CS350: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
|
|
|
- Juliet Terry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Binary Search Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola
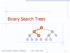
2 Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree that stores keys (or keyelement pairs) in such a way as to satisfy the following: - For every node X in the tree, the values of all the keys in the left subtree are smaller than the key in X - For every node X in the tree, the values of all the keys in the right subtree are larger than the key in X v nodes n in subtree u, key(n) < key(v) nodes n in subtree w, key(n) > key(v) u w 2
3 Binary Search Trees Which of these is not a BST? Why? 6 3
4 Binary Search Trees Which of these is not a BST? Why? This tree is NOT a BST Node 6 must be in the left subtree of node! 6 4
5 Typical Binary Search Tree Operations - isempty - checks to see if the BST is empty - makeempty - empties the BST - find - searches for and returns the node with a specified key in the BST - findmin - returns the node with the smallest key (or the key itself) - findmax - returns the node with the largest key (or the key itself) - insert - inserts a new node into the tree while maintaining the properties of a BST; all nodes are inserted as leaves - remove - removes a node from the tree while maintaining the properties of a BST 5
6 Implementation of a Binary Search Tree BST nodes are implemented similarly to other tree nodes - Contains pointers to left and right subtrees - Contains a data element Some implementation may contain a key-element pair where the key is used to determine where to insert the node in the tree class BinTreeNode<E> { E element; BinTreeNode<E> left, right; } BinTreeNode(E newelement) { element = newelement; } 6
7 The find Operation To find a node with key k - Start at the root node - Compare k with the key at the node Move to left child if k is < the key at the node Move to right child if k is > the key at the node Repeat until either the desired key is found or until a leaf node is found - If a leaf node is found and the desired key has not been found, then the desired key does not exist in the tree, return null
8 The find Operation Example of find operation - find(5)
9 The find Operation Example of find operation - find(5) < > = (1) start at root node (node ) (2) compare 5 to (3) 5 < so move left (4) compare 5 to 3 (5) 5 > 3 so move right (6) compare 5 to 5 () found node
10 A Recursive Implementation of find BinTreeNode<E> find(bintreenode<e> node, E element) { if (node == null) { return node; } else if (element == node.element) { return node; } else if (element < node.element) { return find(node.left, element); } else { return find(node.right, element); } } 10
11 The insert Operation To insert a node with key k - Start at the root node - Compare k with the key at the node If the node is null, insert new node at current location in BST Move to left child if k is < the key at the node Move to right child if k is > the key at the node Repeat until a null location is found in which to insert the new node - All insertions create a new leaf node 11
12 The insert Operation Example of insert operation - insert(6) 12
13 The insert Operation Example of insert operation - insert(6) < > > 6 (1) start at root node (node ) (2) compare 6 to (3) 6 < so move left (4) compare 6 to 3 (5) 6 > 3 so move right (6) compare 6 to 5 () 6 > 5 so move right () found null location, so add new node 6 there 13
14 The insert Operation Example of insert operation - insert(11) > >
15 The insert Operation Example of insert operation - insert(4) < > <
16 A Recursive Implementation of insert BinTreeNode<E> insert(bintreenode<e> node, E element) { if (node == null) { node = new BinTreeNode(element); } else if (element < node.element) { node.left = insert(node.left, element); } else { node.right = insert(node.right, element); } return node; } 16
17 The findmin Operation How can the node with the smallest key be found? To find the node in the tree with the smallest key k - Start at the root node - Repeatedly move to the left child until there are no more left children - Return the node 1
18 The findmin Operation Example of findmin operation - findmin( )
19 The findmin Operation Example of findmin operation - findmin( ) (1) start at root node (node ) (2) move to left child (node 5) (3) move to left child (node 2) (4) no more left children, so return node 2 as minimum key in tree 3 1
20 A Recursive Implementation of findmin BinTreeNode<E> findmin(bintreenode<e> node) { if (node.left == null) { return node; } else { return findmin(node.left); } } 20
21 The findmax Operation How can the node with the largest key be found? To find the node in the tree with the largest key k - Start at the root node - Repeatedly move to the right child until there are no more right children - Return the node 21
22 The remove Operation Find a node N with key k and remove it from the tree - Start at the root node - Find the node requested for removal - Remove the node (there are several different cases that need to be considered when removing a node): 1) Node N is not found -- do nothing 2) Node N is a leaf node -- simply remove node N from tree 3) Node N has only a single child -- remove node N and replace it with its child 4) Node N has two children -- do not delete node N, instead find its inorder successor node (or in-order predecessor) (node R) and replace the values in the node N with those from node R. Then delete node R. 22
23 The remove Operation: Case #2 - Leaf Node Example of remove operation on leaf node - remove() 23
24 The remove Operation: Case #2 - Leaf Node Example of remove operation on leaf node - remove() (1) start at root node (node ) (2) find node (3) node is a leaf node (4) simply delete node from the tree (i.e. set node s right child to null) 24
25 The remove Operation: Case #3 - Single Child Example of remove operation with a single child - remove(10) 25
26 The remove Operation: Case #3 - Single Child Example of remove operation with a single child - remove(10) (1) start at root node (node ) (2) find node 10 (3) node 10 has a single child (4) remove node 10, and replace it with its only child 26
27 The remove Operation: Case #3 - Single Child Example of remove operation with a single child - remove(10) 3 2
28 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove(3) 2
29 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove(3) (1) start at root node (node ) (2) find node 3 (3) node 3 is has two children (4) find the successor of node 3 (i.e. the min value from its right subtree) (5) replace values of node 3 with those from successor (6) remove the successor (may require additional modifications to the tree) 2
30 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove(3)
31 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove(3)
32 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove() 32
33 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove() (1) start at root node (node ) (2) find node (3) node is has two children (4) find the successor of node (i.e. the min value from its right subtree) (5) replace values of node with those from successor (6) remove the successor (may require additional modifications to the tree) 33
34 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove() 34
35 The remove Operation: Case #4 - Two Children Example of remove operation with a two children - remove() 35
36 Analysis of BST Operations Time complexity of BST operations worst case average find O(N) O(log N) insert O(N) O(log N) remove O(N) O(log N) 36
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Binary Search Trees. See Section 11.1 of the text.
 Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
a graph is a data structure made up of nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges
 1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
CS350: Data Structures Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Priority Queue An abstract data type of a queue that associates a priority
Heaps and Priority Queues James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Priority Queue An abstract data type of a queue that associates a priority
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Data Structures. Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748
 Data Structures Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu Search Tree Structures Binary Tree Operations u Tree Traversals u Search O(n) calls to visit() Why? Every recursive has one
Data Structures Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu Search Tree Structures Binary Tree Operations u Tree Traversals u Search O(n) calls to visit() Why? Every recursive has one
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
CIS 121. Binary Search Trees
 CIS 121 Binary Search Trees 1 Binary Search Tree n A Binary Search Tree is a Binary Tree in which, at every node v, the values stored in the left subtree of v are less than the value at v and the values
CIS 121 Binary Search Trees 1 Binary Search Tree n A Binary Search Tree is a Binary Tree in which, at every node v, the values stored in the left subtree of v are less than the value at v and the values
Binary Tree. Preview. Binary Tree. Binary Tree. Binary Search Tree 10/2/2017. Binary Tree
 0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
CS350: Data Structures Tree Traversal
 Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Multi-Way Search Tree
 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
CS350: Data Structures B-Trees
 B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
CSC148-Section:L0301
 Slides adapted from Professor Danny Heap course material winter17 CSC148-Section:L0301 Week#9-Firday Instructed by AbdulAziz Al-Helali a.alhelali@mail.utoronto.ca Office hours: Wednesday 11-1, BA2230.
Slides adapted from Professor Danny Heap course material winter17 CSC148-Section:L0301 Week#9-Firday Instructed by AbdulAziz Al-Helali a.alhelali@mail.utoronto.ca Office hours: Wednesday 11-1, BA2230.
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
CMSC 341. Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST
 CMSC 341 Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST Announcements Homework #3 dues Thursday (10/5/2017) Exam #1 next Thursday (10/12/2017) CMSC 341 BST A Generic Tree CMSC 341 BST Binary Tree CMSC 341 BST The Binary
CMSC 341 Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST Announcements Homework #3 dues Thursday (10/5/2017) Exam #1 next Thursday (10/12/2017) CMSC 341 BST A Generic Tree CMSC 341 BST Binary Tree CMSC 341 BST The Binary
Binary Search Trees. BinaryTree<E> Class (cont.) Section /27/2017
 Binary Search Trees Section.4 BinaryTree Class (cont.) public class BinaryTree { // Data members/fields...just the root is needed - Node root; // Constructor(s) + BinaryTree() + BinaryTree(Node
Binary Search Trees Section.4 BinaryTree Class (cont.) public class BinaryTree { // Data members/fields...just the root is needed - Node root; // Constructor(s) + BinaryTree() + BinaryTree(Node
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
CS350: Data Structures AA Trees
 AA Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to AA Trees A type of balanced binary search tree Developed as a simpler alternative
AA Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to AA Trees A type of balanced binary search tree Developed as a simpler alternative
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees
 CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
CS32%Discussion% Sec.on%1B% Week9% % TA:%Zhou%Ren%
 CS32%Discussion% Sec.on%1B% Week9% % TA:%Zhou%Ren% Tree: Definitions" root node link (edge) parent children siblings leaves H" Tree: Definitions" root node link (edge) X No loop! parent children siblings
CS32%Discussion% Sec.on%1B% Week9% % TA:%Zhou%Ren% Tree: Definitions" root node link (edge) parent children siblings leaves H" Tree: Definitions" root node link (edge) X No loop! parent children siblings
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
8. Binary Search Tree
 8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Search Trees. Data and File Structures Laboratory. DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17
 Search Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17 Binary search trees. Definition. Binary tree in which following property
Search Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17 Binary search trees. Definition. Binary tree in which following property
We have the pointers reference the next node in an inorder traversal; called threads
 Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Threaded Binary Tree Introduction: Threaded Binary Tree is also a binary tree in which all left child pointers that are NULL (in Linked
Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Threaded Binary Tree Introduction: Threaded Binary Tree is also a binary tree in which all left child pointers that are NULL (in Linked
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Spring 2018 Mentoring 8: March 14, Binary Trees
 CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
Binary Search Trees. EECS 214, Fall 2018
 Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed
 Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 Department of Computer Science _ UHD 1 What this Lecture
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 Department of Computer Science _ UHD 1 What this Lecture
SFU CMPT Lecture: Week 9
 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees
 Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
Readings. Priority Queue ADT. FindMin Problem. Priority Queues & Binary Heaps. List implementation of a Priority Queue
 Readings Priority Queues & Binary Heaps Chapter Section.-. CSE Data Structures Winter 00 Binary Heaps FindMin Problem Quickly find the smallest (or highest priority) item in a set Applications: Operating
Readings Priority Queues & Binary Heaps Chapter Section.-. CSE Data Structures Winter 00 Binary Heaps FindMin Problem Quickly find the smallest (or highest priority) item in a set Applications: Operating
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Binary search trees (BST) Binary search trees (BST)
 Tree A tree is a structure that represents a parent-child relation on a set of object. An element of a tree is called a node or vertex. The root of a tree is the unique node that does not have a parent
Tree A tree is a structure that represents a parent-child relation on a set of object. An element of a tree is called a node or vertex. The root of a tree is the unique node that does not have a parent
Binary Trees. Examples:
 Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Search Trees (10.1) Dictionary ADT (9.5.1)
 Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
Binary Trees: Practice Problems
 Binary Trees: Practice Problems College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Warmup Problem 1: Searching for a node public boolean recursivesearch(int
Binary Trees: Practice Problems College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Warmup Problem 1: Searching for a node public boolean recursivesearch(int
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch18d Title: Binary Search Tree Iterator Description: Additional operations first and last; the BST iterator Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook:
Podcast Ch18d Title: Binary Search Tree Iterator Description: Additional operations first and last; the BST iterator Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook:
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Principles of Computer Science
 Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees The Binary Search Property
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees The Binary Search Property
The Binary Search Tree ADT
 The Binary Search Tree ADT Binary Search Tree A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree with an ordering property of its elements, such that the data in any internal node is Greater than the data in
The Binary Search Tree ADT Binary Search Tree A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree with an ordering property of its elements, such that the data in any internal node is Greater than the data in
CS102 Binary Search Trees
 CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
BST Implementation. Data Structures. Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr University of Ain Shams
 Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
A set of nodes (or vertices) with a single starting point
 Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Priority Queues. 04/10/03 Lecture 22 1
 Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
CSC212 Data Structure - Section FG
 CSC212 Data Structure - Section FG Lecture 17 B-Trees and the Set Class Instructor: Feng HU Department of Computer Science City College of New York @ Feng HU, 2016 1 Topics Why B-Tree The problem of an
CSC212 Data Structure - Section FG Lecture 17 B-Trees and the Set Class Instructor: Feng HU Department of Computer Science City College of New York @ Feng HU, 2016 1 Topics Why B-Tree The problem of an
8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))
![8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F)) 8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))](/thumbs/89/97773603.jpg) DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
Binary Tree Applications
 Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
Tree Structures. Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest
 Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
Motivation Computer Information Systems Storage Retrieval Updates. Binary Search Trees. OrderedStructures. Binary Search Tree
 Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates
 Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Outline. An Application: A Binary Search Tree. 1 Chapter 7: Trees. favicon. CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Approaching BST Making a decision We discussed the trade-offs between linked and array-based implementations of sequences (back in Section 4.7). Linked lists
Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Approaching BST Making a decision We discussed the trade-offs between linked and array-based implementations of sequences (back in Section 4.7). Linked lists
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Dictionaries. 2/17/2006 Dictionaries 1
 Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
CISC 235 Topic 3. General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Binary search trees. Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search. Minimum. Maximum. Insert. Delete ...
 Binary search trees Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search Minimum Maximum Insert Delete... Can be used as dictionary, priority queue... you name it Running time depends on height of tree: 1
Binary search trees Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search Minimum Maximum Insert Delete... Can be used as dictionary, priority queue... you name it Running time depends on height of tree: 1
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Data Structure. Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang. National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan
 Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees. Linda Shapiro Spring 2016
 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 nnouncements HW2 due start of class Wednesday pril 13 on paper. Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms
CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 nnouncements HW2 due start of class Wednesday pril 13 on paper. Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Trees. Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano Ronaldo Menezes, Florida Tech
 Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Binary Trees. BSTs. For example: Jargon: Data Structures & Algorithms. root node. level: internal node. edge.
 Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Binary Heaps. COL 106 Shweta Agrawal and Amit Kumar
 Binary Heaps COL Shweta Agrawal and Amit Kumar Revisiting FindMin Application: Find the smallest ( or highest priority) item quickly Operating system needs to schedule jobs according to priority instead
Binary Heaps COL Shweta Agrawal and Amit Kumar Revisiting FindMin Application: Find the smallest ( or highest priority) item quickly Operating system needs to schedule jobs according to priority instead
Binary Trees. Recursive definition. Is this a binary tree?
 Binary Search Trees Binary Trees Recursive definition 1. An empty tree is a binary tree 2. A node with two child subtrees is a binary tree 3. Only what you get from 1 by a finite number of applications
Binary Search Trees Binary Trees Recursive definition 1. An empty tree is a binary tree 2. A node with two child subtrees is a binary tree 3. Only what you get from 1 by a finite number of applications
CSCI Trees. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
Dictionaries. Priority Queues
 Red-Black-Trees.1 Dictionaries Sets and Multisets; Opers: (Ins., Del., Mem.) Sequential sorted or unsorted lists. Linked sorted or unsorted lists. Tries and Hash Tables. Binary Search Trees. Priority Queues
Red-Black-Trees.1 Dictionaries Sets and Multisets; Opers: (Ins., Del., Mem.) Sequential sorted or unsorted lists. Linked sorted or unsorted lists. Tries and Hash Tables. Binary Search Trees. Priority Queues
Outline. Preliminaries. Binary Trees Binary Search Trees. What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications
 Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Outline. Computer Science 331. Insertion: An Example. A Recursive Insertion Algorithm. Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion.
 Outline Computer Science Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture # 2 BST Deletion Case Case 2 Case Case 4 Complexity Discussion
Outline Computer Science Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture # 2 BST Deletion Case Case 2 Case Case 4 Complexity Discussion
CSC148 Week 7. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 7 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 can be picked up in DH-3008 A1 due this Saturday Next week is reading week no lecture, no labs no office hours 2 Recap Last week, learned about binary trees
CSC148 Week 7 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 can be picked up in DH-3008 A1 due this Saturday Next week is reading week no lecture, no labs no office hours 2 Recap Last week, learned about binary trees
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science. Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department
 Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
Binary Search Tree. Revised based on textbook author s notes.
 Binary Search Tree Revised based on textbook author s notes. Search Trees The tree structure can be used for searching. Each node contains a search key as part of its data or payload. Nodes are organized
Binary Search Tree Revised based on textbook author s notes. Search Trees The tree structure can be used for searching. Each node contains a search key as part of its data or payload. Nodes are organized
2-3 and Trees. COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli
 2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
Binary Heaps. CSE 373 Data Structures Lecture 11
 Binary Heaps CSE Data Structures Lecture Readings and References Reading Sections.1-. //0 Binary Heaps - Lecture A New Problem Application: Find the smallest ( or highest priority) item quickly Operating
Binary Heaps CSE Data Structures Lecture Readings and References Reading Sections.1-. //0 Binary Heaps - Lecture A New Problem Application: Find the smallest ( or highest priority) item quickly Operating
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
* Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab
 ===Lab Info=== *100 points * Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab ==Assignment== In this assignment you will work on designing a class for a binary search tree. You
===Lab Info=== *100 points * Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab ==Assignment== In this assignment you will work on designing a class for a binary search tree. You
Binary Search Tree (3A) Young Won Lim 6/2/18
 Binary Search Tree (A) /2/1 Copyright (c) 2015-201 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Binary Search Tree (A) /2/1 Copyright (c) 2015-201 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort
 Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort Complete the Doublets partner(s) evaluation by tonight. Use your individual log to give them useful feedback! Like 230 and have workstudy funding? We are looking for CSSE230
Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort Complete the Doublets partner(s) evaluation by tonight. Use your individual log to give them useful feedback! Like 230 and have workstudy funding? We are looking for CSSE230
