Measurement and Geometry: Area and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects *
|
|
|
- Amice Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OpenStax-CNX module: m Measurement and Geometry: and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses area and volume of geometric gures and objects. By the end of the module students should know the meaning and notation for area, know the area formulas for some common geometric gures, be able to nd the areas of some common geometric gures, know the meaning and notation for volume, know the volume formulas for some common geometric objects and be able to nd the volume of some common geometric objects. 1 Section Overview The Meaning and Notation for Formulas Finding s of Some Common Geometric Figures The Meaning and Notation for Volume Volume Formulas Finding Volumes of Some Common Geometric Objects Quite often it is necessary to multiply one denominate number by another. To do so, we multiply the number parts together and the unit parts together. For example, 8 in. 8 in. = 8 8 in. in. = 64 in. 2 4 mm 4 mm 4 mm = mm mm mm = 64 mm 3 Sometimes the product of units has a physical meaning. In this section, we will examine the meaning of the products (length unit) 2 and (length unit) 3. * Version 1.2: Aug 18, :41 pm
2 OpenStax-CNX module: m The Meaning and Notation for The product (length unit) (length unit) = (length unit) 2, or, square length unit (sq length unit), can be interpreted physically as the area of a surface. The area of a surface is the amount of square length units contained in the surface. For example, 3 sq in. means that 3 squares, 1 inch on each side, can be placed precisely on some surface. (The squares may have to be cut and rearranged so they match the shape of the surface.) We will examine the area of the following geometric gures. 3 Formulas We can determine the areas of these geometric gures using the following formulas. Figure Formula Statement Triangle A T = 1 2 b h of a triangle is one half the base times the height. continued on next page
3 OpenStax-CNX module: m Rectangle A R = l w of a rectangle is the length times the width. Parallelogram A P = b h of a parallelogram is base times the height. Trapezoid A Trap = 1 2 (b 1 + b 2 ) h of a trapezoid is one half the sum of the two bases times the height. Circle A C = πr 2 of a circle is π times the square of the radius. Table 1 4 Finding s of Some Common Geometric Figures 4.1 Sample Set A Example 1 Find the area of the triangle. A T = 1 2 b h = sq ft = 10 6 sq ft = 60 sq ft = 60 ft 2 The area of this triangle is 60 sq ft, which is often written as 60 ft 2. Example 2 Find the area of the rectangle. Let's rst convert 4 ft 2 in. to inches. Since we wish to convert to inches, we'll use the unit 12 in. fraction since it has inches in the numerator. Then, 1 ft
4 OpenStax-CNX module: m ft = 4 ft = 12 in. 1 1 ft 4) ft 12 in. 1 1) ft = 48 in. Thus, 4 ft 2 in. = 48 in. + 2 in. = 50 in. A R = l w = 50 in. 8 in. = 400 sq in. The area of this rectangle is 400 sq in. Example 3 Find the area of the parallelogram. A P = b h = 10.3 cm 6.2 cm = sq cm The area of this parallelogram is sq cm. Example 4 Find the area of the trapezoid. A Trap = 1 2 (b 1 + b 2 ) h = 1 2 (14.5 mm, +, 20.4 mm) (4.1 mm) 1 = 2 (34.9 mm) (4.1 mm) ( sq mm) = 1 2 = sq mm The area of this trapezoid is sq mm. Example 5 Find the approximate area of the circle.
5 OpenStax-CNX module: m A c = π r 2 (3.14) (16.8 ft) 2 (3.14) ( sq ft) sq ft The area of this circle is approximately sq ft. 4.2 Practice Set A Find the area of each of the following geometric gures. Exercise 1 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 2 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 3 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 4 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 5 (Solution on p. 17.)
6 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 6 (Solution on p. 17.) 5 The Meaning and Notation for Volume The product (length unit) (length unit) (length unit) = (length unit) 3, or cubic length unit (cu length unit), can be interpreted physically as the volume of a three-dimensional object. Volume The volume of an object is the amount of cubic length units contained in the object. For example, 4 cu mm means that 4 cubes, 1 mm on each side, would precisely ll some three-dimensional object. (The cubes may have to be cut and rearranged so they match the shape of the object.)
7 OpenStax-CNX module: m Volume Formulas Figure Volume Formula Statement Rectangular solid V R = l w h The volume of a rectangular solid is the length = (area of base) (height) times the width times the height. Sphere V S = 4 3 π r3 The volume of a sphere is 4 3 times π times the cube of the radius. continued on next page
8 OpenStax-CNX module: m Cylinder V Cyl = π r 2 h The volume of a cylinder (height) is π times the square = (area of base) of the radius times the height. Cone V c = 1 3 π r2 h The volume of a cone = (area of base) (height) is 1 3 times π times the square of the radius times the height. Table 2 7 Finding Volumes of Some Common Geometric Objects 7.1 Sample Set B Example 6 Find the volume of the rectangular solid. V R = l w h = 9 in. 10 in. 3 in. = 270 cu in. = 270 in. 3 The volume of this rectangular solid is 270 cu in. Example 7 Find the approximate volume of the sphere.
9 OpenStax-CNX module: m V S = 3 ( π r3 4 3) (3.14) (6 3 cm) ( 4 3) (3.14) (216 cu cm) cu cm The approximate volume of this sphere is cu cm, which is often written as cm 3. Example 8 Find the approximate volume of the cylinder. V Cyl = π r 2 h (3.14) (4.9 ft) 2 (7.8 ft) (3.14) (24.01 sq ft) (7.8 ft) (3.14) ( cu ft) cu ft The volume of this cylinder is approximately cu ft. because we approximated π with Example 9 Find the approximate volume of the cone. Round to two decimal places. The volume is approximate 1 V c = 3 π r2 h ( 1 3) (3.14) (2 mm)2 (5 mm) ( 1 3) (3.14) (4 sq mm) (5 mm) ) (3.14) (20 cu mm) ( cu mm cu mm
10 OpenStax-CNX module: m The volume of this cone is approximately cu mm. The volume is approximate because we approximated π with Practice Set B Find the volume of each geometric object. If π is required, approximate it with 3.14 and nd the approximate volume. Exercise 7 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 8 (Solution on p. 17.) Sphere Exercise 9 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 10 (Solution on p. 17.) 8 Exercises Find each indicated measurement.
11 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 11 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 12 Exercise 13 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 14 Exercise 15 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 16 Exercise 17 (Solution on p. 17.) Exact area
12 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 18 Approximate area Exercise 19 (Solution on p. 17.) Exercise 20 Exercise 21 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate area Exercise 22 Exact area Exercise 23 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate area
13 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 24 Exact area Exercise 25 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate area Exercise 26 Exercise 27 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate area Exercise 28 Volume Exercise 29 (Solution on p. 17.) Volume
14 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 30 Exact volume Exercise 31 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate volume Exercise 32 Approximate volume Exercise 33 (Solution on p. 17.) Exact volume Exercise 34 Approximate volume
15 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 35 (Solution on p. 17.) Approximate volume Exercise 36 Approximate volume 8.1 Exercises for Review Exercise 37 (Solution on p. 17.) () In the number 23,426, how many hundreds are there? Exercise 38 () List all the factors of 32. Exercise 39 (Solution on p. 17.) () Find the value of
16 OpenStax-CNX module: m Exercise 40 () Find the value of Exercise 41 (Solution on p. 18.) () Find the perimeter.
17 OpenStax-CNX module: m Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Exercise (p. 5) 36 sq cm Solution to Exercise (p. 5) sq mm Solution to Exercise (p. 5) sq in. Solution to Exercise (p. 5) sq mi Solution to Exercise (p. 5) sq ft Solution to Exercise (p. 6) sq cm Solution to Exercise (p. 10) 21 cu in. Solution to Exercise (p. 10) cu ft Solution to Exercise (p. 10) 157 cu m Solution to Exercise (p. 10) cu in. Solution to Exercise (p. 10) 16 sq m Solution to Exercise (p. 11) 1.21 sq mm Solution to Exercise (p. 11) 18 sq in. Solution to Exercise (p. 11) (60.5π + 132) sq ft Solution to Exercise (p. 12) 40.8 sq in. Solution to Exercise (p. 12) sq in. Solution to Exercise (p. 12) sq mm Solution to Exercise (p. 13) sq in. Solution to Exercise (p. 13) sq ft Solution to Exercise (p. 13) 512 cu cm Solution to Exercise (p. 14) cu cm Solution to Exercise (p. 14) π cu ft Solution to Exercise (p. 15) cu in. Solution to Exercise (p. 15) 4
18 OpenStax-CNX module: m Solution to Exercise (p. 15) = = 2.58 Solution to Exercise (p. 16) 27.9m
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Sect Volume. 3 ft. 2 ft. 5 ft
 199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
Volume of Cylinders. Volume of Cones. Example Find the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth.
 Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Vocabulary. Triangular pyramid Square pyramid Oblique square pyramid Pentagonal pyramid Hexagonal Pyramid
 CP1 Math 2 Unit 8: S.A., Volume, Trigonometry: Day 7 Name Surface Area Objectives: Define important vocabulary for 3-dimensional figures Find the surface area for various prisms Generalize a formula for
CP1 Math 2 Unit 8: S.A., Volume, Trigonometry: Day 7 Name Surface Area Objectives: Define important vocabulary for 3-dimensional figures Find the surface area for various prisms Generalize a formula for
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon
 Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Section 9.4. Volume and Surface Area. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area What You Will Learn Volume Surface Area 9.4-2 Volume Volume is the measure of the capacity of a three-dimensional figure. It is the amount of material you can put inside
Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area What You Will Learn Volume Surface Area 9.4-2 Volume Volume is the measure of the capacity of a three-dimensional figure. It is the amount of material you can put inside
CCBC Math 081 Geometry Section 2.2
 2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Free Response. Test A. 1. What is the estimated area of the figure?
 Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Arithmetic Review: Decimal Fractions *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m21865 1 Arithmetic Review: Decimal Fractions * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m21865 1 Arithmetic Review: Decimal Fractions * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
3.1 Deepening Understandings of Volume Parts 1_2.notebook. September 05, 2018 M Jun 27 10:28 AM
 M1 115 Jun 27 10:28 AM 1 Learning Targets Jun 20 10:53 AM 2 9/4 /18 # Glue pages 1 & 2 into notebook M1: 3.1 Deepening Understanding of Volume Essential Question: How can you use what you know to calculate
M1 115 Jun 27 10:28 AM 1 Learning Targets Jun 20 10:53 AM 2 9/4 /18 # Glue pages 1 & 2 into notebook M1: 3.1 Deepening Understanding of Volume Essential Question: How can you use what you know to calculate
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
January 23, HW 3 GeometricSolids Key. Fundamentals of Algebra. Geometric Solids. Homework #3. Key
 Fundamentals of Algebra Geometric Solids Homework #3 Key 1 Problem #1 6 2 Problem #1 I Need To 6 I need to find the container that holds the largest volume of water, choosing between two cylinders and
Fundamentals of Algebra Geometric Solids Homework #3 Key 1 Problem #1 6 2 Problem #1 I Need To 6 I need to find the container that holds the largest volume of water, choosing between two cylinders and
Geometry - Additional Questions: Sheet 1
 Geometry - Additional Questions: Sheet 1 Parallel Lines Eercises (G3E) e g f h L1 L1 L2 1.) How many angles do you need to know in order to replace the letters in the diagram to the left? b c a d L2 2.)
Geometry - Additional Questions: Sheet 1 Parallel Lines Eercises (G3E) e g f h L1 L1 L2 1.) How many angles do you need to know in order to replace the letters in the diagram to the left? b c a d L2 2.)
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Someone else might choose to describe the closet by determining how many square tiles it would take to cover the floor. 6 ft.
 Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
February 07, Dimensional Geometry Notebook.notebook. Glossary & Standards. Prisms and Cylinders. Return to Table of Contents
 Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14. Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures
 Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14 Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures Standards of Learning Blueprint Summary Reporting Category Geometry SOL Number of Items Reasoning, Lines, and G.1(a-d),
Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14 Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures Standards of Learning Blueprint Summary Reporting Category Geometry SOL Number of Items Reasoning, Lines, and G.1(a-d),
Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A3; B2; C1. 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can.
 Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A; B2; C1 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can. 2. Name the geometric solid suggested by a beach ball.. Name the geometric solid suggested
Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A; B2; C1 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can. 2. Name the geometric solid suggested by a beach ball.. Name the geometric solid suggested
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME
 29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME Recognise units of measurement used for length, area and volume Know and apply formulae to calculate area of triangles, circles, parallelograms and trapezia Calculate
29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME Recognise units of measurement used for length, area and volume Know and apply formulae to calculate area of triangles, circles, parallelograms and trapezia Calculate
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
Area. Domain 4 Lesson 25. Getting the Idea
 Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade. Name. Integer Operations = 2. (-7)(6)(-4) = = = = 6.
 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16 - + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference between the numbers and keep
Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16 - + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference between the numbers and keep
Practice A Introduction to Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Geometry Surface Area & Volume of Prisms & Cylinders.
 Geometry 11.5 Surface Area & Volume of Prisms & Cylinders mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.5 Essential Question How do you find the surface area and volume of a prism or cylinder? Geometry 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms
Geometry 11.5 Surface Area & Volume of Prisms & Cylinders mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.5 Essential Question How do you find the surface area and volume of a prism or cylinder? Geometry 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms
Reteaching. Solids. These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids. A cylinder has two congruent circular bases.
 9- Solids These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids A B C D cylinder cone prism pyramid A cylinder has two congruent circular bases AB is a radius A cone has one circular base CD is
9- Solids These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids A B C D cylinder cone prism pyramid A cylinder has two congruent circular bases AB is a radius A cone has one circular base CD is
Solid Figures. Name. 22 Topic 18. Reteaching Polyhedrons Prisms
 Solid Figures Polyhedrons Prisms Pyramids Reteaching 8- Properties of polyhedrons include vertices, edges, and faces, and base(s). Square Pyramid K Reteaching 8- Not Polyhedrons Cylinder Cone Sphere H
Solid Figures Polyhedrons Prisms Pyramids Reteaching 8- Properties of polyhedrons include vertices, edges, and faces, and base(s). Square Pyramid K Reteaching 8- Not Polyhedrons Cylinder Cone Sphere H
Unit Map: Grade 3 Math
 Place Value 3.3 Number and operations. The student represents and compares whole numbers and understand relationships related to place value. Place Value of Whole Numbers 3.3A compose and decompose numbers
Place Value 3.3 Number and operations. The student represents and compares whole numbers and understand relationships related to place value. Place Value of Whole Numbers 3.3A compose and decompose numbers
Practice Test Unit 8. Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it!
 Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all its outer surfaces or faces.
 Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS
 STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to fractions and to repeated
STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to fractions and to repeated
Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area
 Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
5.1 Any Way You Slice It
 SECONDARY MATH III // MODULE 5 MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.1 Students in Mrs. Denton s class were given cubes made of clay and asked to slice off a corner of the cube with a piece of dental floss. Jumal sliced
SECONDARY MATH III // MODULE 5 MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.1 Students in Mrs. Denton s class were given cubes made of clay and asked to slice off a corner of the cube with a piece of dental floss. Jumal sliced
Unit 4, Lesson 14: Fractional Lengths in Triangles and Prisms
 Unit 4, Lesson 14: Fractional Lengths in Triangles and Prisms Lesson Goals Use multiplication and division to solve problems involving fractional areas and lengths in triangles. cubes with fractional edge
Unit 4, Lesson 14: Fractional Lengths in Triangles and Prisms Lesson Goals Use multiplication and division to solve problems involving fractional areas and lengths in triangles. cubes with fractional edge
Lesson 9. Three-Dimensional Geometry
 Lesson 9 Three-Dimensional Geometry 1 Planes A plane is a flat surface (think tabletop) that extends forever in all directions. It is a two-dimensional figure. Three non-collinear points determine a plane.
Lesson 9 Three-Dimensional Geometry 1 Planes A plane is a flat surface (think tabletop) that extends forever in all directions. It is a two-dimensional figure. Three non-collinear points determine a plane.
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of
 Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Length and Area. Charles Delman. April 20, 2010
 Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 5: Explaining and Applying Area and Volume Formulas Instruction
 UNIT CIRCLES AND VOLUME Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: calculating with fractions and decimals understanding operations with exponents knowing area, surface area,
UNIT CIRCLES AND VOLUME Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: calculating with fractions and decimals understanding operations with exponents knowing area, surface area,
Number Sense Third Grade Fourth Grade Fifth Grade MA.4.NS.1.a.1: Read, demonstrate, and write whole numbers up to 500.
 Number Sense MA.4.NS.1.a.1: Read, demonstrate, and write whole numbers up to 500. MA.3.NS.1.a.1: Read, demonstrate, and write whole numbers up to 200, in standard and word form. MA.3.NS.2.a.1: Compare
Number Sense MA.4.NS.1.a.1: Read, demonstrate, and write whole numbers up to 500. MA.3.NS.1.a.1: Read, demonstrate, and write whole numbers up to 200, in standard and word form. MA.3.NS.2.a.1: Compare
Standard 1 Students will expand number sense to include integers and perform operations with whole numbers, simple fractions, and decimals.
 Stretch Standard 1 Students will expand number sense to include integers and perform operations with whole numbers, simple fractions, and decimals. Objective 1: Represent whole numbers and decimals from
Stretch Standard 1 Students will expand number sense to include integers and perform operations with whole numbers, simple fractions, and decimals. Objective 1: Represent whole numbers and decimals from
Math Content
 2013-2014 Math Content PATHWAY TO ALGEBRA I Hundreds and Tens Tens and Ones Comparing Whole Numbers Adding and Subtracting 10 and 100 Ten More, Ten Less Adding with Tens and Ones Subtracting with Tens
2013-2014 Math Content PATHWAY TO ALGEBRA I Hundreds and Tens Tens and Ones Comparing Whole Numbers Adding and Subtracting 10 and 100 Ten More, Ten Less Adding with Tens and Ones Subtracting with Tens
Center of a sphere. Radius of a sphere. Chord of a sphere. Diameter of a sphere
 12.6 Surface Area and Volume of Spheres Goal p Find surface areas and volumes of spheres. Your Notes VOCABULARY Sphere Center of a sphere Radius of a sphere Chord of a sphere Diameter of a sphere Tangent
12.6 Surface Area and Volume of Spheres Goal p Find surface areas and volumes of spheres. Your Notes VOCABULARY Sphere Center of a sphere Radius of a sphere Chord of a sphere Diameter of a sphere Tangent
Lesson 26: Volume of Composite Three-Dimensional Objects
 Classwork Example 1 Find the volume of the following three-dimensional object composed of two right rectangular prisms. Exercise 1 Find the volume of the following three-dimensional figure composed of
Classwork Example 1 Find the volume of the following three-dimensional object composed of two right rectangular prisms. Exercise 1 Find the volume of the following three-dimensional figure composed of
Aptitude Volume and Surface Area. Theory
 Aptitude Volume and Surface Area Theory Volume Volume is the amount of space inside a three-dimensional (length, width and height.) object, or its capacity. measured in cubic units. Surfce Area Total area
Aptitude Volume and Surface Area Theory Volume Volume is the amount of space inside a three-dimensional (length, width and height.) object, or its capacity. measured in cubic units. Surfce Area Total area
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
3. Draw the orthographic projection (front, right, and top) for the following solid. Also, state how many cubic units the volume is.
 PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m18877 1 Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m18877 1 Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
S8.6 Volume. Section 1. Surface area of cuboids: Q1. Work out the surface area of each cuboid shown below:
 Things to Learn (Key words, Notation & Formulae) Complete from your notes Radius- Diameter- Surface Area- Volume- Capacity- Prism- Cross-section- Surface area of a prism- Surface area of a cylinder- Volume
Things to Learn (Key words, Notation & Formulae) Complete from your notes Radius- Diameter- Surface Area- Volume- Capacity- Prism- Cross-section- Surface area of a prism- Surface area of a cylinder- Volume
MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 6
 MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 6 MCAS Finish Line Mathematics Grade 6 MCAS Standard DCCAS Standard DCCAS Standard Description Unit 1: Number Sense Lesson 1: Whole Number and Decimal Place
MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 6 MCAS Finish Line Mathematics Grade 6 MCAS Standard DCCAS Standard DCCAS Standard Description Unit 1: Number Sense Lesson 1: Whole Number and Decimal Place
When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
 Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
Summer Math Reinforcement Packet Students Entering into 4th Grade THIRD GRADE GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS IN MATHMATICS When entering fourth grade this is what is expected that your child should already know.
2. a. approximately cm 3 or 9p cm b. 20 layers c. approximately cm 3 or 180p cm Answers will vary.
 Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, D Geometry Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 2.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Backyard Barbecue Introduction to Volume and Surface Area Vocabulary Write the term from the box that best completes each statement. surface area
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Backyard Barbecue Introduction to Volume and Surface Area Vocabulary Write the term from the box that best completes each statement. surface area
Determine the surface area of the following square-based pyramid. Determine the volume of the following triangular prism. ) + 9.
 MPM 1D Name: Unit: Measurement Date: Calculating and of Three Dimensional Figures Use the Formula Sheet attached to help you to answer each of the following questions. Three problems are worked out for
MPM 1D Name: Unit: Measurement Date: Calculating and of Three Dimensional Figures Use the Formula Sheet attached to help you to answer each of the following questions. Three problems are worked out for
Instructional. Essential Standards. Materials. Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4. Envision Topic 2 2-2; 2-3. Envision Topic 2 2-4; 2-5; 2-6
 Time Frame Period 1 Dates: Sept.4 Oct.26 Big Idea/Topic Essential Standards NS1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large and very small numbers. Materials Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4 Envision
Time Frame Period 1 Dates: Sept.4 Oct.26 Big Idea/Topic Essential Standards NS1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large and very small numbers. Materials Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4 Envision
1.1 Metric Systems. Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units. Main Ideas:
 1.1 Metric Systems Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units Formula sheet Multiplying and dividing fractions Definitions Metric System The International System of Units, abbreviated
1.1 Metric Systems Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units Formula sheet Multiplying and dividing fractions Definitions Metric System The International System of Units, abbreviated
Chapter 12 Review Period:
 Chapter 12 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the number of vertices, faces, and edges for the figure. 9. A polyhedron has 6 faces and 7 vertices. How many edges does it have? Explain your answer. 10. Find the
Chapter 12 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the number of vertices, faces, and edges for the figure. 9. A polyhedron has 6 faces and 7 vertices. How many edges does it have? Explain your answer. 10. Find the
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. no no R89. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Mr. Whelan Name: Block:
 Mr. Whelan Name: Block: Geometry/Trig Unit 10 Area and Volume of Solids Notes Packet Day 1 Notes - Prisms Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 6cm Find the area of each face: Front:
Mr. Whelan Name: Block: Geometry/Trig Unit 10 Area and Volume of Solids Notes Packet Day 1 Notes - Prisms Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 6cm Find the area of each face: Front:
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Lesson 6 Reteach. Surface Area of Prisms. Example. Exercises. 232 in^ tt^^ Find the surface area of the rectangular prism.
 Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms T h e s u m of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. T h e surface area of a rectangular prism with length f,
Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms T h e s u m of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. T h e surface area of a rectangular prism with length f,
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula
 Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
CK-12 Geometry: Exploring Similar Solids. Learning Objectives Find the relationship between similar solids and their surface areas and volumes.
 CK-12 Geometry: Exploring Similar Solids Learning Objectives Find the relationship between similar solids and their surface areas and volumes. Review Queue a. We know that every circle is similar, is every
CK-12 Geometry: Exploring Similar Solids Learning Objectives Find the relationship between similar solids and their surface areas and volumes. Review Queue a. We know that every circle is similar, is every
Lesson 6 Reteach. Perimeter of the base = 14. S. A. = area of the 2 bases + lateral area = = 52 m^.
 Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms The sum of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. The area of
Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms The sum of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. The area of
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, D Geometry
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 2D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, 2018 3D Geometry Two-dimensional shapes
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 2D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, 2018 3D Geometry Two-dimensional shapes
Student Outcomes. Classwork. Opening Exercises 1 2 (5 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine an unknown dimension of a cone or a sphere. Students know that a pyramid is a special type of cone with triangular faces and a rectangular
Student Outcomes Students use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine an unknown dimension of a cone or a sphere. Students know that a pyramid is a special type of cone with triangular faces and a rectangular
USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL
 Print this page Chapter Eight USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 8.1 AREAS AND VOLUMES In Chapter 5, we calculated areas under graphs using definite integrals. We obtained the integral by slicing up the region,
Print this page Chapter Eight USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 8.1 AREAS AND VOLUMES In Chapter 5, we calculated areas under graphs using definite integrals. We obtained the integral by slicing up the region,
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Number Sense and Operations Curriculum Framework Learning Standard
 Grade 5 Expectations in Mathematics Learning Standards from the MA Mathematics Curriculum Framework for the end of Grade 6 are numbered and printed in bold. The Franklin Public School System s grade level
Grade 5 Expectations in Mathematics Learning Standards from the MA Mathematics Curriculum Framework for the end of Grade 6 are numbered and printed in bold. The Franklin Public School System s grade level
A plane that is to the base of the figure will create a cross section that is the same shape as the base.
 Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
10-1. Enrichment. You Can Count On It!
 10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
Study Guide and Review
 State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
11.7 Exploring Similar Solids
 11.7 Exploring Similar Solids Learning Objectives Find the relationship between similar solids and their surface areas and volumes. Review Queue 1. We know that every circle is similar, is every sphere
11.7 Exploring Similar Solids Learning Objectives Find the relationship between similar solids and their surface areas and volumes. Review Queue 1. We know that every circle is similar, is every sphere
Lesson 26: Volume of Composite Three-Dimensional Objects
 Lesson 26: Volume of Composite Three-Dimensional Objects Student Outcomes Students compute volumes of three-dimensional objects composed of right prisms by using the fact that volume is additive. Lesson
Lesson 26: Volume of Composite Three-Dimensional Objects Student Outcomes Students compute volumes of three-dimensional objects composed of right prisms by using the fact that volume is additive. Lesson
Chapter 7 Connect Algebra to Geometry
 Lesson 7-1 Volume of Cylinders Page 79 Determine the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth. V Bh V (π r ) h Volume of a cylinder The base is a circle. V π() (5) Replace r with and h with 5.
Lesson 7-1 Volume of Cylinders Page 79 Determine the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth. V Bh V (π r ) h Volume of a cylinder The base is a circle. V π() (5) Replace r with and h with 5.
Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm.
 Page 1 of 17 Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm. Page 1 of 17 Page 2 of 17 2. A regular hexagon
Page 1 of 17 Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm. Page 1 of 17 Page 2 of 17 2. A regular hexagon
r the COR d e s 3 A lg e b r a Alabama Pathways
 BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E Gra 2013 2014 d e s 3 A lg e b r a Alabama Pathways I Grade 3 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Operations and Algebraic Thinking Operations and Algebraic Thinking Number
BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E Gra 2013 2014 d e s 3 A lg e b r a Alabama Pathways I Grade 3 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Operations and Algebraic Thinking Operations and Algebraic Thinking Number
COMMUNITY LEARNING CENTER LESSON PLAN
 COMMUNITY LEARNING CENTER LESSON PLAN Level (preged or GED): Content Area (RLA, Math, Science, Social Studies): General Topic: GED Math Geometry Specific Lesson Title: Surface Area and Volume of pyramids,
COMMUNITY LEARNING CENTER LESSON PLAN Level (preged or GED): Content Area (RLA, Math, Science, Social Studies): General Topic: GED Math Geometry Specific Lesson Title: Surface Area and Volume of pyramids,
Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: and Volume of Solids
 Page 1 of 15 Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and Volume of Solids SOL G.13 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional
Page 1 of 15 Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and Volume of Solids SOL G.13 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
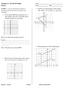 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
r the COR d e s 3 A lg e b r a New York Common Core Pathways
 BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E Gra 2013 2014 d e s 3 A lg e b r a New York Common Core Pathways I Grade 3 Number and Operations - Fractions Measurement and Data Geometry Place Value with Whole Numbers Place
BUI LT fo COM r the MON COR E Gra 2013 2014 d e s 3 A lg e b r a New York Common Core Pathways I Grade 3 Number and Operations - Fractions Measurement and Data Geometry Place Value with Whole Numbers Place
MATHEMATICS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR CHRISTIAN UNIFIED SCHOOLS OF SAN DIEGO. Third Grade Parent Handbook
 MATHEMATICS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR CHRISTIAN UNIFIED SCHOOLS OF SAN DIEGO Third Grade Parent Handbook Standards for Mathematics Number Sense 1.0 Place Value 1.1 Count, read, and write whole numbers to 1,000,000.
MATHEMATICS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR CHRISTIAN UNIFIED SCHOOLS OF SAN DIEGO Third Grade Parent Handbook Standards for Mathematics Number Sense 1.0 Place Value 1.1 Count, read, and write whole numbers to 1,000,000.
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Alignment of Destination Math Courseware with GRADE 4 Benchmarks (B1-B3)
 NUMBER SENSE SAM04101- B1 Read write whole numbers in the millions (1.1) 1.1 Read write whole numbers in the millions. I Number Sense Unit: Large Small Whole to One Million Ordering Rounding Whole SAM04102a-B1
NUMBER SENSE SAM04101- B1 Read write whole numbers in the millions (1.1) 1.1 Read write whole numbers in the millions. I Number Sense Unit: Large Small Whole to One Million Ordering Rounding Whole SAM04102a-B1
