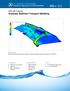
HEC-RAS 2D Flood Modelling Tutorial
|
|
|
- Bethany Ashlynn Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEC-RAS 2D Flood Modelling Tutorial
2 Civil Site Design and HECRAS 2D Flood Modelling HECRAS version 5 and later includes functionality to analyse water flows moving across a surface. this is known as 2D flood modelling and provides more accurate modelling of water movement across a surface than 1d (or section based) flood modelling. If you are using Civil Site Design, you now have functionality to work with HECRAS input and output files via the Export HECRAS 2D and Import HECRAS 2D commands. For this example, we ll use HECRAS to undertake a 2D flow analysis of an existing creek abutting an existing car park being considered for expansion. The existing creek flow performance is to be maintained following the new works, and enhancement of the creek flow may be required if flooding is occurring downstream. A peak flow of 10m 3 /s must be managed in the creek. The Tutorial Data Set The tutorial data is installed with the software installation to the following location (Note: the HEC-RAS menu must be ticked on for inclusion during install): Civil 3D: C:\CSS Training Data\Civil Site Design\HEC-RAS\HECRAS 2D Tutorial Start.dwg CAD: C:\CSS Training Data\Civil Site Design\HEC-RAS\HECRAS 2D Tutorial Start - CAD.dwg This drawing file includes a surface and is located in the MGA-55 Coordinate system. At this stage, there is no surface associated with the data set. This can be remedied using Model Viewer. To do this: Start the ribbon command Roads Tab > Select Panel > Model Viewer. This will start Model Viewer and populate the existing surface name into the Toggle Display form Under Base Surface, click on the picklist dropdown for Style and select Image from Satellite (Aerial Photo) The Satellite Setup form will display. Firstly click on the button, select Australia MGA-55.prj from the list and click OK. Click on Confirm Satellite Data to see the imagery available under the surface location. For AutoCAD and Civil 3D users, an image is also inserted in the drawing. Roll the mouse to zoom out once only (the more zoom out, the less quality) and click the Accept button top left. Click OK to exit the Toggle Display form. An image is associated with the surface in Model Viewer.
3 For BricsCAD users, an image is saved to the Data folder. When inserted into the drawing it will automatically position itself correctly. Exporting Terrain Data to HECRAS The Export HECRAS 2D command will take the combination of your design and existing surfaces and share them across to HECRAS as a single geotiff file. The goetiff describes the surface extents and elevations for HECRAS. The command can be run directly from the ribbon interface, or can be run from inside Model Viewer. If you opt to run the command from the CAD ribbon interface, the Toggle Display form will display for you to confirm what surface data to bring across to HECRAS - you can opt to just include the existing surface conditions, or you could send across a combined surface containing the existing surface as well as your design surfaces. This would enable you to analyse pre and post development conditions. If you run the command from inside Model Viewer, you get the benefit of directly reviewing the surface before export across to HECRAS. In the Export HECRAS 2D command you need to specify a location and name for the geotiff you are exporting, as well as a grid spacing. Set a grid spacing that matches the accuracy of the data you have, to ensure you don't lose information and, conversely, you don't include unnecessary data. Once you have a geotiff file you can use this to generate terrain data in HECRAS. Steps: 1. If you closed Model Viewer, click on the ribbon command Roads Tab > Select Panel > Model Viewer. This will start Model Viewer.
4 2. If required, confirm the settings via Toggle Display. If the previous steps are complete, the surface and image required to be analysed in HECRAS should already by shown. Note: in the above image the exaggeration has been set to 5 to accentuate the shape of the terrain. Exaggeration must be set to 1 before exporting 3. Click on the Analyse Tab > HECRAS 2D Panel > Export button In the Export form you confirm the location, name and grid size of the file to export. 4. Leave the Grid Spacing to the default of 1 5. Note the path to the output HECRAS file, then click Export to create a HECRAS input file.
5 Import and Analysis in HECRAS After starting your HECRAS project and establishing the units and setup, you need to open RAS Mapper and create a terrain. You will firstly set up a projection, or coordinate system, for your data. HECRAS Project Setup 6. Click on File > New. Select a location and name for the new project. 7. Click on Options > Unit System to confirm the units (this example is using Metric units). HECRAS RAS Mapper 8. From the HEC-RAS interface, select GIS Tools > RAS Mapper or else click on the RAS Mapper button. The RAS Mspper form will display with a menu at the top and a list of layers along the side. The first task is to populate the Terrain layer using the.tif created by Civil Site Design. Optionally, a Map Layer can be included for the aerial photo. Assigning a Projection Before creating a terrain, a projection must be set. This is controlled by a projection file, extension.prj. Some typical Australian and other country specific.prj files are contained in the Civil Site Design Settings folder, in the Visualisation and then Projections folders. There is also a website where you can generate.prj files by typing in your location. 9. From the Ras Mapper form, click on Tools > Set Projection for Project. For this example, a.prj has been provided in the same directory as the tutorial drawing: C:\CSS Training Data\Civil Site Design\HEC-RAS 10. Navigate to the above folder location and open Australia MGA-55.prj. This assigns the projection.
6 Adding a Terrain When you open the Terrain form and create a new Terrain, you will have an opportunity to load a terrain file - here you can use the exported file from Civil Site Design to generate the terrain data for HECRAS. 11. Click on Tools > New Terrain 12. Click on + to add a new data source for the terrain. Navigate to the output location of the.tif and open that file This data will be used to create a Terrain in HECRAS the terrain is saved as a file with extension.hdf. 13. Click on Create to import the Terrain. 14. Note under the Terrains layer is a new layer. Make sure that Terrains is ticked on, then right click on Terrain and choose Zoom to Extents to see the full extents of the terrain model in RAS Mapper.
7 Adding an Aerial Photo With RAS Mapper you can also include imagery and other geospatial data. 15. Right click on Map Layers and select Add map data layers When prompted to select a file, use the file type dropdown bottom right to select images. Selecting a.jpg file will then insert it into HECRAS so long as it is accompanied by a world file (.jgw file contains the spatial location for a.jpg file). 16. Select the file C:\CSS Training Data\Civil Site Design\HEC-RAS\Google_Colour.jpg Tick on the image to display it in RAS Mapper. Right click on the image name to edit the Image Display Properties a transparency can be assigned here.
8 After importing data into RAS Mapper it will become available in the HECRAS Geometry Editor. In here you can assign flood data along the boundaries, establish the model grid size for flood analysis, edit the surface breaklines, assign different surface Manning's n values and more. Close RAS Mapper. Creating the 2D Flow Area 17. From the HEC-RAS interface, click on View/Edit Geometric Data A new form will display entitled Geometric Data. The surface will initially display with the colours representing elevations. To show the aerial photo, click on and tick on to display the Map Layer you added.
9 The linework in your original drawing can be included in the Geometric data as a layer, after exporting it out from the drawing in an appropriate format for HECRAS. Now to create a 2D flow area for analysis. To keep it simple, select the extents of the terrain as the boundary. This is a relatively well defined basin, so the extents of the boundary are typically much higher than the creek (excepting the inflow and outflow locations north and south). When you select the area you can establish a calculation mesh across the surface. In our example, a 10m mesh is suitable and matches with the existing surface triangulation. 18. Click on the 2D Flow Area button. Use the left mouse button to sketch the boundaries of a flow area. Double click on the start of the first line drawn to close the area. 19. At the prompt, name the area Total Flow Area and click OK.
10 20. Left click on the new area and select Edit 2D Flow Area In the 2D Flow Areas form you apply a computational mesh across the surface, as well as establish Manning s n values to apply for the default area and for any other Land Cover areas added. 21. Click on Generate Computation Points on Regular Interval with All Breaklines 22. Set DX and DY both to 10 and click Generate Points in 2D Flow Area 23. Click OK to close the 2D Flow Areas form. The pattern on the 2D flow area in the Geometric Editor will change zooming in will expose the individual mesh areas. Zoom in to view the mesh shape. If any are red in colour then you will need to use the Edit > Add Points command to add more mesh point or else adjust the boundary shape.
11 Note: if it is required to edit the outline of the 2D flow area, use the menu command Edit > Move Points/Objects or other edit tool in the Edits menu. The 2D Area Breaklines command can be used to incorporate breaklines into the flow area to better represent ridge and valley lines for the surface. Setting Boundary Conditions (for Incoming and Outgoing flows) Flow comes from the ponding areas along the southern and western boundaries of the surface, so a boundary condition needs to be set along this edge. We can then assign inflow along this boundary to spill across the surface. The low side of the surface is along the eastern boundary, so we can set a boundary condition along there for how water can exit along that boundary. 24. Click on the SA/2D Area BC Lines button 25. Click along the western boundary to set an incoming flow line. Flow will come in uniformly along this line. Double click to finish the boundary 26. Name the boundary Inflow and click OK to create. 27. Repeat the above 3 steps to create an outflow boundary. Run the boundary along the northeastern boundary where the properties are and name the flow area boundary Outflow. Outputs should look similar to below:
12 Note that in the geometry editor you can incorporate both 1D and 2D flow zones into a single model for analysis. Additionally, boundary conditions can be set within the 2D area to represent different hydraulic behaviours. After setting up the surface and boundary conditions, you can move onto assigning the flow conditions. 28. Click on File > Save Geometry Data. 29. Name the file Existing Conditions and click OK Note: Where a boundary is not specified, water is assumed to well up along the boundary as if the boundary edge was a wall. Establish Flow Conditions along the Boundaries In the Flow Conditions form, we can set an inflow for the incoming boundary along the western boundary. In this example, we're working with a peak flow of 20 l/s and describing the storm shape as a simple bell type curve. You can copy and paste from spreadsheet input tools, such as Excel, to quickly create the flow information for HEC- RAS. For the outgoing boundary conditions, we set for a normal depth and apply a friction slope to describe how the exiting flow is handled. 30. From the HECRAS menu click on View/Edit Unsteady Flow data A new form will display entitled Unsteady Flow Data. The form will list the two Boundary Conditions set for the 2D area. 31. Under Add Boundary Condition Location, click on Add SA/2D Flow Area to include the Total Flow area 32. Click on the -> arrow to include the Total Flow Area for analysis and click OK. 33. Under Storage/2D Flow Area, click the flow area entitled Outflow 34. Click on Normal Depth at the top to establish the outflow conditions along this line 35. Type in a Friction Slope of 0.1 and click OK The Boundary Condition for the Inflow will be set to Normal Depth. Now we need to assign incoming flows into the system. 36. Under Storage/2D Flow Area, click on the flow entitled Inflow 37. Click on Flow Hydrograph to assign a time dependent flow to this inflow line
13 38. For Data Time Interval, set the value to 1 hr using the pick list To add flows you can type in a Flow for each time step (0 to 48hrs) and set for a build up to a peak flow of 10m 3 /s, however it is often quicker to spreadsheet out the required flow characteristics, copy them from Excel, and use the paste command to paste them into the Flow column. For this purpose, you may wish to open the file Storm Input Calculator.xls file located in the same directory as the source drawing. In this file, you can type in the Minimum and Maximum flow values at the top of the form and it will populate values for 1hr increments. Set the Maximum Flow to 10m 3 /s. Then highlight the values in the Flow column and copy to clipboard (Ctrl + C or right click and select Copy). In the Flow Hydrograph form, highlight all Flow cells from 0:00 to 48:00 and press Ctrl+V 39. For EG Slope for distributing flow along BC Line, type in Click OK to assign the flow conditions to the boundaries specified 41. Click on Save > Unsteady Flow Data. Name the file Flows and click OK 42. Flick on File > Exit to close the flow data form.
14 Re-establish the Area Conditions You may receive an error if you move directly to analysing the flows, without first returning to the Geometric Data Editor form and re-establishing the grid calculations to ensure they are correctly saved following the flow assignment. To do this: 43. From the HEC-RAS interface, click on View/Edit Geometric Data 44. Click on the 2D area and select Edit 2D Flow Area 45. In the form that displays click on generate Computation Points on Regular Interval with All Breaklines 46. Accept the default spacings you previously applied and click Generate Points in 2D Area. Accept the warning message and click Yes. 47. Click OK to close this form then click on File > Save Geometry Data 48. Close the Geometry Editor form. Analyse the Flows When you analyse the system you set up time stamps for calculating flows, reporting times and total analysis duration. RAS Mapper is then used to review the flood extents over time, assess the peak extents, flow depths and flow velocities. As part of this analysis process, HECRAS has created a file to store this storm flow information. Civil Site Design can import this file and visualise it in 3D in Model Viewer. The Computation Interval is very important if it is too large or too small you will generate instability in your model or miss important calculation outcomes. Because we are on a steep site with fast flow in sections, a small Computation Interval is required we ll be going for 3 seconds. 49. From the HECRAS menu click on Perform and Unsteady Flow Simulation button. 50. Fill out the form as follows: a. Tick ON i. Geometry Preprocessor ii. Unsteady Flow Simulation iii. Post Processor b. Set the Simulation Time Window i. Pick a Starting Date (default selection shown) and Ending Date (same as starting) ii. Set the starting time to 0:00 iii. Set the ending time to 24:00
15 c. Set the Computational Settings i. Set the Computation Interval (how often it calculates levels) to 10 seconds ii. Set the Hydrograph Output Interval to 30 minutes iii. Set the Mapping Output Interval (time increments displayed in RAS Mapper) to 30 minutes iv. Set the Detailed Output Interval to 30 minutes 51. Click on Compute If you receive any information in red text, it is likely that some data has not been saved, data hasn t been fully added or there is an error in the mesh or data input. Review the above steps, ensuring you (again) Save Geometry Data and Save Unsteady Flow Data, and try computing again. You ll have to wait a little while as it processes 4-6 minutes. 52. Close the computations form 53. Click on File > Save Plan to save the applied flow analysis inputs 54. Click Close You can view the results directly inside HECRAS via RAS Mapper. As well, you can generate lines for the flood extents and other flow outcomes and export this to a geospatial file format suitable for import using the Map 3D tools in Civil 3D. To check out the results in RAS Mapper, do the following:
16 From the HECRAS interface, click on the RAS Mapper button. Tick on the Depth layer to show the depth of water. Use the slider at the top to change the flow time to see development of flow over time. The play button will animate the flow. 3D Review and Analysis using Model Viewer The Import HECRAS 2D command lets you import the HECRAS output file (which is a file with extension p##.hdf). After running the command and selecting the file, a new form displays with the calculated time stamps included. 55. Open Model Viewer 56. Click on Analyse > Import HEC-RAS 57. Click on the... button to select an output file. Output files have the name of the HECRAS project file with.p##.hdf, where ## is a 2 digit number. Locate the project folder you saved the HEC-RAS analysis to and
17 you will find the output.hdf file/s there. Select and Open. 58. Select a time stamp and see the extents of flooding at that time. You can play and pause the results to see the development of flooding over time and assess, in 3D, how the flooding may impact downstream properties and infrastructure.
18 Video Output From the Outputs tab, click on Record Video to create an animated video file (.avi) of the water.
19 Adding the Flood Extents Linework into your Drawing You will need to create an export file from HEC-RAS in order to import it into your drawing as linework. Since HEC-RAS interfaces with geospatial systems, you will be generating a geospatial file (ESRI.shp) describing the linework. This needs to then be imported into your drawing. Civil 3D and Map 3D include tools to read.shp files and create objects in the drawing from the file/s. AutoCAD and BricsCAD do not natively have functionality to interface with geospatial files such as.shp. There are third party applications, such as Spatial Manager, that deliver functionality to import, export and interrogate geospatial data. To generate the.shp file of the water extents you need to: 1. Open HEC-RAS and go into RAS Mapper. You should see all the results in RAS mapper from your analysis. 2. In the Selected Layer list, right click on the Results Layer (Plan 01) and select Add new results map layer The following form will display: 3. You can creae a new layer displaying any of the Map Type information, at any particular time. To generate the maximum inundatation a. Select the Map type Inundation Boundary b. Under Unsteady Profile, click on Maximum c. Confirm to create a Polygon Boundary d. Click on Add Map The new layer shows the inundation extents 4. Right click on the new layer and select Export Layer > Save Feature to Shapefile (or KMZ if viewing in Google Earth)
20 5. Save the file and then it can be imported into your drawing via a.shp import. If using Civil 3D, the command MAPIMPORT can be used to include the linework from the file. If using Spatial Manager there are tools to read in the layer of data and display as linework in the drawing. Here is a sample result using Civil 3D Map Import command: This creates polygons or poylines in the image below hatching has been applied in AutoCAD:
HEC-RAS 5.0 Training New Zealand Workshop Guide
 HEC-RAS 5.0 Training New Zealand Workshop Guide Prepared by: Krey Price Surface Water Solutions 57 Bromfield Drive Kelmscott WA 6111 Australia Tel. +61 400 367 542 e-mail: info@surfacewater.biz website:
HEC-RAS 5.0 Training New Zealand Workshop Guide Prepared by: Krey Price Surface Water Solutions 57 Bromfield Drive Kelmscott WA 6111 Australia Tel. +61 400 367 542 e-mail: info@surfacewater.biz website:
Workshop #1: Set Up Project File and RAS Mapper
 Workshop #1: Set Up Project File and RAS Mapper 1 In this workshop, you will: Install and open HEC-RAS 5.0.3 Create a project file Obtain terrain and projection data Import terrain data into RAS Mapper
Workshop #1: Set Up Project File and RAS Mapper 1 In this workshop, you will: Install and open HEC-RAS 5.0.3 Create a project file Obtain terrain and projection data Import terrain data into RAS Mapper
This tutorial introduces the HEC-RAS model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the HEC-RAS software.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
Updated on November 10, 2017
 CIVE 7397 Unsteady flows in Rivers and Pipe Networks/Stormwater Management and Modeling / Optimization in Water Resources Engineering Updated on November 10, 2017 Tutorial on using HEC-GeoRAS 10.1 (or
CIVE 7397 Unsteady flows in Rivers and Pipe Networks/Stormwater Management and Modeling / Optimization in Water Resources Engineering Updated on November 10, 2017 Tutorial on using HEC-GeoRAS 10.1 (or
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
Cross Sections, Profiles, and Rating Curves. Viewing Results From The River System Schematic. Viewing Data Contained in an HEC-DSS File
 C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
v Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
v. 8.4 Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Time minutes
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
TUFLOW 1D/2D SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Background Data
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Exercise Topic: HEC GeoRAS Post-Processing Objectives: This tutorial is designed to walk you
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Exercise Topic: HEC GeoRAS Post-Processing Objectives: This tutorial is designed to walk you
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Prerequisites None Time minutes Requirements Map Module Mesh Module Scatter Module Generic Model SRH-2D
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v SMS Tutorials SRH-2D Prerequisites Requirements SRH-2D Model Map Module Mesh Module Data files Time
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v TUFLOW 1D/2D SMS 11.2 Tutorial Time minutes Prerequisites TUFLOW 2D Tutorial
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
LD20493 From AutoCAD Civil 3D to Storm and Sanitary Analysis - Pond Design Using Volume-Grading Tools
 LD20493 From AutoCAD Civil 3D to Storm and Sanitary Analysis - Pond Design Using Volume-Grading Tools Kevin Larkin LSC Design, Inc. Learning Objectives Learn how to dynamically model stormwater ponds using
LD20493 From AutoCAD Civil 3D to Storm and Sanitary Analysis - Pond Design Using Volume-Grading Tools Kevin Larkin LSC Design, Inc. Learning Objectives Learn how to dynamically model stormwater ponds using
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Quick Guide to MapWindow GIS Desktop Application
 Quick Guide to MapWindow 1 Quick Guide to MapWindow GIS Desktop Application Version 2 January 2007 Adapted by Tom Croft. This is a summary user guide for commonly used tools and capabilities and does not
Quick Guide to MapWindow 1 Quick Guide to MapWindow GIS Desktop Application Version 2 January 2007 Adapted by Tom Croft. This is a summary user guide for commonly used tools and capabilities and does not
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes
 HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ.
 Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
SMS v Simulations. SRH-2D Tutorial. Time. Requirements. Prerequisites. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
Linear Routing: Floodrouting. HEC-RAS Introduction. Brays Bayou. Uniform Open Channel Flow. v = 1 n R2/3. S S.I. units
 Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D.
 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document
 City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
GIS Basics for Urban Studies
 GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation. Requirements
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
Carlson GIS for Surveyors
 Professional Land Surveyors of Ohio 2016 Annual Conference -- Dayton Ohio Carlson GIS for Surveyors Presented by Who Is That CAD Girl? Jennifer DiBona is a long time CAD consultant and trainer doing business
Professional Land Surveyors of Ohio 2016 Annual Conference -- Dayton Ohio Carlson GIS for Surveyors Presented by Who Is That CAD Girl? Jennifer DiBona is a long time CAD consultant and trainer doing business
Watershed Modeling Maricopa Predictive HEC-1 Model. Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v TUFLOW FV SMS 12.2 Tutorial Time Requirements Prerequisites Objectives
 SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
Day 1. HEC-RAS 1-D Training. Rob Keller and Mark Forest. Break (9:45 am to 10:00 am) Lunch (12:00 pm to 1:00 pm)
 Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
SMS v D Summary Table. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives Learn the process of making a summary table to compare the 2D hydraulic model results with 1D hydraulic model results. This tutorial introduces a method of presenting
SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives Learn the process of making a summary table to compare the 2D hydraulic model results with 1D hydraulic model results. This tutorial introduces a method of presenting
SMS v Culvert Structures with HY-8. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
HEC-RAS. A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume)
 HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v Google Earth Files SMS 13.0 Tutorial Prerequisites None Requirements Mesh Module Google Earth Time minutes
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to save SMS data to a KMZ file format. KMZ files are Google Earth files and will allow viewing SMS data in Google Earth. SMS can save any georeferenced data
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to save SMS data to a KMZ file format. KMZ files are Google Earth files and will allow viewing SMS data in Google Earth. SMS can save any georeferenced data
SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS
 Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
v Data Visualization SMS 12.3 Tutorial Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
UTEXAS Embankment on Soft Clay
 GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
Introduction to using QGIS for Archaeology and History Workshop by the Empirical Reasoning Center
 Introduction to using QGIS for Archaeology and History Workshop by the Empirical Reasoning Center In this workshop, we will cover the basics of working with spatial data, as well as its main uses for archaeology.
Introduction to using QGIS for Archaeology and History Workshop by the Empirical Reasoning Center In this workshop, we will cover the basics of working with spatial data, as well as its main uses for archaeology.
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Rational Design
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
v Water Distribution System Modeling Working with WMS Tutorials Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
HEC-RAS River Analysis System
 HEC-RAS River Analysis System Supplemental to HEC-RAS Version 5.0 User's Manual Version 5.0.4 April 2018 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. CPD-68d REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved
HEC-RAS River Analysis System Supplemental to HEC-RAS Version 5.0 User's Manual Version 5.0.4 April 2018 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. CPD-68d REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Help
 Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
Introduction to SAGA GIS
 GIS Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_001 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released under the Creative
GIS Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_001 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released under the Creative
All data is in Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Zone 6 projection, and WGS 84 datum.
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 EXPLORING MOOREA DATA WITH QUANTUM GIS In this exercise, you will be using an open-source FREE GIS software, called Quantum GIS,
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 EXPLORING MOOREA DATA WITH QUANTUM GIS In this exercise, you will be using an open-source FREE GIS software, called Quantum GIS,
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling?
 HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
Floodplain Mapping & Hydraulic Analysis with HEC-GeoRAS and ArcGIS 9.1
 Floodplain Mapping & Hydraulic Analysis with HEC-GeoRAS 4.1.1 and ArcGIS 9.1 Prepared by Sarah Meyer 1 and Francisco Olivera 2, Ph.D., P.E. May 2007 Contents: 1. Goals of Exercise & Additional Resources
Floodplain Mapping & Hydraulic Analysis with HEC-GeoRAS 4.1.1 and ArcGIS 9.1 Prepared by Sarah Meyer 1 and Francisco Olivera 2, Ph.D., P.E. May 2007 Contents: 1. Goals of Exercise & Additional Resources
_Tutorials. Arcmap. Linking additional files outside from Geodata
 _Tutorials Arcmap Linking additional files outside from Geodata 2017 Sourcing the Data (Option 1): Extracting Data from Auckland Council GIS P1 First you want to get onto the Auckland Council GIS website
_Tutorials Arcmap Linking additional files outside from Geodata 2017 Sourcing the Data (Option 1): Extracting Data from Auckland Council GIS P1 First you want to get onto the Auckland Council GIS website
SMS v Culvert Structures. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
PlaceMap. Accommodation. Slide 1
 PlaceMap for Accommodation Slide 1 PlaceMap Using the power of Google Earth to store and display all of your spatial data in a much more dynamic way Google Earth is a free software program that lets you
PlaceMap for Accommodation Slide 1 PlaceMap Using the power of Google Earth to store and display all of your spatial data in a much more dynamic way Google Earth is a free software program that lets you
Readme for Civil Site Design for Civil 3D, AutoCAD and BricsCAD
 Readme for Civil Site Design for Civil 3D, AutoCAD and BricsCAD V18.21 This readme contains important information regarding the installation and use of Civil Site Design versions as described above. Civil
Readme for Civil Site Design for Civil 3D, AutoCAD and BricsCAD V18.21 This readme contains important information regarding the installation and use of Civil Site Design versions as described above. Civil
Objectives Learn how to work with projections in SMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same SMS project.
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in SMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in SMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same SMS project.
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in SMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in SMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same SMS project.
v SMS Tutorials Working with Rasters Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
GIS OPERATION MANUAL
 GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
v Overview SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
Exercise 4: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing
 Exercise 4: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing You can create NEW GIS data layers by digitizing on screen with an aerial photograph or other image as a back-drop. You can also digitize using imported
Exercise 4: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing You can create NEW GIS data layers by digitizing on screen with an aerial photograph or other image as a back-drop. You can also digitize using imported
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x
 Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
Stringer Topo. For BricsCAD and AutoCAD. Getting Started
 Stringer Topo For BricsCAD and AutoCAD Getting Started Table of Contents Typical Surveyors Workflow - Stringer Topo for CAD... 1 Module 1 - Introduction to Stringer Topo for CAD... 2 Module 2: Introduction
Stringer Topo For BricsCAD and AutoCAD Getting Started Table of Contents Typical Surveyors Workflow - Stringer Topo for CAD... 1 Module 1 - Introduction to Stringer Topo for CAD... 2 Module 2: Introduction
Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
Tutorial 7. Water Table and Bedrock Surface
 Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
FrontCounter BC Discovery Tool Instructions. NOTE: You must have Google Earth installed to use this tool.
 NOTE: You must have Google Earth installed to use this tool. These instructions are written for use with a Microsoft Windows Work Station. This tutorial will step you through navigating to and viewing
NOTE: You must have Google Earth installed to use this tool. These instructions are written for use with a Microsoft Windows Work Station. This tutorial will step you through navigating to and viewing
ISIS 1D. Quick Start Guide. Cost effective, integrated software solutions ch2mhill.com/isis
 ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
Data Visualization SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Data sets. 3 Open the Geometry and Solution Files
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Data Visualization 1 Introduction It is useful to view the geospatial data utilized as input and generated as solutions in the process of numerical analysis. It is also helpful
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Data Visualization 1 Introduction It is useful to view the geospatial data utilized as input and generated as solutions in the process of numerical analysis. It is also helpful
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
NMCRIS Map Service Application Feature Editing
 NMCRIS Map Service Application Feature Editing Exercise goal: Users will edit the polygonal boundaries for activities and resources in the NMCRIS Map Service. Important: This exercise is a sample presentation
NMCRIS Map Service Application Feature Editing Exercise goal: Users will edit the polygonal boundaries for activities and resources in the NMCRIS Map Service. Important: This exercise is a sample presentation
Tutorial 18: 3D and Spatial Analyst - Creating a TIN and Visual Analysis
 Tutorial 18: 3D and Spatial Analyst - Creating a TIN and Visual Analysis Module content 18.1. Creating a TIN 18.2. Spatial Analyst Viewsheds, Slopes, Hillshades and Density. 18.1 Creating a TIN Sometimes
Tutorial 18: 3D and Spatial Analyst - Creating a TIN and Visual Analysis Module content 18.1. Creating a TIN 18.2. Spatial Analyst Viewsheds, Slopes, Hillshades and Density. 18.1 Creating a TIN Sometimes
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk SSA
 Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
GIS Workshop Spring 2016
 1/ 14 GIS Geographic Information System. An integrated collection of computer software and data used to view and manage information about geographic places, analyze spatial relationships, and model spatial
1/ 14 GIS Geographic Information System. An integrated collection of computer software and data used to view and manage information about geographic places, analyze spatial relationships, and model spatial
TRIMBLE ACCESS PIPELINES USER GUIDE
 TRIMBLE ACCESS PIPELINES USER GUIDE Version 2018.00 Revision A June 2018 Contents Introduction 4 Jobs, tallies and joint maps 5 Stakeout 9 Pipelines jobs 10 To configure Pipeline options 10 To link weld
TRIMBLE ACCESS PIPELINES USER GUIDE Version 2018.00 Revision A June 2018 Contents Introduction 4 Jobs, tallies and joint maps 5 Stakeout 9 Pipelines jobs 10 To configure Pipeline options 10 To link weld
Create Geomark in Google Earth Tutorial
 Create Geomark in Google Earth Tutorial General business example a potential applicant / user wants to create an area of interest that can be shared electronically to another party eg: another agency,
Create Geomark in Google Earth Tutorial General business example a potential applicant / user wants to create an area of interest that can be shared electronically to another party eg: another agency,
