Maclaurin series. To create a simple version of this resource yourself using Geogebra:
|
|
|
- Maximillian Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Maclaurin series Maclaurin series (Geogebra) This resource is on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI FP2 Power series 1, AQA FP3 Series 1, Edexcel FP2 Maclaurin series 1, OCR FP2 Maclaurin series 1, WJEC FP3 Power Series 1. It s useful for students to connect the derivation of a Maclaurin series with the graphical approximations: the linear approximation has the same first derivative, the quadratic has the same first and second derivatives, and so on. The resource can also be used to look at functions for which the Maclaurin series is valid only for a limited range of values. To create a simple version of this resource yourself using Geogebra: 1. Enter the equation f(x)=e^x. 2. Create a slider called n, with minimum 1, maximum 10 and increment Enter the equation g(x) = TaylorPolynomial[f,0,n]. This creates n terms of the Taylor polynomial for f at x = 0 (i.e. the Maclaurin polynomial). 4. Change the colours and thicknesses of the two graphs if you wish. 5. You may want to use a text box to put the approximation on the screen, e.g. create a text box and type in "Approximation = " +g Moving the slider shows successive approximations. Look at how the approximation improves for a wider range of values of x as the value of n increases. Double click on the function f(x) (either in the Algebra window or the graph itself) to change the function, e.g. f(x)=sin(x), f(x)=ln(1+x). In particular, look at the range of values of x for which the approximation is valid. The version on the website also allows you to compare the values of the derivatives of the function and the approximation. It can be helpful to use a different graph for this, so that the values of the derivatives are more interesting! Alternatively, you can create a similar resource using Autograph: 1. Enter the equation y = e^x. 2. Select the graph, right-click (or go to Object) and choose Maclaurin series 3. Uncheck Show Progressive terms and click OK 4. Select the Maclaurin graph and click the lightning bolt button 5. Use the arrows to increase or decrease the number of terms in the expansion.
2 Intersecting planes (Autograph) Matrices and simultaneous equations This resource is on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI FP2 Matrices 3, AQA FP4 Matrices 4, OCR FP1 Matrices 4, WJEC FP1 Matrices 2. It can be difficult for students to visualise what is happening geometrically when they solve three simultaneous linear equations. This resource allows them to explore the different configurations of three planes, particularly cases in which there is no unique solution. To create this resource yourself using Autograph: 1. Open a new 3D graphs page 2. Choose Equation Enter equation. Enter the equation of a plane and click Plot as 2D equation. Enter two other equations of planes in the same way. Drag the axes round to look at where the graphs intersect, and whether there is a unique solution, infinitely many solutions or no solutions. Choose suitable sets of equations for students to explore. By including variables in the equations you can use the Constant controller. e.g. the default set of planes in the resource on the website are: x + 3y 2z = 7 2x 2y + az = 2 3x + y z = k This gives a triangular prism initially (with a = k = 1). You can get a sheaf of planes by changing k, and a single point by changing a. Have a calculator that handles matrices available, and ask students to check the determinant of the matrices corresponding to each set of equations. Ask students to think about how they might recognise different configurations from the equations of the planes. (Parallel or coinciding places are easily spotted, but a triangular prism or a sheaf of planes requires some algebraic manipulation!) You could ask students to find a set of equations corresponding to each possible configuration.
3 Matrices eigenvalues and eigenvectors Eigenvalues and eigenvectors (Autograph) There is a Flash resource Eigenvalues and eigenvectors on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI FP2 Matrices 4, AQA FP4 Matrices 5, Edexcel FP3 Matrices 2. Students can usually learn the recipe for finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors without too much trouble. However, they often have very little idea of what an eigenvector is. This resource introduces the idea geometrically. To create a similar resource in Autograph: 1. In the Object menu, select Enter shape. Enter the coordinates (0, 0) and (1, 1). This should give you a line segment from the origin to the point (1, 1). 2. With the line segment selected, select Matrix Transformation in the Object menu. Enter the matrix you want to. This should give you the image of the line segment under this transformation. Move the point (1, 1) around until you find a position for which the original line segment and its image lie in the same straight line (for some matrix transformations, they may be in opposite directions). When you have found an appropriate position, look at the results box at the bottom of the page to see the coordinates of the point, and hence write down a vector in the direction of the line segment (or you can rightclick on each point and add a text box to label each point with its coordinates). This is an eigenvector for the matrix. Try to find two different positions for the eigenvector. Note the position vectors of both the original point and its image, and hence find the constant by which the eigenvector must be multiplied to obtain its image. This is the eigenvalue corresponding to the eigenvector you have found. Double-click on the image line to change the matrix. You can also check the Show eigenvectors box to show the direction of both eigenvectors. If you right-click on the image point, you can put a trace on the image (this can t be done in the Flash resource). Investigate!
4 Conic sections (Autograph) The conic as sections of a cone This resource is on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI FP2 Curves 2, AQA FP1 Graphs 3, Edexcel FP3 Coordinate systems 1, WJEC FP2 Loci 1. Students are often not aware of the connections between the different members of the family of conic sections. This resource helps them to visualise the conics as sections of a cone. To create this resource yourself using Autograph: 1. Open a new 3D page in Autograph. Enter the equation r = z (this gives a double cone, using cylindrical polar coordinates). 2. Enter the equation z = a + bx (this gives a general plane initially the values of a and b take their default values of 1). Use the Constant controller to set b to be zero and try different values of a. Move the view round so that you can see the cone from above you should be able to see circles of varying radii. Set a = 2 and try different values of b, starting with values between 0 and 1. These should give ellipses. Next set b = 1. The plane is now parallel to the slope of the cone, and this gives a parabola (you will need to change the view to see this properly). Now try values of b greater than 1. These give hyperbolae. As b gets larger, the plane becomes closer to vertical. To look at a vertical plane, change the equation of the plane to x = c. and the hyperbola approaches a rectangular hyperbola. For the default value of c = 1, you get a rectangular hyperbola. Decrease c to zero, and you have a vertical plane through the origin, which gives a pair of straight lines also part of the family of conic sections!
5 Conic graphs Conics (Geogebra) This resource is on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI FP2 Curves 2, AQA FP1 Graphs 3, Edexcel FP3 Coordinate systems 1, WJEC FP2 Loci 1. This resource helps to show students that the ellipse, parabola and hyperbola are all part of the same family, and explores the focus-directrix property. Not all specifications require this, but it s useful background knowledge which gives students a context for the work they need to cover. To create a simple version of this resource yourself using Geogebra: 1. Mark the point (1, 0) for the focus. The y-axis will be a directrix. 2. Create a slider for e, with e going from zero to Put in the equation (x - 1)² + y² = e²x². 4. Mark a point P on the curve, and draw a segment from P to the focus. Change the label so that it shows the length. 5. Draw a perpendicular from P to the y-axis, and mark the point where this line crosses the y-axis. Then hide the line, and draw a segment from P to the point on the y-axis. Change the label so that it shows the length. Use the slider to vary the value of e and produce hyperbolas, a parabola and ellipses. Divide the length of the first segment by the other (use their labels, e.g. a/b) to show that the ratio is always the same and equal to the eccentricity. Alternatively, you can create a similar resource using Autograph: 1. Create a point on the x-axis for the focus, and draw a vertical line such as x = -1 for the directrix. 2. Select both the point and the line, right-click (or use the Object menu) and choose Conic by Eccentricity. 3. Select the resulting conic and press the lightning bolt button. You can then vary the eccentricity of the conic.
6 Newton-Raphson (Geogebra) Newton-Raphson method This resource is on the Integral website in the following sections: MEI C3 Numerical methods 1, AQA FP1 Numerical methods 1, Edexcel FP1 Numerical methods 1, OCR FP2 Numerical methods 2, WJEC FP3 Numerical methods 1. This resource illustrates the Newton-Raphson iterations graphically. Students can explore how different starting positions result in convergence to different roots, and look at how quickly the iterations converge. To create this resource yourself using Geogebra: 1. Enter the graph in the input box. 2. Put a point A on the x-axis. 3. Go to Spreadsheet view and type x(a) in cell A1. This gives you the x-coordinate of point A the first approximation to the root. 4. In cell A2, type A1 f(a1)/f (A1) and copy this down the column as far as you like. (You can change the number of decimal places shown on Options Rounding. 5. In cell B1, type Segment[(A1, 0), (A1, f(a1))]. This creates a vertical line from point A to the graph. Copy this down the column. 6. In cell C1, type Segment[(A1, f(a1)), (A2, 0)]. This creates the tangent line from the curve to the second approximation. Copy down the column as far as one row before the end of column B entries. You can move the first approximation around to explore convergence to different roots or divergence. Look at column A to see how quickly the iterations converge in some cases they diverge first and then converge. You can change the graph by double-clicking on it Useful links These interactive resources, and many others, as well as a wide range of other resources are available by subscribing to the Integral website Information about subscriptions to the website can be found at Geogebra is freely available open-source software. It can be downloaded from The Geogebra website also contains introductory materials, help documents and a user forum. Autograph is available to purchase from as a single user or site licence. You can download a 30-day trial free of change.
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics
 8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
Quickstart for Desktop Version
 Quickstart for Desktop Version What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematics Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Quickstart for Desktop Version What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematics Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Quickstart for Web and Tablet App
 Quickstart for Web and Tablet App What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematic Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
Quickstart for Web and Tablet App What is GeoGebra? Dynamic Mathematic Software in one easy-to-use package For learning and teaching at all levels of education Joins interactive 2D and 3D geometry, algebra,
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 181. Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Conic Sections Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Conic Sections. College Algebra
 Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff. x h y k r
 NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
CK 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
GeoGebra Workshop. (Short Version)
 GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH. Dr Toh Pee Choon NIE 2 June 2016
 DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
Introduction to Geogebra
 Aims Introduction to Geogebra Using Geogebra in the A-Level/Higher GCSE Classroom To provide examples of the effective use of Geogebra in the teaching and learning of mathematics at A-Level/Higher GCSE.
Aims Introduction to Geogebra Using Geogebra in the A-Level/Higher GCSE Classroom To provide examples of the effective use of Geogebra in the teaching and learning of mathematics at A-Level/Higher GCSE.
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Name. Center axis. Introduction to Conic Sections
 Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
The derivative of a function at one point. 1. Secant lines and tangents. 2. The tangent problem
 1. Secant lines and tangents The derivative of a function at one point A secant line (or just secant ) is a line passing through two points of a curve. As the two points are brought together (or, more
1. Secant lines and tangents The derivative of a function at one point A secant line (or just secant ) is a line passing through two points of a curve. As the two points are brought together (or, more
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for A2 Core
 Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 2 4 x 0
 Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR
 European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 011-01-D-7-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 011-01-D-7-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
MEI Conference Teaching numerical methods using graphing technology
 MEI Conference 2017 Teaching numerical methods using graphing technology Jo Sibley josibley@furthermaths.org.uk Casio CG20 Task Numerical Methods: Change of sign 1. Add a new Graphs screen: p5 5. Generate
MEI Conference 2017 Teaching numerical methods using graphing technology Jo Sibley josibley@furthermaths.org.uk Casio CG20 Task Numerical Methods: Change of sign 1. Add a new Graphs screen: p5 5. Generate
Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties
 Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 8 Conic Sections 8.1 Circle write the definition, provide examples of both the standard
Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 8 Conic Sections 8.1 Circle write the definition, provide examples of both the standard
Today s class. Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods. Numerical Methods, Fall 2011 Lecture 5. Prof. Jinbo Bi CSE, UConn
 Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
, minor axis of length 12. , asymptotes y 2x. 16y
 Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Activity overview. Background. Concepts. Teacher preparation. Technical prerequisites
 The impact of b in By Øystein Nordvik Grade level: secondary (Years 9-1) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview In this activity you will examine the influence parameter b has
The impact of b in By Øystein Nordvik Grade level: secondary (Years 9-1) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview In this activity you will examine the influence parameter b has
ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet
 Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University
 A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University sml4@axe.humboldt.edu The following exploration builds an ellipse based on the geometric definition: An ellipse
A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University sml4@axe.humboldt.edu The following exploration builds an ellipse based on the geometric definition: An ellipse
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
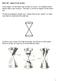 Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. Page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Chapter 10. Exploring Conic Sections
 Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Josef Böhm, ACDCA, DUG and Technical University of Vienna
 Linking Geometry, Algebra and Calculus with GeoGebra Josef Böhm, ACDCA, DUG and Technical University of Vienna nojo.boehm@pgv.at Abstract GeoGebra is free, open-source, and multi-platform software that
Linking Geometry, Algebra and Calculus with GeoGebra Josef Böhm, ACDCA, DUG and Technical University of Vienna nojo.boehm@pgv.at Abstract GeoGebra is free, open-source, and multi-platform software that
Design and Communication Graphics
 An approach to teaching and learning Design and Communication Graphics Solids in Contact Syllabus Learning Outcomes: Construct views of up to three solids having curved surfaces and/or plane surfaces in
An approach to teaching and learning Design and Communication Graphics Solids in Contact Syllabus Learning Outcomes: Construct views of up to three solids having curved surfaces and/or plane surfaces in
Geometry: Conic Sections
 Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Pre-Calculus. 2) Find the equation of the circle having (2, 5) and (-2, -1) as endpoints of the diameter.
 Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
New perspectives on conic sections
 New perspectives on conic sections Abstract Giora Mann, Nurit Zehavi and Thierry Dana-Picard* Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, *Jerusalem College of Technology For a given hyperbola, what are the
New perspectives on conic sections Abstract Giora Mann, Nurit Zehavi and Thierry Dana-Picard* Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, *Jerusalem College of Technology For a given hyperbola, what are the
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study
 Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas. Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School
 Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds
 Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Honors Precalculus: Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically. Page 1
 Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Graphing Techniques. Domain (, ) Range (, ) Squaring Function f(x) = x 2 Domain (, ) Range [, ) f( x) = x 2
 Graphing Techniques In this chapter, we will take our knowledge of graphs of basic functions and expand our ability to graph polynomial and rational functions using common sense, zeros, y-intercepts, stretching
Graphing Techniques In this chapter, we will take our knowledge of graphs of basic functions and expand our ability to graph polynomial and rational functions using common sense, zeros, y-intercepts, stretching
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
 Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Mastery. PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets
 PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets Big Idea: Sequences and Series 1. I can describe a sequence as a function where the domain is the set of natural numbers. Connections (Pictures, Vocabulary, Definitions,
PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets Big Idea: Sequences and Series 1. I can describe a sequence as a function where the domain is the set of natural numbers. Connections (Pictures, Vocabulary, Definitions,
Algebra II. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Slide 4 / 181. Slide 6 / 181. Slide 5 / 181.
 Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
GeoGebra Workshop. Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University
 GeoGebra Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Contents Introduction... 3 What is GeoGebra?... 3 Get GeoGebra... 3 Workshop Sections... 3 Workshop Format...
GeoGebra Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Contents Introduction... 3 What is GeoGebra?... 3 Get GeoGebra... 3 Workshop Sections... 3 Workshop Format...
MEI Desmos Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1
 9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
Put your initials on the top of every page, in case the pages become separated.
 Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
form. We will see that the parametric form is the most common representation of the curve which is used in most of these cases.
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 Curve Representation Welcome everybody to the lectures on computer graphics.
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 Curve Representation Welcome everybody to the lectures on computer graphics.
A new CAS-touch with touching problems
 A new CAS-touch with touching problems T 3 - Conference, Oostende, August 00 Dr. René Hugelshofer, Switzerland rene@hugelshofer.net Parameters provide Maths with a new dynamic and lead sometimes to astonishing
A new CAS-touch with touching problems T 3 - Conference, Oostende, August 00 Dr. René Hugelshofer, Switzerland rene@hugelshofer.net Parameters provide Maths with a new dynamic and lead sometimes to astonishing
Substituting a 2 b 2 for c 2 and using a little algebra, we can then derive the standard equation for an ellipse centred at the origin,
 Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct equation form as listed!! above, then determine the center and radius of each circle.
 Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Standard Equation of a Circle
 Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
OpenGL Graphics System. 2D Graphics Primitives. Drawing 2D Graphics Primitives. 2D Graphics Primitives. Mathematical 2D Primitives.
 D Graphics Primitives Eye sees Displays - CRT/LCD Frame buffer - Addressable pixel array (D) Graphics processor s main function is to map application model (D) by projection on to D primitives: points,
D Graphics Primitives Eye sees Displays - CRT/LCD Frame buffer - Addressable pixel array (D) Graphics processor s main function is to map application model (D) by projection on to D primitives: points,
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Conic Sections and Locii
 Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already familiar with ways of solving
 The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
GeoGebra. 10 Lessons. maths.com. Gerrit Stols. For more info and downloads go to:
 GeoGebra in 10 Lessons For more info and downloads go to: http://school maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements Download GeoGebra from http://www.geogebra.org GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source
GeoGebra in 10 Lessons For more info and downloads go to: http://school maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements Download GeoGebra from http://www.geogebra.org GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source
A function: A mathematical relationship between two variables (x and y), where every input value (usually x) has one output value (usually y)
 SESSION 9: FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Definitions & Terminology Graphs of Functions - Straight line - Parabola - Hyperbola - Exponential Sketching graphs Finding Equations Combinations of graphs TERMINOLOGY
SESSION 9: FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Definitions & Terminology Graphs of Functions - Straight line - Parabola - Hyperbola - Exponential Sketching graphs Finding Equations Combinations of graphs TERMINOLOGY
Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections
 206 Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections Summary: This chapter begins by introducing the idea of representing curves using parameters. These parametric equations of the curves can then
206 Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections Summary: This chapter begins by introducing the idea of representing curves using parameters. These parametric equations of the curves can then
Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots. Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle.
 Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
CURRICULUM MAP. Course / Subject: Precalculus Grade: 11/12 Teacher: Kelly, Kirk, McCollick, Palkovics, Roderick Month: September (19 days)
 Month: September (19 days) - Change from radian to degree measure, & vice versa - Find angles that are coterminal with a given angle - Find reference angle for a given angle Angles & Their Measure (Section
Month: September (19 days) - Change from radian to degree measure, & vice versa - Find angles that are coterminal with a given angle - Find reference angle for a given angle Angles & Their Measure (Section
Math 1314 Lesson 2: An Introduction to Geogebra (GGB) Course Overview
 Math 1314 Lesson : An Introduction to Geogebra (GGB) Course Overview What is calculus? Calculus is the study of change, particularly, how things change over time. It gives us a framework for measuring
Math 1314 Lesson : An Introduction to Geogebra (GGB) Course Overview What is calculus? Calculus is the study of change, particularly, how things change over time. It gives us a framework for measuring
Buds Public School, Dubai
 Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
To be a grade 1 I need to
 To be a grade 1 I need to Order positive and negative integers Understand addition and subtraction of whole numbers and decimals Apply the four operations in correct order to integers and proper fractions
To be a grade 1 I need to Order positive and negative integers Understand addition and subtraction of whole numbers and decimals Apply the four operations in correct order to integers and proper fractions
Unit 3 Higher topic list
 This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
Find and open a GeoGebra Applet. : Instructions for using the GeoGebra Applet
 1 is based on a series of 42 Applets which were created in GeoGebra to help you visualise a range of key concepts in CAPS Mathematics, particularly in the areas of Functions and Euclidean Geometry. Each
1 is based on a series of 42 Applets which were created in GeoGebra to help you visualise a range of key concepts in CAPS Mathematics, particularly in the areas of Functions and Euclidean Geometry. Each
An Introduction to GeoGebra
 Contents Foreword ii Downloading and Installing.......................... 1 Acquiring GeoGebra........................... 1 Installing................................. 1 Necessary Files..............................
Contents Foreword ii Downloading and Installing.......................... 1 Acquiring GeoGebra........................... 1 Installing................................. 1 Necessary Files..............................
Mathematics 6 12 Section 26
 Mathematics 6 12 Section 26 1 Knowledge of algebra 1. Apply the properties of real numbers: closure, commutative, associative, distributive, transitive, identities, and inverses. 2. Solve linear equations
Mathematics 6 12 Section 26 1 Knowledge of algebra 1. Apply the properties of real numbers: closure, commutative, associative, distributive, transitive, identities, and inverses. 2. Solve linear equations
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders
 GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
Properties of Quadratic functions
 Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
UNIT 3 EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Lesson 3: Creating Quadratic Equations in Two or More Variables
 Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
Warm-Up Exercises. Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; y = 2x + 7 ANSWER ; 7
 Warm-Up Exercises Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; 3 2. y = 2x + 7 7 2 ANSWER ; 7 Chapter 1.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form A quadratic function is a function that
Warm-Up Exercises Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; 3 2. y = 2x + 7 7 2 ANSWER ; 7 Chapter 1.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form A quadratic function is a function that
13.1 2/20/2018. Conic Sections. Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
 13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts
 Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
FOUNDATION HIGHER. F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9
 Year: 9 GCSE Mathematics FOUNDATION F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9 HIGHER Integers and place value Decimals Indices, powers and roots Factors,multiples
Year: 9 GCSE Mathematics FOUNDATION F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9 HIGHER Integers and place value Decimals Indices, powers and roots Factors,multiples
Name: Chapter 7 Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Name: Chapter Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: = ax + bx+ c A is a function that can be written in the form = ax + bx+ c where a, b, and c are real numbers
Name: Chapter Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: = ax + bx+ c A is a function that can be written in the form = ax + bx+ c where a, b, and c are real numbers
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
The equation to any straight line can be expressed in the form:
 Student Activity 7 8 9 10 11 12 TI-Nspire Investigation Student 45 min Aims Determine a series of equations of straight lines to form a pattern similar to that formed by the cables on the Jerusalem Chords
Student Activity 7 8 9 10 11 12 TI-Nspire Investigation Student 45 min Aims Determine a series of equations of straight lines to form a pattern similar to that formed by the cables on the Jerusalem Chords
A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks:
 Functions (H) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. (a) The diagram shows a sketch of the graph y = f(x). The
Functions (H) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. (a) The diagram shows a sketch of the graph y = f(x). The
Cambridge IGCSE mapping
 Cambridge IGCSE mapping Specification point Boardworks presentation 1. Number, set notation and language Identify and use natural numbers, integers (positive, negative and zero), prime numbers, square
Cambridge IGCSE mapping Specification point Boardworks presentation 1. Number, set notation and language Identify and use natural numbers, integers (positive, negative and zero), prime numbers, square
7 Fractions. Number Sense and Numeration Measurement Geometry and Spatial Sense Patterning and Algebra Data Management and Probability
 7 Fractions GRADE 7 FRACTIONS continue to develop proficiency by using fractions in mental strategies and in selecting and justifying use; develop proficiency in adding and subtracting simple fractions;
7 Fractions GRADE 7 FRACTIONS continue to develop proficiency by using fractions in mental strategies and in selecting and justifying use; develop proficiency in adding and subtracting simple fractions;
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS. MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June C3 COURSEWORK
 MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June 29 2009 C3 COURSEWORK What is this coursework designed to do and how do we prepare students for it? Presenter: Val Hanrahan The
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June 29 2009 C3 COURSEWORK What is this coursework designed to do and how do we prepare students for it? Presenter: Val Hanrahan The
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2
 EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name
 Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
Using Symbolic Geometry to Teach Secondary School Mathematics - Geometry Expressions Activities for Algebra 2 and Precalculus
 Using Symbolic Geometry to Teach Secondary School Mathematics - Geometry Expressions Activities for Algebra and Precalculus Irina Lyublinskaya, CUNY College of Staten Island, Staten Island, NY, USA and
Using Symbolic Geometry to Teach Secondary School Mathematics - Geometry Expressions Activities for Algebra and Precalculus Irina Lyublinskaya, CUNY College of Staten Island, Staten Island, NY, USA and
9-1 GCSE Maths. GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9).
 9-1 GCSE Maths GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9). In each tier, there are three exams taken at the end of Year 11. Any topic may be assessed on each of
9-1 GCSE Maths GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9). In each tier, there are three exams taken at the end of Year 11. Any topic may be assessed on each of
Integrated Algebra/Geometry 1
 *Ability to add, subtract, multiply and divide integers (without the use of a calculator) Ability to make statements about information presented in: tables and graphs concept maps identify and extend patterns
*Ability to add, subtract, multiply and divide integers (without the use of a calculator) Ability to make statements about information presented in: tables and graphs concept maps identify and extend patterns
Casio 9860 DYNA Investigation and Instructions
 Casio 9860 DYNA Investigation and Instructions Instructions This activity is both a self-guided instruction worksheet and a student investigation of Straight Lines, Parabolas, Cubics, Hyperbolas, and Exponentials.
Casio 9860 DYNA Investigation and Instructions Instructions This activity is both a self-guided instruction worksheet and a student investigation of Straight Lines, Parabolas, Cubics, Hyperbolas, and Exponentials.
Flash Light Reflectors. Fountains and Projectiles. Algebraically, parabolas are usually defined in two different forms: Standard Form and Vertex Form
 Sec 6.1 Conic Sections Parabolas Name: What is a parabola? It is geometrically defined by a set of points or locus of points that are equidistant from a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). To
Sec 6.1 Conic Sections Parabolas Name: What is a parabola? It is geometrically defined by a set of points or locus of points that are equidistant from a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). To
Sketching graphs of polynomials
 Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
5.5 Newton s Approximation Method
 498CHAPTER 5. USING DERIVATIVES TO ANALYZE FUNCTIONS; FURTHER APPLICATIONS 4 3 y = x 4 3 f(x) = x cosx y = cosx 3 3 x = cosx x cosx = 0 Figure 5.: Figure showing the existence of a solution of x = cos
498CHAPTER 5. USING DERIVATIVES TO ANALYZE FUNCTIONS; FURTHER APPLICATIONS 4 3 y = x 4 3 f(x) = x cosx y = cosx 3 3 x = cosx x cosx = 0 Figure 5.: Figure showing the existence of a solution of x = cos
How Many Solutions 2 TEACHER NOTES
 Math Objectives Students will recognize that a system of two equations in two variables can have no solution, one or more solutions, or infinitely many solutions. Students will determine whether a graph
Math Objectives Students will recognize that a system of two equations in two variables can have no solution, one or more solutions, or infinitely many solutions. Students will determine whether a graph
