(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
|
|
|
- Leonard Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
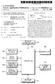
1 (19) United States US 2003O129988A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR CALL ADMISSION FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Sung-Won Lee, Songnam-shi (KR); Young-Ky Kim, Seoul (KR); Dong-Soo Park, Seoul (KR); Dong-Jun Lee, Songnam-shi (KR); Sang-Soo Kim, Songnam-shi (KR); Jin-Sung Cho, Yongin-shi (KR) Correspondence Address: Peter L. Kendall Roylance, Abrams, Berdo & Goodman, L.L.P. Suite th Street, N.W. Washington, DC (US) (21) Appl. No.: 10/338,716 (22) Filed: Jan. 9, 2003 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jan. 9, 2002 (KR) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... H04Q 7/20 (52) U.S. Cl /450; 455/423 (57) ABSTRACT A QoS-based call admission system and method for a mobile communication System. To establish a call for a mobile Station according to the QoS of the call, upon request of Setup of a call requiring a QoS guarantee, a base transceiver Station determines whether a channel element is available. In the presence of an available channel element, the base transceiver Station determines whether a remaining band width can Support a data rate required to guarantee the QoS. If the data rate is Supported, the base transceiver Station assigns the channel element and connects its intra Switch to a base Station controller. Then the base transceiver Station transmits a call accept response Signal to the base Station controller. DLE STATE ALL SETUP REQUEST YES 416 NO TRANSMIT REJECT SIGNAL TO BSC REGURED DA AE AVAILABL YES 4 CE AVAILABLE? ES 4O6 408 CHANNEL RESOURC AVAILABE ES ASSGN CE CONNECT NTFA BTS SWITCH TO BSC TRANSMT ACCEP SIGNAL TO BSC 422
2 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, Sheet 1 of 11 US 2003/ A1 INTERNET/ PSTN/PSDN 6O N BTS-a y W BTS- y \ In Sl / N 7 n Y Y M w 1 N Y N- - 1 N 11
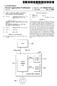
3 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 2 of 11 US 2003/ A1 O- a 2O 40 3O PROF LE BTS BSC SERVER GW/MSC 106 CAC Cal-Establishment-Req (100) w User-Profile-Req (102 User-Profile-Res (104) Call-Establish ment-req (110) CAC 2 Cat-Accept-Res (114-a) Cat-Establish ment -Rej (114-b) Cal-Establishment-Re (108) Cal-Accept-Res (116-a) - CALL ADM IT/CALL REQUEST - - -D CALL REJECT FIG 2
4 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, Sheet 3 of 11 US 2003/ A1
5 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, Sheet 4 of 11 US 2003/ A1
6 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 5 of 11 SW US 2003/ A1 IZ 9 B?IGOW -}} I-QIZ. U-GIZ D-^ HOLMS IZ? HEFT(\CEHOS S18 OS8
7 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, Sheet 6 of 11 US 2003/ A1 TRANSMIT REJECT SIGNAL TO BSC EQUIRED DATA RAE AVAILABLE YES 4 4 ASSGN CE CONNECT NTRA BTS SWITCH TO BSC TRANSMIT ACCEP SIGNAL TO BSC 4. R FIG.5
8 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, Sheet 7 of 11 US 2003/ A1 s C) s S CD
9 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 8 of 11 US 2003/ A1 MSG TYPE SUBSCR BER DENT FER AUTHENT CATION LENGTH FEER FIG.7
10 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 9 of 11 US 2003/ A1 MSG TYPE LENGTH SUBSCRIBER AUTHENT CATION ADDITIONAL DENT FER PARAMETER NFORMATION SERVICE COS PARAMETER RECODER #1 SERVICE SERVICE QoS TYPE #1 PARAMETER RECODER #1 FIG.8A
11 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 10 of 11 US 2003/ A1 MSG TYPE CODE LENGTH SUBSCRIBER AUTHENT CATION ADDITIONAL DENT FER PARAMETER INFORMATION SUBSCRBER CLASS SERVICE QoS PARAMETER RECODER FIG.8B
12 Patent Application Publication Jul. 10, 2003 Sheet 11 of 11 US 2003/ A1 START DLE STATE 5O2 YES 504 Gos SERVICE CAd NO-1AADIO RESOURCE AVAILABLE ES 506 NO YES 52 RAIRESOURCE AVALABLE CALCULATE MINIMUM DATA RATES CALCULATE NUDATA RATE AND BANDVDTS FOR NONOOS GA) AND ANDWDTHF"QoS SERVICE SERVICE AND QOS SERVICE REQUIRED DATA RATE AWA LABLE ENSE TRANSMT REJECT SIGNAL TO GW/MSC YES YES ASSGN BANDWIDTH AND SDL)/RP PROCESS Seanaw 5 2 () CONNECT NTFA BSC SWITCH TO STS 522 GA) TRANSICALESTABLISHENT REQUEST SIGNAL TO BTS FIG.9
13 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, 2003 SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR CALL ADMISSION FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM PRIORITY This application claims priority under 35 U.S.C. S119 to an application entitled Call Admission Method for a Mobile Communication System filed in the Korean Industrial Property Office on Jan. 9, 2002 and assigned Serial No , the contents of which are incorpo rated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002) 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates generally to a call admission System and method in a mobile communication System, and in particular, to a System and method of deter mining whether to admit a new or handover call in a mobile communication System Description of the Related Art A mobile communication system has been devel oped to provide voice and data Service, ensuring user mobility. Thus an MS (Mobile Station) exchanges data with a BTS (Base Transceiver Station) on radio channels. In the mobile communication System, authentication of the mobile Station is performed upon initiation of or request for a call The configuration of the mobile communication system will be described with reference to FIG. 1. FIG. 1 illustrates connections between nodes in a typical mobile communication System Referring to FIG. 1, an MS 1 with mobility con ducts voice or data communications with BTSs (BTS-a to BTS-n) 10-a to 10-in on radio channels. The BTSs 10-a to 10-in are controlled by a BSC (Base Station Controller) 20 and connected to each other over a network Such as a WAN (Wide Area Network). The BSC 20 is connected to the Internet/PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)/ PSDN (Public Switched Data Network) 60 through a gate way/mobile Switching center (GW/MSC) 30, for call con nection. The GW 30 is a logical name and is commonly referred to as a Packet Data Service Node (PDSN), Access Gateway (AGW), or Media Gateway (MGW) A profile server 40 stores information in user profiles such as the Identifier (ID) of each subscriber and authentication parameter. A user profile is illustrated in Table 1 below. TABLE 1. Subscriber ID Authentication Parameter Additional Information In Table 1, the user profile comprises a Subscriber ID that identifies a Subscriber, an Authentication Parameter for authenticating a Subscriber, and Additional Information. The profile server 40 is a logical entity. Physically, it can be integrated into the GW/MSC FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a signal flow for an operation of admitting or rejecting an incoming call in the mobile communication system of FIG When an originating node requests a call setup to the MS 1, the call setup request is connected to the mobile communication System. That is, a System to which the originating node belongs transmits a call Setup request Signal to the GW/MSC 30. The GW/MSC 30 then transmits a Call-Establishment-Req message to the BSC 20 in step 100. The BSC 20 transmits a User-Profile-Req message to the profile server 40 in step 102. In step 104, the profile server 40 generates a User-Profile-Res message by Searching a user profile as illustrated in Table 1 and transmits it to the BSC 20. The User-Profile-Res message is constructed from either a part of or the whole of the contents of Table In step 106, the BSC 20 performs a CAC (Call Admission Control) operation to determine resource avail ability. If it is determined from the result of the resource availability check that the call cannot be admitted, the BSC 20 transmits a Call-Establishment-Rei message to the GW/MSC30 in step 108. If the call is admitted, the BSC 20 transmits a Call-Establishment-Req message to the BTS 10-a in step 110. The BTS 10-a then performs a CAC operation to determine whether to admit the call in Step 112. If the call is admitted, the BTS 10-a transmits a Call-Accept Res message to the BSC 20 in step 114-a. If the call cannot be accepted, the BTS 10-a transmits a Call-Establishment Rei message to the BSC 20 in step 114-b Upon receipt of the Call-Accept-Res message from the BTS 10-a, the BSC 20 forwards the Call-Accept-Res message to the GW/MSC 30 in step 116-a. However, upon receipt of the Call-Establishment-Rei message from the BTS 10-a, the BSC 20 forwards the Call-Establishment-Remes sage to the GW/MSC 30 in step 116-b. In the above procedure, a call is either admitted or rejected during the call Setup Stage. 0014) However, the CAC operations in the BSC 2 and the BTS 10-a involves only resource availability, and excludes the Quality of Service (QoS) of a call from consideration. No problems arise if a voice call, instant message, or simple Internet service is provided. Yet, one of the clear trends these days is the provision of various Services including Video on Demand (VoD), Music on Demand (MoD), and Wireless ISP (W-ISP) to satisfy growing user demand for these services. These Services often require real-time transmission. Thus, while a call is connected, a large amount of data must be transmitted continuously or for a Selected time. If a call is assigned by determining the availability of resources, it may occur that a user-requested data rate is not Supported. If the BTS or BSC assigns a call requiring high-speed data trans mission in the same manner as a voice Service requiring low-speed data transmission, a required data rate cannot be ensured. Therefore, QoS is not guaranteed in the conven tional call Setup This problem is encountered also in handover Situations. For example, in the case where a Source BTS Supports a high data rate but a target BTS does not, QoS is not guaranteed. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is, therefore, an object of the present invention to provide a System and method of admitting a call by taking the QoS of the call into consideration in a mobile commu nication System.
14 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, It is another object of the present invention to provide a System and method of admitting a handover call by considering the QoS of the handover call in a mobile communication System It is a further object of the present invention to provide a System and method of admitting a call to ensure a continuous high data rate for an MS that receives a high Speed data Service in a mobile communication System To achieve the above and other objects, a system and method of establishing a call for an MS according to the QoS of the call in a BTS communicable with the MS in a service system where the MS, the BTS, and a BSC are connected over a selected network, the NTS determines whether a CE (channel element) is available upon request for a call requiring QoS guarantee. If the CE is available, the BTS determines whether a remaining bandwidth can support a data rate required to guarantee the QoS of the call. If the data rate is Supported, the BTS admits the call by assigning the CE and transmitting a call accept response Signal to the BSC In a system and method of establishing a call for an MS according to the QoS of the call in a BSC in a service system where the MS, a BTS communicable with the MS, and the BSC are connected over a selected network, the BSC determines whether radio resources are available upon request of the MS for a call requiring QoS guarantee after the MS is authenticated according to QoS. If the radio resources are available, the BSC determines whether a remaining available bandwidth of the network connected to the BTS can Support a minimum data rata required from the QoS of the call. If the bandwidth can support the minimum data rate, the BSC assigns the bandwidth and radio resources, and transmits a call establishment request Signal to the BTS In a system and method of establishing a call for an MS according to the QoS of the call in a BSC in a service System having a profile Server for Storing the QoS profile information of the MS, where the MS, a BTS communicable with the MS, and the BSC are connected over a selected network, the BSC acquires the user profile information of the MS from the profile server upon receipt of a call setup request message including a QoS parameter, and compares the user profile information with the QoS parameter. If the user profile information includes the QoS parameter, the BSC determines whether radio resources are available within the BSC. If the radio resources are available, the BSC determines whether a remaining available bandwidth of the network connected to the BTS can Support a minimum data rata required from the QoS of the call. If the bandwidth can Support the minimum data rate, the BSC assigns the band width and radio resources, and transmits a call establishment request signal to the BTS. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other objects, features and advan tages of the present invention will become more apparent from the following detailed description when taken in con junction with the accompanying drawings in which: 0023 FIG. 1 illustrates connections between nodes in a conventional mobile communication System; 0024 FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a signal flow for admitting or rejecting a call upon the detection of an incoming call in the mobile communication System; 0025 FIG. 3A illustrates an exemplary structure of a user profile database that includes Quality of Service (QoS) considerations when QoS is Supported on a Service basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; 0026 FIG. 3B illustrates an exemplary structure of a user profile database that includes QoS considerations when QoS is Supported on a Subscriber basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; 0027 FIG. 4 is an example of a block diagram of a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that supports QoS-based service provisioning in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; 0028 FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating an example of steps for performing a QoS-based Call Admission Control (CAC) operation in the BTS in accordance with an embodi ment of the present invention; 0029 FIG. 6 is an example of a block diagram of a Base Station Controller (BSC) that supports QoS-based service provisioning in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; 0030 FIG. 7 illustrates a conceptual format of messages exchanged for call Setup and authentication in the conven tional mobile communication System; 0031 FIG. 8A illustrates an example of a conceptual format for a message transmitted from a profile Server when QoS is Supported on a Service basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; 0032 FIG. 8B illustrates an example of a conceptual format for a message transmitted from the profile Server when QoS is Supported on a Subscriber basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention; and 0033 FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating an example of Steps for performing a QoS-based CAC operation in the BSC in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS 0034 Several embodiments of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the accompa nying drawings. Also, a detailed description of known functions and configurations have been omitted for concise CSS A mobile communication system to which the present invention is applied is the same as the network configuration illustrated in FIG. 1, except for the profile server 40 and the CAC operations in the BTS 10-a and the BSC ) While the profile server 40 has a user profile database as illustrated in Table 1 in the conventional tech nology, the user profile database is formed as illustrated in FIG. 3A or 3B in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The user profile database illustrated in FIG. 3A includes QoS considerations therein on a service basis, and the user profile database illustrated in FIG. 3B includes QoS considerations therein on a Subscriber basis. Different CAC operations are performed in the BTS 10-a and the BSC 20 and thus messages exchanged between BTS
15 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, a and BSC 20 are also different in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the user profile database is configured in the profile server 40 differently depending on whether QoS is applied on a Service basis or on a Subscriber basis. 0038) Referring to FIG. 3A, when QoS is applied on a Service basis, a user profile further includes a Service Type, indicating the type of service and a Service QoS Parameter Recorder containing a Set of parameters related to a QoS level required from the service, in addition to the fields of the conventional user profile, e.g., Subscriber Identifier, Authen tication Parameter, and Additional Information There are provided as many Service Type and Service QoS Parameter Recorder fields as the number of Services with different QoS levels that a Subscriber can receive. Service Type can indicate Voice, VoD, MoD, Web service, or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) The Service QoS parameter Recorder is deter mined according to the definition of QoS that minimum X bits and maximum Z bits are transmitted for y Seconds. 0041) Referring to FIG. 3B, when QoS is applied on a subscriber basis, a user profile further includes a Subscriber Class indicating the QoS class of a subscriber and a Sub Scriber QoS Parameter Recorder indicating a Set of param eters related to a QoS level required from the subscriber class, in addition to the fields of the conventional user profile, Subscriber Identifier, Authentication Parameter, and Additional Information In the same manner as the Service QoS Parameter Recorder, the Subscriber QoS parameter Recorder is deter mined according to the definition of QoS that minimum X bits and maximum Z bits are transmitted for y Seconds Therefore, a different QoS-based CAC operation is performed depending on the QoS profile of a subscriber. From the definition of QoS, a data rate R-rate is defined to be one of the followings. 0044) (1) Method 1: minimum X bits per y second; 0045 (2) Method 2: maximum Z bits per y second; 0046 (3) Method 3: minimum X bits per y second with a weighting factor C.(C.s 1); and 0047 (4) Method 4: maximum Z bits per y second with a weighting factor f3(bs1) In Method 1, a call is admitted if the calls mini mum required bandwidth is Satisfied and a mobile commu nication network must render the minimum band available for the call. In Method 2, a call is admitted if the calls maximum required bandwidth is satisfied and the mobile communication network must render the maximum band width available for the call. Method 3 and Method 4 are based on the principle that packet data Service does not always require a minimum or maximum bandwidth but it does require a minimum and maximum bandwidth when traffic is active on the network. Therefore, for Methods 3 and 4, a bandwidth narrower than actually required is maintained by multiplying the minimum or maximum band by a Selected weighting factor in order to increase the Statistical use efficiency of radio resources. This prevents the ineffi cient use of radio resources as encountered in the use Method 1 and Method 2 in the mobile communication network FIG. 4 is an example of a block diagram of a BTS that Supports QoS-based Service provisioning in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 4, the structure of the BTS, a CAC operation in the BTS, and related messages will be described below A BTS 10 in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention is connected to the BCS 20 via double Network Interface Cards (NICs) or Line Interface Cards (LICs) 212. The NICs 212 are connected to an intra-bts switch (or router) 213. Thus the NICs 212 interface data between the BTS 10 with the BSC 20. The intra-bts Switch 213 Switches received data under the control of a BTS controller The BTS controller 211 manages resources within the BTS 10 and controls each function block. The BTS controller 211 also performs call authentication according to radio channel information of the BTS 10 received from a radio Scheduler e.g., BTS Scheduler 214, depending on whether a received call is a general non-qos-based call or a QoS-based call. The BTS controller 211 receives a QoS message from the BSC 20 and determines whether to admit a new call or a handover call according to the QoS message The BTS 10 is provided with channel cards to 215-n, each card being assigned to one user, for process ing input data for each of the users. That is, each channel card processes data received from an Radio Frequency (RF) module 216 by, for example, decoding, and providing the processed data to the intra-bts Switch 213, processing data received from the intra-bts Switch 213 by, for example, encoding, and providing the processed data to the RF module 216. The RF module 216 upconverts data received from the channel cards to 215-in to RF signals in a transmission band and transmits the RF signals. The RF module 216 also downconverts RF signals received from Mobile Stations (MSs) to signals in a selected transmission band and transmits the signals to the channel cards to 215-n. 0053) The BTS scheduler 214 is used to provide efficient use of radio resources. In an embodiment of the invention, the BSC Scheduler 214 is integrated into the channel cards to 215-in. In another embodiment of the invention, the BSC Scheduler 214 operates as a separate processor. The BTS scheduler 214 controls scheduling in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating an example of steps for performing a QoS-based CAC operation in the BTS in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention Referring to FIG. 5, the BTS controller 211 is in an idle state in step 400. The idle state is a state where the BTS controller 211 waits for a call. In step 402, the BTS con troller 211 determines whether a call Setup request has been received. The call Setup request can be generated from the MS 1, from the MSC 30, or from a handover call. If the MS 1 requests a call Setup, the CAC operation preferably includes the Step of providing authentication in the profile server 40 and QoS-based authentication in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention after step 402.
16 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, Upon request for a call setup, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 404, otherwise, BTS controller 211 returns to step 400. In step 404, the BTS controller 211 determines whether the call requires a QoS guarantee, that is, whether the call is a QoS service call. If a QoS guarantee is required, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 410 and if a QoS guarantee is not required, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 406. In step 406, the BTS controller 211 determines the availability of a channel element (CE) as is performed in the conventional technology. If a CE is avail able, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 408 and otherwise, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 416. In step 408, the BTS controller 211 determines whether a channel resource for Non QoS Subscriber is available. The BTS controller can assign a part of operator's entire channel resources for Non QoS Subscriber or remaining portion except for the channel resources used by QoS Subscriber. 0057) If the channel resource is available, the BTS con troller 211 proceeds to step 418 otherwise, the BTS control ler 211 proceeds to step Meanwhile, if the call requires a QoS guarantee in step 404, the BTS controller 211 determines the availability of a CE in step 410. If a CE is available, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 412 otherwise, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 416. In step 416, the BTS controller 211 transmits a Call-Establishment-Rei message to the BSC In step 412, the BTS controller 211 calculates a remaining available bandwidth using the following formula Remaining Bandwidth=overall available bandwidth badnwidth in use (1) Then the BTS controller 211 determines whether a data rate required to guarantee the QoS of the call can be supported in step 414. If it can, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to step 418 otherwise, the BTS controller 211 proceeds to Step The BTS controller 211 assigns the CE in step 418, and assigns the intra-bts Switch 213 to the BSC 20 and controls the NICs 212 to establish a channel for communi cation with the BSC 20 in step 420. In step 422, the BTS controller 211 transmits a Call-Accept-ReS message to the BSC 20. Thus the BTS 10 establishes a channel with the MS 1 and Sets up the call FIG. 6 is an example of a block diagram of a BSC that Supports QoS-based Service provisioning in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention Referring to FIG. 6, the BSC 20 includes an NIC 312 connected to the GW/MSC 30, for interfacing between the BSC 20 and the GW/MSC 30. Another NIC 314 is connected to the BTS 10, for interfacing between the BSC 20 and the BTS 10. The NICS 312 and 314 are identical to the NICS 212 in the BTS An intra-bsc controller 313 switches data within the BSC 20. That is, the BSC controller 313 is connected between the NICs 312 and 314, for transmitting and receiv ing data to and from the NICs 312 and 314. It also switches data received from the NICS 312 and 314 to a BSC controller 311 or to a traffic Scheduler The BSC controller 311 provides overall control to the BSC 20 and controls the resources of the BSC 20 and part of the resources of the BTS 10. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the BSC controller 311 controls QoS-based call connection. The traffic control ler 315 controls Selection and Distribution Unit/Radio Link Protocol (SDU/RLP) (not shown) processing and signal processing. The SDU extracts the best-quality information from the information received from a plurality of BTSS in a CDMA communication network. The SDU also functions to deliver information to a particular MS through one or a plurality of BTSs A conceptual format of data exchanged for call authentication or admission between the BSC 20 and the BTS 10, and between the BSC 20 and the profile server 40 for a conventional system is illustrated in FIG. 7. Referring to FIG. 7, MSG Type indicates the type of message. MSG Type further identifies Call-Establishment-Req, Call-Estab lishment-res, User-Profile-Req, or User-Profile-Res mes Sages. Information about the code and length of a corre sponding message is Set in Code and Length, respectively of FIG. 7. When user profile information is required, Sub scriber Identifier, Authentication Parameter, and Additional Information are added. That is, the contents of Table 1 are used for authentication or admission. In order to admit or reject a call based on the QoS of the call in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a Service Type or a Subscriber Class must be further included in the message structure of FIG. 7. This embodiment of the invention is described with reference to FIGS. 8A and 8B FIG. 8A illustrates an example of a conceptual structure of a message transmitted from the profile server 40 when QoS is Supported on a Service basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Service Types and Service QoS Parameter Recorders are added to the typical message structure illustrated in FIG. 7. These parameters are delivered from the profile server 40 to the BSC 20 and from the BSC 20 to the BTS 10, in order to determine the availability of required resources when a channel is assigned for a call setup. The message structure of FIG. 8A is constructed to provide corresponding Service Type and Service QoS Parameter Recorder among parameter fields stored in the profile server 40, or to provide all Service Types and Service QoS Parameter Recorders FIG. 8B illustrates an example of a conceptual structure of a message transmitted from the profile server 40 when QoS is Supported on a Subscriber basis in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Subscriber Class and Subscriber QoS Parameter Recorder are added to the typical message structure of FIG. 7. This message structure is constructed to provide Subscriber Class and Subscriber QoS Parameter Recorder stored in the profile server 40. The message structures illustrated in FIGS. 8A and 9B match the user profiles illustrated in FIGS. 3A and 3B, respectively FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating an example of Steps for performing a QoS-based CAC operation in the BSC in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention Referring to FIG.9, the BSC controller 311 is in an idle state in step 500. The idle state is a state prior to an event being generated, where the BSC controller 311 controls call maintenance and System management. The event can be a request for processing to initiate, discontinue, or release a call. In step 502, the BSC controller 311 determines whether
17 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, 2003 a call setup request has been received from the NIC 312 through the intra BSC Switch 313. Upon receipt of the call setup request, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step 504 otherwise, the BSC controller 311 returns to step The BSC controller 311 determines whether the requested call requires a QoS guarantee and checks the Service type of the call and its requirements in a message received from the MSC 30 in step 504. The message is preferably in the format illustrated in FIG. 8A or 8B. The MSC 30 receives the message from the profile server 40 and forwards it to the BSC 20. If the call requires a QoS guarantee, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step 512 otherwise, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step In the conventional technology, the MSC 30 does not provide the message received from the profile server 40 to the BSC 20. As described with reference to FIG. 2, the BSC 20 performs steps 102 and 104 in the conventional call admission method. However, in accordance with an embodi ment of the present invention, the MSC 30 provides the message received from the profile server 40 to the BSC ) If the BSC 20 performs steps 102 and 104 as in the conventional technology, it determines whether the call requires the QoS Service by checking whether a QoS param eter is included in a Call-Establishment-Req message. If the QoS parameter is not included, the BSC 20 requests the profile of a user for which the call is to be set up to the profile server 40 and acquires it. The BSC 20 then determines whether a required QoS parameter can be provided by checking the received user profile in the format of FIG. 8A or 8B. If the service is available, that is, the user profile includes the QoS parameter, the BSC controller 311 goes to step In the case where the call does not require a QoS guarantee, in step 504 the BSC controller 311 determines whether radio resources are available, that is, whether the SDU/RLP resources with which to establish a communica tion path with the MS are available in the BSC 20 in step 506. While the traffic controller 315 assumes control of the SDU/RLP, the BSC controller 311 determines the availabil ity of resources. The traffic controller 315 also manages the resources instead of the BSC controller 311. In the presence of available radio resources, the BSC controller 311 pro ceeds to step 508 otherwise, the BSC controller 311 rejects the call request in step 518. Step 518 will be described later in more detail. 0075). In step 508, the BSC controller 311 calculates minimum data rates and bandwidths between the BSC 20 and the BTS 10 for the cases of QoS service and non-qos service. As described above, the BSC 20 and the BTS 10 are connected over a WAN or via an E1/T1 trunk. The BSC controller 311 determines the availability of the call to the Non-QoS Subscriber based on the remaining bandwidth in step 510. If it is available, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step 520 otherwise, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step Now, a description will be made of the case where the BSC controller 311 proceeds from step 504 to step 512 or the case where a Call-Establishment-Req message con taining a QoS parameter is received and a corresponding called MS can Support the QoS of the service In step 512, the BSC controller 311 determines whether radio resources, that is, SDU/RLP resources are available in the BSC 20. In the presence of radio resources, the BSC controller 311 proceeds to step 514 otherwise, the BSC controller 311 rejects the call request instep 518. In step 514, the BSC controller 311 calculates a minimum data rate and a bandwidth between the BSC 20 and the BTS 10 for the QoS Service and determines whether a requested data rate is supported with the remaining bandwidth in step 516. In step 514, the BSC controller 311 calculate a remaining band width using the following formula; Remaining Bandwidth=overall available bandwidth between BTS and BSC-Bandwidth in used between BTS and BSC In step 520, the BSC controller 311 assigns the bandwidth to the BTS 10 according to the requested data rate and assigns radio resource within the BSC20. Then the BSC controller 311 connects the BSC Switch 313 to the BTS 10 in step 522. Thus, a channel is established between the NSC 20 and the BTS 10. The BSC controller 311 transmits a Call-Establishment-Req message in the format illustrated in FIG. 8A or 8B to the BTS 10 in step Upon receipt of the Call-Establishment-Req mes sage, the BTS 10 performs a CAC operation and transmits a corresponding response to the BSC. Then the call is rejected or admitted according to the QoS of the call In accordance with the present invention, a CAC can provide a QoS guarantee. In the CAC operation, a call is admitted only if a requested data rate corresponding to a Subscriber class or a Service class is Supported. Furthermore, if the Service requires a QoS guarantee, a Subscriber can receive a service reliably even if traffic congestion exists While the invention has been shown and described with reference to a certain preferred embodiment thereof, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing from the Spirit and Scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A method of establishing a call for a Mobile Station (MS) according to the Quality of Service (QoS) of the call in a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) communicable with the MS in a service system where the MS, the BTS, and a Base Station Controller (BSC) are connected over a selected network, the method comprising the Steps of: calculating a remaining available bandwidth; determining whether the remaining available bandwidth can Support a data rate required to guarantee the QoS of the call; admitting the call if the data rate is Supported; and transmitting a call accept response Signal to the BSC. 2. The method of claim 1, further comprising the Step of determining whether a channel element (CE) is available for a call required to guarantee the QoS. 3. The method of claim 1, further comprising the step of assigning the channel element if the data rate is Supported. 4. The method of claim 1, further comprising the step of admitting the call by transmitting the call accept response signal to a BSC, if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is available.
18 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, The method of claim 1, wherein the data rate is Supported if a minimum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter for the call is available. 6. The method of claim 1, wherein the data rate is Supported if a maximum bandwidth required based on the QoS parameter is available. 7. The method of claim 1, wherein the data rate is supported if the product of the minimum bandwidth and a Selected first factor is available. 8. The method of claim 1, wherein the data rate is Supported if the product of the maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available. 9. The method of claim 1, further comprising the step of assigning a BTS Switch to the call if the data rate is Supported; 10. A method of establishing a call for an Mobile Station (MS) according to the Quality of Service (QoS) of the call in a Base Station Controller (BSC) in a service system where the MS, a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) communicable with the MS, and the BSC are connected over a selected network, the method comprising the Steps of: calculating a remaining available bandwidth between the BTS and BSC; determining whether a remaining available bandwidth of the network connected to the BTS can support a minimum data rata required based on the QoS of the call assigning the bandwidth; and transmitting a call establishment request Signal to the BTS, if the bandwidth can support the minimum data rate. 11. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of determining whether a channel element (CE) is available for a call required to guarantee the QoS. 12 The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of assigning the radio resources. 13. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of admitting the call by transmitting a call accept response signal to at least one of a GateWay and an MSC (Mobile Switching Center), if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is available. 14. The method of claim 10, wherein the data rate is Supported if a minimum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter for the call is available. 15. The method of claim 10, wherein the data rate is Supported if a maximum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter is available. 16. The method of claim 10, wherein the data rate is Supported if the product of a minimum bandwidth and a Selected first factor is available. 17. The method of claim 10, wherein the data rate is Supported if the product of a maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available. 18. The method of claim 10, further comprising the step of connecting a BSC Switch to the BTS if the network connected to the BTS has a bandwidth available to support a minimum data rate required based on the QoS of the call. 19. A method of establishing a call for an Mobile Station (MS) according to the QoS Quality of Service (QoS) of the call in a Base Station Controller (BSC) in a service system having a profile Server for Storing the QoS profile informa tion of the MS, where the MS, a Base Transceiver Station (BST) communicable with the MS, and the BSC are con nected over a Selected network, the method comprising the Steps of r requesting the user profile information of the MS containing a QoS parameter to the profile Server upon receipt of a call Setup request message including a QoS parameter, determining whether radio resources are available within the BSC if the user profile information includes the QoS parameter; determining whether a remaining available bandwidth of the network connected to the BTS can support a minimum data rata required based on the QoS require ments of the call if the radio resources are available; assigning the bandwidth and the radio resources, and transmitting a call establishment request signal to the BTS, if the bandwidth can support the minimum data rate. 20. The method of claim 19, further comprising the step of admitting the call by transmitting a call accept response signal to at least one of a GateWay and an Mobile Switching Center (MSC), if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is avail able. 21. The method of claim 19, wherein the data rate is supported if a minimum bandwidth required from the QoS parameter is available. 22. The method of claim 19, wherein the data rate is supported if a maximum bandwidth required from the QoS parameter is available. 23. The method of claim 19, wherein the data rate is Supported if a product of the minimum bandwidth and a Selected first factor is available. 24. The method of claim 19, wherein the data rate is Supported if a product of the maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available. 25. The method of claim 19, further comprising the step of connecting a BSC Switch to the BTS if the network connected to the BTS has a bandwidth available to support a minimum data rate required based on the QoS of the call. 26. A System for establishing a call over a communication network according to the Quality of Service requirement for the call, the System comprising: a mobile Station, a base transceiver Station, a base trans ceiver Station controller, and a base Station controller; Said base Station transceiver controller being adapted to calculate a remaining available bandwidth, determine whether a remaining bandwidth can Support a data rate required to guarantee the QoS of the call, admit the call if the data rate is Supported and transmit a call accept response Signal to the base Station controller. 27. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to determining whether a channel element (CE) is available for a call required to guarantee the QoS. 28. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to assign the channel ele ment if the data rate is Supported. 29. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to admit the call by trans
19 US 2003/ A1 Jul. 10, 2003 mitting the call accept response Signal to the base Station controller, if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is available. 30. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a minimum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter for the call is available. 31. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a maximum bandwidth required based on the QoS parameter is available. 32. The system of claim 26, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of the minimum band width and a selected first factor is available. 33. The system of claim 29, wherein said base station transceiver controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of the maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available. 34. A System for establishing a call over a communication network according to the Quality of Service requirement for the call, the System comprising: a mobile Station, a base transceiver Station, and a base Station controller; Said base Station controller being adapted to calculating a remaining bandwidth between the BTS and BSC, deter mine whether a remaining available bandwidth of the network connected to the base transceiver Station can Support a minimum data rata requirement based on the QoS of the call, assign the bandwidth and transmit a call establishment request signal to the base Station transceiver if the bandwidth available can support the minimum data rate. 35. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to whether a radio resources are avail able for a call required to guarantee the QoS. 36. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to assign the channel element if the data rate is Supported and connect to the base transceiver Station. 37. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to admit the call by transmitting a call accept response Signal to at least one of a GateWay and a Mobile Switching Center, if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is available. 38. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a minimum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter for the call is available. 39. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a maximum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter is available. 40. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of a minimum bandwidth and a Selected first factor is available. 41. The system of claim 34, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of a maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available. 42. A System for establishing a call over a communication network according to the Quality of Service requirement for the call, the System comprising: a mobile Station, a base transceiver Station, and a base Station controller; Said base Station controller being adapted to acquire user profile information of the mobile station from a profile Server upon receipt of a call Setup request message including a QoS parameter, compare the user profile information with the QoS parameter, determine whether radio resources are available if the user profile information includes the QoS parameter, determine whether a remaining available bandwidth of the net work connected to the base transceiver Station can Support a minimum data rata required based on the QoS requirements of the call if the radio resources are available, assign the bandwidth and radio resources, connect the base transceiver Station, and transmit a call establishment request Signal to the base transceiver Station if the bandwidth can Support the minimum data rate. 43. The system of claim 42, wherein said base station controller is adapted to admit the call by transmitting a call accept response Signal to at least one of a GateWay and a Mobile Switching Center, if the call does not require the QoS guarantee and if a channel resource for non QoS Subscriber is available. 44. The system of claim 42, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a minimum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter for the call is available. 45. The system of claim 42, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if a maximum bandwidth required based on a QoS parameter is available. 46. The system of claim 42, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of a minimum bandwidth and a Selected first factor is available. 47. The system of claim 42, wherein said base station controller is adapted to determine whether the data rate is Supported if the product of a maximum bandwidth and a Selected Second factor is available.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008
 (19) United States US 2008.0095244A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0095244 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008 (54) DE-BLOCKING FILTERING METHOD OF Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2008.0095244A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0095244 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2008 (54) DE-BLOCKING FILTERING METHOD OF Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010
 US 20100178904A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0178904 A1 LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010 (54) MESSAGING SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION (30) Foreign Application
US 20100178904A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0178904 A1 LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010 (54) MESSAGING SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,325,795 B2
 US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
United States Patent (19) Boltz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Boltz et al. 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR TIME DEFINED DELIVERY OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE MESSAGES 75 Inventors: David Boltz; David B. Westbrook, both of Garland, TeX. 73 Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Boltz et al. 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR TIME DEFINED DELIVERY OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE MESSAGES 75 Inventors: David Boltz; David B. Westbrook, both of Garland, TeX. 73 Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B1
 US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0072119A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/00721 19 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. CONNECTING WITH
(19) United States US 2013 0072119A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/00721 19 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. CONNECTING WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0301612 A1 Ou et al. US 2013 03.01612A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEM FORMANAGING SERVICES OF WIMAX
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0301612 A1 Ou et al. US 2013 03.01612A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEM FORMANAGING SERVICES OF WIMAX
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070216764A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0216764 A1 KWak (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 20, 2007 (54) ACCESS AUTHENTICATION SYSTEMAND METHOD USING SMART COMMUNICATOR
(19) United States US 20070216764A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0216764 A1 KWak (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 20, 2007 (54) ACCESS AUTHENTICATION SYSTEMAND METHOD USING SMART COMMUNICATOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
isits ar. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 (19) United States y(n) second sub-filter feedback equalizer
 (19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
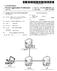 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Dec. 27, 2001 (KR)...
 (19) United States US 2003.01.23482A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0123482 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) METHOD FOR DYNAMICALLY ALLOCATING BANDWIDTH IN ATM
(19) United States US 2003.01.23482A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0123482 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) METHOD FOR DYNAMICALLY ALLOCATING BANDWIDTH IN ATM
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
1a " " " ), Gigi Nii
 USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060200568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200568 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE
(19) United States US 20060200568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200568 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048744 A1 Kimura US 2001 0048744A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) ACCESS POINT DEVICE AND METHOD THEREOF (76) Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048744 A1 Kimura US 2001 0048744A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) ACCESS POINT DEVICE AND METHOD THEREOF (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) United States Patent
 USOO943.2909B2 (12) United States Patent Svedevall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 30, 2016 (54) CONTROL NODE FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION NETWORK AND A METHOD FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES IN
USOO943.2909B2 (12) United States Patent Svedevall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 30, 2016 (54) CONTROL NODE FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION NETWORK AND A METHOD FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES IN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
Printer. Data input/ Printout unit. processor) Control unit. (Raster image RIP. Display unit. Image
 (19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
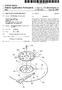 (19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080117477A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0117477 A1 Fujise (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2008 (54) FACSIMILE APPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 20080117477A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0117477 A1 Fujise (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2008 (54) FACSIMILE APPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
(19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
(2GEUs) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States. Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 (19) United States US 2008O177867A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177867 A1 Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2008 (54) CONFIGURATION OF A MEMORY CONTROLLER IN A PARALLEL
(19) United States US 2008O177867A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177867 A1 Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2008 (54) CONFIGURATION OF A MEMORY CONTROLLER IN A PARALLEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
(19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Requena et al. I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US 20020181495Al (10) Pub. No.:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Requena et al. I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US 20020181495Al (10) Pub. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1. Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011
 US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
