C3 Integration 1. June 2010 qu. 4
|
|
|
- Teresa Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
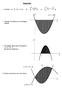
1 C Integration. June qu. 4 k The diagram shows part of the curve y =, where k is a positive constant. The points A and B on the curve have -coordinates and 6 respectively. Lines through A and B parallel to the aes as shown meet at the point C. The region R is bounded by the curve and the lines =, = 6 and y =. The region S is bounded by the curve and the lines AC and BC. It is given that the area of the region R is ln 8. Show that k = 4. [] Find the eact volume of the solid produced when the region S is rotated completely about the -ais. [4]. June qu.7 The diagram shows the curve with equation y = ( ) 4. The point P on the curve has coordinates (, 6) and the tangent to the curve at P meets the -ais at the point Q. The shaded region is bounded by PQ, the -ais and that part of the curve for which. Find the eact area of this shaded region. []. Jan qu. Find ( 7) d. []
2 4. Jan qu. Find, in simplified form, the eact value of 6 d. [] Use Simpson s rule with two strips to find an approimation to 6 d. [] (iii) 5 Use your answers to parts and to show that ln. 6 [] 5. Jan qu.6 Given that ( ke + ( k )e ) d = 85, find the value of the constant k. [7] 6. June 9 qu. ln 4 The diagram shows the curve with equation y = ( ). The shaded region is bounded by the curve and the lines = and y =. Find the eact volume obtained when the shaded region is rotated completely about the -ais. [5] 7. June 9 qu. 4 It is given that a a (e + e )d =, where a is a positive constant. Show that a = ln( + e a e a ). 9 [5] Use an iterative process, based on the equation in part, to find the value of a correct to 4 decimal places. Use a starting value of.6 and show the result of each step of the process. 8. Jan 9 qu. Find 8e d, (4 + 5) 6 d. [5] 9. Jan 9 qu.8 The diagram shows the curve with equation y = 6. The point P has coordinates (, p). The shaded region is bounded by the curve and the lines =, y = and y = p. The shaded region is rotated completely about the y-ais to form a solid of volume V. 7 Show that V = 6π. [6] ( p + ) It is given that P is moving along the y-ais in such a way that, at time t, the variables p and t d p dv are related by = p +. Find the value of at the instant when p = 9. [4] dt dt
3 . June 8 qu. 6 The diagram shows the curves y = e and y = ( ) 4. The shaded region is bounded by the two curves and the line =. The shaded region is rotated completely about the -ais. Find the eact volume of the solid produced. [9]. Jan 8 qu.5 9 Find ( + 7) d. [] (b). June 7 qu. 4 The diagram shows the curve y =. The shaded region is bounded by the curve and the lines =, = 6 and y =. The shaded region is rotated completely about the -ais. Find the eact volume of the solid produced, simplifying your answer. [5] ( The integral I is defined by I = + ) d. Use integration to find the eact value of I. [4] Use Simpson s rule with two strips to find an approimate value for I. Give your answer correct to significant figures. []. June 7 qu. 6 a Given that ( 6e + )d = 4, show that a = ln(5 a ). 6 [5] Use an iterative formula, based on the equation in part, to find the value of a correct to decimal places. Use a starting value of and show the result of each iteration. [4]
4 4. June 7 qu. 8 4ln dy 4 Given that y =, show that =. 4ln + d (4ln + ) [] 4ln Find the eact value of the gradient of the curve y = 4ln + at the point where it crosses the -ais. [4] (iii) y 5. Jan 7 qu.6 O e The diagram shows part of the curve with equation y =. (4ln + ) The region shaded in the diagram is bounded by the curve and the lines =, = e and y =. Find the eact volume of the solid produced when this shaded region is rotated completely about the -ais. [4] The diagram shows the curve with equation y =. The shaded region is bounded by the + curve and the lines =, = and y =. Find the eact area of the shaded region. [4] The shaded region is rotated completely about the -ais. Find the eact volume of the solid formed, simplifying your answer. [5] 6. June 6 qu. 7 Find the eact value of (4 ) d. [4] (b) The diagram shows part of the curve y =. The point P has coordinates a, and the point Q has a coordinates a,, where a is a positive constant. The point R is such that PR is parallel to the -ais a and QR is parallel to the y-ais. The region shaded in the diagram is bounded by the curve and by the lines PR and QR. Show that the area of this shaded region is ln( e ). [6]
5 7. June 6 qu. 9 y y = ln( ) P O The diagram shows the curve with equation y = ln( ). The point P has coordinates (, p). The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and the lines =, y = and y = p. The units on the aes are centimetres. The region R is rotated completely about the y-ais to form a solid. Show that the volume, V cm, of the solid is given byv = π(e P + 4e + p 5). [8] It is given that the point P is moving in the positive direction along the y-ais at a constant rate of. cm min. Find the rate at which the volume of the solid is increasing at the instant when p = 4, giving your answer correct to significant figures. [5] 8. Jan 6 qu. Show that 8 d = ln 64. ` [4] 9. Jan 6 qu.5 P The diagram shows the curves y = ( ) 5 and y = e. The curves meet at the point (, ). Find the eact area of the region (shaded in the diagram) bounded by the y-ais and by part of each curve. [8]. June 5 qu. 4 The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines =, = 5 and y =. The region R is rotated completely about the -ais. Find the eact volume of the solid formed. [4] 5 (b) Use Simpson s rule, with 4 strips, to find an approimate value for ( + ) d, giving your answer correct to decimal places. [4]
(ii) Use Simpson s rule with two strips to find an approximation to Use your answers to parts (i) and (ii) to show that ln 2.
 C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
C3 Numerical methods
 Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
(ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1]
![(ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1] (ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1]](/thumbs/82/84800654.jpg) C Integration. June 00 qu. Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 7 +, the -ais, and the lines = and = 0. Give your answer correct
C Integration. June 00 qu. Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 7 +, the -ais, and the lines = and = 0. Give your answer correct
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1
 PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
(i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line
![(i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line (i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line](/thumbs/90/103919535.jpg) H Math : Integration Apps 0. M p The diagram shows the curve e e and its maimum point M. The -coordinate of M is denoted b p. (i) Find the eact value of p. [] (ii) Show that the area of the shaded region
H Math : Integration Apps 0. M p The diagram shows the curve e e and its maimum point M. The -coordinate of M is denoted b p. (i) Find the eact value of p. [] (ii) Show that the area of the shaded region
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE
 IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet A (1, 1)
 C Worksheet A y You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet y = B A (, ) O The diagram shows the curve y = which passes through the point A (, ) and the point B. a Copy and complete the table
C Worksheet A y You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet y = B A (, ) O The diagram shows the curve y = which passes through the point A (, ) and the point B. a Copy and complete the table
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Edexcel Core Mathematics 4 Integration
 Edecel Core Mathematics 4 Integration Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Edecel Core Mathematics 4 Integration Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
SPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 3 Integration
 SPM Add Math Form Chapter Integration INDEFINITE INTEGRAL CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Integration as the reverse process of differentiation ) y if dy = x. Given that d Integral of ax n x + c = x, where c is
SPM Add Math Form Chapter Integration INDEFINITE INTEGRAL CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Integration as the reverse process of differentiation ) y if dy = x. Given that d Integral of ax n x + c = x, where c is
Pegasys Publishing. CfE Higher Mathematics. Expressions and Functions Practice Assessment A
 Pegasys Publishing CfE Higher Mathematics Epressions and Functions Practice ssessment otes:. Read the question fully before answering it.. lways show your working.. Check your paper at the end if you have
Pegasys Publishing CfE Higher Mathematics Epressions and Functions Practice ssessment otes:. Read the question fully before answering it.. lways show your working.. Check your paper at the end if you have
Integration. Edexcel GCE. Core Mathematics C4
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
x=2 26. y 3x Use calculus to find the area of the triangle with the given vertices. y sin x cos 2x dx 31. y sx 2 x dx
 4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
y 4 y 1 y Click here for answers. Click here for solutions. VOLUMES
 SECTION 7. VOLUMES 7. VOLUMES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 5 Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given curves about the specified line.
SECTION 7. VOLUMES 7. VOLUMES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 5 Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given curves about the specified line.
with x 1 ¼ 1 to find the values of x 2 and x 3, giving your answers to three decimal places
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 Friday 11 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 Friday 11 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Volume of Revolution Paper 2
 Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Answer: Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the shaded region about the given axis. 2) About the x-axis. y = 9 - x π.
 Final Review Study All Eams. Omit the following sections: 6.,.6,., 8. For Ch9 and, study Eam4 and Eam 4 review sheets. Find the volume of the described solid. ) The base of the solid is the disk + y 4.
Final Review Study All Eams. Omit the following sections: 6.,.6,., 8. For Ch9 and, study Eam4 and Eam 4 review sheets. Find the volume of the described solid. ) The base of the solid is the disk + y 4.
Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find
 Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
( ) 2. Integration. 1. Calculate (a) x2 (x 5) dx (b) y = x 2 6x. 2. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite.
 Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form 5 Chapter 3 - Integration
 SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form Chapter - Integration SPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM CHAPTER : INTEGRATION SPM 99 a) Find i) (4 - )(4 ) d, ii) 8 ( - ) d b) Given f ( ) d 8, find
SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form Chapter - Integration SPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM CHAPTER : INTEGRATION SPM 99 a) Find i) (4 - )(4 ) d, ii) 8 ( - ) d b) Given f ( ) d 8, find
11 cm. A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm.
 Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Area and Volume. where x right and x left are written in terms of y.
 Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Euler s Method and Logistic Growth (BC Only)
 Euler s Method Students should be able to: Approximate numerical solutions of differential equations using Euler s method without a calculator. Recognize the method as an recursion formula extension of
Euler s Method Students should be able to: Approximate numerical solutions of differential equations using Euler s method without a calculator. Recognize the method as an recursion formula extension of
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
minutes/question 26 minutes
 st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
In this chapter, we will investigate what have become the standard applications of the integral:
 Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
Trig Practice 09 & Nov The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = 1 + k sin x, defined for 0 x 3π.
 IB Math High Level Year : Trig: Practice 09 & 0N Trig Practice 09 & Nov 0. The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = + k sin x, defined for 0 x. The point A, lies on the curve and B(a, b) is the
IB Math High Level Year : Trig: Practice 09 & 0N Trig Practice 09 & Nov 0. The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = + k sin x, defined for 0 x. The point A, lies on the curve and B(a, b) is the
The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y = 2, below by
 Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Find the volume of a solid with regular cross sections whose base is the region between two functions
 Area Volume Big Ideas Find the intersection point(s) of the graphs of two functions Find the area between the graph of a function and the x-axis Find the area between the graphs of two functions Find the
Area Volume Big Ideas Find the intersection point(s) of the graphs of two functions Find the area between the graph of a function and the x-axis Find the area between the graphs of two functions Find the
Mathematics (JUN11MPC201) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit Pure Core TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 Wednesday 18 May 2011 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 Wednesday 18 May 2011 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Condensed. Mathematics. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Unit Pure Core 3. Time allowed * 1 hour 30 minutes
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Eamination June 01 Mathematics MPC3 Unit Pure Core 3 Thursda 31 Ma 01 9.00 am to 10.30 am For this aer ou must have: the blue AQA booklet of formulae and
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Eamination June 01 Mathematics MPC3 Unit Pure Core 3 Thursda 31 Ma 01 9.00 am to 10.30 am For this aer ou must have: the blue AQA booklet of formulae and
Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors
 Physics 5B Winter 008 Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors 1 General considerations Consider a curved mirror surface that is constructed as follows Start with a curve, denoted by y()
Physics 5B Winter 008 Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors 1 General considerations Consider a curved mirror surface that is constructed as follows Start with a curve, denoted by y()
MATH 19520/51 Class 6
 MATH 19520/51 Class 6 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-06 1 Review partial derivatives. 2 Review equations of planes. 3 Review tangent lines in single-variable calculus. 4 Tangent planes to
MATH 19520/51 Class 6 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-06 1 Review partial derivatives. 2 Review equations of planes. 3 Review tangent lines in single-variable calculus. 4 Tangent planes to
Surname. Other Names. Centre Number. Candidate Number. Candidate Signature. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2014
 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 MPC3 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2014 Leave blank Tuesday 10 June
Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 MPC3 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2014 Leave blank Tuesday 10 June
Exam 3 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 3 Spring Section and/or TA:
 MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X
 Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Chapter 7 curve. 3. x=y-y 2, x=0, about the y axis. 6. y=x, y= x,about y=1
 Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
Wednesday 15 June 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level MATHEMATICS Unit Pure Core 3 Wednesday 15 June 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature A-level MATHEMATICS Unit Pure Core 3 Wednesday 15 June 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 C Differentiation: Tangents & Normals. y A C R P O Q The diagram above shows part of the curve C with equation y = 6 + 8. The curve meets the y-ais at the point A and has a minimum at the point P. (a)
C Differentiation: Tangents & Normals. y A C R P O Q The diagram above shows part of the curve C with equation y = 6 + 8. The curve meets the y-ais at the point A and has a minimum at the point P. (a)
Ch8: Straight Line Graph. x f(x) p 0.5 q 2 4 R 16. (a) Find the values of p, q and r. [3]
![Ch8: Straight Line Graph. x f(x) p 0.5 q 2 4 R 16. (a) Find the values of p, q and r. [3] Ch8: Straight Line Graph. x f(x) p 0.5 q 2 4 R 16. (a) Find the values of p, q and r. [3]](/thumbs/78/77995389.jpg) Ch8: Straight Line Graph. Answer the whole of this question on a sheet of graph paper. The table gives values of f() =, for 4. 0 3 4 f() p 0.5 q 4 R 6 (a) Find the values of p, q and r. [3] Using a scale
Ch8: Straight Line Graph. Answer the whole of this question on a sheet of graph paper. The table gives values of f() =, for 4. 0 3 4 f() p 0.5 q 4 R 6 (a) Find the values of p, q and r. [3] Using a scale
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level CANDIDATE NAME *8968664976* CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER MATHEMATICS 9709/21 Paper 2 Pure Mathematics 2 (P2) May/June
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level CANDIDATE NAME *8968664976* CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER MATHEMATICS 9709/21 Paper 2 Pure Mathematics 2 (P2) May/June
Math 126 Winter CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems.
 Math 126 Winter 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems. This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 1 11 sheet of hand-written
Math 126 Winter 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems. This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 1 11 sheet of hand-written
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com January 2007 2. Figure 1 A a θ α A uniform solid right circular cone has base radius a and semi-vertical angle α, where 1 tanα = 3. The cone is freely suspended by a string attached
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com January 2007 2. Figure 1 A a θ α A uniform solid right circular cone has base radius a and semi-vertical angle α, where 1 tanα = 3. The cone is freely suspended by a string attached
Alternate Angles. Clip 67. Mathswatch
 Clip 67 Alternate Angles ) Line PQ is parallel to line RS If angle PQR is equal to 6 a) What is the size of angle QRS? b) Give a reason for ou answer. P 6 Q R S ) Line DCE is parallel to line AB a) Find
Clip 67 Alternate Angles ) Line PQ is parallel to line RS If angle PQR is equal to 6 a) What is the size of angle QRS? b) Give a reason for ou answer. P 6 Q R S ) Line DCE is parallel to line AB a) Find
ADVANCED GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) 4754A
 ADVANCED GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper A 4754A Candidates answer on the Answer Booklet OCR Supplied Materials: 8 page Answer Booklet Graph paper MEI Examination
ADVANCED GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper A 4754A Candidates answer on the Answer Booklet OCR Supplied Materials: 8 page Answer Booklet Graph paper MEI Examination
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral
 1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES. 4. Function of several variables, their domain. 6. Limit of a function of several variables
 302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
Review for Applications of Definite Integrals Sections
 Review for Applications of Definite Integrals Sections 6.1 6.4 Math 166 Iowa State University http://orion.math.iastate.edu/dstolee/teaching/15-166/ September 4, 2015 1. What type of problem: Volume? Arc
Review for Applications of Definite Integrals Sections 6.1 6.4 Math 166 Iowa State University http://orion.math.iastate.edu/dstolee/teaching/15-166/ September 4, 2015 1. What type of problem: Volume? Arc
Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1)
 5/19/01 Final Eam Review Ch 10,11-Virginia Davis Student: Date: Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1) Assignment: Final Eam Review Ch 10,11 1. Simplif b factoring. Assume
5/19/01 Final Eam Review Ch 10,11-Virginia Davis Student: Date: Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1) Assignment: Final Eam Review Ch 10,11 1. Simplif b factoring. Assume
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator
Segments Proofs Reference
 Segments Proofs Reference Properties of Equality Addition Property Subtraction Property Multiplication Property Division Property Distributive Property Reflexive Property The properties above may only
Segments Proofs Reference Properties of Equality Addition Property Subtraction Property Multiplication Property Division Property Distributive Property Reflexive Property The properties above may only
Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes
 1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
Shape 3 Assessment Calculator allowed for all questions
 Shape Assessment Calculator allowed for all questions Foundation Higher All questions Time for the test: 50 minutes Name: MATHSWATCH ANSWERS Grade Title of clip Marks Score Percentage Clip 7 D Area of
Shape Assessment Calculator allowed for all questions Foundation Higher All questions Time for the test: 50 minutes Name: MATHSWATCH ANSWERS Grade Title of clip Marks Score Percentage Clip 7 D Area of
4754 Mark Scheme June 2006 Mark Scheme 4754 June 2006
 Mark Scheme 75 June 6 1 sin x cos x R sin(x α) R(sin x cos α cos x sin α) R cos α 1, R sin α R 1 + ( ), R tan α /1 α π/ sin x cos x sin(x π/) x coordinate of P is when x π/ π/ x 5π/6 y So coordinates are
Mark Scheme 75 June 6 1 sin x cos x R sin(x α) R(sin x cos α cos x sin α) R cos α 1, R sin α R 1 + ( ), R tan α /1 α π/ sin x cos x sin(x π/) x coordinate of P is when x π/ π/ x 5π/6 y So coordinates are
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
7.8. Approximate Integration
 7.8. Approimate Integration Recall that when we originally defined the definite integral of a function interval, that we did so with the limit of a Riemann sum: on an where is the number of intervals that
7.8. Approimate Integration Recall that when we originally defined the definite integral of a function interval, that we did so with the limit of a Riemann sum: on an where is the number of intervals that
Name Find the area the shaded region.
 Berkele Cit College Due: HW - Chapter 6 - Applications of Integration Name Find the area of the shaded region. 1) = - + + 16 0 = 4 0 1 10 1) - -4 - - -1-1 4-10 -1-0 - -0 ) 6 = - 1 ) 4 = - 4 + 1 - -1 1
Berkele Cit College Due: HW - Chapter 6 - Applications of Integration Name Find the area of the shaded region. 1) = - + + 16 0 = 4 0 1 10 1) - -4 - - -1-1 4-10 -1-0 - -0 ) 6 = - 1 ) 4 = - 4 + 1 - -1 1
AP Calculus. Areas and Volumes. Student Handout
 AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
Revision Pack. Edexcel GCSE Maths (1 9) Non-calculator Questions Shapes
 Edexcel GCSE Maths (1 9) Revision Pack Non-calculator Questions Shapes Edited by: K V Kumaran kvkumaran@gmail.com 07961319548 www.kumarmaths.weebly.com kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Q1. All the measurements
Edexcel GCSE Maths (1 9) Revision Pack Non-calculator Questions Shapes Edited by: K V Kumaran kvkumaran@gmail.com 07961319548 www.kumarmaths.weebly.com kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Q1. All the measurements
Plane Curve [Parametric Equation]
![Plane Curve [Parametric Equation] Plane Curve [Parametric Equation]](/thumbs/89/98510023.jpg) Plane Curve [Parametric Equation] Bander Almutairi King Saud University December 1, 2015 Bander Almutairi (King Saud University) Plane Curve [Parametric Equation] December 1, 2015 1 / 8 1 Parametric Equation
Plane Curve [Parametric Equation] Bander Almutairi King Saud University December 1, 2015 Bander Almutairi (King Saud University) Plane Curve [Parametric Equation] December 1, 2015 1 / 8 1 Parametric Equation
AB Student Notes: Area and Volume
 AB Student Notes: Area and Volume An area and volume problem has appeared on every one of the free response sections of the AP Calculus exam AB since year 1. They are straightforward and only occasionally
AB Student Notes: Area and Volume An area and volume problem has appeared on every one of the free response sections of the AP Calculus exam AB since year 1. They are straightforward and only occasionally
(c) 0 (d) (a) 27 (b) (e) x 2 3x2
 1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
The directional derivative of f x, y in the direction of at x, y u. f x sa y sb f x y (, ) (, ) 0 0 y 0 0
 Review: 0, lim D f u 0 0 0 0 u The directional derivative of f, in the direction of at, is denoted b D f, : u a, b must a unit vector u f sa sb f s 0 (, ) (, ) s f (, ) a f (, ) b 0 0 0 0 0 0 D f, f u
Review: 0, lim D f u 0 0 0 0 u The directional derivative of f, in the direction of at, is denoted b D f, : u a, b must a unit vector u f sa sb f s 0 (, ) (, ) s f (, ) a f (, ) b 0 0 0 0 0 0 D f, f u
Published. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers.
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 404/ Paper May/June 06 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 00 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 404/ Paper May/June 06 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 00 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
8/6/2010 Assignment Previewer
 8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
College Algebra Review for Test 4
 College Algebra Review for Test Evaluate the epression b hand. ) a) /2 b) 27/3 c) 32/ d) 8-/3 Use positive rational eponents to rewrite the epression. 2) 2 Use radical notation to rewrite. 3) a-/2b/7 Solve
College Algebra Review for Test Evaluate the epression b hand. ) a) /2 b) 27/3 c) 32/ d) 8-/3 Use positive rational eponents to rewrite the epression. 2) 2 Use radical notation to rewrite. 3) a-/2b/7 Solve
MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution
 MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution Dr Craig 02 October 2018 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Monday 14h40 15h25 Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h20 12h55 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution Dr Craig 02 October 2018 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Monday 14h40 15h25 Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h20 12h55 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2816863460* MATHEMATICS 0580/41 Paper 4 (Extended) May/June 2018 Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2816863460* MATHEMATICS 0580/41 Paper 4 (Extended) May/June 2018 Candidates answer on the Question
4.1 Angles and Angle Measure. 1, multiply by
 4.1 Angles and Angle Measure Angles can be measured in degrees or radians. Angle measures without units are considered to be in radians. Radian: One radian is the measure of the central angle subtended
4.1 Angles and Angle Measure Angles can be measured in degrees or radians. Angle measures without units are considered to be in radians. Radian: One radian is the measure of the central angle subtended
5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations
 5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations The highest tides in the world are found in the Ba of Fund. Tides in one area of the ba cause the water level to rise to 6 m above average sea level
5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations The highest tides in the world are found in the Ba of Fund. Tides in one area of the ba cause the water level to rise to 6 m above average sea level
m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 1 m 4 m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ m 6 m 2 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true?
 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points.
 MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
Mathematics MPC2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit Pure Core 2
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Direction Fields; Euler s Method
 Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Answer Book (AB16) Graph Paper
Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Answer Book (AB16) Graph Paper
Quiz 6 Practice Problems
 Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
HSC Mathematics - Extension 1. Workshop E2
 HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
Math 20C. Lecture Examples.
 Math 20C. Lecture Eamples. (8/7/0) Section 4.4. Linear approimations and tangent planes A function z = f(,) of two variables is linear if its graph in z-space is a plane. Equations of planes were found
Math 20C. Lecture Eamples. (8/7/0) Section 4.4. Linear approimations and tangent planes A function z = f(,) of two variables is linear if its graph in z-space is a plane. Equations of planes were found
Name: Class: Date: 1. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint.
 . Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
University of Saskatchewan Department of Mathematics & Statistics MATH Final Instructors: (01) P. J. Browne (03) B. Friberg (05) H.
 University of Saskatchewan Department of Mathematics & Statistics MATH. Final Instructors: (0) P. J. Browne (0) B. Friberg (0) H. Teismann December 9, 000 Time: :00-:00 pm This is an open book exam. Students
University of Saskatchewan Department of Mathematics & Statistics MATH. Final Instructors: (0) P. J. Browne (0) B. Friberg (0) H. Teismann December 9, 000 Time: :00-:00 pm This is an open book exam. Students
"Full Coverage": Volumes & Surface Area
 "Full Coverage": Volumes & Surface Area This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by
"Full Coverage": Volumes & Surface Area This worksheet is designed to cover one question of each type seen in past papers, for each GCSE Higher Tier topic. This worksheet was automatically generated by
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Name: Teacher: Form: LEARNER JOURNAL. Set: Mathematics. Module 7 END OF YEAR TARGET: GCSE TARGET:
 Name: Teacher: Form: Set: LEARNER JOURNAL Mathematics Module 7 END OF YEAR TARGET: GCSE TARGET: MODULE 7 Unit 7A - Graphs Use areas of rectangles, triangles and trapeziums to estimate the area under a
Name: Teacher: Form: Set: LEARNER JOURNAL Mathematics Module 7 END OF YEAR TARGET: GCSE TARGET: MODULE 7 Unit 7A - Graphs Use areas of rectangles, triangles and trapeziums to estimate the area under a
Shape, space and measures
 Shape, space and measures Non-Calculator Exam Questions 1. Here is the plan and side elevation of a prism. The side elevation shows the cross section of the prism. On the grid below, draw the front elevation
Shape, space and measures Non-Calculator Exam Questions 1. Here is the plan and side elevation of a prism. The side elevation shows the cross section of the prism. On the grid below, draw the front elevation
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 1300, Calculus 1
 Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect the
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect the
AP Calculus BC. Find a formula for the area. B. The cross sections are squares with bases in the xy -plane.
 AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
Similar shapes.
 Similar shapes www.q8maths.com 4. R C 45 cm 26 cm A 8 cm B P 12 cm Q The two triangles ABC and PQR are mathematically similar. Angle A = angle P. Angle B = angle Q. AB = 8 cm. AC = 26 cm. PQ = 12 cm. QR
Similar shapes www.q8maths.com 4. R C 45 cm 26 cm A 8 cm B P 12 cm Q The two triangles ABC and PQR are mathematically similar. Angle A = angle P. Angle B = angle Q. AB = 8 cm. AC = 26 cm. PQ = 12 cm. QR
4. The following diagram shows the triangle AOP, where OP = 2 cm, AP = 4 cm and AO = 3 cm.
 Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
MA 243 Calculus III Fall Assignment 1. Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals)
 MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA FINAL EXAM Green April 30, 2018 EXAM POLICIES
 MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods
 MD53a HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods student name....................... Monday, 3 May 6 number о number о 3 6 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 a 8 b 9 9 a b a 3 b 4
MD53a HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods student name....................... Monday, 3 May 6 number о number о 3 6 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 a 8 b 9 9 a b a 3 b 4
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
2. Solve for x when x < 22. Write your answer in interval notation. 3. Find the distance between the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 3).
 Math 6 Practice Problems for Final. Find all real solutions x such that 7 3 x = 5 x 3.. Solve for x when 0 4 3x
Math 6 Practice Problems for Final. Find all real solutions x such that 7 3 x = 5 x 3.. Solve for x when 0 4 3x
FURTHER MATHS. WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL
 FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
On Your Own. Applications. Unit 3. b. AC = 8 units y BD = 16 units C(5, 2)
 Applications 1 a. If students use uniform and y scales or ZSquare, they should have a shape that looks like a kite. Using the distance formula, DC = AD = 1 and BC = BA = 0. b. AC = 8 units y BD = 16 units
Applications 1 a. If students use uniform and y scales or ZSquare, they should have a shape that looks like a kite. Using the distance formula, DC = AD = 1 and BC = BA = 0. b. AC = 8 units y BD = 16 units
AP * Calculus Review. Area and Volume
 AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
CBSE Board Paper 2011 (Set-3) Class X
 L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) Ph: 981551, 1-4611 CBSE Board Paper 11 (Set-3) Class X General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four
L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) Ph: 981551, 1-4611 CBSE Board Paper 11 (Set-3) Class X General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four
