(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
|
|
|
- Simon Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 Reitz et al. US 2008O262913A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 23, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) OPTIMIZINGELECTRONIC DISPLAY OF ADVERTISING CONTENT Inventors: James Reitz, San Francisco, CA (US); Paul Deeds, Berkeley, CA (US) Correspondence Address: Trellis Intellectual Property Law Group, PC 1900 EMBARCADERO ROAD, SUITE 109 PALO ALTO, CA (US) Assignee: Appl. No.: 11/738,421 HUBPAGES, INC., San Franscisco, CA (US) Filed: Apr. 20, 2007 Publication Classification Int. C. G06O 30/00 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /14 (57) ABSTRACT In one embodiment, a selection process executing in an opti mizing engine is invoked as users are presented with web pages that include ad content. The selection process provides an initial population of sets of characteristics that specify an initial generation of layouts of ads for the pages. The charac teristics can include anything that affects an ads appearance on the display. For example, ad type, position within a web page, color, size, text font, animation, etc. can be specified. Statistics are obtained as to each ad or page layout's perfor mance or impact on the user, Such as revenue obtained from ads in the layout, how many user's clickanad, how long users view an ad, etc. Once a large enough sample of user impacts is obtained a second population of sets of characteristics is created to improve the overall performance of the initial population. In a preferred embodiment, genetic computa tional procedures are used to create each population and to create new characteristic sets and remove underperforming SetS. Optimizing Engine 102 Ad Characteristics 104. Ad Definitions 106 Ad Characteristic Server 111 Ad Selection 108 Ad Performance Measurement 110 PAGE SERVER 120 INTERNET 150
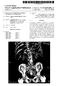
2 Patent Application Publication Oct. 23, 2008 Sheet 1 of 5 US 2008/ A1 1OO LATEST NEWS E Watch Video Stories 24 E World Market E. wim milk 26 Figure 1
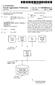
3 Patent Application Publication Oct. 23, 2008 Sheet 2 of 5 US 2008/ A1 Optimizing Engine 102 1OO Ad Characteristics 104. Ad Definitions 106 Ad Characteristic Server 111 Ad Selection 108 Ad Performance Measurement 110 PAGE SERVER 120 INTERNET Figure 2
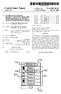
4 Patent Application Publication Oct. 23, 2008 Sheet 3 of 5 US 2008/ A1 OZ9 Sod HTO GV v SOd HTO GV S/WEIN p JONA 9 eun61 Z09
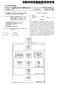
5 Patent Application Publication Oct. 23, 2008 Sheet 4 of 5 US 2008/ A gl gl y z) 7. v 9 gl d
6 Patent Application Publication Oct. 23, 2008 Sheet 5 of 5 US 2008/ A1 009 Z09 p\/ eunseðin?oedu] G?un61
7 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, 2008 OPTIMIZNGELECTRONIC DISPLAY OF ADVERTISING CONTENT TECHNICAL FIELD This disclosure relates in general to electronic dis play of information and more specifically to a system for optimizing the display of advertising content. BACKGROUND 0002 Electronic transmission and display of information is prevalent. Forms of electronic displays of information include web pages, electronic mail ( ) and attachments, text messages, displaying documents such as text and image documents, spreadsheets, or other forms of files or data. Such information display can take place on many types of devices Such as computer systems, billboard displays, cell phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), devices, cameras, etc Along with displaying main content that is the initial Subject of interest to viewers, advertising or other commercial content is often included with the display of the main content. Displaying commercial content is an important revenue Source for many providers of the main content, or for provid ers of other services or equipment that contribute to a user's access to the main content. One approach to providing adver tising content includes ads that are adjacent to or embedded with portions of the main content. When the ad is displayed in a web page many of the ad's characteristics (i.e., ad metadata) Such as ad type, position within a web page, color, size, text font, animation, etc. become very important to whethera user notices the ad and reads the ad or otherwise reacts to the ad Ideally, for the ad's sponsor, the user will click on the ad to be taken to a commercial website to be presented with additional product or service information or, ideally, to complete a sale. Even if the ad is merely noticed by the user, then a psychological attachment to the sponsor's product or service can be achieved which can have significant value to the ad's sponsor Although ad characteristics can be important to the ad's impact on a user, it can be difficult to determine the ideal ad characteristics that will achieve the highest impact. SUMMARY OF EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION 0006 A preferred embodiment of the invention is directed to determining optimal placement and appearance of adver tisements in a web page. Other embodiments can be adapted for different types of content delivery and display such as in the body or attachments of an message, within docu ments or files, within or adjacent to digital video, movie, FlashTM animations, etc A selection process executing in an optimizing engine is invoked as users are presented with web pages that include ad content. The selection process provides an initial population of sets of characteristics that specify an initial generation of layouts of ads for pages. The characteristics can include anything that affects an ads appearance on the display. For example, ad type, position within a web page, color, size, text font, animation, border or other decorative ad features, images within an ad (e.g., internal image size and position), etc. can be specified. Statistics are obtained as to each ad or page layout's performance or impact on the user, Such as revenue obtained from ads in the layout, how many user's click an ad, how long users view an ad, etc Once a large enough sample of user impacts is obtained a second population of sets of characteristics is created to improve the overall performance of the initial population. In a preferred embodiment, a genetic computa tional procedure is used to create each population and to create new characteristic sets and remove underperforming sets. In other embodiments, other computing methods can be used for one or more of the functions described herein In one embodiment the invention provides a method, for displaying ad content with main content on a display device, wherein the display device is operated by a user, the method comprising: generating first characteristics for the display of the ad content; sending display information to a user device to display thead content with the main content according to the first characteristics; accepting a user input signal associated with the user device to indicate an impact of the ad content upon a human user; generating second charac teristics derived at least in part from the first characteristics and the indicated impact; and sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the second characteristics. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0010 FIG. 1 illustrates a web page layout including main content and ad content; 0011 FIG. 2 shows basic components of a system for practicing an embodiment of the invention over a digital network such as the Internet; 0012 FIG. 3 shows an example format for an ad charac teristic definition; 0013 FIG. 4 illustrates a genetic computational procedure example of optimization of slot positions; and 0014 FIG. 5 is an example flowchart illustrating basic steps in a method DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION (0015 FIG. 1 illustrates a layout of web page 100. A web page Such as web page 100 is typically provided in response to a user selection or signal Such as when a user selects or clicks a link, or hyperlink, to the web page. A web browser or other display system or process executing on a device such as a computer is used to display the web page in response to a web page definition that can include text in a standard format such as HyperTextMarkup Language (HTML), Extensible HTML (XHTML), Extensible Markup Language (XML). JavaScript TM, etc. Web pages can include various other mechanisms or definitions to assist in the display or presen tation of information (e.g., image, Sound, executable code, hyperlinks etc.) such as JavaScriptTM, Dynamic HTML (DHTML), Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), C code, etc. Although a preferred embodiment is described with reference to web pages any Suitable system, format or approach to display electronic information may be used Web page 100 would typically be displayed on a display screen Such as display screen 10. All or a portion of the web page might be displayed at any one time. Multiple web pages and/or other types of electronic information can also be displayed on one screen. The web page includes advertising content that can be positioned at slots Such as ad slots 20, 22, 24 and 26. Other content on the page such as text
8 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, 2008 and images is referred to as main content since it is usually the content that is of primary or initial interest to a user who has selected the page. Note that any type of content may be used with features of the present invention. It should be appar ent that FIG. 1 is only an example of a single layout for purposes of discussion and the layout of other pages can vary widely For example, the size, shape, number and position of the ad slots can vary. The type and arrangement of the main content can change. A page may have one or more ad slots and may have no content other than ad content, if desired. Ani mations can be used in the ad and main content. Other mecha nisms such as hyperlinks, digital video, color, font, etc. can be used as is known in the art In a preferred embodiment, ad slots 20, 22, 24 and 26 are areas of the page that can be filled with ad contentator before a time when a user requests the page, or the page is otherwise provided to a device for display. Ad content is defined to be displayed in one or more of the slots according to ad metadata or characteristics such as ad type, color, size, position, etc. An ad may occupy all or a fraction of an ad slot or the slot may be left empty or hidden. Position of the ad can include the slot to which an ad is assigned and the ad's position within the slot. In other embodiments, ad position on a page does not have to be handled with slots but can be by any other positioning scheme. For example, ad x,y coordinates with respect to a position on the page can be used. Orad slot information may be an approximation of where an ad will be placed rather than a mandatory region. In some approaches, ads are allowed to move or float over the main content. Other approaches are possible FIG. 2 illustrates basic components of a system for practicing an embodiment of the invention in a digital net work such as the Internet. System 100 includes an optimizing engine 102 for generating web page layouts using differentad characteristics. Optimizing engine 102 includes stored ad characteristics 104, ad content definitions 106, ad selection process 108, ad characteristic server 111 and ad performance measurement 110. Note that the diagram of FIG. 2 is but one example of an arrangement of components in a system Suit able for use with the invention. Many variations are possible including adding, deleting or modifying components, data paths or other aspects of the example system User 144 operates a computer system that includes display screen 130 and user input devices such as keyboard 140 and mouse 142. Although specific devices are shown, many other types of devices can be used. For example, user input devices can be any Suitable type of device Such as a trackball, touchscreen, motion or gesture detection, image or Voice recognition, etc. Other basic components that may be used in a computer system are not specifically shown. For example, a processor, memory, hard disk drive, input/output ports and connectors, etc. are not shown but it should be apparent that Such devices or hardware are used, as needed. Yet other types of devices such as portable computers, PDAs, cellphones, portable devices, audio players, etc. can be used in place of the computer system of FIG. 2. In general, any Suitable type of device having an associated display and user input device can be employed User 144 operates the computer system to cause a display of a web page such as web page 131. Page server 120 provides web page 131 to the user's computer system or other user device via Internet 150. Web page 131 includes text and/or images that are the main content of the page and also includes ad content such as ads 132,134,136 and 138. In one embodiment the placement of ads within a page is determined by the presence within the page definition of calls to an ad server Such as optimizing engine 102. The calls are text or Script placed within the page definition manually or automati cally to determine the spaces that an ad might occupy. For example, a call can be placed by a human web page author when the page definition is created. Or the call can be inserted by page server 120 or a different device or process when the page is created, or dynamically when the page is formed in real time in response to a user or device requesting the page. Calls can be placed in any other Suitable way Such as with a combination of manual and automated techniques One or more of the calls results in a communication to ad selection process 108 of optimizing engine 102. Ad selection process 108 determines the ad content and charac teristic to be used to display the ad. Ad content is retrieved from ad definitions 106 and ad characteristics are obtained from ad characteristics 104. The ad content and characteris tics are provided to the web browser executing in the user's computer system by ad selection process 108 and ad charac teristics server 111, respectively, to generate the display of web page 131. The displayed page shows the ads embedded within the page and interspersed at different positions within the main content of the page. In a preferred embodiment the characteristics are communicated via serialized JavaScriptTM (JSON) but other embodiments can use XML, or any other Suitable mechanism Note that many variations to this approach are pos sible. For example, some types of page definitions may allow the ads to be placed on the pagearbitrarily at a time of serving the page. In other words, no predetermined positions for the ads need to be coded into an original page definition and the call functions can be achieved by other mechanisms. This would allow the optimizing engine to have more control over ad position in a page as opposed to using set calls at prede termined positions. It is also possible to have ad content and/or ad characteristics reside at a site that is remote from, and not part of optimizing engine 102. So, for example, the ad content can be obtained from a different (i.e., third-party) server or site that is run by a person, company or other entity distinct from the entity operating the optimizing engine and distinct from the user. The ad content can still be displayed according to the ad characteristics which can come from the entity operating the optimizing engine, the entity operating hosting the ad definitions, or from a different entity. Each of these pieces of the ad display information can be conveyed to the user device over a digital network such as Internet 150. As is known in the art, Internet 150 is an open network system that includes many other devices such as routers, Switches, servers, etc. These are shown symbolically by components 152, 154 and 156. The transfer of information via the Internet can use any Suitable type and number of devices and pro cesses and can use with any Suitable data format, protocol, standard or other present or future convention or characteris tic Yet another approach can allow optimizing engine 102 to provide the entire web page definition to a user includ ing ad content. In this approach it is not necessary to have separate calls for ad content since the page's main content and ad content are formed or hosted at a single site. Alternatively, calls can be included to other sites to obtain parts of the ad content to be used for one or more ads. In general, the func tions described herein can be performed by the same or dif
9 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, 2008 ferent devices and/or processes at one or more places and times. For example, although the optimizing engine and its components are described as being remote from the user device and communicating over the Internet, other embodi ments can allow one or more of the optimizing engine com ponents (or a portion of the components functionalities) to operate locally with, or on, the user device User 144's actions with respect to the page are monitored and information that could indicate an ad's impact on the user (i.e., the ad s performance') is provided to ad performance measurement process 110. For example, the act of a user clicking on an ador on text or images within, adjacent to or otherwise associated with an ad can be a factor used in ad performance measurement process 110. A pre ferred embodiment uses actual sales or revenue obtained from ads so user completions of a transaction initiated with an ad are tracked. Other acts such as a user moving a pointer over an ad (so-called mouse over ), the duration of time the ad remains visible on the display, or other types of detected user actions or inactions can be indicated and used by ad perfor mance measurement process 110 to help determine a perfor mance level for the ad. In the preferred embodiement, some of these measurements are gathered via JavaScriptTM and com municated back to process 110 over the Internet. This com munication happens transparently to the user via XMLHTTP requests or as parameters in a hidden image, etc as is known in the art The performance measurements are provided to ad selection process 108 in order to rank each set of character istics used by an ad so that sets that result in better ad perfor mance are used more often and sets that result in worse ad performance are used less often. The ad performance can be weighted with the average or actual revenue associated with the data gathered in process 110. Thus, over time the perfor mance of the ads are improved A particular embodiment focuses on the effective ness of an overall page layout of one or more ads. Genetic computational procedure techniques are used so that a popu lation of layouts changes from generation to generation based on performance, or "fitness of particular characteristics used in the layout. A layout is expressed in digital form as "chromosomes, genotype', 'genome' or 'agent'. As per formance results are obtained, better performing agents are used to generate hybrid agents for the next population 0028 FIG. 3 shows an example format for an ad charac teristic definition 300. Ad characteristic definition 300 includes Active Indicator 302 data for whether the agent is currently enabled or not. Adtype 304 is a pointer to the actual ad content data (e.g., the ad's visual image definition) which can reside at a different server or computer system from the computer system executing the optimizing engine. Color Field 306 indicates one or more colors to be used in display ing the ad. For example, the color of a background upon which the ad content is displayed can be specified along with other color properties such as text and border colors, different colors for different fonts, hyperlink text, etc. Position Field 308 determines where within an ad slot the ad content corre sponding to the Ad Type is displayed. This allows more pre cise control of ad positioning within a page layout Each ad characteristic definition defines how an ad is displayed within an ad slot in a page layout. One or more ad characteristic definitions are combined to form the agent or genome for a layout that corresponds to a particular page of main content. Agent 320 includes ad characteristic definitions for 4 ads named Ad1, Ad 2, Ad 3 and Ad 4. Ad characteristic definition 300 has been reduced in size for purposes of illus tration to be Ad 1's characteristic within agent Each ad characteristic in the set of four ad charac teristics in agent 320 has the same format but in other embodi ments the formats can vary among characteristic definitions. Thus, each of Ads 1, 2, 3 and 4 have their own Active Indi cator, Ad Type, Color Field and Position Field. The position of each ad characteristic definition within the agent deter mines the slot to which the associated ad is assigned. The characteristic definitions are mapped to the page layout by parsing the agent left-to-right while parsing the page in a left-to-right and top-down manner. Any other approach to assigning agent definitions to a page layout is possible. Note that in other embodiments it may not be necessary to have a spatial assignment of ad characteristics with ad slots. So in FIG.3, Ad 1 is in the first position of the agent and is assigned to slot 330, Ad 2 is in the second position of the agent and is assigned to slot 332, Ad 3 is in the third position of the agent and is assigned to slot 334 and Ad 4 is in the fourth position of the agent and is assigned to slot 336. Each Ad is displayed according to its characteristic in the agent. Thus, agent 320 determines the display of ads for a particular layout in a web page FIG. 4 illustrates a genetic computational procedure example of optimization of slot positions which can result in improved ad performance. In FIG. 4, Population 1 is desig nated as P1. It includes four agents 402,404, 406, and 408. Only ad numbers are shown to representa set of the respective ad's characteristic definitions. For example. In agent 402, Ad 11 is in position 1. All of Ad 11's characteristics are assumed to be represented by bits in the position for ad 11 within agent 402. Similarly Ads 2, 7 and 6 in the subsequent positions for agent 402 each have the same characteristic fields as do other ads in other agents of P1, such as agents 404, 406 and For ease of discussion P1 is shown with only 4 agents. In practice the number of agents can vary and is dependent upon the number of different layout possibilities that are desired to be maintained for a page, group of pages, website or other collection of web pages. Agent 404 includes Ads 5, 14, 1 and 16. Agent 406 includes Ads 9, 8, 13 and 3. Agent 408 includes Ads 12, 415 and 10. As described above, the position of eachad's set of characteristics within an agent determines the ad slot within a page layout where the ad associated with the characteristic set will be displayed. For example, ifa page layout for web page 100 is performed using agent 402 then Ad 11 will be in slot 20, Ad 2 will be in slot 22, Ad 7 will be in slot 24 and Ad 6 will be in slot 26. Other types of operators can be used, including but not limited to cross over, double-crossover, mutation, inversion or directed manipulation of the characteristics based on domain knowl edge. Any suitable present or future-discovered operators or techniques can be employed to generate Sucessive agents, genomes, populations or other forms of characteristic descriptions for ad layouts In a preferred embodiment, the first population P1 is generated with random ads in random agents positions. Although each ad is different (they each have a different ad number or identifier) it is possible to have duplicate ads among a population and even within an agent, as desired. Performance statistics are obtained for each layout. Perfor mance can be measured over a short time interval Such as minutes or seconds (or less). Or performance can be mea Sured over longer periods of time depending upon the amount
10 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, 2008 of page "hits (i.e., web traffic for a particular page), the amount of revenue being generated, the number of agents in a population, or depending upon other factors In order to generate a second population, P2, layouts that are performing better than other layouts in P1 are used to derive new agents according to rules. One rule for slot assign ment takes Ad identifiers from better-performing agents and combines them to form new agents In FIG. 4, it is assumed that the measured perfor mance of agent 402 and agent 404 is better than that of agents 406 and 408. One rule for generating new agents uses the first two ads from a first agent with the last two ads from a second agent. In the example, Ads 11 and 2 from agent 402 are combined with Ads 1 and 16 from agent 404 to produce new agent 422 in a second generation, or second population, P2. Similarly, Ads 7 and 6 from agent 402 are combined with Ads 5 and 14 from agent 404 to create new agent 424. Since agents 402 and 404 performed better than other agents they are also propagated to P2. Thus, P2 includes agents 422 and 424 derived from agents 402 and 404; and P2 also includes agents 402 and 404, themselves Similarly, a third population, P3, can be generated by a similar approach. In P2 it is assumed that agents 422 and 426 are the better-performing agents. So the agents 442 and 444 of P3 are derived from Ads 11 and 2 of agent 422 and Ads 7 and 6 of agent 426. Agents 422 and 426 are also propagated to P3. In this manner Subsequent generations of agents can have a higher percentage of better-performing layouts to pro vide better ad performance A preferred embodiment also varies specific ad characteristics among Subsequent population sets by allow ing new agents to have individual characteristics or portions of characteristics from a prior generation of agents. For example, rather than inheriting an entire ad's characteristic set (e.g., Active Indicator, Ad Type, Color and Position) one or more of the characteristics or a portion of a characteristic can be used. Referring to FIG.3, agent 300 may be divided so that, for example, the first half 340 of the characteristic set up to position 342 is used for a new agent while the second half of the new agent is obtained from a different agent. In this manner, the new agent includes the Active Indicator and Ad Type characteristics from agent 300 and also a portion of the color information from agent 300, while also including a remainder of the color information from a different agent and the Position Field from a different agent. By allowing split ting and inheritance of the data representation of specific characteristics and characteristic sets the optimization of a layout or individual ad placement can be performed at a characteristic-based level rather than a slot-based level as described in the discussion above in connection with FIG Thus, a next generation of layout agents can allow inheritance of characteristics of better-performing layouts from the prior generation. Characteristics such as a fine degree of ad placement within a slot, numerous color changes, etc. can be varied among populations until each characteristic set can be optimized. A preferred embodiment uses a 'gray code representation of the characteristic values, but in other embodiments any suitable data format can be used FIG. 5 shows flowchart 500 that illustrates basic steps in a method according to an embodiment of the inven tion. Flowchart 500 is entered at 502 when it is desired to begin to present and optimize a display including ads At step 504 first ad characteristics are generated for the display of ad content. Next, step 506 is executed to use the ad characteristics generated in step 504 in an initial display of ad content with main content. Step 508 is executed to measure an impact of the ad content upon a human user. Step 510 is then executed to generate second characteristics derived at least in part from the first characteristics and the indicated impact Execution then loops back to step 506 where the new characteristics are used to generate new displays of ads and main content. Steps 506, 508 and 510 are repeated, as desired, to optimize a display of ads Note that the flowchart of FIG. 5 is but one illustra tive example of a sequence of basic steps to achieve function ality according to an embodiment of the invention. Many variations can be made to the steps of FIG. 5 including add ing, removing or modifying steps or step execution Although the invention has been described with respect to particular embodiments thereof, these particular embodiments are merely illustrative, and not restrictive. For example, although embodiments have been described as implemented with genetic computational procedure tech niques, any other suitable programming approaches, tech niques or methods can be used. For example, procedural, heuristic or a combination of both methods may be used, as desired. Other factors can be taken into consideration and used in a performance evaluation or to generate Subsequent agent populations. For example, layout optimization can be associated with a time of day, day of the year (e.g., holidays, special events), geographic are, web site, source of a user being referred to a site, etc. This can allow a Valentine's day layout to be optimized differently from the same site or page on a different day of the year. Orifa user is referred to a target page being optimized from a search engine, the optimization can be handled differently than if the user is referred from another page at the target page's site. Many such variations are possible Any suitable programming language can be used to implement the routines of particular embodiments including C, C++, Java, assembly language, etc. Different program ming techniques can be employed such as procedural or object oriented. The routines can execute on a single process ing device or multiple processors. Although the steps, opera tions, or computations may be presented in a specific order, this order may be changed in different particular embodi ments. In some particular embodiments, multiple steps shown as sequential in this specification can be performed at the same time. The sequence of operations described herein can be interrupted, suspended, or otherwise controlled by another process, such as an operating system, kernel, etc. The routines can operate in an operating system environment or as stand-alone routines occupying all, or a Substantial part, of the system processing. Functions can be performed in hardware, software, or a combination of both. Unless otherwise stated, functions may also be performed manually, in whole or in part In the description herein, numerous specific details are provided, such as examples of components and/or meth ods, to provide a thorough understanding of particular embodiments. One skilled in the relevant art will recognize, however, that a particular embodiment can be practiced with out one or more of the specific details, or with otherapparatus, systems, assemblies, methods, components, materials, parts, and/or the like. In other instances, well-known structures,
11 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, 2008 materials, or operations are not specifically shown or described in detail to avoid obscuring aspects of particular embodiments A computer-readable medium' for purposes of particular embodiments may be any medium that can contain, store, communicate, propagate, or transport the program for use by or in connection with the instruction execution system, apparatus, system, or device. The computer readable medium can be, by way of example only but not by limitation, an electronic, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor system, apparatus, system, device, propaga tion medium, or computer memory Particular embodiments can be implemented in the form of control logic in Software or hardware or a combina tion of both. The control logic, when executed by one or more processors, may be operable to perform that what is described in particular embodiments A processor or process includes any human, hardware and/or Software system, mechanism or component that processes data, signals, or other information. A processor can include a system with a general-purpose central process ing unit, multiple processing units, dedicated circuitry for achieving functionality, or other systems. Processing need not be limited to a geographic location, or have temporal limitations. For example, a processor can perform its func tions in real time."offline in a batch mode, etc. Portions of processing can be performed at different times and at different locations, by different (or the same) processing sys tems Reference throughout this specification to one embodiment, an embodiment, a specific embodiment'. or particular embodiment means that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the particular embodiment is included in at least one embodiment and not necessarily in all particular embodiments. Thus, respective appearances of the phrases "inaparticular embodi ment, in an embodiment, or in a specific embodiment' in various places throughout this specification are not necessar ily referring to the same embodiment. Furthermore, the par ticular features, structures, or characteristics of any specific embodiment may be combined in any Suitable manner with one or more other particular embodiments. It is to be under stood that other variations and modifications of the particular embodiments described and illustrated herein are possible in light of the teachings herein and are to be considered as part of the spirit and scope Particular embodiments may be implemented by using a programmed general purpose digital computer, by using application specific integrated circuits, programmable logic devices, field programmable gate arrays, optical, chemi cal, biological, quantum or nanoengineered systems, compo nents and mechanisms may be used. In general, the functions of particular embodiments can beachieved by any means as is known in the art. Distributed, networked systems, compo nents, and/or circuits can be used. Communication, or trans fer, of data may be wired, wireless, or by any other means It will also be appreciated that one or more of the elements depicted in the drawings/figures can also be imple mented in a more separated or integrated manner, or even removed or rendered as inoperable in certain cases, as is useful in accordance with a particular application. It is also within the spirit and scope to implement a program or code that can be stored in a machine-readable medium to permit a computer to perform any of the methods described above Additionally, any signal arrows in the drawings/ Figures should be considered only as exemplary, and not limiting, unless otherwise specifically noted. Furthermore, the term 'or' as used herein is generally intended to mean and/or unless otherwise indicated. Combinations of com ponents or steps will also be considered as being noted, where terminology is foreseen as rendering the ability to separate or combine is unclear As used in the description herein and throughout the claims that follow, a, an, and the includes plural refer ences unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. Also, as used in the description herein and throughout the claims that follow, the meaning of in includes in and on unless the context clearly dictates otherwise The foregoing description of illustrated particular embodiments, including what is described in the Abstract, is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise forms disclosed herein. While specific particular embodiments of, and examples for, the invention are described herein for illustrative purposes only, various equivalent modifications are possible within the spirit and Scope, as those skilled in the relevant art will recognize and appreciate. As indicated, these modifications may be made to the present invention in light of the foregoing description of illustrated particular embodiments and are to be included within the spirit and scope Thus, while the present invention has been described herein with reference to particular embodiments thereof, a latitude of modification, various changes and Sub stitutions are intended in the foregoing disclosures, and it will be appreciated that in Some instances some features of par ticular embodiments will be employed without a correspond ing use of other features without departing from the scope and spirit as set forth. Therefore, many modifications may be made to adapta particular situation or material to the essential scope and spirit. It is intended that the invention not be limited to the particular terms used in following claims and/or to the particular embodiment disclosed as the best mode contem plated for carrying out this invention, but that the invention will include any and all particular embodiments and equiva lents falling within the scope of the appended claims. 1. A method, for displaying ad content with main content on a display device, wherein the display device is operated by a user, the method comprising: generating first characteristics for the display of the ad content; sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the first characteristics; accepting a user input signal associated with the user device to indicate an impact of the ad content upon a human user; generating second characteristics derived at least in part from the first characteristics and the indicated impact; and sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the second characteristics. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein the user device includes a web browser for displaying a web page. 3. The method of claim 1, wherein a user input signal associated with the user device includes a user selection of the ad content.
12 US 2008/ A1 Oct. 23, The method of claim 1, wherein a user input signal associated with the user device includes a time duration of display of the ad content on a display Screen associated with the user device. 5. The method of claim 1, further comprising using genetic computing techniques to achieve one of more of the actions recited in claim The method of claim 1, wherein the first characteristics include first and second agents, wherein generating second characteristics further comprises: determining that the first and second agents are better performing than at least one other agent in the first characteristics; using a portion of the first agent and a portion of the second agent to create a third agent; and using the third agent in the second characteristics. 7. The method of claim 6, wherein a portion of an agent includes a complete characteristic set for an ad. 8. The method of claim 6, wherein a portion of an agent includes one or more characteristics in a characteristic set associated with an ad. 9. The method of claim 8, wherein a characteristic set includes ad position. 10. The method of claim 8, wherein a characteristic set includes enabling of an ad. 11. The method of claim 8, wherein a characteristic set includes a pointer to ad content. 12. The method of claim 8, wherein a characteristic set includes ad color. 13. The method of claim 8, wherein a characteristic set includes ad position. 14. The method of claim 13, wherein ad position includes a position within a slot on a web page. 15. An apparatus, for displaying ad content with main content on a display device, wherein the display device is operated by a user, the apparatus comprising: a processor; one or more instructions executable by the processor for generating first characteristics for the display of the ad content; sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the first characteristics; accepting a user input signal associated with the user device to indicate an impact of the ad content upon a human user; generating second characteristics derived at least in part from the first characteristics and the indicated impact; and sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the second characteristics. 16. A machine-readable storage device including instruc tions for displaying ad content with main content on a display device, wherein the display device is operated by a user, the machine-readable storage device including one or more instructions for: generating first characteristics for the display of the ad content; sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the first characteristics; accepting a user input signal associated with the user device to indicate an impact of the ad content upon a human user; generating second characteristics derived at least in part from the first characteristics and the indicated impact; and sending display information to a user device to display the ad content with the main content according to the second characteristics.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O235.131A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0235131 A1 Ware (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEMORY CONTROLLER FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 711/203; 711/156 NON-HOMOGENEOUS
US 2005O235.131A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0235131 A1 Ware (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEMORY CONTROLLER FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 711/203; 711/156 NON-HOMOGENEOUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013
 (19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O183076A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183076 A1 Colangelo et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BROWSER-INDEPENDENT POP-UP WINDOWS (76) Inventors: Agatha
(19) United States US 2005O183076A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183076 A1 Colangelo et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BROWSER-INDEPENDENT POP-UP WINDOWS (76) Inventors: Agatha
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342470A1 (12) Patent Application Publication () Pub. No.: US 2016/0342470 A1 Cudak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) SEPARATING A HYBRIDASYMMETRIC (52) U.S. Cl. MX OF
(19) United States US 2016.0342470A1 (12) Patent Application Publication () Pub. No.: US 2016/0342470 A1 Cudak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) SEPARATING A HYBRIDASYMMETRIC (52) U.S. Cl. MX OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,103,736 B2. Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006
 United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0070968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0070968 A1 Poulsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 18, 2010 (54) DESKTOP WIDGET ENGINE EMULATOR COMPONENT FOR
(19) United States US 2010.0070968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0070968 A1 Poulsen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 18, 2010 (54) DESKTOP WIDGET ENGINE EMULATOR COMPONENT FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160372114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0372114A1 Klose et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ANNOUNCEMENT SIGNALING ON BOARD H04W 68/00 (2006.01) AN AIRCRAFT
(19) United States US 20160372114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0372114A1 Klose et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ANNOUNCEMENT SIGNALING ON BOARD H04W 68/00 (2006.01) AN AIRCRAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
231 age sins N3 : as a. (12) United States Patent US 8,194,335 B2. Jun. 5, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,548,906 B1. Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013
 United States Patent USOO8548906B1 (12) () Patent No.: Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,272.472 B1* 8/2001 Danneels et al.... 705/27 AUTOMATC SAVINGS UPON EVENT
United States Patent USOO8548906B1 (12) () Patent No.: Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,272.472 B1* 8/2001 Danneels et al.... 705/27 AUTOMATC SAVINGS UPON EVENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050283468A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0283468 A1 Kamvar et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) ANTICIPATED QUERY GENERATION AND PROCESSING IN
(19) United States US 20050283468A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0283468 A1 Kamvar et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) ANTICIPATED QUERY GENERATION AND PROCESSING IN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080243480A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0243480 A1 Bartz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DETERMINING SEMANTICALLY RELATED TERMS (75)
(19) United States US 20080243480A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0243480 A1 Bartz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DETERMINING SEMANTICALLY RELATED TERMS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090089340A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/008934.0 A1 Ohr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) BACKUP CATALOG RECOVERY FROM REPLICATED DATA (76)
(19) United States US 20090089340A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/008934.0 A1 Ohr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) BACKUP CATALOG RECOVERY FROM REPLICATED DATA (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application
 From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O147734A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0147734 A1 Shoup et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) ARCHIVING METHOD AND SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2002O147734A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0147734 A1 Shoup et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 10, 2002 (54) ARCHIVING METHOD AND SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006
 US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701 15488A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0115488 A1 Engelman et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR MULTIPLE Publication
US 200701 15488A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0115488 A1 Engelman et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR MULTIPLE Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O1591.22A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0159122 A1 Biswas et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTIMIZER AS AN APPSTORE SERVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 705/26.1
(19) United States US 2013 O1591.22A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0159122 A1 Biswas et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTIMIZER AS AN APPSTORE SERVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 705/26.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050289474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Master et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) PRESENTATION OF INFORMATION BASED (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/765; 715/744;
(19) United States US 20050289474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Master et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) PRESENTATION OF INFORMATION BASED (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/765; 715/744;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
(19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. combiner box. A/D Data Processing AID 2OO 3O1 203.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/ A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr.
 US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
2c NCPURA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0182258A1 Sakamoto et al. US 2003O182258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003 (54) SEARCH SERVER AND METHOD FOR (75) (73) (21) (22)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0182258A1 Sakamoto et al. US 2003O182258A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2003 (54) SEARCH SERVER AND METHOD FOR (75) (73) (21) (22)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
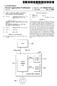 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
