Constructive Search Algorithms
|
|
|
- Ilene Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constructive Search Algorithms! Introduction Historically the major search method for CSPs Reference: S.W.Golomb & L.D.Baumert (1965) Backtrack Programming, JACM 12: Extended for Intelligent Backtracking techniques Plus Constraint Propagation techniques Used in CSPs, tree-search and Constraint Logic Programming (CLP)! Hybrid Algorithms for CSPS Reference: P. Prosser (1993) Hybrid Algorithms for the Constraint Satisfaction Problem, Computational Intelligence 9(3), pp Paper unifies important constructive search + constraint propagation algorithms in a common framework Also defines 4 new variations September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 1 of 24
2 Assumptions in paper 1. Tree search using a stack-based architecture (eg- Prolog, CLP) Efficient but limiting search architecture Elegant implementation in the Warren Abstract Machine (WAM) for Prolog Reference: H. Ait-Kaci, Warren s Abstract Machine - A tutorial reconstruction, MIT Press, Variables instantiated in some arbitrary (fixed) order Variable ordering is an important research issue 3. Strict boundary between past/future variables in ordering (cf- dynamic backtracking) Past Vars = variables already assigned values in tree Future Vars = variables currently unassigned Current Var = variable being instantiated or backtracked 4. All constraints are binary (unnecessary) September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 2 of 24
3 Family of Backtrack Algorithms Horizontal axis = backtracking dimension Vertical axis = constraint propagation dimension 9 possible algorithms in family Caveat: we will cover a subset here September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 3 of 24
4 Top-Level Search Algorithm Given a set of variables v[] of size n, find a first solution such that every constraint c[i,j] in C holds on variables v[i] and v[j]. procedure bcssp(n, status) Note unusal iterative coding style (from Nadel[89]) September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 4 of 24
5 Procedure label() Procedure label(i, consistent) finds an assignment for v[i]. on success, sets reference variable consistent = true and returns the next var, i+1, to instantiate. on failure, sets consistent = false and returns var i (for backtracking)! Cases on label() return values 1. consistent = true and 1< i < n bcssp() will iterate on labelling the next variable i 2. consistent = true and i = n+1 bcssp() will terminate with status = solution 3. consistent = false bcssp() will call procedure unlabel(i, consistent) on var i September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 5 of 24
6 Procedure unlabel() procedure unlabel(i, consistent) performs backtracking on some variable h < i in the static ordering. Resets every domain D j for variable v[j] such that h < j " i Then the current value of v[h] is removed from domain D h Sets consistent = true iff D h is not empty and returns var h Otherwise, D h = {} then consistent = false and returns var h! Cases on unlabel() return values 1. consistent = true and 1 " h " i bcssp() will iterate on labelling variable h 2. consistent = false and 1 " h < i bcssp() will call unlabel() again on the new backtrack point h Deep backtracks recursively 3. consistent = false and h = 0 bcssp() will terminate with status = impossible (no backtrack points left) September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 6 of 24
7 Parmeterizing the Algorithms Forward moves use method x-label for various instances of x Backward moves use method x-unlabel for various instances of x! Traditional chronological backtracking (BT) Earliest and simplest constructive tree search algorithm Still used in Prolog!!! September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 7 of 24
8 procedure bt-label() Consistency checking is performed ONLY backwards against previously instantiated variables When assigning v[i] only predicates v[i,h] for h < i are checked On failure: 1. Algorithm shallow backtracks by selecting another value in D i if possbile 2. Otherwise deep backtracks by return consistent = false and current var i to bcssp() September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 8 of 24
9 procedure bt-unlabel() Definition: the culprit = the variable h selected for backtracking For BT, the culprit is always the previous variable, h = i - 1 The domain D i of var i is reset to full domain (stack architecture again) Current value of v[h] removed from D h consistent = true iff Dh # {} September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 9 of 24
10 BackJumping Algorithm Major problem with BT Culprit may NOT be the actual cause of inconsistency Example CSP C 13 X 1 C 12 C 35 X 3 X 2 C 24 Failure X 5 X 4 Why backtrack from X5 to X4? X4 will choose a new assignment BUT X5 will inevitably fail again? Why? Actual culprit = X3 Called thrashing [Mackworth77] How do you know the real culprit? September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 10 of 24
11 BackJumping method Attempts to backtrack over irrelevant variables Identifies culprit = greatest var h < i such that there exists c[h,i] in C which removes a value from domain Di Method: define a variable maxcheck[i] for each var i which contains the index of the greatest variable constraining var i (as above) maxcheck updated during consistency checking otherwise same method as bt-label() September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 11 of 24
12 procedure bj-unlabel() maxcheck provides culprit for bj-label() resets domains D j, for j = h+1,..., i resets maxcheck[i] = 0! Analysis BJ is an approximation to the real culprit Consider example Prosser figure 3 Suppose no constraint c[1,2] in C What happens when v[2] must backtrack? Thus BJ backtracks chronologically September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 12 of 24
13 Induced Graphs Need to understand the concept of the induced graph Reference: Bayardo&Mirankar (1996) A Complexity Analysis of Space-Bounded Learning Algorithms for the CSP, proc. AAAI-96, pp Explicit representation of culprit dependencies Computed indirectly by CBJ and other Intelligent Backtracking methods Only approximated by BJ Definition: given a constraint graph G = (X, C) plus a total ordering of the variables in X, the induced graph G = (X, C ) contains the following set of edges C : 1. all edges (i,j) $ C are also edges in C 2. if (i,j) $ C and (h,j) $ C such that i<j and h<j then edge (i,h) $ C 3. no other edges are in C September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 13 of 24
14 Examples of Induced Graphs X 1 X 2 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 3 X 4 X 4 X 5 X 5 Directed arcs given by variable ordering New arcs added whenever a node has 2 parents Pathological example Who is the culprit for variable X 2? Why? 5 September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 14 of 24
15 Conflict-Directed Backjumping Method (CBJ) Definition: the conflict set of a variable X i are those past vars which failed consistency with X i. Culprit Identification Rule: the culprit of the conflict set for var X i is Xj where j % h for all X h in the conflict set. Required for complete search CBJ maintains a conflict set conf-set[i] for each variable v[i]. Initially all conf-set[i] = {0} Whenever a constraint c(i,h), h < i, fails then index h is added to confset[i] Thus the conflict set represents those previous variables whose values are in conflict with v[i]. If v[i] fails (via D i = {}) then h = max(conflict-set[i]) according to the culprit identification rule. Plus remaining vars in conflict-set[i] are transferred to conflict-set[h] State of v[i] represented by pair: current-domain[i] and conflict-set[i] September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 15 of 24
16 procedure cbj-label() Same as bj-label() except for lines 9-13 Note: algorithm discovers inconsistency AFTER for-loop exits (yeech!) conf-set[i] maintained as a set of candidate culprits (no duplicates) Why is 0 in the conflict set? September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 16 of 24
17 procedure cbj-unlabel() Again similar to bj-unlabel() Line 3 identifies culprit h for backtracking Line 4 updates conf-set[h] = conf-set[h] & conf-set[i] - {h} September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 17 of 24
18 Analysis of CBJ Smarter than either BT or BJ Computes culprit on failure exactly Algorithm is complete Overhead is still low (polynomial pain for exponential gain) Backtrack method of choice for stack-based (tree) search! Comparison with Induced Graph Note that CBJ is computing the induced graph indirectly See line 4 of cbj-unlabel() But only if a constraint actually removes a value from the current domain ' i. Basis for more sophisticated Intelligent Backtracking scheme (egdynamic backtracking) September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 18 of 24
19 Forward Checking (FC)! Overview Simplest form of constraint propagation in backtrack search Note: we will not cover Backmarking (BM) here Reference: R. Haralick & G. Elliott (1980) Increasing tree search efficiency for CSPs, Aritificial Intelligence 14: Prunes the live domains ' j of future variables v[j] given a particular assignment to variable v[i] for every v[j] connected by a constraint c[i,j]. Thus every future variable v[j] will be consistent with all past variables (but perhaps not with each other) Realizes the basic Arc Consistency condition between pairs of past and future variables. Powerful technique - on domain wipeout of ' j then assignment v[i] is known inconsistent. Original method uses BT as the search control structure September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 19 of 24
20 Implementing Forward Checking First we require the machinery for recording domain reductions Called from v[i] to prune values from the current domain ' j of v[j], i<j and there exists a c[i,j] in C Returns true iff ' j # {} Remember deleted values in reduction Line 9 updates ' j Lines maintains sufficient info for undoing assignment to v[i] September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 20 of 24
21 procedure undo-reduction(i) Undoes the domain reductions on backtracking assignment v[i] Line 5 removes the trail stack entry reduction from last variable to prune ' i Line 6 restores ' i given reduction Ignore line 7 temporarily September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 21 of 24
22 procedure fc-label(i, consistent) Main procedure for FC backtracking Attempts to instantiate v[i] while pruning the lives domains of all future vars v[j] sharing a constraint c[i,j] On domain wipeout, then reductions are reversed and a new assignment for v[i] is attempted. Line 8 calls check-forward(i,j) to do FC Line 12 undoes reductions if assignment is not consistent September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 22 of 24
23 procedure fc-unlabel(i, consistent) Again analogous to bt-unlabel() except Line 4 undoes the reductions to the live domains of future variables Line 5 restores the current live domain of v[i] before backtracking (from only those last reductions on the trail stack) Caveat: undo machinery here is very opaque September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 23 of 24
24 Example: Thrashing in FC FC does NOT avoid thrashing Why? Because control structure is BT v[5] is current variable v[3] has pruned values from domain fo v[6] v[6] has domain wipeout v[5] backtracks to v[4] by mistake. The real culprit = v[3] September 16, 2007 Copyright 2003 by Bill Havens 24 of 24
Constraint (Logic) Programming
 Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint-Directed Backtracking Algorithm. Wanlin Pang. Scott D. Goodwin. May 1996
 Constraint-Directed Backtracking Algorithm for Constraint-Satisfaction Problems Wanlin Pang Scott D. Goodwin Technical Report CS-96-05 May 1996 cwanlin Pang and Scott D. Goodwin Department of Computer
Constraint-Directed Backtracking Algorithm for Constraint-Satisfaction Problems Wanlin Pang Scott D. Goodwin Technical Report CS-96-05 May 1996 cwanlin Pang and Scott D. Goodwin Department of Computer
Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior
 PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
Reduced branching-factor algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems
 Reduced branching-factor algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
Reduced branching-factor algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
Conflict based Backjumping for Constraints Optimization Problems
 Conflict based Backjumping for Constraints Optimization Problems Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels {zivanr,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105,
Conflict based Backjumping for Constraints Optimization Problems Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels {zivanr,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105,
A Uniform View of Backtracking
 A Uniform View of Backtracking Fahiem Bacchus 1 Department. of Computer Science, 6 Kings College Road, University Of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5S 1A4, fbacchus@cs.toronto.edu? Abstract. Backtracking
A Uniform View of Backtracking Fahiem Bacchus 1 Department. of Computer Science, 6 Kings College Road, University Of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5S 1A4, fbacchus@cs.toronto.edu? Abstract. Backtracking
A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor
 A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Look-Back Malte Helmert and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 5, 2007 S. Wölfl, M. Helmert (Universität Freiburg) Constraint Satisfaction Problems June
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Look-Back Malte Helmert and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 5, 2007 S. Wölfl, M. Helmert (Universität Freiburg) Constraint Satisfaction Problems June
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Conflict Directed Backjumping for Max-CSPs
 Conflict Directed Backjumping for Max-CSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels, Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel Abstract Max-CSPs are Constraint
Conflict Directed Backjumping for Max-CSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels, Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel Abstract Max-CSPs are Constraint
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
General Methods and Search Algorithms
 DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Search and Lookahead Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 4/6, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Search and Lookahead Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 4/6, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
Solving Constraint Programs using Conflicts and Backjumping
 Solving onstraint Programs using onflicts and ackjumping Slides draw upon material from: Prof. Patrick Prosser, lasow University rian. Williams 16.410-13 September 29 th, 2010 6/30/11 1 Search Performance
Solving onstraint Programs using onflicts and ackjumping Slides draw upon material from: Prof. Patrick Prosser, lasow University rian. Williams 16.410-13 September 29 th, 2010 6/30/11 1 Search Performance
Modelling CSP Solution Algorithms with Petri Decision Nets
 Modelling CSP Solution Algorithms with Petri Decision Nets Stephan Pontow Technical University of Hamburg-Harburg Department of Process Automation Techniques D-21071 Hamburg, Germany pontow@tu-harburg.de
Modelling CSP Solution Algorithms with Petri Decision Nets Stephan Pontow Technical University of Hamburg-Harburg Department of Process Automation Techniques D-21071 Hamburg, Germany pontow@tu-harburg.de
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint satisfaction problems Backtracking algorithms for CSP Heuristics Local search for CSP Problem structure and difficulty of solving Search Problems The formalism
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint satisfaction problems Backtracking algorithms for CSP Heuristics Local search for CSP Problem structure and difficulty of solving Search Problems The formalism
Implementation of backtrack search
 Fall Semester, 2005 CSCE 421/821: Foundations of Constraint Processing B.Y. Choueiry Homework 3 Assigned: Thursday, September 22, 2005 Due: Tuesday, October 11, 2005 Total value: 100 points. Penalty of
Fall Semester, 2005 CSCE 421/821: Foundations of Constraint Processing B.Y. Choueiry Homework 3 Assigned: Thursday, September 22, 2005 Due: Tuesday, October 11, 2005 Total value: 100 points. Penalty of
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming
 Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint)Programming!
 Just!to!recall! onstraint)programming! Roman! Barták epartment of Theoretical omputer Science and Mathematical Logic Back to generate-and-test: generates a solution candidate (a complete assignment) and
Just!to!recall! onstraint)programming! Roman! Barták epartment of Theoretical omputer Science and Mathematical Logic Back to generate-and-test: generates a solution candidate (a complete assignment) and
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Frank C. Langbein F.C.Langbein@cs.cf.ac.uk Department of Computer Science Cardiff University 13th February 2001 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) A CSP is a high
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Frank C. Langbein F.C.Langbein@cs.cf.ac.uk Department of Computer Science Cardiff University 13th February 2001 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) A CSP is a high
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Logistics. Heuristics & Constraint Satisfaction. Symbolic Integration. 573 Topics. Symbolic Integration. Search. E.g. x 2 e x dx = e x (x 2-2x+2) + C
 Logistics Heuristics & Constraint Satisfaction CSE 573 University of Washington Reading for Monday Ch 6 (Game playing) Guest Speaker Henry Kautz Mini Projects A. Game Playing Choose your own game Experiment
Logistics Heuristics & Constraint Satisfaction CSE 573 University of Washington Reading for Monday Ch 6 (Game playing) Guest Speaker Henry Kautz Mini Projects A. Game Playing Choose your own game Experiment
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Constraint Programming
 Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
A generic framework for solving CSPs integrating decomposition methods
 A generic framework for solving CSPs integrating decomposition methods L. Blet 1,3, S. N. Ndiaye 1,2, and C. Solnon 1,3 1 Université de Lyon - LIRIS 2 Université Lyon 1, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69622 France
A generic framework for solving CSPs integrating decomposition methods L. Blet 1,3, S. N. Ndiaye 1,2, and C. Solnon 1,3 1 Université de Lyon - LIRIS 2 Université Lyon 1, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69622 France
Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Thursday: Chapter 8
 Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Lecture: Iterative Search Methods
 Lecture: Iterative Search Methods Overview Constructive Search is exponential. State-Space Search exhibits better performance on some problems. Research in understanding heuristic and iterative search
Lecture: Iterative Search Methods Overview Constructive Search is exponential. State-Space Search exhibits better performance on some problems. Research in understanding heuristic and iterative search
Determining if (FC-) (conflict-directed) backjumping visits a given node is NP-hard
 Artificial Intelligence 32 (200) 05 7 Research Note Determining if (FC-) (conflict-directed) backjumping visits a given node is NP-hard Bernd S.W. Schröder Program of Mathematics and Statistics, Louisiana
Artificial Intelligence 32 (200) 05 7 Research Note Determining if (FC-) (conflict-directed) backjumping visits a given node is NP-hard Bernd S.W. Schröder Program of Mathematics and Statistics, Louisiana
Search Algorithms in Type Theory
 Search Algorithms in Type Theory James L. Caldwell Ian P. Gent Judith Underwood Revised submission to Theoretical Computer Science: Special Issue on Proof Search in Type-theoretic Languages May 1998 Abstract
Search Algorithms in Type Theory James L. Caldwell Ian P. Gent Judith Underwood Revised submission to Theoretical Computer Science: Special Issue on Proof Search in Type-theoretic Languages May 1998 Abstract
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
Backtracking Search (CSPs)
 CSC384: Intro to Artificial Intelligence Backtracking Search (CSPs STATE REPRESENTATION: Factored representation of state ALGORITHMS: general purpose for particular types of constraints (versus problem
CSC384: Intro to Artificial Intelligence Backtracking Search (CSPs STATE REPRESENTATION: Factored representation of state ALGORITHMS: general purpose for particular types of constraints (versus problem
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides)
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Large Scale: Problems with A* What is Search For? Example: N-Queens
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
In the last six years, since the year 2000, the community of researchers in the field have had at least one yearly workshop. These activities have
 Preface DistributedsearchbyagentsisanimportanttopicofdistributedAIandhas not been treated thoroughly as such. While the scope of work on multi-agent systems has grown steadily over the last decade, very
Preface DistributedsearchbyagentsisanimportanttopicofdistributedAIandhas not been treated thoroughly as such. While the scope of work on multi-agent systems has grown steadily over the last decade, very
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Dynamic Variable Ordering In CSPs?
 Dynamic Variable Ordering In CSPs? Fahiem Bacchus 1 and Paul van Run 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, N2L 3G1, (fbacchus@logos.uwaterloo.ca) 2 ID-Direct
Dynamic Variable Ordering In CSPs? Fahiem Bacchus 1 and Paul van Run 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, N2L 3G1, (fbacchus@logos.uwaterloo.ca) 2 ID-Direct
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence
 CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
Constraint Satisfaction. AI Slides (5e) c Lin
 Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Solving Quantified Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Solving Quantified Constraint Satisfaction Problems Ian P. Gent Peter Nightingale Andrew Rowley School of Computer Science, University of St Andrews St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9SS, UK. {ipg,pn,agdr}@dcs.st-and.ac.uk
Solving Quantified Constraint Satisfaction Problems Ian P. Gent Peter Nightingale Andrew Rowley School of Computer Science, University of St Andrews St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9SS, UK. {ipg,pn,agdr}@dcs.st-and.ac.uk
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D)
 Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Backtracking algorithms for disjunctions of temporal constraints
 Artificial Intelligence 120 (2000) 81 117 Backtracking algorithms for disjunctions of temporal constraints Kostas Stergiou a,, Manolis Koubarakis b,1 a APES Research Group, Department of Computer Science,
Artificial Intelligence 120 (2000) 81 117 Backtracking algorithms for disjunctions of temporal constraints Kostas Stergiou a,, Manolis Koubarakis b,1 a APES Research Group, Department of Computer Science,
Example: Map-Coloring. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Australia. Example: Map-Coloring contd. Outline. Constraint graph
 Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Example: Map coloring
 Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Temporal Constraint Satisfaction Problems An Evaluation of Search Strategies
 Introduction Temporal Constraint Satisfaction Problems An Evaluation of Search Strategies Bruce Lo, John Duchi, and James Connor brucelo@cs.stanford.edu, jduchi@stanford.edu, jconnor@stanford.edu Stanford
Introduction Temporal Constraint Satisfaction Problems An Evaluation of Search Strategies Bruce Lo, John Duchi, and James Connor brucelo@cs.stanford.edu, jduchi@stanford.edu, jconnor@stanford.edu Stanford
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
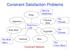 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEM: A CASE STUDY
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 5, May 2015, pg.33
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 5, May 2015, pg.33
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Dynamic Ordering for Asynchronous Backtracking on DisCSPs
 Dynamic Ordering for Asynchronous Backtracking on DisCSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels, Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel No Institute Given
Dynamic Ordering for Asynchronous Backtracking on DisCSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels, Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel No Institute Given
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Solving quantified constraint satisfaction problems
 Artificial Intelligence 172 (2008) 738 771 www.elsevier.com/locate/artint Solving quantified constraint satisfaction problems Ian P. Gent a, Peter Nightingale a, Andrew Rowley a, Kostas Stergiou b, a School
Artificial Intelligence 172 (2008) 738 771 www.elsevier.com/locate/artint Solving quantified constraint satisfaction problems Ian P. Gent a, Peter Nightingale a, Andrew Rowley a, Kostas Stergiou b, a School
On the Space-Time Trade-off in Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems*
 Appeared in Proc of the 14th Int l Joint Conf on Artificial Intelligence, 558-56, 1995 On the Space-Time Trade-off in Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems* Roberto J Bayardo Jr and Daniel P Miranker
Appeared in Proc of the 14th Int l Joint Conf on Artificial Intelligence, 558-56, 1995 On the Space-Time Trade-off in Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems* Roberto J Bayardo Jr and Daniel P Miranker
On the BEAM Implementation
 On the BEAM Implementation Ricardo Lopes 1,Vítor Santos Costa 2, and Fernando Silva 1 1 DCC-FC and LIACC, Universidade do Porto, Portugal {rslopes,fds}@ncc.up.pt 2 COPPE-Sistemas, Universidade Federal
On the BEAM Implementation Ricardo Lopes 1,Vítor Santos Costa 2, and Fernando Silva 1 1 DCC-FC and LIACC, Universidade do Porto, Portugal {rslopes,fds}@ncc.up.pt 2 COPPE-Sistemas, Universidade Federal
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
Path Consistency Revisited. Moninder Singh. University of Pennsylvania. Philadelphia, PA
 Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Articial Intelligence, 318-325, 1995. c Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE). Path Consistency Revisited Moninder
Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Articial Intelligence, 318-325, 1995. c Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE). Path Consistency Revisited Moninder
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
10/11/2017. Constraint Satisfaction Problems II. Review: CSP Representations. Heuristic 1: Most constrained variable
 //7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
//7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. What is Search For? Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
Lecture 18. Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1
 Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Material. Thought Question. Outline For Today. Example: Map-Coloring EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS
 EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
Binary Encodings of Non-binary Constraint Satisfaction Problems: Algorithms and Experimental Results
 Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 24 (2005) 641-684 Submitted 04/05; published 11/05 Binary Encodings of Non-binary Constraint Satisfaction Problems: Algorithms and Experimental Results Nikolaos
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 24 (2005) 641-684 Submitted 04/05; published 11/05 Binary Encodings of Non-binary Constraint Satisfaction Problems: Algorithms and Experimental Results Nikolaos
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Adrian Groza Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca 12 Nov 2014 Outline 1 Constraint Reasoning 2 Systematic Search Methods Improving backtracking
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Adrian Groza Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca 12 Nov 2014 Outline 1 Constraint Reasoning 2 Systematic Search Methods Improving backtracking
Andrew Davenport and Edward Tsang. fdaveat,edwardgessex.ac.uk. mostly soluble problems and regions of overconstrained, mostly insoluble problems as
 An empirical investigation into the exceptionally hard problems Andrew Davenport and Edward Tsang Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Colchester, Essex CO SQ, United Kingdom. fdaveat,edwardgessex.ac.uk
An empirical investigation into the exceptionally hard problems Andrew Davenport and Edward Tsang Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Colchester, Essex CO SQ, United Kingdom. fdaveat,edwardgessex.ac.uk
An Attempt to Map the Performance of a Range of Algorithm and Heuristic Combinations *
 An Attempt to Map the Performance of a Range of Algorithm and Heuristic Combinations * Edward P. K. Tsang, James E. Borrett, & Alvin C. M. Kwan {edward, jborrett, alvin}@essex.ac.uk Department of Computer
An Attempt to Map the Performance of a Range of Algorithm and Heuristic Combinations * Edward P. K. Tsang, James E. Borrett, & Alvin C. M. Kwan {edward, jborrett, alvin}@essex.ac.uk Department of Computer
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
UNIVERSITY OF ALBERTA. A Theoretical Evaluation of Selected Backtracking Algorithms. Grzegorz Kondrak
 UNIVERSITY OF ALBERTA A Theoretical Evaluation of Selected Backtracking Algorithms BY Grzegorz Kondrak A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research in partial fulllment of the requirements
UNIVERSITY OF ALBERTA A Theoretical Evaluation of Selected Backtracking Algorithms BY Grzegorz Kondrak A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research in partial fulllment of the requirements
Announcements. Reminder: CSPs. Today. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
CMU-Q Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev Kask ICS-271:Notes 5: 1 The constraint network model Outline Variables, domains, constraints, constraint graph, solutions Examples: graph-coloring,
Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev Kask ICS-271:Notes 5: 1 The constraint network model Outline Variables, domains, constraints, constraint graph, solutions Examples: graph-coloring,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems: A Deeper Look
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems: A Deeper Look The last problem set covered the topic of constraint satisfaction problems. CSP search and solution algorithms are directly applicable to a number of AI
Constraint Satisfaction Problems: A Deeper Look The last problem set covered the topic of constraint satisfaction problems. CSP search and solution algorithms are directly applicable to a number of AI
Arc Consistency for Dynamic CSPs
 Arc Consistency for Dynamic CSPs Malek Mouhoub mouhoubm@cs.uregina.ca Department of Computer Science, University of Regina 3737 Waskana Parkway, Regina SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 ABSTRACT Constraint Satisfaction
Arc Consistency for Dynamic CSPs Malek Mouhoub mouhoubm@cs.uregina.ca Department of Computer Science, University of Regina 3737 Waskana Parkway, Regina SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 ABSTRACT Constraint Satisfaction
Improving search using indexing: a study with temporal CSPs
 Improving search using indexing: a study with temporal CSPs Nikos Mamoulis Dimitris Papadias Department of Computer Science Hong Kong University of Science Technology Clear Water Bay, Hong Kong http://www.es.ust.hk/{-mamoulis,
Improving search using indexing: a study with temporal CSPs Nikos Mamoulis Dimitris Papadias Department of Computer Science Hong Kong University of Science Technology Clear Water Bay, Hong Kong http://www.es.ust.hk/{-mamoulis,
CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI
 CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI 1 handout: slides asst 1 milestone was due Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 1 / 19 EOLQs Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 2 / 19 Comparison Heuristics Search Algorithms
CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI 1 handout: slides asst 1 milestone was due Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 1 / 19 EOLQs Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 2 / 19 Comparison Heuristics Search Algorithms
Announcements. Homework 1: Search. Project 1: Search. Midterm date and time has been set:
 Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
What is Search For? CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Example: N-Queens. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring 4/7/17
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
Synchronous vs Asynchronous search on DisCSPs
 Synchronous vs Asynchronous search on DisCSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels {zivanr,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel Abstract.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous search on DisCSPs Roie Zivan and Amnon Meisels {zivanr,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel Abstract.
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Some material from: D Lin, J You, JC Latombe
 RN, Chapter 5 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Some material from: D Lin, J You, JC Latombe 1 Search Overview Introduction to Search Blind Search Techniques Heuristic Search Techniques Constraint Satisfaction
RN, Chapter 5 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Some material from: D Lin, J You, JC Latombe 1 Search Overview Introduction to Search Blind Search Techniques Heuristic Search Techniques Constraint Satisfaction
Constraints. CSC 411: AI Fall NC State University 1 / 53. Constraints
 CSC 411: AI Fall 2013 NC State University 1 / 53 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search: state is a black box that supports goal testing, application of an evaluation function, production
CSC 411: AI Fall 2013 NC State University 1 / 53 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search: state is a black box that supports goal testing, application of an evaluation function, production
SAT Solvers. Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego. April 9, 2013
 SAT Solvers Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 9, 2013 Decision Procedures We will look very closely at the following 1. Propositional Logic 2. Theory of Equality 3. Theory of Uninterpreted Functions 4.
SAT Solvers Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 9, 2013 Decision Procedures We will look very closely at the following 1. Propositional Logic 2. Theory of Equality 3. Theory of Uninterpreted Functions 4.
Australia Western Australia Western Territory Northern Territory Northern Australia South Australia South Tasmania Queensland Tasmania Victoria
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Decomposable Constraints
 Decomposable Constraints Ian Gent 1, Kostas Stergiou 2, and Toby Walsh 3 1 University of St Andrews, St Andrews, Scotland. ipg@dcs.st-and.ac.uk 2 University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland. ks@cs.strath.ac.uk
Decomposable Constraints Ian Gent 1, Kostas Stergiou 2, and Toby Walsh 3 1 University of St Andrews, St Andrews, Scotland. ipg@dcs.st-and.ac.uk 2 University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland. ks@cs.strath.ac.uk
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems. Maria Simi
 AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
Announcements. Homework 4. Project 3. Due tonight at 11:59pm. Due 3/8 at 4:00pm
 Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
