Big Data Fall Data Models
|
|
|
- Aubrie Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ghislain Fourny Big Data Fall Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo
2 CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness"" Theorem" 2
3 CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness"" Theorem" ID Last name First name Theory 1 Einstein Albert General, Special Relativity 2 Gödel Kurt "Incompleteness" Theorem This is a data model 3
4 Syntax vs. Data Models Physical view Syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness"" Theorem" 4
5 Syntax vs. Data Models Logical view Data Model ID Last name First name Theory 1 Einstein Albert General, Special Relativity 2 Gödel Kurt "Incompleteness" Theorem Physical view Syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness"" Theorem" 5
6 Syntax vs. Data Models Physical view Syntax <a> <d e="f"/> <c>this is <b>text</b>.</c> </a> 6
7 Syntax vs. Data Models a Logical view Data Model e = f d This is c b. text Physical view Syntax <a> <d e="f"/> <c>this is <b>text</b>.</c> </a> 7
8 Syntax vs. Data Models Physical view Syntax { "foo" : [ 1, 2, 3 ], "bar" : { "a" : 1, "bar" : 2 } } 8
9 Syntax vs. Data Models Object foo bar Logical view Data Model Array a Object bar Physical view Syntax { "foo" : [ 1, 2, 3 ], "bar" : { "a" : 1, "bar" : 2 } } 9
10 Edge vs. Node labeling foo bar Labels are on the edges 10
11 Edge vs. Node labeling Object foobar foobar Object e = f foo bar foo bar Labels are on the edges Labels are on the nodes 11
12 XML Data models Information Set (Infoset) 12
13 XML Data models Information Set (Infoset) Post Schema-Validation Infoset (PSVI) 13
14 XML Data models Information Set (Infoset) Post Schema-Validation Infoset (PSVI) XQuery and XPath Data Model (XDM) 14
15 JSON Data Models "original" (implicit) JSON Data Model 15
16 JSON Data Models "original" (implicit) JSON Data Model JSON Schema Data Model 16
17 JSON Data Models "original" (implicit) JSON Data Model JSON Schema Data Model JSONiq Data Model (JDM) y/html/section-jsoniq-data-model.html 17
18 HTML/XML Data model Document Object Model (DOM) 18
19 grigory_bruev / 123RF Stock Photo XML Information Set 19
20 Information Set <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <dc:metadata xmlns:dc=" <title xml:lang="en" year="2008" >Systems Group</title> <publisher>eth Zurich</publisher> </dc:metadata> 20
21 Information Set 21
22 The 11 XML Information Items Document Element Attribute Processing Instruction Character Comment Namespace Unexpanded Entity Reference DTD Unparsed Entity Notation 22 22
23 The 11 XML Information Items Document Element Attribute Processing Instruction Character Comment Namespace Unexpanded Entity Reference DTD Unparsed Entity Notation 23 23
24 Document Information Items Document Information Item doc [children] Element Information Item metadata [document element] Element Information Item metadata [notations] <empty> [unparsed entities] <empty> [base URI ] file:///users/bigdata/documents/info.xml [character encoding scheme] UTF-8 [standalone] <no value> [version]
25 Element Information Items Element Information Item dc:metadata [namespace name] [local name] metadata [prefix] dc [children] Element Information Items title, publisher [attributes] <empty> [namespace attributes] Attribute Information Item xmlns:dc [in-scope namespaces] Namespace Information Items dc->systems, xml->ns [base URI] file:///users/bigdata/documents/info.xml [parent] Document Information Item doc 25
26 Attribute Information Items Attribute Information Item year [namespace name] none [local name] year [prefix] none [normalized value] 2008 [specified] true [attribute type] <no value> [references] unknown [owner element] Element Information Item dc:title 26
27 Namespace Information Items Namespace Information Item dc->systems [prefix] dc [namespace name] dc->systems Namespace Information Item xml->ns xml->ns [prefix] xml [namespace name] 27
28 XML Infoset - the tree doc xmlns:dc dc:metadata xml->ns dc->systems xml->ns dc->systems dc:title dc:publisher dc->systems xml->ns en xml:lang Systems Group year 2008 ETH Zurich 28
29 Types 29
30 Type Systems Almost all type systems (Java, SQL, PSVI, JDM, Protocol buffers, Avro, Parquet, and so on) share the following properties: 30
31 Type Systems Almost all type systems (Java, SQL, PSVI, JDM, Protocol buffers, Avro, Parquet, and so on) share the following properties: - Distinction between atomic types and structured types 31
32 Type Systems Almost all type systems (Java, SQL, PSVI, JDM, Protocol buffers, Avro, Parquet, and so on) share the following properties: - Distinction between atomic types and structured types - Same categories of atomic types 32
33 Type Systems Almost all type systems (Java, SQL, PSVI, JDM, Protocol buffers, Avro, Parquet, and so on) share the following properties: - Distinction between atomic types and structured types - Same categories of atomic types - Lists and maps as structured types 33
34 Type Systems Almost all type systems (Java, SQL, PSVI, JDM, Protocol buffers, Avro, Parquet, and so on) share the following properties: - Distinction between atomic types and structured types - Same categories of atomic types - Lists and maps as structured types - Sequence type cardinalities 34
35 Types (General) Atomic Types vs. Structured Types 35
36 Atomic Types 36
37 Atomic Types Strings 37
38 Strings (Character sequences with monoid structure) "foo" "Zurich" "Ilsebill salzte nach." f o o Z u r i c h I l s e b i l l s a l z t e n a c h. 38
39 Atomic Types Strings Numbers 39
40 Interval-based integer types (exist as signed and unsigned) 8-bit (Java's byte) 16-bit (Java's short) 32-bit (Java's int) 64-bit (Java's long) 40
41 Arbitrary precision decimals (and integers) Any precision and scale
42 Float and Double IEEE 754 standard 32 bits 64 bits ca. 7 digits ca. 15 digits to to single precision double precision 42
43 Atomic Types Strings Numbers Booleans 43
44 Booleans TRUE t true y yes on 1 FALSE f false n no off 0 44
45 Atomic Types Strings Numbers Booleans Dates and Times 45
46 Dates and times Date Time Timestamp Duration 46
47 Dates (Gregorian calendar) Year + Month + Day 2017 August 1st (AD) 47
48 Times Hours + Minutes + Seconds 10 : 31 :
49 Timestamps Year + Month + Day + Hours + Minutes + Seconds 2017 August 1 st 10 : 31 : (AD) 49
50 Atomic Types Strings Numbers Booleans Dates and Times Time Intervals 50
51 Duration kinds Year Month Day Hour Minute Second Example: 2 years and 4 months 51
52 Duration kinds Year Month Day Hour Minute Second Example: 2 years and 4 months Example: 3 hours and 14 minutes 52
53 Atomic Types Strings Numbers Booleans Dates and Times Time Intervals Binaries 53
54 Atomic Types Strings Numbers Booleans Dates and Times Time Intervals Binaries Null 54
55 Lexical space vs. value space Value space Lexical space 55
56 Lexical space vs. value space "1" "01"... Value space Lexical space 56
57 Lexical space vs. value space "4" "04" "100b"... Value space Lexical space 57
58 Subtypes Supertype's value space Subtype's value space 58
59 Structured Types Data Structure Associative Arrays (a.k.a. maps) Ordered Lists Examples JSON Object, Protobuf Message, Set of XML Attributes JSON Array, XML Element, Protobuf repeated field 59
60 Structured Types Data Structure Associative Arrays (a.k.a. maps) Ordered Lists Examples JSON Object, Set of XML Attributes Protobuf Message, JSON Array, XML Element, Protobuf repeated field 60
61 Cardinality How many? Common sign Common adjective 61
62 Cardinality One How many? Common sign Common adjective required 62
63 Cardinality One How many? Common sign Common adjective required Zero or more * repeated 63
64 Cardinality One How many? Common sign Common adjective required Zero or more * repeated Zero or one? optional 64
65 Cardinality One How many? Common sign Common adjective required Zero or more * repeated Zero or one? optional One or more + 65
66 wklzzz / 123RF Stock Photo JSON Data Model 66
67 JSON Values Strings Objects Numbers Booleans Arrays Null Atomic values Structured values 67
68 JSON Values Strings Numbers Booleans Null Objects String-to-Value map Arrays List of values Atomic values Structured values 68
69 JSON Values Strings Numbers Booleans Null Objects String-to-Value map Recursion Arrays List of values Atomic values Structured values 69
70 Tree-based visual model { } "foo" : true, "bar" : [ { "foobar" : "foo" }, null ] 70
71 Tree-based visual model object { } "foo" : true, "bar" : [ { "foobar" : "foo" }, null ] 71
72 Tree-based visual model object { } "foo" : true, "bar" : [ { "foobar" : "foo" }, null ] true foo bar array 72
73 Tree-based visual model object { } "foo" : true, "bar" : [ { "foobar" : "foo" }, null ] true foo object bar array null 73
74 Tree-based visual model object { } "foo" : true, "bar" : [ { "foobar" : "foo" }, null ] true foo object bar array null foobar foo 74
75 wklzzz / 123RF Stock Photo Protocol Buffers 75
76 Messages message Person { required string last_name = 1; repeated string first_name = 2; optional Title title = 3; optional Person boss = 4; } 76
77 Scalar types double, float int32, int64 and variants bool string bytes 77
78 Enums enum Title { MR = 1; MS = 2; MRS = 3; } 78
79 In C++ person.boss().first_name() 79
80 This is a schema! message Person { required string last_name = 1; repeated string first_name = 2; optional Title title = 3; optional Person boss = 4; } 80
81 JSON/XML vs. Protobufs No schema (heterogeneous) With schema (homogeneous) 81
82 Without schema... { "a" : 1, "b" : [ "foo", true, null, { "foo" : "bar" } ], "c" : { "d" : { "foo" : null }, "e" : [ 1, 2, [ 3, 4 ] ], "f" : 3.14 } } 82
83 With schema... { } "a" : 1, "b" : true, "c" : [ { "foo" : "bar1", "bar" : [ 1, 2 ] }, { "foo" : "bar2", "bar" : [ 3, 4, 5 ] }, { "foo" : "bar3" } ] 83
84 Validation Burak Cakmak / 123RF Stock Photo 84
85 Validation: The Pipeline Document 85
86 Validation: The Pipeline Document Well- Formedness 86
87 Validation: The Pipeline Document Well- Formedness Validation 87
88 On the oxygen Cheat Sheet Validity Well- Formedness 88
89 Validation vs. Annotation Validation 89
90 Validation vs. Annotation Validation Annotation 90
91 Validation 91
92 Validation 92
93 Validation 93
94 Validation 94
95 Validation 95
96 Post-Schema-Validation Infoset (with XML Schema) Infoset + Types Post-Schema-Validation Infoset (PSVI) 96
97 DTD Validation 97
98 Document Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a>& <a>& &&<d&e="f"/>& &&<c>this&is&<b>text</b>.</c>& </a>& & 98
99 Document Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a>& <a>& &&<d&e="f"/>& &&<c>this&is&<b>text</b>.</c>& </a>& & 99
100 Document Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& ]>& <a>& &&<d&e="f"/>& &&<c>this&is&<b>text</b>.</c>& </a>& & 100
101 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& ]>& <a>& &&<d&e="f"/>& &&<c>this&is&<b>text</b>.</c>& </a>& & 101
102 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& ]>& <a/>& & Empty Content 102
103 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&(#PCDATA)>& ]>& <a>& &&This&is&text.& </a>& & Simple Content 103
104 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&(foo,&bar)>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&bar&EMPTY>& ]>& <a>& &&<foo/>& &&<bar/>& </a>& & Complex Content 104
105 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&(foo+,&bar*,&foobar?)>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&bar&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&foobar&EMPTY>& ]>& <a>& &&<foo/>& &&<foo/>& &&<foo/>& &&<foobar/>& </a>& Complex Content 105
106 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&(&bar*& &(foo foobar)+)?>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&foobar&EMPTY>& ]>& <a>& &&<foo/>& &&<foobar/>& &&<foo/>& &&<foobar/>& </a>& & Complex Content 106
107 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&(#PCDATA& &foo)*>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& ]>& <a>& &&<foo/>lorum<foo/>ipsum<foo/>& </a>& & Mixed Content 107
108 Element Type Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&ANY>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&bar&EMPTY>& ]>& <a>& &&<foo/>& &&Lorem& &&<bar/>& &&Ipsum& &&<bar/>& &&<bar/>& </a>& & Mixed Content 108
109 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&CDATA&#REQUIRED>& ]>& <a&foo="this&is&a&"value""></a>& & 109
110 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&CDATA&#IMPLIED>& ]>& <a&foo="this&is&a&"value""></a>& & 110
111 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE a [ <!ELEMENT a EMPTY> <!ATTLIST a foo CDATA #IMPLIED> ]> <a></a> 111
112 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&CDATA&"bar">& ]>& <a&foo="this&is&a&"value""></a>& & 112
113 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&CDATA&"bar">& ]>& <a></a>& & 113
114 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&CDATA&#FIXED&"bar">& ]>& <a&foo="bar"></a>& & 114
115 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&NMTOKEN&#REQUIRED>& ]>& <a&foo="123atoken456"></a>& & 115
116 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&a&[& <!ELEMENT&a&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&a&foo&NMTOKENS&#REQUIRED>& ]>& <a&foo="123atoken&456"></a>& & 116
117 Attribute-List Declaration <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&root&[& <!ELEMENT&root&(foo+,&bar,&barlist)>& <!ELEMENT&foo&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&bar&EMPTY>& <!ELEMENT&barlist&EMPTY>& <!ATTLIST&foo&myid&ID&#REQUIRED>& <!ATTLIST&bar&ref&IDREF&#REQUIRED>& <!ATTLIST&barlist&ref&IDREFS&#REQUIRED>& ]>& <root>& &&<foo&myid="foobar"/>& &&<foo&myid="foobar2"/>& &&<bar&ref="foobar"/>& &&<barlist&ref="foobar&foobar2"/>& </root>& & 117
118 DTD Example: External Subset <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <!DOCTYPE&root&SYSTEM&"schema.dtd">& <a&foo="bar"/>& 118
119 Warning: DTDs and Namespaces <!ELEMENT eth (date, president, Rektor)> <!ATTLIST eth xmlns CDATA #FIXED " xmlns:xmldb CDATA #FIXED " date CDATA #IMPLIED xmldb:date CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ELEMENT date (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT president (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST president number CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ELEMENT Rektor (#PCDATA)> 119
120 XML Schema 120
121 Empty Schema <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <xs:schema& &&xmlns:xs=" </xs:schema>& & 121
122 Simple Scenario <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" <xs:element name="foo" type="xs:string"/> </xs:schema> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd"> This is text. </foo> schema.xsd Schema Instance file.xml 122
123 Simple Scenario <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" <xs:element name="foo" type="xs:string"/> </xs:schema> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd"> This is text. </foo> schema.xsd Schema Instance file.xml 123
124 Simple Scenario <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" <xs:element name="foo" type="xs:string"/> </xs:schema> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd"> This is text. </foo> Schema Instance 124
125 Simple Scenario <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" <xs:element name="foo" type="xs:integer"/> </xs:schema> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd"> </foo> Schema Instance 125
126 Simple Types: Built-in Strings Numbers Booleans string anyuri QName decimal integer float double long int short byte positiveinteger nonnegativeinteger... unsignedlong unsignedint... boolean 126
127 Simple Types: Built-in Dates and Times Time Intervals Binaries Null - datetime time date gyearmonth gmonthday gyear gmonth gday datetimestamp duration yearmonthduration daytimeduration hexbinary base64binary 127
128 Dates T10:15:00Z 01:15:00-08:00 128
129 Durations P1Y2MT3H 129
130 User-defined types 130
131 User-defined types Restriction 131
132 User-defined types Restriction Union Not atomic 132
133 User-defined types Restriction Union Not atomic List Not atomic 133
134 Restriction <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <xs:schema& &&xmlns:xs=" &&<xs:simpletype&name="myfixedlengthstring">& &&&&<xs:restriction&base="xs:string">& &&&&&&<xs:length&value="3"/>& &&&&</xs:restriction>& &&</xs:simpletype>& &&<xs:element&name="foo"&type="myfixedlengthstring"/>& </xs:schema>& <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <foo& &&xmlns:xsi=" &&xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd">zrh</foo>& & & Schema Instance 134
135 Restriction <xs:simpletype,name="myfixedlengthstring">,,,<xs:restriction,base="xs:string">,,,,,<xs:length,value="3"/>,,,</xs:restriction>, </xs:simpletype>,, <foo>zrh</foo>,,, Schema Instance 135
136 List <xs:simpletype,name="mylist">,,,<xs:list,itemtype="xs:string"/>, </xs:simpletype>,, <foo>foo,bar,foobar</foo>,, Schema Instance 136
137 Union <xs:simpletype,name="myunion">,,,<xs:union,membertypes="xs:integer,xs:boolean"/>, </xs:simpletype>,, Schema <foo>true</foo>,,,, Instance 137
138 Complex Types 138
139 Complex Types Empty <foo/> 139
140 Complex Types Empty <foo/> Simple Content <foo>text</foo> 140
141 Complex Types Empty <foo/> Simple Content Complex Content <foo>text</foo> <foo> <a/> <b/> </foo> 141
142 Complex Types Empty <foo/> Simple Content Complex Content Mixed Content <foo>text</foo> <foo> <a/> <b/> </foo> <foo> Text<a/>Text<b/> </foo> 142
143 Complex content <xs:complextype-name="complexcontent">- --<xs:sequence>- ----<xs:element-name="twotofour"-type="xs:string"-minoccurs="2"-maxoccurs="4"/>- ----<xs:element-name="zeroorone"-type="xs:boolean"-minoccurs="0"-maxoccurs="1"/>- --</xs:sequence>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<zeroorone>true</zeroorone>- </foo> Schema Instance 143
144 Complex content <xs:complextype-name="complexcontent">- --<xs:sequence>- ----<xs:element-name="twotofour"-type="xs:string"-minoccurs="2"-maxoccurs="4"/>- ----<xs:element-name="zeroorone"-type="xs:boolean"-minoccurs="0"-maxoccurs="1"/>- --</xs:sequence>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<twotofour>foobar</twotofour>- --<zeroorone>true</zeroorone>- </foo> Schema Instance 144
145 Empty content <xs:complextype-name="emptytype">- --<xs:sequence/>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo/>- - - Schema Instance 145
146 Simple content <xs:complextype-name="datecountry">- --<xs:simplecontent>- ----<xs:extension-base="xs:date"> <xs:attribute-name="country"-type="xs:string"/>- ----</xs:extension>- --</xs:simplecontent>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo-country="switzerland">2014d12d02</foo>- - - Schema Instance 146
147 Mixed content <xs:complextype-name="mixedcontent"-mixed="true">- --<xs:sequence>- ----<xs:element-name="b"-type="xs:string"-minoccurs="0"-maxoccurs="unbounded"/>- --</xs:sequence>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo>some-text-and-some-<b>bold</b>-text.</foo> Schema Instance 147
148 Simple type on attributes <xs:complextype-name="withattribute">- --<xs:sequence/>- --<xs:attribute-name="country" type="xs:string" default="switzerland"/>- </xs:complextype>- - <foo-country="switzerland"/>- - - Schema Instance 148
149 Named Types <xs:complextype name="empty"> <xs:sequence/> </xs:complextype> <xs:element name="c" type="empty"> </xs:element> Schema Instance <c/> 149
150 Anonymous Types <xs:element name="c"> <xs:complextype> <xs:sequence/> </xs:complextype> </xs:element> Schema Instance <c/> 150
151 No namespaces <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <xs:schema& &&xmlns:xs=" &&<xs:element&name="foo"&type="xs:string"/>& </xs:schema>& & & <?xml&version="1.0"&encoding="utf98"?>& <foo& &&xmlns:xsi=" &&xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd">& &&This&is&text.& </foo>& & Schema Instance 151
152 With namespaces <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" targetnamespace=" xmlns:big=" <xs:element name="foo" type="xs:string"/> </xs:schema> Schema <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> Instance <big:foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:schemalocation=" schema.xsd" xmlns:big=" This is text. </big:foo> 152
153 Warning: named types with namespaces <xs:complextype name="empty"> </xs:complextype> implicitly in the target namespace always unprefixed <xs:element name="c" type="big:empty"> </xs:element> Schema Instance <big:c/> 153
154 Multiple namespaces <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <big:foo xmlns:xsi=" xsi:schemalocation=" schema-big.xsd schema-medium.xsd schema-small.xsd " xmlns:big=" xmlns:medium=" xmlns:small=" <medium:page> <small:paragraph/> <small:paragraph/> <small:paragraph/> </medium:page> <medium:page> <small:paragraph/> <small:paragraph/> <small:paragraph/> </medium:page> </big:foo> 154
155 Small schema <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" xmlns:small=" targetnamespace=" <xs:element name="paragraph" type="small:empty-string"/> <xs:simpletype name="empty-string> <xs:restriction base="xs:string"> <xs:length value="0"/> </xs:restriction> </xs:simpletype> </xs:schema> 155
156 Medium schema <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" xmlns:small=" xmlns:medium=" targetnamespace=" <xs:import namespace=" schemalocation="schema-small.xsd"/> <xs:element name="page" type="medium:paragraphs"/> <xs:complextype name="paragraphs"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="small:paragraph" maxoccurs="unbounded"> </xs:sequence> </xs:simpletype> </xs:schema> 156
157 Big schema <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" xmlns:big=" xmlns:medium=" targetnamespace=" <xs:import namespace=" schemalocation="schema-medium.xsd"/> <xs:element name="foo" type="big:pages"/> <xs:complextype name="pages"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="medium:page" maxoccurs="unbounded"> </xs:sequence> </xs:simpletype> </xs:schema> 157
158 Keys <xs:schema* ****xmlns:xs=" **<xs:element*name="root">* ****<xs:complextype>* ******..* ****</xs:complextype>* ****<xs:key*name="foodid">* ******<xs:selector*xpath="foo"/>* ****</xs:key>* **</xs:element>* </xs:schema>* * <?xml*version="1.0"*encoding="utfd8"?>* <root* **xmlns:xsi=" **xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd">* **<foo*id="foo"/>* **<foo*id="bar"/>* **<foo*id="foobar"/>* </root>* * 158
159 Keys <xs:schema* ****xmlns:xs=" **<xs:element*name="root">* ****<xs:complextype>* ******..* ****</xs:complextype>* ****<xs:key*name="foodid">* What must be unique ******<xs:selector*xpath="foo"/>* ****</xs:key>* **</xs:element>* </xs:schema>* * <?xml*version="1.0"*encoding="utfd8"?>* <root* **xmlns:xsi=" **xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd">* **<foo*id="foo"/>* **<foo*id="bar"/>* **<foo*id="foobar"/>* </root>* * 159
160 Keys <xs:schema* ****xmlns:xs=" **<xs:element*name="root">* ****<xs:complextype>* ******..* ****</xs:complextype>* ****<xs:key*name="foodid">* ******<xs:selector*xpath="foo"/>* ****</xs:key>* **</xs:element>* </xs:schema>* * <?xml*version="1.0"*encoding="utfd8"?>* <root* What must be unique What makes it unique **xmlns:xsi=" **xsi:nonamespaceschemalocation="schema.xsd">* **<foo*id="foo"/>* **<foo*id="bar"/>* **<foo*id="foobar"/>* </root>* * 160
161 Bonus material: The Schema of Schemas!!<xs:schema!!!!!xmlns:xs=" 161
162 Avro 162
163 Avro is language neutral 163
164 Interoperability Avro DataFile 164
165 Avro atomic types Category Absence of value Boolean Number String Binary Types null boolean int long float double string enum bytes fixed (list of 8-bit unsigned bytes) 165
166 Avro structured types Category Arrays Objects Types array map record 166
167 Parquet 167
168 Row storage 168
169 Columnar storage 169
170 Columnar storage Row group Row group 170
171 Columnar storage 171
172 Parquet atomic types Category Boolean Number String Binary Date Types boolean int32 int64 int96 double DECIMAL(precision, scale) UTF8 ENUM binary fixed_len_byte_array DATE 172
173 Parquet structured types Category Arrays Objects Types LIST MAP 173
174 Weerapat Kiatdumrong / 123RF Stock Photo XPath and XQuery Data Model (XDM) JSONiq Data Model (JDM) 174
175 XDM/JDM: Sequences of Items (,,,,, ) 175
176 XDM/JDM: Sequence of one item 176
177 XDM/JDM: Sequence of one item = ( ) 177
178 XDM/JDM: Sequences are flat ((, ), ) 178
179 XDM/JDM: Sequences are flat ((, ), )=(,, ) 179
180 XDM: Items Atomic Node 180
181 XDM: Seven Kinds of XML Nodes Document node Element node Attribute node Text node Comment node Processing instruction node Namespace node 181
182 XDM: Seven Kinds of XML Nodes Infoset XDM 182
183 XDM vs. Infoset Infoset XDM xs:untyped 183
184 JSONiq Data Model (JDM): Objects and Arrays lorem ipsum dolor sit amet Atomic Objects Arrays 184
185 Advanced XDM/JDM: Function items Functions 185
186 XDM/JDM and Querying for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression 186
Big Data for Engineers Spring Data Models
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data for Engineers Spring 2018 11. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special
Ghislain Fourny Big Data for Engineers Spring 2018 11. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special
Big Data 9. Data Models
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 9. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Syntax vs. Data Models Physical view Syntax this is text. 2 Syntax vs. Data Models a Logical view
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 9. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Syntax vs. Data Models Physical view Syntax this is text. 2 Syntax vs. Data Models a Logical view
Big Data 11. Data Models
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 11. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness""
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 11. Data Models pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo CSV (Comma separated values) This is syntax ID,Last name,first name,theory, 1,Einstein,Albert,"General, Special Relativity" 2,Gödel,Kurt,"""Incompleteness""
Solution Sheet 5 XML Data Models and XQuery
 The Systems Group at ETH Zurich Big Data Fall Semester 2012 Prof. Dr. Donald Kossmann Prof. Dr. Nesime Tatbul Assistants: Martin Kaufmann Besmira Nushi 07.12.2012 Solution Sheet 5 XML Data Models and XQuery
The Systems Group at ETH Zurich Big Data Fall Semester 2012 Prof. Dr. Donald Kossmann Prof. Dr. Nesime Tatbul Assistants: Martin Kaufmann Besmira Nushi 07.12.2012 Solution Sheet 5 XML Data Models and XQuery
Big Data Exercises. Fall 2018 Week 8 ETH Zurich. XML validation
 Big Data Exercises Fall 2018 Week 8 ETH Zurich XML validation Reading: (optional, but useful) XML in a Nutshell, Elliotte Rusty Harold, W. Scott Means, 3rd edition, 2005: Online via ETH Library 1. XML
Big Data Exercises Fall 2018 Week 8 ETH Zurich XML validation Reading: (optional, but useful) XML in a Nutshell, Elliotte Rusty Harold, W. Scott Means, 3rd edition, 2005: Online via ETH Library 1. XML
Introduction Syntax and Usage XML Databases Java Tutorial XML. November 5, 2008 XML
 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
W3C XML Schemas For Publishing
 W3C XML Schemas For Publishing 208 5.8.xml: Getting Started
W3C XML Schemas For Publishing 208 5.8.xml: Getting Started
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2
 Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Information Systems for Engineers Fall Data Definition with SQL
 Ghislain Fourny Information Systems for Engineers Fall 2018 3. Data Definition with SQL Rare Book and Manuscript Library, Columbia University. What does data look like? Relations 2 Reminder: relation 0
Ghislain Fourny Information Systems for Engineers Fall 2018 3. Data Definition with SQL Rare Book and Manuscript Library, Columbia University. What does data look like? Relations 2 Reminder: relation 0
Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model
 5. XPath/XQuery Data Model 5-1 Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model References: Mary Fernández, Ashok Malhotra, Jonathan Marsh, Marton Nagy, Norman Walsh (Ed.): XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model (XDM).
5. XPath/XQuery Data Model 5-1 Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model References: Mary Fernández, Ashok Malhotra, Jonathan Marsh, Marton Nagy, Norman Walsh (Ed.): XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model (XDM).
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XML Schema (Part 1)
 Data-centric XML XML Schema (Part 1) Schema and DTD Disadvantages of DTD: separate, non-xml syntax very limited constraints on data types (just ID, IDREF, ) no support for sets (i.e. each element type
Data-centric XML XML Schema (Part 1) Schema and DTD Disadvantages of DTD: separate, non-xml syntax very limited constraints on data types (just ID, IDREF, ) no support for sets (i.e. each element type
Using and defining new simple types. Basic structuring of definitions. Copyright , Sosnoski Software Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IRIS Web Services Workshop II Session 1 Wednesday AM, September 21 Dennis M. Sosnoski What is XML? Extensible Markup Language XML is metalanguage for markup Enables markup languages for particular domains
IRIS Web Services Workshop II Session 1 Wednesday AM, September 21 Dennis M. Sosnoski What is XML? Extensible Markup Language XML is metalanguage for markup Enables markup languages for particular domains
Marker s feedback version
 Two hours Special instructions: This paper will be taken on-line and this is the paper format which will be available as a back-up UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Semi-structured Data
Two hours Special instructions: This paper will be taken on-line and this is the paper format which will be available as a back-up UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Semi-structured Data
XML and Web Services
 XML and Web Services Lecture 8 1 XML (Section 17) Outline XML syntax, semistructured data Document Type Definitions (DTDs) XML Schema Introduction to XML based Web Services 2 Additional Readings on XML
XML and Web Services Lecture 8 1 XML (Section 17) Outline XML syntax, semistructured data Document Type Definitions (DTDs) XML Schema Introduction to XML based Web Services 2 Additional Readings on XML
XML Schema. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 28
 1 / 28 XML Schema Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 Elements 3 Simple and complex types 4 Attributes 5 Groups and built-in 6 Import of other schemes
1 / 28 XML Schema Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 Elements 3 Simple and complex types 4 Attributes 5 Groups and built-in 6 Import of other schemes
XML extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
Software Engineering Methods, XML extensible Markup Language. Tutorial Outline. An Example File: Note.xml XML 1
 extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
Restricting complextypes that have mixed content
 Restricting complextypes that have mixed content Roger L. Costello October 2012 complextype with mixed content (no attributes) Here is a complextype with mixed content:
Restricting complextypes that have mixed content Roger L. Costello October 2012 complextype with mixed content (no attributes) Here is a complextype with mixed content:
Big Data 10. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Big Data 12. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
XML. Part II DTD (cont.) and XML Schema
 XML Part II DTD (cont.) and XML Schema Attribute Declarations Declare a list of allowable attributes for each element These lists are called ATTLIST declarations Consists of 3 basic parts The ATTLIST keyword
XML Part II DTD (cont.) and XML Schema Attribute Declarations Declare a list of allowable attributes for each element These lists are called ATTLIST declarations Consists of 3 basic parts The ATTLIST keyword
[MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Integration Services Project Parameter File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Integration Services Project Parameter File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Integration Services Project Parameter File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/72/67554040.jpg) [MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for
[MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for
XML. Document Type Definitions XML Schema. Database Systems and Concepts, CSCI 3030U, UOIT, Course Instructor: Jarek Szlichta
 XML Document Type Definitions XML Schema 1 XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML was designed to describe data. XML has come into common use for the interchange of data over the Internet.
XML Document Type Definitions XML Schema 1 XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML was designed to describe data. XML has come into common use for the interchange of data over the Internet.
XML Format Plug-in User s Guide. Version 10g Release 3 (10.3)
 XML Format Plug-in User s Guide Version 10g Release 3 (10.3) XML... 4 TERMINOLOGY... 4 CREATING AN XML FORMAT... 5 CREATING AN XML FORMAT BASED ON AN EXISTING XML MESSAGE FORMAT... 5 CREATING AN EMPTY
XML Format Plug-in User s Guide Version 10g Release 3 (10.3) XML... 4 TERMINOLOGY... 4 CREATING AN XML FORMAT... 5 CREATING AN XML FORMAT BASED ON AN EXISTING XML MESSAGE FORMAT... 5 CREATING AN EMPTY
PESC Compliant JSON Version /19/2018. A publication of the Technical Advisory Board Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council
 Version 0.5.0 10/19/2018 A publication of the Technical Advisory Board Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council 2018. All Rights Reserved. This document may be copied and furnished to others, and derivative
Version 0.5.0 10/19/2018 A publication of the Technical Advisory Board Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council 2018. All Rights Reserved. This document may be copied and furnished to others, and derivative
[MS-DPAD]: Alert Definition Data Portability Overview. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MS-DPAD]: Alert Definition Data Portability Overview. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MS-DPAD]: Alert Definition Data Portability Overview. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/75/71809355.jpg) [MS-DPAD]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MS-DPAD]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
 [MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Intellectual Property Rights tice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats,
[MS-SSISPARAMS-Diff]: Intellectual Property Rights tice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats,
No Trade Secrets. Microsoft does not claim any trade secret rights in this documentation.
 [MS-DPAD]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-DPAD]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
This Documentation, which includes embedded help systems and electronically distributed materials, (hereinafter referred to
 This Documentation, which includes embedded help systems and electronically distributed materials, (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for your informational purposes only and is subject
This Documentation, which includes embedded help systems and electronically distributed materials, (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for your informational purposes only and is subject
[MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/95/125832960.jpg) [MS-QDEFF]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-QDEFF]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
Markup Languages. Lecture 4. XML Schema
 Markup Languages Lecture 4. XML Schema Introduction to XML Schema XML Schema is an XML-based alternative to DTD. An XML schema describes the structure of an XML document. The XML Schema language is also
Markup Languages Lecture 4. XML Schema Introduction to XML Schema XML Schema is an XML-based alternative to DTD. An XML schema describes the structure of an XML document. The XML Schema language is also
Semantic Web. XML and XML Schema. Morteza Amini. Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95
 ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
BEAWebLogic. Integration. Transforming Data Using XQuery Mapper
 BEAWebLogic Integration Transforming Data Using XQuery Mapper Version: 10.2 Document Revised: March 2008 Contents Introduction Overview of XQuery Mapper.............................................. 1-1
BEAWebLogic Integration Transforming Data Using XQuery Mapper Version: 10.2 Document Revised: March 2008 Contents Introduction Overview of XQuery Mapper.............................................. 1-1
Faster XML data validation in a programming language with XML datatypes
 Faster XML data validation in a programming language with XML datatypes Kurt Svensson Inobiz AB Kornhamnstorg 61, 103 12 Stockholm, Sweden kurt.svensson@inobiz.se Abstract EDI-C is a programming language
Faster XML data validation in a programming language with XML datatypes Kurt Svensson Inobiz AB Kornhamnstorg 61, 103 12 Stockholm, Sweden kurt.svensson@inobiz.se Abstract EDI-C is a programming language
XML Schema Element and Attribute Reference
 E XML Schema Element and Attribute Reference all This appendix provides a full listing of all elements within the XML Schema Structures Recommendation (found at http://www.w3.org/tr/xmlschema-1/). The
E XML Schema Element and Attribute Reference all This appendix provides a full listing of all elements within the XML Schema Structures Recommendation (found at http://www.w3.org/tr/xmlschema-1/). The
Last week we saw how to use the DOM parser to read an XML document. The DOM parser can also be used to create and modify nodes.
 Distributed Software Development XML Schema Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 7-2: Modifying XML programmatically Last week we saw how to use the DOM parser to read
Distributed Software Development XML Schema Chris Brooks Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 7-2: Modifying XML programmatically Last week we saw how to use the DOM parser to read
Syntax XML Schema XML Techniques for E-Commerce, Budapest 2004
 Mag. iur. Dr. techn. Michael Sonntag Syntax XML Schema XML Techniques for E-Commerce, Budapest 2004 E-Mail: sonntag@fim.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.fim.uni-linz.ac.at/staff/sonntag.htm Michael Sonntag 2004
Mag. iur. Dr. techn. Michael Sonntag Syntax XML Schema XML Techniques for E-Commerce, Budapest 2004 E-Mail: sonntag@fim.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.fim.uni-linz.ac.at/staff/sonntag.htm Michael Sonntag 2004
All About <xml> CS193D, 2/22/06
 CS193D Handout 17 Winter 2005/2006 February 21, 2006 XML See also: Chapter 24 (709-728) All About CS193D, 2/22/06 XML is A markup language, but not really a language General purpose Cross-platform
CS193D Handout 17 Winter 2005/2006 February 21, 2006 XML See also: Chapter 24 (709-728) All About CS193D, 2/22/06 XML is A markup language, but not really a language General purpose Cross-platform
[MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MS-QDEFF]: Query Definition File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/93/112712705.jpg) [MS-QDEFF]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MS-QDEFF]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
Framing how values are extracted from the data stream. Includes properties for alignment, length, and delimiters.
 DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 3: DFDL properties In lesson 2 we learned that in the DFDL language, XML Schema conveys the basic structure of the data format being modeled, and DFDL properties
DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 3: DFDL properties In lesson 2 we learned that in the DFDL language, XML Schema conveys the basic structure of the data format being modeled, and DFDL properties
Modelling XML Applications (part 2)
 Modelling XML Applications (part 2) Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2014/2015 Lecture 3 20.10.2014 Common design decisions Natural language Which natural language to use? It would be a nonsense not
Modelling XML Applications (part 2) Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2014/2015 Lecture 3 20.10.2014 Common design decisions Natural language Which natural language to use? It would be a nonsense not
MCS-274 Final Exam Serial #:
 MCS-274 Final Exam Serial #: This exam is closed-book and mostly closed-notes. You may, however, use a single 8 1/2 by 11 sheet of paper with hand-written notes for reference. (Both sides of the sheet
MCS-274 Final Exam Serial #: This exam is closed-book and mostly closed-notes. You may, however, use a single 8 1/2 by 11 sheet of paper with hand-written notes for reference. (Both sides of the sheet
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
Framing how values are extracted from the data stream. Includes properties for alignment, length, and delimiters.
 DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 3: DFDL properties Version Author Date Change 1 S Hanson 2011-01-24 Created 2 S Hanson 2011-03-30 Updated 3 S Hanson 2012-09-21 Corrections for errata 4 S Hanson
DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 3: DFDL properties Version Author Date Change 1 S Hanson 2011-01-24 Created 2 S Hanson 2011-03-30 Updated 3 S Hanson 2012-09-21 Corrections for errata 4 S Hanson
Introducing our First Schema
 1 di 11 21/05/2006 10.24 Published on XML.com http://www.xml.com/pub/a/2000/11/29/schemas/part1.html See this if you're having trouble printing code examples Using W3C XML By Eric van der Vlist October
1 di 11 21/05/2006 10.24 Published on XML.com http://www.xml.com/pub/a/2000/11/29/schemas/part1.html See this if you're having trouble printing code examples Using W3C XML By Eric van der Vlist October
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Big Data Exercises. Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich
 Big Data Exercises Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich Introduction This exercise will cover XQuery. You will be using oxygen (https://www.oxygenxml.com/xml_editor/software_archive_editor.html), AN XML/JSON development
Big Data Exercises Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich Introduction This exercise will cover XQuery. You will be using oxygen (https://www.oxygenxml.com/xml_editor/software_archive_editor.html), AN XML/JSON development
The XQuery Data Model
 The XQuery Data Model 9. XQuery Data Model XQuery Type System Like for any other database query language, before we talk about the operators of the language, we have to specify exactly what it is that
The XQuery Data Model 9. XQuery Data Model XQuery Type System Like for any other database query language, before we talk about the operators of the language, we have to specify exactly what it is that
Oracle Berkeley DB XML. API Reference for C++ 12c Release 1
 Oracle Berkeley DB XML API Reference for C++ 12c Release 1 Library Version 12.1.6.0 Legal Notice This documentation is distributed under an open source license. You may review the terms of this license
Oracle Berkeley DB XML API Reference for C++ 12c Release 1 Library Version 12.1.6.0 Legal Notice This documentation is distributed under an open source license. You may review the terms of this license
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
So far, we've discussed the use of XML in creating web services. How does this work? What other things can we do with it?
 XML Page 1 XML and web services Monday, March 14, 2011 2:50 PM So far, we've discussed the use of XML in creating web services. How does this work? What other things can we do with it? XML Page 2 Where
XML Page 1 XML and web services Monday, March 14, 2011 2:50 PM So far, we've discussed the use of XML in creating web services. How does this work? What other things can we do with it? XML Page 2 Where
PART. Oracle and the XML Standards
 PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
Apache UIMA Regular Expression Annotator Documentation
 Apache UIMA Regular Expression Annotator Documentation Written and maintained by the Apache UIMA Development Community Version 2.3.1 Copyright 2006, 2011 The Apache Software Foundation License and Disclaimer.
Apache UIMA Regular Expression Annotator Documentation Written and maintained by the Apache UIMA Development Community Version 2.3.1 Copyright 2006, 2011 The Apache Software Foundation License and Disclaimer.
About the Data-Flow Complexity of Web Processes
 Cardoso, J., "About the Data-Flow Complexity of Web Processes", 6th International Workshop on Business Process Modeling, Development, and Support: Business Processes and Support Systems: Design for Flexibility.
Cardoso, J., "About the Data-Flow Complexity of Web Processes", 6th International Workshop on Business Process Modeling, Development, and Support: Business Processes and Support Systems: Design for Flexibility.
Part VII. Querying XML The XQuery Data Model. Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153
 Part VII Querying XML The XQuery Data Model Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153 Outline of this part 1 Querying XML Documents Overview 2 The XQuery Data Model The XQuery
Part VII Querying XML The XQuery Data Model Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153 Outline of this part 1 Querying XML Documents Overview 2 The XQuery Data Model The XQuery
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Chapter 3 Brief Overview of XML
 Slide 3.1 Web Serv vices: Princ ciples & Te echno ology Chapter 3 Brief Overview of XML Mike P. Papazoglou & mikep@uvt.nl Slide 3.2 Topics XML document structure XML schemas reuse Document navigation and
Slide 3.1 Web Serv vices: Princ ciples & Te echno ology Chapter 3 Brief Overview of XML Mike P. Papazoglou & mikep@uvt.nl Slide 3.2 Topics XML document structure XML schemas reuse Document navigation and
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
Describing Document Types: The Schema Languages of XML Part 2
 Describing Document Types: The Schema Languages of XML Part 2 John Cowan 1 Copyright Copyright 2005 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTIES; USE AT YOUR OWN RISK
Describing Document Types: The Schema Languages of XML Part 2 John Cowan 1 Copyright Copyright 2005 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTIES; USE AT YOUR OWN RISK
QVX File Format and QlikView Custom Connector
 QVX File Format and QlikView Custom Connector Contents 1 QVX File Format... 2 1.1 QvxTableHeader XML Schema... 2 1.1.1 QvxTableHeader Element... 4 1.1.2 QvxFieldHeader Element... 5 1.1.3 QvxFieldType Type...
QVX File Format and QlikView Custom Connector Contents 1 QVX File Format... 2 1.1 QvxTableHeader XML Schema... 2 1.1.1 QvxTableHeader Element... 4 1.1.2 QvxFieldHeader Element... 5 1.1.3 QvxFieldType Type...
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Request for Comments: Tail-f Systems December Partial Lock Remote Procedure Call (RPC) for NETCONF
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 5717 Category: Standards Track B. Lengyel Ericsson M. Bjorklund Tail-f Systems December 2009 Partial Lock Remote Procedure Call (RPC) for NETCONF Abstract The
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 5717 Category: Standards Track B. Lengyel Ericsson M. Bjorklund Tail-f Systems December 2009 Partial Lock Remote Procedure Call (RPC) for NETCONF Abstract The
CS A1150 Databases, 2017 Exercise Round 6 (( ), Solutions
 CS A1150 Databases, 2017 Exercise Round 6 ((8.5. 12.5.2017), Solutions 1. (6 p.) Consider a database schema which consists of three relations, whose schemas are: Students(ID, name, program, year) Courses(code,
CS A1150 Databases, 2017 Exercise Round 6 ((8.5. 12.5.2017), Solutions 1. (6 p.) Consider a database schema which consists of three relations, whose schemas are: Students(ID, name, program, year) Courses(code,
MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE
 MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE Gabriela Ochoa http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~goc/ OUTLINE XML Elements vs. Attributes Well-formed vs. Valid XML documents Document Type Definitions (DTDs)
MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE Gabriela Ochoa http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~goc/ OUTLINE XML Elements vs. Attributes Well-formed vs. Valid XML documents Document Type Definitions (DTDs)
Web Services. The Pervasive Internet
 Web Services CPSC 328 Spring 2009 The Pervasive Internet Years ago, computers couldn t talk to each other like they can now Researchers wanted to share information The Internet! Gopher & Veronica (text
Web Services CPSC 328 Spring 2009 The Pervasive Internet Years ago, computers couldn t talk to each other like they can now Researchers wanted to share information The Internet! Gopher & Veronica (text
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Oracle Hospitality OPERA Web Self- Service Brochure Web Service Specification Version 5.1. September 2017
 Oracle Hospitality OPERA Web Self- Service Brochure Web Service Specification Version 5.1 September 2017 Copyright 1987, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This software and related
Oracle Hospitality OPERA Web Self- Service Brochure Web Service Specification Version 5.1 September 2017 Copyright 1987, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This software and related
Fall, 2005 CIS 550. Database and Information Systems Homework 5 Solutions
 Fall, 2005 CIS 550 Database and Information Systems Homework 5 Solutions November 15, 2005; Due November 22, 2005 at 1:30 pm For this homework, you should test your answers using Galax., the same XQuery
Fall, 2005 CIS 550 Database and Information Systems Homework 5 Solutions November 15, 2005; Due November 22, 2005 at 1:30 pm For this homework, you should test your answers using Galax., the same XQuery
Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE. M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science. Date: Tuesday 20 th May 2008.
 COMP60370 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Semi-Structured Data and the Web Date: Tuesday 20 th May 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer
COMP60370 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Semi-Structured Data and the Web Date: Tuesday 20 th May 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer
Pattern/Object Markup Language (POML): A Simple XML Schema for Object Oriented Code Description
 Pattern/Object Markup Language (POML): A Simple XML Schema for Object Oriented Code Description Jason McC. Smith Apr 7, 2004 Abstract Pattern/Object Markup Language (or POML) is a simple XML Schema for
Pattern/Object Markup Language (POML): A Simple XML Schema for Object Oriented Code Description Jason McC. Smith Apr 7, 2004 Abstract Pattern/Object Markup Language (or POML) is a simple XML Schema for
Modelling XML Applications
 Modelling XML Applications Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2013/2014 Lecture 2 14.10.2013 XML application (recall) XML application (zastosowanie XML) A concrete language with XML syntax Typically defined
Modelling XML Applications Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2013/2014 Lecture 2 14.10.2013 XML application (recall) XML application (zastosowanie XML) A concrete language with XML syntax Typically defined
QosPolicyHolder:1 Erratum
 Erratum Number: Document and Version: Cross References: Next sequential erratum number Effective Date: July 14, 2006 Document erratum applies to the service document QosPolicyHolder:1 This Erratum has
Erratum Number: Document and Version: Cross References: Next sequential erratum number Effective Date: July 14, 2006 Document erratum applies to the service document QosPolicyHolder:1 This Erratum has
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
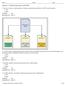 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
Web Computing. Revision Notes
 Web Computing Revision Notes Exam Format The format of the exam is standard: Answer TWO OUT OF THREE questions Candidates should answer ONLY TWO questions The time allowed is TWO hours Notes: You will
Web Computing Revision Notes Exam Format The format of the exam is standard: Answer TWO OUT OF THREE questions Candidates should answer ONLY TWO questions The time allowed is TWO hours Notes: You will
Appendix H XML Quick Reference
 HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
XML DTDs and Namespaces. CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 3, 2007.
 XML DTDs and Namespaces CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 3, 2007. Outline Internal versus External DTDs Namespaces XML Schemas Internal versus External DTDs There are two ways to associate a DTD with an XML document:
XML DTDs and Namespaces CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 3, 2007. Outline Internal versus External DTDs Namespaces XML Schemas Internal versus External DTDs There are two ways to associate a DTD with an XML document:
Document erratum applies to QosDevice:1. List other Erratum s or Documents that this change may apply to or have associated changes with
 Erratum Number: Document and Version: Cross References: QosDevice:1 Erratum Next sequential erratum number Effective Date: July 14, 2006 Document erratum applies to QosDevice:1 List other Erratum s or
Erratum Number: Document and Version: Cross References: QosDevice:1 Erratum Next sequential erratum number Effective Date: July 14, 2006 Document erratum applies to QosDevice:1 List other Erratum s or
Complex type. This subset is enough to model the logical structure of all kinds of non-xml data.
 DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 2: DFDL language basics We have seen in lesson 1 how DFDL is not an entirely new language. Its foundation is XML Schema 1.0. Although XML Schema was created as a
DFDL Introduction For Beginners Lesson 2: DFDL language basics We have seen in lesson 1 how DFDL is not an entirely new language. Its foundation is XML Schema 1.0. Although XML Schema was created as a
Module 4. Implementation of XQuery. Part 2: Data Storage
 Module 4 Implementation of XQuery Part 2: Data Storage Aspects of XQuery Implementation Compile Time + Optimizations Operator Models Query Rewrite Runtime + Query Execution XML Data Representation XML
Module 4 Implementation of XQuery Part 2: Data Storage Aspects of XQuery Implementation Compile Time + Optimizations Operator Models Query Rewrite Runtime + Query Execution XML Data Representation XML
No Trade Secrets. Microsoft does not claim any trade secret rights in this documentation.
 [MS-OXWSXPROP]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-OXWSXPROP]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
Information Systems Modelling Information Systems II: XML
 Information Systems 2 Information Systems 2 2. Modelling Information Systems II: XML Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute for Business Economics and Information
Information Systems 2 Information Systems 2 2. Modelling Information Systems II: XML Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute for Business Economics and Information
extensible Markup Language
 What is XML? The acronym means extensible Markup Language It is used to describe data in a way which is simple, structured and (usually) readable also by humans Developed at the end of the ninenties by
What is XML? The acronym means extensible Markup Language It is used to describe data in a way which is simple, structured and (usually) readable also by humans Developed at the end of the ninenties by
Service Modeling Language (SML) Pratul Dublish Principal Program Manager Microsoft Corporation
 Service Modeling Language (SML) Pratul Dublish Principal Program Manager Microsoft Corporation 1 Outline Introduction to SML SML Model Inter-Document References URI scheme deref() extension function Schema-based
Service Modeling Language (SML) Pratul Dublish Principal Program Manager Microsoft Corporation 1 Outline Introduction to SML SML Model Inter-Document References URI scheme deref() extension function Schema-based
SDPL : XML Basics 2. SDPL : XML Basics 1. SDPL : XML Basics 4. SDPL : XML Basics 3. SDPL : XML Basics 5
 2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
<account_number> A-101 </account_number># <branch_name> Downtown </branch_name># <balance> 500 </balance>#
 Basic structure: # # A-101 # Downtown # 500 # # # # # # # Johnson#
Basic structure: # # A-101 # Downtown # 500 # # # # # # # Johnson#
Introduction to XML. An Example XML Document. The following is a very simple XML document.
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Expires: January 15, 2005 July 17, Extensible Markup Language (XML) Formats for Representing Resource Lists draft-ietf-simple-xcap-list-usage-03
 SIMPLE J. Rosenberg Internet-Draft dynamicsoft Expires: January 15, 2005 July 17, 2004 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Formats for Representing Resource Lists draft-ietf-simple-xcap-list-usage-03 Status
SIMPLE J. Rosenberg Internet-Draft dynamicsoft Expires: January 15, 2005 July 17, 2004 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Formats for Representing Resource Lists draft-ietf-simple-xcap-list-usage-03 Status
Data Presentation and Markup Languages
 Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
SMKI Repository Interface Design Specification TPMAG baseline submission draft version 8 September 2015
 SMKI Repository Interface Design Specification DCC Public Page 1 of 21 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Purpose and Scope 3 1.2 Target Response Times 3 2 Interface Definition 4 2.1 SMKI Repository Portal
SMKI Repository Interface Design Specification DCC Public Page 1 of 21 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Purpose and Scope 3 1.2 Target Response Times 3 2 Interface Definition 4 2.1 SMKI Repository Portal
No Trade Secrets. Microsoft does not claim any trade secret rights in this documentation.
 [MS-CSOM]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-CSOM]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD
![Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD](/thumbs/72/67474201.jpg) Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
[MS-MSL]: Mapping Specification Language File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MS-MSL]: Mapping Specification Language File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MS-MSL]: Mapping Specification Language File Format. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/75/71853798.jpg) [MS-MSL]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MS-MSL]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
Notes. Any feedback/suggestions? IS 651: Distributed Systems
 Notes Grading statistics Midterm1: average 10.60 out of 15 with stdev 2.22 Total: average 15.46 out of 21 with stdev 2.80 A range: [18.26, 23] B range: [12.66, 18.26) C or worse range: [0, 12.66) The curve
Notes Grading statistics Midterm1: average 10.60 out of 15 with stdev 2.22 Total: average 15.46 out of 21 with stdev 2.80 A range: [18.26, 23] B range: [12.66, 18.26) C or worse range: [0, 12.66) The curve
XML Information Set. Working Draft of May 17, 1999
 XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
Chapter 11 XML Data Modeling. Recent Development for Data Models 2016 Stefan Deßloch
 Chapter 11 XML Data Modeling Recent Development for Data Models 2016 Stefan Deßloch Motivation Traditional data models (e.g., relational data model) primarily support structure data separate DB schema
Chapter 11 XML Data Modeling Recent Development for Data Models 2016 Stefan Deßloch Motivation Traditional data models (e.g., relational data model) primarily support structure data separate DB schema
XML databases. Jan Chomicki. University at Buffalo. Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9
 XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML
 ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML Stefan Manegold Stefan.Manegold@cwi.nl http://www.cwi.nl/~manegold/ Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan The Challenge: Comic Strip Finder The Challenge:
ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML Stefan Manegold Stefan.Manegold@cwi.nl http://www.cwi.nl/~manegold/ Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan The Challenge: Comic Strip Finder The Challenge:
Big Data Exam ETH Zürich February 9, 2017 Answer sheet
 Big Data Exam ETH Zürich February 9, 2017 Answer sheet Name: Legi-Number: 1. A B C D 2. A B C D 3. A B C D 4. A B C D 5. A B C D 6. A B C D 7. A B C D 8. A B C D 9. A B C D 10. A B C D 11. A B C D 12.
Big Data Exam ETH Zürich February 9, 2017 Answer sheet Name: Legi-Number: 1. A B C D 2. A B C D 3. A B C D 4. A B C D 5. A B C D 6. A B C D 7. A B C D 8. A B C D 9. A B C D 10. A B C D 11. A B C D 12.
