Geometer s Sketchpad Techno Polly
|
|
|
- Lily Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geometer s Sketchpad Techno Polly Opening an Existing Sketch 1. To open an existing sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad, first click on the icon on your desktop then when the program opens click on File, Open. GSP 4.06.lnk 2. A pop-up window will appear. Follow the directions for your particular computer system to get to the file where the existing sketches are stored. Select the desired file by clicking on it, then click the Open button. TMT 3 Geometry: Engage Technology Tutorial 229
2 Polygarden Landscaping Company Equilateral Triangle with Graph Using the Compass tool and the Straightedge tool, construct a circle and its radius. Be sure the radius is attached to the point that is constructed on the side of the circle this will later allow all vertices of the triangle to act as control points to adjust the size of triangle. With the selection tool, highlight the radius and the point of intersection on the circle. Double click on the center point of the circle to mark it as a point of rotation. There will be a flash of concentric circles around the point as it is marked. From the Menu Bar use the Transform option and choose Rotate. A window will pop up with a box to enter the number of degrees of rotation desired. In this case enter 120 degrees, the number of degrees of the central angle of an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. Click the Rotate button to complete the rotation. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 230
3 After the rotation, the new radius and its point of intersection are highlighted. The center point is still marked as the point of rotation. To rotate the radius, simply use the Transform and Rotate options again. The 120 degrees should still be in the pop-up window; so to complete the rotation, click on the Rotate button. Use the Segment tool to connect the points on the circle forming the equilateral triangle. Construct a line perpendicular to one side of the triangle through the center by first highlighting the side and the center, then using the Construct and Perpendicular options from the Menu Bar. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 231
4 Construct the point of intersection between the side of the triangle and its perpendicular either by using the Point tool and clicking at the intersection when both lines turn blue OR by highlighting the side and the perpendicular and using the Construct and Intersection options from the Menu Bar. To construct the apothem, the only part of the perpendicular needed is the segment connecting the center to the side. Use the Straightedge tool to construct a segment (on top of the perpendicular line) that joins the two points. To hide the circle and the unnecessary lines, simply highlight them and use the Display and Hide Path Objects from the Menu Bar. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 232
5 To measure the length of the apothem, highlight it and use the Measure and Length options from the Menu Bar. The points will automatically be labeled, and the measurement will appear. This measurement will be highlighted, and a click in the blank white area of the screen will deselected it. To use the Measure and Perimeter options from the menu bar, the interior of the triangle must first be constructed. Highlight the vertices. Use the Construct and Triangle Interior options from the Menu Bar. Once constructed, the interior is automatically selected (This is shown by cross hatching.) allowing the Measure and Perimeter options to become available. Click on them to measure. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 233
6 Geometer s Sketchpad labels automatically. In this particular case it used point D as the original point on the circle and D and D as the rotated points. If desired, rename the points by selecting the Text tool. A little outline of a hand will appear as the curser. As the curser becomes lined up with a label, it will change. Double click on a point and a window will pop up with a box allowing for the new name to be entered. As points are changed, the label with their respective measurements will also change. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 234
7 To build a table to explore the relationship between the length of the apothem and the perimeter, highlight in order first the independent variable followed by the dependent variable. In this case, the measurement of the apothem is the independent variable and the perimeter the dependent variable. Once highlighted, use the Graph and Tabulate options from the Menu Bar. A table with each value will appear. This table can be moved anywhere on the screen that is convenient. To plot the points, again highlight the independent then the dependent variable. In this case the length of the apothem then the perimeter. Once highlighted use the Graph and Plot as (x, y) option from the Menu Bar. A coordinate grid appears behind the triangle with the point highlighted. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 235
8 To trace the point, highlight it and use the Display and Trace Plotted Point options from the Menu Bar. The point will trace on the coordinate grid as the triangle is manipulated from any one of its vertices. To add data to the table, double click in the table, adjust the size of the triangle and repeat until the number of data points desired are accumulated. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 236
9 Verify a Function Rule To use Geometer s Sketchpad to verify a function rule, in this case y = 10.39x, use the Graph and Plot New Function options from the Menu Bar. A calculator window will pop up allowing the equation to be entered. After entering the function, click the OK button. The function will graph, hopefully over the existing data, thus verifying the function rule. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 237
10 To verify using a trigonometric function, follow the same procedure, but use the calculator to enter the specific trigonometric function desired. For instance, o y = 6xtan(60 ). The function will then graph verifying the plotted data. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore/Explain 1 Technology Tutorial 238
11 Sketchpad Skills Investigation Opening a New Sketch 1. To open the Geometer s Sketchpad,click on the icon on your desktop GSP 4.06.lnk or click on Start, Programs and find the GSP icon. A new blank sketch will open up. 2. To open a new sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad, click on File, New Sketch. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 239
12 Creating Points Select the Point Tool and click in the white blank space. Notice that the last item created stays highlighted. To deselect the last item, use the Selection Tool to click anywhere in the blank white space. To label points, use the Text Tool. Notice that the curser turns into an outline of a hand. As you line up on a point, the hand fills in. Click the mouse to label the point. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 240
13 Selection Tool The selection tool allows for selection/deselection of items in two different ways. First, simply click on the item to be selected/deselected. An item that is highlighted is pink. The second way is to click and drag. An outline box will appear that will select/deselect everything it touches. Deleting To delete items, simply select them, so they are highlighted, and then hit the Delete key on the keyboard. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 241
14 Circles To construct a circle use the Compass Tool. Notice that the circle forms from the inside out. The point on the side of the circle is a control point that will allow the size of the circle to get larger and smaller by clicking and dragging. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 242
15 Lines, Rays and Segments To create lines, rays or segments, click on the Straightedge tool, then slide the cursor to the right to choose the desired tool. Each figure is formed from two points. The segment has two distinct endpoints; the ray has one endpoint and then travels off the screen, and the line has both ends traveling off the screen. Label the figures by first selecting the Text tool and either clicking on two points on the figure or by clicking on the figure between two points. Labels can be changed by double clicking on the label. A box will pop up that provides a place to edit or delete a label. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 243
16 Measuring an Angle To measure an angle, first highlight it by clicking on three points that could be used to name it, one on a side, then the vertex, and then one on the other side. Use the Measure option on the menu bar and select Angle. The measurement will appear and the program will automatically label points if they weren t labeled prior to measurement. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 244
17 Measuring a Circle To measure a circle, first highlight it by clicking on it. Use the Measure option on the menu bar and select the measurement desired. The measurement will appear, and the program will automatically label points if they weren t labeled prior to measurement. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 245
18 Triangle 1. Draw a horizontal line. If you hold the shift key before letting of the line, it will make it horizontal for you. 2. Construct a perpendicular line by first highlighting the line and one of the points, then clicking on the Construct menu. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 246
19 3. Create the third side by rotating the original line to form either a 30 or 60 degree angle. a) Mark the point of rotation by double clicking on it. There will be a quick flash of concentric circles around the point as it is marked. b) Highlight the original line and use the Transform menu with the Rotate option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 247
20 A box will pop up that allows the number of degrees of rotation to be entered. Notice that a shadow of the rotated line appears. This shadow line is a preview of where the rotated line will go. Geometer s Sketchpad has a default of 90 degrees. Change the number to a multiple of 30 to get the desired effect. Geometer s Sketchpad treats the point of rotation as the origin and rotates from the side of standard position. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 248
21 4. Construct a point of intersection where the perpendicular line meets the rotated line either by using the Point tool and placing a point or by highlighting both lines and using the Construct menu with the Intersection option. Construction Clean Up 1. To clean up a construction, it is often necessary to construct segments, arcs, etc. over the parts of the final product. Follows is an example of a triangle. 1. Use the Straightedge tool to draw segments on top of the sides of the triangle. After drawing the first one, use the Display menu to change the Line Width and Color of the segment. Subsequent segments will then be drawn with this color and thickness. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 249
22 2. To hide construction lines,create a Hide/Show button by highlighting the lines then using the Edit menu and the Action Buttons Hide/Show option. The Hide Lines button appears which works as a toggle switch between Hide and Show when clicked on. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 250
23 Reflecting To transform a figure by reflecting, first mark the line of reflection by double clicking on it. A quick flash of two sets of concentric squares will appear on the line as the marking process is taking place. Next, use the Selection tool to highlight the figure to be reflected. Use the Transform menu and the Reflect option to complete the reflection triangle tessellation by reflection TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 251
24 Explore Geometric Properties in the World Importing Pictures from the Internet 1. Position the cursor on the picture. 2. RIGHT click on your mouse and select COPY. 3. Return to your sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad. Use the Edit and Paste Picture options from the Menu bar. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 2 Technology Tutorial 252
25 Dome Floor Dilemma Sector Construction 1. Circle Construction a) Use the Compass tool to construct a circle. b) Use the Segment tool or the Construct menu to construct a radius of the circle. Connect the radius from the center to the control point on the circle. To use the Construct menu, first select the center and the point on the circle, then use Construct with the Circle By Center+Point option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 253
26 2. Rotate Radius a) To rotate the radius and its endpoint that lies on the circle, first mark the point of rotation by double clicking on the center of the circle. You will see a quick flash of concentric circles as the marking takes place, then highlight the radius and the endpoint that lies on the circle. Use the Transform menu and choose the Rotation option. b) A box will pop up that allows the desired degrees of rotation to be entered. For this construction, enter 60 o, then click on Rotate. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 254
27 3. Construct Intercepted Arc To construct the intercepted arc of the sector, select the endpoints of the radii in a counter clockwise direction. Then select the circle and use the Construct menu to construct Arc on Circle. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 255
28 4. Construct Arc Sector While the newly constructed arc is still highlighted, create the arc sector interior by using the Construct menu with the options, Arc Interior then Arc Sector. 5. Measure Area and Length a) To measure the area of the sector, highlight the sector by clicking in it, then use Measure from the menu bar with the Area option. A highlighted labeled box will appear. Be sure to un-highlight the box by clicking in any white space on the sketch. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 256
29 b) Change the label of the Area to read Arc Sector Area by first selecting the Text tool, then double clicking on the Area label and typing in the new label in the pop-up window. c) To measure the length of the radius, first highlight any radii, then use the Measure menu with the Length option. Again a labeled highlighted box will appear. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 257
30 6. Create a Table To create a table to explore the relationship between the length of the radius and the area of the sector, highlight their measures respectively. Then use Graph from the menu bar with the Tabulate option. A labeled highlighted table will pop up on the sketch. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 258
31 7. Plot Point a) To plot the point represented in the table, again highlight the measure values in the respective order: length of radius then area of sector. Use Graph from the menu bar with the Plot as (x,y) option. b) The coordinate grid appears with the highlighted point on the grid. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 259
32 c) To turn on the trace option, highlight the plotted point and use Display from the menu bar with the Trace Plotted Point option. This will allow any new points added to the table to be plotted automatically. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 260
33 The Arc Segment Construction 1. Construct Arc Segment To construct the arc segment, first select the arc by double clicking on the arc. Then use Construct from the menu bar with the Arc Interior, then Arc Segment options. 2. Change the color of the segment by using Display with the Color option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 261
34 3. Measure Arc Segment Area a) To measure the area of the arc segment, highlight it by clicking in the interior of the arc sector, then use Measure from the menu bar with the Area option. With the measurement still highlighted, you may move it to a new location on the sketch for easier viewing. Remember to click in any blank space to deselect the measurement. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 262
35 b) Change the label of the Area to read Arc Segment Area by first selecting the Text tool, then double clicking on the Area label and typing in the new label in the pop-up window. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 263
36 4. Create Table To create a table to explore the relationship between the length of the radius and the arc segment area, highlight their measures respectively. Then use Graph from the menu bar with the Tabulate option. A labeled highlighted table will pop up on the sketch. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 264
37 5. Plot and Trace Point a) To plot the point represented in the table, highlight the measure values in the respective order: length of radius, then area of the arc segment. Use Graph from the menu bar with the Plot as (x, y) option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 265
38 b) To turn on the trace option, highlight the plotted point and use Display from the menu bar with the Trace Plotted Point option. This will allow any new points added to the table to be plotted automatically. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 266
39 The Triangle Construction 1. Construct Triangle Interior To construct the triangle interior, first select the vertices of the triangle, then use Construct from the menu bar with the Construct Triangle Interior option. The color will change to the last color selected, so use Display from the menu bar with the Color option to make the triangle a different color than the arc segment. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 267
40 2. Measure Triangle Area To measure the area of the triangle, click the triangle interior (may require double clicking to keep from selecting the entire sector) and use Measure from the menu bar with the Area option. With the measurement still highlighted, you may move it to a new location for easier viewing. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 268
41 3. Create Table To create the table to explore the relationship between the length of the radius and the area of the triangle, highlight both measures respectfully. Use Graph from the menu bar with the Tabulate option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 269
42 4. Plot and Trace Point a) To plot the point in the table, highlight the measures again: length of the radius and area of the triangle. Use Graph from the menu bar with the Plot as (x, y) option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 270
43 b) To trace the plotted point, highlight the plotted point and use Display from the menu bar with the Trace Plotted Point option. This will allow any new points added to the table to be plotted automatically.. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 271
44 Dome Floor Dilemma Function Rule Verification Function Rule Verification Geometer s Sketchpad. Geometry 1. Using the existing sketch from the Dome Floor Dilemma Exploration, use Graph with the Plot New Function option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 272
45 A New Function box will pop up, allowing the function rule to be entered. Then click on the OK button. The function will then graph on the coordinate grid. If it is right, it will graph directly on top of its corresponding points, thus verifying the rule. Repeat this process for all function rules. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 273
46 Function Rule Verification TI-Interactive. 1. With your sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad still open, open TI-Interactive by pressing on the TI-Interactive icon. 2. Click on the List Icon to get the Data Editor screen. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 274
47 3. Select one of the tables from your sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad by clicking on it. Use Edit from the menu bar with the Copy option. 4. Return to the Data Editor and click on the Paste icon or use Edit from the menu bar with the Paste option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 275
48 5. Notice that the table headings also transfer. Delete the non-numerical data; and if you like, enter the point of origin in its place. 6. Highlight the data you want to graph and click the Scatter Plot icon. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 276
49 The Functions window and the Graph window will pop up with L1 and L2 listed in the Stat Plots windows and the points plotted on the Graph. 7. To enter the function for verification, click on the f(x) tab. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 277
50 8. To enter the function, press the Symbol Pallet icon. This lets the Symbol Palette pop up. Enter the function and check the box to graph the function. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 278
51 Function Rule Verification Spreadsheet 1. Copy the table from Geometer s Sketchpad by first selecting it, then use Edit from the menu bar with the Copy option. 2. Open a blank Spreadsheet and paste into the spreadsheet by using the Edit from the menu bar with the Paste option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 279
52 3. Highlight the data you want to graph, then click on the Chart Wizard icon. The Chart Wizard box will pop up on the screen. Select XY (Scatter). TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 280
53 4. Click Finish to view the graph. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 281
54 5. Select the graph, then use the Chart menu with the Add Trendline option. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 282
55 6. Since the scatterplot appears to be quadratic, select Polynomial order Click the Options tab. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 283
56 8. Check Display Equation on Chart, then click OK. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 284
57 9. Use the graphing calculator to verify that the function that was developed by the 2 πr spreadsheet is equivalent to A =. 6 Press o. Enter both functions into!. sec Press the % key. If the functions are equivalent, they will graph on top of each other and the graphing window will show what appears to be only one graph. For further verification, press ` % to examine the table values. TMT 3 Geometry: Explore Explain 3 Technology Tutorial 285
58 Geometer s Sketchpad Rose Construction TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 286
59 Opening a New Sketch To open the Geometer s Sketchpad, click on the icon on your desktop GSP 4.06.lnk or click on Start, Programs and find the GSP icon. A new blank sketch will open up. To open a new sketch in Geometer s Sketchpad, click on File, New Sketch. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 287
60 Circle Construction Construct a circle with the Compass Tool. Construct the inner circle. Angle Construction Construct a 30 o angle by rotating a point on the circle. Since there are 12 congruent spokes in the rose, we can use 30 degree rotations in our construction. Highlight the point on the circle, then double click the center of the circle to mark the angle of rotation. You will see concentric circles radiating from the center as it is marked. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 288
61 Use Transform from the menu bar with the Rotate option to rotate. Enter 30 o in the window when the box pops up and click on Rotate. Construct an angle from the center of the circle through each point on the circle. Using the Straightedge tool, select the Ray option. Click on the center of the circle to attach the endpoint, and then line up the point of the ray on top of the point on the circle. Repeat for the second ray. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 289
62 Construct the angle bisector by first selecting the three points of the angle, then using Construct from the menu bar with the Angle Bisector option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 290
63 Construct a point where the angle bisector intersects the circle, either by selecting the angle bisector and the circle, then using Construct from the menu bar with Intersection option or by using the Point tool and placing the point on the intersection (You will know you are on the intersection when both the circle and the angle bisector change color.) We can find the center of the small circle by reflecting the original circle over a line perpendicular to the angle bisector. Construct a tangent to the circle through the point of intersection of the circle and the angle bisector by first selecting the point of intersection and the angle bisector, then using Construct from the menu bar with the Perpendicular Line option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 291
64 Mark the tangent line as a line of reflection by double clicking on the line. You will see a double set of concentric boxes flash as the line is being marked. Reflect the circle across the line of reflection by selecting the circle and using Transform from the menu bar with the Reflect option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 292
65 Construct the intersection of the angle bisector and the circle, then construct a line through it and perpendicular to one side of the angle. Select the point of intersection and the ray that forms one side of the angle, then use Construct from the menu bar with the Perpendicular Line option. We use the fact that a tangent and radius that intersects it are perpendicular to construct a circle tangent to the rays. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 293
66 Construct the point of intersection with the new perpendicular line and the side of the angle. Select the points in the order shown below. Use Construct from the menu bar with the Circle By Center+Point. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 294
67 We need to construct an arc that is tangent to the rays that form the angle as well as tangent to the small circle. We will use proportional reasoning to determine the center of the circle the arc lies on. Construct the intersection of the small circle with the angle bisector by first selecting the circle and the angle bisector, then using Construct from the menu bar with the Intersections option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 295
68 To use points to set up measures to use in the proportion, label points with the Text tool according to the sketch below. To set up the proportion, measure the following distances AB, AC and AD by selecting the endpoints of the segments and using Measure from the menu bar with the Distance option. The center of circle that will be tangent to the sides of the angle and tangent to the small circle at point D will have a proportional distance from A based on the following AB AC proportion: = AD Ax which can be rewritten as AC AD A x =. AB Distances will vary per individual sketches. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 296
69 Use Measure from the menu bar with the Calculate option to compute the distance from AC AD A to the center of the new circle, A x =. AB Click on the desired measure to enter the values in the calculator, then click OK. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 297
70 Select the solution for the distance of the new center from A. Use Transform from the menu bar with the Mark Distance option. The highlighted box with the solution in it will flash as it marked. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 298
71 Select point A and use Transform from the menu bar with the Translate option. A popup box will appear that will allow you to select the following options. A new point will appear in the blank space of the sketch. In order, select point A followed by the newly translated point. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 299
72 Use Construct from the menu bar with Circle By Center+Point. This will create a large circle whose point of intersection with the angle bisector will be the center of the new circle. Construct the intersection. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 300
73 To find the radius of the circle, highlight the new point and the ray that makes the side of the angle. Then use Construct from the menu bar with the Perpendicular Line option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 301
74 Construct a point of intersection where the new perpendicular line intersects with the side of the angle, then deselect it. In order, select the new center point and the new point of intersection (see picture) and use Construct from the menu bar with the Circle By Center+Point option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 302
75 Select the new circle and the other ray that forms the angle. Use Construct from the menu bar with the Intersection option to create a point of tangency. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 303
76 Construct the arc by selecting the points in a counter clockwise order, then selecting the circle. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 304
77 Next use Construct from the menu bar with the Arc on a Circle option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 305
78 Hide all undesired parts of the construction by selecting them and using Display from the menu bar with the Hide Path Objects option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 306
79 With the Straightedge Tool, construct a segment from the original circle to point B (See sketch.) Select point A and one of the endpoints of the arc and use Construct from the menu bar with Circle By Center+Point. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 307
80 Hide the unnecessary points by first selecting them, then use Display from the menu bar with the Hide Points option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 308
81 Shrink the construction by selecting the control point on circle A and moving it toward the center. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 309
82 To rotate the construction around the circle, select the arc, small circle and segment. Double click on point A to mark the center of rotation. There will be concentric circles radiating out from point A as it is marked. Use Transform from the menu bar with the Rotate option. A pop-up window will appear that will allow 30 o to be entered in the window. Then select Rotate. Repeat the rotation until the construction is complete. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 310
83 Hide point A if desired, but leave the control point for adjusting the size of the construction. If you want, you can select the entire construction and adjust the line thickness and color using Display from the menu bar with Line Width/Thick option, then Display with the Color option. TMT3 Geometry: Elaborate Technology Tutorial 311
A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to THE GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD
 A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to the GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD v. 4.0 Dynamic Geometry in the Mathematics Classroom _/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/_/ _/_/ Dr. _/ _/ _/ _/ Distinguished Teaching Professor _/_/_/ _/_/ _/
A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to the GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD v. 4.0 Dynamic Geometry in the Mathematics Classroom _/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/_/ _/_/ Dr. _/ _/ _/ _/ Distinguished Teaching Professor _/_/_/ _/_/ _/
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
GeoGebra. 10 Lessons. maths.com. Gerrit Stols. For more info and downloads go to:
 GeoGebra in 10 Lessons For more info and downloads go to: http://school maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements Download GeoGebra from http://www.geogebra.org GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source
GeoGebra in 10 Lessons For more info and downloads go to: http://school maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements Download GeoGebra from http://www.geogebra.org GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source
For more info and downloads go to: Gerrit Stols
 For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines
 Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Math Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016
 Math 304 - Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via email by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016 As with our second GSP activity for this course, you will email the assignment at the end of this tutorial
Math 304 - Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via email by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016 As with our second GSP activity for this course, you will email the assignment at the end of this tutorial
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop
 Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
GeoGebra Workshop. (Short Version)
 GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
Study Guide - Geometry
 Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Geometry: Traditional Pathway
 GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
Geometric Constructions
 Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
G12 Centers of Triangles
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Lines That Intersect Circles
 LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
Standards to Topics. Common Core State Standards 2010 Geometry
 Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Geometry. Geometry. Domain Cluster Standard. Congruence (G CO)
 Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide,
 Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
Appendix. Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
I can identify reflections, rotations, and translations. I can graph transformations in the coordinate plane.
 Page! 1 of! 14 Attendance Problems. 1. Sketch a right angle and its angle bisector. 2. Draw three different squares with (3, 2) as one vertex. 3. Find the values of x and y if (3, 2) = (x + 1, y 3) Vocabulary
Page! 1 of! 14 Attendance Problems. 1. Sketch a right angle and its angle bisector. 2. Draw three different squares with (3, 2) as one vertex. 3. Find the values of x and y if (3, 2) = (x + 1, y 3) Vocabulary
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
Constructions Quiz Review November 29, 2017
 Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan
 Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 10/8/2003 Class: Geometry Grades: 9/10 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: This is a two part lesson designed to be given over
Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 10/8/2003 Class: Geometry Grades: 9/10 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: This is a two part lesson designed to be given over
Construction: Draw a ray with its endpoint on the left. Label this point B.
 Name: Ms. Ayinde Date: Geometry CC 1.13: Constructing Angles Objective: To copy angles and construct angle bisectors using a compass and straightedge. To construct an equilateral triangle. Copy an Angle:
Name: Ms. Ayinde Date: Geometry CC 1.13: Constructing Angles Objective: To copy angles and construct angle bisectors using a compass and straightedge. To construct an equilateral triangle. Copy an Angle:
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry
 Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards. Geometry. Table of Contents. Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8
 Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Content Skills Assessments Lessons
 Teacher: CORE GEOMETRY Year: 2012-13 Course: GEOMETRY Month: All Months S e p t e m b e r Basic Terminology draw and measure two and threedimensional investigate and analyze two and threedimensional Am
Teacher: CORE GEOMETRY Year: 2012-13 Course: GEOMETRY Month: All Months S e p t e m b e r Basic Terminology draw and measure two and threedimensional investigate and analyze two and threedimensional Am
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders
 GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workshop. Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University
 GeoGebra Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Contents Introduction... 3 What is GeoGebra?... 3 Get GeoGebra... 3 Workshop Sections... 3 Workshop Format...
GeoGebra Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Contents Introduction... 3 What is GeoGebra?... 3 Get GeoGebra... 3 Workshop Sections... 3 Workshop Format...
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
SEU /22/04 Kerry D Snyder. Exterior Angles Investigation
 Exterior Angles Investigation Name Date 1) Start Geometer s Sketchpad if it isn t already running or choose New Sketch from the File menu. A new, blank sketch window titled Untitled N appears. 2) If necessary,
Exterior Angles Investigation Name Date 1) Start Geometer s Sketchpad if it isn t already running or choose New Sketch from the File menu. A new, blank sketch window titled Untitled N appears. 2) If necessary,
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions. ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations REFLECT
 2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5
 UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview
 GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 63 G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP Conics using Locus Definitions Exploration #1 Parabola as a locus Objective: The definition of a parabola is the set of points that
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 63 G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP Conics using Locus Definitions Exploration #1 Parabola as a locus Objective: The definition of a parabola is the set of points that
PARCC Geometry Practice Test Released April,
 Non-Calculator Part 1. The figure shows with side lengths as indicated. Enter your answer in the box. 2. The figure shows two perpendicular lines s and r intersecting at point P in the interior of a trapezoid.
Non-Calculator Part 1. The figure shows with side lengths as indicated. Enter your answer in the box. 2. The figure shows two perpendicular lines s and r intersecting at point P in the interior of a trapezoid.
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
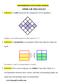 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers:
 Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles
 Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Test #1: Chapters 1, 2, 3 Test #2: Chapters 4, 7, 9 Test #3: Chapters 5, 6, 8 Test #4: Chapters 10, 11, 12
 Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Quickstart for Desktop Version
 Quickstart for Desktop Version What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematics Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Quickstart for Desktop Version What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematics Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview
 South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview In South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry, students build on the conceptual knowledge and skills they mastered in previous
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview In South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry, students build on the conceptual knowledge and skills they mastered in previous
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Ansoft HFSS Windows Screen Windows. Topics: Side Window. Go Back. Contents. Index
 Modifying Coordinates Entering Data in the Side Windows Modifying Snap To Absolute Relative Each screen in divided up into many windows. These windows can allow you to change the coordinates of the model,
Modifying Coordinates Entering Data in the Side Windows Modifying Snap To Absolute Relative Each screen in divided up into many windows. These windows can allow you to change the coordinates of the model,
GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP
 2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, flat ) or three-dimensional ( solid ).
 Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Selects an object on the screen.
 G e t t i n g Sta r t e d w i t h t h e T I - N s p i r e Key Name xclick Key (See Figures 1 and 2.) TouchPad descape Key» Scratch Pad etab Key c Home Key ~ Document Key b Menu Key Function Selects an
G e t t i n g Sta r t e d w i t h t h e T I - N s p i r e Key Name xclick Key (See Figures 1 and 2.) TouchPad descape Key» Scratch Pad etab Key c Home Key ~ Document Key b Menu Key Function Selects an
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test
 LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test Instructions. Answer each question to the best of your ability. If there is more than one answer, put both/all answers down. Try to answer each question, but if there is
LESSON 1: Trigonometry Pre-test Instructions. Answer each question to the best of your ability. If there is more than one answer, put both/all answers down. Try to answer each question, but if there is
Randy H. Shih. Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS
 Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
Geometry Arkansas 1. INTRODUCTION TO GEOMETRY 2. LINES AND ANGLES. Tutorial Outline
 Tutorial Outline Arkansas Tutorials are designed specifically for the Arkansas Standards found in the Curriculum Framework documents to prepare students for the ACT Aspire in English, reading, writing,
Tutorial Outline Arkansas Tutorials are designed specifically for the Arkansas Standards found in the Curriculum Framework documents to prepare students for the ACT Aspire in English, reading, writing,
2003/2010 ACOS MATHEMATICS CONTENT CORRELATION GEOMETRY 2003 ACOS 2010 ACOS
 CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
Unit 8 Plane Geometry
 Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses. Geometry. Course Outline
 The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
Quickstart for Web and Tablet App
 Quickstart for Web and Tablet App What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematic Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Quickstart for Web and Tablet App What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematic Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Curriculum Scope & Sequence
 BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry
 NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
YEAR AT A GLANCE Student Learning Outcomes by Marking Period
 2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
Geometry/Pre AP Geometry Common Core Standards
 1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
TUTORIAL 2. OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs.
 TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
 Tutorial Outline Florida Tutorials are designed specifically for the New Florida Standards for Math and English Language Arts and the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards (NGSSS) for science and social
Tutorial Outline Florida Tutorials are designed specifically for the New Florida Standards for Math and English Language Arts and the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards (NGSSS) for science and social
Geometry. Instructional Activities:
 GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
Activity 1. Simple Constructions. Introduction. Construction. Objective. Cabri Jr. Tools. Part I: Construct a parallelogram.
 Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Triangle Inequality Theorem
 Triangle Inequality Theorem Preparation Open a new GeoGebra file For this construction, we will not use the coordinate axes or the Algebra window. Click on the View menu on the top of the page. Select
Triangle Inequality Theorem Preparation Open a new GeoGebra file For this construction, we will not use the coordinate axes or the Algebra window. Click on the View menu on the top of the page. Select
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Geometry GEOMETRY. Congruence
 Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
High School Geometry. Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics
 High School Geometry Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics Standard 5 : Graphical Representations = ALEKS course topic that addresses
High School Geometry Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics Standard 5 : Graphical Representations = ALEKS course topic that addresses
Test Blueprint Dysart Math Geometry #2 Comp. AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE. 27.9% on Test. # on AP. # on Test. % on Test
 Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
TI- Nspire Testing Instructions
 TI- Nspire Testing Instructions Table of Contents How to Nsolve How to Check Compositions of Functions How to Verify Compositions of Functions How to Check Factoring How to Use Graphs to Backward Factor
TI- Nspire Testing Instructions Table of Contents How to Nsolve How to Check Compositions of Functions How to Verify Compositions of Functions How to Check Factoring How to Use Graphs to Backward Factor
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry Readiness Standard(s) First Six Weeks (29 ) Coordinate Geometry G.7.B use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships, including parallel
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry Readiness Standard(s) First Six Weeks (29 ) Coordinate Geometry G.7.B use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships, including parallel
Russell County Pacing Guide
 August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms:
 Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can
Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can
9 Circles CHAPTER. Chapter Outline. Chapter 9. Circles
 www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles CHAPTER 9 Circles Chapter Outline 9.1 PARTS OF CIRCLES & TANGENT LINES 9.2 PROPERTIES OF ARCS 9.3 PROPERTIES OF CHORDS 9.4 INSCRIBED ANGLES 9.5 ANGLES OF CHORDS, SECANTS,
www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles CHAPTER 9 Circles Chapter Outline 9.1 PARTS OF CIRCLES & TANGENT LINES 9.2 PROPERTIES OF ARCS 9.3 PROPERTIES OF CHORDS 9.4 INSCRIBED ANGLES 9.5 ANGLES OF CHORDS, SECANTS,
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards
 Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
An Introduction to GeoGebra
 An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
Math 460: Homework # 6. Due Monday October 2
 Math 460: Homework # 6. ue Monday October 2 1. (Use Geometer s Sketchpad.) onsider the following algorithm for constructing a triangle with three given sides, using ircle by center and radius and Segment
Math 460: Homework # 6. ue Monday October 2 1. (Use Geometer s Sketchpad.) onsider the following algorithm for constructing a triangle with three given sides, using ircle by center and radius and Segment
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
3ds Max Cottage Step 1. Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch.
 3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
GEOMETRY. Changes to the original 2010 COS is in red. If it is red and crossed out, it has been moved to another course.
 The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
Pearson Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Geometry Common Core to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics High School , Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the Mathematics High School, PARRC Model Content
A Correlation of Geometry Common Core to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics High School , Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the Mathematics High School, PARRC Model Content
