3-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY. 1. Find the distance between the planes, 2x + 3y +4z =4 and 4x +6y +8z =12
|
|
|
- Christina Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 1 Find the distance between the planes, 2x + 3y +4z 4 and 4x +6y +8z 12 Ans Find the length of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane 2x- 3y+6z+21 0 Ans 3 7 unit 3 Find the shortest distance of the plane 3x-4y+12z 3 from the origin Ans 3 13 unit 4 Write the intercept cut-off by plane 2x+y-z5on x-axis Ans5/2 5 Write the distance of following plane from origin, 2x-y+2z +10 Ans 1 3 unit 6 Find the value ofk, so taht the line x 2 plane 3x y-2z 7 Ans -2 y 1 6 k z+5 4 is perpendicular to the 7Write down the distance of a point P(a, b, c)fromx-axis Ans b 2 + c 2
2 8 If the Cartesian equation of a line is 3 x equation for the line y+4 2z , then write the vector Ansr (3i 4j + 3k) + ( 5i + 7j + 3k) 9 Write the equation of the straight line through the point (α, β,γ) and parallel to Z-axis Ans (αi+βj+ γk) + k 10 Find the direction cosines of the line 4 x 2 y 6 1 z 3 Ans (-2/7, 6/7, -3/7) 11 If a unit vector â makes angles π with î, π 3 4 then find the value of θ Ans π/3 with ĵ and an acute angle θ with k, 12 Find the Cartesian equation of the line which passes through the point( 2,4, 5) and is parallel to the line x+3 4 y z Ans x+2 3 y 4 5 z What are the direction cosines of a line which makes equal angles with the coordinate axes? Ans(± 1 3, ± 1 3, ± 1 3 ) 14 Write the vector equation of the line given by x 5 3 y+4 7 z 6 2 Ansr (5i 4j + 6k) + (3i + 7j + 2k) 15 Equation of a line is 4 x to the above line Ans (-2/3, 2/3, 1/3) y+3 z Find the direction cosines of a line parallel
3 16 If the equations of line AB is 3 x the line parallel to above line AB Ans (-1,-2,4) y+2 z Find the distance of a point(2, 3, 4) from X-axis Ans 5 18 Write the equations of a line parallel to the line x 2 through point (1, 2, 3) Ans x 1 z 3 y , then write the direction ratios of y+3 z Write the direction cosines of a line parallel to the line 3 x Ans (-3/7, -2/7, 6/7) 20 The equation of a line is 2x 5 parallel to this line Ans (2/7, 3/7, -6/7) 4 y+4 6 z 3 6 and passing y+2 z Find the direction cosines of the line 4 Marks Questions 21 A plane makes intercepts -6, 3, 4 respectively on the coordinate axes Find the length of the perpendicular from the origin on it Ans units 22Find the distance of the point( 1, 5, 10)from the point of intersection of the line r2i - i +2k +λ(i + 4j + 2k )and the plane r (i j + 2k ) 5 Ans 13 units 23Show that the lines 5 x y 7 z andx 8 2y z 5 are coplanar 3
4 24Find the image of the point having position vectori + 3j + 4k in the plane r (2i j + k ) Ans(-3,5,2) 25Find the vector equation of the plane through the points(2,1, 1)and( 1,3,4) and perpendicular to the plane x 2y+4z10 Ansr (18i+17j+4k) 49 26Find the coordinates of the point,where the line x 2 y+1 z intersects the planex y + z 5 0Also,find the angle between the line and the plane Ans (2, -1, 2 ), sin Find the vector equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planesr(i + 2j + 3k ) 4 0 and r (2i + j k ) and which is perpendicular to the plane r (5i + 3j 6k ) Ans33x+45y+50z Find the equation of plane(s) passing through the intersection of the planes x + 3y and 3x y 4z 0 and whose perpendicular distance from origin is unity Ans 2x+y-2z+30 and x-2y-2z Find the equation of the plane passing through the point A(1,2,1) and perpendicular to the line joining points P(1,4,2) and Q(2,3,5)Also,find the distance of this plane from the line x+3 y 5 z Ans 11 units
5 30 Find the cartesian equation of the plane passing through the origin and (3, 1,2) and is parallel to the line x 4 y+3 z Ans x-19y-11z0 31Find the equation of plane that contains the point(1, 1,2) and is perpendicular to each of planes2x + 3y 2z 5 andx + 2y 3z 8 Ans 5x-4y-z Fnd the coordinates of point, where the line x+1 planex + y + 4z 6 Ans(1,1,1) y+2 z meets the 33Show that the lines r (î + ĵ k ) + λ(3î j ) andr (4î k ) + μ (2î + 3k ) intersect Also, find their point of intersection Ans (4, 0, -1) 34Find the direction cosines of a line x+2 Also, find the vector 2y 7 5 z equation of the line through the point A( 1, 2, 3) and parallel to the given line Ans (2/7, 3/7, -6/7), x+1 2 y 4 z Find the angle between the linesr 2î 5ĵ + k + λ(3î + 2ĵ + 6k ) and r 7i 6ĵ 6k + μ(î + 2ĵ + 2k ) Anscos Show that the lines x+1 their point of intersection Ans (1/2, -1/2, -3/2) y+3 z andx 2 1 y 4 3 z 6 5 intersect Also, find
6 37 Find the distance of a point (2,4-1) from the line x+5 1 y+3 z Ans 7 units 38 Show that the lines r (î + ĵ k ) + λ(3î j ) and r (4î k ) + μ (2î + 3k ) intersect Also, find their point of intersection Ans (4, 0, -1) 39Find the direction cosines of a line x+2 Also, find the vector 2y 7 5 z equation of the line through the point A( 1, 2, 3) and parallel to the given line Ans (2/7, 3/7, -6/7) and x+1 2 y 4 z Find the angle between the linesr 2î 5ĵ + k + λ(3î + 2ĵ + 6k ) and r 7i 6ĵ 6k + μ(î + 2ĵ + 2k ) 1 19 Anscos Show that the lines x+1 their point of intersection Ans (1/2, -1/2, -3/2) y+3 z andx 2 1 y 4 3 z 6 5 intersect Also, find 42 Find the value of p, so that the linesl 1 : 1 x y 5 6 z 1 5 7y 14 3 p z 3 2 and l 2 : 7 7x 3p are perpendicular to each other Also, find theequation of a line passing through a point(3,2, -4) and parallel to line l 1 Ans 3 x 3 y 2 z A line passes through the point (2, -1, 3) and is perpendicular to the linesr (i + j - k ) + x (2i - 2j + k )equation in vector and Cartesian forms Ans 2 x 6 y 1 z 3 3 6
7 44 Find the shortest distance between the lineswhosevector equations are r i + j +x(2i -j + k )and r 2i + j - k + µ(3i - 5j + 2k) Ans 10/ 59 units 45 Find the shortest distance between the twolines whose vector equations are r (i + 2j + 3k ) + x(i - 3j + 2k ) andr (4i + 5j + k ) 9 Ans unit Find the shortest distance between the following lines: x+1 y 5 z Ans y+1 z+1, x Find the distance between the lines l 1 and l 2 given by l 1 : r i + 2j 4k + x(2i + 3j + 6k ),l 2 :r 3i + 3j 5k + µ(4i + 6j + 12k ) Ans 48 Find the vector and Cartesian equations of the line passing through the point (2, 1, 3) and perpendicular to the lines x 1 y 2 z 3 and x y z Ansr 2i + j + 3k + (2i + 7j + 6k) 49 The Cartesian equation of a line is 6x 2 3y + 1 2z -2 Find the direction cosines of the line Write down the Cartesian and vector equations of a line passing through (2, -1, -1) which are parallel to the given line Ansr (2i j k) + ( 1 6 i j k) 50 Find the shortest distance between the two lines whose vector equations are r (6i + 2j ) + x(i 2j + 2k ) andr (-4i k) + µ(3i 2j + 2k ) Ans 9 units 51 Show that the lines r 3i + 2j 4k + x(i + 2j + 2k ); r 5i 2j + µ(3i + 2j + 6k )are intersecting Hence, find their point of intersection
8 Ans (-1, -6, -12) 52 Find the vector and Cartesian equations of line passing through point (1, 2, -4) and perpendicular to two lines x 8 y+19 z Ans r (i+2j-4k)+ (2i+3j+6k) and x 15 3 y 29 8 z Find the angle between following pair of lines x+2 z 5 4 Ans π/2 and check whether the lines are parallel or perpendicular 2 y 1 z+3 x+2 and 2y Find the shortest distance between lines whose vector equations are r (1 t)i + (t 2)j + (3 2t)k and r (s + 1)i + (2s 1)j - (2s + 1)k Ans 8 29 units Find shortest distance between the lines r (i + 2j + k ) + x(i j + k ) and r (2i j k ) + µ(2i + j + 2k ) Ans units 56Find the equation of the perpendicular from point (3, 1,11) to line x 2 y 2 z 3 Also find the coordinates of foot of perpendicular and the length of 4 perpendicular Ans 53 units 57Find the perpendicular distance of point (1,0,0) from the lines x 1 z+10 8 Also, find the coordinates of foot of perpendicular and equation of perpendicular Ans 53 units,(3,4, -2) and x 1 2 y 4 z 2 y
9 58 Find the points on the line x+2 point P(1,3,3) Ans (-2, -1, 3) and (4,3,7) y+1 z Find the shortest distance between the lines l 1 : x 1 z 1 2 Ans 3/ 2 units at a distance of 5 units from the y z 1 1 l 2: x 2 2 y Find the shortest distance between lines r (1 + 2λ)i + (1 λ)j + λk 2i j k ) + μ(2i + j + 2k ) r Ans 3/ 29units 61 Find the value of λ, so that following lines are perpendicular to each other x+5 2 y 1 z and x 2y+1 1 z 5λ λ 3 Ans 1 62 Find the value of λ so that lines 1 x perpendicular to each other Ans -2 63Find the value of λ so that lines 1 x perpendicular to each other Ans 7 y 2 3 2λ 7y λ z 3 2 5z and x+1 3λ and 7 7x 3λ y z 7 are y z 5 are 64Find the length and foot of perpendicular drawn from the point (2, 1,5) to line x 11 y+2 z Ans 14units, (1,2,3)
10 6MARKS QUESTIONS 65Find the equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the plane r (i + j + k ) 1 and r (2i + 3j k) and parallel to X-axis Ansr (i -3k) Find the distance between the point(7,2,4)and the plane determined by the points A(2,5, 3), B( 2, 3,5) and C(5,3, 3) Ans 29 units 67Find the equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planesx + y + z 1and2x + 3y + 4z 5,which is perpendicular to the planex y + z 0Also,find the distance of the plane obtained above, from the origin Ans x z+ 20, distance 2 units 68Find the distance of the point(2,12,5)from the point of intersection of the liner 2i 4j + 2k + λ(3i + 4j + 2k ) and the planer (i 2j + k ) 0 Ans 13 units 69Find the equation of the plane that contains the point(1, 1,2) and is perpendicular to both the planes 2x + 3y 2z 5 and x + 2y 3z 8Hence, find the distance of point P( 2,5,5)from the plane obtained above Ans 42 units 70Show that the linesr (i + j k ) + λ(3i j ) and r (4i k ) + μ(2i + 3k ) are coplanar Also, find the equation of the plane containing them Ans 3x+9y-2z14
11 71Find the distance of the point(1, 2,3)from the plane x y + z 5 measured parallel to the line x 1 y 3 z Ans units 72Find the equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes r (i + 3j ) 6 0andr (3i j 4k 0,whose perpendicular distance from origin is unity Ansr (-2i+4j+4k) Find the vector equation of the line passing through the point(1,2,3) and parallel to the planesr (i j + 2k ) 5 and r (3i + j + k ) 6 Ansr (i + 2j + 3k) + ( 3i + 5j + 4k) 74Find the coordinates of the point, where the line through(3 4, 5) and (2, 3,1) crosses the plane, passing the points (2,2,1), (3,0,1) and (4, 1,0) Ans (1,-2,7) 75 Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the three points with position vectorsi + j 2k, 2i j + k and i + 2j + k Also,find the coordinates of the point of intersection of this plane and the line r 3i j k + λ(2i 2j + k ) Ansr i + j 2k 76Find the equation of the plane determined by pointsa(3, 1,2), B(5,2,4) and C( 1, 1,6)and hence find the distance between plane and point(6,5,9)
12 Ans 6 34 units 77Find the length and foot of perpendicular from the pointp(7,14,5)to plane 2x + 4y z 2Also,find the image of the point P in the plane Ans 189 unitsand(-5,-10,11) 78Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of planes r (i + 2j + 3k ) 4 0, r (2i + j k ) and which is perpendicular to plane r (5i + 3j 6k )8 0 Ansr, (33i + 45j + 50k) 41 79Find the equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of planes 2x + y z 3and5x 3y + 4z and parallel to line x 1 y 3 z Ans 7x+9y-10z Find the equation of plane passing through the point( 1,3,2) and perpendicular to each of the planesx + 2y + 3z 5 and 3x + 3y + z 5 Ans7x-8y+3z Find the vector equation of plane passing through the pointsa(2,2, 1), B(3,4,2) and C(7,0,6)Also,find the Cartesian equation of plane Ansr (5i + 2j 3k) 17 82Find the equation of the plane passing through point(1,1, 1) and perpendicular to planes x + 2y + 3z 7 0 and 2x 3y 4z 0 Ans7x+2y-7z-260
13 83 Find the vector and cartesian equation of a plane containing the two linesr (2i + j 3k ) + λ (i + 2j + 5k ) and r (3i + 3j + 2k ) + μ(3i 2j + 5k ) Also,show that r (2i + 5j + 2k ) + P(3i 2j + 5k ) lies in the plane Ansr (10i + 5j 4k) 37 and 10x + 5y 4z 37 84Find the equation of the plane passing through the point(1,2,1) and perpendicular to line joining points(1,4,2) and (2,3,5)Also,find the coordinates of foot of the perpendicular and the perpendicular distance of the point(4,0,3) from above found plane Ans x-y+3z-20, (3,1,0), Distance 11 units 85Find the equation of the plane passing through point P(1,1,1) and containing the liner ( 3i + j + 5k ) + λ(3i j 5k )Also,show that plane contains the liner + ( i + 2j + 5k ) + μ(i 2j 5k ) Ansr (i 2j + k) 0 86Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular, distance of pointp(3,2,1) from the plane 2x y + z + 1 0Also,find image of the point in the plane Ans(1,3,0) Distance 6 units Image Point (-1,4,1) 87Find the distance of the point(2,3,4)from the line x+3 3 y 2 parallel to the parallel to the plane3x + 2y + 2z 5 0 Ans 33 units 6 z 2 measured
14 88Find the distance of point( 2,3, 4)from the line x+2 parallel to the plane4x + 12y 3z Ans 17/2 units 2y z+4 5 measured 89Find the coordinates of image of point (1, 3, 4) in the plane 2x y + z Ans(-3,5,2) 90 From the point (1, 2, 4), a perpendicular is drawn on the plane 2x + y 2z Find the equation, the length and the coordinates of foot of perpendicular Ans x 1 2 y 2 1 z 4 2, 1/3 unit and(11/9, 19/9, 34/9) 91Find the equation of plane passing through the point ( 1, 1, 2) and perpendicular to each plane 2x + 3y 3z 2and 5x 4y + z 6 Ans 9x+17y+23z Find the equations of plane passing through points (3, 4, 1) and (0, 1, 0) and parallel to line x+3 y 3 z Ans 8x-13y+15z Find the distance of the point P( 1, 5, 10) from the point of intersection of the line joining the points A(2, 1,2) and B(5,3,4) with the plane x y + z 5 Ans 13 units 94 Find the vector and Cartesian forms of the equation of the plane passing through the point (1,2, 4)and parallel to the lines r i + 2j 4k + λ(2i + 3j + 6k )and r i 3j + 5k + μ(i + j k )Also, fnd the distance of the point (9, 8, 10) from the plane thus obtained
15 Ans 146units 95 Find the equation of line passing through points A(0,6, 9) and B( 3, 6,3) If D is the foot of perpendicular drawn from the point C(7,4, 1) on the line AB, then find the coordinates of point D and equation of line CD Ansline x 7 y 4 z Find the image of the point (1,6,3) on the line x 1 y 1 z Also, Write the equation of the line joining the given points and its image and find The length of segment joining given point and its image Ans 52 units 97 Write the vector equations of following lines and hence find the distance between them x 1 y 2 z+4, x 3 y 3 z Ans The points A(4,5,10), B(2,3,4) and C(1,2, 1) are the three vertices of parallelogram ABCD Find the vector equations of sides AB and BC and also find the coordinates of point D Ansr (4i+5j+10k) - (2i+2j+6k) and r (2i+3j+4k) -µ(i+j+5k) 99 Find the coordinates of foot of perpendicular drawn from the point (0,2,3) on the line x+3 y 1 z+4 Also, find the length of perpendicular Ans 21 units 100Find the perpendicular distance of the point (2,3,4) from the line 4 x y z Also, find coordinates of foot of perpendicular 3 Ans (170/49, 78/49, 60/49) 101: If the equations of a line AB are 3 x y+2 z+2, find the direction cosines of a line parallel to AB 3 2 6
16 Ans: 3, 2, : The Cartesian equations of a line are 6x-23y+12z-2 Find the direction cosines of the line Write down the Cartesian and vector equations of the line passing through (2,-1,-1) which is parallel to the given line Ans 1 14, 2 14, : Show that the lines r i +j -k + λ (3i -j ) and r 4i -k + µ(2i +k ) intersect Also find their point of intersection Ans: (4, 0, -1) 104: Find the shortest distance between the lines through the points A (6, 2, 2) and A (-4, 0, -1) in the direction 1, -2, 2 and 3, -2, -2 respectively Ans: 9 units 105: Find the shortest distance between the lines x 1 y 2 z and x 2 3 y 3 4 z 5 5 Ans: 6 6 units 106: By computing the shortest distance between the following pair of lines, determine whether they intersect or not? r i - j +λ (2i -k ), r 2i -j +µ(i -j -k ) Ans: units, No 107: Show that the lines x a+d α j y a α z a d α+j and x b+c β γ γ b β z b c β+γ are coplanar
17 108: A line with direction ratios 2, 7, -5 is drawn to intersect the lines x 5 y 7 z+2 x+3 and y 3 z Find the co-ordinates of the points of intersection and the length intercepted on it Ans: (2, 8, -3), (0, 1, 2), 78 units 109: Show that the line x 1 y z 3 x 4 and y 1 z intersect Find their point of intersection Ans: (-1, -1, -1) 110: Find the image of the point (1, 2, 3) in the line x 6 3 y 7 2 z 7 2 Ans: (5, 8, 15)
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
12 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) = 2. ( d ) - 3. ^i - 2. ^j c 3. ( d )
 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
- THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
Review Exercise. 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the
 Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
Three Dimensional Geometry
 Three Dimensional Geometry Teaching learning points Distance between two given points P(x, y, z ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ = ( x x ) + ( y y ) + ( z z ) Direction ratio of line joining the points (x, y, z
Three Dimensional Geometry Teaching learning points Distance between two given points P(x, y, z ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ = ( x x ) + ( y y ) + ( z z ) Direction ratio of line joining the points (x, y, z
Homework Questions 1 Gradient of a Line using y=mx+c
 (C1-5.1a) Name: Homework Questions 1 Gradient of a Line using y=mx+c 1. State the gradient and the y-intercept of the following linear equations a) y = 2x 3 b) y = 4 6x m= 2 c = -3 c) 2y = 8x + 4 m= -6
(C1-5.1a) Name: Homework Questions 1 Gradient of a Line using y=mx+c 1. State the gradient and the y-intercept of the following linear equations a) y = 2x 3 b) y = 4 6x m= 2 c = -3 c) 2y = 8x + 4 m= -6
Three Dimensional Geometry. Linear Programming
 Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Mathematics (www.tiwariacademy.com)
 () Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
() Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 1 CHAPTER 5. GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS Contents 1 Geometry in R 3 2 1.1 Lines...............................................
1 CHAPTER 5. GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW GEOMETRY IN THREE DIMENSIONS Contents 1 Geometry in R 3 2 1.1 Lines...............................................
Elements of three dimensional geometry
 Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Topic 4: Vectors Markscheme 4.6 Intersection of Lines and Planes Paper 2
 Topic : Vectors Markscheme. Intersection of Lines and Planes Paper. Using an elimination method, x y + z x y z x y x + y 8 y Therefore x, y, z Using matrices, x y z x y z 5 (using a graphic display calculator)
Topic : Vectors Markscheme. Intersection of Lines and Planes Paper. Using an elimination method, x y + z x y z x y x + y 8 y Therefore x, y, z Using matrices, x y z x y z 5 (using a graphic display calculator)
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2. GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) by A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2.3 Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin UNIT 5.2
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) by A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2.3 Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin UNIT 5.2
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
If the center of the sphere is the origin the the equation is. x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 -(2)
 Sphere Definition: A sphere is the locus of a point which remains at a constant distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is the radius of the sphere.
Sphere Definition: A sphere is the locus of a point which remains at a constant distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is the radius of the sphere.
Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations
 Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations Name Date Period Find the x- and y-intercepts and slope of each equation. 1. y = -x 2. x + 3y = 6 3. x = 2 4. y = 0 5. y = 2x - 9 6. 18x 42 y = 210 Graph each
Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations Name Date Period Find the x- and y-intercepts and slope of each equation. 1. y = -x 2. x + 3y = 6 3. x = 2 4. y = 0 5. y = 2x - 9 6. 18x 42 y = 210 Graph each
UNIT NUMBER 5.2. GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) b A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2. Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin 5.2.5 Exercises
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) b A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2. Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin 5.2.5 Exercises
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE
 ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron (solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
TEST 3 REVIEW DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS
 TEST 3 REVIEW DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors 1.1. Form the vector starting at the point P and ending at the point Q: P = (0, 0, 0), Q = (1,, 3). P = (1, 5, 3), Q = (8, 18, 0). P = ( 3, 1, 1), Q = (, 4,
TEST 3 REVIEW DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors 1.1. Form the vector starting at the point P and ending at the point Q: P = (0, 0, 0), Q = (1,, 3). P = (1, 5, 3), Q = (8, 18, 0). P = ( 3, 1, 1), Q = (, 4,
Buds Public School, Dubai
 Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Straight Lines. 2 of 71. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes. 1 Objectives. 2 Assignments. 3 Lecture Notes
 Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
3 CHAPTER. Coordinate Geometry
 3 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius Cartesian Plane Ordered pair A pair of numbers a and b instead in a specific order with a at the first place and b
3 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius Cartesian Plane Ordered pair A pair of numbers a and b instead in a specific order with a at the first place and b
Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position
 Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position IM3 - Santowski IM3 - Santowski 1 Fast Five Opening Exercises! Use your TI 84 calculator:! Evaluate sin(50 ) " illustrate with a diagram! Evaluate sin(130 ) " Q
Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position IM3 - Santowski IM3 - Santowski 1 Fast Five Opening Exercises! Use your TI 84 calculator:! Evaluate sin(50 ) " illustrate with a diagram! Evaluate sin(130 ) " Q
.(3, 2) Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates. Every point has two co-ordinates. Plot the following points on the plane. A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3)
 Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates Every point has two co-ordinates. (3, 2) x co-ordinate y co-ordinate Plot the following points on the plane..(3, 2) A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3) B (3, 3) E ( 4, 4) H (6,
Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates Every point has two co-ordinates. (3, 2) x co-ordinate y co-ordinate Plot the following points on the plane..(3, 2) A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3) B (3, 3) E ( 4, 4) H (6,
Vectors. Section 1: Lines and planes
 Vectors Section 1: Lines and planes Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Reminder: notation and definitions Equation of a line The intersection of two lines Finding the equation of a plane
Vectors Section 1: Lines and planes Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Reminder: notation and definitions Equation of a line The intersection of two lines Finding the equation of a plane
If (x, y, z) are the coordinates of a point P in space, then the position vector of the point P w.r.t. the same origin is.
 7. 3D GEOMETRY. COORDINATE OF A POINT IN SPACE Let P be a point in the space. If a perpendicular from that point is dropped to the xyplane, then the algebraic length of this perpendicular is considered
7. 3D GEOMETRY. COORDINATE OF A POINT IN SPACE Let P be a point in the space. If a perpendicular from that point is dropped to the xyplane, then the algebraic length of this perpendicular is considered
Homogeneous coordinates, lines, screws and twists
 Homogeneous coordinates, lines, screws and twists In lecture 1 of module 2, a brief mention was made of homogeneous coordinates, lines in R 3, screws and twists to describe the general motion of a rigid
Homogeneous coordinates, lines, screws and twists In lecture 1 of module 2, a brief mention was made of homogeneous coordinates, lines in R 3, screws and twists to describe the general motion of a rigid
Notes on Spherical Geometry
 Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
For all questions, E. NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.
 For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
Coordinate Geometry. Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane
 Coordinate Geometry Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane What we will explore in this tutorial (a) Explore gradient I. Identify the gradient of a
Coordinate Geometry Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane What we will explore in this tutorial (a) Explore gradient I. Identify the gradient of a
STRAIGHT LINES. 2) The coordinates of the join of trisection of the points (-2,3), (3,-1) nearer to (-2,3) is
 STRAIGHT LINES Episode :39 Faculty:Prof. A. NAGARAJ 1) The distance between the points a cos, a sin and a cos, asin is a) a cos 2 b) 2a cos c) a sin d) 2a sin 2 2 2 2) The coordinates of the join of trisection
STRAIGHT LINES Episode :39 Faculty:Prof. A. NAGARAJ 1) The distance between the points a cos, a sin and a cos, asin is a) a cos 2 b) 2a cos c) a sin d) 2a sin 2 2 2 2) The coordinates of the join of trisection
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Coordinate Systems, Locus and Straight Line
 Coordinate Systems Locus Straight Line. A line makes zero intercepts on - ax - ax it perpendicular to the line. Then the equation (Karnataka CET 00). If p the length if the perpendicular from the origin
Coordinate Systems Locus Straight Line. A line makes zero intercepts on - ax - ax it perpendicular to the line. Then the equation (Karnataka CET 00). If p the length if the perpendicular from the origin
Year 10 Term 3 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
CHAPTER 40 CARTESIAN AND POLAR COORDINATES
 CHAPTER 40 CARTESIAN AND POLAR COORDINATES EXERCISE 169 Page 462 1. Express (3, 5) as polar coordinates, correct to 2 decimal places, in both degrees and in From the diagram, r = 32 + 52 = 5.83 y and 5
CHAPTER 40 CARTESIAN AND POLAR COORDINATES EXERCISE 169 Page 462 1. Express (3, 5) as polar coordinates, correct to 2 decimal places, in both degrees and in From the diagram, r = 32 + 52 = 5.83 y and 5
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Education Resources. This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
 Education Resources Straight Line Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
Education Resources Straight Line Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D
 1.5. EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES IN 3-D 55 Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from the
1.5. EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES IN 3-D 55 Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from the
Analytic Spherical Geometry:
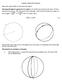 Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( )
 MATHEMATICS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( ) A. TRIANGLES: Distance formula is used to show PERIMETER: sum of all the sides Scalene triangle: 3 unequal sides Isosceles
MATHEMATICS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( ) A. TRIANGLES: Distance formula is used to show PERIMETER: sum of all the sides Scalene triangle: 3 unequal sides Isosceles
Downloaded from Class XI Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Maths
 A point is on the axis. What are its coordinates and coordinates? If a point is on the axis, then its coordinates and coordinates are zero. A point is in the XZplane. What can you say about its coordinate?
A point is on the axis. What are its coordinates and coordinates? If a point is on the axis, then its coordinates and coordinates are zero. A point is in the XZplane. What can you say about its coordinate?
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Math (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines
 Math 18.02 (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines February 12 Reading Material: From Simmons: 17.1 and 17.2. Last time: Square Systems. Word problem. How many solutions?
Math 18.02 (Spring 2009): Lecture 5 Planes. Parametric equations of curves and lines February 12 Reading Material: From Simmons: 17.1 and 17.2. Last time: Square Systems. Word problem. How many solutions?
Intersection of planar figures. Intersection of a parallelogram and a triangle
 Intersection of planar figures Intersection of a parallelogram and a triangle Exercise. Given a parallelogram ABCD and a triangle P QR. Construct the intersection of the two figures. First, we consider
Intersection of planar figures Intersection of a parallelogram and a triangle Exercise. Given a parallelogram ABCD and a triangle P QR. Construct the intersection of the two figures. First, we consider
7.3 3-D Notes Honors Precalculus Date: Adapted from 11.1 & 11.4
 73 3-D Notes Honors Precalculus Date: Adapted from 111 & 114 The Three-Variable Coordinate System I Cartesian Plane The familiar xy-coordinate system is used to represent pairs of numbers (ordered pairs
73 3-D Notes Honors Precalculus Date: Adapted from 111 & 114 The Three-Variable Coordinate System I Cartesian Plane The familiar xy-coordinate system is used to represent pairs of numbers (ordered pairs
CHAPTER 4 LINE PERPENDICULAR TO PLANE
 CHAPTER 4 LINE PERPENDICULAR TO PLANE LEARNING OBJECTIVES mention the definition of line perpendicular to plane prove that a line perpendicular to a plane understand theorems related to line perpendicular
CHAPTER 4 LINE PERPENDICULAR TO PLANE LEARNING OBJECTIVES mention the definition of line perpendicular to plane prove that a line perpendicular to a plane understand theorems related to line perpendicular
ax + by = 0. x = c. y = d.
 Review of Lines: Section.: Linear Inequalities in Two Variables The equation of a line is given by: ax + by = c. for some given numbers a, b and c. For example x + y = 6 gives the equation of a line. A
Review of Lines: Section.: Linear Inequalities in Two Variables The equation of a line is given by: ax + by = c. for some given numbers a, b and c. For example x + y = 6 gives the equation of a line. A
3.0 Trigonometry Review
 3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position
 Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry
 Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Trigonometry Review Day 1
 Name Trigonometry Review Day 1 Algebra II Rotations and Angle Terminology II Terminal y I Positive angles rotate in a counterclockwise direction. Reference Ray Negative angles rotate in a clockwise direction.
Name Trigonometry Review Day 1 Algebra II Rotations and Angle Terminology II Terminal y I Positive angles rotate in a counterclockwise direction. Reference Ray Negative angles rotate in a clockwise direction.
GEOMETRY 1 Basic definitions of some important term:
 GEOMETRY 1 Geometry: The branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, solids, and higher dimensional analogues. GEOMETRY WHT TO STUDY? LSSIFITION OF NGLES
GEOMETRY 1 Geometry: The branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, solids, and higher dimensional analogues. GEOMETRY WHT TO STUDY? LSSIFITION OF NGLES
Visualisation Pipeline : The Virtual Camera
 Visualisation Pipeline : The Virtual Camera The Graphics Pipeline 3D Pipeline The Virtual Camera The Camera is defined by using a parallelepiped as a view volume with two of the walls used as the near
Visualisation Pipeline : The Virtual Camera The Graphics Pipeline 3D Pipeline The Virtual Camera The Camera is defined by using a parallelepiped as a view volume with two of the walls used as the near
UT2-DSE-MATH-CP 1 Solution
 016 017 UT-DSE-MATH-CP 1 Solution SECTION A (70 marks) 1. Factorize x 5x, (b) x y xy x 5x. ( marks) x 5x ( x 1)( x ) (b) x y xy x 5x ( x 1) xy (x 1)( x ) ( xy x )(x 1) 19 4x. Solve the inequality 17 x
016 017 UT-DSE-MATH-CP 1 Solution SECTION A (70 marks) 1. Factorize x 5x, (b) x y xy x 5x. ( marks) x 5x ( x 1)( x ) (b) x y xy x 5x ( x 1) xy (x 1)( x ) ( xy x )(x 1) 19 4x. Solve the inequality 17 x
Grad operator, triple and line integrals. Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures
 Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1
 PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
LECTURE 5: VECTOR GEOMETRY : REPRESENTATION OF PLANES. Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012
 LECTURE 5: VECTOR GEOMETRY : REPRESENTATION OF PLANES Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012 1 Outline: 5. MORE ON VECTOR GEOMETRY 5.1 Vector representation of planes 5.1.1 Plane from vector to Cartesian
LECTURE 5: VECTOR GEOMETRY : REPRESENTATION OF PLANES Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012 1 Outline: 5. MORE ON VECTOR GEOMETRY 5.1 Vector representation of planes 5.1.1 Plane from vector to Cartesian
X-ray Diffraction from Materials
 X-ray Diffraction from Materials 2008 Spring Semester Lecturer; Yang Mo Koo Monday and Wednesday 14:45~16:00 8. Experimental X-ray Diffraction Procedures 8.1 Diffraction Experiments using Films 8.1.1 Laue
X-ray Diffraction from Materials 2008 Spring Semester Lecturer; Yang Mo Koo Monday and Wednesday 14:45~16:00 8. Experimental X-ray Diffraction Procedures 8.1 Diffraction Experiments using Films 8.1.1 Laue
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS 1.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP
 PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
4. The following diagram shows the triangle AOP, where OP = 2 cm, AP = 4 cm and AO = 3 cm.
 Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
7Coordinate. geometry UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. 7.1 Kick off with CAS
 7.1 Kick off with CAS 7Coordinate geometry 7. Distance between two points 7.3 Midpoint of a line segment 7.4 Parallel lines and perpendicular lines 7.5 Applications 7.6 Review 7.1 Kick off with CAS U N
7.1 Kick off with CAS 7Coordinate geometry 7. Distance between two points 7.3 Midpoint of a line segment 7.4 Parallel lines and perpendicular lines 7.5 Applications 7.6 Review 7.1 Kick off with CAS U N
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2
 EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS. Apply Geometric Concepts in Modeling Situations
 UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions
 Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Answers to practice questions for Midterm 1
 Answers to practice questions for Midterm Paul Hacking /5/9 (a The RREF (reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix is So the system of linear equations has exactly one solution given by x =, y =,
Answers to practice questions for Midterm Paul Hacking /5/9 (a The RREF (reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix is So the system of linear equations has exactly one solution given by x =, y =,
Co-ordinate Geometry
 Co-ordinate Geometry 1. Find the value of P for which the points (1, -), (2, -6) and (p, -1) are collinear 2. If the point P (x, y) is equidistant from the points A (1,) and B(4, 1). Prove that 2x+y =
Co-ordinate Geometry 1. Find the value of P for which the points (1, -), (2, -6) and (p, -1) are collinear 2. If the point P (x, y) is equidistant from the points A (1,) and B(4, 1). Prove that 2x+y =
Geo - CH3 Prctice Test
 Geo - CH3 Prctice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Identify the transversal and classify the angle pair 11 and 7. a. The transversal
Geo - CH3 Prctice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Identify the transversal and classify the angle pair 11 and 7. a. The transversal
1 Affine and Projective Coordinate Notation
 CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout #9 Geometric Modeling Original Handout #9 Stanford University Tuesday, 3 November 992 Original Lecture #2: 6 October 992 Topics: Coordinates and Transformations Scribe:
CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout #9 Geometric Modeling Original Handout #9 Stanford University Tuesday, 3 November 992 Original Lecture #2: 6 October 992 Topics: Coordinates and Transformations Scribe:
GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET
 GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET Name Period 1 Day 1 - Directed Line Segments DO NOW Distance formula 1 2 1 2 2 2 D x x y y Midpoint formula x x, y y 2 2 M 1 2 1 2 Slope formula y y m x x 2 1
GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET Name Period 1 Day 1 - Directed Line Segments DO NOW Distance formula 1 2 1 2 2 2 D x x y y Midpoint formula x x, y y 2 2 M 1 2 1 2 Slope formula y y m x x 2 1
Example Items. Geometry
 Example Items Geometry Geometry Example Items are a representative set of items for the ACP. Teachers may use this set of items along with the test blueprint as guides to prepare students for the ACP.
Example Items Geometry Geometry Example Items are a representative set of items for the ACP. Teachers may use this set of items along with the test blueprint as guides to prepare students for the ACP.
INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Mathematics is both the queen and the hand-maiden of all sciences E.T. BELL 1.1 Introduction You may recall that to locate the position of a point in
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Mathematics is both the queen and the hand-maiden of all sciences E.T. BELL 1.1 Introduction You may recall that to locate the position of a point in
Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FREE Study Material at Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry 33 OPTIO
 33 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY You have read in your earlier lessons that given a point in a plane, it is possible to find two numbers, called its co-ordinates in the plane. Conversely,
33 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY You have read in your earlier lessons that given a point in a plane, it is possible to find two numbers, called its co-ordinates in the plane. Conversely,
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
0118geo. Geometry CCSS Regents Exam In the diagram below, a sequence of rigid motions maps ABCD onto JKLM.
 0118geo 1 In the diagram below, a sequence of rigid motions maps ABCD onto JKLM. The graph below shows two congruent triangles, ABC and A'B'C'. If m A = 82, m B = 104, and m L = 121, the measure of M is
0118geo 1 In the diagram below, a sequence of rigid motions maps ABCD onto JKLM. The graph below shows two congruent triangles, ABC and A'B'C'. If m A = 82, m B = 104, and m L = 121, the measure of M is
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
The Humble Tetrahedron
 The Humble Tetrahedron C. Godsalve email:seagods@hotmail.com November 4, 010 In this article, it is assumed that the reader understands Cartesian coordinates, basic vectors, trigonometry, and a bit of
The Humble Tetrahedron C. Godsalve email:seagods@hotmail.com November 4, 010 In this article, it is assumed that the reader understands Cartesian coordinates, basic vectors, trigonometry, and a bit of
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot. Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR. Spring May 6, 2017
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Spring May 6, 2017 Mathematical analysis of disphenoid (isosceles tetrahedron (Derivation of volume, surface area, vertical height, in-radius,
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Spring May 6, 2017 Mathematical analysis of disphenoid (isosceles tetrahedron (Derivation of volume, surface area, vertical height, in-radius,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS LEARNER NOTES
 SENIOR SECONDARY,059(0(7 PROGRAMME 0 GRADE LEARNER NOTES The SSIP is supported by c) Gauteng Department of Education, 0 TABLE OF CONTENTS LEARNER NOTES SESSION TOPIC Revision of Analytical Geometry (Grade
SENIOR SECONDARY,059(0(7 PROGRAMME 0 GRADE LEARNER NOTES The SSIP is supported by c) Gauteng Department of Education, 0 TABLE OF CONTENTS LEARNER NOTES SESSION TOPIC Revision of Analytical Geometry (Grade
CHAPTER 6 : COORDINATE GEOMETRY CONTENTS Page 6. Conceptual Map 6. Distance Between Two Points Eercises Division Of A Line Segment 4 Eercises
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS MODULE 0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY CHAPTER 6 : COORDINATE GEOMETRY CONTENTS Page 6. Conceptual Map 6. Distance Between Two Points Eercises 6. 3 6.3 Division Of A Line Segment 4 Eercises
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS MODULE 0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY CHAPTER 6 : COORDINATE GEOMETRY CONTENTS Page 6. Conceptual Map 6. Distance Between Two Points Eercises 6. 3 6.3 Division Of A Line Segment 4 Eercises
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
62 Basilio Bona - Dynamic Modelling
 6 Basilio Bona - Dynamic Modelling Only 6 multiplications are required compared to the 7 that are involved in the product between two 3 3 rotation matrices...6 Quaternions Quaternions were introduced by
6 Basilio Bona - Dynamic Modelling Only 6 multiplications are required compared to the 7 that are involved in the product between two 3 3 rotation matrices...6 Quaternions Quaternions were introduced by
GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS
 GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS Chapter 3: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Name: Teacher: Pd: 0 Table of Contents DAY 1: (Ch. 3-1 & 3-2) SWBAT: Identify parallel, perpendicular, and skew lines. Identify the angles
GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS Chapter 3: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Name: Teacher: Pd: 0 Table of Contents DAY 1: (Ch. 3-1 & 3-2) SWBAT: Identify parallel, perpendicular, and skew lines. Identify the angles
2D Object Definition (1/3)
 2D Object Definition (1/3) Lines and Polylines Lines drawn between ordered points to create more complex forms called polylines Same first and last point make closed polyline or polygon Can intersect itself
2D Object Definition (1/3) Lines and Polylines Lines drawn between ordered points to create more complex forms called polylines Same first and last point make closed polyline or polygon Can intersect itself
