16.7 OC680 Assignment 6, Due Wednesday Feb. 28
|
|
|
- Mildred Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 292 CHAPTER 16. NOTES Figure 16.30: Profiles of (a) velocity and (b) shear for the separating boundary layer OC680 Assignment 6, Due Wednesday Feb. 28 1: Instability of a separating boundary layer [10] A priori unstable? The profile has an inflection point which represents a shear maximum. Instability will occur if not prevented by viscosity, stratification (not a factor here) or boundaries. Here is my script: % OC680, 2018, script Hmwk6_proj1 % Separating BL problem % W. Smyth, Feb clear close all fs=18; % define parameter values direc= /Users/smyth/Dropbox/HOME/Projects/Book_Instability/figures/ ; Lz=3.0; del=.02; z=[del:del:lz-del] ; N=length(z); U=z.^2.*(6-8*z+3*z.^2); U(z>1)=1; ks=[0:.05:2.1]; Res=10.^linspace(6,1,30); bc= rf ; %
2 16.7. OC680 ASSIGNMENT 6, DUE WEDNESDAY FEB Figure 16.31: Growth rate versus wavenumber and Reynolds number for the separating boundary layer. % plot background profile U* figure subplot(1,2,1) plot(u,z, linewidth,2) xlabel( U*, fontsize,fs, fontangle, italic ) ylabel( z*, fontsize,fs, fontangle, italic ) ylim([0 1.5]) set(gca, fontsize,fs-2) subplot(1,2,2) plot(ddz(z)*u,z, linewidth,2) xlabel( U_z*, fontsize,fs, fontangle, italic ) ylim([0 1.5]) set(gca, fontsize,fs-2) print( -djpeg,[direc hmwk6_1a ]) %% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% % loop to compute sig(k,re) (takes a while!) % loop over k nk=length(ks) nre=length(res) for i=1:nk k=ks(i); % loop over Re for j=1:nre
3 294 CHAPTER 16. NOTES nu=1/res(j); [s]=vsf(z,u,nu,k,0,bc); sig(i,j)=real(s(1)); end disp([num2str(i/nk) done ]) % track progress end %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% % Find the critical Re by fitting a quadratic to sig(re) and finding the % zero. [ms,is]=max(sig,[],1); [mms,js]=max(ms); k_mx=ks(is(js)); Re_mx=Res(js); sss=max(real(sig)); jjj=(max(find(sss>max(sss)/1000))) p=polyfit(log10(res(jjj-2:jjj)),sss(jjj-2:jjj),2) Re_root=10.^roots(p) Re_err=abs(Re_root-Res(jjj)); Re_crit=Re_root(Re_err==min(Re_err)) % plot results figure contourf(ks,res,sig,max(sig(:))*[0:.1:.9]); hold on; plot(xlim,280*[1 1], k ) set(gca, yscale, log ) xlabel( k*, fontsize,fs+2, fontangle, italic ) ylabel( Re, fontsize,fs+2, fontangle, italic ) set(gca, fontsize,fs-2) %title( Growth rates for separating boundary layer, fontsize,16) lab=sprintf( Re_{crit}=%.0f,Re_crit) text(.05,.12,lab, units, normal, fontsize,fs-2) lab=sprintf( max \\sigma = %.2e at Re = %.2e, k = %.2f,mms,Re_mx,k_mx) text(.05,.05,lab, units, normal, fontsize,fs-2) colorbar print( -djpeg,[direc hmwk6_1b ]) return If you use fine enough resolution in Re, the minimum value for instability is 280, consistent with the published result. It helps to interpolate, as shown in the code above. If you got a much smaller result, e.g. 140, it is because you have the upper and lower boundaries reversed in your 4th derivative matrix. At the critical Reynolds number, the frozen flow approximation is absolutely not valid, since the growth rate is zero and therefore cannot possibly be fast in comparison to the viscous spreading of the background flow. The growth rate decreases monotonically with decreasing Reynolds number, so this flow is stabilized by viscosity. In other words, the flow is most unstable in the inviscid limit. This indicates that the instability is driven by the inflection point mechanism that applies in inviscid flow (e.g. assignment #2). Viscosity merely modifies the instability by damping its growth rate. This also assures us, via Squire s theorem, that
4 16.7. OC680 ASSIGNMENT 6, DUE WEDNESDAY FEB Figure 16.32: Echosounder image of instabilities observed in sill flow, from Armi & Farmer, 2002, PRSL. Superimposed are estimates of (1) the wavelength of a stratified shear flow instability, (2) the thickness of the separating boundary layer, and (3) the wavelength of what may be a separating boundary layer instability. the 2D modes we have been investigating are indeed the most unstable. The maximum growth rate at Re=106 growth rate is 0.107, which is about 0.06 times the maximum absolute shear. The wavelength of the fastest growing mode is 2p/1.15 = 5.5. The layer thickness, in this scaling, is just 1 (i.e. the length scale is the layer thickness), so the ratio of the wavelength to the layer thickness is 5.5. In the echosounder image, the wavelength of the dominant disturbance downstream of the separation point looks to me to be about 4 times the original thickness of the boundary layer (indicated by lines 1 and 2 on figure 16.32). Multiplying this by 4 to account for the aspect ratio of the image, I get 16, which is of the same order of magnitude as 6. Another way to make this comparison is to draw a line indicating the predicted wavelength (line 3), so that the reader can compare visually with the scales of the observed waves. Trying to guess the velocity profile from an echosounder image is an extremely uncertain business, and this is about as close as I would expect to come. Ideally, one would look at ADCP velocity measurements and make a more careful estimate but, for an order of magnitude comparison, this will do. 2: The half-holmboe instability [10] (a) The algebra is basically identical to section (i) The dispersion relation is c2 = b0. 2k (16.7.1) (ii) The positive and negative values of c represent right- and left-going interfacial gravity waves. (b) The procedure is similar to sections and
5 296 CHAPTER 16. NOTES Figure 16.33: Growth rate versus wavenumber and bulk Richardson number for the half-holmboe problem. Figure 16.34: (a) Phase speed and (b) growth rate versus wavenumber for the half- Holmboe problem.
6 16.7. OC680 ASSIGNMENT 6, DUE WEDNESDAY FEB (i) The dispersion relation is c 2 Ri b c Ri b 2k 2k 4k 2 e 2k = 0. In the limit of large k, the term with the exponential function drops out and the solution describes three waves with phase speeds given by: and 1/2 Rib c = ±, 2k c = 1 1 2k. The first pair are right- and left-going gravity waves riding on the buoyancy interface. Without the scaling, this is equivalent to (16.7.1). The third wave is a vorticity wave as described in section Its phase speed is between zero and 1. As k is decreased from, the right-going gravity wave phase-locks with the shear wave and resonates to form an instability. (ii) See figure (iii) See figure : Instabilities in a plunging downslope flow [20] See figure (a) I get s = at k = 0.47 The growth rate is much greater than 1/Re, so the frozen flow hypothesis is valid. S mx = 1, so the scaled growth rate is In contrast, the boundary layer instability in project #1 gave a scaled growth rate of 0.06, considerably smaller than this. The main difference is the proximity of the lower boundary in project #1, which tends to damp instabilities. (b) I get s = at k = The growth rate is much greater than 1/Re, so the frozen flow hypothesis is valid. The behavior at large k is an artifact of coarse resolution. It drops away as resolution is increased (see comparison below), while behavior near the FGM is not affected. (c) I get s = at k = The growth rate is a factor of ten greater than 1/Re, so the frozen flow hypothesis is marginally valid. Note that decreasing Re has an effect similar to increasing resolution. It smooths the eigenfunctions, making them easier to resolve on a coarse grid. Thus, the anomalous behavior at high k is removed even when D = 0.2. (d) I get s = at k = The growth rate is similar to 1/Re, so the frozen flow hypothesis is not valid. A typical wavenumber from cases a-c is k = 0.45, which yields a wavelength of 14h, or 7 times the thickness of the shear layer (2h). Correcting for the aspect ratio of the image (4), this wavelength would appear about 7/4 times the thickness of the shear layer (figure 16.32). On the figure, the vertical line indicates my estimate of the initial thickness of the shear layer. The horizontal line is longer by a factor 7/4. This actually agrees pretty well with the typical scale of the earliest deformations of the shear layer (which may be pure luck!) Further downstream, larger structures emerge, possibly as a result of merging of the primary billows.
7 298 CHAPTER 16. NOTES Figure 16.35: Growth rate versus wavenumber for four cases of a stratified shear flow. U = tanhz, B = Ri b tanhz. Impermeable, fixed-buoyancy boundaries at z = ±4. Grid spacing D = 0.2. Note under-resolution and boundary effects at high and low k.
The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model
 The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model The main equation The Spallart Allmaras turbulence model is a one equation model designed especially for aerospace applications; it solves a modelled transport equation
The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model The main equation The Spallart Allmaras turbulence model is a one equation model designed especially for aerospace applications; it solves a modelled transport equation
Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers
 Accepted for presentation at the 9th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Madison, WI. July -9,. Paper #8 Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, and H. G.
Accepted for presentation at the 9th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Madison, WI. July -9,. Paper #8 Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, and H. G.
Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Super-Parameterization of Boundary Layer Roll Vortices in Tropical Cyclone Models PI Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography
Detached-Eddy Simulation of a Linear Compressor Cascade with Tip Gap and Moving Wall *)
 FOI, Stockholm, Sweden 14-15 July, 2005 Detached-Eddy Simulation of a Linear Compressor Cascade with Tip Gap and Moving Wall *) A. Garbaruk,, M. Shur, M. Strelets, and A. Travin *) Study is carried out
FOI, Stockholm, Sweden 14-15 July, 2005 Detached-Eddy Simulation of a Linear Compressor Cascade with Tip Gap and Moving Wall *) A. Garbaruk,, M. Shur, M. Strelets, and A. Travin *) Study is carried out
A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity Waves
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity
Challenges in Boundary- Layer Stability Analysis Based On Unstructured Grid Solutions
 Challenges in Boundary- Layer Stability Analysis Based On Unstructured Grid Solutions Wei Liao National Institute of Aerospace, Hampton, Virginia Collaborators: Mujeeb R. Malik, Elizabeth M. Lee- Rausch,
Challenges in Boundary- Layer Stability Analysis Based On Unstructured Grid Solutions Wei Liao National Institute of Aerospace, Hampton, Virginia Collaborators: Mujeeb R. Malik, Elizabeth M. Lee- Rausch,
Marie Curie Actions. IEF Final report
 Project No : 234782 Project Acronm : 3DZZI Project Full Name : Three-dimensional structure of stratified turbulence Marie Curie Actions IEF Final report Period covered : from 5/5/29 to 3/9/2 Start date
Project No : 234782 Project Acronm : 3DZZI Project Full Name : Three-dimensional structure of stratified turbulence Marie Curie Actions IEF Final report Period covered : from 5/5/29 to 3/9/2 Start date
Graphs of Exponential
 Graphs of Exponential Functions By: OpenStaxCollege As we discussed in the previous section, exponential functions are used for many realworld applications such as finance, forensics, computer science,
Graphs of Exponential Functions By: OpenStaxCollege As we discussed in the previous section, exponential functions are used for many realworld applications such as finance, forensics, computer science,
Backward facing step Homework. Department of Fluid Mechanics. For Personal Use. Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Budapest, 2010 autumn
 Backward facing step Homework Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest, 2010 autumn Updated: October 26, 2010 CONTENTS i Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The problem
Backward facing step Homework Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest, 2010 autumn Updated: October 26, 2010 CONTENTS i Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The problem
Modeling External Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Math 1020 Objectives & Exercises Calculus Concepts Spring 2019
 Section of Textbook 1.1 AND Learning Objectives/Testable Skills Identify four representations of a function. Specify input and output variables, input and output descriptions, and input and output units.
Section of Textbook 1.1 AND Learning Objectives/Testable Skills Identify four representations of a function. Specify input and output variables, input and output descriptions, and input and output units.
Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions
 Optimized corrections for 2D FD modelling Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions Peter M. Manning and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite-difference two-dimensional correction
Optimized corrections for 2D FD modelling Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions Peter M. Manning and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite-difference two-dimensional correction
Applied Reservoir Simulation. Course. Workshop Problems
 Applied Reservoir Simulation Course Workshop Problems Reservoir Simulation Application Training Course and (Eclipse) Workshop GeoQuest Training and Development, And NExT Denver and Houston March 06 Applied
Applied Reservoir Simulation Course Workshop Problems Reservoir Simulation Application Training Course and (Eclipse) Workshop GeoQuest Training and Development, And NExT Denver and Houston March 06 Applied
An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (2000/2001)
 An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (000/001) Summary The objectives of this project were as follows: 1) Investigate iterative
An Investigation into Iterative Methods for Solving Elliptic PDE s Andrew M Brown Computer Science/Maths Session (000/001) Summary The objectives of this project were as follows: 1) Investigate iterative
The viscous forces on the cylinder are proportional to the gradient of the velocity field at the
 Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions. Milovan Perić
 Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
Large Eddy Simulation of Flow over a Backward Facing Step using Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS)
 The 14 th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics - 14ACFM October 15-19, 2013; Hanoi and Halong, Vietnam Large Eddy Simulation of Flow over a Backward Facing Step using Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS) Md. Mahfuz
The 14 th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics - 14ACFM October 15-19, 2013; Hanoi and Halong, Vietnam Large Eddy Simulation of Flow over a Backward Facing Step using Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS) Md. Mahfuz
Moving Interface Problems: Methods & Applications Tutorial Lecture II
 Moving Interface Problems: Methods & Applications Tutorial Lecture II Grétar Tryggvason Worcester Polytechnic Institute Moving Interface Problems and Applications in Fluid Dynamics Singapore National University,
Moving Interface Problems: Methods & Applications Tutorial Lecture II Grétar Tryggvason Worcester Polytechnic Institute Moving Interface Problems and Applications in Fluid Dynamics Singapore National University,
 Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK
 YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK Week Chapter: Topic 1 2 3.1:1: Percentages 3.2:1: Percentages 3 4 3.1:2: Equations and formulae 3.2:2: Equations and formulae 5 6 3.1:3: Polygons 3.2:3: Polygons 6 7 3.1:4: Using
YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK Week Chapter: Topic 1 2 3.1:1: Percentages 3.2:1: Percentages 3 4 3.1:2: Equations and formulae 3.2:2: Equations and formulae 5 6 3.1:3: Polygons 3.2:3: Polygons 6 7 3.1:4: Using
Handout: Turbulent Structures
 058:268 Turbulent Flows G. Constantinescu Handout: Turbulent Structures Recall main properties of turbulence: Three dimensional 2D turbulence exists, interesting mainly in geophysics Unsteady Broad spectrum
058:268 Turbulent Flows G. Constantinescu Handout: Turbulent Structures Recall main properties of turbulence: Three dimensional 2D turbulence exists, interesting mainly in geophysics Unsteady Broad spectrum
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics
 Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation
 Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Thompson/Ocean 420/Winter 2005 Internal Gravity Waves 1
 Thompson/Ocean 420/Winter 2005 Internal Gravity Waves 1 II. Internal waves in continuous stratification The real ocean, of course, is continuously stratified. For continuous stratification, = (z), internal
Thompson/Ocean 420/Winter 2005 Internal Gravity Waves 1 II. Internal waves in continuous stratification The real ocean, of course, is continuously stratified. For continuous stratification, = (z), internal
Computing Nearly Singular Solutions Using Pseudo-Spectral Methods
 Computing Nearly Singular Solutions Using Pseudo-Spectral Methods Thomas Y. Hou Ruo Li January 9, 2007 Abstract In this paper, we investigate the performance of pseudo-spectral methods in computing nearly
Computing Nearly Singular Solutions Using Pseudo-Spectral Methods Thomas Y. Hou Ruo Li January 9, 2007 Abstract In this paper, we investigate the performance of pseudo-spectral methods in computing nearly
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
II. Functions. 61. Find a way to graph the line from the problem 59 on your calculator. Sketch the calculator graph here, including the window values:
 II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
Project #3 MAE 598 Applied CFD
 Project #3 MAE 598 Applied CFD 16 November 2017 H.P. Huang 1 Task 1 (a) Task 1a was to perform a transient analysis of a 2-D chamber that is initially filled with air, and has water flowing through the
Project #3 MAE 598 Applied CFD 16 November 2017 H.P. Huang 1 Task 1 (a) Task 1a was to perform a transient analysis of a 2-D chamber that is initially filled with air, and has water flowing through the
A B C D E. Settings Choose height, H, free stream velocity, U, and fluid (dynamic viscosity and density ) so that: Reynolds number
 Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students:
 AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students: Email (cdhall@vt.edu) by 5 PM Suppose F b is initially aligned with F i and at t = 0 begins to rotate
AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students: Email (cdhall@vt.edu) by 5 PM Suppose F b is initially aligned with F i and at t = 0 begins to rotate
THE FLUCTUATING VELOCITY FIELD ABOVE THE FREE END OF A SURFACE- MOUNTED FINITE-HEIGHT SQUARE PRISM
 THE FLUCTUATING VELOCITY FIELD ABOVE THE FREE END OF A SURFACE- MOUNTED FINITE-HEIGHT SQUARE PRISM Rajat Chakravarty, Noorallah Rostamy, Donald J. Bergstrom and David Sumner Department of Mechanical Engineering
THE FLUCTUATING VELOCITY FIELD ABOVE THE FREE END OF A SURFACE- MOUNTED FINITE-HEIGHT SQUARE PRISM Rajat Chakravarty, Noorallah Rostamy, Donald J. Bergstrom and David Sumner Department of Mechanical Engineering
Name: Math Analytic Geometry and Calculus III - Spring Matlab Project - due on Wednesday, March 30
 Name: Math 275 - Analytic Geometry and Calculus III - Spring 2011 Solve the following problems: Matlab Project - due on Wednesday, March 30 (Section 14.1 # 30) Use Matlab to graph the curve given by the
Name: Math 275 - Analytic Geometry and Calculus III - Spring 2011 Solve the following problems: Matlab Project - due on Wednesday, March 30 (Section 14.1 # 30) Use Matlab to graph the curve given by the
Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube
 Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube Deliverable 5.1.2 of Work Package WP5 (Creating Impact) Authors: Stanislav Knotek Czech Metrology Institute
Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube Deliverable 5.1.2 of Work Package WP5 (Creating Impact) Authors: Stanislav Knotek Czech Metrology Institute
Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Contents.
 Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Preface page 2 Part I Fluid Dynamics and Waves 7 1 Elements of fluid dynamics 9 1.1
Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Preface page 2 Part I Fluid Dynamics and Waves 7 1 Elements of fluid dynamics 9 1.1
3.5D Graphing Rational Functions
 3.5D Graphing Rational Functions A. Strategy 1. Find all asymptotes (vertical, horizontal, oblique, curvilinear) and holes for the function. 2. Find the and intercepts. 3. Plot the and intercepts, draw
3.5D Graphing Rational Functions A. Strategy 1. Find all asymptotes (vertical, horizontal, oblique, curvilinear) and holes for the function. 2. Find the and intercepts. 3. Plot the and intercepts, draw
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. OVERVIEW... 2 2. CHOICE OF MODEL OR FULL SCALE... 2 3. NOMINAL WAKE IN MODEL SCALE... 3 3.1 Pre-processing... 3 3.1.1 Geometry... 3 3.1.2 Computational Domain and Boundary
Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. OVERVIEW... 2 2. CHOICE OF MODEL OR FULL SCALE... 2 3. NOMINAL WAKE IN MODEL SCALE... 3 3.1 Pre-processing... 3 3.1.1 Geometry... 3 3.1.2 Computational Domain and Boundary
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
Comparison of a two-dimensional viscid and inviscid model for rotating stall analysis
 Comparison of a two-dimensional viscid and inviscid model for rotating stall analysis S. LJEVAR, H.C. DE LANGE, A.A. VAN STEENHOVEN Department of Mechanical Engineering Eindhoven University of Technology
Comparison of a two-dimensional viscid and inviscid model for rotating stall analysis S. LJEVAR, H.C. DE LANGE, A.A. VAN STEENHOVEN Department of Mechanical Engineering Eindhoven University of Technology
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Water. Notes. Free surface. Boundary conditions. This week: extend our 3D flow solver to full 3D water We need to add two things:
 Notes Added a 2D cross-section viewer for assignment 6 Not great, but an alternative if the full 3d viewer isn t working for you Warning about the formulas in Fedkiw, Stam, and Jensen - maybe not right
Notes Added a 2D cross-section viewer for assignment 6 Not great, but an alternative if the full 3d viewer isn t working for you Warning about the formulas in Fedkiw, Stam, and Jensen - maybe not right
Mesoscale Ocean Large Eddy Simulation (MOLES)
 Mesoscale Ocean Large Eddy Simulation (MOLES) Baylor Fox-Kemper (Brown) Scott Bachman (Cambridge) Frank Bryan & David Bailey (NCAR) Viscosity Parameterizations GCMs use horizontal eddy viscosity to account
Mesoscale Ocean Large Eddy Simulation (MOLES) Baylor Fox-Kemper (Brown) Scott Bachman (Cambridge) Frank Bryan & David Bailey (NCAR) Viscosity Parameterizations GCMs use horizontal eddy viscosity to account
1
 Zeros&asymptotes Example 1 In an early version of this activity I began with a sequence of simple examples (parabolas and cubics) working gradually up to the main idea. But now I think the best strategy
Zeros&asymptotes Example 1 In an early version of this activity I began with a sequence of simple examples (parabolas and cubics) working gradually up to the main idea. But now I think the best strategy
VOLCANIC DEFORMATION MODELLING: NUMERICAL BENCHMARKING WITH COMSOL
 VOLCANIC DEFORMATION MODELLING: NUMERICAL BENCHMARKING WITH COMSOL The following is a description of the model setups and input/output parameters for benchmarking analytical volcanic deformation models
VOLCANIC DEFORMATION MODELLING: NUMERICAL BENCHMARKING WITH COMSOL The following is a description of the model setups and input/output parameters for benchmarking analytical volcanic deformation models
MATERHORN The immersed boundary method for flow over complex terrain
 MATERHORN The immersed boundary method for flow over complex terrain Tina Katopodes Chow, Jingyi Bao, Jason Simon Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Berkeley Overview p Field
MATERHORN The immersed boundary method for flow over complex terrain Tina Katopodes Chow, Jingyi Bao, Jason Simon Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Berkeley Overview p Field
PC-MATLAB PRIMER. This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens.
 PC-MATLAB PRIMER This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens. >> 2*3 ans = 6 PCMATLAB uses several lines for the answer, but I ve edited this to save space.
PC-MATLAB PRIMER This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens. >> 2*3 ans = 6 PCMATLAB uses several lines for the answer, but I ve edited this to save space.
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION
 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
FLOW VISUALISATION AROUND A SOLID SPHERE ON A ROUGH BED UNDER REGULAR WAVES
 FLOW VISUALISATION AROUND A SOLID SPHERE ON A ROUGH BED UNDER REGULAR WAVES H.P.V.Vithana 1, Richard Simons 2 and Martin Hyde 3 Flow visualization using Volumetric Three-component Velocimetry (V3V) was
FLOW VISUALISATION AROUND A SOLID SPHERE ON A ROUGH BED UNDER REGULAR WAVES H.P.V.Vithana 1, Richard Simons 2 and Martin Hyde 3 Flow visualization using Volumetric Three-component Velocimetry (V3V) was
Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Overview for Families
 unit: Graphing Equations Mathematical strand: Algebra The following pages will help you to understand the mathematics that your child is currently studying as well as the type of problems (s)he will solve
unit: Graphing Equations Mathematical strand: Algebra The following pages will help you to understand the mathematics that your child is currently studying as well as the type of problems (s)he will solve
A Deterministic Viscous Vortex Method for Grid-free CFD with Moving Boundary Conditions
 A Deterministic Viscous Vortex Method for Grid-free CFD with Moving Boundary Conditions M.W. PITMAN, A.D. LUCEY Department of Mechanical Engineering Curtin University of Technology GPO Box U1987, Perth,
A Deterministic Viscous Vortex Method for Grid-free CFD with Moving Boundary Conditions M.W. PITMAN, A.D. LUCEY Department of Mechanical Engineering Curtin University of Technology GPO Box U1987, Perth,
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Ripple Tank. Refraction and Dispersion
 Ripple Tank Refraction and Dispersion There is a distinct relationship between frequency, wave velocity, and wavelength. If you know any two, you can determine the third simply by using the formula v =
Ripple Tank Refraction and Dispersion There is a distinct relationship between frequency, wave velocity, and wavelength. If you know any two, you can determine the third simply by using the formula v =
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
The Bisection Method versus Newton s Method in Maple (Classic Version for Windows)
 The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
ME scope Application Note 19
 ME scope Application Note 19 Using the Stability Diagram to Estimate Modal Frequency & Damping The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-4500 Advanced
ME scope Application Note 19 Using the Stability Diagram to Estimate Modal Frequency & Damping The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-4500 Advanced
Voluntary State Curriculum Algebra II
 Algebra II Goal 1: Integration into Broader Knowledge The student will develop, analyze, communicate, and apply models to real-world situations using the language of mathematics and appropriate technology.
Algebra II Goal 1: Integration into Broader Knowledge The student will develop, analyze, communicate, and apply models to real-world situations using the language of mathematics and appropriate technology.
Edge detection. Convert a 2D image into a set of curves. Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels
 Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Linear, Quadratic, Exponential, and Absolute Value Functions
 Linear, Quadratic, Exponential, and Absolute Value Functions Linear Quadratic Exponential Absolute Value Y = mx + b y = ax 2 + bx + c y = a b x y = x 1 What type of graph am I? 2 What can you tell me about
Linear, Quadratic, Exponential, and Absolute Value Functions Linear Quadratic Exponential Absolute Value Y = mx + b y = ax 2 + bx + c y = a b x y = x 1 What type of graph am I? 2 What can you tell me about
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
DATA PLOTTING WITH MATLAB
 DATA PLOTTING WITH MATLAB Prof. Marco Pilotti marco.pilotti@ing.unibs.it Dr. Giulia Valerio giulia.valerio@ing.unibs.it Giulia Valerio 7Marzo 2014 1 1. WHY MATLAB? WHY MATLAB? Matlab is a high-level programming
DATA PLOTTING WITH MATLAB Prof. Marco Pilotti marco.pilotti@ing.unibs.it Dr. Giulia Valerio giulia.valerio@ing.unibs.it Giulia Valerio 7Marzo 2014 1 1. WHY MATLAB? WHY MATLAB? Matlab is a high-level programming
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
ENGR Socolofsky
 ENGR 102-213 - Socolofsky Date : due 9/3/2018 at 12:40 p.m. Engineering Lab I - Computation Lab Assignment #01b Writing Your Own Programs Return your solution (one per group) as outlined in the activities
ENGR 102-213 - Socolofsky Date : due 9/3/2018 at 12:40 p.m. Engineering Lab I - Computation Lab Assignment #01b Writing Your Own Programs Return your solution (one per group) as outlined in the activities
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL. Tomasz Maliszewski
 Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Straight Lines. 2 of 71. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Stability and Pulsations of Wolf - Rayet Stars
 Stability and Pulsations of Wolf - Rayet Stars Talk presented on the conference Hydrogen - Deficient Stars Tübingen, September 20, 2007 Wolfgang Glatzel Institut für Astrophysik, Universität Göttingen
Stability and Pulsations of Wolf - Rayet Stars Talk presented on the conference Hydrogen - Deficient Stars Tübingen, September 20, 2007 Wolfgang Glatzel Institut für Astrophysik, Universität Göttingen
Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N)
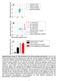 Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N) 6 4 A Individual Trials Subject Average Velocity Average Ideal Performance 2 0 0 0.2 0.4 6 4 2 B 0 0 0.2 0.4 Movement Velocity (m/s)
Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N) Mid-movement Force (N) 6 4 A Individual Trials Subject Average Velocity Average Ideal Performance 2 0 0 0.2 0.4 6 4 2 B 0 0 0.2 0.4 Movement Velocity (m/s)
Numerical Simulation of Coastal Wave Processes with the Use of Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Method
 Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Division of Hydraulics and Environmental Engineering Laboratory of Maritime Engineering Christos V. Makris Dipl.
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Division of Hydraulics and Environmental Engineering Laboratory of Maritime Engineering Christos V. Makris Dipl.
DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS
 DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS Alexandre T. P. Alho Laboratório de Sistemas de Propulsão DENO/POLI, UFRJ INTRODUCTION Motivation Growing demand for high efficiency propulsion
DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS Alexandre T. P. Alho Laboratório de Sistemas de Propulsão DENO/POLI, UFRJ INTRODUCTION Motivation Growing demand for high efficiency propulsion
Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D
 Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Chapter 15. Light Waves
 Chapter 15 Light Waves Chapter 15 is finished, but is not in camera-ready format. All diagrams are missing, but here are some excerpts from the text with omissions indicated by... After 15.1, read 15.2
Chapter 15 Light Waves Chapter 15 is finished, but is not in camera-ready format. All diagrams are missing, but here are some excerpts from the text with omissions indicated by... After 15.1, read 15.2
APPM 2460 PLOTTING IN MATLAB
 APPM 2460 PLOTTING IN MATLAB. Introduction Matlab is great at crunching numbers, and one of the fundamental ways that we understand the output of this number-crunching is through visualization, or plots.
APPM 2460 PLOTTING IN MATLAB. Introduction Matlab is great at crunching numbers, and one of the fundamental ways that we understand the output of this number-crunching is through visualization, or plots.
Rotating Moving Boundary Analysis Using ANSYS 5.7
 Abstract Rotating Moving Boundary Analysis Using ANSYS 5.7 Qin Yin Fan CYBERNET SYSTEMS CO., LTD. Rich Lange ANSYS Inc. As subroutines in commercial software, APDL (ANSYS Parametric Design Language) provides
Abstract Rotating Moving Boundary Analysis Using ANSYS 5.7 Qin Yin Fan CYBERNET SYSTEMS CO., LTD. Rich Lange ANSYS Inc. As subroutines in commercial software, APDL (ANSYS Parametric Design Language) provides
Surface effects in QG dynamics
 Surface effects in QG dynamics Ben Harvey b.j.harvey@reading.ac.uk Supervisor: Maarten Ambaum 2/11/2010 Introduction Surface Outline QG dynamics Surface QG (temperature) 2-d Euler (vorticity) 2/11/2010
Surface effects in QG dynamics Ben Harvey b.j.harvey@reading.ac.uk Supervisor: Maarten Ambaum 2/11/2010 Introduction Surface Outline QG dynamics Surface QG (temperature) 2-d Euler (vorticity) 2/11/2010
MMAE-540 Adv. Robotics and Mechatronics - Fall 2007 Homework 4
 MMAE-54 Adv. Robotics and Mechatronics - Fall 27 Homework 4 Assigned Wednesday Sep. 9th Due Wednesday Sept. 26th.5 Trajectory for t = s.5 Trajectory for t = 2 s.5.5 -.5 -.5 - - -.5 -.5-2 - 2-2 -.5 Trajectory
MMAE-54 Adv. Robotics and Mechatronics - Fall 27 Homework 4 Assigned Wednesday Sep. 9th Due Wednesday Sept. 26th.5 Trajectory for t = s.5 Trajectory for t = 2 s.5.5 -.5 -.5 - - -.5 -.5-2 - 2-2 -.5 Trajectory
List of NEW Maths content
 List of NEW Maths content Our brand new Maths content for the new Maths GCSE (9-1) consists of 212 chapters broken up into 37 titles and 4 topic areas (Algebra, Geometry & Measures, Number and Statistics).
List of NEW Maths content Our brand new Maths content for the new Maths GCSE (9-1) consists of 212 chapters broken up into 37 titles and 4 topic areas (Algebra, Geometry & Measures, Number and Statistics).
10.1 Overview. Section 10.1: Overview. Section 10.2: Procedure for Generating Prisms. Section 10.3: Prism Meshing Options
 Chapter 10. Generating Prisms This chapter describes the automatic and manual procedure for creating prisms in TGrid. It also discusses the solution to some common problems that you may face while creating
Chapter 10. Generating Prisms This chapter describes the automatic and manual procedure for creating prisms in TGrid. It also discusses the solution to some common problems that you may face while creating
Supplemental Material Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations
 Supplemental Material Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations 1. Extended Results 1.1. 2-D Smoke Plume Additional results for the 2-D smoke plume example are shown in Figures
Supplemental Material Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations 1. Extended Results 1.1. 2-D Smoke Plume Additional results for the 2-D smoke plume example are shown in Figures
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions
 Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways
 Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver.
 Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES AND MOMENTS FOR A GRAVITY BASED STRUCTURE PREDICTED USING CFD
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-49593 WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-49593 WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES
Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute Value Square Root Exponential Reciprocal
 Topic 2.0 Review Concepts What are non linear equations? Student Notes Unit 2 Non linear Equations Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute
Topic 2.0 Review Concepts What are non linear equations? Student Notes Unit 2 Non linear Equations Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute
ME422 Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips
 Cal Poly San Luis Obispo Mechanical Engineering ME Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips Ridgely/Owen, last update Jan Building A Model The way in which we construct models for analyzing
Cal Poly San Luis Obispo Mechanical Engineering ME Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips Ridgely/Owen, last update Jan Building A Model The way in which we construct models for analyzing
Projectile Trajectory Scenarios
 Projectile Trajectory Scenarios Student Worksheet Name Class Note: Sections of this document are numbered to correspond to the pages in the TI-Nspire.tns document ProjectileTrajectory.tns. 1.1 Trajectories
Projectile Trajectory Scenarios Student Worksheet Name Class Note: Sections of this document are numbered to correspond to the pages in the TI-Nspire.tns document ProjectileTrajectory.tns. 1.1 Trajectories
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models
 Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
Finite-difference elastic modelling below a structured free surface
 FD modelling below a structured free surface Finite-difference elastic modelling below a structured free surface Peter M. Manning ABSTRACT This paper shows experiments using a unique method of implementing
FD modelling below a structured free surface Finite-difference elastic modelling below a structured free surface Peter M. Manning ABSTRACT This paper shows experiments using a unique method of implementing
Lab 2: Real-Time Automotive Suspension system Simulator
 ENGG*4420 Real Time System Design Lab 2: Real-Time Automotive Suspension system Simulator TA: Aws Abu-Khudhair (aabukhud@uoguelph.ca) Due: Week of Oct. 12th Aws Abu-Khudhair ENGG*4420 1 Today s Activities
ENGG*4420 Real Time System Design Lab 2: Real-Time Automotive Suspension system Simulator TA: Aws Abu-Khudhair (aabukhud@uoguelph.ca) Due: Week of Oct. 12th Aws Abu-Khudhair ENGG*4420 1 Today s Activities
NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES
 NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES Ben R. Hodges 1 (A.M., ASCE) and Sarah Kelly Delavan 2 ABSTRACT Analysis of numerical diffusion and dissipation rates in a hydrostatic
NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES Ben R. Hodges 1 (A.M., ASCE) and Sarah Kelly Delavan 2 ABSTRACT Analysis of numerical diffusion and dissipation rates in a hydrostatic
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. OVERVIEW... 2 2. COMPUTATIONAL PROCEDURE.. 2 2.1 Preliminaries... 2 2.2 Code and Computer... 3 2.3 Ship Geometry, Computational Domain, and Boundary Conditions... 3 2.4
Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. OVERVIEW... 2 2. COMPUTATIONAL PROCEDURE.. 2 2.1 Preliminaries... 2 2.2 Code and Computer... 3 2.3 Ship Geometry, Computational Domain, and Boundary Conditions... 3 2.4
Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves
 Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Lindsay Christine Kirk IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Lindsay Christine Kirk IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA
 Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA Andrew Smyth, P.E. LPI, Inc., New York, NY, USA Abstract Overhead crane wire ropes utilized within manufacturing plants are subject to extensive
Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA Andrew Smyth, P.E. LPI, Inc., New York, NY, USA Abstract Overhead crane wire ropes utilized within manufacturing plants are subject to extensive
Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
 Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
Gravity Methods (VII) wrap up
 Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Gravity Methods (VII) wrap up tom.h.wilson tom.wilson@mail.wvu.edu Department of Geology and Geography West Virginia University Morgantown, WV Items on the list
Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Gravity Methods (VII) wrap up tom.h.wilson tom.wilson@mail.wvu.edu Department of Geology and Geography West Virginia University Morgantown, WV Items on the list
Prentice Hall Pre-Algebra 2004 Correlated to: Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12)
 Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12) NUMBER AND OPERATIONS STANDARD 1: Students understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and
Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12) NUMBER AND OPERATIONS STANDARD 1: Students understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and
Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching
 Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching Paul Groenenboom ESI Group Delft, Netherlands Martin Siemann German Aerospace Center (DLR) Stuttgart, Germany
Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching Paul Groenenboom ESI Group Delft, Netherlands Martin Siemann German Aerospace Center (DLR) Stuttgart, Germany
Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow
 Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow What is Contrast Optimization? Contrast Optimization (CO) is a new technique for improving performance of imaging
Contrast Optimization A new way to optimize performance Kenneth Moore, Technical Fellow What is Contrast Optimization? Contrast Optimization (CO) is a new technique for improving performance of imaging
Numerical Modelling in Fortran: day 6. Paul Tackley, 2017
 Numerical Modelling in Fortran: day 6 Paul Tackley, 2017 Today s Goals 1. Learn about pointers, generic procedures and operators 2. Learn about iterative solvers for boundary value problems, including
Numerical Modelling in Fortran: day 6 Paul Tackley, 2017 Today s Goals 1. Learn about pointers, generic procedures and operators 2. Learn about iterative solvers for boundary value problems, including
