Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
|
|
|
- Lesley Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML
2 Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory Overview Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features UFM and CFM Array Size UFM Memory Organization Map UFM Block Diagrams UFM Operating Modes Intel MAX 10 UFM Design Considerations Guideline: UFM Power Supply Requirement Guideline: Program and Read UFM with JTAG Guideline: UFM Content Initialization Guideline: Erase Before Program Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core UFM Avalon-MM Operating Modes UFM Read Status and Control Register UFM Write Control Register UFM Program (Write) Operation UFM Sector Erase Operation UFM Page Erase Operation UFM Read Operation UFM Burst Read Operation Flash Initialization Files On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Parameters On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Signals On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Registers Sector Address Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Archive Document Revision History for the Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
3 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory Overview Intel Intel MAX 10 FPGAs offer a user flash memory (UFM) block that stores nonvolatile information. The UFM provides an ideal storage solution that you can access using the Avalon Memory Mapped (Avalon-MM) slave interface to UFM. The UFM block also offers the following features. Features Capacity Endurance Data retention (after 10,000 program/ erase cycles) Counts to at least 10,000 program/erase cycles 20 years at 85 ºC 10 years at 100 ºC Maximum operating frequency Serial interface 10M02,10M04, 10M08, 10M16, 10M25: 7.25 MHz 10M40, 10M50: 4.81 MHz Parallel interface 10M02: 7.25 MHz 10M04, 10M08, 10M16, 10M25, 10M40, 10M50: 116 MHz Data length Stores data of up to 32 bits length in parallel Related Information Utilizing the User Flash Memory (UFM) on Intel MAX 10 Devices with a Nios II Processor Putting MAX Series FPGAs in Hibernation Mode Using User Flash Memory Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Archive on page 26 Provides a list of user guides for previous versions of the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
4 2. Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features The UFM architecture of Intel MAX 10 devices is a combination of soft and hard IPs. You can only access the UFM using the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core in the Intel Quartus Prime software UFM and CFM Array Size Each array is organized as various sectors. A page is the smallest amount of flash memory that you can erase at one time. A sector contains a number of pages. You can erase each page or sector independently. The On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core also gives you access to configuration flash memory (CFM) based on your specification in the parameter editor. Table 1. UFM and CFM Array Size This table lists the dimensions of the UFM and CFM arrays. Device Pages per Sector UFM1 UFM0 CFM2 CFM1 (Image 2) (Image 2) CFM0 (Image 1) Page Size (Kb) Total User Flash Memory Size (Kb) (1) Total Configuration Memory Size (Kb) (1) 10M M ,248 2,240 10M ,376 2,240 10M ,368 4,224 10M ,200 5,888 10M ,888 10,752 10M ,888 10, UFM Memory Organization Map The scheme changes based on the configuration mode you specify in the On- Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core parameter editor. The following tables show the dynamic UFM support based on different configuration mode and Intel MAX 10 variant. (1) The maximum possible value, which is dependent on the mode you select. Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
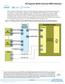
5 2. Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features Table 2. Dynamic Flash Size Support: Flash and Analog Variants Configuration UFM1 UFM0 CFM2 (Image 2) CFM1 (Image 2) CFM0 (Image 1) Dual compressed images UFM space UFM space Single uncompressed image UFM space UFM space UFM space Single compressed image UFM space UFM space UFM space UFM space Single uncompressed image with memory initialization UFM space UFM space Single compressed image with memory initialization UFM space UFM space Table 3. Dynamic Flash Size Support: Compact Variant Configuration UFM1 UFM0 CFM2 (Image 2) CFM1 (Image 2) CFM0 (Image 1) Dual compressed images Not available Single uncompressed image UFM space UFM space Single compressed image UFM space UFM space Single uncompressed image with memory initialization Single compressed image with memory initialization Not available Not available 2.3. UFM Block Diagrams This figure shows the top level view of the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core block diagram. The On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core supports both parallel and serial interfaces for Intel MAX 10 FPGAs. Figure 1. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Block Diagram Avalon-MM Avalon-MM Avalon-MM Avalon-MM Slave Parallel Controller (Data) Avalon-MM Slave Serial Controller (Data) Control Register Status Register Avalon-MM Slave Controller (Control) UFM Block Interface On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA This IP block has two Avalon-MM slave controllers: Data a wrapper of the UFM block that provides and program accesses to the flash. Control the CSR and status register for the flash, which is required only for program and erase operations. 5
6 2. Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features These figures show the detailed overview of the Avalon-MM interface during and program () operation. Figure 2. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Avalon-MM Slave Read and Program (Write) Operation in Parallel Mode This figure shows the standard interface for Intel MAX 10 devices in parallel mode. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA reset_n addr[x:0] data[31:0] data[31:0] datavalid burstcount[x:0] Avalon-MM Slave Parallel Controller (Data) internal internal UFM Block I/F UFM Block Interface Control Register Status Register / Avalon-MM Slave Controller (Control) external external reset_n addr data[31:0] data[31:0] Note: The maximum frequency for all devices in parallel mode, except for 10M02, is 116 MHz. The maximum frequency for 10M02 devices is 7.25 MHz. Figure 3. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Avalon-MM Slave Read and Program (Write) Operation in Serial Mode This figure shows the standard interface for Intel MAX 10 devices in serial mode. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA reset_n addr[x:0] data data datavalid burstcount[x:0] Avalon-MM Slave Serial Controller (Data) internal internal UFM Block I/F UFM Block Interface Control Register Status Register / Avalon-MM Slave Controller (Control) external external reset_n addr data[31:0] data[31:0] These figures show the detailed overview of the Avalon-MM interface during only operation. 6
7 2. Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features Figure 4. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Avalon-MM Slave Read Only Operation in Parallel Mode On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA reset_n addr[x:0] data[31:0] datavalid burstcount[x:0] Avalon-MM Slave Parallel Controller (Data) UFM Block I/F UFM Block Interface Figure 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Avalon-MM Slave Read Only Operation in Serial Mode On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA reset_n addr[x:0] data datavalid burstcount[x:0] Avalon-MM Slave Serial Controller (Data) UFM Block I/F UFM Block Interface 2.4. UFM Operating Modes The UFM block offers the following operating modes: Read Burst Program (Write) Sector erase Page erase Sector protection You can choose one of the following access modes in the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core parameter editor to and control the operations. 7
8 2. Intel MAX 10 UFM Architecture and Features Read and program mode this mode allows both data and control slave interface. This mode is applicable for both UFM and CFM sectors. Read only mode this mode allows only data slave interface, and restricted to only operations. This mode is applicable for both UFM and CFM sectors. Hidden this mode does not allow any or program () operations. This mode is applicable only for CFM sectors. The following table shows the comparison between parallel and serial modes. Table 4. Comparison between Parallel Mode and Serial Mode Feature Parallel Mode Serial Mode Avalon-MM Data Interface Parallel mode with 32-bit data bus Serial mode with 32 bits based burst count Access Mode Read and program Read only Hidden Read Mode Incrementing burst Wrapping burst Read and program Read only Hidden Incrementing burst only Program (Write) Operation Single 32-bit parallel program operation Single 32-bit serial program operation 8
9 3. Intel MAX 10 UFM Design Considerations There are several considerations that require your attention to ensure the success of your designs. Unless noted otherwise, these design guidelines apply to all variants of this device family Guideline: UFM Power Supply Requirement During UFM and CFM operations, make sure to follow the maximum slew rate requirement for power supply ramp down. This setting prevents device damage in case of power loss. Table 5. Maximum Slew Rate Requirement Device Single-supply device Multi-supply device Maximum Slew Rate 0.073V/µs 0.023V/µs 3.3V 0V 2.5V 0V <0.073V/µs Single-Supply Device <0.023V/µs Multi-Supply Device 3.2. Guideline: Program and Read UFM with JTAG You can program UFM using JTAG interface version IEEE Standard The JTAG interface supports Jam Standard Test and Programming Language (STAPL) Format File (.jam), Programmer Object File (.pof), and JAM Byte Code File (.jbc). You can use the Intel Quartus Prime Programmer to program.pof through the JTAG interface. To program.pof, into the flash, follow these steps: Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
10 3. Intel MAX 10 UFM Design Considerations 1. In the Programmer window, click Hardware Setup, and select USB Blaster. 2. In the Mode list, select JTAG. 3. Click Auto Detect on the left pane. 4. Select the device to be programmed, and click Add File. 5. Select the.pof to be programmed to the selected device. 6. Select the UFM in the Program/Configure column. 7. Click Start to start programming. To program through.jam or.jbc files, refer to the Using the Command-Line Jam STAPL Solution for Device Programming application note. Related Information AN 425: Using the Command-Line Jam STAPL Solution for Device Programming 3.3. Guideline: UFM Content Initialization You can initialize the UFM content using software. The initial memory content supports Memory Initialization File (.mif), and Hexadecimal (Intel-Format) File (.hex). You can initialize the UFM content using either one of the following ways: Set the initial memory content through the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Set the initial memory content through the Convert Programming File tool in the Intel Quartus Prime software when you convert.sof to.pof. For more information about the initialization flash content, refer to the Programming Files Generation section in the Embedded Design Handbook. Related Information Programming Files Generation Provides more information about the initialization flash content Guideline: Erase Before Program Make sure to erase the flash location before you perform a program () operation. 10
11 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Related Information Utilizing the User Flash Memory (UFM) on Intel MAX 10 Devices with a Nios II Processor Putting MAX Series FPGAs in Hibernation Mode Using User Flash Memory 4.1. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core The IP core design flow helps you get started with any IP core. The On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core is installed as part of the Intel Quartus Prime installation process. You can select and parameterize any IP core from the Intel FPGA IP library. Intel provides an integrated parameter editor that allows you to customize the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core to support a wide variety of applications. The parameter editor guides you through the setting of parameter values and selection of optional ports. Related Information Introduction to Intel FPGA IP Cores Provides more information about Intel FPGA IP cores UFM Avalon-MM Operating Modes The UFM operating modes use Avalon-MM interface UFM Read Status and Control Register You can access the control register value through the Avalon-MM control slave interface. Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
12 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Figure 6. Read Status and Control Register The figure below shows the timing diagram for the status and control register. addr data value To use the control register, assert the signal and send the control register to the control slave. The flash IP core then sends the register value through the data bus UFM Write Control Register You can program () the control register value through Avalon-MM control slave interface. Figure 7. Program (Write) Control Register The figure below shows the timing diagram for the program control register. addr data value To program the control register, assert the signal. The flash IP core then sends 0 01 (control register) and data (register value) to control the slave interface UFM Program (Write) Operation The UFM offers a single 32-bit program () operation. 12
13 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides To perform a UFM program operation, follow these steps: 1. Disable the protection mode. Write 0 into the protection register for the sector of the given data through the Avalon-MM control interface. 2. Program the following data into flash through the Avalon-MM data interface. Address: legal (from Avalon-MM map) Data: user data Set burst count to 1 (parallel mode) or 32 (serial mode). 3. The flash IP core sets the busy field in the status register to 2'b10 when the program operation is in progress. 4. If the operation goes well, the flash IP core sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b1 or successful. The flash IP core sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b0 (failed) if one of the following conditions takes place: The burst count is not equal to 1 (parallel mode) or 32 (serial mode). The given is out of range. The sector protection mode or protection mode of the corresponding sector is not clear (the value is not 1'b0). 5. Repeat the earlier steps if you want to perform another program operation. 6. You have to enable back the protection mode when the program operation completes. Write 1 into the protection register for the corresponding sector through the Avalon-MM control interface. Note: Check the status register after each to make sure the program operation is successful ( successful). 13
14 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Figure 8. Program Operation in Parallel Mode The figure below shows the data timing diagram in parallel mode. addr burstcount 1 data data Write to UFM UFM Programming Max 305 µs Typical 102 µs Min 34 µs UFM Reset Min 250 ns Figure 9. Program Operation in Serial Mode The figure below shows the data timing diagram in serial mode. addr burstcount 32 data Write to UFM Serial Write 32 bits Data to UFM (32 Cycles) UFM Sector Erase Operation The sector erase operation allows the UFM to erase by sectors. To perform a UFM sector erase operation, follow these steps: 1. Disable the protection mode. Write 0 into the protection register for the sector through the Avalon-MM control interface. 2. Write the appropriate bits into the control register to select the sector erase location. The flash IP core stores the sector erase and initiates the sector erase operation. 14
15 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Note: The IP core only accepts the sector erase when it is in IDLE state; busy field at status register is 2'b00. If the IP core is busy, it will ignore the sector erase. 3. The flash IP core sets the busy field in the status register to 2'b01 when the erase operation is in progress. 4. The flash IP core then asserts the signal if there are any new incoming or commands from the data interface. 5. The flash IP core erases the sector. It stores the physical flash erase result in the erase successful field in the status register when the sector erase operation completes. Note: The maximum erase time is 350 ms. 6. The flash IP core sets the erase successful field in the status register to 1'b0 (failed) if one of the following conditions takes place: You send an illegal sector number. The sector protection mode or protection mode of the corresponding sector is not clear (the value is not 1'b0). 7. Repeat the earlier steps if you want to perform another sector erase operation. 8. You have to enable back the protection mode when the sector erase operation completes. Write 1 into the protection register for the corresponding sector through the Avalon-MM control interface. Note: Check the status register after each erase to make sure the erase operation is successful (erase successful) UFM Page Erase Operation The page erase operation allows the UFM to erase by pages. To perform a UFM page erase operation, follow these steps: 1. Disable the protection mode. Write 0 into the protection register for the sector through the Avalon-MM control interface. 2. Write the appropriate bits into the control register to select the page erase location. The flash IP core stores the page erase and initiates the page erase operation. Note: The IP core only accepts the page erase when the IP is in IDLE state; busy field at status register is 2'b00. If the IP core is busy, it will ignore the page erase. 3. The flash IP core sets the busy field in the status register to 2'b01 when the erase operation is in progress. 4. The flash IP core then asserts the signal if there are any new incoming or commands from the data interface. 5. The flash IP core erases the page. It stores the physical flash erase result in the erase successful field in the status register when the page erase operation completes. Note: The maximum erase time is 350 ms. 15
16 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides 6. The flash IP core sets the erase successful field in the status register to 1b'0 (failed) if you send an illegal. 7. Repeat the earlier steps if you want to perform another page erase operation. 8. You have to enable back the protection mode when the page erase operation completes. Write 1 into the protection register for the corresponding page through the Avalon-MM control interface. Note: Check the status register after each erase to make sure the erase operation is successful (erase successful) UFM Read Operation The UFM offers a single 32-bit operation. To perform a operation, the register must be loaded with the reference where the data is or is going to be located in the UFM. To perform a UFM operation, follow these steps: 1. Assert the signal to send the legal data to the data slave interface. 2. Set the burst count to 1 (parallel mode) or 32 (serial mode). 3. The flash IP core asserts the signal when it is busy. 4. The flash IP core asserts the datavalid signal and sends the data through the data bus. 5. The flash IP core sets the busy field in the status register to 2'b11 when the operation is in progress. 6. If the operation goes well, the flash IP core sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b1 or successful. It sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b0 (failed) and returns empty flash if you try to from an illegal or protected sector. The following figures show the timing diagrams for the operations for the different Intel MAX 10 devices in parallel and serial modes. Figure 10. Read Operation for 10M04, 10M08, 10M16 and 10M25 Devices in Parallel Mode burstcount addr 1 data datavalid data data0 16
17 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Figure 11. Read Operation for 10M40 and 10M50 Devices in Parallel Mode addr burstcount 1 data datavalid data data0 Figure 12. Read Operation for Intel MAX 10 Devices in Serial Mode addr burstcount 32 data datavalid data UFM Burst Read Operation The burst operation is a streaming 32-bit operation. The burst operation offers the following modes: Data incrementing burst allows a maximum of 128 burst counts. Data wrapping burst has fixed burst counts of 2 (10M04/08) and 4 (10M16/25/40/50) To perform a UFM burst operation, follow these steps: 1. Assert the signal and send the legal burst count and legal data es to the data interface. 2. The flash IP core asserts the signal when it is busy. 3. The flash IP core then asserts the datavalid signal and sends the data through the data bus. 17
18 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Note: For data wrapping burst operation, if the reaches the end of the flash, it wraps back to the beginning of the flash and continues ing. 4. The flash IP core sets the busy field in the status register to 2'b11 or busy_ when the operation is in progress. 5. If the operation goes well, the flash IP core sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b1 or successful. It sets the successful field in the status register to 1'b0 (failed) and changes empty flash to 1 if you try to from an illegal or protected sector UFM Data Incrementing Burst Read The following figures show the timing diagrams for the data incrementing burst operations for the different Intel MAX 10 devices. Figure 13. Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M04 and 10M08 Devices in Parallel Mode burstcount data datavalid data addr1 addr2 8 2 data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 data7 data8 data9 Figure 14. Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M16 and 10M25 Devices in Parallel Mode burstcount data datavalid data addr1 8 addr2 8 data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 data7 data8 data9 data10 data11 data12 data13 data14 data15 Figure 15. Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M50 Devices in Parallel Mode burstcount data datavalid data addr1 8 data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 data7 data8 data9 data10 data11 addr2 4 Figure 16. Unaligned Address Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M50 Devices in Parallel Mode burstcount addr 7 data datavalid data data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 18
19 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Figure 17. Incrementing Burst Read Operation for Intel MAX 10 Devices in Serial Mode addr burstcount 64 data datavalid data UFM Data Wrapping Burst Read The UFM supports data wrapping when it receives an unaligned. Note: Table 6. Wrapping burst is available only for parallel interface. Data Wrapping Support for Intel MAX 10 Devices Device Data Register Length Flash IP Data Bus Width Fixed Supported Burst Count Data Wrapping 10M04, or 10M08 10M16, 10M25, 10M40, or 10M The wraps back to the previous boundary after 64 bits or 2 cycles. For example, for a wrapping in a 32-bit data interface: 1. Start is Address sequence will be 0 01, then back to The wraps back to the previous boundary after 128 bits or 4 cycles. For example, for a wrapping in a 32-bit data interface: 1. Start is Address sequence will be 0 02 and 0 03, then back to 0 00 and 0 01 The following figures show the timing diagrams for the data wrapping burst operations for the different Intel MAX 10 devices. Figure 18. Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M04 and 10M08 Devices burstcount data datavalid data addr1 2 addr2 data0 data1 data2 data3 Figure 19. Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M16 and 10M25 Devices burstcount data datavalid data addr1 4 addr2 data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 data7 19
20 4. Intel MAX 10 UFM Implementation Guides Figure 20. Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M40 and 10M50 Devices burstcount data datavalid data addr1 4 addr2 data0 data1 data2 data3 data4 data5 data6 data Flash Initialization Files The On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core supports the.hex,.mif, and.dat files. If the total data size in the initialization file is less the maximum UFM size, the IP core retains blank data (all 1's). If the total data size in the initialization file is larger than the maximum UFM size, the IP core ignores the extra data. Table 7. Types of Flash Initialization File Supported File Type Format Notes.hex.mif Standard Intel hexadecimal file uses byte ing. Standard Intel FPGA memory initialization file uses word ing. For flash initialization in actual hardware. For flash initialization in actual hardware..dat 32-bit data width file uses word ing. For flash initialization in simulation model. 20
21 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References This section provides information about the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core parameters, signals, and registers On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Parameters The following table lists the parameters for the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Table 8. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Parameters Parameters Default Value Description Data interface Parallel Allows you to select the type of interface. You can choose parallel or serial. Read burst mode Incrementing Allows you to select the type of burst mode. You can choose incrementing or wrapping. Incrementing mode Read burst count is 2, 4, 8, Wrapping mode Burst count fixed to 2 or 4 Note: Serial interface supports only incrementing mode. Parallel interface does not support wrapping mode for 10M02 devices. Read burst count 2 Allows you the flexibility to adjust the maximum burst count bus width. Parallel mode: This setting represents the maximum burst count number. Serial mode: This setting supports stream and represents the words to be for each operation. The Avalon-MM interface burst count bus width is equal to 32* burst count. Configuration mode Single uncompressed image Allows you to select the configuration mode. You can choose one of these options: Dual compressed images Single uncompressed image: Accesses CFM2 sector as UFM Single compressed image: Accesses CFM2 and CFM1 sectors as UFM Single uncompressed image with memory initialization Single compressed image with memory initialization Flash Memory The sector ID, range value, and flash type are generated dynamically by hardware.tcl based on the device and configuration mode you select. Indicates the mapping for each sector and adjusts the Access Mode for each sector individually. Note: Only CFM sectors support Hidden access mode. continued... Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
22 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References Parameters Default Value Description Clock frequency MHz Key in the appropriate frequency in MHz. The maximum frequency is MHz for parallel interface and 7.25 MHz for serial interface. Note: If you use 10M02 devices, the maximum frequency for parallel interface is 7.25 MHz. Initialize flash content Off Turn on this option to initialize the flash content. Enable non-default initialization file Off Turn on this option to enable your preferred initialization file. If you choose to have a non-default file, type the filename or select the.hex or.mif file using the browse button. User created hex or mif file This option is only available if you turn on Enable nondefault initialization file. Assign your own.hex or.mif filename. User created dat file for simulation This option is only available if you turn on Enable nondefault initialization file. Assign your own simulation filename On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Signals The following table lists the signals for the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Table 9. Avalon-MM Slave Input and Output Signals for Parallel and Serial Modes. Clock and Reset Signal Width Direction Description 1 Input System signal that s the entire peripheral. reset_n 1 Input System synchronous reset signal that resets the entire peripheral. The IP core asserts this signal asynchronously. This signal becomes synchronous in the IP core after the rising edge of the. Control avmm_csr_addr 1 Input Avalon-MM bus that decodes registers. avmm_csr_ 1 Input Avalon-MM control signal. The IP core asserts this signal to indicate a transfer. If present, the data signal is required. avmm_csr_data 32 Output Avalon-MM back data signal. The IP core asserts this signal during cycles. avmm_csr_ 1 Input Avalon-MM control signal. The IP core asserts this signal to indicate a transfer. If present, the data signal is required. avmm_csr_data 32 Input Avalon-MM data bus. The bus master asserts this bus during cycles. Data avmm_data_addr User-defined Input Avalon-MM bus that indicates the flash data. The width of this depends on your selection of device and configuration mode. avmm_data_ 1 Input Avalon-MM control signal. The IP core asserts this signal to indicate a transfer. If present, the data signal is required. continued... 22
23 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References Signal Width Direction Description avmm_data_data Parallel mode: 32 Serial mode: 1 Output Avalon-MM back data signal. The IP core asserts this signal during cycles. avmm_data_ 1 Input Avalon-MM control signal. The IP core asserts this signal to indicate a transfer. If present, the data signal is required. avmm_data_data Parallel mode: 32 Serial mode: 1 Input Avalon-MM data bus. The bus master asserts this bus during cycles. avmm_data_ 1 Output The IP core asserts this bus to pause the master when the IP core is busy during or operations. avmm_data_dataval id 1 Output The IP core asserts this signal when the data signal is valid during cycles. avmm_data_burstcount User-defined Input The bus master asserts this signal to initiate a burst operation. In operations, the burst count is always fixed to 1 for parallel mode and 32 for serial mode. In incrementing burst mode, the supported burst count range: Parallel mode 1-2 (burstcount width-1) Serial mode 1-128*32 In wrapping burst mode (parallel mode only), the supported burst count is fixed to 2 and 4. 10M04, and 10M M16, 10M25, 10M40 and 10M On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Registers The following table lists the mapping and registers for the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Table 10. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Control Address Mapping Register Address Access Description Status Register 0 00 Read only Stores the status and result of recent operations and sector protection mode. Control Register 0 01 Read/Program Stores the following information: Page erase Sector erase Sector protection mode Table 11. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Status Register Bit Offset Field Default Value Description 1 0 busy 2'b00 2'b00 IDLE 2'b01 BUSY_ERASE 2'b10 BUSY_WRITE continued... 23
24 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References Bit Offset Field Default Value Description 2'b11 BUSY_READ 2 rs ( successful) 1'b0 1'b0 Read failed 1'b1 Read successful 3 ws ( successful) 4 es (erase successful) 1'b0 1'b0 1'b0 Write failed 1'b1 Write successful 1'b0 Erase failed 1'b1 Erase successful 5 sp (Sector ID 1 protection bit) 6 sp (Sector ID 2 protection bit) 7 sp (Sector ID 3 protection bit) 8 sp (Sector ID 4 protection bit) 9 sp (Sector ID 5 protection bit) The IP core sets these bits based on the device, and configuration and access mode settings you specify during instantiation. These settings are fixed. If the IP core sets one of these bits, you cannot or program on the specified sector dummy (padding) All of these bits are set to 1. Table 12. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core Control Register Bit Offset Field Default Value Description 19 0 pe (page erase ) se (sector erase ) All 1's 3'b111 Sets the page erase to initiate a page erase operation. The IP core only accepts the page erase when it is in IDLE state. Otherwise, the page will be ignored. The legal value is any available. The IP core erases the corresponding page of the given. Sets the sector erase to initiate a sector erase operation. The IP core only accepts the sector erase when it is in IDLE state. Otherwise, the page will be ignored. 3'b001 Sector ID 1 3'b010 Sector ID 2 3'b011 Sector ID 3 3'b100 Sector ID 4 3'b101 Sector ID 5 Other values Illegal If the device you selected has only 3 sectors, the value mapped to sectors ID 4 and 5 will become illegal. Note: If you set both sector and page at the same time, the sector erase gets the priority. The IP core accepts and executes the sector erase and ignores the page erase. For more detailed description, refer to Sector Address on page 25. continued... 24
25 5. On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP Core References Bit Offset Field Default Value Description 23 wp (Sector ID 1 protection) 24 wp (Sector ID 2 protection) 25 wp (Sector ID 3 protection) 26 wp (Sector ID 4 protection) 27 wp (Sector ID 5 protection) 1 The IP core uses these bits to protect the sector from and erase operation. You must clear the corresponding sector protection bit before your program or erase 1 the sector 'b0 1'b1 Disable protected mode Enable protected mode dummy (padding) All of these bits are set to Sector Address You need to convert the sector in the parameter editor to 32-bit. The mapping in the parameter editor uses byte. The Avalon-MM interface in the On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core uses 32-bit. Table 13. Address Mapping Example Sector Parameter Editor Address Avalon-MM Address Sector ID 1 0x0000 0x17ff 0x000 0x5ff Sector ID 2 0x1800 0x2fff 0x600 0xBff Sector ID 3 0x3000 0x13fff 0x0C00 0x4fff 25
26 6. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Archive If an IP core version is not listed, the user guide for the previous IP core version applies. IP Core Version User Guide 16.0 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide 15.1 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide 15.0 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide 14.1 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
27 7. Document Revision History for the Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Document Version Intel Quartus Prime Version Changes Beginning from the Intel Quartus Prime software version 18.0, the name of this IP core has been changed from Altera On-Chip Flash IP core to On-Chip Flash Intel FPGA IP core. Added a reference to the Programming Files Generation section of the Embedded Design Handbook for the initialization flash content. Updated the Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M04 and 10M08 Devices in Parallel Mode figure. Updated the Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M16 and 10M25 Devices in Parallel Mode figure. Updated the Incrementing Burst Read Operation for 10M50 Devices in Parallel Mode figure. Updated the Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M04 and 10M08 Devices figure. Updated the Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M16 and 10M25 Devices figure. Updated the Wrapping Burst Read Operation for 10M40 and 10M50 Devices figure. Date Version Changes February Rebranded as Intel. December Updated the description for Altera On-Chip Flash bit offsets 5 9 that the IP core sets these bits based on the device, and configuration and access mode settings you specify during instantiation. These settings are fixed. Updated the description for Altera On-Chip Flash bit offsets to include clearer information about sector. Added Sector Address topic that provides details about converting sector from byte ing to bit ing. May Added the typical and minimum UFM programming time in parallel mode. Corrected the minimum UFM reset time in parallel mode to 250 ns. Added links to archived versions of the MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide. November Added information about the supported flash initialization files. Added serial interface support for 10M40 and 10M50 devices. The maximum frequency for MAX 10 devices is 7.25 MHz, except for 10M40 and 10M50 devices, which is 4.81 MHz. Added parallel interface support for 10M02 devices. The maximum frequency for MAX 10 devices is 116 MHz, except for 10M02 devices, which is 7.25 MHz. Changed instances of Quartus II to Intel Quartus Prime. continued... Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus and Stratix words and logos are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and/or other countries. Intel warrants performance of its FPGA and semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Intel's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Intel assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Intel. Intel customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ISO 9001:2008 Registered
28 7. Document Revision History for the Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Date Version Changes May Changed to industry-standard term program. Added a note to the UFM and CFM Array Size section that the total UFM size is the maximum possible value, which is dependent on the selected mode. Added design consideration information about the maximum slew rate requirement for power supply ramp down. Added design consideration information about erasing the flash location before performing a program operation. December Added support for serial interface. September Initial release. Added maximum operating frequency of 7.25 MHz for serial interface. Updated the UFM block diagram to include serial interface. Added design consideration information about creating initial memory content using the IP core, and programming UFM using JTAG interface version IEEE Standard Added new timing diagrams for and operations in serial mode. Added information for the new serial interface related GUI parameters, signals, and registers. Added information for the following new Avalon-MM slave interface signals for serial mode: addr,, data,, data,, datavalid, and burstcount. Added information for the following new parameters: Data Interface that allows you to choose between Parallel and Serial interface. Configuration Scheme and Configuration Mode that replace Dual Images. The new parameters include all supported configuration modes. Read Burst Count that allows the burst count width to be autoadjusted. 28
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide
 Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide
 Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Customizable Flash Programmer Overview... 3 1.1. Device Family Support...3 1.2. Software Support...
Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Customizable Flash Programmer Overview... 3 1.1. Device Family Support...3 1.2. Software Support...
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide
 Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Intel FPGA Voltage Sensor IP Core User Guide
 Intel FPGA Voltage Sensor IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Voltage Sensor
Intel FPGA Voltage Sensor IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Voltage Sensor
Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide
 Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Parameterizing the Intel Arria 10 Native Floating-Point
Intel Arria 10 Native Floating- Point DSP Intel FPGA IP User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Parameterizing the Intel Arria 10 Native Floating-Point
Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.1 Feature Description...3 1.2 Command & Error Code...4 1.2.1 Commands...
Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.1 Feature Description...3 1.2 Command & Error Code...4 1.2.1 Commands...
Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide
 Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide UG-20051 2017.09.19 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1 Directory Structure... 4 1.2 Design Components...
Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide UG-20051 2017.09.19 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1 Directory Structure... 4 1.2 Design Components...
Stratix 10 Serial Flash Mailbox Client Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Stratix 10 Serial Flash Mailbox Client Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3
Stratix 10 Serial Flash Mailbox Client Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3
NIOS II Processor Booting Methods In MAX 10 Devices
 2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
Intel Stratix 10 Analog to Digital Converter User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Analog to Digital Converter User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix
Intel Stratix 10 Analog to Digital Converter User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix
Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Quick Start Guide...
Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Quick Start Guide...
Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.1. Feature Description...3 1.2. s and Error Codes...4 1.2.1. s... 5 1.2.2. Error
Mailbox Client Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Core User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.1. Feature Description...3 1.2. s and Error Codes...4 1.2.1. s... 5 1.2.2. Error
AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface
 AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon -ST Pass-Through
AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon -ST Pass-Through
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices
 SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Stratix 10 ES Editions Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Stratix 10 ES Editions Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices
 IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start
IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start
Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide
 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide UG-01074 2017.09.14 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents... 3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Features...3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Functional Description...
Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor IP Core User Guide UG-01074 2017.09.14 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents... 3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Features...3 Intel FPGA Temperature Sensor Functional Description...
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. High Bandwidth
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. High Bandwidth
Intel Stratix 10 H-Tile PCIe Link Hardware Validation
 Intel Stratix 10 H-Tile PCIe Link Hardware Validation Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 H-Tile PCIe* Link Hardware Validation... 3 1.1.
Intel Stratix 10 H-Tile PCIe Link Hardware Validation Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 H-Tile PCIe* Link Hardware Validation... 3 1.1.
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design
 AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board
Partial Reconfiguration Solutions IP User Guide
 Partial Reconfiguration Solutions IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1
Partial Reconfiguration Solutions IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide...
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide...
AN822: Intel Configuration Device Migration Guideline
 AN822: Intel Configuration Device Migration Guideline Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Configuration Device Migration Guideline...3 1.1 Migration Considerations...3
AN822: Intel Configuration Device Migration Guideline Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Configuration Device Migration Guideline...3 1.1 Migration Considerations...3
Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
AN822: Intel FPGA Configuration Device Migration Guideline
 AN822: Intel FPGA Configuration Device Migration Guideline Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Configuration Device Migration Guideline...3 1.1 Migration
AN822: Intel FPGA Configuration Device Migration Guideline Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Configuration Device Migration Guideline...3 1.1 Migration
Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata
 Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata Updated for Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs: 1.0 Production Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web:
Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata Updated for Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs: 1.0 Production Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web:
25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. 25G
25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. 25G
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
PCI Express Multi-Channel DMA Interface
 2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 LAB and Overview... 3 2 HyperFlex
Intel Stratix 10 Logic Array Blocks and Adaptive Logic Modules User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 LAB and Overview... 3 2 HyperFlex
AN 797: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Board
 AN 797: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Partially Reconfiguring
AN 797: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Partially Reconfiguring
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design
 AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference
H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Serial Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software
 AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader IP Core
AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader IP Core
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet
 Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...4 1.1 Supported Devices...4 1.2 Features...5 1.3 Operating Conditions...5
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...4 1.1 Supported Devices...4 1.2 Features...5 1.3 Operating Conditions...5
Nios II Performance Benchmarks
 Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit)
 Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
Intel Quartus Prime Software Download and Installation Quick Start Guide
 Intel Quartus Prime Software Download and Installation Quick Start Guide Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus, and Stratix
Intel Quartus Prime Software Download and Installation Quick Start Guide Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel, the Intel logo, Altera, Arria, Cyclone, Enpirion, MAX, Nios, Quartus, and Stratix
Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim
 Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim AN-828 2017.10.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Conventions...3 1.2 Glossary...3 1.3 Introduction...3 1.4 Design...
Intel Xeon with FPGA IP Asynchronous Core Cache Interface (CCI-P) Shim AN-828 2017.10.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Conventions...3 1.2 Glossary...3 1.3 Introduction...3 1.4 Design...
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes
 Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes RN-01082-17.0.0 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Version 17.0... 3 1.1 New Features and Enhancements...3
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes RN-01082-17.0.0 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Version 17.0... 3 1.1 New Features and Enhancements...3
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet
 Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1....4 1.1. Supported Devices...4 1.2. Features...5 1.3. Operating Conditions...5
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1....4 1.1. Supported Devices...4 1.2. Features...5 1.3. Operating Conditions...5
AN 834: Developing for the Intel HLS Compiler with an IDE
 AN 834: Developing for the Intel HLS Compiler with an IDE Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Developing for the Intel HLS Compiler with an Eclipse* IDE...
AN 834: Developing for the Intel HLS Compiler with an IDE Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Developing for the Intel HLS Compiler with an Eclipse* IDE...
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface
 White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide
 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide Subscribe UG-20025 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Quick Start Guide...1-1 Directory Structure... 1-2 Design Components...
Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide Subscribe UG-20025 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Quick Start Guide...1-1 Directory Structure... 1-2 Design Components...
Nios II Embedded Design Suite Release Notes
 Nios II Embedded Design Suite Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Product Revision History... 3 1.2 Nios II EDS v15.0 Updates...4 1.3
Nios II Embedded Design Suite Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Product Revision History... 3 1.2 Nios II EDS v15.0 Updates...4 1.3
AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board
 AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Partially Reconfiguring
AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Partially Reconfiguring
PCI Express*: Migrating to Intel Stratix 10 Devices for the Avalon Streaming Interface
 PCI Express*: Migrating to Intel Stratix 10 Devices for the Avalon Streaming Interface AN791 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: Quartus Prime Pro v17.1 Stratix 10 Editions Subscribe
PCI Express*: Migrating to Intel Stratix 10 Devices for the Avalon Streaming Interface AN791 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: Quartus Prime Pro v17.1 Stratix 10 Editions Subscribe
Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs
 Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs AN-630-1.0 Application Note This application note describes the real-time in-system programmability (ISP) and ISP Clamp programming modes and their usage in
Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs AN-630-1.0 Application Note This application note describes the real-time in-system programmability (ISP) and ISP Clamp programming modes and their usage in
AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines
 AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines AN-756 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Implementing the Altera PHYLite Design... 3 1.1.1 Parameter
AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines AN-756 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Implementing the Altera PHYLite Design... 3 1.1.1 Parameter
AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board
 AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents
AN 825: Partially Reconfiguring a Design on Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents
Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide
 Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
EPCQA Serial Configuration Device Datasheet
 EPCQA Serial Configuration Device Datasheet CF52014 2017.08.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1.1 Supported Devices...3 1.2 Features...3 1.3 Operating Conditions...4 1.3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings...
EPCQA Serial Configuration Device Datasheet CF52014 2017.08.02 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1.1 Supported Devices...3 1.2 Features...3 1.3 Operating Conditions...4 1.3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings...
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet
 2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
AN 807: Configuring the Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit for the Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL
 AN 807: Configuring the Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit for the Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Configuring the Intel Arria
AN 807: Configuring the Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit for the Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Configuring the Intel Arria
AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems
 AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5
AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices
 9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report
 AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and AD9691 Hardware
AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and AD9691 Hardware
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition
 Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Version 18.1 Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Version 18.1 Software
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Version 18.1 Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Version 18.1 Software
Applying the Benefits of Network on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design
 white paper Intel FPGA Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design Authors Kent Orthner Senior Manager, Software and IP Intel Corporation Table of Contents Abstract...1 Introduction...1
white paper Intel FPGA Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design Authors Kent Orthner Senior Manager, Software and IP Intel Corporation Table of Contents Abstract...1 Introduction...1
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide
 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 2017.06.16 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents...3 Device Family Support...
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 2017.06.16 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents...3 Device Family Support...
AN 826: Hierarchical Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board
 AN 826: Hierarchical Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
AN 826: Hierarchical Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Overview
 Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Overview Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3 Key Advantages of Intel MAX 10 Devices... 3 Summary of Intel MAX 10 Device Features...
Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Overview Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3 Key Advantages of Intel MAX 10 Devices... 3 Summary of Intel MAX 10 Device Features...
Avalon Interface Specifications
 Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to the Avalon Interface Specifications... 4 1.1. Avalon
Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to the Avalon Interface Specifications... 4 1.1. Avalon
Avalon Interface Specifications
 Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to the...4 1.1. Avalon Properties and Parameters...5 1.2. Signal Roles...5
Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to the...4 1.1. Avalon Properties and Parameters...5 1.2. Signal Roles...5
Simulating the ASMI Block in Your Design
 2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
9. Functional Description Example Designs
 November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
AN 839: Design Block Reuse Tutorial
 AN 839: Design Block Reuse Tutorial for Intel Arria 10 FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
AN 839: Design Block Reuse Tutorial for Intel Arria 10 FPGA Development Board Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
System Debugging Tools Overview
 9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
Intel Arria 10 and Intel Cyclone 10 Avalon -MM Interface for PCIe* Design Example User Guide
 Intel Arria 10 and Intel Cyclone 10 Avalon -MM Interface for PCIe* Design Example User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1
Intel Arria 10 and Intel Cyclone 10 Avalon -MM Interface for PCIe* Design Example User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1
AN 464: DFT/IDFT Reference Design
 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents About the DFT/IDFT Reference Design... 3 Functional Description for the DFT/IDFT Reference Design... 4 Parameters for the
Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents About the DFT/IDFT Reference Design... 3 Functional Description for the DFT/IDFT Reference Design... 4 Parameters for the
Section III. Transport and Communication
 Section III. Transport and Communication This section describes communication and transport peripherals provided for SOPC Builder systems. This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 16, SPI
Section III. Transport and Communication This section describes communication and transport peripherals provided for SOPC Builder systems. This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 16, SPI
Timing Analyzer Quick-Start Tutorial
 Timing Analyzer Quick-Start Tutorial Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Timing
Timing Analyzer Quick-Start Tutorial Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Timing
Using the Nios Development Board Configuration Controller Reference Designs
 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs July 2006 - ver 1.1 Application Note 346 Introduction Many modern embedded systems utilize flash memory to store processor configuration information
Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs July 2006 - ver 1.1 Application Note 346 Introduction Many modern embedded systems utilize flash memory to store processor configuration information
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices
 11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
White Paper AHB to Avalon & Avalon to AHB Bridges
 White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial
 AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Intel Stratix 10 GX Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Static
AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Intel Stratix 10 GX Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Static
AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial
 AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
AN 818: Static Update Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial for Intel Stratix 10 GX FPGA Development Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
10. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction User Guide
 ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
AN 829: PCI Express* Avalon -MM DMA Reference Design
 AN 829: PCI Express* Avalon -MM DMA Reference Design Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1....3 1.1. Introduction...3 1.1.1.
AN 829: PCI Express* Avalon -MM DMA Reference Design Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1....3 1.1. Introduction...3 1.1.1.
EPCQ-L Serial Configuration Devices Datasheet
 EPCQ-L Serial Configuration Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Supported Devices... 3 Features... 3 Operating Conditions... 4 Absolute
EPCQ-L Serial Configuration Devices Datasheet Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Supported Devices... 3 Features... 3 Operating Conditions... 4 Absolute
3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices
 July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current
 AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
 Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Nios II Custom Instruction Overview...4 1.1 Custom Instruction Implementation... 4
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Nios II Custom Instruction Overview...4 1.1 Custom Instruction Implementation... 4
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes
 Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Version 17.1... 3 1.1 New Features and Enhancements...3
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Version 17.1... 3 1.1 New Features and Enhancements...3
EFEC20 IP Core. Features
 EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
8. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices
 January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design
 2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design AN-642-1.0 Application Note The Altera 2.5G Reed-Solomon (RS) II MegaCore function reference design demonstrates a basic application of the Reed-Solomon
2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design AN-642-1.0 Application Note The Altera 2.5G Reed-Solomon (RS) II MegaCore function reference design demonstrates a basic application of the Reed-Solomon
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes
 Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Version 18.0... 3 1.1. New Features and Enhancements...3
Intel Quartus Prime Pro Edition Software and Device Support Release Notes Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Version 18.0... 3 1.1. New Features and Enhancements...3
Intel FPGA USB Download Cable User Guide
 Intel FPGA USB Download Cable User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to Intel FPGA Download Cable...3 1.1. Intel FPGA Download Cable Revision... 3 1.2.
Intel FPGA USB Download Cable User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Introduction to Intel FPGA Download Cable...3 1.1. Intel FPGA Download Cable Revision... 3 1.2.
Intel Stratix 10 SEU Mitigation User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 SEU Mitigation User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 SEU Mitigation
Intel Stratix 10 SEU Mitigation User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 SEU Mitigation
Intel Arria 10 Native Fixed Point DSP IP Core User Guide
 Intel Arria 0 Native Fixed Point DSP IP Core User Guide UG-06 207.0. Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents Intel Arria Native Fixed Point DSP IP Core User Guide.... Arria 0 Native Fixed Point DSP IP
Intel Arria 0 Native Fixed Point DSP IP Core User Guide UG-06 207.0. Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents Intel Arria Native Fixed Point DSP IP Core User Guide.... Arria 0 Native Fixed Point DSP IP
AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL
 AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread...3 1.1
AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread...3 1.1
Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview...4 2. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Overview...4 2. Intel MAX 10 Embedded Memory Architecture
Quick Start Guide for Intel FPGA Development Tools on the Nimbix Cloud
 Quick Start Guide for Intel FPGA Development Tools on the Nimbix Cloud Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Quick Start Guide for Intel FPGA Development Tools on the Nimbix Cloud Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
