Truss Bracket. Problem:
|
|
|
- Dortha Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem: The truss structure shown above is mounted on the sides of buildings during construction for use as scaffolding for workers. A design team has created a new bracket design (shown below) to use with the truss structure and want to know if the new bracket design is safe. The material for the bracket and the connecting pin is steel with a yield strength of 35 kpsi. The loads on the pin are know to be 14,825 lb in the minus X direction and 4856 lb in the Y direction. Determine if the new bracket design is safe using yielding as the failure criteria. Y X
2 Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 1 hour Tutorial Overview This tutorial is divided into four parts: 1) Tutorial Basics 2) Preprocessing 3) Solution 4) Post Processing Audience This tutorial assumes familiarity of ANSYS 8.0; therefore, it does not go into step by step detail. Prerequisites 1) ANSYS 8.0 in house Structural Tutorial 2) Completion of all Basic Machine Design Tutorials 3) Completion of the 3D Knuckle Pin Joint Tutorial Objectives 1) Create a solid model representation of the bracket 2) Create contact elements to model the interaction between the pin and the bracket 3) Determine if the bracket is a safe design for the given loads. Outcomes 1) Explore possibilities with the graphical user interface (GUI) 2) Learn how to create and mesh a complex geometries 3) Increase efficiency in problem set up and solving speed 2
3 In this tutorial: Instructions appear on the left. Visual aids corresponding to the text appear on the right. Tutorial Basics All commands on the toolbars are labeled. However, only operations applicable to the tutorial are explained. The instructions should be used as follows: Bold > Example: Italics MB1 MB2 MB3 Text in bold are buttons, options, or selections that the user needs to click on > Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/DeleteFile would mean to follow the options as shown to the right to get you to the Element Types window Text in italics are hints and notes Click on the left mouse button Click on the middle mouse button Click on the right mouse button Some basic ANSYS functions are: To rotate the models use Ctrl and MB3. To zoom use Ctrl and MB2 and move the mouse up and down. To translate the models use Ctrl and MB1. 3
4 Problem Planning A log file approach would be an excellent choice for solving this problem. The instructions given in this tutorial follow this approach. You will begin by creating log file commands to define the material properties, the geometry, and the mesh. You will then paste those commands into the ANSYS command line and build the model up to that point. Then you will use the contact wizard in the GUI to define contact surfaces between the pin and the hole. You will open the session editor and copy the commands that ANSYS used while creating the contacts and paste it into your log file. You will finish the tutorial by writing solution and post processing log file commands. The end result will be a log file useful for solving the entire problem. As you work through this tutorial, some new ANSYS features will be explained and the command lines for the log file will be given to you. Other log file commands you have used in other tutorials and will not be given to you. The 3D Knuckle Pin Joint uses many of the commands that you will need to solve this problem as well. It is recommended that you complete the 3D Knuckle Pin Joint tutorial before beginning this one. Drawings of the truss bracket are given below and on the next page. All dimensions are given in inches. 4
5 Problem Planning 5
6 1) Make the first two lines of the log file instructions for ANSYS to clear whatever database it is working on and start a new one. FINISH /CLEAR,NOSTART 2) Add commands to add a file name and title. /FILNAME, /TITLE, Test for Failure 3) One thing nice about a log file is that you can create prompts to allow the user to enter information. This is done through the *ASK command. Information on how to use the *ASK command is found in ANSYS help. For this problem the user will be prompted for the X and Y loads applied to the pin. Add the two lines of command as shown. The user inputted values will be stored in UFX, and UFY respectively. *ASK,UFX,'ENTER THE VALUE OF FX (LB),0 *ASK,UFY,'ENTER THE VALUE OF FY (LB),0 *ASK, Par, Query, DVAL Prompts the user to input a parameter value. Par An alphanumeric name used to identify the scalar parameter. Query Text string to be displayed on the next line as the query (32 characters maximum). Characters having special meaning (such as $!,) should not be included. DVAL Default value assigned to the parameter if the user issues a blank response. 4) Type the command to enter the preprocessor. /PREP7 5) Define the beam element for the model. You are going to use a solid95 element for this model. ET,1,SOLID95 6
7 6) Add the commands to define the material properties. The MP command to add a material model has been used in other tutorials. Additional properties that can be added for a material will now be shown. For this model we will add the density and define data points to map the stress-strain curve for the material. All of the commands needed are briefly explained to the right. See ANSYS help for additional information. MP, Lab, MAT, C0, C1, C2, C3, C4 Defines a linear material property as a constant or a function of temperature. Lab Valid property label. (note only the applicable property labels are shown below). EX -- Elastic moduli (also EY, EZ). PRXY -- Major Poisson's ratios (also PRYZ, PRXZ). For this model a custom stress strain curve will be added. This curve dictates that the material will start to yield at stresses of 35 kpsi. Once you understand how these commands are used, add the following to your log file. MP,EX,1,30e6 MP,PRXY,1,0.3 MP,DENS,1,0.283/386 TB,MISO,1,1,6, TBTEMP,0 TBPT,,.0015,45000 TBPT,,.0133,47000 TBPT,,.0266,54000 TBPT,,.05,62000 TBPT,,.1,70000 TBPT,,.15,73000 After you have entered the commands above you can run your log file up to this point and then view a plot of the materials stress-strain curve by going to > Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models > Material Model Number 1 > Multilinear Isotropic >Then click on the graph button TB, Lab, MAT, NTEMP, NPTS, TBOPT Lab Valid property label. (note only the applicable property label is shown below). MISO -- Multilinear isotropic hardening using von Mises or Hill plasticity MAT Material reference number NTEMP The number of temperatures for which data will be provided NPTS Number of data points to be specified for a given temperature. TBTEMP, TEMP, KMOD TEMP Temperature value (defaults to 0.0 if KMOD is blank). TBPT, Oper, X, Y Oper - Leave blank for this case X value of the point (strain, or H, or closure value). Y The corresponding Y value of the point (stress, or B, or pressure value). 7
8 7) Create the geometry for the bracket and the pin. There are several ways to do this. The challenge of this tutorial will be to build the geometry in an efficient and accurate manner. The geometry can be built using commands that have been demonstrated in other tutorials. The following commands may be helpful: SET - define scalar parameters BLOCK - create solid blocks CYL4 - create cylinders VSBV - subtract volumes VGLUE - glue volumes together For example, you could first build the two plates using the BLOCK command. Second, you could build a solid cylinder and use the VSBV command to subtract it from the plate to create the hole. Then create another cylinder in the same place the size of the pin. Finally, use the VGLUE command to glue the appropriate geometry parts together. (Don t glue the pin and the plate together.) Note: In order to know the appropriate volume numbers to use in this command, you may have to run your log file up to this point, plot the volumes, and turn on the volume numbers. 8
9 8) Set the mesh size for different parts of the model. Use the LESIZE and AESIZE commands to set the number of divisions or element size for the lines and areas indicated. Note: In order to know the appropriate line and area numbers to use in these commands, you may have to run your log file up to this point, plot the line and areas, and turn on the line and area numbers. The numbers below refer to the number of divisions for the lines indicated and the element size for the areas indicated. These are the mesh sizes used in the creation of the tutorial. Feel free to mesh the model in a different manner; however, note that too coarse of mesh will not give the correct result and too dense of a mesh will significantly increase the time the computer needs to solve the model. Area, 0.1 (outer surface of head of pin) Examples: LESIZE,60,,,15,,,,,1 AESIZE,17,0.1, Line, 10 Line, 7 Line, 3 Line, 15 Line, 15 Line, 15 Line, 15 Line, 10 9
10 9) Mesh the model using the volume sweep command. VSWEEP,ALL 10) Add constraints to the bracket and the pin. This can be accomplished using the ASEL,NSLA, and D commands. ASEL - select areas NSLA - select nodes associated with selected areas D - constrain degrees of freedom Constrain the back of the truss in all degrees of freedom and constrain the pin so that it cannot slide out of the bracket. Example code: Back of Truss ASEL,S,AREA,,6 NSLA,S D,ALL,UX,0 D,ALL,UY,0 D,ALL,UZ,0 Pin ASEL,S,AREA,,17 NSLA,S D,ALL,UZ,0 Note: The area numbers given in the code may not be the same as the ones in your model. Verify that you have entered the right area number in your code. 10
11 11) Apply the forces to the ends of the pin. Use the ASEL, NSLA, commands to select the two areas that make up the ends of the pin. Divide the force equally among the nodes on ends of the pin. ASEL,S,AREA,,17 NSLA,S ASEL,A,AREA,,21 NSLA,A Note: The area numbers given in the code may not be the same as the ones in your model. Verify that you have entered the right area number in your code. Run your model up to this point. When you use the ASEL, and NSLA commands ANSYS will count how many nodes you have selected and display that number in the output window. Look in the output window to see how many nodes were selected. If you can t see that number copy and paste the above commands into the command prompt in the GUI and press enter. Check the output window again. Make sure that you have the right area numbers. Based on the mesh used in the tutorial, there were 204 nodes; 102 nodes on each side of the pin. Apply the force evenly over these selected nodes. Remember that UFX, and UFY are variables that contain the user inputted values for the FX and FY forces on the pin. F,ALL,FX,UFX/204 F,ALL,FY,UFY/204 12) Select all the nodes again. ALLSEL,ALL 11
12 13) You will now switch to the GUI and use the contact wizard to generate contact elements between the bracket and the pin. Once you have created the contacts, use the session editor to paste the command lines into your log file. The steps shown in the 3D Knuckle Pin Joint explain the process for creating the contacts. Use the following information as you create the contacts using the contact wizard. Use inner surface of the hole in the bracket as the target area. Target Surface = Areas Target Type = Flexible Use the outer surface of the hole (that makes contact with the bracket) as the contact surface Contact Surface = Areas Contact Element Type = Surface-to- Surface Unselect the option to include initial penetration. Select the option to create a symmetric pair. Enter a coefficient of friction of 0.2. Leave the other setting as the defaults. Once you have created the contact pair, open the session editor in the ANSYS main menu and copy all the commands used to create the contact pair. Paste them into your log file. 14) Add a command to reselect all the nodes. ALLSEL,ALL 12
13 15) When the contact pair was created, coincident nodes were created at the interface of the pin and the bracket. Some unneeded degrees of freedom in these nodes can be removed by defining coupled degrees of freedom between these coincident nodes (within a tolerance), which will decrease the solution time. Add the following command. CPINTF,ALL, ) Add commands to setup the solution and then solve the model. FINISH /SOL ANTYPE,0 NLGEOM,1 NSUBST,10,1000,1 AUTOTS,1 SOLVE FINISH FINISH Exits normally from a processor. /SOL Enters the solution processor. ANTYPE, Antype Specifies the analysis type and restart status. STATIC or 0 -- Perform a static analysis. Valid for all degrees of freedom NLGEOM, Key Includes large-deflection effects in a static or full transient analysis. ON -- 1 Large-deflection effects are to be included NSUBST, NSBSTP, NSBMX, NSBMN Specifies the number of substeps to be taken this load step NSBSTP Number of substeps to be used for this load step NSBMX Maximum number of substeps to be taken NSBMN Minimum number of substeps to be taken AUTOTS, Key Specifies whether to use automatic time stepping or load stepping ON -- 1 Use automatic time stepping SOLVE Starts a solution 13
14 17) Add commands to enter the post processor and to view the stresses. Review the command explanations to the right and then add the following code: /POST1 AVPRIN,0,, PLNSOL,S,EQV,0,1 /REPLOT /POST1 Enters the database results postprocessor. AVPRIN, KEY, EFFNU Specifies how principal and vector sums are to be calculated KEY Averaging key: 0 -- Average the component values from the elements at a common node PLNSOL, Item, Comp, KUND, Fact Displays results as continuous contours Item - S Component stress Comp - EQV Equivalent stress KUND - 0 Do not overlay undeformed structure display Fact - 1 (default) Scale factor for 2-D display for contact items. /REPLOT, Label Automatically reissues the last display command for convenience 18) Run your log file and view the results. When you run the log file you should get two user prompts asking for the FX and FY loads applied to the pin. Enter the following values in these prompts: For FX enter For FY enter 4856 Note depending on the speed of your computer it may take ten minutes or more for the solution to solve. 14
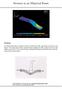
15 Post Processing 19) If everything was done correctly you should see a stress plot of the bracket and the pin similar to the one shown. Look at the stresses around the interface of the pin and the bracket. Under these loads the stress in the bracket exceeds the yield strength (35kpsi) and thus failure can occur. The bracket is not a safe design for the loads given. Try running the solution under different loads. 15
Truss Optimization. Problem:
 Problem: Assuming that the compression members of the truss showing in the figure will not buckle, find the minimum cross sectional area of each member using an allowable stress of 50 MPa. The dimensions
Problem: Assuming that the compression members of the truss showing in the figure will not buckle, find the minimum cross sectional area of each member using an allowable stress of 50 MPa. The dimensions
Statically Indeterminate Beam
 Problem: A rectangular aluminum bar.5 inches thick and 2 inches wide is welded to fixed supports at the ends, and the bar supports a load W=800 lb, acting through the pin as shown. Find the reactions at
Problem: A rectangular aluminum bar.5 inches thick and 2 inches wide is welded to fixed supports at the ends, and the bar supports a load W=800 lb, acting through the pin as shown. Find the reactions at
Bell Crank. Problem: Joseph Shigley and Charles Mischke. Mechanical Engineering Design 5th ed (New York: McGraw Hill, May 2002) page 87.
 Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Stresses in an Elliptical Beam
 Problem: An offset tensile link is shaped to clear an obstruction with a geometry as shown in the figure. The cross section at the critical location is elliptical, with a major axis of 4 in and a minor
Problem: An offset tensile link is shaped to clear an obstruction with a geometry as shown in the figure. The cross section at the critical location is elliptical, with a major axis of 4 in and a minor
Latch Spring. Problem:
 Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Stiffness of Tapered Beam
 Problem: A bar in tension has a conical shape of length L. The task is to find the stiffness of the tapered section. Compare the stiffness given by ANSYS to the theoretical stiffness given by: EA1 ( r2
Problem: A bar in tension has a conical shape of length L. The task is to find the stiffness of the tapered section. Compare the stiffness given by ANSYS to the theoretical stiffness given by: EA1 ( r2
NonLinear Materials AH-ALBERTA Web:
 NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
Statically Indeterminate Beam
 Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
Buckling of Euler Column
 Problem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 GPa). The cross sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the
Problem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 GPa). The cross sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial
 Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
file://c:\documents and Settings\sala\Configuración local\temp\~hha54f.htm
 Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Two Dimensional Truss
 Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline the steps required to do a simple nonlinear analysis of the beam
NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline the steps required to do a simple nonlinear analysis of the beam
Module 1.2: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel.
 Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 3: Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam
 Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
ANSYS. Geometry. Material Properties. E=2.8E7 psi v=0.3. ansys.fem.ir Written By:Mehdi Heydarzadeh Page 1
 Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial
 Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Tutorial Week 10 Internal bone remodelling
 Introduction Tutorial Week 10 Internal bone remodelling This tutorial will introduce the necessary steps to simulate internal bone remodelling of an implanted femur using ANSYS. You will learn to: Setup
Introduction Tutorial Week 10 Internal bone remodelling This tutorial will introduce the necessary steps to simulate internal bone remodelling of an implanted femur using ANSYS. You will learn to: Setup
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis
 Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
ANSYS Tutorials. Table of Contents. Grady Lemoine
 ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
Transient Thermal Conduction Example
 Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
Buckling (with sections)
 roblem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 Ga). The oss sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the column
roblem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 Ga). The oss sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the column
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Workshop 15. Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate
 Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6
 ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
IJMH - International Journal of Management and Humanities ISSN:
 EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior Initial Project Space Setup Static Structural ANSYS ZX Plane
 TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models
 Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Background on Gaskets
 Gasket Materials 1 Background on Gaskets Example of Gaskets used in Engines Gaskets serve two main purposes in many structural assemblies: Provide tight and durable seal between parts Transfer mechanical
Gasket Materials 1 Background on Gaskets Example of Gaskets used in Engines Gaskets serve two main purposes in many structural assemblies: Provide tight and durable seal between parts Transfer mechanical
Modelling and Analysis Lab (FEA)
 Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading
 Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading This exercise will focus on setting up a model for analysis. At the end of this exercise, you will run an analysis in OptiStruct. While this exercise is focused
Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading This exercise will focus on setting up a model for analysis. At the end of this exercise, you will run an analysis in OptiStruct. While this exercise is focused
Melting Using Element Death
 Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Linear Static Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 Fergyanto E. Gunawan (f.e.gunawan@gmail.com) Department of Mechanical Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Objectives: Modeling a symmetric structure Bottom-up and top-down approaches in modeling
Fergyanto E. Gunawan (f.e.gunawan@gmail.com) Department of Mechanical Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Objectives: Modeling a symmetric structure Bottom-up and top-down approaches in modeling
Truss Analysis using Multiframe
 Truss Analysis using Multiframe 1. The software is on the teaching computers in the College of Architecture in Programs under the Windows Start menu. Multiframe is under the Bentley Engineering menu. It
Truss Analysis using Multiframe 1. The software is on the teaching computers in the College of Architecture in Programs under the Windows Start menu. Multiframe is under the Bentley Engineering menu. It
ME Week 12 Piston Mechanical Event Simulation
 Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing
 Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss
 TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
Introduction to MSC.Patran
 Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
[ ] u 1. ME309 Homework #2 $ % & u = 1 s 2 " # u 2. s,u. A,E constant along length. 4Etc
![[ ] u 1. ME309 Homework #2 $ % & u = 1 s 2 # u 2. s,u. A,E constant along length. 4Etc [ ] u 1. ME309 Homework #2 $ % & u = 1 s 2 # u 2. s,u. A,E constant along length. 4Etc](/thumbs/73/69550715.jpg) ME09 Homework # OBJECTIVES: Introduction to convergence issues and modeling approaches Postprocessing procedures Element selection Experience with shape functions and stiffness terms NOTES: Problems 1and
ME09 Homework # OBJECTIVES: Introduction to convergence issues and modeling approaches Postprocessing procedures Element selection Experience with shape functions and stiffness terms NOTES: Problems 1and
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
The part to be analyzed is the bracket from the tutorial of Chapter 3.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis
 Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Course in ANSYS. Example0303. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Problem description. The FCBI-C element is used in the fluid part of the model.
 Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Example Plate with a hole
 Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Example Cantilever beam
 Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench
 Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench Course Curriculum (Duration: 120 Hrs.) Section I: ANSYS Mechanical APDL Chapter 1: Before you start using ANSYS a. Introduction to
Finite Element Analysis using ANSYS Mechanical APDL & ANSYS Workbench Course Curriculum (Duration: 120 Hrs.) Section I: ANSYS Mechanical APDL Chapter 1: Before you start using ANSYS a. Introduction to
MAE 323: Lab 7. Instructions. Pressure Vessel Alex Grishin MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1
 Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer
 Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
This tutorial will take you all the steps required to set up and run a basic simulation using ABAQUS/CAE and visualize the results;
 ENGN 1750: Advanced Mechanics of Solids ABAQUS TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University This tutorial will take you all the steps required to set up and run a basic simulation using ABAQUS/CAE and
ENGN 1750: Advanced Mechanics of Solids ABAQUS TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University This tutorial will take you all the steps required to set up and run a basic simulation using ABAQUS/CAE and
Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks
 Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: 1819-4818 Delivering Quality Science to the World Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks Chenling Zheng 1, a, Hang Li 1, b and Jianyong Li 1, c 1 Shandong University
Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: 1819-4818 Delivering Quality Science to the World Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks Chenling Zheng 1, a, Hang Li 1, b and Jianyong Li 1, c 1 Shandong University
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
FEMAP Tutorial 2. Figure 1: Bar with defined dimensions
 FEMAP Tutorial 2 Consider a cantilevered beam with a vertical force applied to the right end. We will utilize the same geometry as the previous tutorial that considered an axial loading. Thus, this tutorial
FEMAP Tutorial 2 Consider a cantilevered beam with a vertical force applied to the right end. We will utilize the same geometry as the previous tutorial that considered an axial loading. Thus, this tutorial
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
ME Optimization of a Truss
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Truss Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus and optimized using HEEDS. 4 5 8 2 11 3 10 6 9 1 7 12 6 m 300 kn 300 kn 22 m 35 m Figure
ME 475 - Optimization of a Truss Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus and optimized using HEEDS. 4 5 8 2 11 3 10 6 9 1 7 12 6 m 300 kn 300 kn 22 m 35 m Figure
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4. ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I. Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC
 Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses
 Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Analysis of ANSI W W 6x9-118,
 Page 1 of 8 Analysis of ANSI W W 6x9-118,110236220472 Author: Analysis Created: Analysis Last Modified: Report Created: Introduction Administrator, 08:29:09, 08:29:09 09:26:02 Database: Z:\ENGENHARIA\ESTUDOS
Page 1 of 8 Analysis of ANSI W W 6x9-118,110236220472 Author: Analysis Created: Analysis Last Modified: Report Created: Introduction Administrator, 08:29:09, 08:29:09 09:26:02 Database: Z:\ENGENHARIA\ESTUDOS
Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post
 Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Course in ANSYS. Example Truss 2D. Example0150
 Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
LAB MANUAL. Dharmapuri ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS. Regulation : Branch : B.E. Mechanical Engineering
 Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Release 10. Kent L. Lawrence. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
 ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Simulation of RF HEat Test
 Simulation of RF HEat Test Date: Tuesday, December 22, 2015 Designer: Solidworks Study name: Stress One Third Emissivity Analysis type: Nonlinear - Dynamic Description No Data Table of Contents Description...
Simulation of RF HEat Test Date: Tuesday, December 22, 2015 Designer: Solidworks Study name: Stress One Third Emissivity Analysis type: Nonlinear - Dynamic Description No Data Table of Contents Description...
FEA TUTORIAL 2D STRESS ANALYSIS OF A THIN BAR (Using ProMechanica Wildfire 1.0)
 FEA TUTORIAL 2D STRESS ANALYSIS OF A THIN BAR (Using ProMechanica Wildfire 1.0) Introduction: A simple 2D stress analysis of a thin bar with a hole will be performed using Pro/Mechanica. The bar will be
FEA TUTORIAL 2D STRESS ANALYSIS OF A THIN BAR (Using ProMechanica Wildfire 1.0) Introduction: A simple 2D stress analysis of a thin bar with a hole will be performed using Pro/Mechanica. The bar will be
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS.
 Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0
 ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
11. Push-over analysis
 . Push-over analysis Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 90 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type: Push Over Element
. Push-over analysis Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 90 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type: Push Over Element
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis
 Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06)
 Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005
 University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005 Running ANSYS on the CADE lab workstations CADE Lab Accounts You need to get account information in EMCB 224 from the operators
University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005 Running ANSYS on the CADE lab workstations CADE Lab Accounts You need to get account information in EMCB 224 from the operators
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials
 ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench
 Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
