3D Resistivity Logging Instruments
|
|
|
- Cecily Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M.Paszyński (1), D.Pardo (2), L.Demkowicz (3), C.Torres-Verdin (2) (1) Department of Modeling and Information Technology, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland (2) Department of Petroleum and Geosystems Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin, USA (3) Institute for Computational Engineering Sciences The University of Texas at Austin, USA CE th ISPE International Conference on Concurrent Engineering
2 Motivation 3D DC resistivity measurements simulations in deviated wells are of great interest to the oil industry. There is a need to solve at least 40 positions of the receiver and transmitter antennas. Each position requires fully 3D Finite Element Method computations of the Poisson equation. The electric field is given by E = u where u is a scalar potential defined by σ ( u ) = f Main challenge: 3D computations are expensive
3 Why distributed parallel computations? Parallel distributed software is better than execution of serial code for many logging positions simultaneously, because: It utilizes less memory. It can be utilized in large parallel machines (number of processors is NOT limited by number of logging positions). It re-utilizes information about results from previous logging positions. It is more suitable for inverse problems. It provides faster first results, which speeds up the developing and debugging process. It supports parallel hp adaptive computations
4 Why distributed parallel computations? Distributed memory architecture 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB Less memory on each processor - cheaper computations
5 Why distributed parallel computations? We can utilize hundreds and thousands of processors Faster computations wrt. parallel execution of serial code for each position of antenna
6 CE infrastructure For each logging position, the Main component generates distributed FE mesh based on the geometry of the domain prescribed in the Geometry Modeling Package, and executes the Parallel multifrontal solver solving the Poisson equation prescribed in the Integration component.
7 CE infrastructure
8 Application of Parallel 3D Code to Resistivity Logging Simulations 3D Mesh designed by hand
9 Antenna radiating into a homogenous space. Mesh designed by hand. 3D solution coincides with the exact solution and with result of 2D goal-oriented code 1 4ΠRσ
10 Axially symmetric layers, mesh designed by hand. Fixed position of Tx and Rx. 3D Code Result: D Code Result: 1.04
11 Full 3D problem for deviated wells. 0 deg 30 deg Front view Side view Crosssection Zoom 15x
12 Full 3D problem for deviated wells. 45 deg 60 deg Front view Side view Crosssection Zoom 15x
13 Full 3D problem for deviated wells. The problem with deviated wells requires introduction of the mesh refinement strategy to minimize the numerical error.
14 Parallel performance same for all above problems More then 90% relative efficiency (6.7 times faster by utilizing 7 processors)
15 One transmitter and three receiver antennas 2 nd differenve of potentials in vertical direction
16 Generation of the optimal 2D mesh The optimal hp mesh for the axially symmetric problem generated by the 2D selfadaptive goal-oriented hp Finite Element Method code. The mesh contains elements with various size h, and various polynomial orders of approximation p over finite element edges and interiors.
17 hp Finite Element Graphical notation for various polynomial orders of approximation on element edges and faces
18 Transfer of grids The optimal 2D mesh generated by self-adaptive goal-oriented hp adaptive code was transferred into 3D mesh by full revolution of the 2D mesh. The obtained 3D mesh was tilted by 30, 45 and 60 degrees.
19 Results - 2 nd difference of potentials in vertical direction Processor 5 Processor 6 Processor 1 Processor 7 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor 4 Domain decomposition for optimal hp refined mesh Processor 8
20 Results for axisymmetric problem 2 nd difference of potential (V)
21 Results for 30 degrees deviated wells 2 nd difference of potential (V)
22 Results for 45 degrees deviated wells 2 nd difference of potential (V)
23 Results for 60 degrees deviated wells 2 nd difference of potential (V)
24 Comparison of results 2 nd difference of potential (V)
25 Efficiency measurements Problem size: d.o.f. Efficiency measurements of parallel solver executed on 2, 4 and 8 processors
26 Conclusions CE infrastructure which automatically solves 3D ressistivity measurement problems in a sequence of logging positions in an efficient way has been developed. The 3D finite element mesh was obtained by revolution of the 2D optimal mesh produced by the 2D goal-oriented self-adaptive hp finite element code, minimizing the numerical error at the receiver antennas. The parallel 3D code supports automatic hp adaptivity driven by energy norm. The code will be extended to support 3D goal-oriented hp adaptivity. The future work will include goal-oriented hp adaptive computations of 3D problems in deviated wells, possibly with mandrel or casing, and with several layers in the formation. An anisotropy and invasion effects will be also studied.
27 Acknowledgments Presented work was sponsored by Polish MEiN grant no. 3 T08B and by The University of Texas at Austin Research Consortium on Formation Evaluation, jointly sponsored by:
Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments
 Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M. Paszyński 1,3, D. Pardo 1,2, L. Demkowicz 1, C. Torres-Verdin 2 1 Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences 2
Parallel hp-finite Element Simulations of 3D Resistivity Logging Instruments M. Paszyński 1,3, D. Pardo 1,2, L. Demkowicz 1, C. Torres-Verdin 2 1 Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences 2
The Development of a 3D Self-Adaptive Goal-Oriented hp-finite Element Software for Simulations of Resistivity Logging Instruments
 A Progress Report on: The Development of a 3D Self-Adaptive Goal-Oriented hp-finite Element Software for Simulations of Resistivity Logging Instruments David Pardo (dzubiaur@yahoo.es), L. Demkowicz, C.
A Progress Report on: The Development of a 3D Self-Adaptive Goal-Oriented hp-finite Element Software for Simulations of Resistivity Logging Instruments David Pardo (dzubiaur@yahoo.es), L. Demkowicz, C.
ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT
 Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
Modeling the Acoustic Scattering from Axially Symmetric Fluid, Elastic, and Poroelastic Objects due to Nonsymmetric Forcing Using COMSOL Multiphysics
 Modeling the Acoustic Scattering from Axially Symmetric Fluid, Elastic, and Poroelastic Objects due to Nonsymmetric Forcing Using COMSOL Multiphysics Anthony L. Bonomo *1 and Marcia J. Isakson 1 1 Applied
Modeling the Acoustic Scattering from Axially Symmetric Fluid, Elastic, and Poroelastic Objects due to Nonsymmetric Forcing Using COMSOL Multiphysics Anthony L. Bonomo *1 and Marcia J. Isakson 1 1 Applied
HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES
 HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland email: paszynsk@agh.edu.pl
HYBRID DIRECT AND ITERATIVE SOLVER FOR H ADAPTIVE MESHES WITH POINT SINGULARITIES Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland email: paszynsk@agh.edu.pl
Nanostructures with HFSS
 . May 9 leidenberger@ifh.ee.ethz.ch / 9 Nanostructures with HFSS Patrick Leidenberger. May 9 . May 9 leidenberger@ifh.ee.ethz.ch / 9 Table of contents HFSS Features Mie Benchmark Possible Simulation Mistakes
. May 9 leidenberger@ifh.ee.ethz.ch / 9 Nanostructures with HFSS Patrick Leidenberger. May 9 . May 9 leidenberger@ifh.ee.ethz.ch / 9 Table of contents HFSS Features Mie Benchmark Possible Simulation Mistakes
A direct solver with reutilization of previously-computed LU factorizations for h-adaptive finite element grids with point singularities
 Maciej Paszynski AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunication Department of Computer Science al. A. Mickiewicza 30 30-059 Krakow, Poland tel.
Maciej Paszynski AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunication Department of Computer Science al. A. Mickiewicza 30 30-059 Krakow, Poland tel.
Using multifrontal hierarchically solver and HPC systems for 3D Helmholtz problem
 Using multifrontal hierarchically solver and HPC systems for 3D Helmholtz problem Sergey Solovyev 1, Dmitry Vishnevsky 1, Hongwei Liu 2 Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics SB RAS 1 EXPEC ARC,
Using multifrontal hierarchically solver and HPC systems for 3D Helmholtz problem Sergey Solovyev 1, Dmitry Vishnevsky 1, Hongwei Liu 2 Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics SB RAS 1 EXPEC ARC,
Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications
 Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications Charles Crook July 30, 2013 Abstract The finite element method is a fast computational method that also has a solid mathematical theory
Finite Element Methods for the Poisson Equation and its Applications Charles Crook July 30, 2013 Abstract The finite element method is a fast computational method that also has a solid mathematical theory
HPC Algorithms and Applications
 HPC Algorithms and Applications Dwarf #5 Structured Grids Michael Bader Winter 2012/2013 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids, Winter 2012/2013 1 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids 1. dense linear algebra 2. sparse linear
HPC Algorithms and Applications Dwarf #5 Structured Grids Michael Bader Winter 2012/2013 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids, Winter 2012/2013 1 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids 1. dense linear algebra 2. sparse linear
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM
 Computer Science 7 (3) 26 http://dx.doi.org/.7494/csci.26.7.3.297 Maciej Woźniak Maciej Paszyński APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM Abstract In this paper,
Computer Science 7 (3) 26 http://dx.doi.org/.7494/csci.26.7.3.297 Maciej Woźniak Maciej Paszyński APPLICATION OF PROJECTION-BASED INTERPOLATION ALGORITHM FOR NON-STATIONARY PROBLEM Abstract In this paper,
Exploring unstructured Poisson solvers for FDS
 Exploring unstructured Poisson solvers for FDS Dr. Susanne Kilian hhpberlin - Ingenieure für Brandschutz 10245 Berlin - Germany Agenda 1 Discretization of Poisson- Löser 2 Solvers for 3 Numerical Tests
Exploring unstructured Poisson solvers for FDS Dr. Susanne Kilian hhpberlin - Ingenieure für Brandschutz 10245 Berlin - Germany Agenda 1 Discretization of Poisson- Löser 2 Solvers for 3 Numerical Tests
Implicit Matrix Representations of Rational Bézier Curves and Surfaces
 Implicit Matrix Representations of Rational Bézier Curves and Surfaces Laurent Busé INRIA Sophia Antipolis, France Laurent.Buse@inria.fr GD/SPM Conference, Denver, USA November 11, 2013 Overall motivation
Implicit Matrix Representations of Rational Bézier Curves and Surfaces Laurent Busé INRIA Sophia Antipolis, France Laurent.Buse@inria.fr GD/SPM Conference, Denver, USA November 11, 2013 Overall motivation
An Example Eddy Currents
 An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
HFSS Hybrid Finite Element and Integral Equation Solver for Large Scale Electromagnetic Design and Simulation
 HFSS Hybrid Finite Element and Integral Equation Solver for Large Scale Electromagnetic Design and Simulation Laila Salman, PhD Technical Services Specialist laila.salman@ansys.com 1 Agenda Overview of
HFSS Hybrid Finite Element and Integral Equation Solver for Large Scale Electromagnetic Design and Simulation Laila Salman, PhD Technical Services Specialist laila.salman@ansys.com 1 Agenda Overview of
MAE 323: Lab 7. Instructions. Pressure Vessel Alex Grishin MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1
 Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 18 (2013 ) 1545 1554 2013 International Conference on Computational Science Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 18 (2013 ) 1545 1554 2013 International Conference on Computational Science Hypergraph Grammars in hp-adaptive Finite Element Method
ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION
 Scientific Research of the Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION Ewa Węgrzyn-Skrzypczak, Tomasz Skrzypczak Institute of Mathematics, Czestochowa
Scientific Research of the Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION Ewa Węgrzyn-Skrzypczak, Tomasz Skrzypczak Institute of Mathematics, Czestochowa
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5
 ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
Real-Time Shape Editing using Radial Basis Functions
 Real-Time Shape Editing using Radial Basis Functions, Leif Kobbelt RWTH Aachen Boundary Constraint Modeling Prescribe irregular constraints Vertex positions Constrained energy minimization Optimal fairness
Real-Time Shape Editing using Radial Basis Functions, Leif Kobbelt RWTH Aachen Boundary Constraint Modeling Prescribe irregular constraints Vertex positions Constrained energy minimization Optimal fairness
Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
AllScale Pilots Applications AmDaDos Adaptive Meshing and Data Assimilation for the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 671603 An Exascale Programming, Multi-objective Optimisation and Resilience
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 671603 An Exascale Programming, Multi-objective Optimisation and Resilience
Optimization of Execution Time, Energy Consumption, and Accuracy during Finite Element Method Simulations
 Optimization of Execution Time, Energy Consumption, and Accuracy during Finite Element Method Simulations Maciej Woźniak, Marcin Łoś, Leszek Siwik, Darusz Król, Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer
Optimization of Execution Time, Energy Consumption, and Accuracy during Finite Element Method Simulations Maciej Woźniak, Marcin Łoś, Leszek Siwik, Darusz Król, Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer
Time domain construction of acoustic scattering by elastic targets through finite element analysis
 Time domain construction of acoustic scattering by elastic targets through finite element analysis Aaron Gunderson*, Blake Simon, Anthony Bonomo, Marcia Isakson Applied Research Laboratories University
Time domain construction of acoustic scattering by elastic targets through finite element analysis Aaron Gunderson*, Blake Simon, Anthony Bonomo, Marcia Isakson Applied Research Laboratories University
2. Convex sets. x 1. x 2. affine set: contains the line through any two distinct points in the set
 2. Convex sets Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes dual
2. Convex sets Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes dual
Contents. I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1
 page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
Leveraging Integrated Concurrent Engineering for vehicle dynamics simulation. Manuel CHENE MSC.Software France
 Leveraging Integrated Concurrent Engineering for vehicle dynamics simulation Manuel CHENE MSC.Software France Agenda Challenge of vehicle dynamic simulation: frequency domain coverage necessity for a multi
Leveraging Integrated Concurrent Engineering for vehicle dynamics simulation Manuel CHENE MSC.Software France Agenda Challenge of vehicle dynamic simulation: frequency domain coverage necessity for a multi
Convex Optimization. Convex Sets. ENSAE: Optimisation 1/24
 Convex Optimization Convex Sets ENSAE: Optimisation 1/24 Today affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes
Convex Optimization Convex Sets ENSAE: Optimisation 1/24 Today affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes
Eulerian Techniques for Fluid-Structure Interactions - Part II: Applications
 Published in Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering Vol. 103, Proceedings of ENUMATH 2013, pp. 755-762, Springer, 2014 Eulerian Techniques for Fluid-Structure Interactions - Part II: Applications
Published in Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering Vol. 103, Proceedings of ENUMATH 2013, pp. 755-762, Springer, 2014 Eulerian Techniques for Fluid-Structure Interactions - Part II: Applications
Hydro-elastic analysis of a propeller using CFD and FEM co-simulation
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Hydro-elastic analysis of a propeller using CFD and FEM co-simulation Vesa Nieminen 1 1 VTT Technical Research Centre
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Hydro-elastic analysis of a propeller using CFD and FEM co-simulation Vesa Nieminen 1 1 VTT Technical Research Centre
The Finite Element Method
 The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
A Framework for the Upscaling of the Electrical Conductivity in the Quasi-static Maxwell s Equations
 A Framework for the Upscaling of the Electrical Conductivity in the Quasi-static Maxwell s Equations arxiv:1610.02948v1 [math.na] 7 Oct 2016 L. A. Caudillo-Mata*, E. Haber, L. J. Heagy, and C. Schwarzbach
A Framework for the Upscaling of the Electrical Conductivity in the Quasi-static Maxwell s Equations arxiv:1610.02948v1 [math.na] 7 Oct 2016 L. A. Caudillo-Mata*, E. Haber, L. J. Heagy, and C. Schwarzbach
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute What are the DH parameters for describing the relative pose of the two frames?
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute What are the DH parameters for describing the relative pose of the two frames?
2. Convex sets. affine and convex sets. some important examples. operations that preserve convexity. generalized inequalities
 2. Convex sets Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes dual
2. Convex sets Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe affine and convex sets some important examples operations that preserve convexity generalized inequalities separating and supporting hyperplanes dual
HEAT A PC-program for heat transfer in two dimensions Update manual. BLOCON
 Software within building physics and ground heat storage HEAT2 7.0 A PC-program for heat transfer in two dimensions Update manual August 8, 2006 BLOCON www.buildingphysics.com Contents 1. WHAT S NEW IN
Software within building physics and ground heat storage HEAT2 7.0 A PC-program for heat transfer in two dimensions Update manual August 8, 2006 BLOCON www.buildingphysics.com Contents 1. WHAT S NEW IN
Two-view geometry Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 10
 Two-view geometry http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 10 Course announcements Homework 2 is due on February 23 rd. - Any questions about the homework? - How many of
Two-view geometry http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 10 Course announcements Homework 2 is due on February 23 rd. - Any questions about the homework? - How many of
THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS. Alekseí Yu. Chekunov. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIQKI VESNIK Corrected proof Available online 01.10.2016 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS Alekseí Yu. Chekunov Abstract. In this paper
MATEMATIQKI VESNIK Corrected proof Available online 01.10.2016 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS Alekseí Yu. Chekunov Abstract. In this paper
computational Fluid Dynamics - Prof. V. Esfahanian
 Three boards categories: Experimental Theoretical Computational Crucial to know all three: Each has their advantages and disadvantages. Require validation and verification. School of Mechanical Engineering
Three boards categories: Experimental Theoretical Computational Crucial to know all three: Each has their advantages and disadvantages. Require validation and verification. School of Mechanical Engineering
Finite element method, Matlab implementation
 TIES594 PDE-solvers Lecture 6, 2016 Olli Mali Finite element method, Matlab implementation Main program The main program is the actual finite element solver for the Poisson problem. In general, a finite
TIES594 PDE-solvers Lecture 6, 2016 Olli Mali Finite element method, Matlab implementation Main program The main program is the actual finite element solver for the Poisson problem. In general, a finite
HFSS: Optimal Phased Array Modeling Using Domain Decomposition
 HFSS: Optimal Phased Array Modeling Using Domain Decomposition 15. 0 Release Authors: Dane Thompson Nick Hirth Irina Gordion Sara Louie Presenter: Dane Thompson Motivation Electronically scannable antenna
HFSS: Optimal Phased Array Modeling Using Domain Decomposition 15. 0 Release Authors: Dane Thompson Nick Hirth Irina Gordion Sara Louie Presenter: Dane Thompson Motivation Electronically scannable antenna
Multi-Mesh CFD. Chris Roy Chip Jackson (1 st year PhD student) Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Department Virginia Tech
 Multi-Mesh CFD Chris Roy Chip Jackson (1 st year PhD student) Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Department Virginia Tech cjroy@vt.edu May 21, 2014 CCAS Program Review, Columbus, OH 1 Motivation Automated
Multi-Mesh CFD Chris Roy Chip Jackson (1 st year PhD student) Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Department Virginia Tech cjroy@vt.edu May 21, 2014 CCAS Program Review, Columbus, OH 1 Motivation Automated
New developments in Statistics on Structures. Sebastian Wolff
 New developments in Statistics on Structures Sebastian Wolff New developments in SoS Overview Releases since WOST 2016 SoS 3.3.0 March 2017 for optislang 6.0 SoS 3.3.1 May 2017 for optislang 6.1 Major
New developments in Statistics on Structures Sebastian Wolff New developments in SoS Overview Releases since WOST 2016 SoS 3.3.0 March 2017 for optislang 6.0 SoS 3.3.1 May 2017 for optislang 6.1 Major
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models
 Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR)
 Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR) Gail Heath 1, John M. Svoboda 1, Birsen Canan 2, Shannon Ansley 1, David Alumbaugh 3, Douglas LaBrecque 4, Roger Sharpe 4,Roelof Versteeg
Combined Electrical and Magnetic Resistivity Tomography (ERT/MMR) Gail Heath 1, John M. Svoboda 1, Birsen Canan 2, Shannon Ansley 1, David Alumbaugh 3, Douglas LaBrecque 4, Roger Sharpe 4,Roelof Versteeg
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
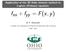 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
BEARING CAPACITY OF CIRCULAR FOOTING
 This document describes an example that has been used to verify the ultimate limit state capabilities of PLAXIS. The problem involves the bearing capacity of a smooth circular footing on frictional soil.
This document describes an example that has been used to verify the ultimate limit state capabilities of PLAXIS. The problem involves the bearing capacity of a smooth circular footing on frictional soil.
Introduction to Multigrid and its Parallelization
 Introduction to Multigrid and its Parallelization! Thomas D. Economon Lecture 14a May 28, 2014 Announcements 2 HW 1 & 2 have been returned. Any questions? Final projects are due June 11, 5 pm. If you are
Introduction to Multigrid and its Parallelization! Thomas D. Economon Lecture 14a May 28, 2014 Announcements 2 HW 1 & 2 have been returned. Any questions? Final projects are due June 11, 5 pm. If you are
Georgia Institute of Technology An attempt at the classification of energy-decaying schemes for structural and multibody dynamics
 Politecnico di Milano Georgia Institute of Technology An attempt at the classification of energy-decaying schemes for structural and multibody dynamics Carlo L. Bottasso Georgia Institute of Technology,
Politecnico di Milano Georgia Institute of Technology An attempt at the classification of energy-decaying schemes for structural and multibody dynamics Carlo L. Bottasso Georgia Institute of Technology,
2008 JINST 3 S Online System. Chapter System decomposition and architecture. 8.2 Data Acquisition System
 Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
2. Optimization problems 6
 6 2.1 Examples... 7... 8 2.3 Convex sets and functions... 9 2.4 Convex optimization problems... 10 2.1 Examples 7-1 An (NP-) optimization problem P 0 is defined as follows Each instance I P 0 has a feasibility
6 2.1 Examples... 7... 8 2.3 Convex sets and functions... 9 2.4 Convex optimization problems... 10 2.1 Examples 7-1 An (NP-) optimization problem P 0 is defined as follows Each instance I P 0 has a feasibility
Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis
 Electrical Interconnect and Packaging Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis Jason Morsey Barry Rubin, Lijun Jiang, Lon Eisenberg, Alina Deutsch Introduction Fast
Electrical Interconnect and Packaging Advanced Surface Based MoM Techniques for Packaging and Interconnect Analysis Jason Morsey Barry Rubin, Lijun Jiang, Lon Eisenberg, Alina Deutsch Introduction Fast
THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS. Alekseí Yu. Chekunov. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 1 (2017), 12 22 March 2017 research paper originalni nauqni rad THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS Alekseí Yu. Chekunov Abstract. In this
MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 1 (2017), 12 22 March 2017 research paper originalni nauqni rad THE COMPUTER MODELLING OF GLUING FLAT IMAGES ALGORITHMS Alekseí Yu. Chekunov Abstract. In this
Best Practices Workshop: Overset Meshing
 Best Practices Workshop: Overset Meshing Overview Introduction to Overset Meshes Range of Application Workflow Demonstrations and Best Practices What are Overset Meshes? Overset meshes are also known as
Best Practices Workshop: Overset Meshing Overview Introduction to Overset Meshes Range of Application Workflow Demonstrations and Best Practices What are Overset Meshes? Overset meshes are also known as
Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method
 Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method Jakub Šístek Includes joint work with P. Burda, M. Čertíková, J. Mandel, J. Novotný, B. Sousedík. Institute of Mathematics of the AS CR, Prague
Approaches to Parallel Implementation of the BDDC Method Jakub Šístek Includes joint work with P. Burda, M. Čertíková, J. Mandel, J. Novotný, B. Sousedík. Institute of Mathematics of the AS CR, Prague
Metafor FE Software. 2. Operator split. 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction
 ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays
 Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. Getting Started Launching ANSYS Electronics Desktop 2015 Select Programs > ANSYS Electromagnetics >
Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. Getting Started Launching ANSYS Electronics Desktop 2015 Select Programs > ANSYS Electromagnetics >
Analysis of a Tension Coupon
 Y Z X Objectives: Manually define material and element properties. Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions. Apply symmetric boundary constraints. Convert the pressure
Y Z X Objectives: Manually define material and element properties. Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions. Apply symmetric boundary constraints. Convert the pressure
Implementation of a XFEM toolbox in Diffpack
 Implementation of a XFEM toolbox in Diffpack 1 Md Naim Hossain, 2 Daniel Alves Paladim, 1 Frank Vogel, 2 Prof. tephane P.A. Bordas 1 inutech GmbH, NuremBerg, Germany 2 Cardiff chool of Engineering, Institute
Implementation of a XFEM toolbox in Diffpack 1 Md Naim Hossain, 2 Daniel Alves Paladim, 1 Frank Vogel, 2 Prof. tephane P.A. Bordas 1 inutech GmbH, NuremBerg, Germany 2 Cardiff chool of Engineering, Institute
SUMMARY. solve the matrix system using iterative solvers. We use the MUMPS codes and distribute the computation over many different
 Forward Modelling and Inversion of Multi-Source TEM Data D. W. Oldenburg 1, E. Haber 2, and R. Shekhtman 1 1 University of British Columbia, Department of Earth & Ocean Sciences 2 Emory University, Atlanta,
Forward Modelling and Inversion of Multi-Source TEM Data D. W. Oldenburg 1, E. Haber 2, and R. Shekhtman 1 1 University of British Columbia, Department of Earth & Ocean Sciences 2 Emory University, Atlanta,
Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method
 Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method Andrea Cangiani, John Chapman, Emmanuil Georgoulis and Max Jensen Abstract For the stationary advection-diffusion problem the
Implementation of the Continuous-Discontinuous Galerkin Finite Element Method Andrea Cangiani, John Chapman, Emmanuil Georgoulis and Max Jensen Abstract For the stationary advection-diffusion problem the
Overview and Recent Developments of Dynamic Mesh Capabilities
 Overview and Recent Developments of Dynamic Mesh Capabilities Henrik Rusche and Hrvoje Jasak h.rusche@wikki-gmbh.de and h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Wikki Gmbh, Germany Wikki Ltd, United Kingdom 6th OpenFOAM Workshop,
Overview and Recent Developments of Dynamic Mesh Capabilities Henrik Rusche and Hrvoje Jasak h.rusche@wikki-gmbh.de and h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Wikki Gmbh, Germany Wikki Ltd, United Kingdom 6th OpenFOAM Workshop,
3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 7th Workshop on Numerical Methods in Applied Science and Engineering (NMASE 8) Vall de Núria, 9 a 11 de enero de 28 c LaCàN, www.lacan-upc.es 3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD R. Sevilla, S. Fernández-Méndez
7th Workshop on Numerical Methods in Applied Science and Engineering (NMASE 8) Vall de Núria, 9 a 11 de enero de 28 c LaCàN, www.lacan-upc.es 3D NURBS-ENHANCED FINITE ELEMENT METHOD R. Sevilla, S. Fernández-Méndez
Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles
 Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium
 Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
Course in. FEM ANSYS Classic
 Course in Geometric modeling Modeling Programme for Lesson: Modeling considerations Element Type Real Constants Material Properties Sections Geometry/Modeling WorkPlane & Coordinate systems Keypoints Lines
Course in Geometric modeling Modeling Programme for Lesson: Modeling considerations Element Type Real Constants Material Properties Sections Geometry/Modeling WorkPlane & Coordinate systems Keypoints Lines
What is Cactus? Cactus is a framework for developing portable, modular applications
 What is Cactus? Cactus is a framework for developing portable, modular applications What is Cactus? Cactus is a framework for developing portable, modular applications focusing, although not exclusively,
What is Cactus? Cactus is a framework for developing portable, modular applications What is Cactus? Cactus is a framework for developing portable, modular applications focusing, although not exclusively,
Solid and shell elements
 Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii
 Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii Timo Heister, Texas A&M University 2012-02-16 SIAM PP2012 joint work with: Wolfgang Bangerth, Carsten Burstedde, Thomas Geenen, Martin Kronbichler
Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii Timo Heister, Texas A&M University 2012-02-16 SIAM PP2012 joint work with: Wolfgang Bangerth, Carsten Burstedde, Thomas Geenen, Martin Kronbichler
C / 35. C18 Computer Vision. David Murray. dwm/courses/4cv.
 C18 2015 1 / 35 C18 Computer Vision David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/4cv Michaelmas 2015 C18 2015 2 / 35 Computer Vision: This time... 1. Introduction; imaging geometry;
C18 2015 1 / 35 C18 Computer Vision David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/4cv Michaelmas 2015 C18 2015 2 / 35 Computer Vision: This time... 1. Introduction; imaging geometry;
istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics
 istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics Jeffcott Rotor Analysis Example istrdyn Modeling, Solutions, and Result Processing July 2007 This presentation shows an analysis sequence using
istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics Jeffcott Rotor Analysis Example istrdyn Modeling, Solutions, and Result Processing July 2007 This presentation shows an analysis sequence using
Summary of the C2.3 test case results
 1st International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods, Nashville, January 7-8, 2012 Institute of Aerodynamics and Flow Technology German Aerospace Center 8. Jan. 2012 1 / 19 Test case C2.3 Compressible
1st International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods, Nashville, January 7-8, 2012 Institute of Aerodynamics and Flow Technology German Aerospace Center 8. Jan. 2012 1 / 19 Test case C2.3 Compressible
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
2 The Elliptic Test Problem
 A Comparative Study of the Parallel Performance of the Blocking and Non-Blocking MPI Communication Commands on an Elliptic Test Problem on the Cluster tara Hafez Tari and Matthias K. Gobbert Department
A Comparative Study of the Parallel Performance of the Blocking and Non-Blocking MPI Communication Commands on an Elliptic Test Problem on the Cluster tara Hafez Tari and Matthias K. Gobbert Department
Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using Ansys
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 9 ǁ September 2014 ǁ PP.18-23 Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 9 ǁ September 2014 ǁ PP.18-23 Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using
Fourteen years of Cactus Community
 Fourteen years of Cactus Community Frank Löffler Center for Computation and Technology Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA September 6th 2012 Outline Motivation scenario from Astrophysics Cactus
Fourteen years of Cactus Community Frank Löffler Center for Computation and Technology Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA September 6th 2012 Outline Motivation scenario from Astrophysics Cactus
PROGRAMMING OF MULTIGRID METHODS
 PROGRAMMING OF MULTIGRID METHODS LONG CHEN In this note, we explain the implementation detail of multigrid methods. We will use the approach by space decomposition and subspace correction method; see Chapter:
PROGRAMMING OF MULTIGRID METHODS LONG CHEN In this note, we explain the implementation detail of multigrid methods. We will use the approach by space decomposition and subspace correction method; see Chapter:
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
Ezequiel Martin, Pablo Carrica, IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering, University of Iowa. Ralph Noack, Celeritas Simulation Technology, LLC
 12 th Overset Grid Symposium, Atlanta, GA October 6-9, 2014 Multiple Body Overset Connectivity Method with Application to Wind Farm Simulations Ezequiel Martin, Pablo Carrica, IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering,
12 th Overset Grid Symposium, Atlanta, GA October 6-9, 2014 Multiple Body Overset Connectivity Method with Application to Wind Farm Simulations Ezequiel Martin, Pablo Carrica, IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering,
Simulation of Transition Radiation from a flat target using CST particle studio.
 Simulation of Transition Radiation from a flat target using CST particle studio. K. Lekomtsev 1, A. Aryshev 1, P. Karataev 2, M. Shevelev 1, A. Tishchenko 3 and J. Urakawa 1 1. High Energy Accelerator
Simulation of Transition Radiation from a flat target using CST particle studio. K. Lekomtsev 1, A. Aryshev 1, P. Karataev 2, M. Shevelev 1, A. Tishchenko 3 and J. Urakawa 1 1. High Energy Accelerator
Pole Shape Optimization Using a Tabu Search Scheme P. J. Leonard and A. M. Connor
 Pole Shape Optimization Using a Tabu Search Scheme P. J. Leonard and A. M. Connor Abstract: The pole shape optimization of an electromagnet typical of an MRI type application is investigated. We compare
Pole Shape Optimization Using a Tabu Search Scheme P. J. Leonard and A. M. Connor Abstract: The pole shape optimization of an electromagnet typical of an MRI type application is investigated. We compare
CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING LINKAGES USED FOR SHAFTS COUPLING
 Mechanical Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 2012 (II), Volume 4, 19-27 CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING LINKAGES USED FOR SHAFTS COUPLING Stelian ALACI, Florina Carmen CIORNEI, Constantin FILOTE, Luminiţa
Mechanical Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 2012 (II), Volume 4, 19-27 CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING LINKAGES USED FOR SHAFTS COUPLING Stelian ALACI, Florina Carmen CIORNEI, Constantin FILOTE, Luminiţa
A High-Order Accurate Unstructured GMRES Solver for Poisson s Equation
 A High-Order Accurate Unstructured GMRES Solver for Poisson s Equation Amir Nejat * and Carl Ollivier-Gooch Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of British Columbia, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada
A High-Order Accurate Unstructured GMRES Solver for Poisson s Equation Amir Nejat * and Carl Ollivier-Gooch Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of British Columbia, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada
Second Conference on Parallel, Distributed, Grid and Cloud Computing for Engineering
 State of the art distributed parallel computational techniques in industrial finite element analysis Second Conference on Parallel, Distributed, Grid and Cloud Computing for Engineering Ajaccio, France
State of the art distributed parallel computational techniques in industrial finite element analysis Second Conference on Parallel, Distributed, Grid and Cloud Computing for Engineering Ajaccio, France
Design Intent of Geometric Models
 School of Computer Science Cardiff University Design Intent of Geometric Models Frank C. Langbein GR/M78267 GR/S69085/01 NUF-NAL 00638/G Massey University 22nd September 2004; Version 1.0 Design Intent
School of Computer Science Cardiff University Design Intent of Geometric Models Frank C. Langbein GR/M78267 GR/S69085/01 NUF-NAL 00638/G Massey University 22nd September 2004; Version 1.0 Design Intent
3D Finite Difference Time-Domain Modeling of Acoustic Wave Propagation based on Domain Decomposition
 3D Finite Difference Time-Domain Modeling of Acoustic Wave Propagation based on Domain Decomposition UMR Géosciences Azur CNRS-IRD-UNSA-OCA Villefranche-sur-mer Supervised by: Dr. Stéphane Operto Jade
3D Finite Difference Time-Domain Modeling of Acoustic Wave Propagation based on Domain Decomposition UMR Géosciences Azur CNRS-IRD-UNSA-OCA Villefranche-sur-mer Supervised by: Dr. Stéphane Operto Jade
Fast solvers for mesh-based computations
 Fast solvers for mesh-based computations Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science AGH University, Krakow, Poland home.agh.edu.pl/paszynsk Collaborators: Anna Paszyńska (Jagiellonian University,Poland)
Fast solvers for mesh-based computations Maciej Paszyński Department of Computer Science AGH University, Krakow, Poland home.agh.edu.pl/paszynsk Collaborators: Anna Paszyńska (Jagiellonian University,Poland)
Robot Vision: Projective Geometry
 Robot Vision: Projective Geometry Ass.Prof. Friedrich Fraundorfer SS 2018 1 Learning goals Understand homogeneous coordinates Understand points, line, plane parameters and interpret them geometrically
Robot Vision: Projective Geometry Ass.Prof. Friedrich Fraundorfer SS 2018 1 Learning goals Understand homogeneous coordinates Understand points, line, plane parameters and interpret them geometrically
TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics. The University of Texas at Austin. Taylor Hall Abstract
 A New Cloud-Based hp Finite Element Method J. T. Oden, C. A. M. Duarte y and O. C. Zienkiewicz z TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics The University of Texas at Austin Taylor
A New Cloud-Based hp Finite Element Method J. T. Oden, C. A. M. Duarte y and O. C. Zienkiewicz z TICAM - Texas Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics The University of Texas at Austin Taylor
High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties
 High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties Joachim Schöberl and Sabine Zaglmayr Institute for Computational Mathematics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria E-mail: {js,sz}@jku.at
High Order Nédélec Elements with local complete sequence properties Joachim Schöberl and Sabine Zaglmayr Institute for Computational Mathematics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria E-mail: {js,sz}@jku.at
A design influence on the mechanical compliance and fracture resistance of railway wheel
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 5 (2011) 197 204 A design influence on the mechanical compliance and fracture resistance of railway wheel P. Navrátil a,,p.janíček a, L. Brabenec a, M. Matug a, P. Marcián
Applied and Computational Mechanics 5 (2011) 197 204 A design influence on the mechanical compliance and fracture resistance of railway wheel P. Navrátil a,,p.janíček a, L. Brabenec a, M. Matug a, P. Marcián
ITU/FAA Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics
 S. Banu YILMAZ, Mehmet SAHIN, M. Fevzi UNAL, Istanbul Technical University, 34469, Maslak/Istanbul, TURKEY 65th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics November 18-20, 2012, San Diego, CA
S. Banu YILMAZ, Mehmet SAHIN, M. Fevzi UNAL, Istanbul Technical University, 34469, Maslak/Istanbul, TURKEY 65th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics November 18-20, 2012, San Diego, CA
Analysis of a Tension Coupon
 WORKSHOP 14 Analysis of a Tension Coupon Objectives: Manually define material and element properties. Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions. Apply symmetric boundary
WORKSHOP 14 Analysis of a Tension Coupon Objectives: Manually define material and element properties. Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions. Apply symmetric boundary
Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU. San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA
 Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA Overview Astrophysical motivation & the Enzo code Finite volume method and adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) CUDA
Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA Overview Astrophysical motivation & the Enzo code Finite volume method and adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) CUDA
Motivation Patch tests Numerical examples Conclusions
 Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: from sub- and super- geometric analysis to Geometry Independent Field approximation (GIFT) Elena Atroshchenko, Gang
Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: from sub- and super- geometric analysis to Geometry Independent Field approximation (GIFT) Elena Atroshchenko, Gang
The following models are not allowed in examinations under any circumstances.
 Use of calculators in examinations 2015 Note: From May 2014, statistical tables are not allowed in mathematics examinations, rather candidates should be using the statistical features on their GDC. Calculator
Use of calculators in examinations 2015 Note: From May 2014, statistical tables are not allowed in mathematics examinations, rather candidates should be using the statistical features on their GDC. Calculator
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization
 Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4. Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010
 ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.

