Alignment ABC. Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures
|
|
|
- Kristina West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alignment ABC Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures
2 Complete genomes
3 Evolution
4 Evolution at the DNA level C ACGGTGCAGTCACCA ACGTTGCAGTCCACCA SEQUENCE EDITS REARRANGEMENTS
5 Sequence conservation implies function Interleukin region in human and mouse
6 Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC--- TAG-CTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCGATTTGCCCGAC Definition Given two strings x = x 1 x 2...x M, y = y 1 y 2 y N, an alignment is an assignment of gaps to positions 0,, N in x, and 0,, N in y, so as to line up each letter in one sequence with either a letter, or a gap in the other sequence
7 What is a good alignment? Alignment: The best way to match the letters of one sequence with those of the other How do we define best? Alignment: A hypothesis that the two sequences come from a common ancestor through sequence edits Parsimonious explanation: Find the minimum number of edits that transform one sequence into the other
8 Scoring Function Sequence edits: Mutations Insertions Deletions Scoring Function: Match: +m Mismatch: -s Gap: -d AGGCCTC AGGACTC AGGGCCTC AGG.CTC Score F = (# matches) m - (# mismatches) s (#gaps) d
9 Scoring the gaps more accurately Current model: (n) Gap of length incurs penalty n n d However, gaps usually occur in bunches Convex gap penalty function: (n) (n): for all n, (n + 1) (n) (n) (n 1)
10 How do we compute the best alignment? AGTGCCCTGGAACCCTGACGGTGGGTCACAAAACTTCTGGA AGTGACCTGGGAAGACCCTGACCCTGGGTCACAAAACTC Too many possible alignments: O( 2 M+N )
11 Dynamic Programming We will now describe a dynamic programming algorithm Suppose we wish to align x 1 x M y 1 y N Let F(i,j) = optimal score of aligning x 1 x i y 1 y j
12 Dynamic Programming (cont d) Notice three possible cases: 1. x i aligns to y j x 1 x i-1 y 1 y j-1 x i y j F(i,j) = F(i-1, j-1) + m, if x i = y j -s, if not 2. x i aligns to a gap x 1 x i-1 y 1 y j - x i 3. y j aligns to a gap x 1 x i - y 1 y j-1 y j F(i,j) = F(i-1, j) - d F(i,j) = F(i, j-1) - d
13 Dynamic Programming (cont d) How do we know which case is correct? Inductive assumption: F(i, j-1), F(i-1, j), F(i-1, j-1) are optimal Then, F(i, j) = max F(i-1, j-1) + s(x i, y j ) F(i-1, j) d F( i, j-1) d Where s(x i, y j ) = m, if x i = y j ; -s, if not
14 Example x = AGTA m = 1 y = ATA s = -1 F(i,j) i = d = -1 j = A G T A A T A Optimal Alignment: F(4,3) = 2 AGTA A - TA
15 The Needleman Wunsch Algorithm 1. Initialization. a. F(0, 0) = 0 b. F(0, j) = - j d c. F(i, 0) = - i d 2. Main Iteration. Filling-in partial alignments a. For each i = 1 M For each j = 1 N F(i-1,j) d [case 1] F(i, j) = max F(i, j-1) d [case 2] F(i-1, j-1) + s(x i, y j ) [case 3] UP, if [case 1] Ptr(i,j) = LEFT if [case 2] DIAG if [case 3] 3. Termination. F(M, N) is the optimal score, and from Ptr(M, N) can trace back optimal alignment
16 Performance Time: O(NM) Space: O(NM) There are more efficient methods
17 A variant of the basic algorithm: Maybe it is OK to have an unlimited # of gaps in the beginning and end: CTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCCCTTCCGGC GCGAGTTCATCTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCG Then, we don t want to penalize gaps in the ends
18 Different types of overlaps
19 The Overlap Detection variant x 1 x M Changes: y 1 y N 1. Initialization For all i, j, F(i, 0) = 0 F(0, j) = 0 2. Termination max i F(i, N) F OPT = max max j F(M, j)
20 Bounded Dynamic Programming Initialization: F(i,0), F(0,j) undefined for i, j > k y 1 y Nx1 xm k(n) Iteration: For i = 1 M For j = max(1, i k) min(n, i+k) F(i, j) = max Termination: F(i 1, j 1)+ s(x i, y j ) F(i, j 1) d, if j > i k(n) F(i 1, j) d, if j < i + k(n) same Easy to extend to the affine gap case
21 The local alignment problem Given two strings x = x 1 x M, y = y 1 y N Find substrings x, y whose similarity (optimal global alignment value) is maximum e.g. x = aaaacccccgggg y = cccgggaaccaacc
22 Why local alignment Genes are shuffled between genomes Portions of proteins (domains) are often conserved
23 The Smith Waterman algorithm Idea: Ignore badly aligning regions Modifications to Needleman Wunsch: Initialization: F(0, j) = F(i, 0) = 0 0 Iteration: F(i, j) = max F(i 1, j) d F(i, j 1) d F(i 1, j 1) + s(x i, y j )
24 The Smith Waterman algorithm Termination: 1. If we want the best local alignment F OPT = max i,j F(i, j) 2. If we want all local alignments scoring > t For all i, j find F(i, j) > t, and trace back
25 Multiple Sequence Alignments
26 Definition Given N sequences x 1, x 2,, x N : Insert gaps ( ) in each sequence x i, such that All sequences have the same length L Score of the global map is maximum The sum of pairs score of an alignment is the sum of the scores of all induced pairwise alignments s(m k, m l ): S(m) = k<l s(m k, m l ) score of induced alignment (k,l)
27 Multidimensional Dynamic Example: in 3D (three sequences): Programming 7 neighbors/cell F(i,j,k) = max{ F(i-1,j-1,k-1)+S(x i, x j, x k ), F(i-1,j-1,k )+S(x i, x j, - ), F(i-1,j,k-1)+S(x i, -, x k ), F(i-1,j,k )+S(x i, -, - ), F(i,j-1,k-1)+S( -, x j, x k ), F(i,j-1,k )+S( -, x j, x k ), F(i,j,k-1)+S( -, -, x k ) }
28 Progressive Alignment Multiple Alignment is NP complete Most used heuristic: Progressive Alignment Algorithm: 1. Align two of the sequences x i, x j 2. Fix that alignment 3. Align a third sequence x k to the alignment x i,x j 4. Repeat until all sequences are aligned Running Time: O( N L 2 )
29 Progressive Alignment When evolutionary tree is known: Align closest first, in the order of the tree x y z w Example: Order of alignments: 1. (x,y) 2. (z,w) 3. (xy, zw)
30 Progressive Alignment: CLUSTALW CLUSTALW: most popular multiple protein alignment Algorithm: 1. Find all d ij : alignment dist (x i, x j ) 2. Construct a tree (Neighbor joining hierarchical clustering) 3. Align nodes in order of decreasing similarity + a large number of heuristics
31 CLUSTALW
32 MLAGAN: Multiple Alignment 1. Multi Anchoring 2. Progressive Alignment 3. Iterative Refinement
33 1. Multi anchoring To anchor the (X/Y), and (Z) alignments: X Z Y Z X/Y Z
34 2. Progressive Alignment Human Baboon Mouse Rat Given N sequences, phylogenetic tree Align pairwise, in order of the tree (LAGAN)
35 3. Iterative Refinement For each sequence y 1. Remove y 2. Anchor good spots 3. Realign y using LAGAN y z x x,z fixed projection
36 Cystic Fibrosis (CFTR), 12 species The zoo project Cow Chicken Chimp Pig Human Baboon Cat Dog Rat Fugu Mouse Human sequence length: 1.8 Mb Total genomic sequence: 13 Mb Zebrafish
37 Performance in the CFTR region Exons Perfect Exons > 90% TIME (sec) MAX MEMORY (Mb) MUMmer Mammals 25% 40% Chicken & Fishes 0% 0% 7 40 AVID Mammals 95% 98% Chicken & Fishes 23% 27% LAGAN Mammals 98% 99.7% Chicken & Fishes 80% 84% MLAGAN Mammals 98% 99.8% Chicken & Fishes 82% 91%
38 MLAGAN
LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient Tools for Large-Scale Multiple Alignment of Genomic DNA
 LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient Tools for Large-Scale Multiple Alignment of Genomic DNA Michael Brudno, Chuong B. Do, Gregory M. Cooper, et al. Presented by Xuebei Yang About Alignments Pairwise Alignments
LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient Tools for Large-Scale Multiple Alignment of Genomic DNA Michael Brudno, Chuong B. Do, Gregory M. Cooper, et al. Presented by Xuebei Yang About Alignments Pairwise Alignments
Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC--
 Sequence Alignment Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC-- TAG-CTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCGATTTGCCCGAC Distance from sequences
Sequence Alignment Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC-- TAG-CTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCGATTTGCCCGAC Distance from sequences
Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements Definition Given N sequences x 1, x 2,, x N : Insert gaps (-) in each sequence x i, such that All sequences have the same length L Score of
Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements Definition Given N sequences x 1, x 2,, x N : Insert gaps (-) in each sequence x i, such that All sequences have the same length L Score of
Lecture 10. Sequence alignments
 Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
TCCAGGTG-GAT TGCAAGTGCG-T. Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners. Review: Probabilistic Interpretation. Chance or true homology?
 Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners Lectures 18 Nov 28, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall
Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners Lectures 18 Nov 28, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 04: Variations of sequence alignments http://www.pitt.edu/~mcs2/teaching/biocomp/tutorials/global.html Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 04: Variations of sequence alignments http://www.pitt.edu/~mcs2/teaching/biocomp/tutorials/global.html Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University
Minimum Edit Distance. Definition of Minimum Edit Distance
 Minimum Edit Distance Definition of Minimum Edit Distance How similar are two strings? Spell correction The user typed graffe Which is closest? graf graft grail giraffe Computational Biology Align two
Minimum Edit Distance Definition of Minimum Edit Distance How similar are two strings? Spell correction The user typed graffe Which is closest? graf graft grail giraffe Computational Biology Align two
Multiple Sequence Alignment. With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University
 Multiple Sequence Alignment With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University Definition: Multiple sequence alignment Given a set of sequences, a multiple sequence alignment
Multiple Sequence Alignment With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University Definition: Multiple sequence alignment Given a set of sequences, a multiple sequence alignment
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
Principles of Bioinformatics. BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010
 Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it.
 Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10)
 Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10) Early Evolutionary Studies Anatomical features were the dominant criteria used to derive evolutionary relationships between species since Darwin till early
Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10) Early Evolutionary Studies Anatomical features were the dominant criteria used to derive evolutionary relationships between species since Darwin till early
Alignment of Long Sequences
 Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2009 Mark Craven craven@biostat.wisc.edu Pairwise Whole Genome Alignment: Task Definition Given a pair of genomes (or other large-scale
Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2009 Mark Craven craven@biostat.wisc.edu Pairwise Whole Genome Alignment: Task Definition Given a pair of genomes (or other large-scale
In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace.
 5 Multiple Match Refinement and T-Coffee In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace. This exposition
5 Multiple Match Refinement and T-Coffee In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace. This exposition
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
Stephen Scott.
 1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
Pairwise alignment II
 Pairwise alignment II Agenda - Previous Lesson: Minhala + Introduction - Review Dynamic Programming - Pariwise Alignment Biological Motivation Today: - Quick Review: Sequence Alignment (Global, Local,
Pairwise alignment II Agenda - Previous Lesson: Minhala + Introduction - Review Dynamic Programming - Pariwise Alignment Biological Motivation Today: - Quick Review: Sequence Alignment (Global, Local,
Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD
 Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD Assumptions: Biological sequences evolved by evolution. Micro scale changes: For short sequences (e.g. one
Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD Assumptions: Biological sequences evolved by evolution. Micro scale changes: For short sequences (e.g. one
WordNet Similarity & Edit Distance
 WordNet Similarity & Edit Distance Nathan Schneider ANLP 18 September 2017 Most slides from Jurafsky & Martin SLP3 lectures 1 Computing with a thesaurus Word Similarity: Thesaurus Methods Word Similarity
WordNet Similarity & Edit Distance Nathan Schneider ANLP 18 September 2017 Most slides from Jurafsky & Martin SLP3 lectures 1 Computing with a thesaurus Word Similarity: Thesaurus Methods Word Similarity
Sequence alignment algorithms
 Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004
 CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
Today s Lecture. Edit graph & alignment algorithms. Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment
 Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment. Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences
 SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014
 Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
human chimp mouse rat
 Michael rudno These notes are based on earlier notes by Tomas abak Phylogenetic Trees Phylogenetic Trees demonstrate the amoun of evolution, and order of divergence for several genomes. Phylogenetic trees
Michael rudno These notes are based on earlier notes by Tomas abak Phylogenetic Trees Phylogenetic Trees demonstrate the amoun of evolution, and order of divergence for several genomes. Phylogenetic trees
PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT MOTIVATION: BACKGROUND: Marina Sirota
 Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Algorithms for Bioinformatics
 Adapted from slides by Leena Salmena and Veli Mäkinen, which are partly from http: //bix.ucsd.edu/bioalgorithms/slides.php. 582670 Algorithms for Bioinformatics Lecture 6: Distance based clustering and
Adapted from slides by Leena Salmena and Veli Mäkinen, which are partly from http: //bix.ucsd.edu/bioalgorithms/slides.php. 582670 Algorithms for Bioinformatics Lecture 6: Distance based clustering and
Using multiple alignments to improve seeded local alignment algorithms
 Published online August 12, 2005 Using multiple alignments to improve seeded local alignment algorithms Jason Flannick* and Serafim Batzoglou Department of Computer Science, Stanford University, Stanford,
Published online August 12, 2005 Using multiple alignments to improve seeded local alignment algorithms Jason Flannick* and Serafim Batzoglou Department of Computer Science, Stanford University, Stanford,
Dynamic Programming & Smith-Waterman algorithm
 m m Seminar: Classical Papers in Bioinformatics May 3rd, 2010 m m 1 2 3 m m Introduction m Definition is a method of solving problems by breaking them down into simpler steps problem need to contain overlapping
m m Seminar: Classical Papers in Bioinformatics May 3rd, 2010 m m 1 2 3 m m Introduction m Definition is a method of solving problems by breaking them down into simpler steps problem need to contain overlapping
Profiles and Multiple Alignments. COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA.
 Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms. COMP Spring 2015 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 - Spring 2015 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if
Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 - Spring 2015 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
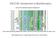 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment
 Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow February 10, 2018 Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow Basic issues What is a multiple sequence alignment? Evolutionary processes operating
Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow February 10, 2018 Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow Basic issues What is a multiple sequence alignment? Evolutionary processes operating
EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES INFERRING PHYLOGENIES
 EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES INFERRING PHYLOGENIES Luca Bortolussi 1 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste luca@dmi.units.it Trieste, 28 th November 2007 OUTLINE 1 INFERRING
EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCES INFERRING PHYLOGENIES Luca Bortolussi 1 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste luca@dmi.units.it Trieste, 28 th November 2007 OUTLINE 1 INFERRING
Quiz section 10. June 1, 2018
 Quiz section 10 June 1, 2018 Logistics Bring: 1 page cheat-sheet, simple calculator Any last logistics questions about the final? Logistics Bring: 1 page cheat-sheet, simple calculator Any last logistics
Quiz section 10 June 1, 2018 Logistics Bring: 1 page cheat-sheet, simple calculator Any last logistics questions about the final? Logistics Bring: 1 page cheat-sheet, simple calculator Any last logistics
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh
 Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
6.047 / Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.047 / 6.878 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Sequence Alignment. part 2
 Sequence Alignment part 2 Dynamic programming with more realistic scoring scheme Using the same initial sequences, we ll look at a dynamic programming example with a scoring scheme that selects for matches
Sequence Alignment part 2 Dynamic programming with more realistic scoring scheme Using the same initial sequences, we ll look at a dynamic programming example with a scoring scheme that selects for matches
Multiple Sequence Alignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW. Ulf Leser
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW Ulf Leser This Lecture Multiple Sequence Alignment The problem Theoretical approach: Sum-of-Pairs scores Practical approach: ClustalW Ulf Leser: Bioinformatics,
Multiple Sequence Alignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW Ulf Leser This Lecture Multiple Sequence Alignment The problem Theoretical approach: Sum-of-Pairs scores Practical approach: ClustalW Ulf Leser: Bioinformatics,
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST
 An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
Sequence clustering. Introduction. Clustering basics. Hierarchical clustering
 Sequence clustering Introduction Data clustering is one of the key tools used in various incarnations of data-mining - trying to make sense of large datasets. It is, thus, natural to ask whether clustering
Sequence clustering Introduction Data clustering is one of the key tools used in various incarnations of data-mining - trying to make sense of large datasets. It is, thus, natural to ask whether clustering
Brief review from last class
 Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
A multiple alignment tool in 3D
 Outline Department of Computer Science, Bioinformatics Group University of Leipzig TBI Winterseminar Bled, Slovenia February 2005 Outline Outline 1 Multiple Alignments Problems Goal Outline Outline 1 Multiple
Outline Department of Computer Science, Bioinformatics Group University of Leipzig TBI Winterseminar Bled, Slovenia February 2005 Outline Outline 1 Multiple Alignments Problems Goal Outline Outline 1 Multiple
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms
 Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 8: Multiple alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 8: Multiple alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution
 Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 11/12/2013 Comp 465 Fall 2013 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other vertex A clique
Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 11/12/2013 Comp 465 Fall 2013 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other vertex A clique
Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh
 Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh We saw earlier how we can use a concave gap penalty function γ, i.e. one that satisfies γ(x+1) γ(x)
Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh We saw earlier how we can use a concave gap penalty function γ, i.e. one that satisfies γ(x+1) γ(x)
Sequence comparison: Local alignment
 Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution
 Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 11/11/2014 Comp 555 Bioalgorithms (Fall 2014) 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other
Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 11/11/2014 Comp 555 Bioalgorithms (Fall 2014) 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other
Lecture 3: February Local Alignment: The Smith-Waterman Algorithm
 CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
Multiple sequence alignment. November 20, 2018
 Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20
 Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
What is a phylogenetic tree? Algorithms for Computational Biology. Phylogenetics Summary. Di erent types of phylogenetic trees
 What is a phylogenetic tree? Algorithms for Computational Biology Zsuzsanna Lipták speciation events Masters in Molecular and Medical Biotechnology a.a. 25/6, fall term Phylogenetics Summary wolf cat lion
What is a phylogenetic tree? Algorithms for Computational Biology Zsuzsanna Lipták speciation events Masters in Molecular and Medical Biotechnology a.a. 25/6, fall term Phylogenetics Summary wolf cat lion
Sequencing Alignment I
 Sequencing Alignment I Lectures 16 Nov 21, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline: Sequence
Sequencing Alignment I Lectures 16 Nov 21, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline: Sequence
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Lecture 10: Local Alignments
 Lecture 10: Local Alignments Study Chapter 6.8-6.10 1 Outline Edit Distances Longest Common Subsequence Global Sequence Alignment Scoring Matrices Local Sequence Alignment Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties
Lecture 10: Local Alignments Study Chapter 6.8-6.10 1 Outline Edit Distances Longest Common Subsequence Global Sequence Alignment Scoring Matrices Local Sequence Alignment Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties
Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics. Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo
 Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo 1 Multiple Alignment: Motivations Common structure, function, or origin may be only
Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo 1 Multiple Alignment: Motivations Common structure, function, or origin may be only
Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee
 More Alignments 1 Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee Mouse to Human Chimpanzee to Human 2 Mouse v.s. Human Chromosome X of Mouse to Human 3 Local Alignment Given: two sequences S and T Find: substrings of S and
More Alignments 1 Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee Mouse to Human Chimpanzee to Human 2 Mouse v.s. Human Chromosome X of Mouse to Human 3 Local Alignment Given: two sequences S and T Find: substrings of S and
Gene expression & Clustering (Chapter 10)
 Gene expression & Clustering (Chapter 10) Determining gene function Sequence comparison tells us if a gene is similar to another gene, e.g., in a new species Dynamic programming Approximate pattern matching
Gene expression & Clustering (Chapter 10) Determining gene function Sequence comparison tells us if a gene is similar to another gene, e.g., in a new species Dynamic programming Approximate pattern matching
Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment. Chaochun Wei Spring 2018
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
CLUSTERING IN BIOINFORMATICS
 CLUSTERING IN BIOINFORMATICS CSE/BIMM/BENG 8 MAY 4, 0 OVERVIEW Define the clustering problem Motivation: gene expression and microarrays Types of clustering Clustering algorithms Other applications of
CLUSTERING IN BIOINFORMATICS CSE/BIMM/BENG 8 MAY 4, 0 OVERVIEW Define the clustering problem Motivation: gene expression and microarrays Types of clustering Clustering algorithms Other applications of
BLAST MCDB 187. Friday, February 8, 13
 BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
Lecture Overview. Sequence search & alignment. Searching sequence databases. Sequence Alignment & Search. Goals: Motivations:
 Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Recent Research Results. Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods
 Recent Research Results Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods Indo-European Languages After Tandy Warnow What is the purpose? Understand evolutionary history (relationship between species). Uderstand how
Recent Research Results Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods Indo-European Languages After Tandy Warnow What is the purpose? Understand evolutionary history (relationship between species). Uderstand how
Sequence Alignment & Search
 Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
FASTA. Besides that, FASTA package provides SSEARCH, an implementation of the optimal Smith- Waterman algorithm.
 FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
Multiple Sequence Alignment Augmented by Expert User Constraints
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Augmented by Expert User Constraints A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Master of
Multiple Sequence Alignment Augmented by Expert User Constraints A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Master of
11/17/2009 Comp 590/Comp Fall
 Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 Problem Set #5 will be available tonight 11/17/2009 Comp 590/Comp 790-90 Fall 2009 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph with every vertex connected
Lecture 20: Clustering and Evolution Study Chapter 10.4 10.8 Problem Set #5 will be available tonight 11/17/2009 Comp 590/Comp 790-90 Fall 2009 1 Clique Graphs A clique is a graph with every vertex connected
BLAST & Genome assembly
 BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
Biological Sequence Analysis. CSEP 521: Applied Algorithms Final Project. Archie Russell ( ), Jason Hogg ( )
 Biological Sequence Analysis CSEP 521: Applied Algorithms Final Project Archie Russell (0638782), Jason Hogg (0641054) Introduction Background The schematic for every living organism is stored in long
Biological Sequence Analysis CSEP 521: Applied Algorithms Final Project Archie Russell (0638782), Jason Hogg (0641054) Introduction Background The schematic for every living organism is stored in long
Bioinformatics for Biologists
 Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Phylogenetics. Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, Lectures: Sven Rahmann. Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst
 Phylogenetics Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, 16.-20.07.2007 Lectures: Sven Rahmann Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst 1 Phylogenetics phylum = tree phylogenetics: reconstruction of evolutionary
Phylogenetics Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, 16.-20.07.2007 Lectures: Sven Rahmann Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst 1 Phylogenetics phylum = tree phylogenetics: reconstruction of evolutionary
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17
 Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment 2 The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if gaps are allowed)
1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment 2 The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if gaps are allowed)
Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment
 UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
Introduction to Trees
 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow December 28, 2016 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow Clades of a rooted tree Every node v in a leaf-labelled rooted tree defines a subset of the leafset that is below
Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow December 28, 2016 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow Clades of a rooted tree Every node v in a leaf-labelled rooted tree defines a subset of the leafset that is below
Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference for Informatics and Information Technology
 Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference for Informatics and Information Technology Held at Hotel Molika, Bitola, Macedonia 11-13th April, 2014 Editors: Vangel V. Ajanovski Gjorgji Madjarov ISBN
Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference for Informatics and Information Technology Held at Hotel Molika, Bitola, Macedonia 11-13th April, 2014 Editors: Vangel V. Ajanovski Gjorgji Madjarov ISBN
Chapter 6. Multiple sequence alignment (week 10)
 Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Efficient Implementation of a Generalized Pair HMM for Comparative Gene Finding. B. Majoros M. Pertea S.L. Salzberg
 Efficient Implementation of a Generalized Pair HMM for Comparative Gene Finding B. Majoros M. Pertea S.L. Salzberg ab initio gene finder genome 1 MUMmer Whole-genome alignment (optional) ROSE Region-Of-Synteny
Efficient Implementation of a Generalized Pair HMM for Comparative Gene Finding B. Majoros M. Pertea S.L. Salzberg ab initio gene finder genome 1 MUMmer Whole-genome alignment (optional) ROSE Region-Of-Synteny
4/4/16 Comp 555 Spring
 4/4/16 Comp 555 Spring 2016 1 A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other vertex A clique graph is a graph where each connected component is a clique The concept of clustering
4/4/16 Comp 555 Spring 2016 1 A clique is a graph where every vertex is connected via an edge to every other vertex A clique graph is a graph where each connected component is a clique The concept of clustering
1. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh und G. Mitchison: Biological sequence analysis, Cambridge, 1998
 7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert, in particular last years lectures
 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 4.1 Sources for this lecture Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut
4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 4.1 Sources for this lecture Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut
Sequence Alignment. COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016
 Sequence Alignment COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016 Why do we want to compare DNA or protein sequences? Find genes similar to known genes IdenGfy important (funcgonal) sequences by finding conserved regions As
Sequence Alignment COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016 Why do we want to compare DNA or protein sequences? Find genes similar to known genes IdenGfy important (funcgonal) sequences by finding conserved regions As
Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples. Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, / 77
 Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, 2011 1 / 77 Dynamic Programming Recall: the Change Problem Other problems: Manhattan
Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, 2011 1 / 77 Dynamic Programming Recall: the Change Problem Other problems: Manhattan
Darwin-WGA. A Co-processor Provides Increased Sensitivity in Whole Genome Alignments with High Speedup
 Darwin-WGA A Co-processor Provides Increased Sensitivity in Whole Genome Alignments with High Speedup Yatish Turakhia*, Sneha D. Goenka*, Prof. Gill Bejerano, Prof. William J. Dally * Equal contribution
Darwin-WGA A Co-processor Provides Increased Sensitivity in Whole Genome Alignments with High Speedup Yatish Turakhia*, Sneha D. Goenka*, Prof. Gill Bejerano, Prof. William J. Dally * Equal contribution
Multiple Sequence Alignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW. Ulf Leser
 Multiple Sequence lignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW Ulf Leser This Lecture Multiple Sequence lignment The problem Theoretical approach: Sum-of-Pairs scores Practical approach: ClustalW Ulf Leser: Bioinformatics,
Multiple Sequence lignment Sum-of-Pairs and ClustalW Ulf Leser This Lecture Multiple Sequence lignment The problem Theoretical approach: Sum-of-Pairs scores Practical approach: ClustalW Ulf Leser: Bioinformatics,
Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description Length
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Volume 2007, Article ID 72936, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2007/72936 Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Volume 2007, Article ID 72936, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2007/72936 Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description
Pairwise Sequence Alignment. Zhongming Zhao, PhD
 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Zhongming Zhao, PhD Email: zhongming.zhao@vanderbilt.edu http://bioinfo.mc.vanderbilt.edu/ Sequence Similarity match mismatch A T T A C G C G T A C C A T A T T A T G C G A T
Pairwise Sequence Alignment Zhongming Zhao, PhD Email: zhongming.zhao@vanderbilt.edu http://bioinfo.mc.vanderbilt.edu/ Sequence Similarity match mismatch A T T A C G C G T A C C A T A T T A T G C G A T
BLAST & Genome assembly
 BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies November 17, 2012 1 Introduction Introduction 2 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 3 Genome assembly De
BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies November 17, 2012 1 Introduction Introduction 2 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 3 Genome assembly De
Multiple Sequence Alignment. Mark Whitsitt - NCSA
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
Regular Expression Constrained Sequence Alignment
 Regular Expression Constrained Sequence Alignment By Abdullah N. Arslan Department of Computer science University of Vermont Presented by Tomer Heber & Raz Nissim otivation When comparing two proteins,
Regular Expression Constrained Sequence Alignment By Abdullah N. Arslan Department of Computer science University of Vermont Presented by Tomer Heber & Raz Nissim otivation When comparing two proteins,
FastA & the chaining problem
 FastA & the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 1 Sources for this lecture: Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert,
FastA & the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 1 Sources for this lecture: Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert,
Dynamic Programming: Sequence alignment. CS 466 Saurabh Sinha
 Dynamic Programming: Sequence alignment CS 466 Saurabh Sinha DNA Sequence Comparison: First Success Story Finding sequence similarities with genes of known function is a common approach to infer a newly
Dynamic Programming: Sequence alignment CS 466 Saurabh Sinha DNA Sequence Comparison: First Success Story Finding sequence similarities with genes of known function is a common approach to infer a newly
FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:
 FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:56 4001 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem
FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:56 4001 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem
Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional. Biological Motivation
 Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional Dynamic Programming Boston University Biological Motivation Compare a new sequence with the sequences in a protein family. Proteins can be categorized into
Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional Dynamic Programming Boston University Biological Motivation Compare a new sequence with the sequences in a protein family. Proteins can be categorized into
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Fall 2013 Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) Generalize
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Fall 2013 Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) Generalize
1. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh und G. Mitchison: Biological sequence analysis, Cambridge, 1998
 7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens Gröpl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens Gröpl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
