NUMB3RS Activity: Sinks & Sources. Episode: Hot Shot
|
|
|
- Clemence Johnston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NUM3RS ctivity Teacher Page 1 pisode: Hot Shot NUM3RS ctivity: Sinks & Sources pisode: Hot Shot Topic: irected graphs Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: Investigate paths and flow in directed graphs Time: 30 minutes Introduction In Hot Shot, the FI is looking for a serial criminal. harlie suggests that by looking at the victims daily routines, he may be able to determine where the killer made contact with the victims. He suggests analyzing the information as a directed network flow problem, a mathematical topic that uses directed graphs. directed graph can be represented with vertices (points) and edges (arrows) connecting two vertices. ach edge has a direction indicated by the arrow. n example is shown below. very vertex has an indegree (the number of edges with arrows leading into a vertex) and an outdegree (the number of edges with arrows pointing away from a vertex). For example vertex has indegree of 1 and outdegree of 2. Suppose this graph represents the movements of three victims on a given day. Movements of the victims in a single day include the following: Victim 1 goes from shop to shop, and then to shop ; Victim 2 goes from shop to shop, and then to shop ; Victim 3 goes from shop to shop to shop, and then back to shop as shown. In graph theory uler paths are routes in which every edge is traveled once. This activity considers uler paths for which the start vertex and the end vertex are different. (Note: uler paths and other graph theory topics have been explored in other NUM3RS activities, which are listed on the xtensions page.) directed network flow problem assigns a value to each edge of a directed graph. Much like the uler paths, the amount of flow into a vertex must equal the amount of flow out, with two exceptions: a source (a vertex with only outgoing flow) and a sink (a vertex with only incoming flow). This setup can represent situations such as traffic flow, movement in a pipe system, or an electrical current. education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
2 NUM3RS ctivity Teacher Page 2 pisode: Hot Shot iscuss with Students 1. etermine the indegree and outdegree for each vertex in the sample graph. 2. Is there an uler path in the sample graph using the directed arrows in the directions given? 3. Is there an uler path if the directions of the arrows are not used? If so, what is it? iscuss with Students nswers: 1. Node Indegree Outdegree There is no uler path that follows the directions of the arrows. 3. There is an uler path but it does not follow the directions of the arrows. For example, Student Page nswers: 1a. indegree=7 1b. outdegree=7 1c. These values are equal for any directed graph; the value also equals the number of edges, because indegree counts the number of arrow heads and outdegree counts the number of arrow tails. 2. Graphs 1 and 4 contain uler paths, Graphs 2 and 3 do not. 3. directed graph must have one node with outdegree = indegree + 1 (this is the start), one node with outdegree = indegree 1 (this is the end), and for all other nodes indegree = outdegree 4a. Vertices and are sources; the refrigerator and the pantry are where the food is stored, and where it moves from. 4b. Vertex is a sink; this is a model in which all food eventually goes to the trashcan. It is unrealistic in most circumstances to have that happen. 4c. Normally, not all of the food goes from the table to the trashcan, because most of it is eaten. The leftover food could also be returned to the refrigerator. 5. The table is being used less; maybe it is being used for something else; food is served at the counter. 6. nswers will vary, but the outdegree should be greater than the indegree and there should be a path back to both the pantry and the refrigerator. education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
3 NUM3RS ctivity Student Page 1 pisode: Hot Shot Name ate NUM3RS ctivity: Sinks & Sources In Hot Shot, the FI is looking for a serial criminal. harlie suggests that by looking at the victims daily routines, he may be able to determine where the killer made contact with the victims. He suggests analyzing the information as a directed network flow problem, a mathematical topic that uses directed graphs. directed graph can be represented with vertices (points) and edges (arrows) connecting two vertices. ach edge has a direction indicated by the arrow. Suppose the graph below represents the movements of three victims on a given day. Movements of the victims include the following: Victim 1 goes from shop to shop, and then to shop ; Victim 2 goes from shop to shop, and then to shop ; Victim 3 goes from shop to shop to shop, and back to shop as shown. very vertex of a graph has an indegree (the number of edges with arrows leading into a vertex) and an outdegree (the number of edges with arrows pointing away from a vertex). 1. a. What is the sum of the indegrees for the graph above? b. The sum of the outdegrees? c. Is it a coincidence that they are equal? n uler path is a route that covers every edge exactly once. In a directed graph, edges can only be traveled in the indicated direction. This activity considers uler paths that start and end at different vertices. There are several reasons why the graph above does not contain such a path. onsider vertex : a path cannot start at vertex because there are no outgoing edges. When one of the edges going into is traveled, there is no new edge to take and the path must end. education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
4 NUM3RS ctivity Student Page 2 pisode: Hot Shot 2. etermine whether each graph below contains an uler path such that the start vertex and end vertex are different. Graph 1 Graph 2 Graph 3 Graph 4 3. etermine the indegree and outdegree for each vertex of the graphs in Question 2. ased on your findings, make a conjecture about uler paths and directed graphs. directed network flow problem assigns a value to each edge of a directed graph. ecause these graphs model the flow of material within a system, the amount of flow into a vertex must equal the amount of flow out, with two exceptions: a source (a vertex with only outgoing flow) and a sink (a vertex with only incoming flow). n example is shown below. Notice that the flow into vertex is 5 (from vertex ) and the flow out is also 5 (2 to and 3 to ). Vertex is a source, only sending material and vertex is a sink, only receiving material education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
5 NUM3RS ctivity Student Page 3 pisode: Hot Shot In the NUM3RS episode, harlie compares the victims routines to movements in a kitchen between the table, kitchen sink, refrigerator, and so on. onsider the possible flow of food in a kitchen with vertices representing refrigerator (), pantry (), counter (), trashcan (), and table (). The flow value on each edge is a measure of the amount of material transported between locations a. Which two vertices above are sources? Why does it make sense in this situation that those locations be the sources? b. Which vertex is a sink? oes this make sense for the situation? Why? c. In a normal situation, would you expect all the food to go from vertex to vertex? Why or why not? 5. harlie could look for changes in routine as a clue to finding the killer. Look at the revised kitchen flow graph and make a conjecture about how the routine in the kitchen has changed In reality, the directed flow graph in Question 5 is not realistic. The indegree and outdegree would not be equal in a kitchen because some of the food is eaten. lso, the refrigerator and pantry would not be strict sources because some of the food is returned to both of them. Modify the graph from Question 5 to more realistically model what takes place in a kitchen. education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
6 NUM3RS ctivity pisode: Hot Shot The goal of this activity is to give your students a short and simple snapshot into a very extensive math topic. TI and NTM encourage you and your students to learn more about this topic using the extensions provided below and through your own independent research. xtensions Three aspects of directed graphs (or digraphs) are components, cuts, and connectivity. Research these ideas, starting at escribe the activity in your school building between classes or after school as a directed graph. an you use your results to make a proposal to the administration about easing any congestion in the hallways? Other Resources There are additional NUM3RS activities that cover other graph theory topics. These activities can be downloaded for free from the Web sites below. ct3_koenigsburgbridge_toxin_final.pdf ct1_partyofsix_protest_final.pdf This Web site includes more information on graph theory, including directed graphs. The idea for using this topic in this episode originated from an interview of onald Knuth on NPR. Knuth designed his entire kitchen dictated by a graph theory analysis with the central point being the trashcan. You can listen to this interview on the Web site below. This Web site, from High School Operations Research, features an activity in which students use graph theory to find the shortest route for a delivery truck. This Web site, from the University of olorado at oulder, provides activities and information on the use of discrete mathematics, including graph theory. For more work on graph theory, this publication contains an introduction to a variety of topics, including directed graphs. Montana ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics (2003). "Our Town" in SIMMS Integrated Mathematics: Modeling pproach Using Technology Level 3. ubuque, I: Kendall/Hunt Publishing ompany, pp, education.ti.com/go/num3rs Kathy rickson, Monument Mountain Regional High School, Great arrington, M
NUMB3RS Activity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "Bones of Contention"
 NUMRS ctivity Teacher Page Episode: "ones of ontention NUMRS ctivity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "ones of ontention" Topic: Voronoi Diagrams Grade Level: 8 - Objectives: Understand the basic
NUMRS ctivity Teacher Page Episode: "ones of ontention NUMRS ctivity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "ones of ontention" Topic: Voronoi Diagrams Grade Level: 8 - Objectives: Understand the basic
NUMB3RS Activity: Dial the Phone. Episode: Brutus
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Dial the Phone Topic: Triangular Numbers, Networks Grade Level: 9-10 Objective: Students will generate a function rule for triangular numbers as they investigate the relationship
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Dial the Phone Topic: Triangular Numbers, Networks Grade Level: 9-10 Objective: Students will generate a function rule for triangular numbers as they investigate the relationship
NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock. Episode: In Plain Sight
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock Topic: Introduction to Flock Behavior Grade Level: 8-12 Objective: Use a mathematical model to simulate an aspect of birds flying in a flock Time: 30 minutes
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock Topic: Introduction to Flock Behavior Grade Level: 8-12 Objective: Use a mathematical model to simulate an aspect of birds flying in a flock Time: 30 minutes
Directed Graph and Binary Trees
 and Dr. Nahid Sultana December 19, 2012 and Degrees Paths and Directed graphs are graphs in which the edges are one-way. This type of graphs are frequently more useful in various dynamic systems such as
and Dr. Nahid Sultana December 19, 2012 and Degrees Paths and Directed graphs are graphs in which the edges are one-way. This type of graphs are frequently more useful in various dynamic systems such as
Chapter 4 Review. 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter. 2. Draw a graph for the following task table.
 hapter Review 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. raw a graph for the following task table. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 None 1 5,, I, inish. a. List the
hapter Review 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. raw a graph for the following task table. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 None 1 5,, I, inish. a. List the
1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map
![1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map 1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map](/thumbs/83/88762945.jpg) 1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7/8 Math ircles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory What is graph theory? Graph theory is the
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7/8 Math ircles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory What is graph theory? Graph theory is the
Mathematical Foundations
 Mathematical Foundations Steve Borgatti Revised 7/04 in Colchester, U.K. Graphs Networks represented mathematically as graphs A graph G(V,E) consists of Set of nodes vertices V representing actors Set
Mathematical Foundations Steve Borgatti Revised 7/04 in Colchester, U.K. Graphs Networks represented mathematically as graphs A graph G(V,E) consists of Set of nodes vertices V representing actors Set
Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4
 Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4 What Solutions are Available? Lesson 1: page 258, Modeling Task 1; page 260, Modeling Task 4; page 261, Organizing Task 1; page 271, Modeling Task 2; page 272, Modeling
Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4 What Solutions are Available? Lesson 1: page 258, Modeling Task 1; page 260, Modeling Task 4; page 261, Organizing Task 1; page 271, Modeling Task 2; page 272, Modeling
11-5 Networks. Königsberg Bridge Problem
 Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics
 Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
G5-20 Introduction to Slides
 WORKBOOK 5:2 PAGE 317 G5-20 Introduction to Slides GOALS Students will slide a dot on a grid. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED Ability to count Distinguish between right and left VOCABULARY slide For this lesson,
WORKBOOK 5:2 PAGE 317 G5-20 Introduction to Slides GOALS Students will slide a dot on a grid. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED Ability to count Distinguish between right and left VOCABULARY slide For this lesson,
Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10
 CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10 GRAPH THEORY Directed Graphs Directed graphs (a.k.a. digraphs) are an important mathematical modeling tool in Computer Science,
CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10 GRAPH THEORY Directed Graphs Directed graphs (a.k.a. digraphs) are an important mathematical modeling tool in Computer Science,
Materials Voyage 200/TI-92+ calculator with Cabri Geometry Student activity sheet Shortest Distance Problems. Introduction
 s (Adapted from T 3 Geometry/C. Vonder Embse) Concepts Triangle inequality Distance between two points Distance between a point and a line Distance between two points and a line Perpendicularity Materials
s (Adapted from T 3 Geometry/C. Vonder Embse) Concepts Triangle inequality Distance between two points Distance between a point and a line Distance between two points and a line Perpendicularity Materials
Math 100 Homework 4 B A C E
 Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Angle Theorems for Triangles 8.8.D
 ? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
NUMB3RS Activity: Creating Codes. Episode: Backscatter
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Creating Codes Topic: Codes Grade Level: 10-12 Objective: Explore several coding methods Time: 30+ minutes Materials: TI-83/84 Plus calculator Introduction While lecturing
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Creating Codes Topic: Codes Grade Level: 10-12 Objective: Explore several coding methods Time: 30+ minutes Materials: TI-83/84 Plus calculator Introduction While lecturing
7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Source. Sink. Chapter 10: Iterative Programming Maximum Flow Problem. CmSc250 Intro to Algorithms
 Chapter 10: Iterative Programming Maximum Flow Problem CmSc20 Intro to Algorithms A flow network is a model of a system where some material is produced at its source, travels through the system, and is
Chapter 10: Iterative Programming Maximum Flow Problem CmSc20 Intro to Algorithms A flow network is a model of a system where some material is produced at its source, travels through the system, and is
Some Graph Theory for Network Analysis. CS 249B: Science of Networks Week 01: Thursday, 01/31/08 Daniel Bilar Wellesley College Spring 2008
 Some Graph Theory for Network Analysis CS 9B: Science of Networks Week 0: Thursday, 0//08 Daniel Bilar Wellesley College Spring 008 Goals this lecture Introduce you to some jargon what we call things in
Some Graph Theory for Network Analysis CS 9B: Science of Networks Week 0: Thursday, 0//08 Daniel Bilar Wellesley College Spring 008 Goals this lecture Introduce you to some jargon what we call things in
Graph Theory(Due with the Final Exam)
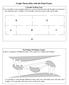 Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
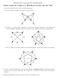 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
Patterning and Algebra 2010/2011 Circle 1 Problem 6. Polygons: How Many Degrees per Vertex? (For pairs or groups of students) B 5.
 Patterning and lgebra 2010/2011 ircle 1 Problem 6 Problem Polygons: How Many egrees per Vertex? (For pairs or groups of students) a) elow are several triangles. For each triangle, measure the angles at
Patterning and lgebra 2010/2011 ircle 1 Problem 6 Problem Polygons: How Many egrees per Vertex? (For pairs or groups of students) a) elow are several triangles. For each triangle, measure the angles at
Chapter 4. Relations & Graphs. 4.1 Relations. Exercises For each of the relations specified below:
 Chapter 4 Relations & Graphs 4.1 Relations Definition: Let A and B be sets. A relation from A to B is a subset of A B. When we have a relation from A to A we often call it a relation on A. When we have
Chapter 4 Relations & Graphs 4.1 Relations Definition: Let A and B be sets. A relation from A to B is a subset of A B. When we have a relation from A to A we often call it a relation on A. When we have
Building Concepts: Building Expressions
 Lesson Overview Algebraic Focus: What does it mean to say two expressions are equivalent? In this lesson students view expressions as objects in their own right and interpret the form and structure of
Lesson Overview Algebraic Focus: What does it mean to say two expressions are equivalent? In this lesson students view expressions as objects in their own right and interpret the form and structure of
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1
 Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles
 Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles By Adam Sheffer The Bridges of Königsberg Can we travel the city while crossing every bridge exactly once? 1 How Graph Theory was Born Leonhard Euler 1736 Eulerian Cycle
Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles By Adam Sheffer The Bridges of Königsberg Can we travel the city while crossing every bridge exactly once? 1 How Graph Theory was Born Leonhard Euler 1736 Eulerian Cycle
NUMB3RS Activity: I It Itera Iteration. Episode: Rampage
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: I It Itera Iteration Topic: Iterative processes Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: Examine random iterative processes and their outcomes Time: about 45 minutes Materials: TI-83/84
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: I It Itera Iteration Topic: Iterative processes Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: Examine random iterative processes and their outcomes Time: about 45 minutes Materials: TI-83/84
The University of Sydney MATH 2009
 The University of Sydney MTH 009 GRPH THORY Tutorial 10 Solutions 004 1. In a tournament, the score of a vertex is its out-degree, and the score sequence is a list of all the scores in non-decreasing order.
The University of Sydney MTH 009 GRPH THORY Tutorial 10 Solutions 004 1. In a tournament, the score of a vertex is its out-degree, and the score sequence is a list of all the scores in non-decreasing order.
incident to X and W, and X is incident to W and Z. (a) Choose the correct digraph below. A. B. C. D. (b) Choose the correct digraph below. A. B. C. D.
 1. (a) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = {,,,D} and arc-set = { D,,,D,D}. (b) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = {,,,D,E} and arc-set = { ED,E,,,D,D,}. (c) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = { W,X,Y,Z}
1. (a) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = {,,,D} and arc-set = { D,,,D,D}. (b) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = {,,,D,E} and arc-set = { ED,E,,,D,D,}. (c) Draw a digraph with vertex-set V = { W,X,Y,Z}
15 Graph Theory Counting the Number of Relations. 2. onto (surjective).
 2. onto (surjective). You should convince yourself that if these two properties hold, then it is always going to be the case that f 1 is a function. In order to do this, you should remember the definition
2. onto (surjective). You should convince yourself that if these two properties hold, then it is always going to be the case that f 1 is a function. In order to do this, you should remember the definition
Translations Lesson Bundle
 We are excited that you will be using these interactive investigations to assist your students in exploring and learning about Transformational Geometry. They are designed so that students investigate
We are excited that you will be using these interactive investigations to assist your students in exploring and learning about Transformational Geometry. They are designed so that students investigate
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
Undirected graphs and networks
 Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Building Concepts: Moving from Proportional Relationships to Linear Equations
 Lesson Overview In this TI-Nspire lesson, students use previous experience with proportional relationships of the form y = kx to consider relationships of the form y = mx and eventually y = mx + b. Proportional
Lesson Overview In this TI-Nspire lesson, students use previous experience with proportional relationships of the form y = kx to consider relationships of the form y = mx and eventually y = mx + b. Proportional
11.4 AA Similarity of Triangles
 Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore G.7. pply the ngle-ngle criterion to verify similar triangles and apply the proportionality
Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore G.7. pply the ngle-ngle criterion to verify similar triangles and apply the proportionality
Lesson 2. Investigation. Name: a. Identify the shape of the sign and describe the symmetries
 Check Your Understanding Being able to recognize traffic signs by their shape and color is important when Unit driving 6and is often tested on exams for a driver s license. Examine the school crossing
Check Your Understanding Being able to recognize traffic signs by their shape and color is important when Unit driving 6and is often tested on exams for a driver s license. Examine the school crossing
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
Lesson 3: Solving for Unknown Angles Using Equations
 Student Outcomes Students solve for unknown angles in word problems and in diagrams involving all learned angle facts. lasswork Opening xercise (5 minutes) Opening xercise Two lines meet at the common
Student Outcomes Students solve for unknown angles in word problems and in diagrams involving all learned angle facts. lasswork Opening xercise (5 minutes) Opening xercise Two lines meet at the common
Geometry Summer Packet Instructions
 Geometry Summer Packet Instructions Dear Student, You are receiving this summer packet as a review of previously covered math topics needed to be successful in the upcoming math class you will be taking
Geometry Summer Packet Instructions Dear Student, You are receiving this summer packet as a review of previously covered math topics needed to be successful in the upcoming math class you will be taking
11.4 AA Similarity of Triangles
 Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore xploring ngle-ngle Similarity for Triangles Two triangles are similar when their corresponding
Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore xploring ngle-ngle Similarity for Triangles Two triangles are similar when their corresponding
SAMPLE. Networks. A view of Königsberg as it was in Euler s day.
 ack to Menu >>> How are graphs used to represent networks? H P T R 10 Networks How do we analyse the information contained in graphs? How do we use graphs to represent everyday situations? 10.1 Graph theory
ack to Menu >>> How are graphs used to represent networks? H P T R 10 Networks How do we analyse the information contained in graphs? How do we use graphs to represent everyday situations? 10.1 Graph theory
Properties of Parallelograms
 Properties of Parallelograms U-OU PUZZ! Objective: tudents will practice identifying and applying the properties of parallelograms to solve for sides and angles. everal problems require that students solve
Properties of Parallelograms U-OU PUZZ! Objective: tudents will practice identifying and applying the properties of parallelograms to solve for sides and angles. everal problems require that students solve
The Join the Club Interpretation of Some. Graph Algorithms
 The Join the Club Interpretation of Some Graph Algorithms Harold Reiter Isaac Sonin June 8, 2000 Abstract Several important tree construction algorithms of graph theory are described and discussed using
The Join the Club Interpretation of Some Graph Algorithms Harold Reiter Isaac Sonin June 8, 2000 Abstract Several important tree construction algorithms of graph theory are described and discussed using
Transformations Reflections, and Rotations
 Grade level: 9-12 Subject: mathematics Time required: 30 minutes Transformations Reflections, and Rotations by Lynne B. Uebelhoer Activity overview This activity is designed to be used in a middle-school
Grade level: 9-12 Subject: mathematics Time required: 30 minutes Transformations Reflections, and Rotations by Lynne B. Uebelhoer Activity overview This activity is designed to be used in a middle-school
APPM 4120/5120 Exam #2 Practice Solutions Spring 2015
 APPM 4120/5120 Exam #2 Practice Solutions Spring 2015 You are not allowed to use textbooks, class notes. Problem #1 (20 points): Consider the following activity-on-arc project network, where the 12 arcs
APPM 4120/5120 Exam #2 Practice Solutions Spring 2015 You are not allowed to use textbooks, class notes. Problem #1 (20 points): Consider the following activity-on-arc project network, where the 12 arcs
TImath.com. Geometry. Triangle Inequalities
 Triangle Inequalities ID: 9425 TImath.com Time required 30 minutes Topic: Right Triangles & Trigonometric Ratios Derive the Triangle Inequality as a corollary of the Pythagorean Theorem and apply it. Derive
Triangle Inequalities ID: 9425 TImath.com Time required 30 minutes Topic: Right Triangles & Trigonometric Ratios Derive the Triangle Inequality as a corollary of the Pythagorean Theorem and apply it. Derive
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
Saturday Morning Math Group Austin Math Circle Austin Area Problem Solving Challenge
 Saturday Morning Math Group Austin Math Circle Austin Area Problem Solving Challenge Rules 1. The Austin Area Problem Solving Challenge (AAPSC) is a competition for teams of up to five students each. Any
Saturday Morning Math Group Austin Math Circle Austin Area Problem Solving Challenge Rules 1. The Austin Area Problem Solving Challenge (AAPSC) is a competition for teams of up to five students each. Any
Applications. 72 Variables and Patterns
 Applications. Sean bought a DVD player and a receiver. The store offered him an interest-free payment plan with weekly installments. Sean figured out that after n weeks of payments, he would still owe
Applications. Sean bought a DVD player and a receiver. The store offered him an interest-free payment plan with weekly installments. Sean figured out that after n weeks of payments, he would still owe
c. Will this coordinate rule hold true for any figure reflected over the x-axis? Why or why not?
 9.1b lass ctivity: Properties of Reflections 1. In the grid below, has been reflected over the y-axis to obtain. 10 a. Describe the movement of a figure that has been reflected. ' b. In the table below,
9.1b lass ctivity: Properties of Reflections 1. In the grid below, has been reflected over the y-axis to obtain. 10 a. Describe the movement of a figure that has been reflected. ' b. In the table below,
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 11 April 16, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
System Analysis and Design. Data Flow Diagram. System Analysis and Design
 Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
SAS Triangle Congruence
 Locker LSSON 5.3 SS Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Locker LSSON 5.3 SS Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
MEI Further Mathematics Support Programme
 Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs
 University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program Spring 4-2015 Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs Claire A. Sonneborn Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program Spring 4-2015 Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs Claire A. Sonneborn Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
GAP CLOSING. Grade 9. Facilitator s Guide
 GAP CLOSING Grade 9 Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions... 5 Using Intervention Materials...8
GAP CLOSING Grade 9 Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions... 5 Using Intervention Materials...8
Graph Algorithms. CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures. Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University
 Graph Algorithms CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University 1 Network Flow How much freight can flow from Seattle to
Graph Algorithms CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University 1 Network Flow How much freight can flow from Seattle to
Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009.
 Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009. Describing Graphs (8.2) A graph is a mathematical way of describing
Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009. Describing Graphs (8.2) A graph is a mathematical way of describing
Graph Theory and its Applications
 Department of Mathematics and Statistics deeringj@goldmail.etsu.edu October 17, 2012 What is a Graph? Introduction Graphs Graph Theory Simply a modeling tool or set of relationships Graphs Graph Theory
Department of Mathematics and Statistics deeringj@goldmail.etsu.edu October 17, 2012 What is a Graph? Introduction Graphs Graph Theory Simply a modeling tool or set of relationships Graphs Graph Theory
Logic: The Big Picture. Axiomatizing Arithmetic. Tautologies and Valid Arguments. Graphs and Trees
 Axiomatizing Arithmetic Logic: The Big Picture Suppose we restrict the domain to the natural numbers, and allow only the standard symbols of arithmetic (+,, =, >, 0, 1). Typical true formulas include:
Axiomatizing Arithmetic Logic: The Big Picture Suppose we restrict the domain to the natural numbers, and allow only the standard symbols of arithmetic (+,, =, >, 0, 1). Typical true formulas include:
ASA Triangle Congruence
 Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
2. CONNECTIVITY Connectivity
 2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
Figure 1: A directed graph.
 1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
Network Flow I. Lecture Overview The Network Flow Problem
 Lecture Network Flow I. Overview In these next two lectures we are going to talk about an important algorithmic problem called the Network Flow Problem. Network flow is important because it can be used
Lecture Network Flow I. Overview In these next two lectures we are going to talk about an important algorithmic problem called the Network Flow Problem. Network flow is important because it can be used
Position and Piecewise Velocity
 Math Objectives Students will modify a piecewise linear graph of velocity to model a scenario. Students will make connections between a graph of an object s velocity and a corresponding graph of an object
Math Objectives Students will modify a piecewise linear graph of velocity to model a scenario. Students will make connections between a graph of an object s velocity and a corresponding graph of an object
SURIEM 2016 Final Report: Games on Graphs
 SURIEM 2016 Final Report: Games on Graphs Julie Anne Bowman, Arthur Diep-Nguyen, Rashmika Goswami, Dylan King, Nicholas Lindell, Emily Olson, Robert W. Bell July 14, 2016 1 Introduction The game of Cops
SURIEM 2016 Final Report: Games on Graphs Julie Anne Bowman, Arthur Diep-Nguyen, Rashmika Goswami, Dylan King, Nicholas Lindell, Emily Olson, Robert W. Bell July 14, 2016 1 Introduction The game of Cops
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00. Networks. Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow
 Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Learn to use the vector and translation tools in GX.
 Learning Objectives Horizontal and Combined Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 00 50 min. This lesson adds horizontal translations to our previous work with vertical translations and
Learning Objectives Horizontal and Combined Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 00 50 min. This lesson adds horizontal translations to our previous work with vertical translations and
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound
 CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
Sec 7.1 EST Graphs Networks & Graphs
 Sec 7.1 ST raphs Networks & raphs Name: These graphs are models to find the RLIST TIM any particular job can STRT. What do you think is meant in a team by the following statement? You are only as fast
Sec 7.1 ST raphs Networks & raphs Name: These graphs are models to find the RLIST TIM any particular job can STRT. What do you think is meant in a team by the following statement? You are only as fast
-Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim Gleason FROM: Deborah Britt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005
 -Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim leason FOM: Deborah ritt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005 Section 4.6 Exploratory #3 Exercises (2,4,6,10,11) Section 5.1 Exercises (4,5,6,10,14)
-Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim leason FOM: Deborah ritt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005 Section 4.6 Exploratory #3 Exercises (2,4,6,10,11) Section 5.1 Exercises (4,5,6,10,14)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
CS 5540 Spring 2013 Assignment 3, v1.0 Due: Apr. 24th 11:59PM
 1 Introduction In this programming project, we are going to do a simple image segmentation task. Given a grayscale image with a bright object against a dark background and we are going to do a binary decision
1 Introduction In this programming project, we are going to do a simple image segmentation task. Given a grayscale image with a bright object against a dark background and we are going to do a binary decision
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 28 Chinese Postman Problem In this lecture we study the Chinese postman
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 28 Chinese Postman Problem In this lecture we study the Chinese postman
Congruence Transformations and Triangle Congruence
 ongruence Transformations and Triangle ongruence Truss Your Judgment Lesson 11-1 ongruent Triangles Learning Targets: Use the fact that congruent triangles have congruent corresponding parts. etermine
ongruence Transformations and Triangle ongruence Truss Your Judgment Lesson 11-1 ongruent Triangles Learning Targets: Use the fact that congruent triangles have congruent corresponding parts. etermine
9.2 Conditions for Parallelograms
 Name lass ate 9.2 onditions for Parallelograms Essential Question: What criteria can you use to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? Explore G.6.E Prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram...
Name lass ate 9.2 onditions for Parallelograms Essential Question: What criteria can you use to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? Explore G.6.E Prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram...
Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer!
 Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Using Cabri Geometry Final Part A Problem 1
 Using Cabri Geometry Final Part A Problem 1 By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 11/10/2002 Class: Geometry Grades: 11/12 Problem 1: Use Cabri-Jr. to create a triangle with vertices labeled A, B, and C. Then: a)
Using Cabri Geometry Final Part A Problem 1 By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 11/10/2002 Class: Geometry Grades: 11/12 Problem 1: Use Cabri-Jr. to create a triangle with vertices labeled A, B, and C. Then: a)
7.NS.2d Decimal Expansions of
 7.NS.2d Decimal Expansions of Fractions Alignments to Content Standards: 7.NS.A.2.d Task Sarah learned that in order to change a fraction to a decimal, she can use the standard division algorithm and divide
7.NS.2d Decimal Expansions of Fractions Alignments to Content Standards: 7.NS.A.2.d Task Sarah learned that in order to change a fraction to a decimal, she can use the standard division algorithm and divide
Rational Number Operations on the Number Line
 The Mathematics Enthusiast Volume 14 Number 1 Numbers 1, 2, & 3 Article 18 1-2017 Rational Number Operations on the Number Line Christopher Yakes Let us know how access to this document benefits you. Follow
The Mathematics Enthusiast Volume 14 Number 1 Numbers 1, 2, & 3 Article 18 1-2017 Rational Number Operations on the Number Line Christopher Yakes Let us know how access to this document benefits you. Follow
Algebra II Honors Summer Packet Summer 2017
 Algebra II Honors Summer Packet Summer 2017 Name: The following packet contains content that you should have learned in previous Mathematics courses. You will be expected to demonstrate proficiency with
Algebra II Honors Summer Packet Summer 2017 Name: The following packet contains content that you should have learned in previous Mathematics courses. You will be expected to demonstrate proficiency with
POSTER PROBLEMS LAUNCH POSE A PROBLEM WORKSHOP POST, SHARE, COMMENT STRATEGIC TEACHER-LED DISCUSSION FOCUS PROBLEM: SAME CONCEPT IN A NEW CONTEXT
 POSTER PROLEMS Triangles To Order Seventh Grade Poster Problem Geometry In this poster problem, students try to build triangles to particular specifications (specs). The specs can include side lengths,
POSTER PROLEMS Triangles To Order Seventh Grade Poster Problem Geometry In this poster problem, students try to build triangles to particular specifications (specs). The specs can include side lengths,
A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole.
 Math 4. Class work. Algebra. Fractions. A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole. Look at the picture on the right: the whole chocolate bar is divided into equal pieces:
Math 4. Class work. Algebra. Fractions. A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole. Look at the picture on the right: the whole chocolate bar is divided into equal pieces:
Functions and Inverses
 Math Objectives Students will graphically explore functions and their inverses. Students will find the inverse of a given function algebraically. Students will reason abstractly and quantitatively (CCSS
Math Objectives Students will graphically explore functions and their inverses. Students will find the inverse of a given function algebraically. Students will reason abstractly and quantitatively (CCSS
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is where a least cost Hamiltonian circuit is found. CHAPTER 1 URBAN SERVICES
 Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Week 5 Video 5. Relationship Mining Network Analysis
 Week 5 Video 5 Relationship Mining Network Analysis Today s Class Network Analysis Network Analysis Analysis of anything that can be seen as connections between nodes Most common social networks Connections
Week 5 Video 5 Relationship Mining Network Analysis Today s Class Network Analysis Network Analysis Analysis of anything that can be seen as connections between nodes Most common social networks Connections
Geometry Honors Semester 1
 Geometry Honors Semester 1 Final Exam Review 2017-2018 Name: ate: Period: Formulas: efinitions: 1. Slope - 1. omplementary 2. Midpoint - 2. Supplementary 3. isect 3. istance - 4. Vertical ngles 4. Pythagorean
Geometry Honors Semester 1 Final Exam Review 2017-2018 Name: ate: Period: Formulas: efinitions: 1. Slope - 1. omplementary 2. Midpoint - 2. Supplementary 3. isect 3. istance - 4. Vertical ngles 4. Pythagorean
CTB/McGraw-Hill. 4th Grade Quiz and Test Review 2 24 Test ID:
 Page 1 of 43 eveloped and published by T/McGraw-Hill LL, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc., 20 Ryan Ranch Road, Monterey, alifornia 93940-5703. ll rights reserved. Only authorized customers
Page 1 of 43 eveloped and published by T/McGraw-Hill LL, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc., 20 Ryan Ranch Road, Monterey, alifornia 93940-5703. ll rights reserved. Only authorized customers
Reading. Graph Terminology. Graphs. What are graphs? Varieties. Motivation for Graphs. Reading. CSE 373 Data Structures. Graphs are composed of.
 Reading Graph Reading Goodrich and Tamassia, hapter 1 S 7 ata Structures What are graphs? Graphs Yes, this is a graph. Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices) dges (arcs) node ut we are interested in a
Reading Graph Reading Goodrich and Tamassia, hapter 1 S 7 ata Structures What are graphs? Graphs Yes, this is a graph. Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices) dges (arcs) node ut we are interested in a
15.2 Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals
 Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection
 Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection He Sun School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Leader of a computation Many distributed computations need a coordinator of server processors
Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection He Sun School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Leader of a computation Many distributed computations need a coordinator of server processors
Problem Set 7 Solutions
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 0, 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 7 Solutions Problem Set 7 Solutions
Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 0, 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 7 Solutions Problem Set 7 Solutions
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics. Chapter 10 Graph Theory
 Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Chapter 10 Graph Theory Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Chapter 10 Graph Theory Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall
GAP CLOSING. Integers. Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide
 GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
llj EXERCISES 938 CHAPTER 15 Graph Theory 11. For Exercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13.
 938 HAPTR 15 Graph Theory 15.1 XRISS or xercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13. 1. 2. (a) (b) 3. 4. 14. (al (b) s. 15. (a) L. (b) 7.-10. or xercises 7-10, refer
938 HAPTR 15 Graph Theory 15.1 XRISS or xercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13. 1. 2. (a) (b) 3. 4. 14. (al (b) s. 15. (a) L. (b) 7.-10. or xercises 7-10, refer
7 Next choice is 4, not 3...
 Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
