Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winkler foundation
|
|
|
- Antony Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, 211 / pp (UDC: : ) Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation R. J. Aziz 1, A. A. Al-Azzawi 2 and Ali A. Al-Ani 3 1 Nahrian University, Baghdad, Iraq riyadh1948@yahoo.com 2 Nahrian University, Baghdad, Iraq dr_adel_azzawi@yahoo.com 3 Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq ali1972@yahoo.com Abstract In this research, the hyperbolic paraboloidal shell is investigated. The two components of the interacting system; the soil and the shell foundation, are modelled using the finite element method. In this study, 9-node isoparametric degenerated shell element with five degrees of freedom at each node was used. The soil-structure interaction between the shell elements and the supporting medium are model in this study by representing the soil medium by certain analytical equivalent such as Winler model with both normal compressional and tangential frictional resistances. A parametric studies have been carried out to investigate the effect of some important parameters on the behaviour of shell foundations. These parameters are: shell thicness, shell warp, ridge and edge beams cross-sectional dimensions. Comparison between the results obtained by the present analysis and those obtained by many other investigations are made. The present analysis shows satisfactory results when compared with those obtained by other studies with largest percentage difference of % in the value of the vertical displacement value. Key words: Elastic analysis, finite element, hypar shell, Winler foundation. 1. Introduction Shells, because their curved topology, have larger stiffness and strength than comparable and corresponding plane surface structural elements. This form enables shells to put a minimum of material to maximum structural advantages. While a plain element lie a roof slab undergoes bending when subjected to a vertical loads including self-weight, a shell which is non-planar or a spatial system sustains the applied loads primarily by direct in-plane or membrane forces (compression or tension). Bending forces, even when present, it normally assumes only a place of secondary importance. Among the shells, which have come into wider use in foundations, the hyperbolic paraboloid (or briefly hypar) shell has been the most important type. Besides its geometric simplicity, resulting from its straight-lines property, the hypar shell has high structural efficiency. Four such shell quadrants jointed together by a system of edge and ridge beams, the latter terminating at the column base (Fig. 1) have been widely used as column foundation in many parts of the world (Kurian 1982). A typical folded plate than can be
2 2 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation considered for use as foundation is the pyramidal combination of four inclined trapezoidal plate elements, that can support a column at its centre. Since these pyramidal folded plates can be rendered square or rectangular in plan, they can be combined to form multiple units to serve as combined footings. The construction is simpler as hypar footing. The pyramid shell foundation can be modeled by flat shell finite elements. Fig. 1. Individual hypar footing. The literature pertaining to the theoretical studies on the behavior of shell foundations is reviewed herein. Bairagi and Buragohain, (1985) have applied the finite element technique to study the stress analysis of a square hypar footing under axial and moment loads. In that study, various three dimensional isoparametric finite elements have been used to model the shell and the soil half space. Melersi, (1986) presented an approximate elastic solution to the statical problem of a reinforced concrete shell foundation, the method of analysis being based on the finite difference procedure in the variational formulation. Kurian, (1993) investigated the performance of shell foundations on soft soils. Two types of shell foundations have been used, which were the hypar and the conical shell foundations. The soil was represented by Winler springs, in which the subgrade reaction ( n ) of the soil is varied to simulate a wide range of soil conditions. Kurian, (1994) studied the behavior of shell foundations under subsidence of core soil. This problem has been addressed in respect of shell foundations in a single cone, a double cone and a hyperbolic paraboloid. These systems were analyzed by the finite element method. In his third paper, Kurian (1995) presented a parametric study on the behavior of conical shell foundations. The finite element method was also used with simulating the soil as a Winler medium. The study was conducted to investigate the influence of the rise and thicness of the shell and the existence of ring beams at top and bottom.
3 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Al-Azzawi, (2) studied the nonlinearity in material and geometry by using the finite element method for the analysis of reinforced concrete shell foundations under static loading. The response of reinforced concrete shell foundation was traced through its elastic, inelastic and ultimate load ranges. He also used a layered approach in his analysis by dividing the concrete into eight layers. Also, a number of steel reinforcement layers were smeared into the concrete layers at appropriate position. The shell was modeled by using nine-node curved shell element. Hassan, (22) investigated the behavior of hypar and conical shells on Winler foundations. The two components of the interaction system; the soil and the foundation, were modeled using the finite element method. Four-node elements with six and five degrees of freedom per node were used in the analysis. 2. Finite element method The Ahmad-type degenerated isoparametric shell elements based on independent rotational and translational displacement interpolation have become popular in recent years. In this element, the Mindlin-type theory is employed. The normal to the middle surface of the three-dimensional element is constrained to remain straight after deformation in order to overcome the numerical difficulty associated with the large stiffness ratio in the through-thicness direction. Also, this element neglects the strain energy associated with stresses perpendicular to the local ' ' x y surface and constrains the normal stress component to zero to simplify the constitutive equations. By adopting the isoparametric geometric description, the element can be used to represent thin and thic shells with arbitrary shapes, circumventing the complexities of classical shell theory and differential geometry (Ahmad et al. 197). The four coordinate systems used in the degenerated shell element formulations are shown in Fig. 2. (1) Global Cartesian coordinate system (x, y, z or x i ). (2) Natural coordinate system (,,). (3) Local Cartesian coordinate system ( ' ' ' ' x, y,z or xi ). (4) Nodal Cartesian coordinate system ( V 1,V2, V 3 ).
4 4 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Fig. 2. Coordinate systems for the degenerated shell element. 3. Elastic foundation For a foundation represented by Winler model for both compressional and frictional resistances, the stiffness matrix is given by Al-Azzawi (1995): [R w ].. [R w ].. Kf [R w ] nn where n is the total number of nodes per element, and R w is defined as: (1)
5 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, R w K f1 K f2 K f3 K f4 Kf5 The stiffness of foundation is distributed on the nodes of the element lie the distribution of pressure load on the bottom surface of the element ( = 1), thus at node 11 (3) K f1 ' x N (ξ,η) J(ξ,η,ζ ) dξ dη 11 K K f4 K K f2 f5 f3 11 y z 11 x y 11 ' ' ' N (ξ,η) J(ξ,η,ζ ) dξ dη N (ξ,η) J(ξ,η,ζ ) dξ dη s h 2 ' s N (ξ,η) J(ξ,η,ζ ) dξ dη h N (ξ,η) J(ξ,η,ζ ) dξ dη 2 ', ' and ' are the subgrade reaction coefficients in the local coordinates where x y z ' ' ' x, y and z, hs is the thicness of the shell at node, N (ξ, η) is the shape function at node and J(ξ,η, ζ) is the determinant of the Jacobian matrix. (2) (4) (5) (6) (7) 4. Applications and discussions In this paper, an example have been analyzed by a computer program named SFAP (Shell Foundation Analysis Program), (Al-Azzawi 2) which is developed from a program named PLAST (Huang 1989) by adding subroutines of foundation properties and stiffnesses in order to be capable of solving different types of shell foundations. 4.1 Hyperbolic paraboloidal shell foundation Melersi (1986) analyzed a square hypar shell foundation by the finite difference method. The square hypar footing has 5m 5m in plan with.5m rise and.1m thicness. The edge and ridge beams cross sectional dimensions are.2m.3m and the footing is subjected to a central vertical load of 16N. The elastic properties of the hypar shell are (E = N/m 2 and = ). The footing is resting on a Winler foundation with K x = K y = K z = 12 N/m 2 /m).
6 6 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation The problem is solved by the finite element method and due to symmetry one quadrant of the shell is taen for the analysis. Due to symmetry, one quadrant of footing is analyzed by using 9- node isoparametric degenerated shell elements as shown in Fig. 3. This problem was also solved by Hassan (22) who used a different finite element model. In the present study, the results are compared with both Melersi (1986) and Hassan (22). Figure 4 shows the variation of the vertical displacement along the diagonal of the footings. Figures 5 and 6 show the variation of axial force and the bending moment in the edge beam, respectively. Figures 7 and 8 show the variation of axial force and bending moment in ridge beam, respectively. The percentage difference in results (for the vertical displacement) between the present study and Melersi (1986) is about 4.49 %. The percentage difference in results between the present study and Hassan (22) is about 7.83 %. Fig. 3. Finite element mesh for hyperbolic paraboloidal footing with edge and ridge beams.
7 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Fig. 4. Variation of vertical displacement along the diagonal of hypar shell. Fig. 5. Variation of axial force in ridge beam. Fig. 6. Variation of bending moment in ridge beam.
8 8 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Fig. 7. Variation of axial force in edge beam. Fig. 8. Variation of bending moment in edge beam. 4.2 Parametric study In order to study the influence of variation of selected parameters on the behavior of the hypar shell foundations, four parameters are considered which are: shell warp, shell thicness, ridge beam cross sectional dimensions and edge beam cross sectional dimensions Shell warp The influence of variation of shell warp ( f ab ) on its behavior is now considered. Different values are taen ( =.8,.16,.24,.32,.4m -1 ). Figure 9 shows the variation of the vertical displacement along the diagonal. From this figure, it is seen that with increasing the shell warp, the vertical displacement decreases near and at the center of the hypar shell while it increases when it approaches the edges. This behavior is due to the increase in the concentrated load component towards the edges of the shell with the increase in the shell warp. Figures 1 and 11 show the variation of the bending moment and shear force in the ridge beam, respectively. From these figures, it can be noticed that the bending moment and the shearing force decreases with the increasing in the shell warp, this is due to the decreases in the concentrated load normal component which causes the bending moment and the shear force in
9 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, the ridge beam. Figure 12 shows that the variation of the axial force in the ridge beam decreases. From this figure, it is seen that the axial force decreases with the increase in the shell warp which is due to reason that the increase in the shell warp will cause a decrease in the membrane shearing stress in the shell Shell thicness The influence of variation of shell thicness is now considered. Five values of shell thicness were considered in this study (h =.1,.15,.2,.25 and.3m). Figure 13 shows the variation of the vertical displacement along the diagonal of the hypar footing. From this figure it is found that the vertical displacement decreases at the center of the footing (i.e. under the concentrated load) and increases near the edges. This behavior is the result of increasing the shell rigidity, i.e. the hypar shell tries to reduce the vertical displacement. Figures 14 and 15 show the variation in the bending moment and the shearing force in the ridge beams, respectively. It is seen that the bending moments and the shearing forces decreases with the increase in the shell thicness which is due to the decrease in the variation of the vertical displacement. Figure 16 shows the variation of the axial force in the ridge beam. From this figure it is seen that the axial force decreases with the increase in the shell thicness Ridge beam cross sectional dimensions Four values of ridge beam cross sectional dimensions are taen (.2m.2m,.2m.25m,.2m.3m and.2m.35m). Figure 17 shows the variation of the vertical displacement along the ridge beam. It is seen that with increasing the cross sectional dimensions of the ridge beam, the vertical displacement at the center of the hypar shell will decrease. This behavior is due to the four ridge beams meeting at the center of the hypar shell and they will increase the hypar shell stiffness and so to decrease the vertical displacement at the same position. Figures 18, 19 and 2 show the variation of the bending moment, shear force and axial force in the ridge beam, respectively. The values of the bending moment, shearing force and axial force in the ridge beam will increases with increasing its cross sectional dimensions. This behavior is due to the fact that the ridge beam stiffness is increased and will attract more forces Edge beam cross sectional dimensions Four values of edge beam cross sectional dimensions are taen (.2m.2m,.2m.25m,.2m.3m and.2m.35m). Figure 21 shows the variation of the vertical displacement along the edge beam. It is seen that with increasing the cross sectional dimensions of the edge beam, the vertical displacement at the center of the beams will decrease while it will increase near edges. This behavior is due to the increase in the edge beam rigidity by increasing its cross sectional dimensions. Figures 22 and 23 show the variation of the bending moment and the shear force in the edge beam. It is seen that with increasing the cross sectional dimensions of the edge beam, the bending moment and the axial force in the edge beam will increase which is due to the increase in the beam stiffness. Figure 24 shows the variation of Axial force in the edge beam. It is seen that the shear force increases at the center of the beam with increasing its cross sectional dimensions which is due to the increase in its stiffness.
10 1 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Fig. 9. Effect of variation of shell warp on the vertical displacement along the diagonal. Fig. 1. Effect of variation of shell warp on the bending moment in ridge beam. Fig. 11. Effect of variation of shell warp on the shear force in ridge beam.
11 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Fig. 12. Effect of variation of shell warp on the axial force in ridge beam. Fig. 13. Effect of variation of shell thicness on the vertical displacement along thediagonal. Fig. 14. Effect of variation of shell thicness on the bending moment in ridge beam.
12 12 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Fig. 15. Effect of variation of shell thicness on the shear force in ridge beam. Fig. 16. Effect of variation of shell thicness on the axial force in ridge beam Fig. 17. Effect of variation of ridge beam cross sectional dimensions on the vertical displacement along ridge beam.
13 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Fig. 18. Effect of variation of ridge beam cross sectional dimensions on the bending moment in ridge beam. Fig. 19. Effect of variation of ridge beam cross sectional dimensions on the shear force in ridge beam. Fig. 2. Effect of variation of ridge beam cross sectional dimensions on the axial force in ridge beam.
14 14 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Fig. 21. Effect of variation of edge beam cross sectional dimensions on the vertical displacement along edge beam. Fig. 22. Effect of variation of edge beam cross sectional dimensions on the bending moment in edge beam.
15 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Fig. 23. Effect of variation of edge beam cross sectional dimensions on the shear force in edge beam. Fig..24. Effect of variation of edge beam cross sectional dimensions on the axial force in edge beam. 5. Conclusions The major conclusions obtained from the study of the hypar shell foundation are: 1. Increasing the shell warp from.8m -1 to.16m -1. decreases the vertical displacement by about (31.5 %) near and at the center of the hypar shell while it increases by about (7.11 %) when it approaches the edges. decreases the bending moments in the ridge beams by about (53.53 %). decreases the shearing forces in the ridge beams by about (24.94 %). decreases the axial forces in the ridge beams by about (16.33 %). 2. Increasing shell thicness from.1 m to.15 m.
16 16 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation decreases the vertical displacement by about (5.2 %) at the center of the hypar shell while it increases by about (1.78 %) when it approaches the edges. decreases the bending moments in the ridge beams by about (21.22 %). decreases the shearing forces in the ridge beams by about (15.97 %). decreases the axial force in the ridge beams by about (2.48 %). 3. Increasing edge beam cross sectional dimensions from.2m.2m to.2m.25m. decreases the vertical displacement by about (1.25 %) at the center of the edge beams while it increases about (19.53 %) when it approaches the edges. increasing the bending moments in the edge beams by about (41.46 %). increasing the axial forces in the edge beams by about (11.43 %). increasing the shearing forces by about (29.59 %) at the center of edge beams while it decreases by about (23.6 %) at the ends of those beams. 4. Increasing ridge beam cross sectional dimensions from.2m.2m to.2m.25m. decreases the vertical displacement by about (2.95 %) at the center of the hypar shell foundation. increasing the bending moments in the ridge beams by about (41.42 %). increasing the shearing forces in the ridge beams by about (23.53 %). increasing the axial forces in the ridge beams by about (6.6 %). 5. The most important aspect of the geometry of the hypar shell is its straight-line property, which renders its construction practically as simple as that of plain structure. In the in-situ method of construction, the foundation is poured on soil that is cut and dressed to the correct profile of the shell.
17 Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics / Vol. 5 / No. 1, Извод Еластична анализа коначним елементима хyпар (хипербполично параболоидне) љуске на Винклеровој подлози R. J. Aziz 1, A. A. Al-Azzawi 2 and Ali A. Al-Ani 3 1 Nahrian University, Baghdad, Iraq riyadh1948@yahoo.com 2 Nahrian University, Baghdad, Iraq dr_adel_azzawi@yahoo.com 3 Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq ali1972@yahoo.com Резиме У овом раду, проучавана је хиперболична параболоидна љуска. Две компоненте система интеракције, тло и подлоге од љуске су моделиране користећи методу коначних елемената. У овој студији је коришћен деветоцворни изопараметарски дегенерисани елемент љуске са пет степена слободе у сваком чвору. Интеракција тло-структура измедју елемената љуске и потпорног слоја је моделована у овој студији представљањем слоја тла одређеним аналитичким еквивалентима као што су Винклеров модел са нормалним компресивним и тангецијалним фрикционалним отпорима. Изведене су параметарске студије како би се истражио утицај неких важних параметара на понашање подлоге од љуске. Ти параметри су: дебљина љуске, витоперење љуске и димензије гредних пресека ивица. Извршена су поређења резултата добијених садашњом анализом и оних добијених многим другим истраживањима. Садашња анализа показује задовљавајуће резултате када се пореде са онима који су добијени другим студијама, са највецим процентом разлике од % у вредностима вертикалних померања. Клучне речи: Еластична анализа, коначни елементи, хyпар љуска, Wинклерова подлога References Ahmad S., Irons B. M. and Zieniewicz O. C. (197). Analysis of Thic and Thin Shell Structures by Curved Finite Elements, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2, Al-Ani A. A. (26).Finite Element Elastic Analysis of Shells on Winler Foundations, M.Sc. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq. Al-Azzawi A. A. (1995).Thic Circular Plates on Elastic Foundations. M.Sc. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq. Al-Azzawi A. A. (2). Finite Element Analysis of Thin and Thic Reinforced Concrete Shell Foundations. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq.
18 18 R. J. Aziz et al: Finite element elastic analysis of hypar shells on winler foundation Bairagi N. K. and Buragohain D.N. (1985). Application of Finite Element to Hypar Shell Footings. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Aided Analysis and Design in Civil Engineering, Rooree, III, Hassan S. A. (22). Finite Element Analysis of Shell Footings. M.Sc. Thesis, College of Engineering, Al-Mustansiria University, Baghdad, Iraq. Huang H. C. (1989). Static and Dynamic Analysis of Plates and Shells, Springer-Verlag, London, UK. Kurian N. P. (1982). Modern Foundations: Introduction to Advanced Techniques. Tata- MacGraw Hill, New Delhi. Kurian N. P. (1993). Performance of Shell Foundation on Soft Soil. Proceedings of the International Conference on Soft Soil Engineering, Guangzhou, November, Kurian N. P. (1994). Behavior of Shell Foundations under Subsidence of Core Soil. Proceedings XIII of the International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, New Delhi, Jan., 2, Kurian N. P. (1995). Parametric Studies on the Behavior of Conical Shell Foundations. Proceedings V East Asia-Pacific Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction, Gold Coast, Australia, July, II, Melersi E. (1986). Numerical Analysis of Hyperbolic Paraboloid Shell. Proceedings of the 1th Australian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials, Adelaide,
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla
 Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia redzuan@utm.my Keywords:
Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia redzuan@utm.my Keywords:
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Finite Element Buckling Analysis Of Stiffened Plates
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 2 (February 2014), PP.79-83 Finite Element Buckling Analysis Of Stiffened
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 2 (February 2014), PP.79-83 Finite Element Buckling Analysis Of Stiffened
A MODELING METHOD OF CURING DEFORMATION FOR CFRP COMPOSITE STIFFENED PANEL WANG Yang 1, GAO Jubin 1 BO Ma 1 LIU Chuanjun 1
 21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 A MODELING METHOD OF CURING DEFORMATION FOR CFRP COMPOSITE STIFFENED PANEL WANG Yang 1, GAO Jubin 1 BO Ma 1 LIU Chuanjun
21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 A MODELING METHOD OF CURING DEFORMATION FOR CFRP COMPOSITE STIFFENED PANEL WANG Yang 1, GAO Jubin 1 BO Ma 1 LIU Chuanjun
Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis. Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis
 25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
Second-order shape optimization of a steel bridge
 Computer Aided Optimum Design of Structures 67 Second-order shape optimization of a steel bridge A.F.M. Azevedo, A. Adao da Fonseca Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal Email: alvaro@fe.up.pt,
Computer Aided Optimum Design of Structures 67 Second-order shape optimization of a steel bridge A.F.M. Azevedo, A. Adao da Fonseca Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal Email: alvaro@fe.up.pt,
Performance of railway track system under harmonic loading by finite element method
 Performance of railway track system under harmonic by finite element method Ammar Shuber 1, Mohammed Hamood 1, * and Walaa Jawad 1 1 Building and Construction Engineering Department, University of Technology,
Performance of railway track system under harmonic by finite element method Ammar Shuber 1, Mohammed Hamood 1, * and Walaa Jawad 1 1 Building and Construction Engineering Department, University of Technology,
 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Strain-Based Finite Element Analysis of Stiffened Cylindrical Shell Roof
 American Journal of Civil Engineering 2017; 5(4): 225-230 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20170504.15 ISSN: 2330-8729 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8737 (Online) Strain-Based Finite
American Journal of Civil Engineering 2017; 5(4): 225-230 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20170504.15 ISSN: 2330-8729 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8737 (Online) Strain-Based Finite
1. INTRODUCTION. A shell may be defined as the solid material enclosed. between two closely spaced curved surfaces (1), the distance
 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. GENERAL A shell may be defined as the solid material enclosed between two closely spaced curved surfaces (1), the distance between these two surfaces being the thickness of the shell.
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. GENERAL A shell may be defined as the solid material enclosed between two closely spaced curved surfaces (1), the distance between these two surfaces being the thickness of the shell.
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 2 BACKGROUND AND LITERATURE REVIEW... 3 SECTION 3 WAVE REFLECTION AND TRANSMISSION IN RODS Introduction...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Objectives... 1 1.3 Report organization... 2 SECTION 2 BACKGROUND AND LITERATURE REVIEW... 3 2.1 Introduction... 3 2.2 Wave propagation
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Objectives... 1 1.3 Report organization... 2 SECTION 2 BACKGROUND AND LITERATURE REVIEW... 3 2.1 Introduction... 3 2.2 Wave propagation
Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure
 Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure In the final year of his engineering degree course a student was introduced to finite element analysis and conducted an assessment
Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure In the final year of his engineering degree course a student was introduced to finite element analysis and conducted an assessment
MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF LATTICE TOWERS WITH MORE ACCURATE MODELS
 Advanced Steel Construction Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 565-582 (2007) 565 MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF LATTICE TOWERS WITH MORE ACCURATE MODELS Wenjiang Kang 1, F. Albermani 2, S. Kitipornchai 1 and Heung-Fai Lam
Advanced Steel Construction Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 565-582 (2007) 565 MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF LATTICE TOWERS WITH MORE ACCURATE MODELS Wenjiang Kang 1, F. Albermani 2, S. Kitipornchai 1 and Heung-Fai Lam
Solid and shell elements
 Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Embedded Reinforcements
 Embedded Reinforcements Gerd-Jan Schreppers, January 2015 Abstract: This paper explains the concept and application of embedded reinforcements in DIANA. Basic assumptions and definitions, the pre-processing
Embedded Reinforcements Gerd-Jan Schreppers, January 2015 Abstract: This paper explains the concept and application of embedded reinforcements in DIANA. Basic assumptions and definitions, the pre-processing
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS ARCHINEER INSTITUTES FOR MEMBRANE AND SHELL TECHNOLOGIES, BUILDING AND REAL ESTATE e.v. ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURES IN FEM-BASED SOFTWARE MASTER THESIS ARCHINEER INSTITUTES FOR MEMBRANE AND SHELL TECHNOLOGIES, BUILDING AND REAL ESTATE e.v. ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES
Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method
 Structural Studies, Repairs and Maintenance of Heritage Architecture XI 279 Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method S. B. Yuksel
Structural Studies, Repairs and Maintenance of Heritage Architecture XI 279 Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method S. B. Yuksel
Figure 30. Degrees of freedom of flat shell elements
 Shell finite elements There are three types of shell finite element; 1) flat elements, 2) elements based on the Sanders-Koiter equations and 3) elements based on reduction of a solid element. Flat elements
Shell finite elements There are three types of shell finite element; 1) flat elements, 2) elements based on the Sanders-Koiter equations and 3) elements based on reduction of a solid element. Flat elements
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance
 Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
An optimization method for generating self-equilibrium shape of curved surface from developable surface
 25-28th September, 2017, Hamburg, Germany Annette Bögle, Manfred Grohmann (eds.) An optimization method for generating self-equilibrium shape of curved surface from developable surface Jinglan CI *, Maoto
25-28th September, 2017, Hamburg, Germany Annette Bögle, Manfred Grohmann (eds.) An optimization method for generating self-equilibrium shape of curved surface from developable surface Jinglan CI *, Maoto
The Dynamic Response of an Euler-Bernoulli Beam on an Elastic Foundation by Finite Element Analysis using the Exact Stiffness Matrix
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series The Dynamic Response of an Euler-Bernoulli Beam on an Elastic Foundation by Finite Element Analysis using the Exact Stiffness Matrix To cite this article: Jeong Soo
Journal of Physics: Conference Series The Dynamic Response of an Euler-Bernoulli Beam on an Elastic Foundation by Finite Element Analysis using the Exact Stiffness Matrix To cite this article: Jeong Soo
Settlement Analysis of Piled Raft Foundation System (PRFS) in Soft Clay
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 62-68 www.iosrjournals.org Settlement Analysis of Piled
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 62-68 www.iosrjournals.org Settlement Analysis of Piled
Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post
 Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint
 Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint Jose M. Cabrero Assistant Professor University of Navarra, Department of Structural Analysis and Design,
Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint Jose M. Cabrero Assistant Professor University of Navarra, Department of Structural Analysis and Design,
ANALYSIS OF BOX CULVERT - COST OPTIMIZATION FOR DIFFERENT ASPECT RATIOS OF CELL
 ANALYSIS OF BOX CULVERT - COST OPTIMIZATION FOR DIFFERENT ASPECT RATIOS OF CELL M.G. Kalyanshetti 1, S.A. Gosavi 2 1 Assistant professor, Civil Engineering Department, Walchand Institute of Technology,
ANALYSIS OF BOX CULVERT - COST OPTIMIZATION FOR DIFFERENT ASPECT RATIOS OF CELL M.G. Kalyanshetti 1, S.A. Gosavi 2 1 Assistant professor, Civil Engineering Department, Walchand Institute of Technology,
EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY
 EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY J. Sauvé 1*, M. Dubé 1, F. Dervault 2, G. Corriveau 2 1 Ecole de technologie superieure, Montreal, Canada 2 Airframe stress, Advanced Structures,
EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY J. Sauvé 1*, M. Dubé 1, F. Dervault 2, G. Corriveau 2 1 Ecole de technologie superieure, Montreal, Canada 2 Airframe stress, Advanced Structures,
Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering. Introduction
 Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections
 A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections Dawit Hailu +, Adil Zekaria ++, Samuel Kinde +++ ABSTRACT After the 1994 Northridge earthquake
A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections Dawit Hailu +, Adil Zekaria ++, Samuel Kinde +++ ABSTRACT After the 1994 Northridge earthquake
Development of Eight Node Isoparametric Quadrilateral (QUAD8) Elements in Java
 709 Development of Eight Node Isoparametric Quadrilateral (QUAD8) Elements in Java I.E Umeonyiagu 1, N.P Ogbonna 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu University, Uli. Nigeria
709 Development of Eight Node Isoparametric Quadrilateral (QUAD8) Elements in Java I.E Umeonyiagu 1, N.P Ogbonna 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu University, Uli. Nigeria
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling. Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling
 CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA
 Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA Blessing O Fatola, Patrick Keogh and Ben Hicks Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Corresponding author bf223@bath.ac.uk Abstract. This paper
Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA Blessing O Fatola, Patrick Keogh and Ben Hicks Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Corresponding author bf223@bath.ac.uk Abstract. This paper
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM
 Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
LATERALLY LOADED PILE GROUPS
 LATERALLY LOADED PILE GROUPS Pedro Meneses Key words: Group Interaction, Lateral Response, Piles, p-multipliers, p-y Curves. Introduction The lateral resistance of pile foundations is a particularly important
LATERALLY LOADED PILE GROUPS Pedro Meneses Key words: Group Interaction, Lateral Response, Piles, p-multipliers, p-y Curves. Introduction The lateral resistance of pile foundations is a particularly important
Introduction. Section 3: Structural Analysis Concepts - Review
 Introduction In this class we will focus on the structural analysis of framed structures. Framed structures consist of components with lengths that are significantly larger than crosssectional areas. We
Introduction In this class we will focus on the structural analysis of framed structures. Framed structures consist of components with lengths that are significantly larger than crosssectional areas. We
Mixed Mode Fracture of Through Cracks In Nuclear Reactor Steam Generator Helical Coil Tube
 Journal of Materials Science & Surface Engineering Vol. 3 (4), 2015, pp 298-302 Contents lists available at http://www.jmsse.org/ Journal of Materials Science & Surface Engineering Mixed Mode Fracture
Journal of Materials Science & Surface Engineering Vol. 3 (4), 2015, pp 298-302 Contents lists available at http://www.jmsse.org/ Journal of Materials Science & Surface Engineering Mixed Mode Fracture
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction GTU Paper Analysis (New Syllabus) Sr. No. Questions 26/10/16 11/05/16 09/05/16 08/12/15 Theory 1. What is graphic standard? Explain different CAD standards. 2. Write Bresenham s
Chapter 1 Introduction GTU Paper Analysis (New Syllabus) Sr. No. Questions 26/10/16 11/05/16 09/05/16 08/12/15 Theory 1. What is graphic standard? Explain different CAD standards. 2. Write Bresenham s
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES
 17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A COMPOSITE CATAMARAN
 NAFEMS WORLD CONGRESS 2013, SALZBURG, AUSTRIA FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A COMPOSITE CATAMARAN Dr. C. Lequesne, Dr. M. Bruyneel (LMS Samtech, Belgium); Ir. R. Van Vlodorp (Aerofleet, Belgium). Dr. C. Lequesne,
NAFEMS WORLD CONGRESS 2013, SALZBURG, AUSTRIA FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A COMPOSITE CATAMARAN Dr. C. Lequesne, Dr. M. Bruyneel (LMS Samtech, Belgium); Ir. R. Van Vlodorp (Aerofleet, Belgium). Dr. C. Lequesne,
Recent Advances on Higher Order 27-node Hexahedral Element in LS-DYNA
 14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Simulation Recent Advances on Higher Order 27-node Hexahedral Element in LS-DYNA Hailong Teng Livermore Software Technology Corp. Abstract This paper
14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Simulation Recent Advances on Higher Order 27-node Hexahedral Element in LS-DYNA Hailong Teng Livermore Software Technology Corp. Abstract This paper
CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING
 113 CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING 6.1 INTRODUCTION Superplastic properties are exhibited only under a narrow range of strain rates. Hence, it
113 CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING 6.1 INTRODUCTION Superplastic properties are exhibited only under a narrow range of strain rates. Hence, it
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL AND ANALYTICAL METHODS IN GEOMECHANICS, VOL. 7, 135-141 (1983) LETTERS TO THE EDITOR NUMERICAL PREDICTION OF COLLAPSE LOADS USING FINITE ELEMENT METHODS by S. W. Sloan
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL AND ANALYTICAL METHODS IN GEOMECHANICS, VOL. 7, 135-141 (1983) LETTERS TO THE EDITOR NUMERICAL PREDICTION OF COLLAPSE LOADS USING FINITE ELEMENT METHODS by S. W. Sloan
Effect of Type of Connection on Dynamic Response of Double layer Grid Space Frames
 Effect of Type of Connection on Dynamic Response of Double layer Grid Space Frames Dr. Ihab Sabri Salih 1, Dr. Saddam Khalaf Faleh 2, Zeinab A. Abdulrasool 3 Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering,
Effect of Type of Connection on Dynamic Response of Double layer Grid Space Frames Dr. Ihab Sabri Salih 1, Dr. Saddam Khalaf Faleh 2, Zeinab A. Abdulrasool 3 Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering,
Modeling Foundations in RS
 Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
Shape optimization of compression structures
 26 30 September, 2016, Tokyo, Japan K. Kawaguch M. Ohsak T. Takeuchi (eds.) Shape optimization of compression structures Petra GIDAK*, Mario UROŠ a, Damir LAZAREVIĆ a *Faculty of civil engineering, University
26 30 September, 2016, Tokyo, Japan K. Kawaguch M. Ohsak T. Takeuchi (eds.) Shape optimization of compression structures Petra GIDAK*, Mario UROŠ a, Damir LAZAREVIĆ a *Faculty of civil engineering, University
Three Dimensional Seismic Simulation of a Two-Bay, Two-Story Reinforced Concrete Building
 Three Dimensional Seismic Simulation of a Two-Bay, Two-Story Reinforced Concrete Building Catherine Joseph, REU Student Rachel Howser, Graduate Advisor Dr. Y.L Mo, Faculty Advisor Final Report Department
Three Dimensional Seismic Simulation of a Two-Bay, Two-Story Reinforced Concrete Building Catherine Joseph, REU Student Rachel Howser, Graduate Advisor Dr. Y.L Mo, Faculty Advisor Final Report Department
FE ANALYSES OF STABILITY OF SINGLE AND DOUBLE CORRUGATED BOARDS
 Proceedings of ICAD26 FE ANALYSES OF STABILITY OF SINGLE AND DOUBLE CORRUGATED BOARDS ICAD-26-43 Enrico Armentani enrico.armentani@unina.it University of Naples P.le V. Tecchio, 8 8125 Naples Italy Francesco
Proceedings of ICAD26 FE ANALYSES OF STABILITY OF SINGLE AND DOUBLE CORRUGATED BOARDS ICAD-26-43 Enrico Armentani enrico.armentani@unina.it University of Naples P.le V. Tecchio, 8 8125 Naples Italy Francesco
ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAME STRUCTURE WITH MATLAB AND SAP2000 PROGRAMS
 ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAME STRUCTURE WITH MATLAB AND SAP2000 PROGRAMS Abdul Ahad FAIZAN Master Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University, Sakarya, Turkey ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAME STRUCTURE WITH MATLAB AND SAP2000 PROGRAMS Abdul Ahad FAIZAN Master Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University, Sakarya, Turkey ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Example 24 Spring-back
 Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
First Order Analysis for Automotive Body Structure Design Using Excel
 Special Issue First Order Analysis 1 Research Report First Order Analysis for Automotive Body Structure Design Using Excel Hidekazu Nishigaki CAE numerically estimates the performance of automobiles and
Special Issue First Order Analysis 1 Research Report First Order Analysis for Automotive Body Structure Design Using Excel Hidekazu Nishigaki CAE numerically estimates the performance of automobiles and
A METHOD TO MODELIZE THE OVERALL STIFFNESS OF A BUILDING IN A STICK MODEL FITTED TO A 3D MODEL
 A METHOD TO MODELIE THE OVERALL STIFFNESS OF A BUILDING IN A STICK MODEL FITTED TO A 3D MODEL Marc LEBELLE 1 SUMMARY The aseismic design of a building using the spectral analysis of a stick model presents
A METHOD TO MODELIE THE OVERALL STIFFNESS OF A BUILDING IN A STICK MODEL FITTED TO A 3D MODEL Marc LEBELLE 1 SUMMARY The aseismic design of a building using the spectral analysis of a stick model presents
Industrial Applications of Computational Mechanics Plates and Shells Mesh generation static SSI. Prof. Dr.-Ing. Casimir Katz SOFiSTiK AG
 Industrial Applications of Plates and Shells Mesh generation static SSI Prof. Dr.-Ing. Casimir Katz SOFiSTiK AG FEM - Reminder A mathematical method The real (continuous) world is mapped on to a discrete
Industrial Applications of Plates and Shells Mesh generation static SSI Prof. Dr.-Ing. Casimir Katz SOFiSTiK AG FEM - Reminder A mathematical method The real (continuous) world is mapped on to a discrete
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
midas Civil Advanced Webinar Date: February 9th, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas Civil Presenter: Abhishek Das Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
 Advanced Webinar Date: February 9th, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas Civil Presenter: Abhishek Das Contents: Overview Modeling Boundary Conditions Loading Analysis Results Design and Misc. Introduction
Advanced Webinar Date: February 9th, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas Civil Presenter: Abhishek Das Contents: Overview Modeling Boundary Conditions Loading Analysis Results Design and Misc. Introduction
FAILURE ANALYSIS OF CURVED LAYERED TIMBER CONSTRUCTIONS
 FAILURE ANALYSIS OF CURVED LAYERED TIMBER CONSTRUCTIONS Stevan Maksimovic 1) and Milorad Komnenovic ) 1) VTI Aeronautical Institute, Ratka Resanovica 1, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro e-mail: s.maksimovic@net.yu
FAILURE ANALYSIS OF CURVED LAYERED TIMBER CONSTRUCTIONS Stevan Maksimovic 1) and Milorad Komnenovic ) 1) VTI Aeronautical Institute, Ratka Resanovica 1, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro e-mail: s.maksimovic@net.yu
Beams. Lesson Objectives:
 Beams Lesson Objectives: 1) Derive the member local stiffness values for two-dimensional beam members. 2) Assemble the local stiffness matrix into global coordinates. 3) Assemble the structural stiffness
Beams Lesson Objectives: 1) Derive the member local stiffness values for two-dimensional beam members. 2) Assemble the local stiffness matrix into global coordinates. 3) Assemble the structural stiffness
Optimization of Arch Supported Tensile Roofs
 Paper 241 Optimization of Arch Supported Tensile Roofs Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp
Paper 241 Optimization of Arch Supported Tensile Roofs Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp
SCIA stands for scientific analyser. The C in SCIA Engineering is not pronounced. Note that the first c in science is not pronounced either.
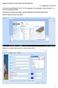 Design of a reinforced concrete 4-hypar shell with edge beams P.C.J. Hoogenboom, 22 May 2016 SCIA stands for scientific analyser. The C in SCIA Engineering is not pronounced. Note that the first c in science
Design of a reinforced concrete 4-hypar shell with edge beams P.C.J. Hoogenboom, 22 May 2016 SCIA stands for scientific analyser. The C in SCIA Engineering is not pronounced. Note that the first c in science
ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION TO CAD
 Computer Aided Design(2161903) ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION TO CAD Theory 1. Discuss the reasons for implementing a CAD system. 2. Define computer aided design. Compare computer aided design and conventional
Computer Aided Design(2161903) ASSIGNMENT 1 INTRODUCTION TO CAD Theory 1. Discuss the reasons for implementing a CAD system. 2. Define computer aided design. Compare computer aided design and conventional
Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket Gowtham K L*, Shivashankar R. Srivatsa** *(Department of Mechanical Engineering, B. M.
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Study of Convergence of Results in Finite Element Analysis of a Plane Stress Bracket Gowtham K L*, Shivashankar R. Srivatsa** *(Department of Mechanical Engineering, B. M.
SIMULATION OF METAL FORMING PROCESSES. Konstantin SOLOMONOV a, Victor SVIRIN b
 SIMULATION OF METAL FORMING PROCESSES Konstantin SOLOMONOV a, Victor SVIRIN b a Moscow State University of Railway Engineering (Voronezh branch), 75а, Uritskogo street, 394026, Voronezh, Russia, E-mail
SIMULATION OF METAL FORMING PROCESSES Konstantin SOLOMONOV a, Victor SVIRIN b a Moscow State University of Railway Engineering (Voronezh branch), 75а, Uritskogo street, 394026, Voronezh, Russia, E-mail
C. Topkaya, J. A. Yura, E. B. Williamson, and K. H. Frank Research Report
 Technical Report Documentation Page 1. Report No. 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient s Catalog No. FHWA/TX-03/1898-3 4. Title and Subtitle 5. Report Date UTrAp: Finite-Element-Based Software for
Technical Report Documentation Page 1. Report No. 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient s Catalog No. FHWA/TX-03/1898-3 4. Title and Subtitle 5. Report Date UTrAp: Finite-Element-Based Software for
Isogeometric Analysis Application to Car Crash Simulation
 Isogeometric Analysis Application to Car Crash Simulation S. Bouabdallah 2, C. Adam 2,3, M. Zarroug 2, H. Maitournam 3 De Vinci Engineering Lab, École Supérieure d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci 2 Direction
Isogeometric Analysis Application to Car Crash Simulation S. Bouabdallah 2, C. Adam 2,3, M. Zarroug 2, H. Maitournam 3 De Vinci Engineering Lab, École Supérieure d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci 2 Direction
EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE
 EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE ABSTRACT: K. Kocamaz 1, K. Tuncay 2 and B. Binici 3 1 Res. Assist., Civil Eng. Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara
EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE ABSTRACT: K. Kocamaz 1, K. Tuncay 2 and B. Binici 3 1 Res. Assist., Civil Eng. Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara
ixcube 4-10 Brief introduction for membrane and cable systems.
 ixcube 4-10 Brief introduction for membrane and cable systems. ixcube is the evolution of 20 years of R&D in the field of membrane structures so it takes a while to understand the basic features. You must
ixcube 4-10 Brief introduction for membrane and cable systems. ixcube is the evolution of 20 years of R&D in the field of membrane structures so it takes a while to understand the basic features. You must
Deep Beam With Web Opening
 Deep Beam With Web Opening Name: Path: Keywords: DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam /Examples//DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam analys: linear static. constr: suppor. elemen: cq16m ct12m pstres. load: force
Deep Beam With Web Opening Name: Path: Keywords: DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam /Examples//DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam analys: linear static. constr: suppor. elemen: cq16m ct12m pstres. load: force
Computer modelling and simulation of the mechanical response of composite lattice structures
 22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Computer modelling and simulation of the mechanical response of composite
22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Computer modelling and simulation of the mechanical response of composite
A Quadratic Pipe Element in LS-DYNA
 A Quadratic Pipe Element in LS-DYNA Tobias Olsson, Daniel Hilding DYNAmore Nordic AB 1 Bacground Analysis of long piping structures can be challenging due to the enormous number of shell/solid elements
A Quadratic Pipe Element in LS-DYNA Tobias Olsson, Daniel Hilding DYNAmore Nordic AB 1 Bacground Analysis of long piping structures can be challenging due to the enormous number of shell/solid elements
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 2, Issue 3, September 2012
 Mitigation Curves for Determination of Relief Holes to Mitigate Concentration Factor in Thin Plates Loaded Axially for Different Discontinuities Shubhrata Nagpal, S.Sanyal, Nitin Jain Abstract In many
Mitigation Curves for Determination of Relief Holes to Mitigate Concentration Factor in Thin Plates Loaded Axially for Different Discontinuities Shubhrata Nagpal, S.Sanyal, Nitin Jain Abstract In many
Strength of Overlapping Multi-Planar KK Joints in CHS Sections
 Strength of Overlapping Multi-Planar KK Joints in CHS Sections Peter Gerges 1, Mohamed Hussein 1, Sameh Gaawan 2 Structural Engineer, Department of Structures, Dar Al-Handasah Consultants, Giza, Egypt
Strength of Overlapping Multi-Planar KK Joints in CHS Sections Peter Gerges 1, Mohamed Hussein 1, Sameh Gaawan 2 Structural Engineer, Department of Structures, Dar Al-Handasah Consultants, Giza, Egypt
Topology Optimization of Two Linear Elastic Bodies in Unilateral Contact
 2 nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization September 6-9, 2010, Lisbon, Portugal Topology Optimization of Two Linear Elastic Bodies in Unilateral Contact Niclas Strömberg Department of Mechanical
2 nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization September 6-9, 2010, Lisbon, Portugal Topology Optimization of Two Linear Elastic Bodies in Unilateral Contact Niclas Strömberg Department of Mechanical
Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
Advanced Professional Training
 Advanced Professional Training Non Linea rand Stability All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part of this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database
Advanced Professional Training Non Linea rand Stability All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part of this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
JAVA APPLETS FOR TEACHING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 JAVA APPLETS FOR TEACHING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Kamal B. Rojiani 1, Suryanarayana Raju S.V.N. 2 ABSTRACT An applet for teaching fundamental concepts of finite element analysis is developed. An applet
JAVA APPLETS FOR TEACHING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Kamal B. Rojiani 1, Suryanarayana Raju S.V.N. 2 ABSTRACT An applet for teaching fundamental concepts of finite element analysis is developed. An applet
Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate
 Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate Outline 1 Description 2 Modeling approach 3 Finite Element Model 3.1 Units 3.2 Geometry definition 3.3 Properties 3.4 Boundary conditions 3.5 Loads 3.6 Meshing 4 Structural
Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate Outline 1 Description 2 Modeling approach 3 Finite Element Model 3.1 Units 3.2 Geometry definition 3.3 Properties 3.4 Boundary conditions 3.5 Loads 3.6 Meshing 4 Structural
E and. L q. AE q L AE L. q L
 STRUTURL NLYSIS [SK 43] EXERISES Q. (a) Using basic concepts, members towrds local axes is, E and q L, prove that the equilibrium equation for truss f f E L E L E L q E q L With f and q are both force
STRUTURL NLYSIS [SK 43] EXERISES Q. (a) Using basic concepts, members towrds local axes is, E and q L, prove that the equilibrium equation for truss f f E L E L E L q E q L With f and q are both force
An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
Large Rotation Analysis of thin-walled shells
 Large Rotation Analysis of thin-walled shells Y. Başar, O. Kintzel Ruhr-University Bochum Bochum, Germany Summary The objective of this contribution is to develop an isoparametric -node shell element by
Large Rotation Analysis of thin-walled shells Y. Başar, O. Kintzel Ruhr-University Bochum Bochum, Germany Summary The objective of this contribution is to develop an isoparametric -node shell element by
Advanced model of steel joints loaded by internal forces from 3D frame structures
 Advanced model of steel joints loaded by internal forces from 3D frame structures Lubomír Šabatka, IDEA RS s.r.o František Wald, FSv ČVUT Praha Jaromír Kabeláč, Hypatia Solutions s.r.o Drahoslav Kolaja,
Advanced model of steel joints loaded by internal forces from 3D frame structures Lubomír Šabatka, IDEA RS s.r.o František Wald, FSv ČVUT Praha Jaromír Kabeláč, Hypatia Solutions s.r.o Drahoslav Kolaja,
ANSYS Element. elearning. Peter Barrett October CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved.
 ANSYS Element Selection elearning Peter Barrett October 2012 2012 CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS Element Selection What is the best element type(s) for my analysis? Best
ANSYS Element Selection elearning Peter Barrett October 2012 2012 CAE Associates Inc. and ANSYS Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS Element Selection What is the best element type(s) for my analysis? Best
Simplified Design Procedure for Piles Affected by Lateral Spreading based on 3D Nonlinear FEA Using OpenSees. University of Washington
 Simplified Design Procedure for Piles Affected by Lateral Spreading based on 3D Nonlinear FEA Using OpenSees Christopher R. McGann, Ph.D. Student Pedro Arduino Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein University of Washington
Simplified Design Procedure for Piles Affected by Lateral Spreading based on 3D Nonlinear FEA Using OpenSees Christopher R. McGann, Ph.D. Student Pedro Arduino Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein University of Washington
Configuration Optimization of Anchoring Devices of Frame-Supported Membrane Structures for Maximum Clamping Force
 6 th China Japan Korea Joint Symposium on Optimization of Structural and Mechanical Systems June 22-25, 200, Kyoto, Japan Configuration Optimization of Anchoring Devices of Frame-Supported Membrane Structures
6 th China Japan Korea Joint Symposium on Optimization of Structural and Mechanical Systems June 22-25, 200, Kyoto, Japan Configuration Optimization of Anchoring Devices of Frame-Supported Membrane Structures
LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results
 LIGO-T980125-00-D HYTEC-TN-LIGO-31 LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results Eric Swensen and Franz Biehl August 30, 1998 Abstract Static structural tests were conducted on the LIGO scissors
LIGO-T980125-00-D HYTEC-TN-LIGO-31 LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results Eric Swensen and Franz Biehl August 30, 1998 Abstract Static structural tests were conducted on the LIGO scissors
Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process
 Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process Kyriaki G. DATSIOU *, Mauro OVEREND a * Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK kd365@cam.ac.uk
Behaviour of cold bent glass plates during the shaping process Kyriaki G. DATSIOU *, Mauro OVEREND a * Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Trumpington Street, Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK kd365@cam.ac.uk
studying of the prying action effect in steel connection
 studying of the prying action effect in steel connection Saeed Faraji Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Ahar Branch S-faraji@iau-ahar.ac.ir Paper Reference Number:
studying of the prying action effect in steel connection Saeed Faraji Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Ahar Branch S-faraji@iau-ahar.ac.ir Paper Reference Number:
TABLE OF CONTENTS WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN? INSTALLING ADVANCE DESIGN... 8 System requirements... 8 Advance Design installation...
 Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
Finite Element Analysis of Slab and a Comparative Study with Others Analytical Solution
 7 th ICCT Finite Element Analysis of Slab and a Comparative Study with Others Analytical Solution M. W. Bari, Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology, BANGLADESH M. M. Rahman, Rajshahi University
7 th ICCT Finite Element Analysis of Slab and a Comparative Study with Others Analytical Solution M. W. Bari, Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology, BANGLADESH M. M. Rahman, Rajshahi University
Global to Local Model Interface for Deepwater Top Tension Risers
 Global to Local Model Interface for Deepwater Top Tension Risers Mateusz Podskarbi Karan Kakar 2H Offshore Inc, Houston, TX Abstract The water depths from which oil and gas are being produced are reaching
Global to Local Model Interface for Deepwater Top Tension Risers Mateusz Podskarbi Karan Kakar 2H Offshore Inc, Houston, TX Abstract The water depths from which oil and gas are being produced are reaching
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
RELIABILITY OF THE FEM CALCULATIONS OF THE FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS
 International Conference on Economic Engineering and Manufacturing Systems Braşov, 26 27 November 2009 RELIABILITY OF THE FEM CALCULATIONS OF THE FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS Galina TODOROVA, Valentin
International Conference on Economic Engineering and Manufacturing Systems Braşov, 26 27 November 2009 RELIABILITY OF THE FEM CALCULATIONS OF THE FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS Galina TODOROVA, Valentin
Finite Element Modeling and Failure Analysis of Roll Bending. Forming of GLARE Laminates
 Finite Element Modeling and Failure Analysis of Roll Bending Forming of GLARE Laminates Jingming Tian, Gang Tao, Cheng Liu, Huaguan Li, Xian Zhang, Jie Tao* College of Materials Science and Technology,
Finite Element Modeling and Failure Analysis of Roll Bending Forming of GLARE Laminates Jingming Tian, Gang Tao, Cheng Liu, Huaguan Li, Xian Zhang, Jie Tao* College of Materials Science and Technology,
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering
 Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Multiframe May 2010 Release Note
 Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
