Advanced Tree Structures
|
|
|
- Della Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap
2 ST Recall, inar Search Tree (ST)is a special case of inar Tree ll elements stored in the left subtreeof a node with value K have values < K ll elements stored in the right subtreeof a node with value K have values >= K alanced ST 40 Problem of ST? Unbalance ctuall affects the operating time We need a ST which can be self-balanced
3 alanced ST: VL Tree n VL (delson-velskii and Landis) Tree is a binar search tree with a balanced condition alanced condition is relaed a little bit Ever node in the tree, the height of the left and right subtreesdiffer b at most 1 alanced ST: VL Tree Node 40 violates the VL propert VL tree 6
4 VL Tree 7 alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion asicall follows insertion strateg of ST Ma cause violation of VL tree propert Rebalance is needed For Eample fter adding, 4, 6 The Tree becomes unbalance Height = 0 Height = Rebalance is needed 4 6 8
5 alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion nl nodes that are on the path from the insertion point to the root might have their balance altered Rebalance the tree at the deepest such node guarantees that the entire tree satisfies the VL propert The rebalance method is called Rotation alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion Four situations of violation: Subtrees: z 1 z Insertion happens in z 1 or z 9 h h h+ Right-Right z 1 z z 1 z Left-Left Right-Left z 1 z z 1 z Left-Right
6 alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion k z 1 z z 1 z z 1 z Right-Right z z 1 Left-Left Right-Left Left-Right RL 1 RR LL LR LR RL 17 LR 11 alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion Right-Right Left-Left Right-Left Left-Right 1
7 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Rotation Two Rotations: Single Rotation Handle Left-Left and Right-Right situation Double Rotation Handle Left-Right and Left-Right situation 13 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Single Rotation Right-Right z 1 z z 1 z
8 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Single Rotation z 1 z 3 3 Left-Left 3 8 z 1 z alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Single Rotation How about Right-Left or Left-Right? Single Rotationcannot solve Right-Left and Left-Right cases Right-Left z 1 z z 1 z Left-Right 16
9 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Double Rotation z 1 z z 1 z Right-Left z 1 z 17 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Double Rotation Right-Left z 1 z z 1 z z 1 z
10 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Double Rotation Left-Right z 1 z z 1 z z 1 z alanced ST VL Tree: Insertion Right-Right Left-Left Right-Left Left-Right Single Rotation Single Rotation Double Rotation Double Rotation 0
11 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Rotation lgorithm Insert the nodeas the same as ST insertion Trace the path from the inserted node towards the root For each node encountered, check if heights of left and right subtree differ b at most 1 If es, go to net node If no, perform an appropriate rotation Stops When rotation is performed r, we ve checked all nodes in the path 1 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion Rotation Insert,, 3, 1, 19, Single Single Double
12 alanced ST: VL Tree: Insertion ompleit ompleit for VL Insertion is Ο(log n) 1. Insert a value to the tree: Ο(log n) Same as ordinar ST. Trace the path from the new leaf towards the root, for each node on the path: Ο(log n) heck height difference: Ο(1) If satisfies VL propert, proceed to net node If not, perform a rotation: Ο(1) hecking stops When a single rotation is performed r, we ve checked all nodes in the path 3 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion lgorithm Delete the nodeas the same as ST deletion Trace the path from the last node deleted towards the root For each node encountered, check if heights of left and right subtree differ b at most 1 If es, go to net node If no, perform an appropriate rotation ontinue to trace the path until we reach the root Unlike insertion, more than one node ma need rotation 4
13 alanced ST: VL Tree: Deletion Single Rotation h Delete in X I h+1 h-1 X I h+1 h+1 X I h h I h-1 * The height of Inside subtree (I) can be h-1 alanced ST: VL Tree: Deletion Double Rotation I h+1 h h+1 h-1 I 1 I Delete in X I 1 I X h I 1 I X h I X I 1 h I I 1 I h-1 6
14 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion Single Rotation h-1 h+1 k I I Double Rotation h-1 h+1 I I 1 I I 1 I 1 I 7 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion Single Rotation I k I Double Rotation k I I 1 I I 1 I 1 I 8
15 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion 1 6 Single Rotation Single Rotation 9 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion 1 6 Single Rotation Double Rotation
16 alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion Delete 46, 9, 6, 9, in this VL Tree alanced ST VL Tree: Deletion Delete 46, 9, 6, 9, Single Double 3
17 Interval Heap Locate both Ma and Min values ombine with Ma- and Min-heap omplete binar tree Each node Must has elements ecept the last one [a, b] is the interval, a b The interval is contained in its parent s interval 0,70,60 30,0 1,80 18,90 1,0 46,60 30,60 3,0 Left values define a min heap Right values define a ma heap 33 Interval Heap Insert dd the value to the last node (dd new node if needed). If the node alread has a value, compare new value is bigger, the right value new value is smaller, the left value 3. Repeat to swap if the new value is bigger than the upper bound of its parent (Ma-heap) 4. Repeat to swap if the new value is smaller than the lower bound of its parent (Min-heap),90 1,80 30,60 0,70 1,0 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 18,19 34
18 Interval Heap Insert dd the value to the last node (dd new node if needed). If the node alread has a value, compare new value is bigger, the right value new value is smaller, the left value 3. Repeat to swap if the new value is bigger than the upper bound of its parent (Ma-heap) 4. Repeat to swap if the new value is smaller than the lower bound of its parent (Min-heap),90 1,80 30,60 0,70 1,0 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 16, Interval Heap Insert 8 1. dd the value to the last node (dd new node if needed). If the node alread has a value, compare new value is bigger, the right value new value is smaller, the left value 3. Repeat to swap if the new value is bigger than the upper bound of its parent (Ma-heap) 4. Repeat to swap if the new value is smaller than the lower bound of its parent (Min-heap),90 1,80 1,8 30,60 0,70 1,0 1,8 18,80 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 18,8 18,0 36
19 Interval Heap Insert 1. dd the value to the last node (dd new node if needed). If the node alread has a value, compare new value is bigger, the right value new value is smaller, the left value 3. Repeat to swap if the new value is bigger than the upper bound of its parent (Ma-heap) 4. Repeat to swap if the new value is smaller than the lower bound of its parent (Min-heap),90,90,80 1,80 30,60 0,70 1,0 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 1, Interval Heap Insert 1. dd the value to the last node (dd new node if needed). If the node alread has a value, compare new value is bigger, the right value new value is smaller, the left value 3. Repeat to swap if the new value is bigger than the upper bound of its parent (Ma-heap) 4. Repeat to swap if the new value is smaller than the lower bound of its parent (Min-heap),90 1,80 30,60 0,70 1,0 1, 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 18,
20 Interval Heap Remove Min 1. Replace the left value of root with the left value of the last node. Shift down with the lower bound if necessar 3. Swap two values if lower bound > upper bound,90 18,90 1,90 18,80 1,80 30,60 0,70 18,0 1,0 46,60 3,0,60 30,0 18, Interval Heap Remove Ma 1. Replace the left value of root with the left value of the last node. Shift down with the upper bound if necessar 3. Swap two values if lower bound > upper bound,90,19,80 1,80 1,19 1,70 30,60 0,70 0,19 19,0 19,60 1,0 46,60 3,0,60,0 0, 30,
21 Heap Time ompleit Time ompleit Heap Interval Heap Insert Remove (log(n)) (log(n)) (log(n)) (log(n)) 41
Advanced Tree. Structures. AVL Tree. Outline. AVL Tree Recall, Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special case of. Splay Tree (Ch 13.2.
 ttp://1...0/csd/ Data tructure Capter 1 Advanced Tree tructures Dr. atrick Can cool of Computer cience and Engineering out Cina Universit of Tecnolog AVL Tree Recall, Binar earc Tree (BT) is a special
ttp://1...0/csd/ Data tructure Capter 1 Advanced Tree tructures Dr. atrick Can cool of Computer cience and Engineering out Cina Universit of Tecnolog AVL Tree Recall, Binar earc Tree (BT) is a special
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
AVL Trees / Slide 2. AVL Trees / Slide 4. Let N h be the minimum number of nodes in an AVL tree of height h. AVL Trees / Slide 6
 COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
Lecture Overview. Readings. Recall: Binary Search Trees (BSTs) The importance of being balanced. AVL trees. Balance Insert. Other balanced trees
 alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
AVL Trees. Version of September 6, AVL Trees Version of September 6, / 22
 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
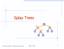 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Data Structure. Chapter 10 Search Structures (Part II)
 Data Structure Chapter 1 Search Structures (Part II) Instructor: ngela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline VL trees Introduction
Data Structure Chapter 1 Search Structures (Part II) Instructor: ngela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline VL trees Introduction
More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees. CS300 Data Structures (Fall 2013)
 More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both
More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both
More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete
 More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both subtrees are
More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both subtrees are
AVL Trees. Reading: 9.2
 AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Chapter 6 Heapsort 1
 Chapter 6 Heapsort 1 Introduce Heap About this lecture Shape Property and Heap Property Heap Operations Heapsort: Use Heap to Sort Fixing heap property for all nodes Use Array to represent Heap Introduce
Chapter 6 Heapsort 1 Introduce Heap About this lecture Shape Property and Heap Property Heap Operations Heapsort: Use Heap to Sort Fixing heap property for all nodes Use Array to represent Heap Introduce
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
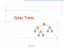 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
Splay Trees 3/20/14. Splay Trees. Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees. note that two keys of equal value may be wellseparated (7,T) (1,Q) (1,C) (5,H)
 Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A)
 ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari, PEng, SMIEEE Associate Professor Software Technologies Applied Research (STAR) Group Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University
ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari, PEng, SMIEEE Associate Professor Software Technologies Applied Research (STAR) Group Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
CS Transform-and-Conquer
 CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2009-2010 Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) The bad news about BSTs... Problem with BSTs is that there
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2009-2010 Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) The bad news about BSTs... Problem with BSTs is that there
Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 7 DCI FEEI TUKE. Balanced Trees
 Balanced Trees AVL trees reconstruction of perfect balance can be quite expensive operation less rigid criteria of balance (e.g. AVL) [2] inorder, self-balancing binary search tree (BST) Definition: AVL
Balanced Trees AVL trees reconstruction of perfect balance can be quite expensive operation less rigid criteria of balance (e.g. AVL) [2] inorder, self-balancing binary search tree (BST) Definition: AVL
Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms
 Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
Balanced BST. Balanced BSTs guarantee O(logN) performance at all times
 Balanced BST Balanced BSTs guarantee O(logN) performance at all times the height or left and right sub-trees are about the same simple BST are O(N) in the worst case Categories of BSTs AVL, SPLAY trees:
Balanced BST Balanced BSTs guarantee O(logN) performance at all times the height or left and right sub-trees are about the same simple BST are O(N) in the worst case Categories of BSTs AVL, SPLAY trees:
Best-Case upper limit on the time for insert/delete/find of an element for a BST withnelements?
 S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
Data Structures Lesson 7
 Data Structures Lesson 7 BSc in Computer Science University of New York, Tirana Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba 1-1 Binary Search Trees For large amounts of input, the linear access time of linked lists
Data Structures Lesson 7 BSc in Computer Science University of New York, Tirana Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba 1-1 Binary Search Trees For large amounts of input, the linear access time of linked lists
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 26 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Balanced Binary Search trees AVL trees Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College - CS
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 26 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Balanced Binary Search trees AVL trees Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College - CS
[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium
![[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists, Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium [6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists, Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium](/thumbs/88/117928360.jpg) [6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. Mcreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \ new representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth nnual M Smposium on Theor of omputing, (1977), pp.49-60. [7] L. J. Guibas, R. Sedgewick,
[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. Mcreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \ new representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth nnual M Smposium on Theor of omputing, (1977), pp.49-60. [7] L. J. Guibas, R. Sedgewick,
B Tree. Also, every non leaf node must have at least two successors and all leaf nodes must be at the same level.
 B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
AVL Trees Heaps And Complexity
 AVL Trees Heaps And Complexity D. Thiebaut CSC212 Fall 14 Some material taken from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~kube/cls/0/lectures/lec4.avl/lec4.pdf Complexity Of BST Operations or "Why Should We Use BST Data
AVL Trees Heaps And Complexity D. Thiebaut CSC212 Fall 14 Some material taken from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~kube/cls/0/lectures/lec4.avl/lec4.pdf Complexity Of BST Operations or "Why Should We Use BST Data
Graduate Algorithms CS F-07 Red/Black Trees
 Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)
Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)
2. We ll add new nodes to the AVL as leaves just like we did for Binary Search Trees (BSTs). a) Add the key 90 to the tree?
 eam #: bsent:. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that
eam #: bsent:. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that
Data Structures (CS 1520) Lecture 23 Name:
 ata Structures (S 152) Lecture 23 Name: 1. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his
ata Structures (S 152) Lecture 23 Name: 1. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES STUDY NOTES. The left subtree of each node contains values that are smaller than the value in the given node.
 UNIT 2 TREE STRUCTURES ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES STUDY NOTES Binary Search Trees- AVL Trees- Red-Black Trees- B-Trees-Splay Trees. HEAP STRUCTURES: Min/Max heaps- Leftist Heaps- Binomial Heaps- Fibonacci
UNIT 2 TREE STRUCTURES ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES STUDY NOTES Binary Search Trees- AVL Trees- Red-Black Trees- B-Trees-Splay Trees. HEAP STRUCTURES: Min/Max heaps- Leftist Heaps- Binomial Heaps- Fibonacci
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees
 Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
CMPT 225. Red black trees
 MPT 225 Red black trees Red-black Tree Structure red-black tree is a BST! Each node in a red-black tree has an etra color field which is red or black In addition false nodes are added so that every (real)
MPT 225 Red black trees Red-black Tree Structure red-black tree is a BST! Each node in a red-black tree has an etra color field which is red or black In addition false nodes are added so that every (real)
Search Structures. Kyungran Kang
 Search Structures Kyungran Kang (korykang@ajou.ac.kr) Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni and Susan Anderson-Freed, Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, 2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2007. Contents Binary Search
Search Structures Kyungran Kang (korykang@ajou.ac.kr) Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni and Susan Anderson-Freed, Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, 2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2007. Contents Binary Search
CS 314H Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012 Programming Assignment #6 Treaps Due November 11/14/16, 2012
 CS H Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 202 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November //, 202 In this assignment ou will work in pairs to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure
CS H Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 202 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November //, 202 In this assignment ou will work in pairs to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Data Structures (CS 1520) Lecture 19 Name:
 . n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that a VL tree
. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that a VL tree
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
l Heaps very popular abstract data structure, where each object has a key value (the priority), and the operations are:
 DDS-Heaps 1 Heaps - basics l Heaps very popular abstract data structure, where each object has a key value (the priority), and the operations are: l insert an object, find the object of minimum key (find
DDS-Heaps 1 Heaps - basics l Heaps very popular abstract data structure, where each object has a key value (the priority), and the operations are: l insert an object, find the object of minimum key (find
l So unlike the search trees, there are neither arbitrary find operations nor arbitrary delete operations possible.
 DDS-Heaps 1 Heaps - basics l Heaps an abstract structure where each object has a key value (the priority), and the operations are: insert an object, find the object of minimum key (find min), and delete
DDS-Heaps 1 Heaps - basics l Heaps an abstract structure where each object has a key value (the priority), and the operations are: insert an object, find the object of minimum key (find min), and delete
Implementation of Dictionaries using AVL Tree
 Implementation of Dictionaries using VL Tree Kanimozhi alaraman Indiana State University Terre Haute IN, US kbalaraman@cs.indstate.edu November 8, 2011 bstract The paper is to implement Sorted Dictionaries
Implementation of Dictionaries using VL Tree Kanimozhi alaraman Indiana State University Terre Haute IN, US kbalaraman@cs.indstate.edu November 8, 2011 bstract The paper is to implement Sorted Dictionaries
AVL trees and rotations
 AVL trees and rotations Part of written assignment 5 Examine the Code of Ethics of the ACM Focus on property rights Write a short reaction (up to 1 page single-spaced) Details are in the assignment Operations
AVL trees and rotations Part of written assignment 5 Examine the Code of Ethics of the ACM Focus on property rights Write a short reaction (up to 1 page single-spaced) Details are in the assignment Operations
CS 314H Honors Data Structures Fall 2017 Programming Assignment #6 Treaps Due November 12/15/17, 2017
 CS H Honors Data Structures Fall 207 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November 2//7, 207 In this assignment ou will work individuall to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure called
CS H Honors Data Structures Fall 207 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November 2//7, 207 In this assignment ou will work individuall to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure called
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees
 Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
CS 234. Module 8. November 15, CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22
 CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE Data Structures and Algoritms Capter 4: Trees (AVL Trees) Text: Read Weiss, 4.4 Izmir University of Economics AVL Trees An AVL (Adelson-Velskii and Landis) tree is a binary searc tree wit a balance
CE Data Structures and Algoritms Capter 4: Trees (AVL Trees) Text: Read Weiss, 4.4 Izmir University of Economics AVL Trees An AVL (Adelson-Velskii and Landis) tree is a binary searc tree wit a balance
Binary Trees. Binary Search Trees
 Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Binary search trees. We can define a node in a search tree using a Python class definition as follows: class SearchTree:
 Binary search trees An important use of binary trees is to store values that we may want to look up later. For instance, a binary search tree could be used to store a dictionary of words. A binary search
Binary search trees An important use of binary trees is to store values that we may want to look up later. For instance, a binary search tree could be used to store a dictionary of words. A binary search
1-1. Functions. Lesson 1-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary. Scan Lesson 1-1. Write two things that you already know about functions.
 1-1 Functions What You ll Learn Scan Lesson 1- Write two things that ou alread know about functions. Lesson 1-1 Active Vocabular New Vocabular Write the definition net to each term. domain dependent variable
1-1 Functions What You ll Learn Scan Lesson 1- Write two things that ou alread know about functions. Lesson 1-1 Active Vocabular New Vocabular Write the definition net to each term. domain dependent variable
Priority Queues and Binary Heaps
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis. Spring 2013
 CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
Fundamental Algorithms
 WS 2007/2008 Fundamental Algorithms Dmytro Chibisov, Jens Ernst Fakultät für Informatik TU München http://www14.in.tum.de/lehre/2007ws/fa-cse/ Fall Semester 2007 1. AVL Trees As we saw in the previous
WS 2007/2008 Fundamental Algorithms Dmytro Chibisov, Jens Ernst Fakultät für Informatik TU München http://www14.in.tum.de/lehre/2007ws/fa-cse/ Fall Semester 2007 1. AVL Trees As we saw in the previous
CS350: Data Structures B-Trees
 B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
Data Structure Chapter 6
 ata Structure hapter Non-inary Trees r. Patrick han School of omputer Science and ngineering South hina University of Technology Outline Non-inary (eneral) Tree (h.) Parent Pointer mplementation (h.) ist
ata Structure hapter Non-inary Trees r. Patrick han School of omputer Science and ngineering South hina University of Technology Outline Non-inary (eneral) Tree (h.) Parent Pointer mplementation (h.) ist
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Splay tree, tree Marko Berezovský Radek Mařík PAL 2012
 Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y To read x--y [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y To read x--y [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
9. Heap : Priority Queue
 9. Heap : Priority Queue Where We Are? Array Linked list Stack Queue Tree Binary Tree Heap Binary Search Tree Priority Queue Queue Queue operation is based on the order of arrivals of elements FIFO(First-In
9. Heap : Priority Queue Where We Are? Array Linked list Stack Queue Tree Binary Tree Heap Binary Search Tree Priority Queue Queue Queue operation is based on the order of arrivals of elements FIFO(First-In
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Lecture No. 10. Reference Variables. 22-Nov-18. One should be careful about transient objects that are stored by. reference in data structures.
 Lecture No. Reference Variables One should be careful about transient objects that are stored by reference in data structures. Consider the following code that stores and retrieves objects in a queue.
Lecture No. Reference Variables One should be careful about transient objects that are stored by reference in data structures. Consider the following code that stores and retrieves objects in a queue.
CSC 263 Lecture 4. September 13, 2006
 S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
Part 2: Balanced Trees
 Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
Splay tree, tree Marko Berezovský Radek Mařík PAL 2012
 Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y x--y To read [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y x--y To read [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
A red-black tree is a balanced binary search tree with the following properties:
 Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Lecture 9: Balanced Binary Search Trees, Priority Queues, Heaps, Binary Trees for Compression, General Trees
 Lecture 9: Balanced Binary Search Trees, Priority Queues, Heaps, Binary Trees for Compression, General Trees Reading materials Dale, Joyce, Weems: 9.1, 9.2, 8.8 Liang: 26 (comprehensive edition) OpenDSA:
Lecture 9: Balanced Binary Search Trees, Priority Queues, Heaps, Binary Trees for Compression, General Trees Reading materials Dale, Joyce, Weems: 9.1, 9.2, 8.8 Liang: 26 (comprehensive edition) OpenDSA:
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Adding a Node to (Min) Heap. Lecture16: Heap Sort. Priority Queue Sort. Delete a Node from (Min) Heap. Step 1: Add node at the end
 Adding a Node to (Min) Heap (F) Lecture16: Heap Sort Takes log steps if nodes are added Step 1: Add node at the end Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Step 2: Make swap if parent is bigger Step
Adding a Node to (Min) Heap (F) Lecture16: Heap Sort Takes log steps if nodes are added Step 1: Add node at the end Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Step 2: Make swap if parent is bigger Step
Outline. Definition. 2 Height-Balance. 3 Searches. 4 Rotations. 5 Insertion. 6 Deletions. 7 Reference. 1 Every node is either red or black.
 Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
Multiway searching. In the worst case of searching a complete binary search tree, we can make log(n) page faults Everyone knows what a page fault is?
 Multiway searching What do we do if the volume of data to be searched is too large to fit into main memory Search tree is stored on disk pages, and the pages required as comparisons proceed may not be
Multiway searching What do we do if the volume of data to be searched is too large to fit into main memory Search tree is stored on disk pages, and the pages required as comparisons proceed may not be
Data Structures and Algorithms(12)
 Ming Zhang "Data s and Algorithms" Data s and Algorithms(12) Instructor: Ming Zhang Textbook Authors: Ming Zhang, Tengjiao Wang and Haiyan Zhao Higher Education Press, 28.6 (the "Eleventh Five-Year" national
Ming Zhang "Data s and Algorithms" Data s and Algorithms(12) Instructor: Ming Zhang Textbook Authors: Ming Zhang, Tengjiao Wang and Haiyan Zhao Higher Education Press, 28.6 (the "Eleventh Five-Year" national
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
Lecture 7. Transform-and-Conquer
 Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSC : Lecture 7 CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique CSC : Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a
CSC : Lecture 7 CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique CSC : Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps and Priority Queues From here, we will look at some ways that trees are used in other structures. First,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps and Priority Queues From here, we will look at some ways that trees are used in other structures. First,
Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps ( 7.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic
 1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 7. Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique. Transform and Conquer
 // CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more
// CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more
Advanced Tree Data Structures
 Advanced Tree Data Structures Fawzi Emad Chau-Wen Tseng Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Binary trees Traversal order Balance Rotation Multi-way trees Search Insert Overview
Advanced Tree Data Structures Fawzi Emad Chau-Wen Tseng Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Binary trees Traversal order Balance Rotation Multi-way trees Search Insert Overview
CSE100. Advanced Data Structures. Lecture 8. (Based on Paul Kube course materials)
 CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 8 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs
CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 8 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs
Red-Black Trees 10/19/2009. Red-Black Trees. Example. Red-Black Properties. Black Height. Example
 lgorithms Red-lak Trees 13-2 Red-lak Trees Red-lak Trees ll binar searh tree operations take O(h) time, here h is the height of the tree Therefore, it is important to `balane the tree so that its height
lgorithms Red-lak Trees 13-2 Red-lak Trees Red-lak Trees ll binar searh tree operations take O(h) time, here h is the height of the tree Therefore, it is important to `balane the tree so that its height
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees:
 DATA STRUCTERS WITH C 10CS35 UNIT 8 : EFFICIENT BINARY SEARCH TREES 8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees: An optimal binary search tree is a binary search tree for which the nodes are arranged on levels such
DATA STRUCTERS WITH C 10CS35 UNIT 8 : EFFICIENT BINARY SEARCH TREES 8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees: An optimal binary search tree is a binary search tree for which the nodes are arranged on levels such
B + -trees. Kerttu Pollari-Malmi
 B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
