the following property: Given an input
CS371m - Mobile Computing Responsiveness An App Idea From Nifty Assignments Draw a picture use randomness Pick an equation at random Operators in the equation have the following property: Given an input
Announcements. Android: n-puzzle Walkthrough. Tommy MacWilliam. Dynamic GUIs. ListViews. Bitmaps. Gameplay. Saving State. Menus
 Harvard University February 22, 2012 Announcements Lecture videos: https://www.cs76.net/lectures Section videos: https://www.cs76.net/sections videos: https://www.cs76.net/projects Today dynamic GUIs bitmaps
Harvard University February 22, 2012 Announcements Lecture videos: https://www.cs76.net/lectures Section videos: https://www.cs76.net/sections videos: https://www.cs76.net/projects Today dynamic GUIs bitmaps
Android Volley Tutorial
 Android Volley Tutorial by Kapil - Monday, May 16, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/android-volley-tutorial/ YouTube Video Volley is an HTTP library developed by Google to ease networking
Android Volley Tutorial by Kapil - Monday, May 16, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/android-volley-tutorial/ YouTube Video Volley is an HTTP library developed by Google to ease networking
API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine. Version 1.3
 API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine Version 1.3 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 Gesture Recognition API...3 API URI... 3 Communication Protocol... 3 Getting Started...4 Protobuf... 4 WebSocket
API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine Version 1.3 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 Gesture Recognition API...3 API URI... 3 Communication Protocol... 3 Getting Started...4 Protobuf... 4 WebSocket
Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters. Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Google 28/5/2009
 Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Team @ Google 28/5/2009 Agenda Tool tour logcat traceview hierarchyviewer Real world usage Pop quiz! Q&A (pop quiz for me)
Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Team @ Google 28/5/2009 Agenda Tool tour logcat traceview hierarchyviewer Real world usage Pop quiz! Q&A (pop quiz for me)
CS371m - Mobile Computing. User Interface Basics
 CS371m - Mobile Computing User Interface Basics Clicker Question Have you ever implemented a Graphical User Interface (GUI) as part of a program? A. Yes, in another class. B. Yes, at a job or internship.
CS371m - Mobile Computing User Interface Basics Clicker Question Have you ever implemented a Graphical User Interface (GUI) as part of a program? A. Yes, in another class. B. Yes, at a job or internship.
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG. CSIS0801 Final Year Project. WhozzUp - A Novel Big Data App for HK (Individual Report)
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG CSIS0801 Final Year Project WhozzUp - A Novel Big Data App for HK (Individual Report) Nundraj NARAYEN (2012518487) 4/17/2016 Page 2 Page 3 Page
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG CSIS0801 Final Year Project WhozzUp - A Novel Big Data App for HK (Individual Report) Nundraj NARAYEN (2012518487) 4/17/2016 Page 2 Page 3 Page
Views & View Events View Groups, AdapterViews & Layouts Menus & ActionBar Dialogs
 Views & View Events View Groups, AdapterViews & Layouts Menus & ActionBar Dialogs Activities usually display a user interface Android provides many classes for constructing user interfaces Key building
Views & View Events View Groups, AdapterViews & Layouts Menus & ActionBar Dialogs Activities usually display a user interface Android provides many classes for constructing user interfaces Key building
8/30/15 MOBILE COMPUTING. CSE 40814/60814 Fall How many of you. have implemented a command-line user interface?
 MOBILE COMPUTING CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 How many of you have implemented a command-line user interface? 1 How many of you have implemented a graphical user interface? HTML/CSS Java Swing.NET Framework
MOBILE COMPUTING CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 How many of you have implemented a command-line user interface? 1 How many of you have implemented a graphical user interface? HTML/CSS Java Swing.NET Framework
Topics of Discussion
 Reference CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Fragments, ActionBar and Menus Part 3 of 5 Android Programming Concepts, by Trish Cornez and Richard Cornez, pubslihed by Jones
Reference CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Fragments, ActionBar and Menus Part 3 of 5 Android Programming Concepts, by Trish Cornez and Richard Cornez, pubslihed by Jones
Android Programming - Jelly Bean
 1800 ULEARN (853 276) www.ddls.com.au Android Programming - Jelly Bean Length 5 days Price $4235.00 (inc GST) Overview This intensive, hands-on five-day course teaches programmers how to develop activities,
1800 ULEARN (853 276) www.ddls.com.au Android Programming - Jelly Bean Length 5 days Price $4235.00 (inc GST) Overview This intensive, hands-on five-day course teaches programmers how to develop activities,
CS 370 Android Basics D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L
 CS 370 Android Basics D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Activity Basics Manifest File AndroidManifest.xml Central configuration of Android application Defines: Name of application Icon for
CS 370 Android Basics D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Activity Basics Manifest File AndroidManifest.xml Central configuration of Android application Defines: Name of application Icon for
Produced by. Design Patterns. MSc in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
Fragments. Lecture 11
 Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
Required Core Java for Android application development
 Required Core Java for Android application development Introduction to Java Datatypes primitive data types non-primitive data types Variable declaration Operators Control flow statements Arrays and Enhanced
Required Core Java for Android application development Introduction to Java Datatypes primitive data types non-primitive data types Variable declaration Operators Control flow statements Arrays and Enhanced
TextView. A label is called a TextView. TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input
 1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts
 Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
Android Application Development 101. Jason Chen Google I/O 2008
 Android Application Development 101 Jason Chen Google I/O 2008 Goal Get you an idea of how to start developing Android applications Introduce major Android application concepts Provide pointers for where
Android Application Development 101 Jason Chen Google I/O 2008 Goal Get you an idea of how to start developing Android applications Introduce major Android application concepts Provide pointers for where
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Layout and Permission Present
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Layout and Permission Present
Android Data Binding: This is the DSL you're looking for
 Android Data Binding: This is the DSL you're looking for Maksim Lin Freelance Android Developer www.manichord.com The plan Why Data Binding? Brief intro to Data Binding Library Adding Data Binding to an
Android Data Binding: This is the DSL you're looking for Maksim Lin Freelance Android Developer www.manichord.com The plan Why Data Binding? Brief intro to Data Binding Library Adding Data Binding to an
MC Android Programming
 MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
Android Programming (5 Days)
 www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
Small talk with the UI thread. Landon Cox March 9, 2017
 Small talk with the UI thread Landon Cox March 9, 2017 Android threads Thread: a sequence of executing instructions Every app has a main thread Processes UI events (taps, swipes, etc.) Updates the UI Apps
Small talk with the UI thread Landon Cox March 9, 2017 Android threads Thread: a sequence of executing instructions Every app has a main thread Processes UI events (taps, swipes, etc.) Updates the UI Apps
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Android Services
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Android Services APP COMPONENTS Activity: a single screen with a user interface Broadcast receiver: responds to system-wide broadcast events. No user interface Service:
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Android Services APP COMPONENTS Activity: a single screen with a user interface Broadcast receiver: responds to system-wide broadcast events. No user interface Service:
Android HelloWorld - Example. Tushar B. Kute,
 Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
Java for Programmers Course (equivalent to SL 275) 36 Contact Hours
 Java for Programmers Course (equivalent to SL 275) 36 Contact Hours Course Overview This course teaches programmers the skills necessary to create Java programming system applications and satisfies the
Java for Programmers Course (equivalent to SL 275) 36 Contact Hours Course Overview This course teaches programmers the skills necessary to create Java programming system applications and satisfies the
Android. Broadcasts Services Notifications
 Android Broadcasts Services Notifications Broadcast receivers Application components that can receive intents from other applications Broadcast receivers must be declared in the manifest They have an associated
Android Broadcasts Services Notifications Broadcast receivers Application components that can receive intents from other applications Broadcast receivers must be declared in the manifest They have an associated
