Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) Solutions
|
|
|
- Roy Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) s Problem 1 (5x2 = 10 points) Label the following statements as True or False, with a one- or two-sentence explanation for why you chose your answer. Even if you get the answer correct, you will receive no credit unless your explanation is clear. a. In order to have total internal reflection for light, you must be in a medium that has a smaller index of refraction than the surrounding medium. b. When you walk away from a flat mirror, the size of your image does not change. c. A lens can produce an upright, magnified, real image. d. When looking at the intensity distribution for diffraction from a small single slit, projected onto a screen very far away from the slit, the width of the central bright spot is twice that of surrounding bright spots. e. To resolve two very close objects, it is helpful to use light with a small wavelength. a. False: The opposite is true according to Snell's Law. If you start in a medium with index of refraction n 1 < n 2, there is always an angle θ 2 such that n 1 sin(θ 1 ) = n 2 sin(θ 2 ). b. True: The size of the image is always equal to the size of the object for a flat mirror, since 1/p + 1/q = 1/f = 0 q = -p M = -q/p = 1 = h' / h. c. False: For a single lens, real images are only produced by converging lenses, which can only form inverted real images on the opposite side of the lens as the object. d. True: This is why the formula for diffraction minima excludes m=0. e. True: Rayleigh's criterion says that the limiting angle of resolution for a slit of width a is θ min = λ / a. The lower the wavelength, the smaller θ min, and the better we are able to see two objects separated by a very small angle.
2 Problem 2 (5+5 = 10 points) A laser beam strikes one end of a slab of material as shown in the figure below. The index of refraction of the slab is a. Determine the number of internal reflections of the beam before it emerges from the opposite end of the slab. b. Is there an incident angle ψ (instead of ) such that the beam inside leaks out of the slab (that is, the beam is not undergoing total internal reflection)? a. (Copied from the solution to P25.35 in the course textbook). As the beam enters the end of the slab, the angle of refraction is found from Snell's law: sin(θ) = (n air /n slab ) sin( ) = θ = 31.2 degrees. This is the angle of refraction of the beam just as it enters the slab. The beam then strikes the top of the slab, at an incident angle φ = = Note that this is greater than the critical angle of θ c = sin -1 (1/1.48) = , and so the beam inside the slab undergoes total internal reflection. Suppose we make a right triangle in the above picture by taking the dotted line (inside the slab) as the base, and the arrow pointing up and to the right as the hypotenuse. The distance the beam travels down the length of the slab for each reflection is 2d, where d is the base of that triangle. Then: d = h / tan(θ) = (3.10mm/2) / tan(θ) 2d = (3.10 x 10-1 cm) / tan( ) = 5.12x10-1 cm. The number of internal reflections made before reaching the opposite end of the slab is then N = (length of slab) / (2d) = (42.0cm) / (5.12x10-1 cm) = 82 reflections. b. The critical angle was found in part a to be , which means that light will leak out if the light hitting the top edge of the slab is less than This means that the angle of the refractred beam that enters the slab is greater than = Using Snell's law, we find n air sin(ψ) = n slab sin( ) sin(ψ) = 1.09 There is no solution for ψ. Therefore, there is no incoming angle for which light will leak out of the slab.
3 Problem 3 (5+5 = 10 points) Light of wavelength 590 nm passes through two narrow slits 0.60 mm apart. The screen is 1.70 m away, perpendicular to the line connecting the slits to the screen. a. How far away from the central maximum is the second-order fringe? The secondorder fringe is not the bright spot next to the central maximum, but the bright spot that is two away from the central maximum. b. A second source of unknown wavelength produces its second-order fringe 1.33 mm closer to the central maximum than the 590-nm light. What is the wavelength of the unknown light? a. dsin(θ) = d(y/l) = mλ y = (mlλ)/d = (2)(1.7)(590 x 10^-9)/(0.60 x 10^-3) meters. Therefore, y = 3.34 mm is the distance from the central maximum to the 2 nd -order fringe. b. The distance of the new light's second-order fringe is 3.34 mm 1.33 mm = 2.01 mm. y new = (mlλ new )/d λ new = (y new d)/(ml) = (2.01 x 10^-3)(0.60 x 10^-3) / [2(1.7)] meters. Thus, λ new = 355 nm. Problem 4 (6+3+3 = 12 points) A collimated laser beam (meaning the light is coming out parallel) emerging from a commerial HeNe laser has a diameter of 1.00 mm. In order to convert this beam into a well-collimated beam of diameter 10.0 mm, two convex lenses are to be used. The first lens is of focal length 1.50 cm and is to be mounted at the output of the laser. a. Draw a (neat) ray diagram to show the beam's width as it passes through the two lenses. Make sure you include the location of the focal points of the lenses. b. What is the focal length of the second lens? c. How far from the first lens should the second lens be placed?
4 a. See the following picture: b. The focal length of the second lens needs to be 15 cm. This is evident from the above picture: in the region between both lenses, the beam grows 1.0 mm in width for every 1.5cm from the focal point. c. The 2 nd lens should be placed 16.5 cm from the 1 st lens, also evident from the picture. Problem 5 (8 points) Blue light of wavelength 480 nanometers is most strongly reflected off a thin film of oil on a glass slide when viewed near normal incidence. The index of refraction of the oil is 1.2 and that of the glass is 1.6. What is the minimum thickness of the oil film (other than zero)? The following picture shows what's going on (the picture assumes the incident light has a maximum at the air-oil interface). Incident waves have two options: 1. to bounce off the oil at the air-oil interface, which comes with a phase difference of 180 degrees, or 2. to go though the oil-glass interface, bounce off the oil-glass interface (which also comes with a phase difference of 180 degrees), and then travel back through the air-oil interface. The picture shows the minimum possible thickness for the two reflected waves to add
5 together with constructive interference. It is evident from the picture the thickness should be half of the wavelength of blue light in the oil. Since λ n = λ / n for light in a material with index of refraction n, the wavelength of blue light in oil is (480nm)/1.2 = 400nm, and the thickness of the oil film is therefore 200nm. Extra Credit (2+2 = 4 points) Suppose we have light of initial intensity 2I 0, and three polarizers. The first polarizer is fixed in the +x-direction, the third polarizer is fixed in the +y-direction, and the second polarizer (in between the two) can be rotated to lie at an angle θ with respect the +x-axis toward the +y-axis. a. What is the intensity of the light passing through the entire system, as a function of θ? b. Graph the intensity of light as a function of theta, for 0 <= θ <= a. After passing through the first polarizer, the intensity of light is I 0. After passing through the second, the intensity is I 0 *cos 2 (θ). After passing through the third, the intensity is I 0 *cos 2 (θ)*cos 2 (90 0 -θ). b.
Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 2002 Session I
 Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 00 Session I Name: Last 4 digits of ID: Total Score: ) Two converging lenses, L and L, are placed on an optical bench, 6 cm apart. L has a 0 cm focal length and is placed to
Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 00 Session I Name: Last 4 digits of ID: Total Score: ) Two converging lenses, L and L, are placed on an optical bench, 6 cm apart. L has a 0 cm focal length and is placed to
Review Session 1. Dr. Flera Rizatdinova
 Review Session 1 Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the object
Review Session 1 Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the object
Physics 214 Midterm Fall 2003 Form A
 1. A ray of light is incident at the center of the flat circular surface of a hemispherical glass object as shown in the figure. The refracted ray A. emerges from the glass bent at an angle θ 2 with respect
1. A ray of light is incident at the center of the flat circular surface of a hemispherical glass object as shown in the figure. The refracted ray A. emerges from the glass bent at an angle θ 2 with respect
1. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page)
 . (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
PHYS2002 Spring 2012 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 25, 26, 27) Constants
 PHYS00 Spring 01 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 5, 6, 7) Constants m m q q p e ε = 8.85 o o p e = 1.67 = 9.11 7 9 7 31 = + 1.60 = 1.60 μ = 4π k = 8.99 g = 9.8 m/s 1 kg 19 19 C kg T m/a N m C / N m C / C 1. A convex
PHYS00 Spring 01 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 5, 6, 7) Constants m m q q p e ε = 8.85 o o p e = 1.67 = 9.11 7 9 7 31 = + 1.60 = 1.60 μ = 4π k = 8.99 g = 9.8 m/s 1 kg 19 19 C kg T m/a N m C / N m C / C 1. A convex
The liquid s index of refraction is. v liquid = nm = = 460 nm 1.38
 HMWK 5 Ch 17: P 6, 11, 30, 31, 34, 42, 50, 56, 58, 60 Ch 18: P 7, 16, 22, 27, 28, 30, 51, 52, 59, 61 Ch. 17 P17.6. Prepare: The laser beam is an electromagnetic wave that travels with the speed of light.
HMWK 5 Ch 17: P 6, 11, 30, 31, 34, 42, 50, 56, 58, 60 Ch 18: P 7, 16, 22, 27, 28, 30, 51, 52, 59, 61 Ch. 17 P17.6. Prepare: The laser beam is an electromagnetic wave that travels with the speed of light.
Physics Midterm I
 Phys121 - February 6, 2009 1 Physics 121 - Midterm I Last Name First Name Student Number Signature Tutorial T.A. (circle one): Ricky Chu Firuz Demir Maysam Emadi Alireza Jojjati Answer ALL 10 questions.
Phys121 - February 6, 2009 1 Physics 121 - Midterm I Last Name First Name Student Number Signature Tutorial T.A. (circle one): Ricky Chu Firuz Demir Maysam Emadi Alireza Jojjati Answer ALL 10 questions.
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 Young College - PHY2054C Wave Optics: 10/29/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline Young 1 2 3 Young 4 5 Assume a thin soap film rests on a flat glass surface. Young Young
Young College - PHY2054C Wave Optics: 10/29/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline Young 1 2 3 Young 4 5 Assume a thin soap film rests on a flat glass surface. Young Young
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions Page 1 of 15 Photometry Questions 1. When an upright object is placed between the focal point of a lens and a converging
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions Page 1 of 15 Photometry Questions 1. When an upright object is placed between the focal point of a lens and a converging
UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE
 58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Photometry Questions 1. When an upright object is placed between the focal point of a lens and a converging
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry Solution Manual 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Photometry Questions 1. When an upright object is placed between the focal point of a lens and a converging
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
2t = (m+ 1 /2) λ = (m+ 1 /2)(λ/n); min, m = 0, 1, 2,... n1 < n2 < n3 2t = m λ = m(λ/n); min, m = 0, 1, 2,... n1 < n2 > n3
 PHY1160C Exam #3 July 8, 1997 Possibly useful information: For reflection, θinc = θref For refraction, image equation apparent depth Young s Double Slit: n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 n = c/v M = h i = d i h o
PHY1160C Exam #3 July 8, 1997 Possibly useful information: For reflection, θinc = θref For refraction, image equation apparent depth Young s Double Slit: n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 n = c/v M = h i = d i h o
College Physics 150. Chapter 25 Interference and Diffraction
 College Physics 50 Chapter 5 Interference and Diffraction Constructive and Destructive Interference The Michelson Interferometer Thin Films Young s Double Slit Experiment Gratings Diffraction Resolution
College Physics 50 Chapter 5 Interference and Diffraction Constructive and Destructive Interference The Michelson Interferometer Thin Films Young s Double Slit Experiment Gratings Diffraction Resolution
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics hitt1 An upright object is located a distance from a convex mirror that is less than the mirror's focal length. The image formed by the mirror is (1) virtual, upright, and larger
Chapter 24 Wave Optics hitt1 An upright object is located a distance from a convex mirror that is less than the mirror's focal length. The image formed by the mirror is (1) virtual, upright, and larger
Wave Optics. April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1
 Wave Optics April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Exam tomorrow! We/Thu: Relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday, April 30, 8-10 PM Location: WH B115 (Wells Hall)
Wave Optics April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Exam tomorrow! We/Thu: Relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday, April 30, 8-10 PM Location: WH B115 (Wells Hall)
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
Young s Double Slit Experiment
 Young s Double Slit Experiment Light as a Wave? If light behaves like a wave, an experiment similar to a ripple tank using two light sources should reveal bright areas (constructive interference) and dark
Young s Double Slit Experiment Light as a Wave? If light behaves like a wave, an experiment similar to a ripple tank using two light sources should reveal bright areas (constructive interference) and dark
Textbook Reference: Physics (Wilson, Buffa, Lou): Chapter 24
 AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics
 Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Chapter 8: Physical Optics
 Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Unit 11 Light and Optics Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction
 Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch ) Diffraction (Ch )
 Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Chapter 25. Wave Optics
 Chapter 25 Wave Optics Interference Light waves interfere with each other much like mechanical waves do All interference associated with light waves arises when the electromagnetic fields that constitute
Chapter 25 Wave Optics Interference Light waves interfere with each other much like mechanical waves do All interference associated with light waves arises when the electromagnetic fields that constitute
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Single slit diffraction
 Single slit diffraction Book page 364-367 Review double slit Core Assume paths of the two rays are parallel This is a good assumption if D >>> d PD = R 2 R 1 = dsin θ since sin θ = PD d Constructive interference
Single slit diffraction Book page 364-367 Review double slit Core Assume paths of the two rays are parallel This is a good assumption if D >>> d PD = R 2 R 1 = dsin θ since sin θ = PD d Constructive interference
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
PHYSICS 106 TEST #3 May 5, 2010
 NAME: PHYSICS 106 TEST #3 May 5, 010 ID NUMBER: LECTURE SECTION: [ ] A1 (8 am) [ ] B1/HP ( pm) [ ] C1 (6 pm) INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not turn over this cover sheet until instructed to do so.. No talking is
NAME: PHYSICS 106 TEST #3 May 5, 010 ID NUMBER: LECTURE SECTION: [ ] A1 (8 am) [ ] B1/HP ( pm) [ ] C1 (6 pm) INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not turn over this cover sheet until instructed to do so.. No talking is
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 13 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away,
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 13 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away,
Diffraction Challenge Problem Solutions
 Diffraction Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Measuring the Wavelength of Laser Light Suppose you shine a red laser through a pair of narrow slits (a = 40 μm) separated by a known distance and allow
Diffraction Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Measuring the Wavelength of Laser Light Suppose you shine a red laser through a pair of narrow slits (a = 40 μm) separated by a known distance and allow
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law
 Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Physics 202 Homework 9
 Physics 202 Homework 9 May 29, 2013 1. A sheet that is made of plastic (n = 1.60) covers one slit of a double slit 488 nm (see Figure 1). When the double slit is illuminated by monochromatic light (wavelength
Physics 202 Homework 9 May 29, 2013 1. A sheet that is made of plastic (n = 1.60) covers one slit of a double slit 488 nm (see Figure 1). When the double slit is illuminated by monochromatic light (wavelength
Assignment 10 Solutions Due May 1, start of class. Physics 122, sections and 8101 Laura Lising
 Physics 122, sections 502-4 and 8101 Laura Lising Assignment 10 Solutions Due May 1, start of class 1) Revisiting the last question from the problem set before. Suppose you have a flashlight or a laser
Physics 122, sections 502-4 and 8101 Laura Lising Assignment 10 Solutions Due May 1, start of class 1) Revisiting the last question from the problem set before. Suppose you have a flashlight or a laser
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 27 Chapter 33 sec. 7-8 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Clicker Question Bright light of wavelength 585 nm is incident perpendicularly on a soap film (n =
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 27 Chapter 33 sec. 7-8 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Clicker Question Bright light of wavelength 585 nm is incident perpendicularly on a soap film (n =
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
The location of the bright fringes can be found using the following equation.
 What You Need to Know: In the past two labs we ve been thinking of light as a particle that reflects off of a surface or refracts into a medium. Now we are going to talk about light as a wave. If you take
What You Need to Know: In the past two labs we ve been thinking of light as a particle that reflects off of a surface or refracts into a medium. Now we are going to talk about light as a wave. If you take
About the Final Exam(1)
 About the Final Exam(1) The exam will be on 7:45-9:45am, Wednesday, Dec 22 in: 2103 Chamberlin, and 810 Ingraham (Allocation to be announced) It will be exactly 120 minutes. Distribution of tests starts
About the Final Exam(1) The exam will be on 7:45-9:45am, Wednesday, Dec 22 in: 2103 Chamberlin, and 810 Ingraham (Allocation to be announced) It will be exactly 120 minutes. Distribution of tests starts
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems
 Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
Lecture 4 Recap of PHYS110-1 lecture Physical Optics - 4 lectures EM spectrum and colour Light sources Interference and diffraction Polarization
 Lecture 4 Recap of PHYS110-1 lecture Physical Optics - 4 lectures EM spectrum and colour Light sources Interference and diffraction Polarization Lens Aberrations - 3 lectures Spherical aberrations Coma,
Lecture 4 Recap of PHYS110-1 lecture Physical Optics - 4 lectures EM spectrum and colour Light sources Interference and diffraction Polarization Lens Aberrations - 3 lectures Spherical aberrations Coma,
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Thin Lenses 4/16/2018 1
 Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version
 Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light
 AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Diffraction. Factors that affect Diffraction
 Diffraction What is one common property the four images share? Diffraction: Factors that affect Diffraction TELJR Publications 2017 1 Young s Experiment AIM: Does light have properties of a particle? Or
Diffraction What is one common property the four images share? Diffraction: Factors that affect Diffraction TELJR Publications 2017 1 Young s Experiment AIM: Does light have properties of a particle? Or
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
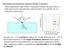 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
About the Final Exam(1)
 About the Final Exam(1) The exam will be on 2:45-4:45pm, Wednesday, Dec 19 th (See my earlier email for room allocation) It will be exactly 120 minutes. Four (3+1) 8½ x 11 formula sheets are allowed. Must
About the Final Exam(1) The exam will be on 2:45-4:45pm, Wednesday, Dec 19 th (See my earlier email for room allocation) It will be exactly 120 minutes. Four (3+1) 8½ x 11 formula sheets are allowed. Must
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3*
 PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Wave Optics. April 9, 2014 Chapter 34 1
 Wave Optics April 9, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Remainder of this week: Wave Optics! Next week: Last of biweekly exams, then relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday,
Wave Optics April 9, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Remainder of this week: Wave Optics! Next week: Last of biweekly exams, then relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday,
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Interference of Light
 Interference of Light Review: Principle of Superposition When two or more waves interact they interfere. Wave interference is governed by the principle of superposition. The superposition principle says
Interference of Light Review: Principle of Superposition When two or more waves interact they interfere. Wave interference is governed by the principle of superposition. The superposition principle says
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics
 Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser
 Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser WARNING NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT LASER LIGHT Index of Refraction: Snell's Law 1. Read the section on physical optics in some introductory physics text. 2. Set the semicircular
Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser WARNING NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT LASER LIGHT Index of Refraction: Snell's Law 1. Read the section on physical optics in some introductory physics text. 2. Set the semicircular
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
22.4. (a) (b) (c) (d)
 mλl 22.2. Because ym = increasing λ and L increases the fringe spacing. Increasing d decreases the fringe d spacing. Submerging the experiment in water decreases λ and decreases the fringe spacing. So
mλl 22.2. Because ym = increasing λ and L increases the fringe spacing. Increasing d decreases the fringe d spacing. Submerging the experiment in water decreases λ and decreases the fringe spacing. So
Solution to PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1B
 n observer O, facing a mirror, observes a light urce S. Where does O perceive the mirror age of S to be located? Physics 1112. 1. 2. 3. 4 Solution to PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1B Thu. Feb. 5, 2009, 2:00pm-3:15pm
n observer O, facing a mirror, observes a light urce S. Where does O perceive the mirror age of S to be located? Physics 1112. 1. 2. 3. 4 Solution to PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1B Thu. Feb. 5, 2009, 2:00pm-3:15pm
Interference. Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location.
 Interference Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location. Thus, interacting electromagnetic waves also add together.
Interference Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location. Thus, interacting electromagnetic waves also add together.
UNIT 102-9: INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION
 Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section Group # UNIT 102-9: INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION Patterns created by interference of light in a thin film. OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the creation of double-slit
Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section Group # UNIT 102-9: INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION Patterns created by interference of light in a thin film. OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the creation of double-slit
LIGHT & OPTICS. Fundamentals of Physics 2112 Chapter 34 1
 LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
Recap: Refraction. Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium. (n 2 > n 1 ) n 2
 Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
1. What is the law of reflection?
 Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Chapter 37. Interference of Light Waves
 Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION
 CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION INTERFERENCE CONSTRUCTIVE DESTRUCTIVE YOUNG S EXPERIMENT THIN FILMS NEWTON S RINGS DIFFRACTION SINGLE SLIT MULTIPLE SLITS RESOLVING POWER 1 IN PHASE 180 0 OUT OF
CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION INTERFERENCE CONSTRUCTIVE DESTRUCTIVE YOUNG S EXPERIMENT THIN FILMS NEWTON S RINGS DIFFRACTION SINGLE SLIT MULTIPLE SLITS RESOLVING POWER 1 IN PHASE 180 0 OUT OF
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light. Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle
 Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES
 Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
Stevens High School AP Physics II Work for Not-school
 1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
Physics 123 Optics Review
 Physics 123 Optics Review I. Definitions & Facts concave converging convex diverging real image virtual image real object virtual object upright inverted dispersion nearsighted, farsighted near point,
Physics 123 Optics Review I. Definitions & Facts concave converging convex diverging real image virtual image real object virtual object upright inverted dispersion nearsighted, farsighted near point,
Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics
 Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics Physical Optics Phase Difference & Coherence Thin Film Interference 2-Slit Interference Single Slit Interference Diffraction Patterns Diffraction Grating Diffraction & Resolution
Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics Physical Optics Phase Difference & Coherence Thin Film Interference 2-Slit Interference Single Slit Interference Diffraction Patterns Diffraction Grating Diffraction & Resolution
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
EM Waves Practice Problems
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first physicists to study light. What properties of light did he explain by using the particle model? 2. Who was the first person who was credited
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first physicists to study light. What properties of light did he explain by using the particle model? 2. Who was the first person who was credited
Light and Lenses Notes
 Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Phys 104: College Physics EXAM 3
 Phys 14: College Physics Key Name I. VERY SHORT ANSWER: EXAM 3 FRIDAY, APRIL 16, 21 1) 3 A cat plays with a butterfly at dawn and looks directly up at light from the sun rising in the east that has been
Phys 14: College Physics Key Name I. VERY SHORT ANSWER: EXAM 3 FRIDAY, APRIL 16, 21 1) 3 A cat plays with a butterfly at dawn and looks directly up at light from the sun rising in the east that has been
Chapter 18 Ray Optics
 Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Optics Final Exam Name
 Instructions: Place your name on all of the pages. Do all of your work in this booklet. Do not tear off any sheets. Show all of your steps in the problems for full credit. Be clear and neat in your work.
Instructions: Place your name on all of the pages. Do all of your work in this booklet. Do not tear off any sheets. Show all of your steps in the problems for full credit. Be clear and neat in your work.
Experiment 1: Diffraction from a Single Slit
 012-05880D Slit Accessory Experiment 1: Diffraction from a Single Slit Purpose Theory EQUIPMENT REQUIRED track and from the Basic Optics System (OS-8515) Diode Laser (OS-8525) Single Slit Disk (OS-8523)
012-05880D Slit Accessory Experiment 1: Diffraction from a Single Slit Purpose Theory EQUIPMENT REQUIRED track and from the Basic Optics System (OS-8515) Diode Laser (OS-8525) Single Slit Disk (OS-8523)
Interference Effects. 6.2 Interference. Coherence. Coherence. Interference. Interference
 Effects 6.2 Two-Slit Thin film is a general property of waves. A condition for is that the wave source is coherent. between two waves gives characteristic patterns due to constructive and destructive.
Effects 6.2 Two-Slit Thin film is a general property of waves. A condition for is that the wave source is coherent. between two waves gives characteristic patterns due to constructive and destructive.
22.1. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.1. Solve: (a)
 22.. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.. Solve: (a) (b) The initial light pattern is a double-slit interference pattern. It is centered behind the midpoint of the slits. The slight decrease in intensity
22.. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.. Solve: (a) (b) The initial light pattern is a double-slit interference pattern. It is centered behind the midpoint of the slits. The slight decrease in intensity
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
PHYSICS. Chapter 34 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
25-1 Interference from Two Sources
 25-1 Interference from Two Sources In this chapter, our focus will be on the wave behavior of light, and on how two or more light waves interfere. However, the same concepts apply to sound waves, and other
25-1 Interference from Two Sources In this chapter, our focus will be on the wave behavior of light, and on how two or more light waves interfere. However, the same concepts apply to sound waves, and other
Lab 7 Interference and diffraction
 Prep this lab, as usual. You may paste this entire lab into your notebook, including the data tables. All this should be completed prior to the start of lab on Wednesday, and I will score your completed
Prep this lab, as usual. You may paste this entire lab into your notebook, including the data tables. All this should be completed prior to the start of lab on Wednesday, and I will score your completed
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Version 001 Interference jean (AP Phy MHS 2012) 1
 Version 001 Interference jean AP Phy MHS 01) 1 This print-out should have 11 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. sound m Concept
Version 001 Interference jean AP Phy MHS 01) 1 This print-out should have 11 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. sound m Concept
Physics 2c Lecture 25. Chapter 37 Interference & Diffraction
 Physics 2c Lecture 25 Chapter 37 Interference & Diffraction Outlook for rest of quarter Today: finish chapter 37 Tomorrow & Friday: E&M waves (Chapter 34) Next Monday, June 4 th : Quiz 8 on Chapter 37
Physics 2c Lecture 25 Chapter 37 Interference & Diffraction Outlook for rest of quarter Today: finish chapter 37 Tomorrow & Friday: E&M waves (Chapter 34) Next Monday, June 4 th : Quiz 8 on Chapter 37
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
What is light? This question sparked a huge debate in physics.
 Optics Sol PH. 11 What is light? This question sparked a huge debate in physics. Light is a Stream of Particles. Newton called corpuscles Colors travel at different speeds. Einstein called quanti Light
Optics Sol PH. 11 What is light? This question sparked a huge debate in physics. Light is a Stream of Particles. Newton called corpuscles Colors travel at different speeds. Einstein called quanti Light
Interference and Diffraction of Light
 Name Date Time to Complete h m Partner Course/ Section / Grade Interference and Diffraction of Light Reflection by mirrors and refraction by prisms and lenses can be analyzed using the simple ray model
Name Date Time to Complete h m Partner Course/ Section / Grade Interference and Diffraction of Light Reflection by mirrors and refraction by prisms and lenses can be analyzed using the simple ray model
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
