Evaluation of Hessian-based filters to enhance the axis of coronary arteries in CT images
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Congress Series 1256 (2003) Evaluation of Hessian-based filters to enhance the axis of coronary arteries in CT images S.D. Olabarriaga a, *, M. Breeuwer b, W.J. Niessen a a University Medical Center Utrecht, Image Sciences Institute, Heidelberglaan 100-E , 3584 CX Utrecht, The Netherlands b Philips Medical Systems, Medical IT-Advanced Development, Building QV 162, P.O. Box 10000, 5680 DA Best, The Netherlands Received 13 March 2003; received in revised form 13 March 2003; accepted 17 March 2003 Abstract This work describes an evaluation of three Hessian-based filters for enhancement of the central axis of coronary arteries in multi-detector CT images acquired with contrast injection. These filters analyze the main modes of 2nd-order variation in image intensity to determine the type of local structure present in the image (tubular-like). The average filter response obtained with different parameter configurations was measured at fixed distances from a reference central axis determined manually. Results were compared with two objective measures, namely the response decay rate at the center and the overall response within 5 mm. D 2003 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. Keywords: Coronary arteries; Vessel; Axis; Cardiac CT; Enhancement; Evaluation 1. Introduction Developments in multi-detector CT and reconstruction techniques allow for fast acquisition of high-resolution images, with large impact on cardiac imaging. Images acquired with contrast injection (CMDCT) contain much detail of the complex heart structure, with promising perspectives for assessment of coronary artery disease in a less invasive manner than conventional angiography. * Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: silvia@isi.uu.nl (S.D. Olabarriaga) /03 D 2003 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. doi: /s (03)
2 1192 S.D. Olabarriaga et al. / International Congress Series 1256 (2003) The analysis of such images requires digital post-processing to isolate the coronary arteries from the complex background. Several methods for vessel enhancement and segmentation are based on the knowledge that vessels are tubular structures that could be described by their central axes and width. Some methods for central vessel axis (CVA) segmentation (e.g., Refs. [1,2]) extract information from 2nd-order derivatives at multiple scales to identify the type of local structure present in the image (e.g., tubular-like) by inspecting the main modes of variation in the Hessian matrix. Hessian-based vessel enhancement filters (HBVF) have been proposed by Lorenz et al. [3], Sato et al. [4], and Frangi et al. [5]. These have been shown to be applicable to various imaging modalities (e.g., DSA [3,5], CTA[4], and 3D MRA [1,4,5]) and several types of vessels (cerebral [3,4], peripheral [5], hepatic [4], pulmonary [4], and cardiac [1]). In this work, we investigate and compare their capabilities to enhance the coronary artery axis in CMDCT images. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Filters In a multi-scale framework, a HBVF is defined as F(x) = max r f (x,r), where x is a position in the image, f is the filter, and r is the scale for calculating Gaussian image derivatives. In this study, the filter response is calculated for 10 exponentially distributed scales in the interval [0.5, 5] mm. The filters calculate 2nd-order derivatives, build the Hessian matrix H decompose it into eigenvalues k 1, k 2, and k 3, and analyze them to determine the likelihood of x belonging to a vessel. This analysis is based on the following hypotheses (for bright vessels, dark background, Ak 1 A < Ak 2 A < Ak 3 A): (a) k 1 c 0 corresponds to the eigenvector tangent to the CVA; (b) k 2 c k 3 < 0; and (c) Ak 1 AbAk 2 A. The filters differ in how they test the hypotheses and generate a quantity indicating vessel-likelihood. In all cases, f(x, r)=0 if k 2 >0 or k 3 >0. The filter defined by Lorenz et al. [3] was implemented as: LðxÞ ¼r g k 2 þ k 3 2:0 ; ð1þ where g normalizes responses across scales. The filter defined by Sato et al. in Ref. [4] was implemented as follows: 8 >< SðxÞ >: r 2 Ak 3 A k 2 k 3 r 2 Ak 3 A k 2 k 3 n 1 þ k s; 1 k3 < k 2 < k 1 < 0 Ak 2 A n 1 q k 1 Ak 2 A s; k3 < k 2 < 0 < k 1 < Ak 2A q ð2þ where n z 0 controls cross-section asymmetry, s z 0 controls the sensitivity to blob-like structures, 0 < q V 1.0 controls sensitivity to the vessel curvature, and r 2 normalizes responses across scales.
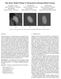
3 S.D. Olabarriaga et al. / International Congress Series 1256 (2003) The filter defined by Frangi et al. in Ref. [5] was implemented as follows: A2 B2 FðxÞ ¼ 1 e 2a 2 e 2b 2 S2 1 e 2c 2 ð3þ where A ¼ p Ak ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 2 A=Ak 3 A (controlled by a) discriminates plate- from line-like structures; B ¼ Ak 1 A= Ak 2 k 3 A (controlled by c) discriminates from blob-like structures and S ¼ qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi k 2 1 þk2 2 þk2 3 (controlled by c) eliminates background noise. Scale normalization is achieved by multiplying H by r 2 before eigenvalue decomposition Evaluation Fourteen coronary artery segments (CAS) in five CMDCT images acquired with fourdetector Philips CT scanners at different sites were used (spacing: in-planea[0.4,0.55] mm, slicea[0.6,1.3] mm). The images were resampled to obtain isotropic voxels. The CVA of 14 CAS, with lengthsa[30,100] mm, were traced manually by one operator using the Path Tracking Tool of the Philips EasyVision workstation. The axes were exported as curves p(t), where t is position on the path (in millimeters), and adopted as reference to generate a straightened vessel representation used for evaluation. At each t, the tangent pv(t) to the curve determines the normal vector to the crosssectional plane (see Fig. 1, left) spanned by the vectors! v and! u. Vectors are determined as follows for angular continuity between cross sections at t i and t i 1 (see Ref. [6]):! n ¼ pvðtþ NpVðtÞN ;! uðt i Þ¼! uðt i 1 Þ! nðt i Þð! uðt i 1 Þ! nðt i ÞÞ N! uðt i 1 Þ! nðt i Þð! uðt i 1 Þ! nðt i ÞÞN ;! v ¼! u! n: The straightened vessel representation consists of a pile of vessel cross-sections obtained with trilinear interpolation (spacing: path = 0.3 mm, in-plane = 0.2 mm). This representation is used to calculate the mean filter response at concentrical and equally spaced regions around the CVA (Fig. 1, center), and to generate curves such as illustrated in Fig. 1, right. Two objective measures are extracted from the normalized curves to compare the response of different HBVF configurations: the decrease rate of response near the CVA (R) and the area under the curve (A). The measure R corresponds to the curve Fig. 1. Left: Cross-sectional plane vectors. Center: Concentrical regions for response analysis. Right: Curve used for HBVF evaluation (normalized filter response vs. distance to the axis), and the objective measures (decrease rate and area under the curve).
4 1194 S.D. Olabarriaga et al. / International Congress Series 1256 (2003) Fig. 2. Lorenz filter: normalized responses (left) and objective measures (right). slope at 0.5 mm from the CVA. Small values of A and large values of R are preferred for CVA enhancement. 3. Results 3.1. Lorenz filter The value of g in Eq. (1) was varied in [0,4] at steps of c 0.25; see mean results obtained for 14 CAS in Fig. 2. In the majority of cases (10 CAS), the two criteria (area and rate) point to g = 0 as the optimal configuration. This in practice means that no scale normalization took place and the maximum filter response was obtained at small r ( mm). In other words, the structures actually detected by the filter are thinner than the actual coronary arteries, which should not be a problem for axis enhancement. Only in two cases, with large vessel width variation, better results were obtained with g = Sato filter The values of q, s, and n in Eq. (2) were independently varied in the range [0,1], with steps of 0.1. The values assumed by the fixed parameters were q = 0.1, s = 0.25, and n = Results are quite insensitive to q, with very small differences between the best Fig. 3. Sato filter: responses (left) and objective measures (right) for varying n.
5 S.D. Olabarriaga et al. / International Congress Series 1256 (2003) Fig. 4. Frangi filter: objective measures for varying a (left), b (center), and c (right). and worst cases, although q = 1 is pointed out as the optimal value for all images. For variation in s, the difference between results is insignificant ( V 0.01 for area and rate), and no preferred optimal value could be found. The influence of n seems to be predominant, indicating that optimal results are obtained when n = 1 in most cases (12 CAS) (see Fig. 3) Frangi filter Each parameter in Eq. (3) was varied independently in the following ranges: aa[0,1], ba[0.1,1] and ca[1,500]. The values assumed by the fixed parameters were a = 0.4, b = 0.6 and c = 200. The objective measures obtained from mean results for 14 CAS are presented in Fig. 4. For the large majority of cases (11 CAS), the best results are obtained for a = 1 and b = 0.1, although the filter response is quite insensitive to these parameters. The parameter c seems to dominate the filter outcome, with optimal performance obtained when c z 100 in most cases (10 CAS). 4. Discussion and conclusions From the results presented in Section 3, we chose the following parameter configurations to obtain good CVA enhancement in the average of all CAS evaluated in this study: Lorenz, Eq. (1): c = 0; Sato, Eq. (2): a =1, b = 0.5, c = 1; Frangi, Eq. (3): a =1, b = 0.1, c = 100. Fig. 5 shows mean results for 14 CAS obtained with the optimal configuration of each filter. Note that the Frangi filter provides better CVA enhancement in general (11 and 13 CAS, respectively, for rate or area measures). Since the response of this filter is largely dominated by the background noise suppression term (parameter c in Eq. (3)), we conclude that, in the case of the images considered in this study, this is an important factor to be taken into account for CVA enhancement, besides the relationships among eigenvalues. The results obtained with this study show that the hypotheses about relationships among the eigenvalues of the Hessian matrix (Section 2) influence the filter response differently for CVA enhancement. The hypothesis (b) is built into all filters as a test, and explicitly as a ratio in Sato and Frangi. This term seems to be important, given its weight in the optimal configuration determined experimentally (n = 1 for Sato, a = 1 for Frangi). The hypothesis (c) is incorporated into the Sato and Frangi filters as a ratio between k 1 and the other eigenvalues. This term, however, does not seem to have an important role, since the filter
6 1196 S.D. Olabarriaga et al. / International Congress Series 1256 (2003) Fig. 5. Results for all filters with the optimal parameter configuration (see text). Left: area. Right: rate. response is quite insensitive to s and b, which control the term s weight respectively in Eqs. (2) and (3). The hypothesis (a) is partially incorporated into the Sato filter, but it does not seem to influence the result in the optimal configuration (q = 1 in Eq. (2)). To conclude, note that the objective measures adopted in this study can only capture the average filter behaviour near the CVA. Other aspects could be investigated for a more thorough evaluation, such as the amount of false positive responses far from the CVA, or the behaviour at special cases such as stenosis, plaque and calcifications. This is the target of our current research. Acknowledgements We are grateful to the following institutions for providing the data for this study: Univ. Hosp. Cleveland (USA), Klinik Mue-Pasing (Prof. Haberl, Germany), Rad. Klinik Univ. Bonn (Germany) and Diagnostico Maipu. This research is funded by Philips Medical Systems, Medical IT-Advanced Development, Best (NL). References [1] O. Wink, et al., 3D MRA coronary axis determination using a minimum cost approach, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 47 (6) (2002) [2] S.R. Aylward, E. Bullit, Initialization, noise, singularities, and scale in height ridge traversal for tubular object centerline extraction, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 21 (2) (2002) [3] C. Lorenz, et al., Multi-scale line segmentation with automatic estimation of width, contrast and tangential direction in 2D and 3D medical images, CRVMed-MRCAS Proceedings, Springer Verlag, 1997, pp [4] Y. Sato, et al., 3-D multi-scale line filter for segmentation and visualization of curvilinear structures in medical images, Medical Image Analysis 2 (2) (1998) [5] A.F. Frangi, et al., Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering, MICCAI Proceedings, Springer Verlag, 1998, pp [6] P.J. Yim, et al., Vessel surface reconstruction with a tubular deformable model, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 20 (12) (2001)
Accurate Quantification of Small-Diameter Tubular Structures in Isotropic CT Volume Data Based on Multiscale Line Filter Responses
 Accurate Quantification of Small-Diameter Tubular Structures in Isotropic CT Volume Data Based on Multiscale Line Filter Responses Yoshinobu Sato 1, Shuji Yamamoto 2, and Shinichi Tamura 1 1 Division of
Accurate Quantification of Small-Diameter Tubular Structures in Isotropic CT Volume Data Based on Multiscale Line Filter Responses Yoshinobu Sato 1, Shuji Yamamoto 2, and Shinichi Tamura 1 1 Division of
Vessel Centerline Tracking in CTA and MRA Images Using Hough Transform
 Vessel Centerline Tracking in CTA and MRA Images Using Hough Transform Maysa M.G. Macedo 1, Choukri Mekkaoui 2, and Marcel P. Jackowski 1 1 University of São Paulo, Department of Computer Science, Rua
Vessel Centerline Tracking in CTA and MRA Images Using Hough Transform Maysa M.G. Macedo 1, Choukri Mekkaoui 2, and Marcel P. Jackowski 1 1 University of São Paulo, Department of Computer Science, Rua
Automatic Vascular Tree Formation Using the Mahalanobis Distance
 Automatic Vascular Tree Formation Using the Mahalanobis Distance Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab, Department of Radiology The University
Automatic Vascular Tree Formation Using the Mahalanobis Distance Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab, Department of Radiology The University
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE
 Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Package vesselr. R topics documented: April 3, Type Package
 Type Package Package vesselr April 3, 2017 Title Gradient and Vesselness Tools for Arrays and NIfTI Images Version 0.2.1 Maintainer Jordan D. Dworkin Simple functions for calculating
Type Package Package vesselr April 3, 2017 Title Gradient and Vesselness Tools for Arrays and NIfTI Images Version 0.2.1 Maintainer Jordan D. Dworkin Simple functions for calculating
Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images
 Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images Clemens M. Hentschke, Oliver Beuing, Rosa Nickl and Klaus D. Tönnies Abstract We propose a system to automatically detect cerebral
Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images Clemens M. Hentschke, Oliver Beuing, Rosa Nickl and Klaus D. Tönnies Abstract We propose a system to automatically detect cerebral
Application of level set based method for segmentation of blood vessels in angiography images
 Lodz University of Technology Faculty of Electrical, Electronic, Computer and Control Engineering Institute of Electronics PhD Thesis Application of level set based method for segmentation of blood vessels
Lodz University of Technology Faculty of Electrical, Electronic, Computer and Control Engineering Institute of Electronics PhD Thesis Application of level set based method for segmentation of blood vessels
Generalizing vesselness with respect to dimensionality and shape Release 1.00
 Generalizing vesselness with respect to dimensionality and shape Release 1.00 Luca Antiga 1 August 3, 2007 1 Medical Imaging Unit Mario Negri Institute, Bergamo, Italy email: antiga at marionegri.it Abstract
Generalizing vesselness with respect to dimensionality and shape Release 1.00 Luca Antiga 1 August 3, 2007 1 Medical Imaging Unit Mario Negri Institute, Bergamo, Italy email: antiga at marionegri.it Abstract
Characterizing Vascular Connectivity from microct Images
 Characterizing Vascular Connectivity from microct Images Marcel Jackowski 1, Xenophon Papademetris 1,2,LawrenceW.Dobrucki 1,3, Albert J. Sinusas 1,3, and Lawrence H. Staib 1,2 1 Departments of Diagnostic
Characterizing Vascular Connectivity from microct Images Marcel Jackowski 1, Xenophon Papademetris 1,2,LawrenceW.Dobrucki 1,3, Albert J. Sinusas 1,3, and Lawrence H. Staib 1,2 1 Departments of Diagnostic
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations Using STAPLE
 Comparison of Vessel Segmentations Using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations Using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Multiscale Vessel Enhancement Filtering*
 Multiscale Vessel Enhancement Filtering* Alejandro F. Frangi, Wiro J. Niessen, Koen L. Vincken, Max A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, Utrecht University Hospital Room E.01.334, Heidelberglaan 100,
Multiscale Vessel Enhancement Filtering* Alejandro F. Frangi, Wiro J. Niessen, Koen L. Vincken, Max A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, Utrecht University Hospital Room E.01.334, Heidelberglaan 100,
Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures
 Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures Stefan Wörz, William J. Godinez, Karl Rohr University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB, and DKFZ Heidelberg, Dept. Bioinformatics
Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures Stefan Wörz, William J. Godinez, Karl Rohr University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB, and DKFZ Heidelberg, Dept. Bioinformatics
Guide wire tracking in interventional radiology
 Guide wire tracking in interventional radiology S.A.M. Baert,W.J. Niessen, E.H.W. Meijering, A.F. Frangi, M.A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, rm E 01.334, P.O.Box
Guide wire tracking in interventional radiology S.A.M. Baert,W.J. Niessen, E.H.W. Meijering, A.F. Frangi, M.A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, rm E 01.334, P.O.Box
4D Motion Modeling of the Coronary Arteries from CT Images for Robotic Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
 4D Motion Modeling of the Coronary Arteries from CT Images for Robotic Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery Dong Ping Zhang 1, Eddie Edwards 1,2, Lin Mei 1,2, Daniel Rueckert 1 1 Department of Computing,
4D Motion Modeling of the Coronary Arteries from CT Images for Robotic Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery Dong Ping Zhang 1, Eddie Edwards 1,2, Lin Mei 1,2, Daniel Rueckert 1 1 Department of Computing,
Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography
 Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
MRA Image Segmentation with Capillary Active Contour
 MRA Image Segmentation with Capillary Active Contour Pingkun Yan and Ashraf A. Kassim Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore {pingkun,ashraf}@nus.edu.sg Abstract.
MRA Image Segmentation with Capillary Active Contour Pingkun Yan and Ashraf A. Kassim Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore {pingkun,ashraf}@nus.edu.sg Abstract.
Image Acquisition Systems
 Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Rigid and Deformable Vasculature-to-Image Registration : a Hierarchical Approach
 Rigid and Deformable Vasculature-to-Image Registration : a Hierarchical Approach Julien Jomier and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel
Rigid and Deformable Vasculature-to-Image Registration : a Hierarchical Approach Julien Jomier and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel
Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery
 Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery Refael Vivanti Computer Aided Surgery and Medical Image Processing Lab Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Advisor: Prof. Leo Joskowicz Clinical
Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery Refael Vivanti Computer Aided Surgery and Medical Image Processing Lab Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Advisor: Prof. Leo Joskowicz Clinical
2D Vessel Segmentation Using Local Adaptive Contrast Enhancement
 2D Vessel Segmentation Using Local Adaptive Contrast Enhancement Dominik Schuldhaus 1,2, Martin Spiegel 1,2,3,4, Thomas Redel 3, Maria Polyanskaya 1,3, Tobias Struffert 2, Joachim Hornegger 1,4, Arnd Doerfler
2D Vessel Segmentation Using Local Adaptive Contrast Enhancement Dominik Schuldhaus 1,2, Martin Spiegel 1,2,3,4, Thomas Redel 3, Maria Polyanskaya 1,3, Tobias Struffert 2, Joachim Hornegger 1,4, Arnd Doerfler
A Hybrid Method for Coronary Artery Stenoses Detection and Quantification in CTA Images
 A Hybrid Method for Coronary Artery Stenoses Detection and Quantification in CTA Images İlkay Öksüz 1, Devrim Ünay 2, Kamuran Kadıpaşaoğlu 2 1 Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bahçeşehir University,
A Hybrid Method for Coronary Artery Stenoses Detection and Quantification in CTA Images İlkay Öksüz 1, Devrim Ünay 2, Kamuran Kadıpaşaoğlu 2 1 Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bahçeşehir University,
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets
 Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Coronary Artery Tracking from Dynamic Cardiac CT Sequences
 Coronary Artery Tracking from Dynamic Cardiac CT Sequences Dong Ping Zhang a, Ose Pedro a, Kensaku Mori b, Philip Edwards a,c and Daniel Rueckert a a Department of Computing, Imperial College London, UK
Coronary Artery Tracking from Dynamic Cardiac CT Sequences Dong Ping Zhang a, Ose Pedro a, Kensaku Mori b, Philip Edwards a,c and Daniel Rueckert a a Department of Computing, Imperial College London, UK
Mimics Innovation Suite Mimics Centerline Extraction: Quantitative Validation
 Mimics Innovation Suite Mimics Centerline Extraction: Quantitative Validation Verhoelst Eefje, Shtankevych Oleksii, Schepers Jan, Maes Jan, Sindhwani Nikhil, Lysogor Andriy, Veeckmans Bart 1 / Introduction
Mimics Innovation Suite Mimics Centerline Extraction: Quantitative Validation Verhoelst Eefje, Shtankevych Oleksii, Schepers Jan, Maes Jan, Sindhwani Nikhil, Lysogor Andriy, Veeckmans Bart 1 / Introduction
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning
 Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
DETECTING and extracting blood vessels in magnetic resonance
 1224 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2007 Weighted Local Variance-Based Edge Detection and Its Application to Vascular Segmentation in Magnetic Resonance Angiography Max
1224 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2007 Weighted Local Variance-Based Edge Detection and Its Application to Vascular Segmentation in Magnetic Resonance Angiography Max
Model-Based Respiratory Motion Compensation for Image-Guided Cardiac Interventions
 Model-Based Respiratory Motion Compensation for Image-Guided Cardiac Interventions February 8 Matthias Schneider Pattern Recognition Lab Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg Imaging and Visualization
Model-Based Respiratory Motion Compensation for Image-Guided Cardiac Interventions February 8 Matthias Schneider Pattern Recognition Lab Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg Imaging and Visualization
Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images
 Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images Attila Budai 1, Georg Michelson 2, Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Pattern Recognition Lab and Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies(SAOT),
Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images Attila Budai 1, Georg Michelson 2, Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Pattern Recognition Lab and Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies(SAOT),
Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images
 Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images Attila Budai 1, Georg Michelson 2, Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Pattern Recognition Lab and Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies(SAOT),
Multiscale Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Fundus Images Attila Budai 1, Georg Michelson 2, Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Pattern Recognition Lab and Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies(SAOT),
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 23, NO. 10, OCTOBER Jian Chen and Amir A. Amini*, Senior Member, IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 23, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2004 1251 Quantifying 3-D Vascular Structures in MRA Images Using Hybrid PDE and Geometric Deformable Models Jian Chen and Amir A. Amini*,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 23, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2004 1251 Quantifying 3-D Vascular Structures in MRA Images Using Hybrid PDE and Geometric Deformable Models Jian Chen and Amir A. Amini*,
The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography
 The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography Matúš Straka M. Šrámek, A. La Cruz E. Gröller, D. Fleischmann Contents Motivation:» Why again a new visualization method for vessel data?
The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography Matúš Straka M. Šrámek, A. La Cruz E. Gröller, D. Fleischmann Contents Motivation:» Why again a new visualization method for vessel data?
Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography
 Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography Erik Meijering 1, Wiro Niessen 1, Joachim Weickert 2, and Max Viergever
Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography Erik Meijering 1, Wiro Niessen 1, Joachim Weickert 2, and Max Viergever
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation
 Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Identify the Centerline of Tubular Structure in Medical Images
 Identify the Centerline of Tubular Structure in Medical Images Yu-Tai Ching a and Carlos Yeh a a Department of Computer and Information Science, National Chiao Tung University, HsunChu, Taiwan. ABSTRACT
Identify the Centerline of Tubular Structure in Medical Images Yu-Tai Ching a and Carlos Yeh a a Department of Computer and Information Science, National Chiao Tung University, HsunChu, Taiwan. ABSTRACT
Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication
 Serveur Académique Lausannois SERVAL serval.unil.ch Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication This paper has been peer-reviewed but dos not include the final publisher proof-corrections
Serveur Académique Lausannois SERVAL serval.unil.ch Author Manuscript Faculty of Biology and Medicine Publication This paper has been peer-reviewed but dos not include the final publisher proof-corrections
XI Conference "Medical Informatics & Technologies" VALIDITY OF MRI BRAIN PERFUSION IMAGING METHOD
 XI Conference "Medical Informatics & Technologies" - 2006 medical imaging, MRI, brain perfusion Bartosz KARCZEWSKI 1, Jacek RUMIŃSKI 1 VALIDITY OF MRI BRAIN PERFUSION IMAGING METHOD Brain perfusion imaging
XI Conference "Medical Informatics & Technologies" - 2006 medical imaging, MRI, brain perfusion Bartosz KARCZEWSKI 1, Jacek RUMIŃSKI 1 VALIDITY OF MRI BRAIN PERFUSION IMAGING METHOD Brain perfusion imaging
Vessel Segmentation Using A Shape Driven Flow
 Vessel Segmentation Using A Shape Driven Flow Delphine Nain, Anthony Yezzi and Greg Turk Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332, USA {delfin, turk}@cc.gatech.edu, ayezzi@ece.gatech.edu Abstract.
Vessel Segmentation Using A Shape Driven Flow Delphine Nain, Anthony Yezzi and Greg Turk Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332, USA {delfin, turk}@cc.gatech.edu, ayezzi@ece.gatech.edu Abstract.
Multi-resolution Vessel Segmentation Using Normalized Cuts in Retinal Images
 Multi-resolution Vessel Segmentation Using Normalized Cuts in Retinal Images Wenchao Cai and Albert C.S. Chung Lo Kwee-Seong Medical Image Analysis Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Multi-resolution Vessel Segmentation Using Normalized Cuts in Retinal Images Wenchao Cai and Albert C.S. Chung Lo Kwee-Seong Medical Image Analysis Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Blood Vessel Visualization on CT Data
 WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 88 93, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-224-5 MATFYZPRESS Blood Vessel Visualization on CT Data J. Dupej Charles University Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 88 93, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-224-5 MATFYZPRESS Blood Vessel Visualization on CT Data J. Dupej Charles University Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
A Geometric Flow for Segmenting Vasculature in Proton-Density Weighted MRI
 A Geometric Flow for Segmenting Vasculature in Proton-Density Weighted MRI Maxime Descoteaux a D. Louis Collins b Kaleem Siddiqi c, a Odyssée Project Team, INRIA, Sophia-Antipolis, France b McConnell Brain
A Geometric Flow for Segmenting Vasculature in Proton-Density Weighted MRI Maxime Descoteaux a D. Louis Collins b Kaleem Siddiqi c, a Odyssée Project Team, INRIA, Sophia-Antipolis, France b McConnell Brain
Model-Based Detection of Tubular Structures in 3D Images
 Model-Based Detection of Tubular Structures in 3D Images Karl Krissian, Grégoire Malandain, Nicholas Ayache, Régis Vaillant, Yves Trousset To cite this version: Karl Krissian, Grégoire Malandain, Nicholas
Model-Based Detection of Tubular Structures in 3D Images Karl Krissian, Grégoire Malandain, Nicholas Ayache, Régis Vaillant, Yves Trousset To cite this version: Karl Krissian, Grégoire Malandain, Nicholas
Vessel Segmentation and Catheter Detection in X-Ray Angiograms Using Superpixels
 1 Vessel Segmentation and Catheter Detection in X-Ray Angiograms Using Superpixels Hamid R. Fazlali 1, Nader Karimi 2, S.M. Reza Soroushmehr 3,4, Shahram Shirani 1, Brahmajee.K. Nallamothu 4, Kevin R.
1 Vessel Segmentation and Catheter Detection in X-Ray Angiograms Using Superpixels Hamid R. Fazlali 1, Nader Karimi 2, S.M. Reza Soroushmehr 3,4, Shahram Shirani 1, Brahmajee.K. Nallamothu 4, Kevin R.
Efficient 3D-3D Vascular Registration Based on Multiple Orthogonal 2D Projections
 Efficient 3D-3D Vascular Registration Based on Multiple Orthogonal 2D Projections Ho-Ming Chan and Albert C. S. Chung Dept. of Computer Science, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, HK {hmchan,achung}@cs.ust.hk
Efficient 3D-3D Vascular Registration Based on Multiple Orthogonal 2D Projections Ho-Ming Chan and Albert C. S. Chung Dept. of Computer Science, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, HK {hmchan,achung}@cs.ust.hk
 Multiscale Detection of Curvilinear Structures in -D and 3-D Image Data Th. M. Koller, G. Gerig, G. Szekely, and D. Dettwiler Communication Technology Laboratory, Image Science, ETH-Zentrum, CH-89 Zurich,
Multiscale Detection of Curvilinear Structures in -D and 3-D Image Data Th. M. Koller, G. Gerig, G. Szekely, and D. Dettwiler Communication Technology Laboratory, Image Science, ETH-Zentrum, CH-89 Zurich,
Precise Segmentation of Vessels from MRA Brain Images
 Precise Segmentation of Vessels from MRA Brain Images D.Jenefa Magdalene 1 PG Scholar Department Of Computer Science & Engineering Dr.sivanthi Aditanar College of Engineering Tiruchendur, Tamil Nadu. G.R.Jainish
Precise Segmentation of Vessels from MRA Brain Images D.Jenefa Magdalene 1 PG Scholar Department Of Computer Science & Engineering Dr.sivanthi Aditanar College of Engineering Tiruchendur, Tamil Nadu. G.R.Jainish
18 3 Model-based quantitation of 3-D MRA images investigation [91, 92]. These findings support the relevance of accurate measurement techniques of vas
![18 3 Model-based quantitation of 3-D MRA images investigation [91, 92]. These findings support the relevance of accurate measurement techniques of vas 18 3 Model-based quantitation of 3-D MRA images investigation [91, 92]. These findings support the relevance of accurate measurement techniques of vas](/thumbs/81/83607791.jpg) People seldom improve when they have no other model but themselves to copy after. O. Goldsmith, 1730-1774 Chapter 3 Model-based quantitation of 3-D Magnetic Resonance angiographic images Abstract Quantification
People seldom improve when they have no other model but themselves to copy after. O. Goldsmith, 1730-1774 Chapter 3 Model-based quantitation of 3-D Magnetic Resonance angiographic images Abstract Quantification
Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data
 Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data Sahla Bouattour and Dietrich Paulus Institute of Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau,
Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data Sahla Bouattour and Dietrich Paulus Institute of Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau,
Robust and Accurate Coronary Artery Centerline Extraction in CTA by Combining Model-Driven and Data-Driven Approaches
 Robust and Accurate Coronary Artery Centerline Extraction in CTA by Combining Model-Driven and Data-Driven Approaches Yefeng Zheng, Huseyin Tek, and Gareth Funka-Lea Imaging and Computer Vision, Siemens
Robust and Accurate Coronary Artery Centerline Extraction in CTA by Combining Model-Driven and Data-Driven Approaches Yefeng Zheng, Huseyin Tek, and Gareth Funka-Lea Imaging and Computer Vision, Siemens
arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 28 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 28 Jan 2019 arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 28 Jan 2019](/thumbs/95/122566453.jpg) Improving Myocardium Segmentation in Cardiac CT Angiography using Spectral Information Steffen Bruns a, Jelmer M. Wolterink a, Robbert W. van Hamersvelt b, Majd Zreik a, Tim Leiner b, and Ivana Išgum a
Improving Myocardium Segmentation in Cardiac CT Angiography using Spectral Information Steffen Bruns a, Jelmer M. Wolterink a, Robbert W. van Hamersvelt b, Majd Zreik a, Tim Leiner b, and Ivana Išgum a
Automatic Hepatic Vessel Segmentation Using Graphics Hardware
 Automatic Hepatic Vessel Segmentation Using Graphics Hardware Marius Erdt 1, Matthias Raspe 2, and Michael Suehling 3 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Graphics, Cognitive Computing & Medical Imaging,
Automatic Hepatic Vessel Segmentation Using Graphics Hardware Marius Erdt 1, Matthias Raspe 2, and Michael Suehling 3 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Graphics, Cognitive Computing & Medical Imaging,
Direction-adaptive grey-level morphology. Application to 3D vascular brain imaging
 Direction-adaptive grey-level morphology. Application to 3D vascular brain imaging Olena Tankyevych, Hugues Talbot, Petr Dokládal, Nicolas Passat To cite this version: Olena Tankyevych, Hugues Talbot,
Direction-adaptive grey-level morphology. Application to 3D vascular brain imaging Olena Tankyevych, Hugues Talbot, Petr Dokládal, Nicolas Passat To cite this version: Olena Tankyevych, Hugues Talbot,
Phantom-based evaluation of a semi-automatic segmentation algorithm for cerebral vascular structures in 3D ultrasound angiography (3D USA)
 Phantom-based evaluation of a semi-automatic segmentation algorithm for cerebral vascular structures in 3D ultrasound angiography (3D USA) C. Chalopin¹, K. Krissian², A. Müns 3, F. Arlt 3, J. Meixensberger³,
Phantom-based evaluation of a semi-automatic segmentation algorithm for cerebral vascular structures in 3D ultrasound angiography (3D USA) C. Chalopin¹, K. Krissian², A. Müns 3, F. Arlt 3, J. Meixensberger³,
Vessels as 4D Curves: Global Minimal 4D Paths to Extract 3D Tubular Surfaces
 Vessels as 4D Curves: Global Minimal 4D Paths to Extract 3D Tubular Surfaces Hua Li Anthony Yezzi School of ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA {hua.li, ayezzi}@ece.gatech.edu Abstract
Vessels as 4D Curves: Global Minimal 4D Paths to Extract 3D Tubular Surfaces Hua Li Anthony Yezzi School of ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA {hua.li, ayezzi}@ece.gatech.edu Abstract
A Quadrature Filter Approach for Registration Accuracy Assessment of Fundus Images
 A Quadrature Filter Approach for Registration Accuracy Assessment of Fundus Images Kedir M. Adal 1,3, Rosalie Couvert, D.W.J. Meijer, Jose P. Martinez 2, Koenraad A. Vermeer 1, L.J. van Vliet 3 1 Rotterdam
A Quadrature Filter Approach for Registration Accuracy Assessment of Fundus Images Kedir M. Adal 1,3, Rosalie Couvert, D.W.J. Meijer, Jose P. Martinez 2, Koenraad A. Vermeer 1, L.J. van Vliet 3 1 Rotterdam
A novel noise removal using homomorphic normalization for multi-echo knee MRI
 A novel noise removal using homomorphic normalization for multi-echo knee MRI Xuenan Cui 1a),HakilKim 1b), Seongwook Hong 1c), and Kyu-Sung Kwack 2d) 1 School of Information and Communication Engineering,
A novel noise removal using homomorphic normalization for multi-echo knee MRI Xuenan Cui 1a),HakilKim 1b), Seongwook Hong 1c), and Kyu-Sung Kwack 2d) 1 School of Information and Communication Engineering,
ICA vs. PCA Active Appearance Models: Application to Cardiac MR Segmentation
 ICA vs. PCA Active Appearance Models: Application to Cardiac MR Segmentation M. Üzümcü 1, A.F. Frangi 2, M. Sonka 3, J.H.C. Reiber 1, B.P.F. Lelieveldt 1 1 Div. of Image Processing, Dept. of Radiology
ICA vs. PCA Active Appearance Models: Application to Cardiac MR Segmentation M. Üzümcü 1, A.F. Frangi 2, M. Sonka 3, J.H.C. Reiber 1, B.P.F. Lelieveldt 1 1 Div. of Image Processing, Dept. of Radiology
THE leading causes of retina-related vision impairment and
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2006 1531 Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka*, Student Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2006 1531 Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka*, Student Member,
Explorative Building of 3D Vessel Tree Models 1) Technology, Inffeldgasse 16 2.OG, A-8010 Graz, Austria
 Explorative Building of 3D Vessel Tree Models 1) Georg Langs 123, Petia Radeva 3, Francesc Carreras 4 1 Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology, Inffeldgasse 16 2.OG,
Explorative Building of 3D Vessel Tree Models 1) Georg Langs 123, Petia Radeva 3, Francesc Carreras 4 1 Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology, Inffeldgasse 16 2.OG,
Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis
 ISSN -7X Volume, Issue June 7 Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis Tamojay Deb, Anjan K Ghosh, Anjan Mukherjee Tripura University (A Central University),
ISSN -7X Volume, Issue June 7 Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis Tamojay Deb, Anjan K Ghosh, Anjan Mukherjee Tripura University (A Central University),
Segmentation of hepatic artery in multi-phase liver CT using directional dilation and connectivity analysis
 Segmentation of hepatic artery in multi-phase liver CT using directional dilation and connectivity analysis Lei Wang a, Alena-Kathrin Schnurr b, Yue Zhao c, Stephan Zidowitz a, Joachim Georgii a, Horst
Segmentation of hepatic artery in multi-phase liver CT using directional dilation and connectivity analysis Lei Wang a, Alena-Kathrin Schnurr b, Yue Zhao c, Stephan Zidowitz a, Joachim Georgii a, Horst
Extracting the Geometry of Branching Slabs via Cores
 Extracting the Geometry of Branching Slabs via Cores Yonatan Fridman, Stephen M. Pizer Medical Image Display & Analysis Group University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC fridman@cs.unc.edu Abstract.
Extracting the Geometry of Branching Slabs via Cores Yonatan Fridman, Stephen M. Pizer Medical Image Display & Analysis Group University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC fridman@cs.unc.edu Abstract.
Clinical Importance. Aortic Stenosis. Aortic Regurgitation. Ultrasound vs. MRI. Carotid Artery Stenosis
 Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
A statistical arteriovenous cerebral atlas
 A statistical arteriovenous cerebral atlas A. Dufour (a,b),o.tankyevych (c),h.talbot (d),c.ronse (a),j.baruthio (b),andn.passat (a) (a) Université de Strasbourg, LSIIT, UMR CNRS 7005, France (b) Université
A statistical arteriovenous cerebral atlas A. Dufour (a,b),o.tankyevych (c),h.talbot (d),c.ronse (a),j.baruthio (b),andn.passat (a) (a) Université de Strasbourg, LSIIT, UMR CNRS 7005, France (b) Université
Globally-Optimal Anatomical Tree Extraction from 3D Medical Images using Pictorial Structures and Minimal Paths
 Globally-Optimal Anatomical Tree Extraction from 3D Medical Images using Pictorial Structures and Minimal Paths Zahra Mirikharaji, Mengliu Zhao, Ghassan Hamarneh Medical Image Analysis Lab, Simon Fraser
Globally-Optimal Anatomical Tree Extraction from 3D Medical Images using Pictorial Structures and Minimal Paths Zahra Mirikharaji, Mengliu Zhao, Ghassan Hamarneh Medical Image Analysis Lab, Simon Fraser
Medical Image Analysis
 Medical Image Analysis 14 (1) 16 171 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Medical Image Analysis journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/media Multiple hypothesis template tracking of small 3D vessel
Medical Image Analysis 14 (1) 16 171 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Medical Image Analysis journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/media Multiple hypothesis template tracking of small 3D vessel
MULTIVARIATE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION USING A PRINCIPAL GEODESIC CLASSIFIER
 MULTIVARIATE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION USING A PRINCIPAL GEODESIC CLASSIFIER A.Shabbir 1, 2 and G.Verdoolaege 1, 3 1 Department of Applied Physics, Ghent University, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium 2 Max Planck Institute
MULTIVARIATE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION USING A PRINCIPAL GEODESIC CLASSIFIER A.Shabbir 1, 2 and G.Verdoolaege 1, 3 1 Department of Applied Physics, Ghent University, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium 2 Max Planck Institute
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA
 FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
Non-linear Model Fitting to Parameterize Diseased Blood Vessels
 Non-linear Model Fitting to Parameterize Diseased Blood Vessels Alexandra La Cruz Vienna University of Technology Miloš Šrámek Austrian Academy of Sciences Matúš Straka Austrian Academy of Sciences Eduard
Non-linear Model Fitting to Parameterize Diseased Blood Vessels Alexandra La Cruz Vienna University of Technology Miloš Šrámek Austrian Academy of Sciences Matúš Straka Austrian Academy of Sciences Eduard
Research Article Automated Segmentation of Coronary Arteries Based on Statistical Region Growing and Heuristic Decision Method
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3530251, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3530251 Research Article Automated Segmentation of Coronary Arteries Based on Statistical Region Growing
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3530251, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3530251 Research Article Automated Segmentation of Coronary Arteries Based on Statistical Region Growing
ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma
 ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma ORAL DEFENSE 8 th of September 2017 Charlotte MARTIN Supervisor: Pr. MP REVEL M2 Bio Medical
ANALYSIS OF PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN MRI, USING AN ELASTIC REGISTRATION TECHNIQUE IN A MODEL OF FIBROSIS: Scleroderma ORAL DEFENSE 8 th of September 2017 Charlotte MARTIN Supervisor: Pr. MP REVEL M2 Bio Medical
Measurements using three-dimensional product imaging
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 3/2010 41 46 7/3 Measurements using
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 3/2010 41 46 7/3 Measurements using
Matching 3D Lung Surfaces with the Shape Context Approach. 1)
 Matching 3D Lung Surfaces with the Shape Context Approach. 1) Martin Urschler, Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, TU Graz Inffeldgasse 16, A-8010 Graz E-Mail: {urschler, bischof}@icg.tu-graz.ac.at
Matching 3D Lung Surfaces with the Shape Context Approach. 1) Martin Urschler, Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, TU Graz Inffeldgasse 16, A-8010 Graz E-Mail: {urschler, bischof}@icg.tu-graz.ac.at
Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures
 Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka, and Charles V. Stewart July 2, 2006 Abstract Motivated by the goals of improving detection
Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka, and Charles V. Stewart July 2, 2006 Abstract Motivated by the goals of improving detection
Spinal Crawlers: Deformable Organisms for Spinal Cord Segmentation and Analysis
 Spinal Crawlers: Deformable Organisms for Spinal Cord Segmentation and Analysis Chris McIntosh and Ghassan Hamarneh Medical Image Analysis Lab, School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University, BC,
Spinal Crawlers: Deformable Organisms for Spinal Cord Segmentation and Analysis Chris McIntosh and Ghassan Hamarneh Medical Image Analysis Lab, School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University, BC,
A Fast Technique for Motion Correction in DSA using a Feature-Based, Irregular Grid
 A Fast Technique for Motion Correction in DSA using a Feature-Based, Irregular Grid Erik H. W. Meijering, Karel J. Zuiderveld, Max A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, Utrecht University, Heidelberglaan
A Fast Technique for Motion Correction in DSA using a Feature-Based, Irregular Grid Erik H. W. Meijering, Karel J. Zuiderveld, Max A. Viergever Image Sciences Institute, Utrecht University, Heidelberglaan
Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation
 Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation Anil Sethi, PhD Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL 60153 November 2015 I. Introduction: The MR distortion grid, used as an insert with Lucy 3D QA phantom, is
Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation Anil Sethi, PhD Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL 60153 November 2015 I. Introduction: The MR distortion grid, used as an insert with Lucy 3D QA phantom, is
48 4 Quantitative 3-D MRA: in vitro and in vivo results Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) [216] and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) [92], both e
![48 4 Quantitative 3-D MRA: in vitro and in vivo results Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) [216] and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) [92], both e 48 4 Quantitative 3-D MRA: in vitro and in vivo results Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) [216] and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) [92], both e](/thumbs/79/79296189.jpg) True genius resides in the capacity for evaluation of uncertain, hazardous, and conflicting information. W. Churchill, 1874-1965 Chapter 4 Quantitative analysis of vascular morphology from 3-D MRA: in
True genius resides in the capacity for evaluation of uncertain, hazardous, and conflicting information. W. Churchill, 1874-1965 Chapter 4 Quantitative analysis of vascular morphology from 3-D MRA: in
An Advanced Automatic Fuzzy Rule-Based Algorithm for 3D Vessel Segmentation
 An Advanced Automatic Fuzzy Rule-Based Algorithm for 3D Vessel Segmentation Mohamed A. Abdou *1, Ashraf El-Sayed 2, Eman Ali 2 1 Informatics Research Institute, City for Scientific, Research & Technology
An Advanced Automatic Fuzzy Rule-Based Algorithm for 3D Vessel Segmentation Mohamed A. Abdou *1, Ashraf El-Sayed 2, Eman Ali 2 1 Informatics Research Institute, City for Scientific, Research & Technology
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc.
 Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Computational methods to predict and enhance decision-making with biomedical data.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2015 Computational methods to predict and enhance decision-making with biomedical
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2015 Computational methods to predict and enhance decision-making with biomedical
An Automatic Seeding Method For Coronary Artery Segmentation and Skeletonization in CTA Release 0.00
 An Automatic Seeding Method For Coronary Artery Segmentation and Skeletonization in CTA Release 0.00 Chunliang Wang 1 and Örjan Smedby 1 July 8, 2008 1 Linkping University, CMIV Abstract An automatic seeding
An Automatic Seeding Method For Coronary Artery Segmentation and Skeletonization in CTA Release 0.00 Chunliang Wang 1 and Örjan Smedby 1 July 8, 2008 1 Linkping University, CMIV Abstract An automatic seeding
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings
 Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging
 Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging J. SEQUEIRA Laboratoire d'informatique de Marseille - FRE CNRS 2246 Faculté des Sciences de Luminy, 163 avenue de Luminy,
Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging J. SEQUEIRA Laboratoire d'informatique de Marseille - FRE CNRS 2246 Faculté des Sciences de Luminy, 163 avenue de Luminy,
A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data
 A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Grünauer, E. Vuçini,
A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Grünauer, E. Vuçini,
Three-Dimensional Model-Based Stenosis Quantification of the Carotid Arteries from Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography
 Three-Dimensional Model-Based Stenosis Quantification of the Carotid Arteries from Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Alejandro F. Frangi, Wiro J. Niessen, Paul J. Nederkoorn, Otto E.H. Elgersma, Max A.
Three-Dimensional Model-Based Stenosis Quantification of the Carotid Arteries from Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Alejandro F. Frangi, Wiro J. Niessen, Paul J. Nederkoorn, Otto E.H. Elgersma, Max A.
SEPARATION AND SEGMENTATION OF THE HEPATIC VASCULATURE IN CT IMAGES. Qingyang Shang. Dissertation. Submitted to the Faculty of the
 SEPARATION AND SEGMENTATION OF THE HEPATIC VASCULATURE IN CT IMAGES By Qingyang Shang Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment of the
SEPARATION AND SEGMENTATION OF THE HEPATIC VASCULATURE IN CT IMAGES By Qingyang Shang Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment of the
Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 2, DECEMBER 26 53 Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka*, Student Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 2, DECEMBER 26 53 Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measures Michal Sofka*, Student Member, IEEE,
RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges
 27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
Medical Image Analysis
 Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy
 The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
Implementation and evaluation of a fully 3D OS-MLEM reconstruction algorithm accounting for the PSF of the PET imaging system
 Implementation and evaluation of a fully 3D OS-MLEM reconstruction algorithm accounting for the PSF of the PET imaging system 3 rd October 2008 11 th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation
Implementation and evaluation of a fully 3D OS-MLEM reconstruction algorithm accounting for the PSF of the PET imaging system 3 rd October 2008 11 th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation
Linköping University Post Print. Phase Based Level Set Segmentation of Blood Vessels
 Post Print Phase Based Level Set Segmentation of Blood Vessels Gunnar Läthén, Jimmy Jonasson and Magnus Borga N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2009 IEEE. Personal use of this material
Post Print Phase Based Level Set Segmentation of Blood Vessels Gunnar Läthén, Jimmy Jonasson and Magnus Borga N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2009 IEEE. Personal use of this material
Respiratory Motion Estimation using a 3D Diaphragm Model
 Respiratory Motion Estimation using a 3D Diaphragm Model Marco Bögel 1,2, Christian Riess 1,2, Andreas Maier 1, Joachim Hornegger 1, Rebecca Fahrig 2 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg 2
Respiratory Motion Estimation using a 3D Diaphragm Model Marco Bögel 1,2, Christian Riess 1,2, Andreas Maier 1, Joachim Hornegger 1, Rebecca Fahrig 2 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg 2
TECHNICAL REPORT. Smart Linking of 2D and 3D Views in Medical Applications
 Institut für Computergraphik und Algorithmen Technische Universität Wien Karlsplatz 13/186/2 A-1040 Wien AUSTRIA Tel: +43 (1) 58801-18601 Fax: +43 (1) 58801-18698 Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms
Institut für Computergraphik und Algorithmen Technische Universität Wien Karlsplatz 13/186/2 A-1040 Wien AUSTRIA Tel: +43 (1) 58801-18601 Fax: +43 (1) 58801-18698 Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms
Tutorial Syllabus. Surface Visualization. (20 min.) Direct Volume Visualization. (30 min.) Medical Training and Surgical Planning
 Tutorial Syllabus Surface Visualization - Marching Cubes and its improvements - Smoothing of surface visualizations Direct Volume Visualization - Ray casting and texture-based approaches - Projection methods
Tutorial Syllabus Surface Visualization - Marching Cubes and its improvements - Smoothing of surface visualizations Direct Volume Visualization - Ray casting and texture-based approaches - Projection methods
Elastic registration of medical images using finite element meshes
 Elastic registration of medical images using finite element meshes Hartwig Grabowski Institute of Real-Time Computer Systems & Robotics, University of Karlsruhe, D-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany. Email: grabow@ira.uka.de
Elastic registration of medical images using finite element meshes Hartwig Grabowski Institute of Real-Time Computer Systems & Robotics, University of Karlsruhe, D-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany. Email: grabow@ira.uka.de
A 3-D Modeling Scheme for Cerebral Vasculature from MRA Datasets
 3-D Modeling Scheme for Cerebral Vasculature from MR Datasets Zhongyuan Qin, Xuanqin Mou Institute of Image Processing Xi'an Jiaotong University Xi'an, Shaanxi 710049, P. R. China Ruofei Zhang Department
3-D Modeling Scheme for Cerebral Vasculature from MR Datasets Zhongyuan Qin, Xuanqin Mou Institute of Image Processing Xi'an Jiaotong University Xi'an, Shaanxi 710049, P. R. China Ruofei Zhang Department
Abstract. 1. Introduction
 A New Automated Method for Three- Dimensional Registration of Medical Images* P. Kotsas, M. Strintzis, D.W. Piraino Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotelian University, 54006 Thessaloniki,
A New Automated Method for Three- Dimensional Registration of Medical Images* P. Kotsas, M. Strintzis, D.W. Piraino Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotelian University, 54006 Thessaloniki,
Comparison of HK and SC curvature description methods
 Comparison of and SC curvature description methods H. Cantzler and R. B. Fisher Machine Vision Unit, Institute for Perception, Action and Behaviour, Division of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh,
Comparison of and SC curvature description methods H. Cantzler and R. B. Fisher Machine Vision Unit, Institute for Perception, Action and Behaviour, Division of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh,
