Part II: Data Center Software Architecture: Topic 2: Key-value Data Management Systems. SkimpyStash: Key Value Store on Flash-based Storage
|
|
|
- Rosanna Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part II: Data Center Software Architecture: Topic 2: Key-value Data Management Systems SkimpyStash: Key Value Store on Flash-based Storage Presented by Aravind Mohan
2 Distinct Features Designed for High Throughput and Low Latency server applications. Low RAM at about 1 byte per key value pair, scale key-value stores on Flash on a lean RAM size budget. Implemented by using the Hash table directory in RAM to index (K,V) pairs stored in a log structured manner in Flash. Move most of the pointers that locate each key-value pair from RAM to Flash itself. (Break barrier of Flash pointer 4 bytes worth of RAM)
3 Background Server side applications require persistent and high throughput key-value stores to function. Flash Memory using Solid state devices getting popular in Desktop and Server applications.
4 Background MySpace.com switched from hard disk to flash storage as primary storage for data center operations. Facebook release Flash Cache by caching data in SSDs for faster read and writes. Challenges of Flash memory can be addressed by two approaches: 1)Device driver software level inside the device. 2)Operating system level. (SkimpyStash uses app 2) To get maximum benefit out of SSDs it is required to use Flash aware data structures and algorithms. Example Avoid random writes high latency and reduce Flash device life time through increased page wearing.
5 Contribution Design Innovation: Move pointers to Flash to break flash pointer barrier. It is implemented by 1) Resolving hash table collisions by linear chaining where multiple keys that collide to the same hash table buckets are chained in a linked list. 2) Storing linked list on Flash with a pointer in each hash table bucket in RAM pointing to the beginning record of the chain on flash. (Multiple flash reads per lookup) 3) Two-choice based load balancing. At most one bucket chain on flash needs to be searched during a lookup. 4) Compaction procedures to pack bucket chain records contiguously onto the flash pages.
6 Contribution Evaluation on data center server applications: SkimpyStash can be used as a high throughput persistent key-value storage layer for many server side applications. Real world use cases: Xbox LIVE Primitive online multi player games, Inline storage deduplication. SkimpyStash provides throughputs from few 10,000s to upwards of 100,000 get-set operations/sec on the evaluated applications.
7 Flash Memory Advantages: Fast read operations for both random and sequential read operations. (No mechanical head movement). Disadvantage: Does not allow in-place update(overwrites). Write performed after Erase In-place update problem: Write performed in pages granularity, erase performed in Block granularity. Read 25 us Write 200 us Erase 1500 us Block Pages
8 FTL Flash transition layer (FTL) is an intermediate software inside SSD makes linear flash memory device act like virtual disk. Logical read Flash memory commands Logical write Mapping physical pages and logical pages, flag current physical page for garbage collection. Flash block can be erased for limited no of times. Effective for sequential access and show poor Performance for random access.
9 Key Value Store Use Cases Online multi player gaming: Requirement: To scale multiple users per game To scale multiple game instances run thru online service To persist the server side game state. (Resume from interrupted state, offline analysis, verification of player action). Set and Get key operation impacts the response time and Throughput. Deduplication: Eliminate redundancy of data across full and incremental backup.
10 Key Value Store Use Cases Requirement: To scale tens of terabytes to petabytes of data volume. To provide high throughput (Disk storage fails) and inline storage deduplication system is desired. Chunk hash index is too big to fit in RAM. Existing solutions do not offer much performance than lookup hitting in RAM. SkimpyStash can be used as chunk hash index for inline deduplication systems. Serving lookups from flash memory.
11 SkimpyStash Design. Flash Constraints: Random Write Random writes need to update the data portions within pages. (New physical pages need to be created and data movement). Write less than flash page size Writing an amount less than the page size, leads to unwanted page wasting. SkimpyStash Components: RAM Write Buffer Buffer (K,V) writes before writing to flash. (Avoid wasting pages 2 or 4 KB in size) RAM Hash Table(HT) Directory (K,V) contains a pointer to the next record and hence chaining.
12 SkimpyStash Design. Two-choice based load balancing to reduce wide variation in bucket sizes (hence, chain lengths and associated lookup times). Bloom filter in each hash table directory slot in RAM for summarizing the records in that bucket so that at most one bucket chain on flash needs to be searched during a lookup. Flash Store -- Persistent storage for the key,value pairs. Circular append log. Writes are inserted to the tail of the log. Garbage recycled from the head of the log. Valid entries moved back to the tail of the log.
13 SkimpyStash Design.
14 SkimpyStash Operations Key Lookup(Get) First lookup the RAM write buffer. If there is a Miss then lookup the HT directory and search the linked list in Flash in respective bucket. Key Insert(Set) First write to the RAM write buffer. When write buffer threshold occurs, at configurable time interval, entries in Write buffer are written to Flash and inserted into RAM HT directory. Delete Insertion of null value for the key. Garbage collector comes into action eventually.
15 HT Directory Design RAM Overhead in FAWN and ChunkStash is 6 bytes. SkimpyStash reduces the overhead to 4 bytes by moving most of the pointers to (K,V) to Flash itself. Multiple Flash reads upon lookup of a key. (Because of chain of key,value pairs in a bucket) This tradeoff is needed to avoid RAM Overhead. Average no of keys in a bucket (k) is used as a parameter to control the tradeoff factor.
16 Base Design Map Function(h) maps keys to slots in HT. Avg no of records in a bucket = k. Accommodate n key value pairs we need n/k slots in Hash Table. For example let us assume k = 4 and n =16 then we have: (4 slots) HT Buckets `
17 HT Directory Design Lookup operation Hash function h is used to obtain the bucket and the pointer in the slot is followed to chain of records to find the key. Avg Case flash read (k/2) Worst case (size of bucket) Insert operation Hash function h is used to obtain the bucket and the new record is inserted into the head of the linked list. (New records always in the beginning of the list, old records are in the end of the list) Delete Operation Same as Lookup and Insert with null values for the key
18 HT Directory Design RAM Overhead in FAWN and ChunkStash is 6 bytes. SkimpyStash reduces the overhead to 4 bytes by moving most of the pointers to (K,V) to Flash itself. Multiple Flash reads upon lookup of a key. (Because of chain of key,value pairs in a bucket) This tradeoff is needed to avoid RAM Overhead. Average no of keys in a bucket (k) is used as a parameter to control the tradeoff factor.
19 Load Balancing across Buckets Maintain bucket chain of same size (Avoid Skewing). Power of two choice idea. Each key would be hashed to two candidate buckets. Two hash functions h1 and h2 used but actual insert is done into the bucket that has fewer elements. Load balancing is implemented by adding 1 byte of storage to each slot in HT.
20 Bloom Filter Mechanism Lookup in both candidate buckets is a bottleneck. (As number of flash reads doubles.) Bloom filter added per each HT slot to summarize keys inserted into each bucket. (1 byte/key) Lookup Search buckets only if the bloom filter associated with the bucket indicates key exist. Insert Records inserted into the same bucket as early one. (Do not follow the load balancing strategy as it goes against the design principles.) In short it reduce variations in the the number of keys assigned to each bucket (hence, chain lengths and associated lookup times).
21 Compaction Mechanism Bucket size is inversely proportional to that of the Lookup time. Compacting the chain on a flash in a bucket by placing valid keys contiguously in more than on page. If m (K,V) pairs can be Packed in one page, no of flash reads in a bucket of k records is (k/2m) average case and (k/m) -- worst case
22 Garbage Collection Mechanism Garbage records (holes) accumulate in the log as a result of compaction and key update/delete operations. When a certain threshold of garbage accumulates, cleaning operation is performed to clean and compact the logs. Scan Lookup HT match match Valid Invalid
23 Summary SkimpyStash is used as high throughput persistent key-value storage layer for a broad range of server class applications. Low RAM footprint at about 1 byte per key-value pair, which is more aggressive than earlier designs. Evaluation done in real world datasets from Xbox LIVE Primetime online multi-player game and inline storage dedu- plication
24 Questions How is SkimpyStash design useful? Refer section 3.1 and 3.2 What are the different operations permitted in SkimpyStash and how are they implemented? Refer section 4.4 What is the Base deign of Hash Table? How does the based deign improved in this paper to address the challenges in Base Design? Refer section 4.5
25 Questions (1) What s advantage and disadvantage of the design that only keeps a hash table directory in RAM and moving the hash table buckets to the flash? (Section 1 Our Contribution ) (2) What s the issue that the Power of two choice idea is adopted to address? What s the issue Bloom Filter is adopted to address? Provide a few specifics on how the two issues are addressed respectively. (Section 4.5 Load Balancing across Buckets and Bloom Filter per Bucket )
Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture PRESENTATION REPORT Semester: Winter 2015 Course: ECE 7650
 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture PRESENTATION REPORT Semester: Winter 2015 Course: ECE 7650 SUBMITTED BY: Yashwanth Boddu fq9316@wayne.edu (1) Our base design uses less than 1 byte
Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture PRESENTATION REPORT Semester: Winter 2015 Course: ECE 7650 SUBMITTED BY: Yashwanth Boddu fq9316@wayne.edu (1) Our base design uses less than 1 byte
Speeding Up Cloud/Server Applications Using Flash Memory
 Speeding Up Cloud/Server Applications Using Flash Memory Sudipta Sengupta and Jin Li Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA Contains work that is joint with Biplob Debnath (Univ. of Minnesota) Flash Memory
Speeding Up Cloud/Server Applications Using Flash Memory Sudipta Sengupta and Jin Li Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA Contains work that is joint with Biplob Debnath (Univ. of Minnesota) Flash Memory
ChunkStash: Speeding Up Storage Deduplication using Flash Memory
 ChunkStash: Speeding Up Storage Deduplication using Flash Memory Biplob Debnath +, Sudipta Sengupta *, Jin Li * * Microsoft Research, Redmond (USA) + Univ. of Minnesota, Twin Cities (USA) Deduplication
ChunkStash: Speeding Up Storage Deduplication using Flash Memory Biplob Debnath +, Sudipta Sengupta *, Jin Li * * Microsoft Research, Redmond (USA) + Univ. of Minnesota, Twin Cities (USA) Deduplication
20-EECE-4029 Operating Systems Spring, 2013 John Franco
 20-EECE-4029 Operating Systems Spring, 2013 John Franco Second Exam name: Question 1: Translation Look-aside Buffer (a) Describe the TLB. Include its location, why it is located there, its contents, and
20-EECE-4029 Operating Systems Spring, 2013 John Franco Second Exam name: Question 1: Translation Look-aside Buffer (a) Describe the TLB. Include its location, why it is located there, its contents, and
BloomStore: Bloom-Filter based Memory-efficient Key-Value Store for Indexing of Data Deduplication on Flash
 BloomStore: Bloom-Filter based Memory-efficient Key-Value Store for Indexing of Data Deduplication on Flash Guanlin Lu EMC 2 Santa Clara, CA Guanlin.Lu@emc.com Young Jin Nam Daegu University Gyeongbuk,
BloomStore: Bloom-Filter based Memory-efficient Key-Value Store for Indexing of Data Deduplication on Flash Guanlin Lu EMC 2 Santa Clara, CA Guanlin.Lu@emc.com Young Jin Nam Daegu University Gyeongbuk,
Optimizing Flash-based Key-value Cache Systems
 Optimizing Flash-based Key-value Cache Systems Zhaoyan Shen, Feng Chen, Yichen Jia, Zili Shao Department of Computing, Hong Kong Polytechnic University Computer Science & Engineering, Louisiana State University
Optimizing Flash-based Key-value Cache Systems Zhaoyan Shen, Feng Chen, Yichen Jia, Zili Shao Department of Computing, Hong Kong Polytechnic University Computer Science & Engineering, Louisiana State University
SILT: A MEMORY-EFFICIENT, HIGH-PERFORMANCE KEY- VALUE STORE PRESENTED BY PRIYA SRIDHAR
 SILT: A MEMORY-EFFICIENT, HIGH-PERFORMANCE KEY- VALUE STORE PRESENTED BY PRIYA SRIDHAR AGENDA INTRODUCTION Why SILT? MOTIVATION SILT KV STORAGE SYSTEM LOW READ AMPLIFICATION CONTROLLABLE WRITE AMPLIFICATION
SILT: A MEMORY-EFFICIENT, HIGH-PERFORMANCE KEY- VALUE STORE PRESENTED BY PRIYA SRIDHAR AGENDA INTRODUCTION Why SILT? MOTIVATION SILT KV STORAGE SYSTEM LOW READ AMPLIFICATION CONTROLLABLE WRITE AMPLIFICATION
BUFFER HASH KV TABLE
 BUFFER HASH KV TABLE CHEAP AND LARGE CAMS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE DATA-INTENSIVE NETWORKED SYSTEMS PAPER BY ASHOK ANAND, CHITRA MUTHUKRISHNAN, STEVEN KAPPES, ADITYA AKELLA AND SUMAN NATH PRESENTED BY PRAMOD
BUFFER HASH KV TABLE CHEAP AND LARGE CAMS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE DATA-INTENSIVE NETWORKED SYSTEMS PAPER BY ASHOK ANAND, CHITRA MUTHUKRISHNAN, STEVEN KAPPES, ADITYA AKELLA AND SUMAN NATH PRESENTED BY PRAMOD
Cheap and Large CAMs for High Performance Data-Intensive Networked Systems- The Bufferhash KV Store
 Cheap and Large CAMs for High Performance Data-Intensive Networked Systems- The Bufferhash KV Store Presented by Akhila Nookala M.S EE Wayne State University ECE7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services
Cheap and Large CAMs for High Performance Data-Intensive Networked Systems- The Bufferhash KV Store Presented by Akhila Nookala M.S EE Wayne State University ECE7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services
A Caching-Oriented FTL Design for Multi-Chipped Solid-State Disks. Yuan-Hao Chang, Wei-Lun Lu, Po-Chun Huang, Lue-Jane Lee, and Tei-Wei Kuo
 A Caching-Oriented FTL Design for Multi-Chipped Solid-State Disks Yuan-Hao Chang, Wei-Lun Lu, Po-Chun Huang, Lue-Jane Lee, and Tei-Wei Kuo 1 June 4, 2011 2 Outline Introduction System Architecture A Multi-Chipped
A Caching-Oriented FTL Design for Multi-Chipped Solid-State Disks Yuan-Hao Chang, Wei-Lun Lu, Po-Chun Huang, Lue-Jane Lee, and Tei-Wei Kuo 1 June 4, 2011 2 Outline Introduction System Architecture A Multi-Chipped
File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4. COMP3231 Operating Systems
 File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4 COMP3231 Operating Systems Architecture of the OS storage stack Application File system: Hides physical location of data on the disk Exposes: directory hierarchy,
File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4 COMP3231 Operating Systems Architecture of the OS storage stack Application File system: Hides physical location of data on the disk Exposes: directory hierarchy,
The What, Why and How of the Pure Storage Enterprise Flash Array. Ethan L. Miller (and a cast of dozens at Pure Storage)
 The What, Why and How of the Pure Storage Enterprise Flash Array Ethan L. Miller (and a cast of dozens at Pure Storage) Enterprise storage: $30B market built on disk Key players: EMC, NetApp, HP, etc.
The What, Why and How of the Pure Storage Enterprise Flash Array Ethan L. Miller (and a cast of dozens at Pure Storage) Enterprise storage: $30B market built on disk Key players: EMC, NetApp, HP, etc.
Part II: Software Infrastructure in Data Centers: Key-Value Data Management Systems
 ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part II: Software Infrastructure in Data Centers: Key-Value Data Management Systems 1 Key-Value Store Clients
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part II: Software Infrastructure in Data Centers: Key-Value Data Management Systems 1 Key-Value Store Clients
Foster B-Trees. Lucas Lersch. M. Sc. Caetano Sauer Advisor
 Foster B-Trees Lucas Lersch M. Sc. Caetano Sauer Advisor 14.07.2014 Motivation Foster B-Trees Blink-Trees: multicore concurrency Write-Optimized B-Trees: flash memory large-writes wear leveling defragmentation
Foster B-Trees Lucas Lersch M. Sc. Caetano Sauer Advisor 14.07.2014 Motivation Foster B-Trees Blink-Trees: multicore concurrency Write-Optimized B-Trees: flash memory large-writes wear leveling defragmentation
C13: Files and Directories: System s Perspective
 CISC 7310X C13: Files and Directories: System s Perspective Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 4/19/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 File Systems: Requirements Long
CISC 7310X C13: Files and Directories: System s Perspective Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 4/19/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 File Systems: Requirements Long
Chapter 11: File System Implementation. Objectives
 Chapter 11: File System Implementation Objectives To describe the details of implementing local file systems and directory structures To describe the implementation of remote file systems To discuss block
Chapter 11: File System Implementation Objectives To describe the details of implementing local file systems and directory structures To describe the implementation of remote file systems To discuss block
Memory management. Last modified: Adaptation of Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne slides for the textbook Applied Operating Systems Concepts
 Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
File System Interface and Implementation
 Unit 8 Structure 8.1 Introduction Objectives 8.2 Concept of a File Attributes of a File Operations on Files Types of Files Structure of File 8.3 File Access Methods Sequential Access Direct Access Indexed
Unit 8 Structure 8.1 Introduction Objectives 8.2 Concept of a File Attributes of a File Operations on Files Types of Files Structure of File 8.3 File Access Methods Sequential Access Direct Access Indexed
Integrating Flash Memory into the Storage Hierarchy
 Integrating Flash Memory into the Storage Hierarchy A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Biplob Kumar Debnath IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Integrating Flash Memory into the Storage Hierarchy A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Biplob Kumar Debnath IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Main Memory (Part II)
 Main Memory (Part II) Amir H. Payberah amir@sics.se Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Main Memory 1393/8/17 1 / 50 Reminder Amir H. Payberah
Main Memory (Part II) Amir H. Payberah amir@sics.se Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Main Memory 1393/8/17 1 / 50 Reminder Amir H. Payberah
Physical Disk Structure. Physical Data Organization and Indexing. Pages and Blocks. Access Path. I/O Time to Access a Page. Disks.
 Physical Disk Structure Physical Data Organization and Indexing Chapter 11 1 4 Access Path Refers to the algorithm + data structure (e.g., an index) used for retrieving and storing data in a table The
Physical Disk Structure Physical Data Organization and Indexing Chapter 11 1 4 Access Path Refers to the algorithm + data structure (e.g., an index) used for retrieving and storing data in a table The
Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems. Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,
 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods
Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods
Database Technology. Topic 7: Data Structures for Databases. Olaf Hartig.
 Topic 7: Data Structures for Databases Olaf Hartig olaf.hartig@liu.se Database System 2 Storage Hierarchy Traditional Storage Hierarchy CPU Cache memory Main memory Primary storage Disk Tape Secondary
Topic 7: Data Structures for Databases Olaf Hartig olaf.hartig@liu.se Database System 2 Storage Hierarchy Traditional Storage Hierarchy CPU Cache memory Main memory Primary storage Disk Tape Secondary
EI 338: Computer Systems Engineering (Operating Systems & Computer Architecture)
 EI 338: Computer Systems Engineering (Operating Systems & Computer Architecture) Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Chentao Wu wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn User:
EI 338: Computer Systems Engineering (Operating Systems & Computer Architecture) Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Chentao Wu wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn User:
SILT: A Memory-Efficient, High- Performance Key-Value Store
 SILT: A Memory-Efficient, High- Performance Key-Value Store SOSP 11 Presented by Fan Ni March, 2016 SILT is Small Index Large Tables which is a memory efficient high performance key value store system
SILT: A Memory-Efficient, High- Performance Key-Value Store SOSP 11 Presented by Fan Ni March, 2016 SILT is Small Index Large Tables which is a memory efficient high performance key value store system
Cascade Mapping: Optimizing Memory Efficiency for Flash-based Key-value Caching
 Cascade Mapping: Optimizing Memory Efficiency for Flash-based Key-value Caching Kefei Wang and Feng Chen Louisiana State University SoCC '18 Carlsbad, CA Key-value Systems in Internet Services Key-value
Cascade Mapping: Optimizing Memory Efficiency for Flash-based Key-value Caching Kefei Wang and Feng Chen Louisiana State University SoCC '18 Carlsbad, CA Key-value Systems in Internet Services Key-value
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems. Lecture 23 File System Implementation II (Allocation Methods, Free-Space Management) Summer 2018
 CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 23 File System Implementation II (Allocation Methods, Free-Space Management) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To discuss how the disk is managed for a
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 23 File System Implementation II (Allocation Methods, Free-Space Management) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To discuss how the disk is managed for a
Hashing Techniques. Material based on slides by George Bebis
 Hashing Techniques Material based on slides by George Bebis https://www.cse.unr.edu/~bebis/cs477/lect/hashing.ppt The Search Problem Find items with keys matching a given search key Given an array A, containing
Hashing Techniques Material based on slides by George Bebis https://www.cse.unr.edu/~bebis/cs477/lect/hashing.ppt The Search Problem Find items with keys matching a given search key Given an array A, containing
Chapter 12: File System Implementation
 Chapter 12: File System Implementation Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management
Chapter 12: File System Implementation Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 11: File System Implementation Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) File-System Structure File structure Logical storage unit Collection
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 11: File System Implementation Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) File-System Structure File structure Logical storage unit Collection
Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies
 Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
Open-Channel SSDs Offer the Flexibility Required by Hyperscale Infrastructure Matias Bjørling CNEX Labs
 Open-Channel SSDs Offer the Flexibility Required by Hyperscale Infrastructure Matias Bjørling CNEX Labs 1 Public and Private Cloud Providers 2 Workloads and Applications Multi-Tenancy Databases Instance
Open-Channel SSDs Offer the Flexibility Required by Hyperscale Infrastructure Matias Bjørling CNEX Labs 1 Public and Private Cloud Providers 2 Workloads and Applications Multi-Tenancy Databases Instance
Scalable Locking. Adam Belay
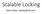 Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
A New Key-Value Data Store For Heterogeneous Storage Architecture
 A New Key-Value Data Store For Heterogeneous Storage Architecture brien.porter@intel.com wanyuan.yang@intel.com yuan.zhou@intel.com jian.zhang@intel.com Intel APAC R&D Ltd. 1 Agenda Introduction Background
A New Key-Value Data Store For Heterogeneous Storage Architecture brien.porter@intel.com wanyuan.yang@intel.com yuan.zhou@intel.com jian.zhang@intel.com Intel APAC R&D Ltd. 1 Agenda Introduction Background
Operating Systems Design Exam 2 Review: Spring 2011
 Operating Systems Design Exam 2 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 CPU utilization tends to be lower when: a. There are more processes in memory. b. There are fewer processes
Operating Systems Design Exam 2 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 CPU utilization tends to be lower when: a. There are more processes in memory. b. There are fewer processes
Secondary storage. CS 537 Lecture 11 Secondary Storage. Disk trends. Another trip down memory lane
 Secondary storage CS 537 Lecture 11 Secondary Storage Michael Swift Secondary storage typically: is anything that is outside of primary memory does not permit direct execution of instructions or data retrieval
Secondary storage CS 537 Lecture 11 Secondary Storage Michael Swift Secondary storage typically: is anything that is outside of primary memory does not permit direct execution of instructions or data retrieval
File Management By : Kaushik Vaghani
 File Management By : Kaushik Vaghani File Concept Access Methods File Types File Operations Directory Structure File-System Structure File Management Directory Implementation (Linear List, Hash Table)
File Management By : Kaushik Vaghani File Concept Access Methods File Types File Operations Directory Structure File-System Structure File Management Directory Implementation (Linear List, Hash Table)
Chapter 1 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing.
 Chapter 1 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing. Adapted from the slides of Fundamentals of Database Systems (Elmasri et al., 2003) 1 Chapter Outline Disk Storage Devices Files of Records Operations
Chapter 1 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing. Adapted from the slides of Fundamentals of Database Systems (Elmasri et al., 2003) 1 Chapter Outline Disk Storage Devices Files of Records Operations
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
CS 416: Opera-ng Systems Design March 23, 2012
 Question 1 Operating Systems Design Exam 2 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu CPU utilization tends to be lower when: a. There are more processes in memory. b. There are fewer processes
Question 1 Operating Systems Design Exam 2 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu CPU utilization tends to be lower when: a. There are more processes in memory. b. There are fewer processes
CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
 CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES OBJECTIVES Detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware Various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide
CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES OBJECTIVES Detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware Various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT. By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed.
 CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
Chapter 8: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
OPERATING SYSTEM. Chapter 12: File System Implementation
 OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 12: File System Implementation Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management
OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 12: File System Implementation Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
 What is File? A file is a collection of records where a record consists of one or more fields. Each contains the same sequence of fields. Each field is normally of fixed length. A sample file with four
What is File? A file is a collection of records where a record consists of one or more fields. Each contains the same sequence of fields. Each field is normally of fixed length. A sample file with four
Flash Memory Based Storage System
 Flash Memory Based Storage System References SmartSaver: Turning Flash Drive into a Disk Energy Saver for Mobile Computers, ISLPED 06 Energy-Aware Flash Memory Management in Virtual Memory System, islped
Flash Memory Based Storage System References SmartSaver: Turning Flash Drive into a Disk Energy Saver for Mobile Computers, ISLPED 06 Energy-Aware Flash Memory Management in Virtual Memory System, islped
Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems
 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems Operating System Concepts 99h Edition DM510-14 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation
Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems Operating System Concepts 99h Edition DM510-14 Chapter 11: Implementing File Systems File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 12: File System Implementation
 Chapter 12: File System Implementation Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management Efficiency
Chapter 12: File System Implementation Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods Free-Space Management Efficiency
Indexing: Overview & Hashing. CS 377: Database Systems
 Indexing: Overview & Hashing CS 377: Database Systems Recap: Data Storage Data items Records Memory DBMS Blocks blocks Files Different ways to organize files for better performance Disk Motivation for
Indexing: Overview & Hashing CS 377: Database Systems Recap: Data Storage Data items Records Memory DBMS Blocks blocks Files Different ways to organize files for better performance Disk Motivation for
Topics. File Buffer Cache for Performance. What to Cache? COS 318: Operating Systems. File Performance and Reliability
 Topics COS 318: Operating Systems File Performance and Reliability File buffer cache Disk failure and recovery tools Consistent updates Transactions and logging 2 File Buffer Cache for Performance What
Topics COS 318: Operating Systems File Performance and Reliability File buffer cache Disk failure and recovery tools Consistent updates Transactions and logging 2 File Buffer Cache for Performance What
pblk the OCSSD FTL Linux FAST Summit 18 Javier González Copyright 2018 CNEX Labs
 pblk the OCSSD FTL Linux FAST Summit 18 Javier González Read Latency Read Latency with 0% Writes Random Read 4K Percentiles 2 Read Latency Read Latency with 20% Writes Random Read 4K + Random Write 4K
pblk the OCSSD FTL Linux FAST Summit 18 Javier González Read Latency Read Latency with 0% Writes Random Read 4K Percentiles 2 Read Latency Read Latency with 20% Writes Random Read 4K + Random Write 4K
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing. Basic Concepts
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
IBM Spectrum NAS. Easy-to-manage software-defined file storage for the enterprise. Overview. Highlights
 IBM Spectrum NAS Easy-to-manage software-defined file storage for the enterprise Highlights Reduce capital expenditures with storage software on commodity servers Improve efficiency by consolidating all
IBM Spectrum NAS Easy-to-manage software-defined file storage for the enterprise Highlights Reduce capital expenditures with storage software on commodity servers Improve efficiency by consolidating all
Don t stack your Log on my Log
 Don t stack your Log on my Log Jingpei Yang, Ned Plasson, Greg Gillis, Nisha Talagala, Swaminathan Sundararaman Oct 5, 2014 c 1 Outline Introduction Log-stacking models Problems with stacking logs Solutions
Don t stack your Log on my Log Jingpei Yang, Ned Plasson, Greg Gillis, Nisha Talagala, Swaminathan Sundararaman Oct 5, 2014 c 1 Outline Introduction Log-stacking models Problems with stacking logs Solutions
SASS: A High-Performance Key-Value Store Design for Massive Hybrid Storage
 SASS: A High-Performance Key-Value Store Design for Massive Hybrid Storage Jiangtao Wang, Zhiliang Guo, and Xiaofeng Meng (B) School of Information, Renmin University of China, Beijing, China {jiangtaow,zhiliangguo,xfmen}@ruc.edu.cn
SASS: A High-Performance Key-Value Store Design for Massive Hybrid Storage Jiangtao Wang, Zhiliang Guo, and Xiaofeng Meng (B) School of Information, Renmin University of China, Beijing, China {jiangtaow,zhiliangguo,xfmen}@ruc.edu.cn
File Systems. ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring 2018
 File Systems ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring 2018 File Systems Abstract the interaction with important I/O devices Secondary storage (e.g. hard disks, flash drives) i.e.
File Systems ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring 2018 File Systems Abstract the interaction with important I/O devices Secondary storage (e.g. hard disks, flash drives) i.e.
Main Memory CHAPTER. Exercises. 7.9 Explain the difference between internal and external fragmentation. Answer:
 7 CHAPTER Main Memory Exercises 7.9 Explain the difference between internal and external fragmentation. a. Internal fragmentation is the area in a region or a page that is not used by the job occupying
7 CHAPTER Main Memory Exercises 7.9 Explain the difference between internal and external fragmentation. a. Internal fragmentation is the area in a region or a page that is not used by the job occupying
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL
Flash File Systems Overview
 Table of contents 1.0 Overview 3 1.1 Flash architecture 3 1.1.1 Partitions 3 1.1.2 Blocks 3 1.2 Programming data 3 1.3 Data integrity 4 2.0 Flash file system functions 4 2.1 Wear leveling 4 2.2 Reclaim
Table of contents 1.0 Overview 3 1.1 Flash architecture 3 1.1.1 Partitions 3 1.1.2 Blocks 3 1.2 Programming data 3 1.3 Data integrity 4 2.0 Flash file system functions 4 2.1 Wear leveling 4 2.2 Reclaim
Chapter 13 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing.
 Chapter 13 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Outline Disk Storage Devices Files of Records Operations on Files Unordered Files Ordered Files
Chapter 13 Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Outline Disk Storage Devices Files of Records Operations on Files Unordered Files Ordered Files
Chapter 13: Indexing. Chapter 13. ? value. Topics. Indexing & Hashing. value. Conventional indexes B-trees Hashing schemes (self-study) record
 Chapter 13: Indexing (Slides by Hector Garcia-Molina, http://wwwdb.stanford.edu/~hector/cs245/notes.htm) Chapter 13 1 Chapter 13 Indexing & Hashing value record? value Chapter 13 2 Topics Conventional
Chapter 13: Indexing (Slides by Hector Garcia-Molina, http://wwwdb.stanford.edu/~hector/cs245/notes.htm) Chapter 13 1 Chapter 13 Indexing & Hashing value record? value Chapter 13 2 Topics Conventional
From server-side to host-side:
 From server-side to host-side: Flash memory for enterprise storage Jiri Schindler et al. (see credits) Advanced Technology Group NetApp May 9, 2012 v 1.0 Data Centers with Flash SSDs iscsi/nfs/cifs Shared
From server-side to host-side: Flash memory for enterprise storage Jiri Schindler et al. (see credits) Advanced Technology Group NetApp May 9, 2012 v 1.0 Data Centers with Flash SSDs iscsi/nfs/cifs Shared
COS 318: Operating Systems. NSF, Snapshot, Dedup and Review
 COS 318: Operating Systems NSF, Snapshot, Dedup and Review Topics! NFS! Case Study: NetApp File System! Deduplication storage system! Course review 2 Network File System! Sun introduced NFS v2 in early
COS 318: Operating Systems NSF, Snapshot, Dedup and Review Topics! NFS! Case Study: NetApp File System! Deduplication storage system! Course review 2 Network File System! Sun introduced NFS v2 in early
NetApp Data Compression, Deduplication, and Data Compaction
 Technical Report NetApp Data Compression, Deduplication, and Data Compaction Data ONTAP 8.3.1 and Later Karthik Viswanath, NetApp February 2018 TR-4476 Abstract This technical report focuses on implementing
Technical Report NetApp Data Compression, Deduplication, and Data Compaction Data ONTAP 8.3.1 and Later Karthik Viswanath, NetApp February 2018 TR-4476 Abstract This technical report focuses on implementing
FlashCache. Mohan Srinivasan Mark Callaghan July 2010
 FlashCache Mohan Srinivasan Mark Callaghan July 2010 FlashCache at Facebook What We want to use some Flash storage on existing servers We want something that is simple to deploy and use Our IO access patterns
FlashCache Mohan Srinivasan Mark Callaghan July 2010 FlashCache at Facebook What We want to use some Flash storage on existing servers We want something that is simple to deploy and use Our IO access patterns
[537] Flash. Tyler Harter
![[537] Flash. Tyler Harter [537] Flash. Tyler Harter](/thumbs/92/108094213.jpg) [537] Flash Tyler Harter Flash vs. Disk Disk Overview I/O requires: seek, rotate, transfer Inherently: - not parallel (only one head) - slow (mechanical) - poor random I/O (locality around disk head) Random
[537] Flash Tyler Harter Flash vs. Disk Disk Overview I/O requires: seek, rotate, transfer Inherently: - not parallel (only one head) - slow (mechanical) - poor random I/O (locality around disk head) Random
Today s Papers. Array Reliability. RAID Basics (Two optional papers) EECS 262a Advanced Topics in Computer Systems Lecture 3
 EECS 262a Advanced Topics in Computer Systems Lecture 3 Filesystems (Con t) September 10 th, 2012 John Kubiatowicz and Anthony D. Joseph Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
EECS 262a Advanced Topics in Computer Systems Lecture 3 Filesystems (Con t) September 10 th, 2012 John Kubiatowicz and Anthony D. Joseph Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
1. a. Show that the four necessary conditions for deadlock indeed hold in this example.
 Tutorial 7 (Deadlocks) 1. a. Show that the four necessary conditions for deadlock indeed hold in this example. b. State a simple rule for avoiding deadlocks in this system. a. The four necessary conditions
Tutorial 7 (Deadlocks) 1. a. Show that the four necessary conditions for deadlock indeed hold in this example. b. State a simple rule for avoiding deadlocks in this system. a. The four necessary conditions
Asynchronous Logging and Fast Recovery for a Large-Scale Distributed In-Memory Storage
 Asynchronous Logging and Fast Recovery for a Large-Scale Distributed In-Memory Storage Kevin Beineke, Florian Klein, Michael Schöttner Institut für Informatik, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Outline
Asynchronous Logging and Fast Recovery for a Large-Scale Distributed In-Memory Storage Kevin Beineke, Florian Klein, Michael Schöttner Institut für Informatik, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Outline
Run-Time Environments/Garbage Collection
 Run-Time Environments/Garbage Collection Department of Computer Science, Faculty of ICT January 5, 2014 Introduction Compilers need to be aware of the run-time environment in which their compiled programs
Run-Time Environments/Garbage Collection Department of Computer Science, Faculty of ICT January 5, 2014 Introduction Compilers need to be aware of the run-time environment in which their compiled programs
DELL EMC DATA DOMAIN SISL SCALING ARCHITECTURE
 WHITEPAPER DELL EMC DATA DOMAIN SISL SCALING ARCHITECTURE A Detailed Review ABSTRACT While tape has been the dominant storage medium for data protection for decades because of its low cost, it is steadily
WHITEPAPER DELL EMC DATA DOMAIN SISL SCALING ARCHITECTURE A Detailed Review ABSTRACT While tape has been the dominant storage medium for data protection for decades because of its low cost, it is steadily
Memory Management william stallings, maurizio pizzonia - sistemi operativi
 Memory Management 1 summary goals and requirements techniques that do not involve virtual memory 2 memory management tracking used and free memory primitives allocation of a certain amount of memory de-allocation
Memory Management 1 summary goals and requirements techniques that do not involve virtual memory 2 memory management tracking used and free memory primitives allocation of a certain amount of memory de-allocation
System and Algorithmic Adaptation for Flash
 System and Algorithmic Adaptation for Flash The FAWN Perspective David G. Andersen, Vijay Vasudevan, Michael Kaminsky* Amar Phanishayee, Jason Franklin, Iulian Moraru, Lawrence Tan Carnegie Mellon University
System and Algorithmic Adaptation for Flash The FAWN Perspective David G. Andersen, Vijay Vasudevan, Michael Kaminsky* Amar Phanishayee, Jason Franklin, Iulian Moraru, Lawrence Tan Carnegie Mellon University
Project 0: Implementing a Hash Table
 Project : Implementing a Hash Table CS, Big Data Systems, Spring Goal and Motivation. The goal of Project is to help you refresh basic skills at designing and implementing data structures and algorithms.
Project : Implementing a Hash Table CS, Big Data Systems, Spring Goal and Motivation. The goal of Project is to help you refresh basic skills at designing and implementing data structures and algorithms.
File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4. COMP3231 Operating Systems
 File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4 COMP3231 Operating Systems Summary of the FS abstraction User's view Hierarchical structure Arbitrarily-sized files Symbolic file names Contiguous address space
File system internals Tanenbaum, Chapter 4 COMP3231 Operating Systems Summary of the FS abstraction User's view Hierarchical structure Arbitrarily-sized files Symbolic file names Contiguous address space
ECE 550D Fundamentals of Computer Systems and Engineering. Fall 2017
 ECE 550D Fundamentals of Computer Systems and Engineering Fall 2017 Input/Output (IO) Prof. John Board Duke University Slides are derived from work by Profs. Tyler Bletsch and Andrew Hilton (Duke) IO:
ECE 550D Fundamentals of Computer Systems and Engineering Fall 2017 Input/Output (IO) Prof. John Board Duke University Slides are derived from work by Profs. Tyler Bletsch and Andrew Hilton (Duke) IO:
UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT
 UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Memory management 3.2 Contiguous allocation i Partitioned memory allocation ii Fixed & variable partitioning iii Swapping iv Relocation v Protection
UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Memory management 3.2 Contiguous allocation i Partitioned memory allocation ii Fixed & variable partitioning iii Swapping iv Relocation v Protection
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Final Examination CS 111, Fall 2016 UCLA. Name:
 Final Examination CS 111, Fall 2016 UCLA Name: This is an open book, open note test. You may use electronic devices to take the test, but may not access the network during the test. You have three hours
Final Examination CS 111, Fall 2016 UCLA Name: This is an open book, open note test. You may use electronic devices to take the test, but may not access the network during the test. You have three hours
Chapter 4 File Systems. Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved
 Chapter 4 File Systems File Systems The best way to store information: Store all information in virtual memory address space Use ordinary memory read/write to access information Not feasible: no enough
Chapter 4 File Systems File Systems The best way to store information: Store all information in virtual memory address space Use ordinary memory read/write to access information Not feasible: no enough
Che-Wei Chang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University
 Che-Wei Chang chewei@mail.cgu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University Chapter 10: File System Chapter 11: Implementing File-Systems Chapter 12: Mass-Storage
Che-Wei Chang chewei@mail.cgu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University Chapter 10: File System Chapter 11: Implementing File-Systems Chapter 12: Mass-Storage
Shared snapshots. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction. Mikulas Patocka Red Hat Czech, s.r.o. Purkynova , Brno Czech Republic
 Shared snapshots Mikulas Patocka Red Hat Czech, s.r.o. Purkynova 99 612 45, Brno Czech Republic mpatocka@redhat.com 1 Abstract Shared snapshots enable the administrator to take many snapshots of the same
Shared snapshots Mikulas Patocka Red Hat Czech, s.r.o. Purkynova 99 612 45, Brno Czech Republic mpatocka@redhat.com 1 Abstract Shared snapshots enable the administrator to take many snapshots of the same
LH*Algorithm: Scalable Distributed Data Structure (SDDS) and its implementation on Switched Multicomputers
 LH*Algorithm: Scalable Distributed Data Structure (SDDS) and its implementation on Switched Multicomputers Written by: Salman Zubair Toor E-Mail: salman.toor@it.uu.se Teacher: Tore Risch Term paper for
LH*Algorithm: Scalable Distributed Data Structure (SDDS) and its implementation on Switched Multicomputers Written by: Salman Zubair Toor E-Mail: salman.toor@it.uu.se Teacher: Tore Risch Term paper for
Chapter 10: File System Implementation
 Chapter 10: File System Implementation Chapter 10: File System Implementation File-System Structure" File-System Implementation " Directory Implementation" Allocation Methods" Free-Space Management " Efficiency
Chapter 10: File System Implementation Chapter 10: File System Implementation File-System Structure" File-System Implementation " Directory Implementation" Allocation Methods" Free-Space Management " Efficiency
File Structures and Indexing
 File Structures and Indexing CPS352: Database Systems Simon Miner Gordon College Last Revised: 10/11/12 Agenda Check-in Database File Structures Indexing Database Design Tips Check-in Database File Structures
File Structures and Indexing CPS352: Database Systems Simon Miner Gordon College Last Revised: 10/11/12 Agenda Check-in Database File Structures Indexing Database Design Tips Check-in Database File Structures
Memory Management. Memory
 Memory Management These slides are created by Dr. Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at GMU can make a single machine readable copy and print a single copy of
Memory Management These slides are created by Dr. Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at GMU can make a single machine readable copy and print a single copy of
Advanced Database Systems
 Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Memory Allocation. Static Allocation. Dynamic Allocation. Dynamic Storage Allocation. CS 414: Operating Systems Spring 2008
 Dynamic Storage Allocation CS 44: Operating Systems Spring 2 Memory Allocation Static Allocation (fixed in size) Sometimes we create data structures that are fixed and don t need to grow or shrink. Dynamic
Dynamic Storage Allocation CS 44: Operating Systems Spring 2 Memory Allocation Static Allocation (fixed in size) Sometimes we create data structures that are fixed and don t need to grow or shrink. Dynamic
Outline. V Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Advantages of Multi-level Page Tables
 Outline V22.0202-001 Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Lecture 15 Memory Management (cont d) Virtual Memory March 30, 2005 Announcements Lab 4 due next Monday (April
Outline V22.0202-001 Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Lecture 15 Memory Management (cont d) Virtual Memory March 30, 2005 Announcements Lab 4 due next Monday (April
KVFTL - Optimization of Storage Space Utilization for Key-Value-Specific Flash Storage Devices
 KVFTL - Optimization of Storage Space Utilization for Key-Value-Specific Flash Storage Devices ASP-DAC 217 Yen-Ting Chen, Ming-Chang Yang, Yuan-Hao Chang, Tseng-Yi Chen, Hsin-Wen Wei, and Wei-Kuan Shih
KVFTL - Optimization of Storage Space Utilization for Key-Value-Specific Flash Storage Devices ASP-DAC 217 Yen-Ting Chen, Ming-Chang Yang, Yuan-Hao Chang, Tseng-Yi Chen, Hsin-Wen Wei, and Wei-Kuan Shih
Chapter 12: File System Implementation. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 12: File System Implementation Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods
Chapter 12: File System Implementation Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 12: File System Implementation File-System Structure File-System Implementation Directory Implementation Allocation Methods
Memory Management. Reading: Silberschatz chapter 9 Reading: Stallings. chapter 7 EEL 358
 Memory Management Reading: Silberschatz chapter 9 Reading: Stallings chapter 7 1 Outline Background Issues in Memory Management Logical Vs Physical address, MMU Dynamic Loading Memory Partitioning Placement
Memory Management Reading: Silberschatz chapter 9 Reading: Stallings chapter 7 1 Outline Background Issues in Memory Management Logical Vs Physical address, MMU Dynamic Loading Memory Partitioning Placement
Ricardo Rocha. Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto
 Ricardo Rocha Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Slides based on the book Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B. Galvin and Greg Gagne,
Ricardo Rocha Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Slides based on the book Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B. Galvin and Greg Gagne,
CSE 124: Networked Services Lecture-17
 Fall 2010 CSE 124: Networked Services Lecture-17 Instructor: B. S. Manoj, Ph.D http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa10/cse124 11/30/2010 CSE 124 Networked Services Fall 2010 1 Updates PlanetLab experiments
Fall 2010 CSE 124: Networked Services Lecture-17 Instructor: B. S. Manoj, Ph.D http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa10/cse124 11/30/2010 CSE 124 Networked Services Fall 2010 1 Updates PlanetLab experiments
Operating Systems. File Systems. Thomas Ropars.
 1 Operating Systems File Systems Thomas Ropars thomas.ropars@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr 2017 2 References The content of these lectures is inspired by: The lecture notes of Prof. David Mazières. Operating
1 Operating Systems File Systems Thomas Ropars thomas.ropars@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr 2017 2 References The content of these lectures is inspired by: The lecture notes of Prof. David Mazières. Operating
The Google File System
 October 13, 2010 Based on: S. Ghemawat, H. Gobioff, and S.-T. Leung: The Google file system, in Proceedings ACM SOSP 2003, Lake George, NY, USA, October 2003. 1 Assumptions Interface Architecture Single
October 13, 2010 Based on: S. Ghemawat, H. Gobioff, and S.-T. Leung: The Google file system, in Proceedings ACM SOSP 2003, Lake George, NY, USA, October 2003. 1 Assumptions Interface Architecture Single
Storage and File Structure
 C H A P T E R 10 Storage and File Structure Practice Exercises 10.1 Answer: This arrangement has the problem that P i and B 4i 3 are on the same disk. So if that disk fails, reconstruction of B 4i 3 is
C H A P T E R 10 Storage and File Structure Practice Exercises 10.1 Answer: This arrangement has the problem that P i and B 4i 3 are on the same disk. So if that disk fails, reconstruction of B 4i 3 is
FFS: The Fast File System -and- The Magical World of SSDs
 FFS: The Fast File System -and- The Magical World of SSDs The Original, Not-Fast Unix Filesystem Disk Superblock Inodes Data Directory Name i-number Inode Metadata Direct ptr......... Indirect ptr 2-indirect
FFS: The Fast File System -and- The Magical World of SSDs The Original, Not-Fast Unix Filesystem Disk Superblock Inodes Data Directory Name i-number Inode Metadata Direct ptr......... Indirect ptr 2-indirect
