GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms?
|
|
|
- Dennis Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. Hundreds of graph algorithms known. Thousands of practical applications. 1 of 38
2 2 of 38
3 Graph Terminology 3 of 38
4 Some Graph Problems Path. Is there a path between s to t? Shortest path. What is the shortest path between s and t? Longest path. What is the longest simple path between s and t? Cycle. Is there a cycle in the graph? Euler tour. Is there a cycle that uses each edge exactly once? Hamilton tour. Is there a cycle that uses each vertex exactly once? Connectivity. Is there a way to connect all of the vertices? MST. What is the best way to connect all of the vertices? Biconnectivity. Is there a vertex whose removal disconnects the graph? Planarity. Can you draw the graph in the plane with no crossing edges? Isomorphism. Do two adjacency matrices represent the same graph? Graph Representation 4 of 38
5 Vertex representation. We use integers between 0 and V 1. Real world: convert between names and integers with symbol table. Other issues. Parallel edges, self-loops. 5 of 38
6 Graph API class Graph graph data type Graph(int V) create an empty graph with V vertices Graph(int V, int E) create a random graph with V vertices, E edges int V() return number of vertices void insert(int v, int w) add an edge v-w int* adj(int v) return the starting value of an iterator over the neighbors of v int* nadj(int v) return the upper barrier of an iterator over the neighbors of v 6 of 38
7 Example: iterate through all edges: Graph* G = new Graph(5, 4); for (int v = 0; v < G->V(); v++) { cout << v << " :"; for(int* pw = G->adj(v); pw!= G->nadj(v); pw++) cout << " " << *pw; cout << endl; } 7 of 38
8 Set of edge representation. Store list of edges. 8 of 38
9 Adjacency matrix representation. Two-dimensional V by V boolean array. Edge v-w in graph adj[v][w] = adj[w][v] = true. 9 of 38
10 Adjacency List Representation Vertex indexed array of lists. Two representations of each undirected edge. 10 of 38
11 Graph Representations Graphs are abstract mathematical objects. ADT implementation requires specific representation. Efficiency depends on matching algorithms to representations. 11 of 38
12 Graphs in practice. [use adjacency list representation] Real world graphs are sparse. Bottleneck is iterating over edges incident to v. 12 of 38
13 Maze graphs. Vertex = intersections. Edge = passage. Goal. Explore every passage in the maze. 13 of 38
14 History. Theseus entered labyrinth to kill the monstrous Minotaur; Ariadne held ball of string. Unroll a ball of string behind you. Mark each visited intersection by turning on a light. Mark each visited passage by opening a door. 14 of 38
15 15 of 38
16 Depth First Search. Find all vertices connected to s. DFS (to visit a vertex v) Mark v as visited. Visit all unmarked vertices w adjacent to v. Running time: O(E) since each edge examined at most twice. 16 of 38
17 Reachability Application: Flood Fill Given lime green pixel in an image, change color of entire blob of neighboring lime pixels to blue. Vertex: pixel. Edge: between two adjacent lime pixels. Blob: all pixels reachable from chosen lime pixel. 17 of 38
18 Path. Is there a path from s to t? If so, find one. 18 of 38
19 19 of 38
20 Quick-Find [eager approach] Data structure. Integer array id[] of size N. Interpretation: p and q are connected if they have the same id. Find. Check if p and q have the same id. (id[3] = 9; id[6] = 6; 3 and 6 not connected) 20 of 38
21 Union. To merge components containing p and q, change all entries with id[p] to id[q]. 21 of 38
22 Quick-Find: Example 22 of 38
23 Quick-Union [lazy approach] Data structure. Integer array id[] of size N. Interpretation: id[i] is parent of i. Root of i is id[id[id[...id[i]...]]]. 23 of 38
24 Find. Check if p and q have the same root. Union. Set the id of q's root to the id of p's root. 24 of 38
25 Quick-Union: Example 25 of 38
26 UF advantage. Can intermix query and edge insertion. DFS advantage. Can recover path itself in same running time. Keep Track of Path DFS tree. Upon visiting a vertex v for the first time, remember from where you came pred[v]. Retrace path. To find path between s and v, follow pred[] values back from v. 26 of 38
27 27 of 38
28 DFS Summary Enables direct solution of simple graph problems. Find path between s to t. Connected components. Euler tour. Cycle detection. Bipartiteness checking. Basis for solving more difficult graph problems. Biconnected components. Planarity testing. 28 of 38
29 Breadth First Search Depth-first search. Put unvisited vertices on a stack. Breadth-first search. Put unvisited vertices on a queue. Shortest path. Find path from s to t that uses fewest number of edges. BFS (from source vertex s) Put s onto a FIFO queue. Repeat until the queue is empty: remove the least recently added vertex v add each of v's unvisited neighbors to the queue, and mark them as visited. Property. BFS examines vertices in increasing distance from s. 29 of 38
30 Connectivity Queries Def. Vertices v and w are connected if there is a path between them. Property. Symmetric and transitive. Goal. Preprocess graph to answer queries: is v connected to w? Connected component. Maximal set of mutually connected vertices. Brute force. Run DFS from each vertex v: quadratic time and space. 30 of 38
31 Connected components Initialize all vertices v as unmarked. For each unmarked vertex v, run DFS and identify all vertices discovered as part of the same connected component. 31 of 38
32 63 connected components 32 of 38
33 A cut vertex (articulation point) is a vertex of a graph such that removal of the vertex causes an increase in the number of connected components. If the graph was connected before the removal of the vertex, it will be disconnected afterwards. A bridge is an edge analogous to a cut vertex; that is, the removal of a bridge increases the number of connected components of the graph. In a tree, every vertex with degree greater than 1 is a cut vertex. A biconnected graph is a connected graph with no articulation vertices. In other words, a biconnected graph is nonseparable, meaning if any edge were to be removed, the graph will remain connected. This property is especially useful in maintaining a graph with a two-fold redundancy, to prevent disconnection upon the removal of a single edge (or connection). 33 of 38
34 The use of biconnected graphs is very important in the field of networking, because of this property of redundancy. Example: The articulation points of this graph are A (because it connects B to the rest of the graph), H (because it connects I to the rest of the graph), J (because it connects K to the rest of the graph), and G (because the graph would fall into three pieces if G were deleted). There are six biconnected components: ACGDEF, GJLM, and the individual nodes B, H, I, and K. 34 of 38
35 Determining the articulation points turns out to be a simple extension of depth-first search. To see this, consider the depth-first search tree for this graph: Deleting node E will not disconnect the graph because G and D both have dotted links that point above E, giving alternate paths from them to F (E s father in the tree). On the other hand, deleting G will disconnect the graph because there are no such alternate paths from L or H to E (L s father). A vertex x is not an articulation point if every son y has some node lower in the tree connected (via a dotted link) to a node higher in the tree than x, thus providing an alternate connection from x to y. 35 of 38
36 This test doesn t quite work for the root of the depth-first search tree, since there are no nodes higher in the tree. The root is an articulation point if it has two or more sons, since the only path connecting sons of the root goes through the root. These tests are easily incorporated into depth-first search by changing the node-visit procedure into a function which returns the highest point in the tree (lowest p value) seen during the search: 36 of 38
37 Graph* G; int* p; int c; int mdfs(int v) { int min=c; p[v]=c; c++; for(int* pw = G->adj(v); pw!= G->nadj(v); pw++) if(p[*pw]==-1) {int m=mdfs(*pw); if(m<min)min=m; if(m>=p[v]) cout << v << endl;} else if(p[*pw]<min) min=p[*pw]; return min; } int main() { G = new Graph(); int size=g->v(); p=new int[size]; memset(p,-1,size*sizeof(int)); p[0]=0;c=0;mdfs(0); } 37 of 38
38 This function recursively determines the highest point in the tree reachable (via a dotted link) from any descendant of vertex v and uses this information to determine if v is an articulation point (and prints it). Normally this calculation simply involves testing whether the minimum value reachable from a son is higher up in the tree, but we need an extra test to determine whether v is the root of a depth-first search tree (or, equivalently, whether this is the first call to visit for the connected component containing v. This test is properly performed outside the recursive function, so it does not appear in the code above. Since it is a depth-first search function, the running time is proportional to V + E. 38 of 38
! Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. ! Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. ! Hundreds of graph algorithms known.
 Undirected Graphs Undirected Graphs Graph. Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms?! Interesting and broadly useful abstraction.! Challenging branch of computer science and
Undirected Graphs Undirected Graphs Graph. Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms?! Interesting and broadly useful abstraction.! Challenging branch of computer science and
Undirected Graphs. introduction Graph API maze exploration depth-first search breadth-first search connected components challenges.
 Undirected Graphs Graph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by edges. Undirected Graphs Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and
Undirected Graphs Graph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by edges. Undirected Graphs Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and
Undirected Graphs. graph API maze exploration depth-first search breadth-first search connected components challenges.
 Undirected graphs Graph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by edges. Undirected Graphs References: Algorithms in Java, Chapters and Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction.
Undirected graphs Graph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by edges. Undirected Graphs References: Algorithms in Java, Chapters and Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction.
UNDIRECTED GRAPHS BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES DEPT. OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton Uniersity. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Undirected Graphs
Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton Uniersity. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Undirected Graphs
UNDIRECTED GRAPHS BBM ALGORITHMS DEPT. OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 BBM - ALGORIHMS DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton Uniersity. Undirected Graphs
BBM - ALGORIHMS DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton Uniersity. Undirected Graphs
Algorithms: Lecture 10. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
CSE202 Greedy algorithms. Fan Chung Graham
 CSE202 Greedy algorithms Fan Chung Graham Announcement Reminder: Homework #1 has been posted, due April 15. This lecture includes material in Chapter 5 of Algorithms, Dasgupta, Papadimitriou and Vazirani,
CSE202 Greedy algorithms Fan Chung Graham Announcement Reminder: Homework #1 has been posted, due April 15. This lecture includes material in Chapter 5 of Algorithms, Dasgupta, Papadimitriou and Vazirani,
UNDIRECTED GRAPHS TODAY BBM ALGORITHMS DEPT. OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING. Undirected graphs. Graph applications
 BBM - ALGORIHMS ODAY DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Undirected Graphs Graph API Depth-first search Challenges Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick
BBM - ALGORIHMS ODAY DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING UNDIRECED GRAPHS Undirected Graphs Graph API Depth-first search Challenges Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Konigsberg Bridge Problem
 Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
Undirected Graphs. Hwansoo Han
 Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Union-Find Algorithms
 Union-Find Algorithms Network connectivity Basic abstractions set of objects union command: connect two objects find query: is there a path connecting one object to another? network connectivity quick
Union-Find Algorithms Network connectivity Basic abstractions set of objects union command: connect two objects find query: is there a path connecting one object to another? network connectivity quick
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Algorithms. Algorithms 1.5 UNION-FIND. dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE
 Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1.5 UNION-FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1.5 UNION-FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
Union-Find Algorithms. network connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications
 Union-Find Algorithms network connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications 1 Subtext of today s lecture (and this course) Steps to developing a usable algorithm. Define the problem. Find
Union-Find Algorithms network connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications 1 Subtext of today s lecture (and this course) Steps to developing a usable algorithm. Define the problem. Find
Algorithms 1.5 UNION FIND. dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications
 1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications R O B E R T S E D G E W I C K K E V I N W A Y N E Algorithms, 4 th Edition Robert
1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications R O B E R T S E D G E W I C K K E V I N W A Y N E Algorithms, 4 th Edition Robert
Algorithms 1.5 UNION FIND. dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications
 1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications R O B E R T S E D G E W I C K K E V I N W A Y N E Algorithms, 4 th Edition Robert
1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N dynamic connectivity quick find quick union improvements applications R O B E R T S E D G E W I C K K E V I N W A Y N E Algorithms, 4 th Edition Robert
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
Graphs. The ultimate data structure. graphs 1
 Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II DIRECTED GRAPHS Graphs slides are modified from COS 126 slides of Dr. Robert Sedgewick. 1 Directed graphs Digraph Set of vertices connected pairwise by directed
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II DIRECTED GRAPHS Graphs slides are modified from COS 126 slides of Dr. Robert Sedgewick. 1 Directed graphs Digraph Set of vertices connected pairwise by directed
Undirected Graphs. DSA - lecture 6 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1
 Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Index. stack-based, 400 A* algorithm, 325
 Index Abstract transitive closure, 174-175, 217-221 Active vertex, 411 Acyclic graph. See Digraph; Directed acyclic graph (DAG) Acyclic network, 313-321, 334-335 maxflow, 427-429 Adjacency-lists representation,
Index Abstract transitive closure, 174-175, 217-221 Active vertex, 411 Acyclic graph. See Digraph; Directed acyclic graph (DAG) Acyclic network, 313-321, 334-335 maxflow, 427-429 Adjacency-lists representation,
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms
 Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
國立清華大學電機工程學系. Outline
 國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions.
 UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
Searching in Graphs (cut points)
 0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
DIRECTED GRAPHS BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES DEPT. OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton University. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING DIRECED GRAPHS Directed Graphs Digraph
Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton University. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING DIRECED GRAPHS Directed Graphs Digraph
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS. UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture Slides No Lecture Slides No
 GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
Graphs. The ultimate data structure. graphs 1
 Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Instructor: Professor Aaron Sidford (sidford@stanford.edu) January 11, 2018 Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1 In this lecture
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Instructor: Professor Aaron Sidford (sidford@stanford.edu) January 11, 2018 Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1 In this lecture
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs. CMSC 420: Lecture 3
 Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory
 CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms
 COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Chapter 3. Graphs. Undirected Graphs. Some Graph Applications
 Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Basic Graph Search. Algorithms and Data Structures, Fall Rasmus Pagh. Based on slides by Kevin Wayne, Princeton
 Algorithms and Data Structures, Fall Basic Graph Search Rasmus Pagh Based on slides by Kevin Wayne, Princeton Algorithms, th Edition Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright Mid-term evaluation Thanks
Algorithms and Data Structures, Fall Basic Graph Search Rasmus Pagh Based on slides by Kevin Wayne, Princeton Algorithms, th Edition Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright Mid-term evaluation Thanks
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Chapter 3. Graphs CLRS Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Graphs CLRS 12-13 Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V
Chapter 3 Graphs CLRS 12-13 Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V
Graphs and Algorithms
 Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graphs. The ultimate data structure. graphs 1
 Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
UNIT 5 GRAPH. Application of Graph Structure in real world:- Graph Terminologies:
 UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Graph and Digraph Glossary
 1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker
 Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Graphs A graph is a set of vertices that are pairwise connected by edges. We distinguish between directed and undirected graphs. Why are we interested in graphs? Graphs
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Graphs A graph is a set of vertices that are pairwise connected by edges. We distinguish between directed and undirected graphs. Why are we interested in graphs? Graphs
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Directed Graphs. digraph API digraph search transitive closure topological sort strong components. Directed graphs
 Directed graphs Digraph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by oriented edges. Directed Graphs digraph API digraph search transitive closure topological sort strong components References: Algorithms in
Directed graphs Digraph. Set of vertices connected pairwise by oriented edges. Directed Graphs digraph API digraph search transitive closure topological sort strong components References: Algorithms in
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
10/31/18. About A6, Prelim 2. Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Facts about trees. Undirected trees
 //8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
//8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this
![Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this](/thumbs/80/81612702.jpg) Lecture Notes Array Review An array in C++ is a contiguous block of memory. Since a char is 1 byte, then an array of 5 chars is 5 bytes. For example, if you execute the following C++ code you will allocate
Lecture Notes Array Review An array in C++ is a contiguous block of memory. Since a char is 1 byte, then an array of 5 chars is 5 bytes. For example, if you execute the following C++ code you will allocate
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 19. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 19 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 19 1 Search Algorithms Search algorithms are fundamental techniques applied to solve a wide range of optimization problems.
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 19 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 19 1 Search Algorithms Search algorithms are fundamental techniques applied to solve a wide range of optimization problems.
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))
![8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F)) 8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))](/thumbs/89/97773603.jpg) DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Linear Time: O(n) CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis 2.4 A Survey of Common Running Times Merge. Combine two sorted lists A = a 1,a 2,,a n with B = b 1,b 2,,b n into sorted whole. Jeremiah Blocki Purdue
Linear Time: O(n) CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis 2.4 A Survey of Common Running Times Merge. Combine two sorted lists A = a 1,a 2,,a n with B = b 1,b 2,,b n into sorted whole. Jeremiah Blocki Purdue
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 NPTEL MOOC,JAN-FEB 0 Week, Module DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Depth first search (DFS) MADHAVAN MUKUND, CHENNAI MATHEMATICAL INSTITUTE http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan Depth first search Start from
NPTEL MOOC,JAN-FEB 0 Week, Module DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Depth first search (DFS) MADHAVAN MUKUND, CHENNAI MATHEMATICAL INSTITUTE http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan Depth first search Start from
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
Outlines: Graphs Part-2
 Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
Algorithms. Algorithms 1.5 UNION FIND. union find data type quick-find quick-union improvements applications ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE
 Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE union find data type quick-find quick-union improvements applications http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1.5 UNION FIND Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE union find data type quick-find quick-union improvements applications http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
(Refer Slide Time: 06:01)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
COS 226 Lecture 19: Minimal Spanning Trees (MSTs) PFS BFS and DFS examples. Classic algorithms for solving a natural problem
 COS Lecture 9: Minimal Spanning Trees (MSTs) PFS BFS and DFS examples Classic algorithms for solving a natural problem MINIMAL SPANNING TREE Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm Boruvka s algorithm Long
COS Lecture 9: Minimal Spanning Trees (MSTs) PFS BFS and DFS examples Classic algorithms for solving a natural problem MINIMAL SPANNING TREE Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm Boruvka s algorithm Long
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers
 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers Lecture 7. István Szapudi Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii February 21, 2018 Outline 1 Reminder 2 Reminder We have seen that
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers Lecture 7. István Szapudi Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii February 21, 2018 Outline 1 Reminder 2 Reminder We have seen that
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko. Graphs
 CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Goals. Chapter 3. Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
E.G.S. PILLAY ENGINEERING COLLEGE (An Autonomous Institution, Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Nagore Post, Nagapattinam , Tamilnadu.
 17CA 104DATA STRUCTURES Academic Year : 018-019 Programme : MCA Year / Semester : I / I Question Bank Course Coordinator: Mrs. C.Mallika Course Objectives The student should be able to 1. To understand
17CA 104DATA STRUCTURES Academic Year : 018-019 Programme : MCA Year / Semester : I / I Question Bank Course Coordinator: Mrs. C.Mallika Course Objectives The student should be able to 1. To understand
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
CS521 \ Notes for the Final Exam
 CS521 \ Notes for final exam 1 Ariel Stolerman Asymptotic Notations: CS521 \ Notes for the Final Exam Notation Definition Limit Big-O ( ) Small-o ( ) Big- ( ) Small- ( ) Big- ( ) Notes: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
CS521 \ Notes for final exam 1 Ariel Stolerman Asymptotic Notations: CS521 \ Notes for the Final Exam Notation Definition Limit Big-O ( ) Small-o ( ) Big- ( ) Small- ( ) Big- ( ) Notes: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
Figure 1: A directed graph.
 1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
Graph Search. Adnan Aziz
 Graph Search Adnan Aziz Based on CLRS, Ch 22. Recall encountered graphs several weeks ago (CLRS B.4) restricted our attention to definitions, terminology, properties Now we ll see how to perform basic
Graph Search Adnan Aziz Based on CLRS, Ch 22. Recall encountered graphs several weeks ago (CLRS B.4) restricted our attention to definitions, terminology, properties Now we ll see how to perform basic
Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs
 Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017
 Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017 Instructor: Professor Edward Reingold TA: Jiahui Hou, Haohua Du Solutions 1. 10 pts) Algorithm 1 Basic Euler Circuit Algorithm. procedure Euler(G
Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017 Instructor: Professor Edward Reingold TA: Jiahui Hou, Haohua Du Solutions 1. 10 pts) Algorithm 1 Basic Euler Circuit Algorithm. procedure Euler(G
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms
 COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
Mystery Algorithm! ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v )
 Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
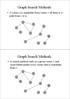 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
CS 161 Lecture 11 BFS, Dijkstra s algorithm Jessica Su (some parts copied from CLRS) 1 Review
 1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
