Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths. April 18, 2010
|
|
|
- Marjorie Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last time: Recall that an even city is a city that has an even number of tunnels connecting to it, and an odd city is a city that has an odd number of tunnels connecting to it. Label the cities above with the number of tunnels connecting to it. Which cities are even? Which cities are odd? We are now going to generalize this idea. The insect worlds we have seen are all examples of graphs. A graph is a set of vertices (cities) and edges (tunnels) connecting them. An even vertex has an even number of edges connecting to it and an odd vertex has an odd number of edges connecting to it. The number of edges attached to a vertex is called its degree.
2 Just like how insects travel from one city to another city by tunnel, we want to trace out a path from one vertex to another along the edges in the graph. A circuit is a type of path where we start and at end at the same vertex. Let s examine the graphs below. 1. a.) Draw a circuit on each of the graphs below. b.) On which graphs can you make a circuit without going over the same edge twice? c.) What is the special name (from our last meeting) for graphs where there is only one path between two points? Do these graphs have circuits?
3 A special type of circuit around a graph is called an Euler Circuit. Here is an example of a graph which has an Euler Circuit: In an Euler Circuit, we start at one vertex and walk through every edge in the graph and go back to our original vertex, but we can only go along each edge once! Here is another example of a graph which has an Euler Circuit: Notice that in an Euler Circuit, you can visit the same vertex several times, but you cannot go along an edge more than once! The graph below does not have an Euler Circuit. Why?
4 2. a.) Which of the graphs below have Euler Circuits and which do not? b.) For each of the graphs above, label each vertex with the number of edges connecting to it. c.) Do any of the graphs have only even vertices? Which ones? d.) Using your answers in parts (a.) and (c.), what do you notice about the graphs that have Euler circuits?
5 3. Here is a picture of the city of Konigsberg, which has 7 bridges. The people of this city want to find out if there is a way to start at on a piece of land and walk across every single bridge exactly one time. a. Let s start by converting this picture into a graph. We represent the 4 pieces of land in the picture above as 4 vertices: Now we connect the vertices. Each bridge represents an edge between two vertices. Can you draw the 7 bridges above? (Notice that some pieces of land are connected by more than one bridge). Starting at some vertex, can you draw a path over each edge, without going over the same edge more than once?
6 b. On the graph, mark which vertices are even and which vertices are odd: c. Can you remove one vertex so that it becomes possible to cross each bridge exactly once? Draw the new graph below. How many odd vertices are there? d. Starting from our original graph, now remove a different vertex and draw the graph. Is there a path to cross each bridge exactly once? How many odd vertices are there? e. Can we remove any one of the vertices from our original graph and still get a path to cross each bridge exactly one? How many odd vertices do we have in each case?
7 4. The path we wanted to take in Problem #3 is called an Euler path. In an Euler path, we want to cross each edge exactly once, but we don t have to come back to the vertex we started at. a. In which of the graphs below can you make an Euler path? b. For each of the graphs, mark which vertices are even and which are odd. c. Using your results in Problem #3 and this problem, how many odd vertices can you have in a graph that has an Euler path?
8 5. a. In the examples above, we have seen that a graph with an Euler Circuit only has even vertices. Draw your own example of a graph with an Euler Circuit. Try to make only one of the vertices odd. Is this possible? Why or why not? b. In the examples above, we have also seen that a graph with an Euler path can only have 0 or 2 odd vertices. Draw a picture of a graph with an Euler path that has exactly 2 odd vertices. Try to make only one more of the vertices odd. Is this possible? Why or why not?
9 6. a. Connect the 3 vertices below in such a way that there is NO Euler Circuit. b. Connect the 4 vertices below in such a way that there is NO Euler path. c. Recall that we have learned that the number of odd vertices is even. How many odd vertices are there in your graph in part (b.)? Could there be any fewer odd vertices? Why or why not?
10 7. There are 6 people at a party. Many of the people at the party do not know each other, so they introduce themselves to each other and shake hands. a. Draw a sample graph to represent this party with some number of people shaking hands with each other (you can choose the number). Draw the 6 people as vertices and draw edges between the pairs of people who shake hands. Label the degree of each of the vertices. b. How many people shake an odd number of people s hands? Does this number surprise you? c. What is the sum of the degrees of the vertices? How does this number relate to the number of edges? d. Do your results depend on the graph you chose? Try drawing a different graph (with different pairs of people shaking hands). What do you notice?
Circuits and Paths. April 13, 2014
 Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study.
 Graph Theory Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However, it wasn t studied too systematically until
Graph Theory Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However, it wasn t studied too systematically until
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology
 Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology The Konigsberg Problem: The Foundation of Topology The Konigsberg Bridge Problem is a very famous problem solved by Euler in 1735. The process he
Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology The Konigsberg Problem: The Foundation of Topology The Konigsberg Bridge Problem is a very famous problem solved by Euler in 1735. The process he
AQR UNIT 7. Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures. Packet #
 AQR UNIT 7 NETWORKS AND GRAPHS: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures Packet # BY: Introduction to Networks and Graphs: Try drawing a path for a person to walk through each door exactly once without going
AQR UNIT 7 NETWORKS AND GRAPHS: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures Packet # BY: Introduction to Networks and Graphs: Try drawing a path for a person to walk through each door exactly once without going
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, Graph Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4
 MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
Networks and Graphs: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures VII.A Student Activity Sheet 1: Euler Circuits and Paths
 The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
Networks and Graphs: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures VII.A Student Activity Sheet 1: Euler Circuits and Paths
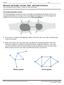 The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
14.2 Euler Paths and Circuits filled in.notebook November 18, Euler Paths and Euler Circuits
 14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III
 1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
An Introduction to Graph Theory
 An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
Graph Theory. 26 March Graph Theory 26 March /29
 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
MA 111 Review for Exam 3
 MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
Graph Theory
 Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Young Won Lim 4/26/18
 Eulerian Cycle (2A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any
#30: Graph theory May 25, 2009
 #30: Graph theory May 25, 2009 Graph theory is the study of graphs. But not the kind of graphs you are used to, like a graph of y = x 2 graph theory graphs are completely different from graphs of functions.
#30: Graph theory May 25, 2009 Graph theory is the study of graphs. But not the kind of graphs you are used to, like a graph of y = x 2 graph theory graphs are completely different from graphs of functions.
How can we lay cable at minimum cost to make every telephone reachable from every other? What is the fastest route between two given cities?
 1 Introduction Graph theory is one of the most in-demand (i.e. profitable) and heavily-studied areas of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. May graph theory questions are applied in this
1 Introduction Graph theory is one of the most in-demand (i.e. profitable) and heavily-studied areas of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. May graph theory questions are applied in this
Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths
 Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths For Next Time. Read Section 6.1 Circuit Training (p. 386ff) for more background on this material. Review the definition of a graph. Make sure you understand
Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths For Next Time. Read Section 6.1 Circuit Training (p. 386ff) for more background on this material. Review the definition of a graph. Make sure you understand
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Simple Graph. General Graph
 Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
An Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory
 An Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory An Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory Chris K. Caldwell 1995 This the first of a series of interactive tutorials introducing the basic concepts of graph
An Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory An Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory Chris K. Caldwell 1995 This the first of a series of interactive tutorials introducing the basic concepts of graph
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Introduction to Graphs
 Introduction to Graphs Historical Motivation Seven Bridges of Königsberg Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia) around 1735 Problem: Find a walk through the city that would cross each bridge once and only
Introduction to Graphs Historical Motivation Seven Bridges of Königsberg Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia) around 1735 Problem: Find a walk through the city that would cross each bridge once and only
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
6.2. Paths and Cycles
 6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees. March 23, 2008
 Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Graph Theory CS/Math231 Discrete Mathematics Spring2015
 1 Graphs Definition 1 A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set and E is a binary relation on V. The set V is called the vertex set of G, and its elements are called vertices
1 Graphs Definition 1 A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set and E is a binary relation on V. The set V is called the vertex set of G, and its elements are called vertices
Vertex-Edge Graphs. Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards. Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University
 Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. 24 and 26 October, 2018
 (1/32) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 24 and 26 October, 2018 1 Graph theory A network of mathematicians Water-Electricity-Broadband
(1/32) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 24 and 26 October, 2018 1 Graph theory A network of mathematicians Water-Electricity-Broadband
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles
 14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
Brief History. Graph Theory. What is a graph? Types of graphs Directed graph: a graph that has edges with specific directions
 Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Displaying Data with Graphs. Chapter 6 Mathematics of Data Management (Nelson) MDM 4U
 Displaying Data with Graphs Chapter 6 Mathematics of Data Management (Nelson) MDM 4U Cause and Effect Diagrams Developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in 1943 (Japan) Picture composed of lines and symbols designed
Displaying Data with Graphs Chapter 6 Mathematics of Data Management (Nelson) MDM 4U Cause and Effect Diagrams Developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in 1943 (Japan) Picture composed of lines and symbols designed
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs
 Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Characterization of Graphs with Eulerian Circuits
 Eulerian Circuits 3. 73 Characterization of Graphs with Eulerian Circuits There is a simple way to determine if a graph has an Eulerian circuit. Theorems 3.. and 3..2: Let G be a pseudograph that is connected
Eulerian Circuits 3. 73 Characterization of Graphs with Eulerian Circuits There is a simple way to determine if a graph has an Eulerian circuit. Theorems 3.. and 3..2: Let G be a pseudograph that is connected
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles
 Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles By Adam Sheffer The Bridges of Königsberg Can we travel the city while crossing every bridge exactly once? 1 How Graph Theory was Born Leonhard Euler 1736 Eulerian Cycle
Ma/CS 6a Class 8: Eulerian Cycles By Adam Sheffer The Bridges of Königsberg Can we travel the city while crossing every bridge exactly once? 1 How Graph Theory was Born Leonhard Euler 1736 Eulerian Cycle
FINDING THE RIGHT PATH
 Task 1: Seven Bridges of Konigsberg! Today we are going to begin with the story of Konigsberg in the 18 th century, its geography, bridges, and the question asked by its citizens. FINDING THE RIGHT PATH
Task 1: Seven Bridges of Konigsberg! Today we are going to begin with the story of Konigsberg in the 18 th century, its geography, bridges, and the question asked by its citizens. FINDING THE RIGHT PATH
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
EECS 203 Lecture 20. More Graphs
 EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
WUCT121. Discrete Mathematics. Graphs
 WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Graphs WUCT121 Graphs 1 Section 1. Graphs 1.1. Introduction Graphs are used in many fields that require analysis of routes between locations. These areas include communications,
WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Graphs WUCT121 Graphs 1 Section 1. Graphs 1.1. Introduction Graphs are used in many fields that require analysis of routes between locations. These areas include communications,
Unit 7 Day 2 Section Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths
 Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Graph Theory. 1 Introduction to Graphs. Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC January 26, 2011
 Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 15 and 17 November, 2017
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition. Chapter 5 Euler Circuits. The Circuit Comes to Town. Peter Tannenbaum
 Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
Introduction to Networks
 LESSON 1 Introduction to Networks Exploratory Challenge 1 One classic math puzzle is the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem which laid the foundation for networks and graph theory. In the 18th century
LESSON 1 Introduction to Networks Exploratory Challenge 1 One classic math puzzle is the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem which laid the foundation for networks and graph theory. In the 18th century
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm
 Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk):describes a route from one vertex
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk):describes a route from one vertex
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
Pre-Calculus. Slide 1 / 192. Slide 2 / 192. Slide 3 / 192. Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Pre-Calculus Slide 2 / 192 Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Slide 1 / 192 Pre-Calculus Slide 2 / 192 Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Pre-Calculus Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
Pre-Calculus. Introduction to Matrices. Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192. Slide 3 / 192. Slide 4 / 192. Slide 6 / 192. Slide 5 / 192. Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology
 MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Winter Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction to Topology 2 Topology and Childrens Drawings 3 Networks 4 Conclusion Geometric Topology
MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Winter Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction to Topology 2 Topology and Childrens Drawings 3 Networks 4 Conclusion Geometric Topology
Undirected Network Summary
 Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours.
 Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours. CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 11 (B00), Day 7 (A00) February 3, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Exam Announcements Seating Chart on Website Good
Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours. CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 11 (B00), Day 7 (A00) February 3, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Exam Announcements Seating Chart on Website Good
Questions? You are given the complete graph of Facebook. What questions would you ask? (What questions could we hope to answer?)
 P vs. NP What now? Attribution These slides were prepared for the New Jersey Governor s School course The Math Behind the Machine taught in the summer of 2011 by Grant Schoenebeck Large parts of these
P vs. NP What now? Attribution These slides were prepared for the New Jersey Governor s School course The Math Behind the Machine taught in the summer of 2011 by Grant Schoenebeck Large parts of these
Euler and Hamilton paths. Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas
 Euler and Hamilton paths Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas 1 Paths and the adjacency matrix The powers of the adjacency matrix A r (with normal, not boolean multiplication) contain the number
Euler and Hamilton paths Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas 1 Paths and the adjacency matrix The powers of the adjacency matrix A r (with normal, not boolean multiplication) contain the number
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13. An Introduction to Graphs
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
08. First and second degree equations
 08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006
 Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006 THE KIT: This kit contains materials for two Instant Insanity games, a student activity sheet with answer key and this instructor
Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006 THE KIT: This kit contains materials for two Instant Insanity games, a student activity sheet with answer key and this instructor
Logic: The Big Picture. Axiomatizing Arithmetic. Tautologies and Valid Arguments. Graphs and Trees
 Axiomatizing Arithmetic Logic: The Big Picture Suppose we restrict the domain to the natural numbers, and allow only the standard symbols of arithmetic (+,, =, >, 0, 1). Typical true formulas include:
Axiomatizing Arithmetic Logic: The Big Picture Suppose we restrict the domain to the natural numbers, and allow only the standard symbols of arithmetic (+,, =, >, 0, 1). Typical true formulas include:
2. Line up the digits from 1 to 9 so that any two digit number made of two adjacent digits is divisible by either 7 or 13.
 Graphs Graphs. Part 1 In some situations it is convenient to use graphs. Objects are represented by dots while connections between them are represented by lines or arrows. In the language of graphs, dots
Graphs Graphs. Part 1 In some situations it is convenient to use graphs. Objects are represented by dots while connections between them are represented by lines or arrows. In the language of graphs, dots
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY. 1. Definitions
 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
Born in Tulsa in 1914 and passed away in Norman in 2010.
 Sooner Math Bowl 2012 November 15, 2012 Photo Martin Gardner by Alex Bellos in 2008 in Norman Born in Tulsa in 1914 and passed away in Norman in 2010. 1 Stage 1 2 Stage 1, Round 1 (2 Questions, 3 Minutes)
Sooner Math Bowl 2012 November 15, 2012 Photo Martin Gardner by Alex Bellos in 2008 in Norman Born in Tulsa in 1914 and passed away in Norman in 2010. 1 Stage 1 2 Stage 1, Round 1 (2 Questions, 3 Minutes)
Graphs And Algorithms
 Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Graphs. Reading Assignment. Mandatory: Chapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2. Peeking into Computer Science. Jalal Kawash 2010
 Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
Eulerian tours. Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck. April 20, 2016
 Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
CS70 - Lecture 6. Graphs: Coloring; Special Graphs. 1. Review of L5 2. Planar Five Color Theorem 3. Special Graphs:
 CS70 - Lecture 6 Graphs: Coloring; Special Graphs 1. Review of L5 2. Planar Five Color Theorem 3. Special Graphs: Trees: Three characterizations Hypercubes: Strongly connected! Administration You need
CS70 - Lecture 6 Graphs: Coloring; Special Graphs 1. Review of L5 2. Planar Five Color Theorem 3. Special Graphs: Trees: Three characterizations Hypercubes: Strongly connected! Administration You need
Graphs II: Trailblazing
 Graphs II: Trailblazing Paths In an undirected graph, a path of length n from u to v, where n is a positive integer, is a sequence of edges e 1,, e n of the graph such that f(e 1 )={x 0,x 1 }, f(e 2 )={x
Graphs II: Trailblazing Paths In an undirected graph, a path of length n from u to v, where n is a positive integer, is a sequence of edges e 1,, e n of the graph such that f(e 1 )={x 0,x 1 }, f(e 2 )={x
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 192 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 192 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Graph Theory. Defining a Graph
 Graph Theory This topic is one of the most applicable to real-life applications because all networks (computer, transportation, communication, organizational, etc.) can be represented with a graph. For
Graph Theory This topic is one of the most applicable to real-life applications because all networks (computer, transportation, communication, organizational, etc.) can be represented with a graph. For
11-5 Networks. Königsberg Bridge Problem
 Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Euler and Hamilton circuits. Euler paths and circuits
 1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 3, 2008 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 3, 2008 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Graph Theory Problems Instructor: Natalya St. Clair. 1 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg Problem
 Graph Theory Problems erkeley Math ircles 2015 Lecture Notes Graph Theory Problems Instructor: Natalya St. lair 1 The Seven ridges of Königsberg Problem Königsberg is an ancient city of Prussia, now Kalingrad,
Graph Theory Problems erkeley Math ircles 2015 Lecture Notes Graph Theory Problems Instructor: Natalya St. lair 1 The Seven ridges of Königsberg Problem Königsberg is an ancient city of Prussia, now Kalingrad,
Varying Applications (examples)
 Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Walking with Euler through Ostpreußen and RNA
 Walking with Euler through Ostpreußen and RNA Mark Muldoon February 4, 2010 Königsberg (1652) Kaliningrad (2007)? The Königsberg Bridge problem asks whether it is possible to walk around the old city in
Walking with Euler through Ostpreußen and RNA Mark Muldoon February 4, 2010 Königsberg (1652) Kaliningrad (2007)? The Königsberg Bridge problem asks whether it is possible to walk around the old city in
Graph Theory. Part of Texas Counties.
 Graph Theory Part of Texas Counties. We would like to visit each of the above counties, crossing each county only once, starting from Harris county. Is this possible? This problem can be modeled as a graph.
Graph Theory Part of Texas Counties. We would like to visit each of the above counties, crossing each county only once, starting from Harris county. Is this possible? This problem can be modeled as a graph.
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
Introduction III. Graphs. Motivations I. Introduction IV
 Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes
 Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Chapter 1. Urban Services. Chapter Outline. Chapter Summary
 Chapter 1 Urban Services Chapter Outline Introduction Section 1.1 Euler Circuits Section 1.2 Finding Euler Circuits Section 1.3 Beyond Euler Circuits Section 1.4 Urban Graph Traversal Problems Chapter
Chapter 1 Urban Services Chapter Outline Introduction Section 1.1 Euler Circuits Section 1.2 Finding Euler Circuits Section 1.3 Beyond Euler Circuits Section 1.4 Urban Graph Traversal Problems Chapter
Launch problem: Lining streets
 Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
Study Guide Mods: Date:
 Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Using Euler s Theorem
 Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around
 Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers
 Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers Bilkent University, Laurence Barker, 19 October 2017 Do not forget to justify your answers in terms which could be understood by people who know the background theory
Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers Bilkent University, Laurence Barker, 19 October 2017 Do not forget to justify your answers in terms which could be understood by people who know the background theory
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm
 Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering. Qian Zhu 2/23/2011
 Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Math 311. Trees Name: A Candel CSUN Math
 1. A simple path in a graph is a path with no repeated edges. A simple circuit is a circuit without repeated edges. 2. Trees are special kinds of graphs. A tree is a connected graph with no simple circuits.
1. A simple path in a graph is a path with no repeated edges. A simple circuit is a circuit without repeated edges. 2. Trees are special kinds of graphs. A tree is a connected graph with no simple circuits.
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 21 and 23 November, 2018
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
