OBJECT ADAPTER ORB CORE I/O SUBSYSTEM. struct RT_Info { wc_exec_time_; period_; importance_; dependencies_; }; 1: CONSTRUCT CALL 6: SUPPLY RUN-TIME
|
|
|
- Darleen Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 L. Levine David University, St. Louis Washington Simplify distribution automating by Object location activation and Parameter marshaling Demultiplexing Error handling Provide foundation higher-level for ORB-endsystem.ps.gz Many applications require guarantees QoS e.g., telecom, avionics, WWW Existing middleware doesn't QoS eectively support Lack of QoS specications Lack of QoS enforcement Lack of real-time programming features Lack of performance Motivation for Real-time Middleware Architectural Considerations for Real-Time CORBA ORBs and Applications e.g., CORBA, DCOM, DCE 19 May 1998 Solutions must be integrated Vertically and horizontally Sponsors: Sprint, Siemens MED and ZT, OTI, NSF grant NCR , GDIS, DARPA contract , and Boeing Washington University, St. Louis 1 Candidate Solution: CORBA Goals of CORBA Limitations Limitations of CORBA for Real-time Systems optimizations services Washington University, St. Louis 3 Washington University, St. Louis 2
2 A high-performance, ORB real-time Telecom and focus avionics Leverages the ACE framework Runs on RTOSs, and Win32 POSIX, U. RIèMITRE ARMADA, U. Mich. Specifying QoS requirements Meeting operation deadlines scheduling Alleviating priority and inversion non-determinism Reducing latencyèjitter Specifyingèenforcing QoS requirements Focus on Operations upon Objects Rather than communication channels threadsèsynchronization or Static scheduling Non-distributed Servants publish resource, e.g., CPU, and èperiodicè deadlines requirements The ACE ORB ètaoè TAO Overview Scope: Real-time Features and Optimizations in TAO Related work QuO, BBN Washington University, St. Louis 4 Washington University, St. Louis 5 Problem: Meeting End-to-End QoS Requirements Problem: Providing QoS to CORBA Operations Design Challenges Design Challenges for demultiplexing Initial focus Solution Approach Most clients are also servants Washington University, St. Louis 7 Washington University, St. Louis 6
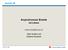
3 Integrate RT dispatcher into endsystem ORB Support multiple request strategies scheduling e.g., RMS, EDF, and MUF Requests ordered across priorities by OS thread dispatcher Requests ordered within based on data priorities Solution: TAO's Real-time Static Scheduling Service Solution: TAO's Real-time ORB Endsystem Solution Approach dependencies and importance Washington University, St. Louis 9 Washington University, St. Louis 8 Real-time ORB Endsystem Use-case struct RT_Info { wc_exec_time_; period_; criticality_; importance_; dependencies_; }; 1: CONSTRUCT CALL CHAINS OF RT_OPERATIONS RT Operation RT Operation RT Operation OBJECT ADAPTER ORB CORE I/O SUBSYSTEM OFF-LINE SCHEDULER TAO's Real-time Dynamic Scheduling Service DEPENDS UPON = DISPATCHED AFTER 2: POPULATE RT_INFO REPOSITORY 5: ASSIGN DYNAMIC SUBPRIORITY 6: SUPPLY URGENCY TO ORB RUN-TIME SCHEDULER ENTRY PER DISPATCH OF RT_OPERATION RT_INFO REPOSITORY 3: ASSESS SCHEDULABILITY 4: ASSIGN STATIC PRIORITY (QUEUE#), STATIC SUBPRIORITY Washington University, St. Louis 11 Washington University, St. Louis 10
4 Decoupled and consumers suppliers Transparent group communication Asynchronous communication Abstraction for distribution Abstraction for Stream-based architecture Enhanced pluggability Subscriptionèltering Source and type-based ltering Event correlations Conjunctions èa+b+cè Disjunctions èajbjcè Real-time scheduling support Priority-based dispatching Priority-based preemption Interval timeouts Server factory implements thread-per-priority Highest real-time for high-priority priority client Lowest real-time for low-priority priority clients COS Event Service Features push (event) TAO's Event Service Features EVENT CHANNEL Proxies Dispatching Module Event Correlation Event Flow Subscription & Filtering Priority Timers Proxies push (event) concurrency Deadline timeouts Washington University, St. Louis 12 Washington University, St. Louis 13 RT Event Channel Use-cases Priority Inversion Experiments C 0 C C n Servants Object Adapter ORB Core SCHEDULER RUNTIME One high-priority client 1..n low-priority clients Requests Client I/O SUBSYSTEM Server ATM Switch Ultra 2 Ultra Network management Avionics Washington University, St. Louis 15 Washington University, St. Louis 14
5 52 CORBAplus High Priority MT-ORBIX High Priority minicool High Priority CORBAplus Low Priority MT-ORBIX Low Priority minicool Low Priority TAO High Priority TAO Low Priority Synopsis of results Number of Low Priority Clients CORBAplus Low Priority CORBAplus High Priority 50 MT-ORBIX Low Priority MT-ORBIX High Priority minicool Low Priority 0 minicool High Priority TAO Low Priority TAO High Priority Number of Low Priority Clients ORB Latency and Priority Inversion Results COOL's latency is lower small è of clients for TAO's latency is lowest large è of clients for TAO avoids priority inversion i.e., high priority always has client lowest latency Washington University, St. Louis 16 Concluding Remarks Developers of distributed applications confront recurring challenges that largely application-independent are e.g., service initialization and distribution, error handling, ow scheduling, event demultiplexing, concurrency control, control, persistence, fault tolerance Successful developers resolve these challenges by applying appropriate patterns to create communication frameworks and components design ORBs are an eective way to achieve reuse of distributed software components The next generation of ORBs will provide much better support for QoS real-time Washington University, St. Louis 18 ORB Jitter Results Denition Variance from latency average Synopsis of results TAO's jitter is and most lowest consistent MT-Orbix's is highest jitter more and variable Washington University, St. Louis 17 For Further Information These slides: More detail on TAO: TAO Event Channel: TAO static scheduling: TAO dynamic scheduling: ORB Endsystem Architecture: Washington University, St. Louis 19 Latency per Two-way Request in Milliseconds Jitter in milliseconds
6 Performance Measurements: For Further Information Demultiplexing latency: SII throughput: DII throughput: Latency, scalability: IIOP: More detail on CORBA: ADAPTIVE Communication Environment èaceè: Washington University, St. Louis 20
Latency Reliability Partitioning Ordering Low-level APIs Poor debugging tools Algorithmic decomposition Components Self-contained, ëpluggable" ADTs Fr
 C. Schmidt Douglas schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington www.cs.wustl.eduèçschmidtètao4.ps.gz Sponsors Boeing, CDI, DARPA, Kodak, Bellcore, Motorola, NSF, OTI, SAIC, Lucent, SCR, Siemens
C. Schmidt Douglas schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington www.cs.wustl.eduèçschmidtètao4.ps.gz Sponsors Boeing, CDI, DARPA, Kodak, Bellcore, Motorola, NSF, OTI, SAIC, Lucent, SCR, Siemens
Vertically and horizontally High-performance, Real-time ORBs Motivation Many applications require æ guarantees QoS e.g., telecom, avionics, WWW Existi
 Principles and Patterns of High-performance, Real-time Object Request Brokers C. Schmidt Douglas schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington http:èèwww.cs.wustl.eduèçschmidtètao.html Typeset
Principles and Patterns of High-performance, Real-time Object Request Brokers C. Schmidt Douglas schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington http:èèwww.cs.wustl.eduèçschmidtètao.html Typeset
The Center for Distributed Object Computing Research Synopsis
 The Center for Distributed Object Computing Director, Center for Distributed Object Computing Research Synopsis David L. Levine www.cs.wustl.edu/levine/ Computer Science Dept. Sponsors NSF, DARPA, Bellcore/Telcordia,
The Center for Distributed Object Computing Director, Center for Distributed Object Computing Research Synopsis David L. Levine www.cs.wustl.edu/levine/ Computer Science Dept. Sponsors NSF, DARPA, Bellcore/Telcordia,
Patterns and Performance of Real-time Middleware for Embedded Systems
 Patterns and Performance of Real-time Middleware for Embedded Systems Associate Professor & Director of the Center for Distributed Object Computing Computer Science Dept. Lockheed Martin November st, 999
Patterns and Performance of Real-time Middleware for Embedded Systems Associate Professor & Director of the Center for Distributed Object Computing Computer Science Dept. Lockheed Martin November st, 999
Motivation: the Distributed Software Crisis Symptoms Hardware gets smaller, cheaper faster, Software gets larger, slower, more expensive Culprits Acci
 Using the ACE Framework and Patterns to Develop OO Communication Software schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Sponsors DARPA, Bellcore, Boeing, CDI/GDIS,
Using the ACE Framework and Patterns to Develop OO Communication Software schmidt@cs.wustl.edu University, St. Louis Washington http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Sponsors DARPA, Bellcore, Boeing, CDI/GDIS,
Patterns and Performance of Real-time Object Request Brokers
 Patterns and Performance of Real-time Object Request Brokers Associate Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. schmidt@uci.edu University of California, Irvine www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901 Sponsors
Patterns and Performance of Real-time Object Request Brokers Associate Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. schmidt@uci.edu University of California, Irvine www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901 Sponsors
The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service
 The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fcdgill,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington
The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fcdgill,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington
OS atop Today, more and more apps atop middleware built Middleware has several layers Quality of Service (QoS) Software architecture & System call-lev
 Using OS System-Hiding Frameworks www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901 Developing Distributed RT Systems Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. Associate University of California, Irvine schmidt@uci.edu
Using OS System-Hiding Frameworks www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901 Developing Distributed RT Systems Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. Associate University of California, Irvine schmidt@uci.edu
The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service
 The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fcdgill,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington
The Design and Performance of a Real-Time CORBA Scheduling Service Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fcdgill,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington
The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA Event Service
 The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA Event Service Timothy H. Harrison, Carlos O Ryan, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fharrison,coryan,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer
The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA Event Service Timothy H. Harrison, Carlos O Ryan, David L. Levine, and Douglas C. Schmidt fharrison,coryan,levine,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer
Developing Distributed Real-time Systems Using OS System-Hiding Frameworks
 Developing Distributed Real-time Systems Using OS System-Hiding Frameworks Associate Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. schmidt@uci.edu University of California, Irvine www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901
Developing Distributed Real-time Systems Using OS System-Hiding Frameworks Associate Professor Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept. schmidt@uci.edu University of California, Irvine www.ece.uci.edu/schmidt/ (949) 824-1901
The Design and Performance of a Pluggable Protocols Framework for Real-time Distributed Object Computing Middleware
 The Design and Performance of a Pluggable Protocols Framework for Real-time Distributed Object Computing Middleware, Fred Kuhns, Douglas C. Schmidt, Ossama Othman and Jeff Parsons coryan@uci.edu http://www.ece.uci.edu/coryan/
The Design and Performance of a Pluggable Protocols Framework for Real-time Distributed Object Computing Middleware, Fred Kuhns, Douglas C. Schmidt, Ossama Othman and Jeff Parsons coryan@uci.edu http://www.ece.uci.edu/coryan/
The Design of the TAO Real-Time Object Request Broker
 The Design of the TAO Real-Time Object Request Broker Douglas C. Schmidt, David L. Levine, and Sumedh Mungee fschmidt,levine,sumedhg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington University St.
The Design of the TAO Real-Time Object Request Broker Douglas C. Schmidt, David L. Levine, and Sumedh Mungee fschmidt,levine,sumedhg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington University St.
An Empirical Evaluation of OS Support for Real-time CORBA Object Request Brokers
 An Empirical Evaluation of OS Support for Real-time CORBA Object Request Brokers David L. Levine, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, and Douglas C. Schmidt flevine,sergio,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer
An Empirical Evaluation of OS Support for Real-time CORBA Object Request Brokers David L. Levine, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, and Douglas C. Schmidt flevine,sergio,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer
Design and Performance of an Asynchronous Method handling Mechanism for CORBA
 Design and Performance of an Asynchronous Method handling Mechanism for CORBA Mayur Deshpande, Douglas C. Schmidt & Carlos O Ryan {deshpanm,schmidt,coryan}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Design and Performance of an Asynchronous Method handling Mechanism for CORBA Mayur Deshpande, Douglas C. Schmidt & Carlos O Ryan {deshpanm,schmidt,coryan}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Evaluating Policies and Mechanisms to Support Distributed Real-Time Applications with CORBA
 Evaluating Policies and Mechanisms to Support Distributed Real-Time Applications with CORBA Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept. University
Evaluating Policies and Mechanisms to Support Distributed Real-Time Applications with CORBA Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept. University
Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers
 Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California,
Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California,
Implementing Real-time CORBA with Real-time Java
 Implementing Real-time CORBA with Real-time Java Ray Klefstad, Mayur Deshpande, Carlos O Ryan, & Doug Schmidt {coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu {klefstad,mayur}@ics.uci.edu Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept Info. & Comp.
Implementing Real-time CORBA with Real-time Java Ray Klefstad, Mayur Deshpande, Carlos O Ryan, & Doug Schmidt {coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu {klefstad,mayur}@ics.uci.edu Elec. & Comp. Eng. Dept Info. & Comp.
Weapon Systems Open Architecture Overview
 Weapon Systems Open Architecture Overview OMG Real-Time and Embedded Distributed Object Computing Workshop July 24-27, 2000 . Vision for Joint Theater Operations Joint Joint Forces Forces Global Global
Weapon Systems Open Architecture Overview OMG Real-Time and Embedded Distributed Object Computing Workshop July 24-27, 2000 . Vision for Joint Theater Operations Joint Joint Forces Forces Global Global
Real-time & Embedded Systems Workshop July 2007 Building Successful Real-time Distributed Systems in Java
 Real-time & Embedded Systems Workshop July 2007 Building Successful Real-time Distributed Systems in Java Andrew Foster Product Manager PrismTech Corporation The Case for Java in Enterprise Real-Time Systems
Real-time & Embedded Systems Workshop July 2007 Building Successful Real-time Distributed Systems in Java Andrew Foster Product Manager PrismTech Corporation The Case for Java in Enterprise Real-Time Systems
A Generative Programming Approach to Middleware Development
 A Generative Programming Approach to Middleware Development Venkita Subramonian and Christopher Gill Washington University, St. Louis {venkita,cdgill}@cse.wustl.edu OMG Workshop on Distributed Object Computing
A Generative Programming Approach to Middleware Development Venkita Subramonian and Christopher Gill Washington University, St. Louis {venkita,cdgill}@cse.wustl.edu OMG Workshop on Distributed Object Computing
short long double char octet struct Throughput in Mbps Sender Buffer size in KBytes short long double char octet struct
 Motivation Optimizations for High Performance ORBs Douglas C. Schmidt (www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt) Aniruddha S. Gokhale (www.cs.wustl.edu/gokhale) Washington University, St. Louis, USA. Typical state of
Motivation Optimizations for High Performance ORBs Douglas C. Schmidt (www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt) Aniruddha S. Gokhale (www.cs.wustl.edu/gokhale) Washington University, St. Louis, USA. Typical state of
Middleware Support for Aperiodic Tasks in Distributed Real-Time Systems
 Outline Middleware Support for Aperiodic Tasks in Distributed Real-Time Systems Yuanfang Zhang, Chenyang Lu and Chris Gill Department of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in St. Louis
Outline Middleware Support for Aperiodic Tasks in Distributed Real-Time Systems Yuanfang Zhang, Chenyang Lu and Chris Gill Department of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in St. Louis
Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers
 Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers Douglas C. Schmidt, Sumedh Mungee, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, and Aniruddha Gokhale fschmidt,sumedh,sergio,gokhaleg@cs.wustl.edu
Software Architectures for Reducing Priority Inversion and Non-determinism in Real-time Object Request Brokers Douglas C. Schmidt, Sumedh Mungee, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, and Aniruddha Gokhale fschmidt,sumedh,sergio,gokhaleg@cs.wustl.edu
Applying Patterns to Design a High-performance, Real-time Pluggable Protocols Framework for OO Communication Middleware
 Applying Patterns to Design a High-performance, Real-time Pluggable Protocols Framework for OO Communication Middleware Carlos O Ryan, Fred Kuhns, Douglas C. Schmidt and Jeff Parsons fcoryan,fredk,schmidt,parsonsg@cs.wustl.edu
Applying Patterns to Design a High-performance, Real-time Pluggable Protocols Framework for OO Communication Middleware Carlos O Ryan, Fred Kuhns, Douglas C. Schmidt and Jeff Parsons fcoryan,fredk,schmidt,parsonsg@cs.wustl.edu
The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA ORB Endsystem
 The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA ORB Endsystem Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept. University of California, Irvine Irvine,
The Design and Performance of a Real-time CORBA ORB Endsystem Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept. University of California, Irvine Irvine,
Applying a Scalable CORBA Events Service to Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations
 Applying a Scalable CORBA Events Service to Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and David L. Levine fcoryan,levineg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington University
Applying a Scalable CORBA Events Service to Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and David L. Levine fcoryan,levineg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science, Washington University
A QoS-aware CCM for DRE System Development
 A QoS-aware CCM for DRE System Development Nanbor Wang Tech-X Corporation 5561 Arapahoe Ave., Suite A Boulder, CO 33 Chris Gill Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University One Brookings
A QoS-aware CCM for DRE System Development Nanbor Wang Tech-X Corporation 5561 Arapahoe Ave., Suite A Boulder, CO 33 Chris Gill Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University One Brookings
70 64k socket queue. C over ATM (64k socket queue) ACE Orbix Sequence. ACE over ATM (64k socket queue) Throughput (Mbps) 40. Throughput (Mbps) 40
 Measuring the Performance of CORBA for High-speed Networking Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Washington University, St. Louis Introduction Distributed object computing
Measuring the Performance of CORBA for High-speed Networking Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Washington University, St. Louis Introduction Distributed object computing
Techniques for Enhancing Real-time CORBA Quality of Service
 Techniques for Enhancing Real-time CORBA Quality of Service Irfan Pyarali y Douglas C. Schmidt Ron K. Cytron irfan@oomworks.com schmidt@uci.edu cytron@cs.wustl.edu OOMWorks, LLC Electrical & Computer Engineering
Techniques for Enhancing Real-time CORBA Quality of Service Irfan Pyarali y Douglas C. Schmidt Ron K. Cytron irfan@oomworks.com schmidt@uci.edu cytron@cs.wustl.edu OOMWorks, LLC Electrical & Computer Engineering
Design Principles and Optimizations for High-performance, Real-time CORBA
 Design Principles and Optimizations for High-performance, Real-time CORBA Aniruddha S. Gokhale gokhale@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/ gokhale/ Advisor: Dr. Douglas C. Schmidt May 13th, 1998 (Funded
Design Principles and Optimizations for High-performance, Real-time CORBA Aniruddha S. Gokhale gokhale@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/ gokhale/ Advisor: Dr. Douglas C. Schmidt May 13th, 1998 (Funded
Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 29-31, Middleware in Context: 2016 David E. Bakken
 Middleware in Context Prof. Dave Bakken Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 29-31, 2017 1 Sources of Info D. Bakken, Middleware, unpublished article (from an Encyclopedia
Middleware in Context Prof. Dave Bakken Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 29-31, 2017 1 Sources of Info D. Bakken, Middleware, unpublished article (from an Encyclopedia
An Overview of the Real-time CORBA Specification
 An Overview of the Real-time CORBA Specification Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@uci.edu Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. University of California, Irvine, 92697 Fred Kuhns fredk@cs.wustl.edu Computer
An Overview of the Real-time CORBA Specification Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@uci.edu Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. University of California, Irvine, 92697 Fred Kuhns fredk@cs.wustl.edu Computer
Today: Distributed Middleware. Middleware
 Today: Distributed Middleware Middleware concepts Case study: CORBA Lecture 24, page 1 Middleware Software layer between application and the OS Provides useful services to the application Abstracts out
Today: Distributed Middleware Middleware concepts Case study: CORBA Lecture 24, page 1 Middleware Software layer between application and the OS Provides useful services to the application Abstracts out
Middleware Techniques and Optimizations for Real-time, Embedded Systems. 1 Introduction: Why We Need Middleware for Real-time Embedded Systems
 Middleware Techniques and Optimizations for Real-time, Embedded Systems Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis St. Louis, MO, 63130 This
Middleware Techniques and Optimizations for Real-time, Embedded Systems Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis St. Louis, MO, 63130 This
Applying Patterns to Develop a Pluggable Protocols Framework for ORB Middleware
 Applying Patterns to Develop a Pluggable Protocols Framework for ORB Middleware Douglas C. Schmidt, Carlos O Ryan, and Ossama Othman fschmidt,coryan,ossamag@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Department
Applying Patterns to Develop a Pluggable Protocols Framework for ORB Middleware Douglas C. Schmidt, Carlos O Ryan, and Ossama Othman fschmidt,coryan,ossamag@uci.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Department
Applying Adaptive Middleware to Manage End-to-End QoS for Next-generation Distributed Applications
 Applying Adaptive Middleware to Manage End-to-End QoS for Next-generation Distributed Applications Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Fred Kuhns fcdgill,levine,fredkg@cs.wustl.edu Department of
Applying Adaptive Middleware to Manage End-to-End QoS for Next-generation Distributed Applications Christopher D. Gill, David L. Levine, and Fred Kuhns fcdgill,levine,fredkg@cs.wustl.edu Department of
A QoS-aware CORBA Component Model for Distributed Real-time and Embedded System Development
 A -aware CORBA Model for Distributed Real-time and Embedded System Development Nanbor Wang and Chris Gill {nanbor,cdgill}@cse.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University
A -aware CORBA Model for Distributed Real-time and Embedded System Development Nanbor Wang and Chris Gill {nanbor,cdgill}@cse.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University
Measuring OS Support for Real-time CORBA ORBs
 Measuring OS Support for Real-time CORBA ORBs David L. Levine, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, Christopher D. Gill, and Douglas C. Schmidt flevine,sergio,cdgill,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science,
Measuring OS Support for Real-time CORBA ORBs David L. Levine, Sergio Flores-Gaitan, Christopher D. Gill, and Douglas C. Schmidt flevine,sergio,cdgill,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science,
Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA
 CprE 450/550x Distributed Systems and Middleware Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA Yong Guan 3216 Coover Tel: (515) 294-8378 Email: guan@ee.iastate.edu March 30, 2004 2 Readings for Today s Lecture!
CprE 450/550x Distributed Systems and Middleware Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA Yong Guan 3216 Coover Tel: (515) 294-8378 Email: guan@ee.iastate.edu March 30, 2004 2 Readings for Today s Lecture!
Middleware in Context: 2016 David E. Bakken. Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 30, 2019
 Middleware in Context Prof. Dave Bakken Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 30, 2019 Sources of Info D. Bakken, Middleware, unpublished article (from an Encyclopedia of Distributed
Middleware in Context Prof. Dave Bakken Cpt. S 464/564 Lecture Auxiliary Material (not from text) January 30, 2019 Sources of Info D. Bakken, Middleware, unpublished article (from an Encyclopedia of Distributed
Real-Time Platforms. Ø Real-Time OS: Linux Ø Real-Time Middleware: TAO
 Real-Time Platforms Ø Real-Time OS: Linux Ø Real-Time Middleware: TAO q Event service q Single-processor scheduling q End-to-end scheduling q Aperiodic scheduling Ø Real-Time Virtualization: RT-Xen Ø Real-Time
Real-Time Platforms Ø Real-Time OS: Linux Ø Real-Time Middleware: TAO q Event service q Single-processor scheduling q End-to-end scheduling q Aperiodic scheduling Ø Real-Time Virtualization: RT-Xen Ø Real-Time
Fine-grained Middleware Composition for the Boeing NEST OEP
 Fine-grained Middleware Composition for the Boeing NEST OEP Venkita Subramonian,Chris Gill, Huang-Ming Huang, Stephen Torri Washington University, St. Louis {venkita,cdgill,hh1,storri} @cs.wustl.edu Jeanna
Fine-grained Middleware Composition for the Boeing NEST OEP Venkita Subramonian,Chris Gill, Huang-Ming Huang, Stephen Torri Washington University, St. Louis {venkita,cdgill,hh1,storri} @cs.wustl.edu Jeanna
Real-time CORBA Trade Study Volume 2 Basic IDL Scenario 1a
 CAGE Code 81205 Real-time CORBA Trade Study Volume 2 Basic IDL Scenario 1a DOCUMENT NUMBER: RELEASE/REVISION: RELEASE/REVISION DATE: D204-31159-2 ORIG CONTENT OWNER: Phantom Works Advanced Information
CAGE Code 81205 Real-time CORBA Trade Study Volume 2 Basic IDL Scenario 1a DOCUMENT NUMBER: RELEASE/REVISION: RELEASE/REVISION DATE: D204-31159-2 ORIG CONTENT OWNER: Phantom Works Advanced Information
EECS 571 Principles of Real-Time Embedded Systems. Lecture Note #10: More on Scheduling and Introduction of Real-Time OS
 EECS 571 Principles of Real-Time Embedded Systems Lecture Note #10: More on Scheduling and Introduction of Real-Time OS Kang G. Shin EECS Department University of Michigan Mode Changes Changes in mission
EECS 571 Principles of Real-Time Embedded Systems Lecture Note #10: More on Scheduling and Introduction of Real-Time OS Kang G. Shin EECS Department University of Michigan Mode Changes Changes in mission
Providing Real-Time and Fault Tolerance for CORBA Applications
 Providing Real-Time and Tolerance for CORBA Applications Priya Narasimhan Assistant Professor of ECE and CS University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Sponsored in part by the CMU-NASA High Dependability Computing
Providing Real-Time and Tolerance for CORBA Applications Priya Narasimhan Assistant Professor of ECE and CS University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Sponsored in part by the CMU-NASA High Dependability Computing
Patterns and Performance of Distributed Real-time and Embedded Publisher/Subscriber Architectures
 Patterns and Performance of Distributed Real-time and Embedded Publisher/Subscriber Architectures Douglas C. Schmidt and Carlos O Ryan fschmidt,coryang@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Patterns and Performance of Distributed Real-time and Embedded Publisher/Subscriber Architectures Douglas C. Schmidt and Carlos O Ryan fschmidt,coryang@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Priya Narasimhan. Assistant Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA
 OMG Real-Time and Distributed Object Computing Workshop, July 2002, Arlington, VA Providing Real-Time and Fault Tolerance for CORBA Applications Priya Narasimhan Assistant Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie
OMG Real-Time and Distributed Object Computing Workshop, July 2002, Arlington, VA Providing Real-Time and Fault Tolerance for CORBA Applications Priya Narasimhan Assistant Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie
Today: Distributed Objects. Distributed Objects
 Today: Distributed Objects Case study: EJBs (Enterprise Java Beans) Case study: CORBA Lecture 23, page 1 Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote object with client-side proxy.
Today: Distributed Objects Case study: EJBs (Enterprise Java Beans) Case study: CORBA Lecture 23, page 1 Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote object with client-side proxy.
Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations
 Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt {coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt {coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Using Quality Objects (QuO) Middleware for QoS Control of Video Streams
 Using Quality Objects (QuO) Middleware for QoS Control of Streams BBN Technologies Cambridge, MA http://www.dist-systems.bbn.com/tech/quo/ Craig Rodrigues crodrigu@bbn.com OMG s Third Workshop on Real-Time
Using Quality Objects (QuO) Middleware for QoS Control of Streams BBN Technologies Cambridge, MA http://www.dist-systems.bbn.com/tech/quo/ Craig Rodrigues crodrigu@bbn.com OMG s Third Workshop on Real-Time
Enhancing Adaptivity via Standard Dynamic Scheduling Middleware
 Enhancing Adaptivity via Standard Dynamic Scheduling Middleware Christopher Gill, Louis Mgeta, Yuanfang Zhang, and Stephen Torri 1 Washington University, St. Louis, MO {cdgill, lmm1, yfzhang, storri}@cse.wustl.edu
Enhancing Adaptivity via Standard Dynamic Scheduling Middleware Christopher Gill, Louis Mgeta, Yuanfang Zhang, and Stephen Torri 1 Washington University, St. Louis, MO {cdgill, lmm1, yfzhang, storri}@cse.wustl.edu
The Design and Implementation of Real-Time CORBA 2.0: Dynamic Scheduling in TAO
 The Design and Implementation of Real-Time CORBA 2.0: Dynamic Scheduling in TAO Yamuna Krishnamurthy and Irfan Pyarali OOMWORKS LLC Metuchen, NJ {yamuna, irfan} @oomworks.com Christopher Gill, Louis Mgeta,
The Design and Implementation of Real-Time CORBA 2.0: Dynamic Scheduling in TAO Yamuna Krishnamurthy and Irfan Pyarali OOMWORKS LLC Metuchen, NJ {yamuna, irfan} @oomworks.com Christopher Gill, Louis Mgeta,
Benchmarking Real-Time and Embedded CORBA ORBs
 Benchmarking Real-Time and Embedded CORBA ORBs Objective Interface 13873 Park Center Road, Suite 36 Herndon, VA 2171-3247 73/295-65 (voice) 73/295-651 (fax) http://www.ois.com/ mailto:info@ois.com 22 Objective
Benchmarking Real-Time and Embedded CORBA ORBs Objective Interface 13873 Park Center Road, Suite 36 Herndon, VA 2171-3247 73/295-65 (voice) 73/295-651 (fax) http://www.ois.com/ mailto:info@ois.com 22 Objective
Short Title: High-performance CORBA Gokhale, D.Sc. 1998
 Short Title: High-performance CORBA Gokhale, D.Sc. 1998 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SEVER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND OPTIMIZATIONS FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE, REAL-TIME
Short Title: High-performance CORBA Gokhale, D.Sc. 1998 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SEVER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND OPTIMIZATIONS FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE, REAL-TIME
C, ACE C++, Blob Streaming, and Orbix over ATM
 The Performance of Object-Oriented Components for High-speed Network Programming Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Washington University, St. Louis Introduction æ Distributed object computing èdocè
The Performance of Object-Oriented Components for High-speed Network Programming Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Washington University, St. Louis Introduction æ Distributed object computing èdocè
Adaptive & Reflective Middleware. Andreas Rasche
 Adaptive & Reflective Middleware Andreas Rasche Roadmap Quality of Service Adaptive Middleware Classification of Adaptive Middleware Reflective Middleware & Reflection & Metaprogramming Overview Adaptive
Adaptive & Reflective Middleware Andreas Rasche Roadmap Quality of Service Adaptive Middleware Classification of Adaptive Middleware Reflective Middleware & Reflection & Metaprogramming Overview Adaptive
Agrowing class of real-time systems require
 COVER FEATURE An Overview of the Real-Time CA Specification OMG s Real-Time CA provides standard policies and mechanisms that support quality-of-service requirements end to end. Such support enhances the
COVER FEATURE An Overview of the Real-Time CA Specification OMG s Real-Time CA provides standard policies and mechanisms that support quality-of-service requirements end to end. Such support enhances the
Overview. Distributed Systems. Distributed Software Architecture Using Middleware. Components of a system are not always held on the same host
 Distributed Software Architecture Using Middleware Mitul Patel 1 Overview Distributed Systems Middleware What is it? Why do we need it? Types of Middleware Example Summary 2 Distributed Systems Components
Distributed Software Architecture Using Middleware Mitul Patel 1 Overview Distributed Systems Middleware What is it? Why do we need it? Types of Middleware Example Summary 2 Distributed Systems Components
Designing an Efficient & Scalable Server-side Asynchrony Model for CORBA
 Designing an Efficient & Scalable Server-side Asynchrony Model for CORBA Darrell Brunsch, Carlos O Ryan, & Douglas C. Schmidt {brunsch,coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Designing an Efficient & Scalable Server-side Asynchrony Model for CORBA Darrell Brunsch, Carlos O Ryan, & Douglas C. Schmidt {brunsch,coryan,schmidt}@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Distributed Objects. Object-Oriented Application Development
 Distributed s -Oriented Application Development Procedural (non-object oriented) development Data: variables Behavior: procedures, subroutines, functions Languages: C, COBOL, Pascal Structured Programming
Distributed s -Oriented Application Development Procedural (non-object oriented) development Data: variables Behavior: procedures, subroutines, functions Languages: C, COBOL, Pascal Structured Programming
Applying Optimization Principle Patterns to Design Real-Time ORBs
 THE ADVANCED COMPUTING SYSTEMS ASSOCIATION The following paper was originally published in the 5 th USENIX Conference on Object-Oriented Technologies and Systems (COOTS '99) San Diego, California, USA,
THE ADVANCED COMPUTING SYSTEMS ASSOCIATION The following paper was originally published in the 5 th USENIX Conference on Object-Oriented Technologies and Systems (COOTS '99) San Diego, California, USA,
3C05 - Advanced Software Engineering Thursday, April 29, 2004
 Distributed Software Architecture Using Middleware Avtar Raikmo Overview Middleware What is middleware? Why do we need middleware? Types of middleware Distributed Software Architecture Business Object
Distributed Software Architecture Using Middleware Avtar Raikmo Overview Middleware What is middleware? Why do we need middleware? Types of middleware Distributed Software Architecture Business Object
Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan.
 Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan Reading List Remote Object Invocation -- Tanenbaum Chapter 2.3 CORBA
Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan Reading List Remote Object Invocation -- Tanenbaum Chapter 2.3 CORBA
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation. Programming Models for Distributed Applications
 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation
 Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
Software Architecture Patterns
 Software Architecture Patterns *based on a tutorial of Michael Stal Harald Gall University of Zurich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch/ase www.infosys.tuwien.ac.at Overview Goal Basic architectural understanding
Software Architecture Patterns *based on a tutorial of Michael Stal Harald Gall University of Zurich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch/ase www.infosys.tuwien.ac.at Overview Goal Basic architectural understanding
Institute for Software Integrated Systems Vanderbilt University Nashville, Tennessee
 Architectural and Optimization Techniques for Scalable, Real-time and Robust Deployment and Configuration of DRE Systems Gan Deng Douglas C. Schmidt Aniruddha Gokhale Institute for Software Integrated
Architectural and Optimization Techniques for Scalable, Real-time and Robust Deployment and Configuration of DRE Systems Gan Deng Douglas C. Schmidt Aniruddha Gokhale Institute for Software Integrated
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Recommendations for a CORBA Language Mapping for RTSJ
 CORBA Language Mapping Victor Giddings Objective Interface Systems victor.giddings@ois.com Outline Real-time Specification for Java Background Memory Management Thread Types Thread Priorities IDL to RTSJ
CORBA Language Mapping Victor Giddings Objective Interface Systems victor.giddings@ois.com Outline Real-time Specification for Java Background Memory Management Thread Types Thread Priorities IDL to RTSJ
Pattern Usage in an Avionics Mission Processing Product Line
 Pattern Usage in an Avionics Mission Processing Product Line David Sharp and Wendy Roll, The Boeing Company, St. Louis, MO 1 Introduction Within the Boeing Company s Phantom Works research and development
Pattern Usage in an Avionics Mission Processing Product Line David Sharp and Wendy Roll, The Boeing Company, St. Louis, MO 1 Introduction Within the Boeing Company s Phantom Works research and development
Interprocess Communication Tanenbaum, van Steen: Ch2 (Ch3) CoDoKi: Ch2, Ch3, Ch5
 Interprocess Communication Tanenbaum, van Steen: Ch2 (Ch3) CoDoKi: Ch2, Ch3, Ch5 Fall 2008 Jussi Kangasharju Chapter Outline Overview of interprocess communication Remote invocations (RPC etc.) Message
Interprocess Communication Tanenbaum, van Steen: Ch2 (Ch3) CoDoKi: Ch2, Ch3, Ch5 Fall 2008 Jussi Kangasharju Chapter Outline Overview of interprocess communication Remote invocations (RPC etc.) Message
Chapter 4 Communication
 DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 4 Communication Layered Protocols (1) Figure 4-1. Layers, interfaces, and protocols in the OSI
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 4 Communication Layered Protocols (1) Figure 4-1. Layers, interfaces, and protocols in the OSI
F6COM: A Case Study in Extending Container Services through Connectors
 F6COM: A Case Study in Extending Container Services through Connectors Abhishek Dubey, Andy Gokhale, Gabor Karsai, William R. Otte; Vanderbilt University/ISIS Johnny Willemsen; Remedy IT Paul Calabrese,
F6COM: A Case Study in Extending Container Services through Connectors Abhishek Dubey, Andy Gokhale, Gabor Karsai, William R. Otte; Vanderbilt University/ISIS Johnny Willemsen; Remedy IT Paul Calabrese,
Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations
 Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Patterns and Performance of a CORBA Event Service for Large-scale Distributed Interactive Simulations Carlos O Ryan and Douglas C. Schmidt fcoryan,schmidtg@uci.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
A Predictable RTOS. Mantis Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Victoria
 A Predictable RTOS Mantis Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Victoria Outline I. Analysis of Timeliness Requirements II. Analysis of IO Requirements III. Time in Scheduling IV. IO in Scheduling
A Predictable RTOS Mantis Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Victoria Outline I. Analysis of Timeliness Requirements II. Analysis of IO Requirements III. Time in Scheduling IV. IO in Scheduling
(D)COM Microsoft s response to CORBA. Alessandro RISSO - PS/CO
 (D)COM Microsoft s response to CORBA Alessandro RISSO - PS/CO Talk Outline DCOM What is DCOM? COM Components COM Library Transport Protocols, Security & Platforms Availability Services Based on DCOM DCOM
(D)COM Microsoft s response to CORBA Alessandro RISSO - PS/CO Talk Outline DCOM What is DCOM? COM Components COM Library Transport Protocols, Security & Platforms Availability Services Based on DCOM DCOM
Applying Patterns to Develop Extensible ORB Middleware
 Applying Patterns to Develop Extensible ORB Middleware Douglas C. Schmidt and Chris Cleeland fschmidt,cleelandg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130, USA
Applying Patterns to Develop Extensible ORB Middleware Douglas C. Schmidt and Chris Cleeland fschmidt,cleelandg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130, USA
CPU Scheduling. Daniel Mosse. (Most slides are from Sherif Khattab and Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013)
 CPU Scheduling Daniel Mosse (Most slides are from Sherif Khattab and Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013) Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained with multiprogramming CPU I/O Burst Cycle Process
CPU Scheduling Daniel Mosse (Most slides are from Sherif Khattab and Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013) Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained with multiprogramming CPU I/O Burst Cycle Process
An Object-level Gateway Supporting Integrated-Property Quality of Service
 An Object-level Gateway Supporting Integrated-Property Quality of Service Richard Schantz, John Zinky, David Karr, David Bakken, James Megquier, Joseph Loyall BBN Technologies/GTE Internetworking 10 Moulton
An Object-level Gateway Supporting Integrated-Property Quality of Service Richard Schantz, John Zinky, David Karr, David Bakken, James Megquier, Joseph Loyall BBN Technologies/GTE Internetworking 10 Moulton
A Family of Design Patterns for Application-Level Gateways
 A Family of Design Patterns for Application-Level Gateways Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis 63130
A Family of Design Patterns for Application-Level Gateways Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu http://www.cs.wustl.edu/schmidt/ Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis 63130
Middleware Scheduling Optimization Techniques for Distributed Real-Time and Embedded Systems
 Middleware Scheduling Optimization Techniques for Distributed Real-Time and Embedded Systems Christopher Gill and Ron Cytron fcdgill, cytrong@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University,
Middleware Scheduling Optimization Techniques for Distributed Real-Time and Embedded Systems Christopher Gill and Ron Cytron fcdgill, cytrong@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University,
Static Component Configuration Support for Real-Time Platforms
 Static Component Configuration Support for Real-Time Platforms Chris Gill, Venkita Subramonian, and Liang-Jui Shen Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130 {cdgill,venkita,ls1}@cse.wustl.edu
Static Component Configuration Support for Real-Time Platforms Chris Gill, Venkita Subramonian, and Liang-Jui Shen Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130 {cdgill,venkita,ls1}@cse.wustl.edu
PROCESS SCHEDULING II. CS124 Operating Systems Fall , Lecture 13
 PROCESS SCHEDULING II CS124 Operating Systems Fall 2017-2018, Lecture 13 2 Real-Time Systems Increasingly common to have systems with real-time scheduling requirements Real-time systems are driven by specific
PROCESS SCHEDULING II CS124 Operating Systems Fall 2017-2018, Lecture 13 2 Real-Time Systems Increasingly common to have systems with real-time scheduling requirements Real-time systems are driven by specific
Using CORBA Asynchronous Messaging, Pluggable Protocols and the Real-Time Event Service in a Real-Time Embedded System
 Using CORBA Asynchronous Messaging, Pluggable Protocols and the Real-Time Event Service in a Real-Time Embedded System Bruce Trask Contact Systems 50 Miry Brook Rd Danbury, CT 06810 btrask@contactsystems.com
Using CORBA Asynchronous Messaging, Pluggable Protocols and the Real-Time Event Service in a Real-Time Embedded System Bruce Trask Contact Systems 50 Miry Brook Rd Danbury, CT 06810 btrask@contactsystems.com
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Motivation. This thesis presents the necessary extensions to the CORBA standard and CORBA
 Chapter 1 Introduction This thesis presents the necessary extensions to the CORBA standard and CORBA Services to support requirements of a real-time distributed system. It also describes a prototype implementation
Chapter 1 Introduction This thesis presents the necessary extensions to the CORBA standard and CORBA Services to support requirements of a real-time distributed system. It also describes a prototype implementation
Asynchronous Events on Linux
 Asynchronous Events on Linux Frederic.Rossi@Ericsson.CA Open System Lab Systems Research June 25, 2002 Ericsson Research Canada Introduction Linux performs well as a general purpose OS but doesn t satisfy
Asynchronous Events on Linux Frederic.Rossi@Ericsson.CA Open System Lab Systems Research June 25, 2002 Ericsson Research Canada Introduction Linux performs well as a general purpose OS but doesn t satisfy
Evaluating CORBA Latency and Scalability Over High-Speed ATM Networks
 Evaluating CORBA Latency and Scalability Over High-Speed ATM Networks Aniruddha S. Gokhale and Douglas C. Schmidt fgokhale,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University St.
Evaluating CORBA Latency and Scalability Over High-Speed ATM Networks Aniruddha S. Gokhale and Douglas C. Schmidt fgokhale,schmidtg@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University St.
DS 2009: middleware. David Evans
 DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
Scheduling. CSC400 - Operating Systems. 7: Scheduling. J. Sumey. one of the main tasks of an OS. the scheduler / dispatcher
 CSC400 - Operating Systems 7: Scheduling J. Sumey Scheduling one of the main tasks of an OS the scheduler / dispatcher concerned with deciding which runnable process/thread should get the CPU next occurs
CSC400 - Operating Systems 7: Scheduling J. Sumey Scheduling one of the main tasks of an OS the scheduler / dispatcher concerned with deciding which runnable process/thread should get the CPU next occurs
Applying Patterns and Frameworks to Develop Object-Oriented Communication Software
 Applying Patterns and Frameworks to Develop Object-Oriented Communication Software Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis, MO 63130 This
Applying Patterns and Frameworks to Develop Object-Oriented Communication Software Douglas C. Schmidt schmidt@cs.wustl.edu Department of Computer Science Washington University, St. Louis, MO 63130 This
Applying CORBA Fault Tolerant Mechanisms to Network Management. B. Natarajan, F. Kuhns, and C. O Ryan
 Applying CORBA Fault Tolerant Mechanisms to Network Management Aniruddha Gokhale Shalini Yajnik Bell Laboratories Lucent Technologies Douglas Schmidt B. Natarajan, F. Kuhns, and C. O Ryan Distributed Object
Applying CORBA Fault Tolerant Mechanisms to Network Management Aniruddha Gokhale Shalini Yajnik Bell Laboratories Lucent Technologies Douglas Schmidt B. Natarajan, F. Kuhns, and C. O Ryan Distributed Object
CPU Scheduling. Operating Systems (Fall/Winter 2018) Yajin Zhou ( Zhejiang University
 Operating Systems (Fall/Winter 2018) CPU Scheduling Yajin Zhou (http://yajin.org) Zhejiang University Acknowledgement: some pages are based on the slides from Zhi Wang(fsu). Review Motivation to use threads
Operating Systems (Fall/Winter 2018) CPU Scheduling Yajin Zhou (http://yajin.org) Zhejiang University Acknowledgement: some pages are based on the slides from Zhi Wang(fsu). Review Motivation to use threads
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms
 Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Chapter 09 (version 27th November 2001) Maarten van Steen Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Faculty of Science Dept. Mathematics and Computer Science Room R4.20.
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Chapter 09 (version 27th November 2001) Maarten van Steen Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Faculty of Science Dept. Mathematics and Computer Science Room R4.20.
Strategized, Coordinated Services for Real-Time Middleware
 Strategized, Coordinated s for Real-Time Middleware Lisa Cingiser DiPippo, Victor Fay-Wolfe, Matthew Murphy, Priyanka Gupta, Jiangyin Zhang, Jianming Ye, Kevin Bryan, Tim Henry Sponsors: URI Real-Time
Strategized, Coordinated s for Real-Time Middleware Lisa Cingiser DiPippo, Victor Fay-Wolfe, Matthew Murphy, Priyanka Gupta, Jiangyin Zhang, Jianming Ye, Kevin Bryan, Tim Henry Sponsors: URI Real-Time
Designing High Performance IEC61499 Applications on Top of DDS
 ETFA2013 4th 4DIAC Users Workshop Designing High Performance IEC61499 Applications on Top of DDS Industrial communications Complex Different solutions at the different layers Fieldbus at bottom layers:
ETFA2013 4th 4DIAC Users Workshop Designing High Performance IEC61499 Applications on Top of DDS Industrial communications Complex Different solutions at the different layers Fieldbus at bottom layers:
Commercial Real-time Operating Systems An Introduction. Swaminathan Sivasubramanian Dependable Computing & Networking Laboratory
 Commercial Real-time Operating Systems An Introduction Swaminathan Sivasubramanian Dependable Computing & Networking Laboratory swamis@iastate.edu Outline Introduction RTOS Issues and functionalities LynxOS
Commercial Real-time Operating Systems An Introduction Swaminathan Sivasubramanian Dependable Computing & Networking Laboratory swamis@iastate.edu Outline Introduction RTOS Issues and functionalities LynxOS
Dassault Enovia, a Case Study of CORBA. Introduction Distributed Architecture Orbix Im plem entation Detail Conlcusion
 Dassault Enovia, a Case Study of CORBA Introduction Distributed Architecture Orbix Im plem entation Detail Conlcusion Introduction What's a PLM solution? Who uses PLM products? The distributed requirem
Dassault Enovia, a Case Study of CORBA Introduction Distributed Architecture Orbix Im plem entation Detail Conlcusion Introduction What's a PLM solution? Who uses PLM products? The distributed requirem
Intelligent Event Processing in Quality of Service (QoS) Enabled Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) Middleware
 Intelligent Event Processing in Quality of Service (QoS) Enabled Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) Middleware Joe Hoffert jhoffert@dre.vanderbilt.edu http://www.dre.vanderbilt.edu/~jhoffert/ CS PhD Student Vanderbilt
Intelligent Event Processing in Quality of Service (QoS) Enabled Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) Middleware Joe Hoffert jhoffert@dre.vanderbilt.edu http://www.dre.vanderbilt.edu/~jhoffert/ CS PhD Student Vanderbilt
Real-Time CORBA Experiences in an Avionics Domain
 Real-Time CORBA Experiences in an Avionics Domain Jeanna Gossett, David Corman and David Sharp The Boeing Company OMG Real-Time Embedded and Distributed Object Computing Workshop June 7, 2001 Bold Stroke
Real-Time CORBA Experiences in an Avionics Domain Jeanna Gossett, David Corman and David Sharp The Boeing Company OMG Real-Time Embedded and Distributed Object Computing Workshop June 7, 2001 Bold Stroke
