Seat Number PHYSICS SPRING EXAM 3. Name: Recitation Section Number:
|
|
|
- Lionel Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seat Number PHYSICS SPRING EXAM 3 Name: Recitation Section Number: NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED - BUT, LUCKILY, NO CALCULATORS NEEDED. SHOW YOUR WORK! Full credit will be given only if you explain how you arrived at your answer. Either show your work (especially in a calculation) or give a short explanation. Nothing elaborate is required, but the grader must be able to follow your reasoning clearly. 1. A metal bar rests on metal rails having a large Y -shaped piece, as shown. The width between the parallel rails is Pœ0.50 m. The bar is being pulled to the right with speed 3.0 m/s through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T directed down ( Œ ). At the instant when the bar is at a distance Bœ2.0 m from the endpiece of the rails, the circuit including the metal bar has resistance Vœ20 H. Determine at that instant: (a) [2 points] The magnitude of the magnetic flux through the circuit. (b) [2 points] The rate of change of the magnitude of the magnetic flux (c) [2 points] The magnitude of the induced electric current (d) [2 points] The direction of the induced electric current through the bar (e) [2 points] Suppose the magnetic field in this problem had been directed up ÐŒÑinstead of down. Which answer(s) (a)-(d), if any, would have been different, and how?
2 2. As shown in the diagram below, an electromagnetic wave of wavelength 1.0. m traveling through glass with an index of refraction of 1.40 is incident at an angle ) œ 30 at an interface with air ( 8œ1.00). Possibly useful information: cos 0 œ 1 œ sin 90 ; cos 30 œ 0.9 œ sin 60 ; cos 45 œ 0.7 œ sin 45 ; sin 30 œ 0.5 œ cos 60 ; sin 0 œ 0 œ cos 90. (a) [2 points] What is the speed of the wave in the glass? (b) [2 points] What is the frequency of this wave? (c) [2 points] At an instant when the electric field of the incident wave is directed up out of the plane Ð Ñ, what is the direction of the magnetic field of the wave at that point at that time (show it on the diagram at the point marked A)? (d) [5 points] Sketch the reflected and refracted rays and determine the angles they make with the normal to the interface at the point where the wave strikes it. (e) [2 points] What is the speed of the refracted wave? (f) [1 point] What is the frequency of the refracted wave?
3 3. An object is located on the principal axis of a convergent lens at a a distance of 6.0 cm from the lens. The focal points of the lens are on either side of the lens at a distance of 12.0 cm. (a) [5 points] Sketch a diagram of this system below, placing the object on the left side. (The principal axis is shown, together with the focal points and the vertex of the lens). Then draw three different rays that permit you to locate the image formed by the lens F v F (b) [3 points] Characterize the image (real or virtual, orientation, size relative to object). (c) [4 points] Use the lens equation to determine the image distance and magnification (including their correct signs!). (d) Check that your results in (c) agree with your characterization of the image in (b). Do they? (If not, find your error!) (e) [4 points] If the object is moved closer to the lens, will the image move to the left or right? Explain how you know this.
4 PHYSICS SPRING EXAM 3 - PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED - BUT, LUCKILY, NO CALCULATORS NEEDED. SHOW YOUR WORK! Full credit will be given only if you explain how you arrived at your answer. Either show your work (especially in a calculation) or give a short explanation. Nothing elaborate is required, but the grader must be able to follow your reasoning clearly. 1. A metal bar rests on metal rails having a large Y -shaped piece, as shown. The width between the parallel rails is Pœ0.50 m. The bar is being pulled to the right with speed 3.0 m/s through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T directed down ( Œ ). At the instant when the bar is at a distance Bœ2.0 m from the endpiece of the rails, the circuit including the metal bar has resistance Vœ20 H. Determine at that instant: (a) [2 points] The magnitude of the magnetic flux through the circuit. 2 F œfecos ) œfpbcos ) œð0.40 TÑÐ0.50 mñð2.0 mñðcos 0 Ñœ 0.40 T m. (b) [2 points] The rate of change of the magnitude of the magnetic flux The only factor in F that is changing is B, so?f Î? >œfpð? BÎ? >Ñ) œfp@ ) œð0.40 TÑÐ0.50 mñð3.0 m/sñðcos 0 Ñœ0.60 V. This can also be found by recognizing that F œ 0 at > œ 0, the time when the bar is at the far left, 2 and that >œ(2.0 m)/(3.0 m/s) œ(2/3) s at the time when F œ 0.40 T m, so that?f Î? > œ ( F F Ñ /? > œ (0.40 T m Ñ/(2/3) s œ 0.60 V. f i (c) [2 points] The magnitude of the induced electric current M œ Ð?F Î? >ÑÎV œ Ð0.60 VÑÎÐ20 HÑ œ 0.03 A. (d) [2 points] The direction of the induced electric current through the bar 2 The magnetic field is down ÐŒÑand the flux is increasing, so the induced magnetic field of the circuit must be up Ð Ñto counteract the decrease, so the current is counterclockwise, and the induced current in the bar is directed up the bar. (e) [2 points] Suppose the magnetic field in this problem had been directed up Ð Ñinstead of down. Which answer(s) (a)-(d), if any, would have been different, and how? Only (d) would have been different: the current would have been in the opposite direction.
5 2. As shown in the diagram below, an electromagnetic wave of wavelength 1.0. m traveling through glass with an index of refraction of 1.40 is incident at an angle ) œ 30 at an interface with air ( 8œ1.00). Possibly useful information: cos 0 œ 1 œ sin 90 ; cos 30 œ 0.9 œ sin 60 ; cos 45 œ 0.7 œ sin 45 ; sin 30 œ 0.5 œ cos 60 ; sin 0 œ 0 œ cos 90. (a) (b) [2 points] What is the speed of the wave in the glass? ms/ ÑÎÐ1.50Ñœ m/s. [2 points] What is the frequency of this wave? œ@Î-œÐ m/sñîð mñœ Hz. (c) [2 points] At an instant when the electric field of the incident wave is directed up out of the plane Ð Ñ, what is the direction of the magnetic field of the wave at that point at that time (show it on the diagram at the point marked A)? Using the right-hand-rule, with the electric field up Ð Ñand the direction of propagation directed up and to the right on the diagram, the magnetic field would have been directed down and to the right. (d) [5 points] Sketch the reflected and refracted rays and determine the angles they make with the normal to the interface at the point where the wave strikes it. The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence (30 ), and the angle of refraction ) 2 is found by Snell's law: 82 sin ) 2 œ 81 sin ) 1 so Ð1.00ÑÐsin ) 2Ñ œ Ð1.40 Ñ Ðsin 30 Ñ and sin ) 2 œ (1.40)(0.50) œ 0.7, corresponding to ) 2 œ 45 (e) [2 points] What is the speed of the refracted wave? The refracted ray is in air, so its speed œ -Î8 œ -Î1.00 œ - œ m/s (f) [1 point] What is the frequency of the refracted wave? It will be the same as the frequency of the incident wave, Hz.
6 3. An object is located on the principal axis of a convergent lens at a a distance of 6.0 cm from the lens. The focal points of the lens are on either side of the lens at a distance of 12.0 cm. (a) [5 points] Sketch a diagram of this system below, placing the object on the left side. (The principal axis is shown, together with the focal points and the vertex of the lens). Then draw three different rays that permit you to locate the image formed by the lens. (b) [3 points] Characterize the image (real or virtual, orientation, size relative to object). The image is virtual, erect, and about twice as large as the object. (c) [4 points] Use the lens equation to determine the image distance and magnification (including their correct signs!). Using the lens equation "Î3 "Î9 œ "Î0, recognizing that for a convergent lens 0 0, "Î3 œ "Î0 "Î9 œ "ÎÐ"# cm) "ÎÐ' cm Ñ œ Ð" #ÑÎÐ"# cm Ñ œ "ÎÐ"# cmñ so 3œ 12 cm and 7 œ 3Î9 œ Ð "# cm ÑÎÐ' cmñ œ #Þ (d) Check that your results in (c) agree with your characterization of the image in (b). Do they? (If not, find your error!) Yes, they agree. (e) [4 points] If the object is moved closer to the lens, will the image move to the left or right? Explain how you know this. From "Î3 œ "Î0 "Î9 we can see that moving the object closer makes 9 smaller and "Î9 larger, so "Î3 will become a larger negative number and 3 will become a smaller in magnitude (a smaller but still negative number). This can also be determined by changing the ray traces. What would happen to the magnification? This is harder to determine, since 7œ 3Î9 and both 3 and 9 have become smaller. But if we solve the lens equation for 3 to get 3 œ 09ÎÐ9 0Ñ then 7 œ 3Î9 œ 0ÎÐ9 0Ñ œ 0ÎÐ0 9Ñ and we can see that as 9 (which is less than 0) becomes smaller, the denominator becomes larger so 7becomes smaller.
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Geometric Optics. The Law of Reflection. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/20/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
General Physics II. Mirrors & Lenses
 General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may draw a diagram.
 1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
1 (a) (i) A ray of light passes through a length of curved optical fibre. Draw a diagram showing the fibre and the path of the ray of light. [1] Describe one use of optical fibres in medicine. You may
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Quest Chapter 30. Same hint as in #1. Consider the shapes of lenses that make them converge or diverge.
 1 Consider the light rays depicted in the figure. 1. diverging mirror 2. plane mirror 3. converging mirror 4. converging lens 5. diverging lens 6. Unable to determine. 2 Consider the light rays depicted
1 Consider the light rays depicted in the figure. 1. diverging mirror 2. plane mirror 3. converging mirror 4. converging lens 5. diverging lens 6. Unable to determine. 2 Consider the light rays depicted
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
Reflection and Refraction
 Reflection and Refraction Theory: Whenever a wave traveling in some medium encounters an interface or boundary with another medium either (or both) of the processes of (1) reflection and (2) refraction
Reflection and Refraction Theory: Whenever a wave traveling in some medium encounters an interface or boundary with another medium either (or both) of the processes of (1) reflection and (2) refraction
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 24. Geometrical Optics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Thin Lenses 4/16/2018 1
 Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics
 PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
Ch. 26: Geometrical Optics
 Sec. 6-1: The Reflection of Light Wave Fronts and Rays Ch. 6: Geometrical Optics Wave front: a surface on which E is a maximum. Figure 5-3: Plane Wave *For this wave, the wave fronts are a series of planes.
Sec. 6-1: The Reflection of Light Wave Fronts and Rays Ch. 6: Geometrical Optics Wave front: a surface on which E is a maximum. Figure 5-3: Plane Wave *For this wave, the wave fronts are a series of planes.
Self-assessment practice test questions Block 3
 elf-assessment practice test questions Block 3 1 A student is trying to measure the speed of sound in air. he stands at a distance of 50 m from a high wall. he bangs a hammer on a metal block. he hears
elf-assessment practice test questions Block 3 1 A student is trying to measure the speed of sound in air. he stands at a distance of 50 m from a high wall. he bangs a hammer on a metal block. he hears
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Topic 7. Ray (Geometrical) Optics
 Topic 7. Ray (Geometrical) Optics Reflection and Refraction Geometrical optics is that branch of optics which treats light as made up of rays that move in straight lines until they encounter an interface
Topic 7. Ray (Geometrical) Optics Reflection and Refraction Geometrical optics is that branch of optics which treats light as made up of rays that move in straight lines until they encounter an interface
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Light, Photons, and MRI
 Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) Solutions
 Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) s Problem 1 (5x2 = 10 points) Label the following statements as True or False, with a one- or two-sentence explanation for why you chose
Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) s Problem 1 (5x2 = 10 points) Label the following statements as True or False, with a one- or two-sentence explanation for why you chose
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Stevens High School AP Physics II Work for Not-school
 1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION. Wave Fronts and Rays
 Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Optics Worksheet. Chapter 12: Optics Worksheet 1
 Optics Worksheet Triangle Diagram: This represents a triangular prism. We want to follow the path of a light ray striking one of the surfaces as it passes through the prism and exits one of the other surfaces.
Optics Worksheet Triangle Diagram: This represents a triangular prism. We want to follow the path of a light ray striking one of the surfaces as it passes through the prism and exits one of the other surfaces.
Physics 11 - Waves Extra Practice Questions
 Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3*
 PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
The Lens. Refraction and The Lens. Figure 1a:
 Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors.
 Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend...
 SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
Optics INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION OF PRINCIPLES. Reflection by a Plane Mirror
 Optics INTRODUCTION Geometric optics is one of the oldest branches of physics, dealing with the laws of reflection and refraction. Reflection takes place on the surface of an object, and refraction occurs
Optics INTRODUCTION Geometric optics is one of the oldest branches of physics, dealing with the laws of reflection and refraction. Reflection takes place on the surface of an object, and refraction occurs
Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law
 Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
M = h' h = #i. n = c v
 Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
LAST REVIEW (Covers to the End of the Semester)
 Physics 2020 Suggested for final. There is no final review. LAST REVIEW (Covers to the End of the Semester) 1. A metal rod slides at a constant velocity v over frictionless rails separated by a distance
Physics 2020 Suggested for final. There is no final review. LAST REVIEW (Covers to the End of the Semester) 1. A metal rod slides at a constant velocity v over frictionless rails separated by a distance
Conceptual Practice Problems for PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1A+1B
 Conceptual Practice Problems for PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1A+1B Thu. Feb. 4, 2010, 9:30am-10:45am and 11:00am-12:15pm CP 1.01: A student runs westward at 3m/s, away from a vertical plane mirror, while
Conceptual Practice Problems for PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1A+1B Thu. Feb. 4, 2010, 9:30am-10:45am and 11:00am-12:15pm CP 1.01: A student runs westward at 3m/s, away from a vertical plane mirror, while
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
The branch of physics which studies light
 Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Solution and Grading Key PHYS1212 / PHYS1252 Quiz #1.04 Ray Diagrams
 (A) Solution and Grading Key PHYS1212 / PHYS1252 Quiz #1.04 Ray Diagrams Only the object is shown here. The image is hidden and you have to infer its location and orientation from the rays as drawn. Red
(A) Solution and Grading Key PHYS1212 / PHYS1252 Quiz #1.04 Ray Diagrams Only the object is shown here. The image is hidden and you have to infer its location and orientation from the rays as drawn. Red
Chapter 18 Ray Optics
 Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS
 PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 (a) Fig. 1.1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at X. The incident ray makes an angle of 50 with the surface of the mirror. (i) Complete Fig. 1.1 to show the normal and
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 (a) Fig. 1.1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at X. The incident ray makes an angle of 50 with the surface of the mirror. (i) Complete Fig. 1.1 to show the normal and
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics
 Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Figure 27a3See Answer T5. A convex lens used as a magnifying glass.
 F1 Figure 27a (in Answer T5) shows a diagram similar to that required, but with different dimensions. The object is between the first focus and the lens. The image is erect and virtual. The lateral magnification
F1 Figure 27a (in Answer T5) shows a diagram similar to that required, but with different dimensions. The object is between the first focus and the lens. The image is erect and virtual. The lateral magnification
Refraction and Lenses. Honors Physics
 Refraction and Lenses Honors Physics Refraction Refraction is based on the idea that LIGHT is passing through one MEDIUM into another. The question is, WHAT HAPPENS? Suppose you are running on the beach
Refraction and Lenses Honors Physics Refraction Refraction is based on the idea that LIGHT is passing through one MEDIUM into another. The question is, WHAT HAPPENS? Suppose you are running on the beach
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
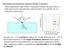 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23)
 Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
P H Y L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S
 P H Y 1 4 3 L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S Introduction Optics is the study of the way light interacts with other objects. This behavior can be extremely complicated. However, if the objects in
P H Y 1 4 3 L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S Introduction Optics is the study of the way light interacts with other objects. This behavior can be extremely complicated. However, if the objects in
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course Physics UNIT 9. Ray Optics. surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
 Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Physics 212 Spring 2009 Final Exam Version B (872413)
 Physics 212 Spring 2009 Final Exam Version B (872413) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Instructions Be sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the first page for filling in the Scantron form.
Physics 212 Spring 2009 Final Exam Version B (872413) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Instructions Be sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the first page for filling in the Scantron form.
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK:
 LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
On Fig. 7.1, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of this image.
 1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
Part Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. This Chapter. Phys. 281B Geometric Optics. Chapter 2 : Image Formation. Chapter 2: Image Formation
 Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Optics and Images. Lenses and Mirrors. Matthew W. Milligan
 Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light. Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle
 Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Light, Lenses, Mirrors
 Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
Recap: Refraction. Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium. (n 2 > n 1 ) n 2
 Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Figure 1 - Refraction
 Geometrical optics Introduction Refraction When light crosses the interface between two media having different refractive indices (e.g. between water and air) a light ray will appear to change its direction
Geometrical optics Introduction Refraction When light crosses the interface between two media having different refractive indices (e.g. between water and air) a light ray will appear to change its direction
Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. (Gauss s law for magnetism) (Faraday s law)
 Electromagnetic Waves Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. E da= B d A= Q encl ε E B d l = ( ic + ε ) encl (Gauss s law) (Gauss s law for magnetism) dφ µ (Ampere s law) dt dφ
Electromagnetic Waves Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. E da= B d A= Q encl ε E B d l = ( ic + ε ) encl (Gauss s law) (Gauss s law for magnetism) dφ µ (Ampere s law) dt dφ
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law
 Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
History of Light. 5 th Century B.C.
 History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
1. What is the law of reflection?
 Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Light and Lenses Notes
 Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
 L10-1 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law. To observe total internal reflection. To understand and use the lens equations. To find the focal length
L10-1 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law. To observe total internal reflection. To understand and use the lens equations. To find the focal length
Physics 1230 Light and Color Fall 2012 M. Goldman. Practice Exam #1 Tuesday, Sept 25, Your full name: Last First and middle.
 Physics 1230 Light and Color Fall 2012 M. Goldman Practice Exam #1 Tuesday, Sept 25, 2012 This exam will be worth 100 points. There are 10 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each and 3 problems worth
Physics 1230 Light and Color Fall 2012 M. Goldman Practice Exam #1 Tuesday, Sept 25, 2012 This exam will be worth 100 points. There are 10 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each and 3 problems worth
A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will
 Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Index of Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
 Index of Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different transparent blocks, two letter size white pages, pencil, protractor, two nails,
Index of Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different transparent blocks, two letter size white pages, pencil, protractor, two nails,
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Reflection and Refraction
 rev 05/2018 Equipment List and Refraction Qty Items Part Numbers 1 Light Source, Basic Optics OS-8517 1 Ray Optics Set OS-8516 2 White paper, sheet 1 Metric ruler 1 Protractor Introduction The purpose
rev 05/2018 Equipment List and Refraction Qty Items Part Numbers 1 Light Source, Basic Optics OS-8517 1 Ray Optics Set OS-8516 2 White paper, sheet 1 Metric ruler 1 Protractor Introduction The purpose
Refraction of Light. This bending of the ray is called refraction
 Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
EE119 Homework 3. Due Monday, February 16, 2009
 EE9 Homework 3 Professor: Jeff Bokor GSI: Julia Zaks Due Monday, February 6, 2009. In class we have discussed that the behavior of an optical system changes when immersed in a liquid. Show that the longitudinal
EE9 Homework 3 Professor: Jeff Bokor GSI: Julia Zaks Due Monday, February 6, 2009. In class we have discussed that the behavior of an optical system changes when immersed in a liquid. Show that the longitudinal
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Geometrical Optics. 1 st year physics laboratories. University of Ottawa
 Geometrical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Geometrical optics deals with light as a ray that can be bounced (reflected)
Geometrical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Geometrical optics deals with light as a ray that can be bounced (reflected)
Physics Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 - Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: SID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. ONE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 - Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: SID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. ONE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
OPTI-502 Midterm Exam John E. Greivenkamp Page 1/12 Fall, 2016
 Page 1/12 Fall, 2016 October 19, 2016 Lecture 17 Name SOLUTIONS Closed book; closed notes. Time limit: 75 minutes. An equation sheet is attached and can be removed. A spare raytrace sheet is also attached.
Page 1/12 Fall, 2016 October 19, 2016 Lecture 17 Name SOLUTIONS Closed book; closed notes. Time limit: 75 minutes. An equation sheet is attached and can be removed. A spare raytrace sheet is also attached.
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
PHYSICS 106. Assignment #10 Due by 10 pm Tuesday April 13, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D1 W 9 am [ ] D2 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am
![PHYSICS 106. Assignment #10 Due by 10 pm Tuesday April 13, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D1 W 9 am [ ] D2 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am PHYSICS 106. Assignment #10 Due by 10 pm Tuesday April 13, DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D1 W 9 am [ ] D2 W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am](/thumbs/95/123249088.jpg) PHYSICS 106 Assignment #10 Due by 10 pm Tuesday April 13, 010 NAME: DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D1 W 9 am [ ] D W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am [ ] D3 W 11 am [ ] D4 W 1 pm [ ] D5 W 1 pm (Sophie) [ ] D6 W 1 pm (Nima)
PHYSICS 106 Assignment #10 Due by 10 pm Tuesday April 13, 010 NAME: DISCUSSION SECTION: [ ] D1 W 9 am [ ] D W 10 am [ ] HS W 10 am [ ] D3 W 11 am [ ] D4 W 1 pm [ ] D5 W 1 pm (Sophie) [ ] D6 W 1 pm (Nima)
Unit 11 Light and Optics Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction
 Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
